Abstract
Invasive marine invertebrates are increasingly recognized as a potential disturbance to coastal ecosystems. We sought to better document the taxonomic composition of subtidal communities around Long Island to obtain a baseline that can be used to monitor current and future invasions of non-indigenous species. We placed settlement blocks at 18 sites along the coast of Long Island, New York, for three months. After recovering blocks at 12 sites, we analyzed the taxonomic composition of fouling communities on the blocks. We observed 64 invertebrate and 3 algal taxa, with large variation in taxon richness among sites. Multivariate analyses revealed that although taxon composition was significantly dissimilar between north and south shores, variation in dissimilarity did not differ significantly between shores. The high variability in taxon composition observed among sites indicates that additional research is needed to expand our knowledge of invertebrate diversity in the waters surrounding Long Island. Adding more sites and replicate blocks within sites could improve future sampling designs. This research will benefit continuing efforts to monitor, manage, and prevent the establishment of marine invasive species.
1. Introduction
Interest in biodiversity is growing as natural environments face ever-greater repercussions from anthropogenic changes occurring on a global scale [1,2]. One of the greatest threats to biodiversity is the introduction of invasive species [3,4]. Once these species establish, they are nearly impossible to remove [5], such that invasive species have the ability to irreversibly alter an ecosystem as well as to cause socio-economic harm [6].
While invasive species are a global issue, examining biofouling communities is a key step in beginning to understand their spread and containment [7,8]. Although Long Island, New York, is home to several invasive species [9,10,11], few publications document the subtidal fouling communities of Long Island. Since a baseline record of extant taxa is required for the identification of future invasive taxa, we seek to document the current biodiversity of subtidal marine invertebrates in the waters surrounding Long Island. In this study, we examined a subset of the near-shore communities of fouling marine invertebrates by placing benthic settlement blocks at 18 sites. We tested the hypothesis that community structure differs between north and south shore habitats and compared the composition and diversity of taxa among locations.
2. Materials and Methods
Long Island parallels the coastline of the northeastern United States. Along with the state of Connecticut, it encapsulates the Long Island Sound to its north; the Atlantic Ocean borders it to the south. We hypothesized that biofouling invertebrates on the north shore of Long Island would be less diverse than on the south shore of Long Island because the north shore borders Long Island Sound and may therefore not be as freely colonized by planktonic larvae as the south shore or exposed to the same intensity of wave disturbance as the south shore, which faces the open Atlantic.
The north and south shores of Long Island differ as follows: Long Island Sound is a navigable estuary that runs predominantly east to west between Connecticut to the north and Long Island, New York, to the south. It is approximately 176 km long and 37 km wide at its widest point [12]. The tides reach the Sound through a small entrance on the west end and a larger entrance on the east end. Because of these differences in size, the range of the tide is largest but the velocity of the tide is lowest at the west end of the Sound, while the range of the tide is lower but the velocity of the tide is much greater at the east end of the Sound [12]. The water at the west end of the Sound is less saline than the east end due to freshwater inflow from the Hudson River. The bottom waters of the western sound experience anoxia late in the summer due to the high degree of urbanization and consequent nitrogen runoff [13,14]. Water movement and sea levels through the sound are driven by the tides [12] and the wind [15]. The tides of Long Island Sound are forced through the opening at the east end of the Sound. While there are both semi-diurnal and diurnal tides within Long Island Sound, the diurnal tides are stronger and are amplified approximately four times due to resonance, while the diurnal tides are much weaker and exhibit little amplification [15]. By contrast, the south shore of Long Island is directly exposed to the Atlantic Ocean, but includes a complex series of barrier islands, sheltered bays, headlands, and coastal plains [16]. It is more highly urbanized than the north shore of Long Island, though both shores have small towns and rural areas too. Both the north and south shores contain a variety of habitats such as beaches, tidal marshes, and rocky intertidal zones [9]; this heterogeneity leads to a wide array of organisms inhabiting both coasts.
To begin the development of a database of marine invertebrates existing in a variety of habitats, we placed settlement blocks at 18 locations in the waters surrounding Long Island (Figure 1). The locations were selected for ease of public access and permissions, and to diversify the types of habitats sampled across both north and south shores. While these habitats and locations vary from natural rock outcroppings surrounded by sand to harbors with infrequent dredging activity, they can broadly be described as exposed or sheltered with rocky, rock/sandy, or sandy substrates (Table 1). South shore blocks were placed in more sheltered habitats than north shore blocks; thus, comparisons between north and south shore locations were confounded by differences in exposure and substrate.
