Tidal-Phase Discharge Strategy Significantly Enhances Sewage Dilution Trapped in Deep Tidal Passages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
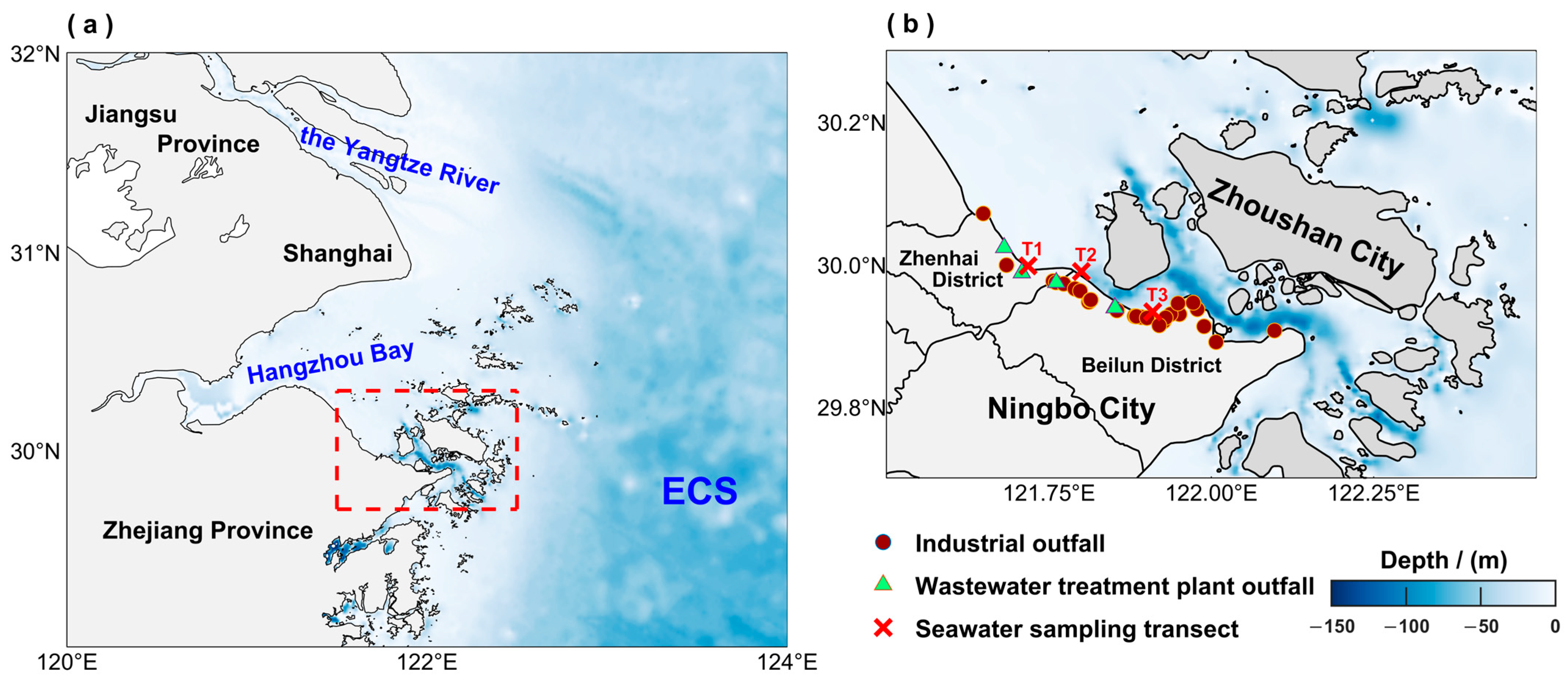
2.1. Study Area and Field Survey
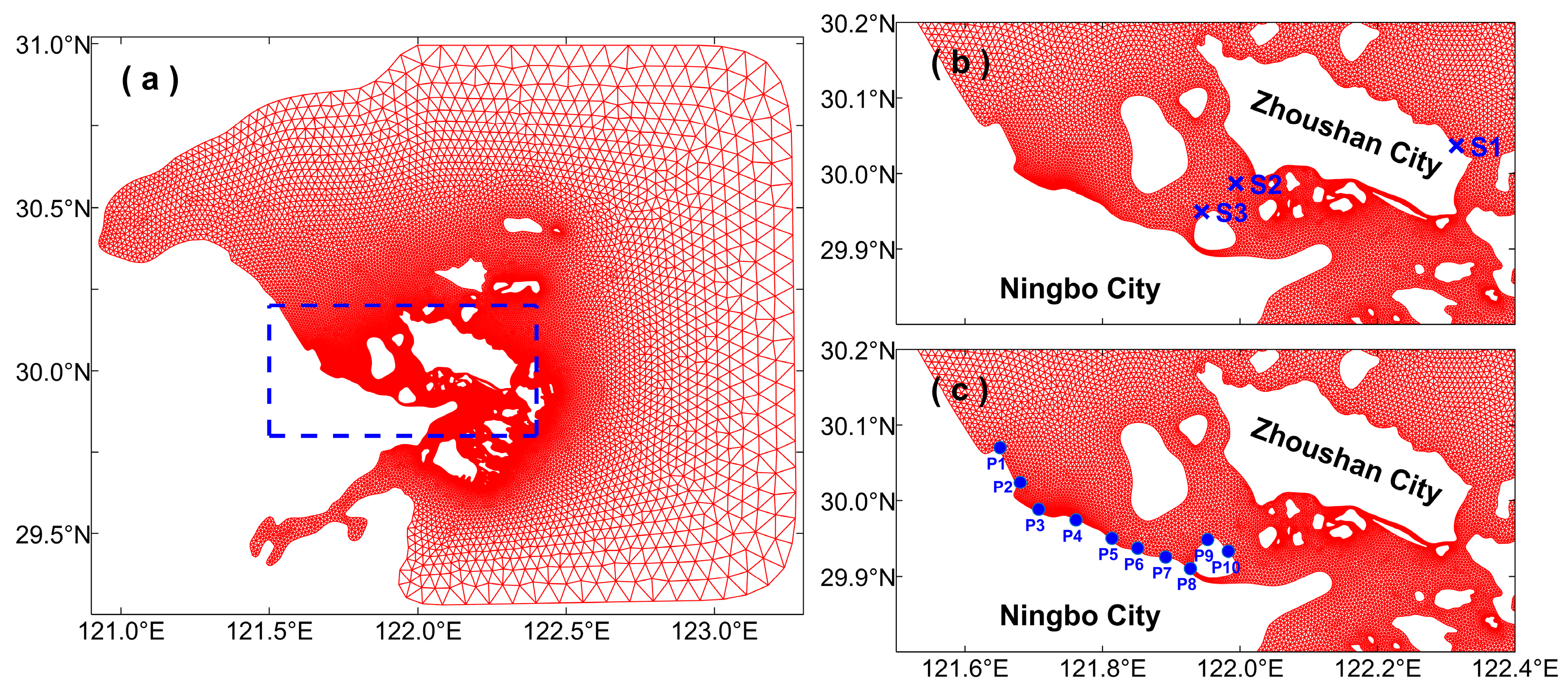
2.2. Hydrodynamic Model
2.2.1. Input Data for Modeling
2.2.2. Skill Assessment and Validation
2.3. The Dye-Tracking Module
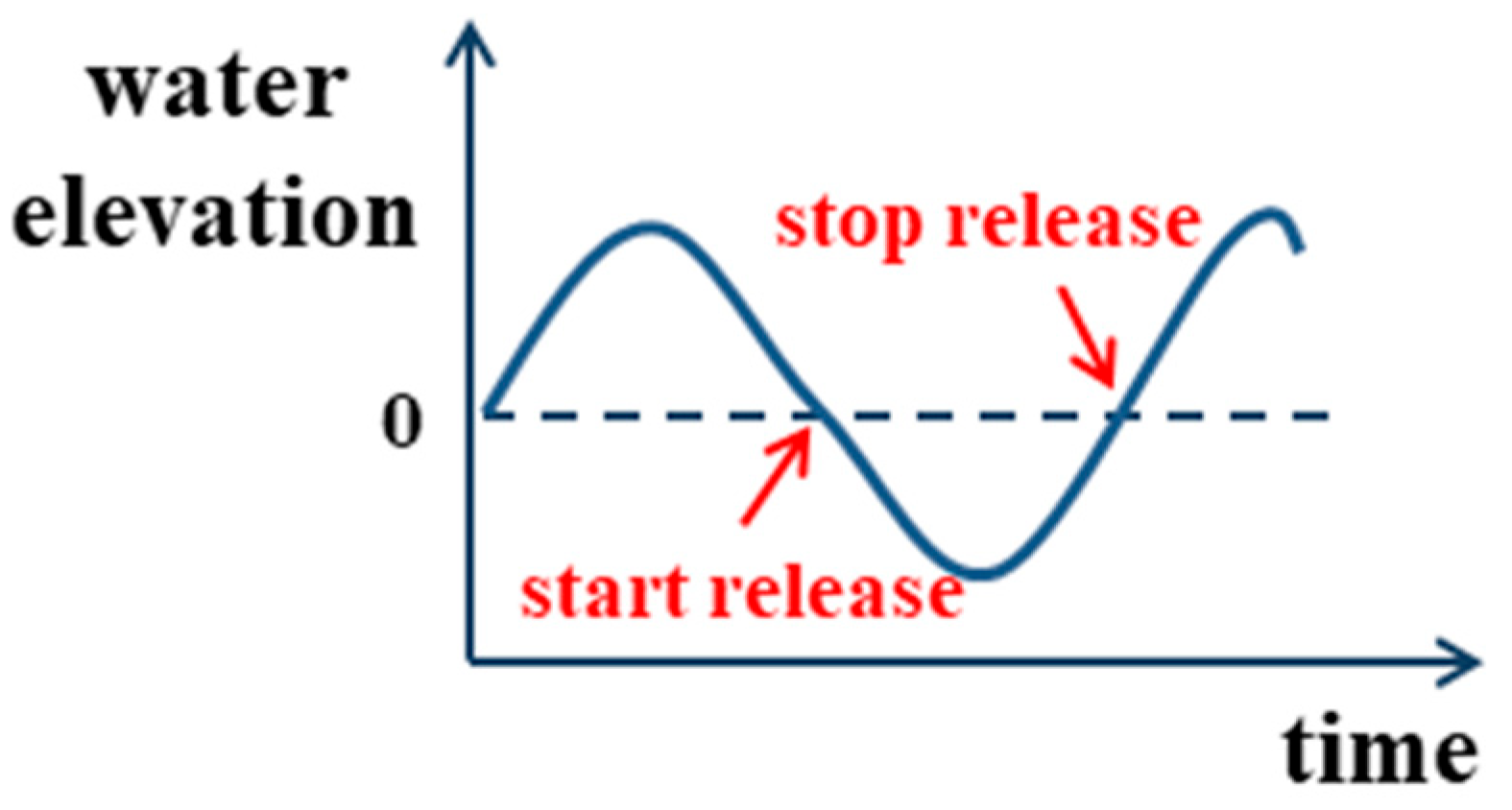
2.4. Experimental Design
3. Results
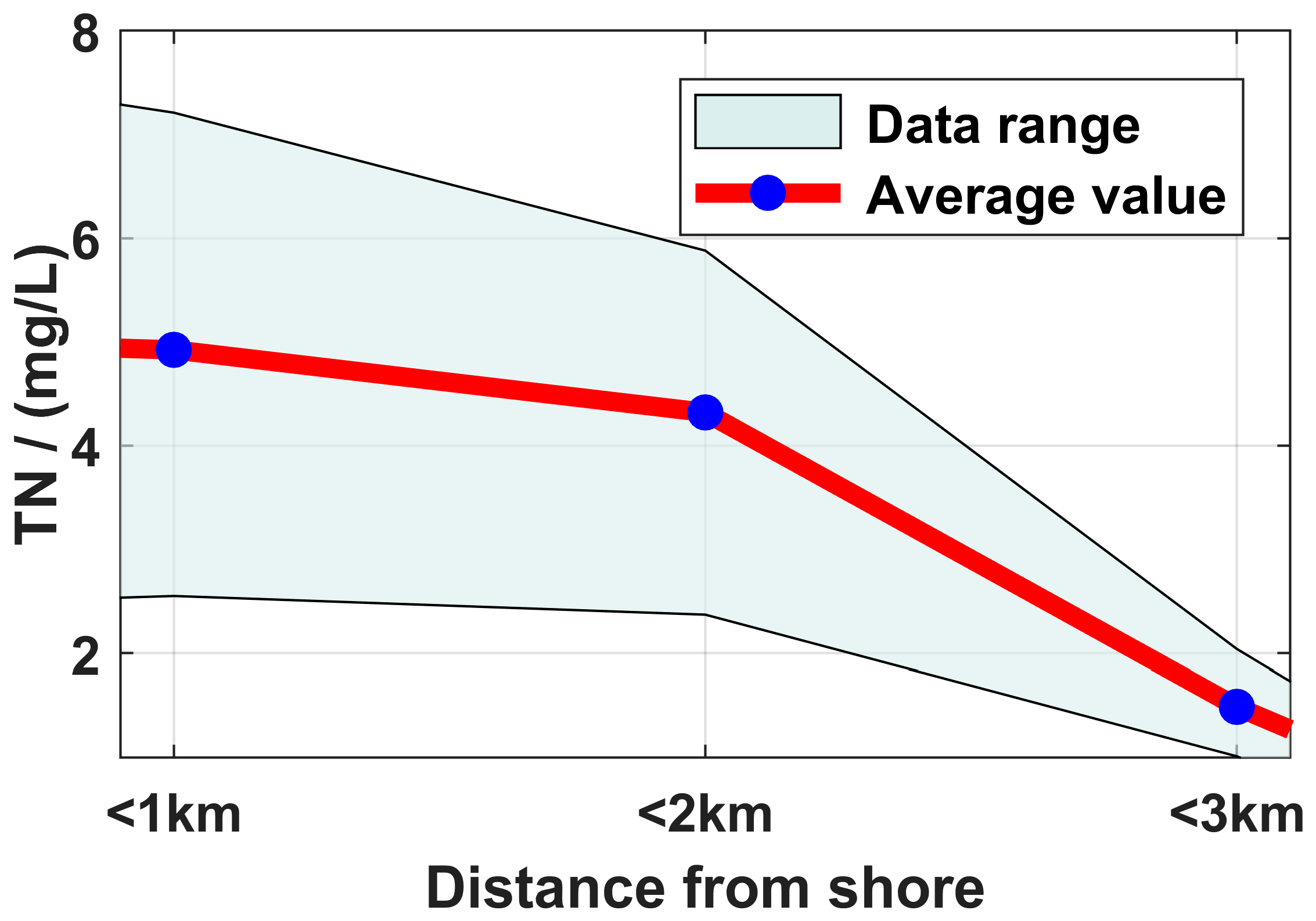
3.1. Field Survey
3.2. Model Validation
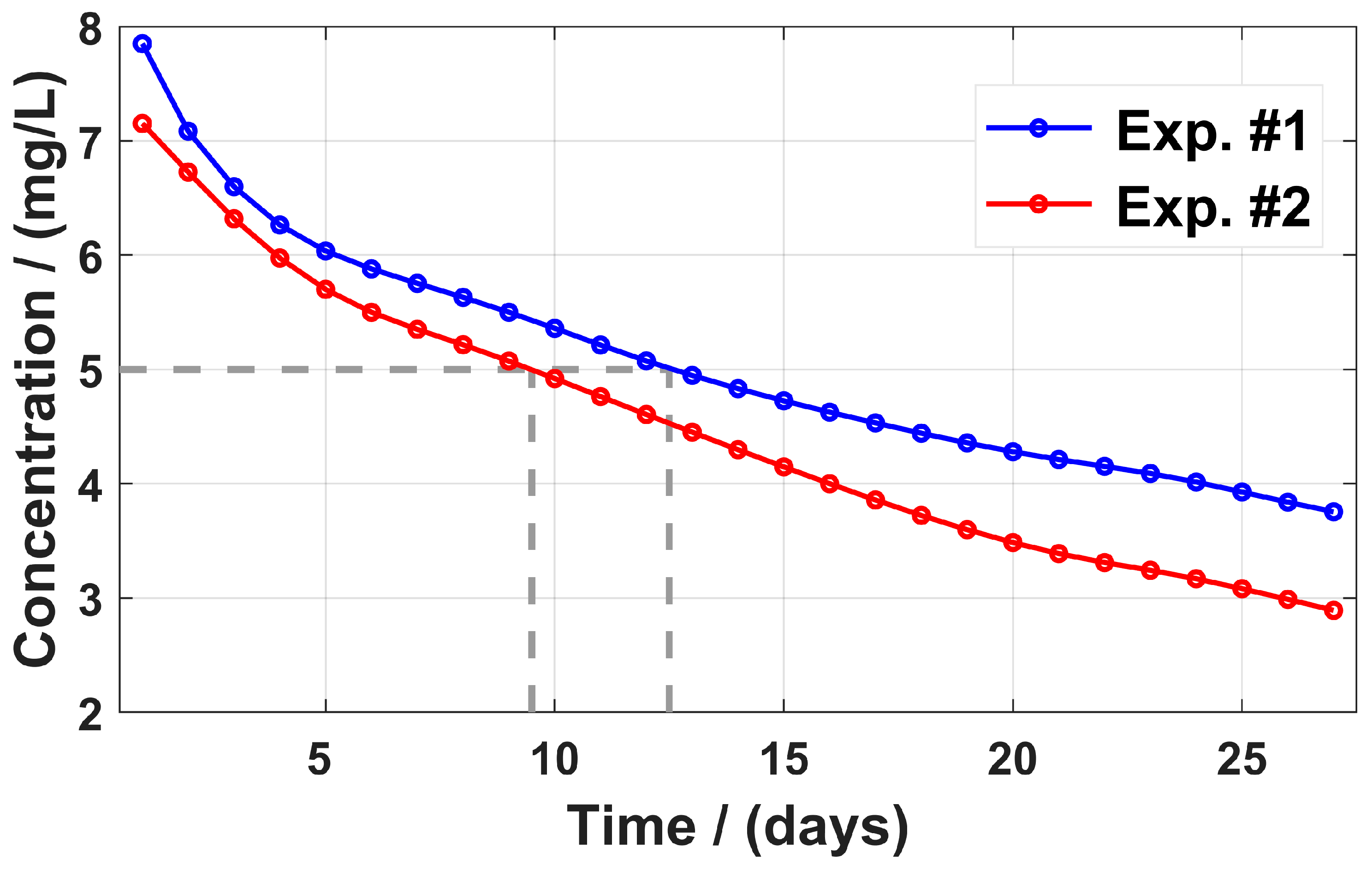
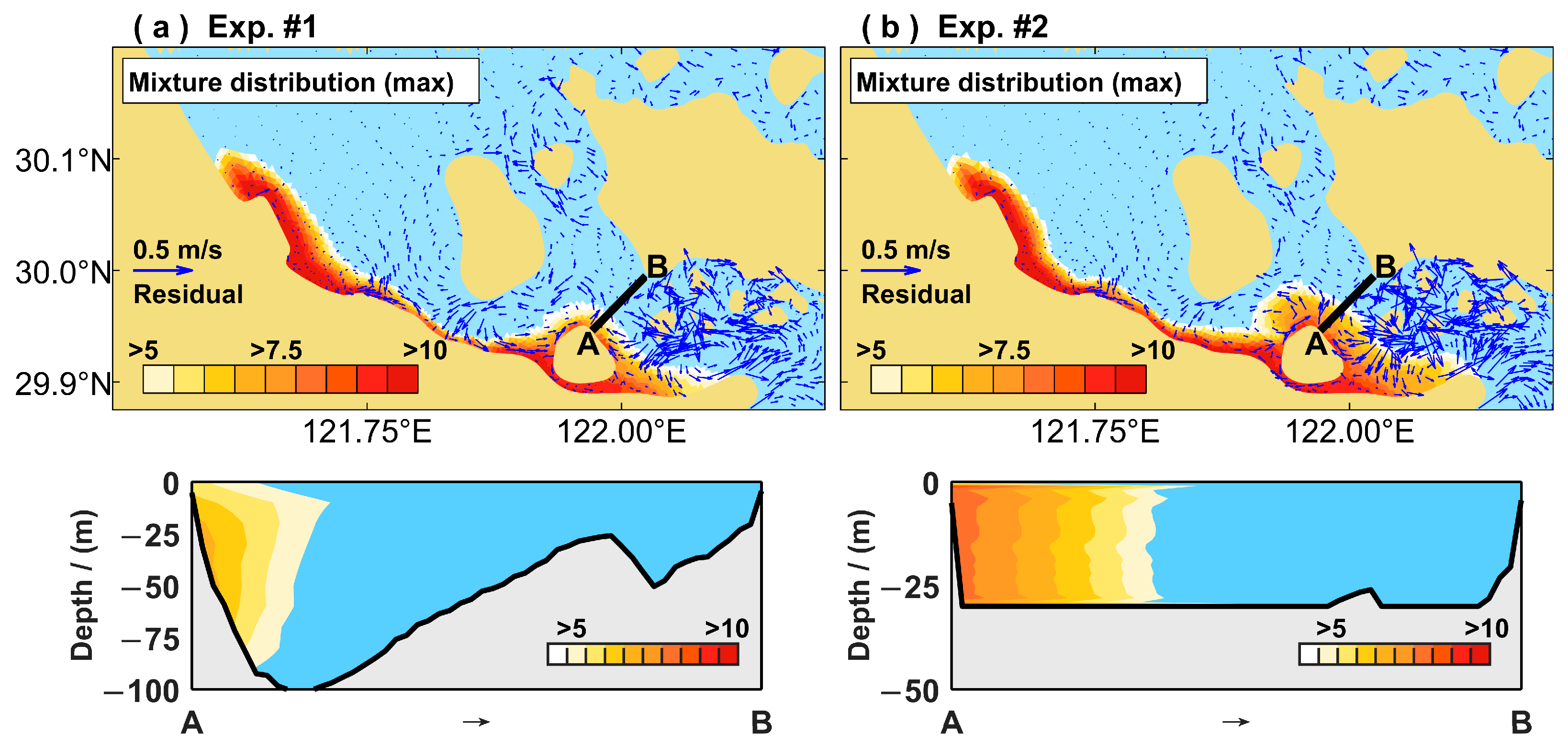
3.3. Sewage Retention Effect
3.4. Seasonal Variations
3.5. Discharge Strategies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, H.X.; Grifoll, M.; Zheng, P.J. From a feeder port to a hub port: The evolution pathways, dynamics and perspectives of Ningbo-Zhoushan port (China). Transp. Policy 2019, 76, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningbo Municipal Ecology and Environment Bureau. Report on the State of the Eco-environment in Ningbo 2018. Available online: http://sthjj.ningbo.gov.cn/art/2019/6/4/art_1229051263_52545151.html (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Law, A.W.K.; Tang, C.Y. Industrial water treatment and industrial marine outfalls: Achieving the right balance. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Galgani, F.; Neal, W.J. Addressing the global challenge of coastal sewage pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammetoglu, A.; Yalcin, O.B.; Ozcan, T. Prediction of wastewater dilution and indicator bacteria concentrations for marine outfall systems. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 78, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, F.; Lessa, G.C.; Wild, C.; Kikuchi, R.K.P.; Naumann, M.S. Impacts of a high-discharge submarine sewage outfall on water quality in the coastal zone of Salvador (Bahia, Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.Y.; Li, K.Q.; Wang, X.l.; Shi, X.Y.; Qiao, X.D.; Liu, J. Environmental capacity of nitrogen and phosphorus pollutions in Jiaozhou Bay, China: Modeling and assessing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premathilake, L.; Khangaonkar, T. Explicit quantification of residence and flushing times in the Salish Sea using a sub-basin scale shoreline resolving model. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 276, 108022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.B.; Sanders, B.F.; Winant, C.D. Cross-shelf transport at Huntington Beach. Implications for the fate of sewage discharged through an offshore ocean outfall. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scroccaro, I.; Ostoich, M.; Umgiesser, G.; De Pascalis, F.; Colugnati, L.; Mattassi, G.; Vazzoler, M.; Cuomo, M. Submarine wastewater discharges: Dispersion modelling in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2010, 17, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.A.; Haverson, D.; Bacon, J. Modelling pollution dispersal around Solomon Islands and Vanuatu. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MrŠAHaber, I.V.A.; LegoviĆ, T.; KranjČEviĆ, L.; Cukrov, M. Simulation of pollutants spreading from a sewage outfall in the Rijeka Bay. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2020, 21, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Bridgen, P.; Dunshea, G.; Galton-Fenzi, B.; Hunter, J.; Johnstone, G.; King, C.; Leeming, R.; Palmer, A.; Smith, J.; et al. Dispersal and dilution of wastewater from an ocean outfall at Davis Station, Antarctica, and resulting environmental contamination. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedri, Z.; O’Sullivan, J.J.; Deering, L.A.; Demeter, K.; Masterson, B.; Meijer, W.G.; O’Hare, G. Assessing the water quality response to an alternative sewage disposal strategy at bathing sites on the east coast of Ireland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 330–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Soussa, H.; Hamed, A.M.; El Safty, H. Numerical modeling of hydrodynamic and water quality impacts of wastewater discharges in coastal Lagoons: A case study of Ria Formosa. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2025, 16, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ligaray, M.; Kwon, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Baek, S.; Pyo, J.; Baek, G.; Shin, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.; et al. Designing a marine outfall to reduce microbial risk on a recreational beach: Field experiment and modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, Q.; Fang, J. Study on layout optimization of sewage outfalls: A case study of wastewater treatment plants in Xiamen. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.W.; Salas, H.J.; Reiff, F.M.; Libhaber, M.; Labbe, A.; Thomson, J.C. Marine Wastewater Outfalls and Treatment Systems; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Borja, Á.; Elliott, M.; Carstensen, J.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; van de Bund, W. Marine management—Towards an integrated implementation of the European Marine Strategy Framework and the Water Framework Directives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Harrison, J.A.; D€urr, H.H.; Bouwman, A.F.; Laruelle, G.G. Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Ecological Studies; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.Q.; Shi, X.Y.; Bao, X.W.; Ma, Q.M.; Wang, X.L. Modeling total maximum allocated loads for heavy metals in Jinzhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Liu, H.D.; Beardsley, R.C. An Unstructured Grid, Finite-Volume, Three-Dimensional, Primitive Equations Ocean Model: Application to Coastal Ocean and Estuaries. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Beardsley, R.C.; Cowles, G.; Qi, J.; Lai, Z.G.; Gao, G.P.; Stuebe, D.; Xu, Q.C.; Xue, P.F.; Ge, J.Z.; et al. An Unstructured Grid, Finite-Volume Community Ocean Model FVCOM User Manual; University of Massachusetts Dartmouth: New Bedford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, G.L.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagorinsky, J. General Circulation Experiments with the Primitive Equations: I The Basic Experiment. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1962, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Bennett, A.F.; Foreman, M.G.G. TOPEX/POSEIDON tides estimated using a global inverse model. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 821–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Erofeeva, S.Y. Efficient Inverse Modeling of Barotropic Ocean Tides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, B.; Sandwell, D.T.; Smith, W.H.F.; Olson, C.; Beale, J.R.; Wessel, P. Global Bathymetry and Topography at 15 Arc Sec: SRTM15+. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1847–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the Validation of Models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Xu, Q.C.; Houghton, R.; Beardsley, R.C. A model—Dye comparison experiment in the tidal mixing front zone on the southern flank of Georges Bank. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C02005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Townsend, D.W.; Chen, C.S.; Cowles, G.; Beardsley, R.C.; Ji, R.B.; Houghton, R.W. Tidal pumping and nutrient fluxes on Georges Bank: A process-oriented modeling study. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S. Improved vertical algorithm for finite volume coastal and ocean model with unstructured-grid. Chin. J. Hydrodyn. 2011, 26, 430–436. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safak, I.; Wiberg, P.L.; Richardson, D.L.; Kurum, M.O. Controls on residence time and exchange in a system of shallow coastal bays. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 97, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, R.H.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Murawski, S.; Hu, C.M.; Paul, J. Did Deepwater Horizon hydrocarbons transit to the west Florida continental shelf? Deep. Sea Res. Part II 2016, 129, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.P.; Yang, Z.Q. A modeling study of tidal energy extraction and the associated impact on tidal circulation in a multi-inlet bay system of Puget Sound. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, Q.S.; HU, S.; WANG, X.H.; LIU, P.X.; Liu, X.; GAO, Z.Q. Simulation of degradation, diffusion and distribution of total nitrogen pollution influenced by tide and runoff in Yongjiang River. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 344–351. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Lai, Z.G.; Beardsley, R.C.; Sasaki, J.; Lin, J.; Lin, H.C.; Ji, R.B.; Sun, Y.F. The March 11, 2011 Tōhoku M9.0 earthquake-induced tsunami and coastal inundation along the Japanese coast: A model assessment. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 123, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

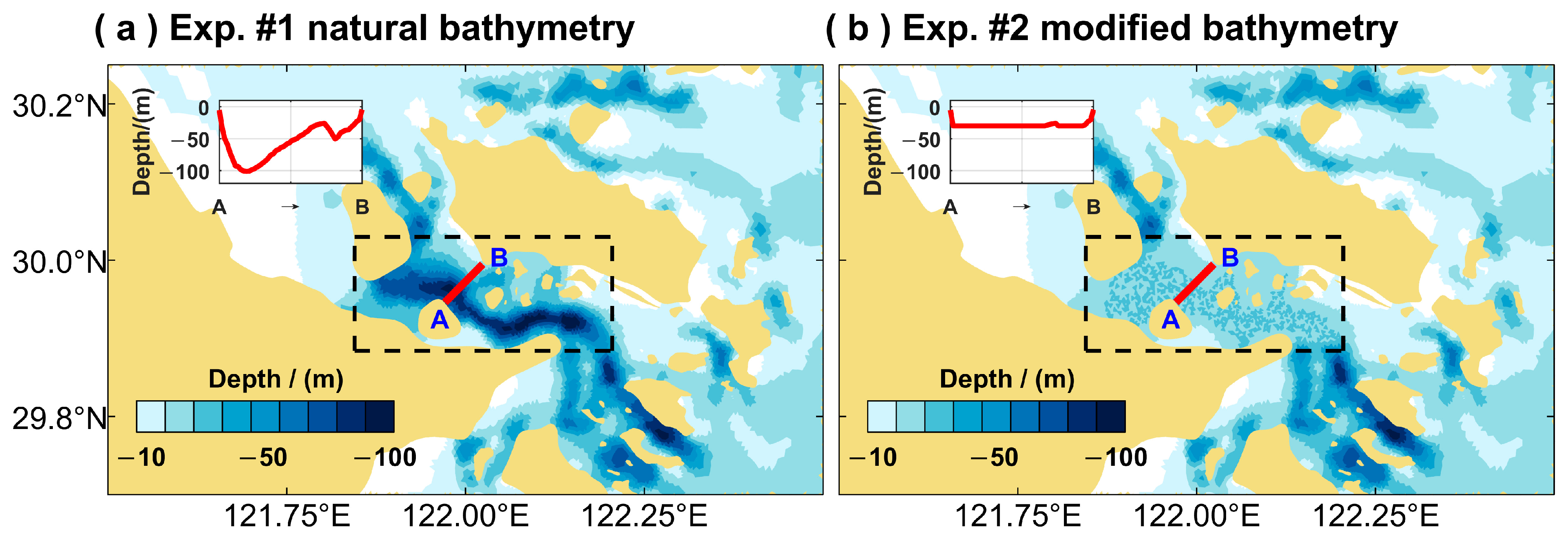



| No. | Case | Dyeing Sigma Layer | Depth | Force |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. #1 | Exp. #1—natural bathymetry | 1, 15, 30 | real depth | tidal forcing |
| Exp. #2 | Exp. #2—modified bathymetry | 1, 15, 30 | comparative depth (water depths exceeding 30 m were filled in as a flat bottom across the tidal passages) | tidal forcing |
| Exp. #3 | Exp. #3—Jan. Exp. #3—Feb. Exp. #3—Mar. Exp. #3—Apr. Exp. #3—May. Exp. #3—Jun. Exp. #3—Jul. Exp. #3—Aug. Exp. #3—Sep. Exp. #3—Oct. Exp. #3—Nov. Exp. #3—Dec. | 1, 15, 30 | real depth | tidal forcing and atmospheric forcing |