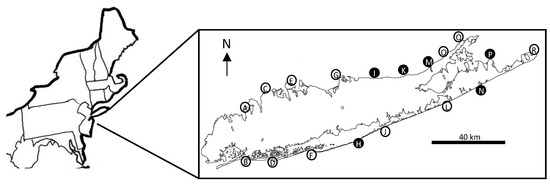
Figure 1.
Sites where settlement blocks were placed. Closed circles indicate sites where no settlement plates were collected either because the plates or the entire block were lost. Open circles represent sites where at least one settlement plate was collected. Site names are as follows: A = Kings Point; B = Silver Point; C = East Island; D = Point Lookout; E = Lloyd Harbor; F = Sore Thumb, Gilgo State Park; G = Crane Neck; H = Smith Point; I = Wildwood; J = Cupsogue Beach; K = Reeves Beach; L = Shinnecock Inlet; M = Bailie Beach; N = W. Scott Cameron Beach; O = Horton Point; P = Hog Creek Point; Q = Orient Point; R = Montauk Point. GPS coordinates for each location are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Locations of settlement blocks, including site letter (used in Figure 1), site name, site description, shore, latitude, and longitude. Sites described as rocky consisted of primarily rocks of various sizes with some sand or small grain substrate in between. Sites described as sandy were purely or nearly purely sand. Sites characterized as rocky/sandy consisted of rocks of various sizes embedded in a matrix of sand. Depths are represented as deviation from mean lower low water (MLLW) at each site. “Plates” represents the number of settlement plates recovered from each site and used in our analyses.
Settlement blocks were constructed using a cement block (19.5 cm × 19.5 cm × 40 cm) with four attached settlement plates. Each plate was a sanded plastic Petri dish (100 mm × 15 mm) that was attached to the cement block using cable ties (Figure 2). Blocks were placed at subtidal depths, less than one meter below the extreme low tide level at each site (Table 1), so that they would remain permanently submerged but could be easily retrieved. Blocks were placed in May 2018 and retrieved in August 2018. At six locations, the block was lost and unable to be retrieved; these locations were removed from the dataset, leaving 12 remaining locations (Figure 1). At some of the remaining sites, individual plates had been detached from the block and could not be retrieved (Table 1).
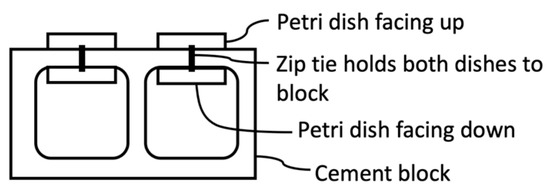
Figure 2.
Diagram of cement block and Petri dish settlement plates. Blocks were placed at subtidal depths such that the settlement plates remained submerged throughout the tidal cycle.
Upon retrieval of each block, plates were removed and immediately placed in 95% EtOH, transported to Long Island University (Brookville, NY), and stored until they were processed in the lab. We identified organisms to the lowest taxon possible based on morphological characteristics, following taxonomic keys for invertebrates of New England [17,18]. While we are confident that each taxon (Table 2) represents a single species, we restricted our analyses to higher taxa (e.g., Caprellidae) when identifications at lower taxonomic levels were uncertain; this procedure potentially underestimated species diversity if multiple species were contained within the higher taxon. Since numerous changes in species names and other taxonomic designations have occurred since these keys were originally published, we used the World Register of Marine Species [19] to identify the most recently accepted scientific name of each taxon and to locate additional taxonomic references that provide specialized morphological descriptions for each taxon (Table 2), taxon-specific keys, and distribution maps.

Table 2.
Invertebrate and algal taxa present on settlement plates, including their phyla, scientific name, common name, distribution status, and additional taxonomic references. Each line represents a unique species, even though some specimens could only be identified to higher taxonomic levels. Shore refers to whether the species was found on the north shore (N) of Long Island, the south shore (S), or both north and south shores (N/S). Bold font on scientific names indicates species widely recognized as invasive. Distribution status includes C: cryptogenic; I: indigenous, NI: non-indigenous, and U: unresolved.