| Exp. #4 | Exp. #4—surface discharge | 1, 2, 3 | real depth | tidal forcing |
| Exp. #4—submerged discharge | 28, 29, 30 | |||
| Exp. #5 | Exp. #5—continuous discharge | 1, 15, 30 | real depth | tidal forcing |
| Exp. #5—intermittent discharge | 1, 2, 14, 15, 29, 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Tan, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, P.; Liu, X. Tidal-Phase Discharge Strategy Significantly Enhances Sewage Dilution Trapped in Deep Tidal Passages. Oceans 2025, 6, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040073
Chen Q, Tan Y, Hu S, Wang X, Zhao H, Liu P, Liu X. Tidal-Phase Discharge Strategy Significantly Enhances Sewage Dilution Trapped in Deep Tidal Passages. Oceans. 2025; 6(4):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040073
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qinsi, Yingyu Tan, Song Hu, Xiaohua Wang, Heng Zhao, Pengxia Liu, and Xing Liu. 2025. "Tidal-Phase Discharge Strategy Significantly Enhances Sewage Dilution Trapped in Deep Tidal Passages" Oceans 6, no. 4: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040073
APA StyleChen, Q., Tan, Y., Hu, S., Wang, X., Zhao, H., Liu, P., & Liu, X. (2025). Tidal-Phase Discharge Strategy Significantly Enhances Sewage Dilution Trapped in Deep Tidal Passages. Oceans, 6(4), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6040073