We tabulated the presence or absence of each taxon occurring on each settlement plate. Each taxon was placed into one of four categories to reflect the status of their distribution: indigenous, non-indigenous, cryptogenic, or unresolved. Indigenous was assigned to taxa that have a known origin in the waters surrounding Long Island or the Northeastern region of the United States. Non-indigenous was assigned to taxa that have a known origin in areas outside the Northeastern US. Cryptogenic was assigned to taxa that could not be identified as indigenous or non-indigenous [59], often due to a lack of knowledge about the biogeographic history of the taxon [60]. Unresolved taxa were not resolved to species and could not be reliably assigned to the other three categories. To assign distribution status, we used multiple approaches. First, we consulted databases containing species range information, including WoRMS, the Global Biodiversity Information Facility [61], and Nemesis [62]. Second, we consulted previous surveys of fouling communities in the Northwestern Atlantic [10,11,63]. We also categorized each taxon as invasive or non-invasive. To consider a taxon as invasive, we required that the taxon has a known detrimental effect in the waters surrounding Long Island or in the Northeastern US, as reported in databases such as Nemesis [62] or in the scientific literature [11].
Data analyses were completed in R [64] and RStudio [65] using taxon presence or absence only. After creating a presence–absence table, a metadata table, and a taxonomic table in spreadsheet software, we imported these files into RStudio. All three tables were then combined into a phyloseq object using the R package phyloseq 1.48.0 [66] to manipulate the data more easily. The dataset was filtered to remove plates with a single or no taxon observations prior subsequent analyses. We used the vegan package 2.6.6.1 [67] to analyze diversity and community similarity among locations. We compared the taxon richness of plates at locations on the north shore of Long Island to those of the south shore using a Wilcoxon rank sum test after testing for normality using a Shapiro–Wilk test and testing for homogeneity of variances using a Fligner–Killeen test. We used rarefaction analyses to compare the accumulation of taxa by sites for the north and south shores and the combined dataset, using vegan functions specaccum and specpool. We tabulated the number of indigenous, nonindigenous, cryptogenic, and unresolved taxa among locations and used a chi-square test to explore whether their occurrence statistically differed. Using Petri dishes to collect individual invertebrates standardizes the community with regard to substrate availability and substrate type at each site. We, therefore, calculated a Jaccard dissimilarity index among plates at the different sites to compare similarity in community composition between the north and south shores of Long Island based on the presence–absence of taxa. We conducted multivariate analyses of community composition by employing a permutational analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) in the vegan function adonis2 to test whether Jaccard dissimilarities significantly varied among individual settlement plates from north and south shores of Long Island, treating shore as a fixed factor. We also included plate angle as a fixed factor to compare upward-facing plates to downward-facing plates. We performed non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) using the Jaccard index to visualize dissimilarity among individual settlement plates. The function betadisper was used to test whether variation in dissimilarity was significantly different between north and south shores. Since NMDS analyses occasionally detect patterns where no such pattern exists, we performed a similarity profile analysis with SIMPROF [68], as implemented in R package clustsig 1.1 [69], to confirm the existence of an a priori group structure. Plots were made utilizing the R packages ggplot2 3.5.1 [70] and RColorBrewer 1.1.3 [71]. The tidyr package 1.3.1 [72] was used throughout the analysis to organize the data.
3. Results
We recorded 64 invertebrate and 3 algal taxa among all settlement plates; we included the algal taxa in our subsequent analyses because they were dominant components of biomass on six upward-facing settlement plates. We could not resolve species names for all taxa. This lack of taxonomic resolution applies to 34% of the taxa listed in Table 2, which represent 29% of the observations of taxa present on settlement plates. We found substantial variation within and among sites in the number of taxa found per settlement plate (Figure 3), with the highest taxon richness observed at Kings Point, East Island, and Point Lookout. The three sites with the lowest taxon richness were Cupsogue, Montauk, and Crane Neck. At some locations, not all plates were retrieved (Figure 1); in addition, some plates had only one taxon or no taxa settle.
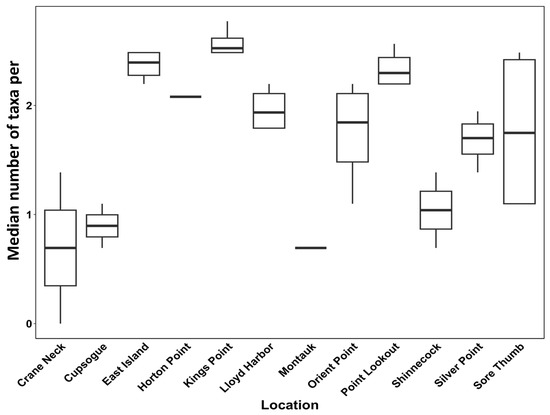
Figure 3.
The median number of taxa found per settlement plate at each location. Bold lines indicate the median values, while boxes delimit the second and third quartiles, and lines indicate the maximum and minimum values. Locations with a single bar indicate that only one plate could be analyzed at that location.
Although we observed more taxa on the north shore of Long Island compared to the south shore (Figure 4; north shore = 8.6 ± 0.83; south shore = 6.2 ± 0.93; mean ± SE), these data were not normally distributed on both shores (Shapiro–Wilk normality test; north shore W = 0.977, p = 0.89; south shore W = 0.885, p = 0.038), despite homogeneous variances (Fligner–Killeen chi-square = 0.26, p = 0.61).
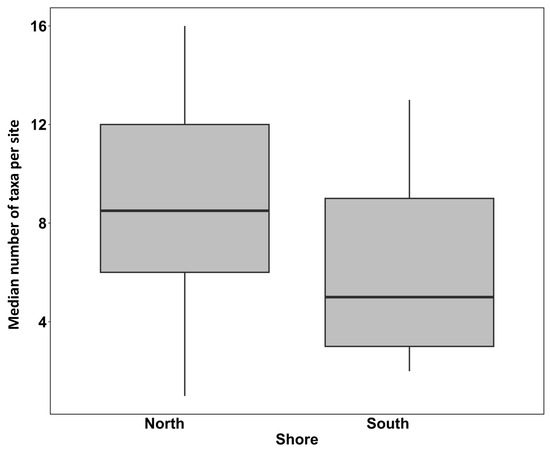
Figure 4.
The median number of taxa found per site on north and south shores of Long Island. Bold lines indicate the median values among sites, while boxes delimit the second and third quartiles, and lines indicate the maximum and minimum values.
A Wilcoxon rank sum test revealed that the observed difference in taxon richness was not statistically significant (W = 227.5, p = 0.081). Rarefaction curves of the number of taxa found across sites on the north and south shores show similar patterns of taxon accumulation (Figure 5), while the Chao1 estimates of the total taxon pools were 56 ± 9 for the north shore, 92 ± 25 for the south shore, and 117 ± 25 for the combined dataset. These data suggest that our surveys represent 57% (67/117) of the estimated taxon diversity. Similarity profile analysis revealed nine significant (p < 0.05) clusters in the dataset, confirming the existence of an a priori group structure. Despite the comparable number of taxa on north and south shores, taxon composition was significantly dissimilar between the north and south shores (Table 3; nMDS stress = 0.134, R2 = 0.116; Figure 6).
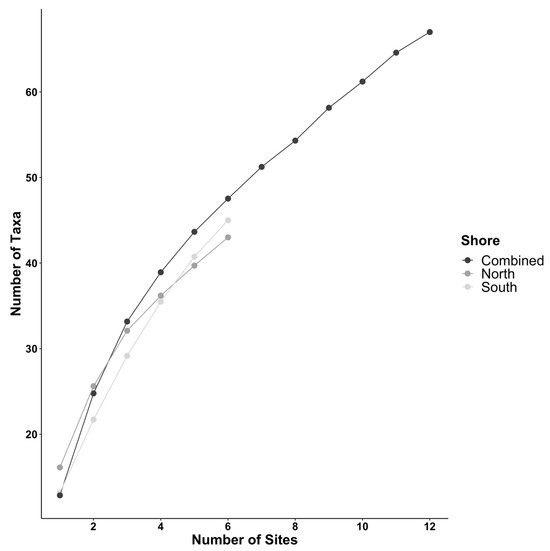
Figure 5.
Rarefaction curves describing the accumulation of unique taxa across sites on the north (dark gray) and south (light gray) shores of Long Island, as well as on both shores combined (black).

Table 3.
The results of the two-factor PERMANOVA test considering “Shore” (two levels, fixed) and “Plate Angle” (two levels, fixed) as factors to compare dissimilarity in species composition among settlement plates on the north and south shores of Long Island, NY. df: degrees of freedom; MS: mean squares; Pseudo-F: pseudo-F ratio; P (perm): p-value based on 1000 permutations.
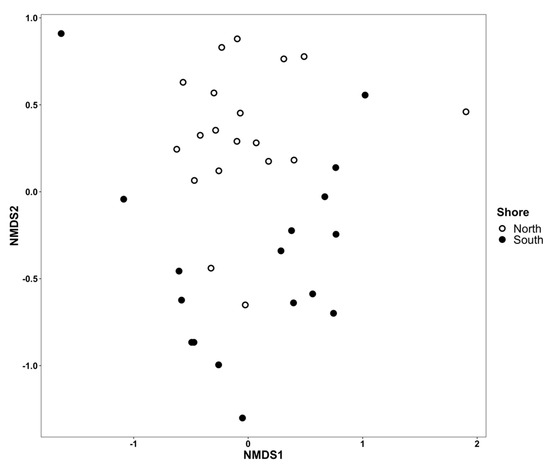
Figure 6.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling plot comparing each settlement plate’s taxonomic dissimilarity as measured by the Jaccard index (stress = 0.198, non-metric fit R2 = 0.97). Open circles represent sites on the north shore of Long Island, while filled circles represent sites on the south shore. Plate angle is not indicated since it was not found to be a significant factor (p = 0.804).
Variation in dissimilarity did not statistically differ among communities within north and south shore locations (Figure 6; betadisper: F1,35 = 1.597, p = 0.215). Taxon richness was similar on upward-facing and downward-facing plates (upward = 7.4 ± 0.9; downward 7.6 ± 0.9; mean ± SE; Wilcoxon rank sum test: W = 179, p = 0.795). Taxon composition was not significantly dissimilar between upward- and downward-facing plates (Table 3).
Of the 64 invertebrate and 3 algal taxa recorded, 23 were categorized as indigenous taxa, while 4 taxa were categorized as non-indigenous, 17 were considered cryptogenic, and 23 lacked sufficient taxonomic resolution (Table 2). The proportions of indigenous, non-indigenous, cryptogenic, and unresolved taxa were not significantly different among the locations (chi-square = 19.12, df = 33, p = 0.974; Figure 7). Only four taxa were categorized as non-indigenous, invasive species: a bryozoan (Membranipora membranacea), two tunicates (Botrylloides violaceus and Botryllus schlosseri), and a gastropod (Littorina littorea). Notably, at least one of these non-indigenous species was found at 10 of 12 locations (Figure 7).
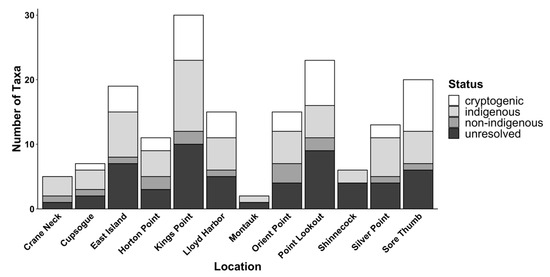
Figure 7.
Number of cryptogenic, indigenous, non-indigenous, and unresolved taxa at each location. The relative abundances of these categories were not significantly different among locations (chi-square = 19.12, df = 33, p = 0.974).
4. Discussion
Across all locations, a total of 64 invertebrate and 3 algal taxa were found; rarefaction analyses suggest these observations reflect less than 60% of the actual biodiversity of these communities. Although we could not fully resolve the taxonomic identity of every species in our study, our rarefaction analyses treated each taxon as a unique species, thereby underestimating species diversity if multiple species were contained within higher taxa. As indicated by our rarefaction analyses, increasing the number of locations sampled would likely provide more confidence in these estimates and reveal the presence of additional species. The betadisper test for the homogeneity of dispersion of dissimilarity among the north and south shores revealed no significant difference, potentially because variation was reduced by transforming the data to presence–absence.
Statistically distinct taxon composition of fouling communities was observed when comparing similarity of the north and south shores of Long Island, despite these communities having a similar taxon richness. These differences are potentially due to physical differences between habitats that remain to be quantified. North shore locations were primarily in Long Island Sound, while the south shore locations faced the Atlantic Ocean. In addition, some individual locations such as Kings Point (north shore) and Point Lookout (south shore) had greater taxon diversity. In contrast, blocks at Crane Neck (north shore) and Montauk (south shore) had very low observed numbers of taxa and were exposed habitats heavily impacted by wave action.
Our survey detected four frequently reported non-indigenous species that are often cited as invasive introduced species along New England shores [11,63]: a bryozoan (Membranipora membranacea), two tunicates (Botrylloides violaceus and Botryllus schlosseri), and a gastropod (Littorina littorea). Notably, some regionally common taxa were not found during this study, including two invasive crabs, Carcinus maenas and Hemigrapsus sanguineus, that have been previously reported from locations in Long Island Sound [10,11]. Other regionally abundant fouling organisms that were not encountered include Ciona intestinalis, Didemnum vexillum, and Diplosoma listerianum. We also did not encounter a barnacle whose range is reported to be expanding northward, Amphibalanus subalbidus (Henry, 1973), despite previous observations in our study area [11]. Our lack of observations of these taxa highlights the potential variability associated with short-term studies of biofouling communities. Settlement of marine invertebrates is highly seasonal in the western North Atlantic [73,74] and elsewhere (e.g., [75,76]). Our plates were placed in May and removed in August, meaning that we likely missed organisms that would have settled on the plates had they been placed before May or removed after August. These data therefore suggest that continued monitoring is needed to track anticipated range expansions.
5. Conclusions
Although our survey of marine invertebrate communities on settlement plates revealed differences in community composition between the north shore and south shores of Long Island, there was no significant difference in the proportion of non-indigenous taxa found at each site. Indeed, non-indigenous taxa were found at all but two locations, suggesting that non-indigenous, invasive taxa are pervasive on our shores. We suggest that future research combines the morphological identifications used here with DNA barcoding approaches [77,78] to improve our knowledge of the identity and geographic distribution of marine invertebrates. Furthermore, increasing both the number of locations surveyed and the number of settlement plates within each location is highly likely to augment the recorded biodiversity of Long Island. Additional survey methods, such as substrate scrapes, devices that would sample the settlement higher in the water column, or more frequent rapid assessments, could also be employed to increase the recorded invertebrate biodiversity of Long Island. Creating a better understanding of what species surround us is the first step in protecting our ecosystems and is crucial for the detection, prevention, and management of marine invasive species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.A.H. and R.W.T.; methodology, K.A.H. and R.W.T.; formal analysis, R.W.T.; investigation, J.H.R. and K.A.H.; resources, K.A.H. and R.W.T.; data curation, E.R., J.H.R. and R.W.T.; writing—original draft preparation, E.R.; writing—review and editing, K.A.H. and R.W.T.; visualization, E.R., K.A.H. and R.W.T.; supervision, K.A.H. and R.W.T. project administration, K.A.H. and R.W.T.; funding acquisition, K.A.H. and R.W.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation grant number EF-2025009 to K.A.H. and EF-2025121 to R.T.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The majority of data used in this paper were originally collected by J.H.R. as part of his high school research course. We would therefore like to thank North Shore High School (Glen Head, NY) and Molly Mordechai for supporting J.H.R. in this research. Without their support, the collection and initial analysis of the data by J.H.R. would not have been possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Burivalova, Z.; Butler, R.A.; Wilcove, D.S. Analyzing Google search data to debunk myths about the public’s interest in conservation. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 16, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, A.; González-Roca, F.; Portflitt-Toro, M.; Fortt, J.A.; Luna, N.; Cerda, O.; Carranza, D.M.; Squeo, F.A.; Gaymer, C.F. National trends in the biodiversity interest in digital media. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 101, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellard, C.; Genovesi, P.; Jeschke, J.M. Global patterns in threats to vertebrates by biological invasions. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20152454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueñas, M.A.; Ruffhead, H.J.; Wakefield, N.H.; Roberts, P.D.; Hemming, D.J.; Diaz-Soltero, H. The role played by invasive species in interactions with endangered and threatened species in the United States: A systematic review. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 3171–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, K.; Holt, R.H.F.; Sharp, R.; Griffith, K.; Roche, R.C.; Newstead, R.G.; Wyn, G.; Jenkins, S.R. Capacity, capability and cross-border challenges associated with marine eradication programmes in Europe: The attempted eradication of an invasive non-native ascidian, Didemnum vexillum in Wales, United Kingdom. Mar. Policy 2014, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boero, F.; Bonsdorff, E. A conceptual framework for marine biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Mar. Ecol. Evol. Perspect. 2007, 28, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsch, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Dasgupta, R.; Mader, A.D.; Johnson, B.A.; Kumar, P. Invasive alien species and local communities in socio-ecological production landscapes and seascapes: A systematic review and analysis. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 112, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadchatheeswaran, S.; Branch, G.M.; Moloney, C.L.; Robinson, T.B. Impacts of alien e‘cosystem engineers’ overwhelm interannual and seasonal shifts in rocky-shore community composition on Marcus Island South Africa. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 40, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.; Carey, D.; Carolton, J.; Cerrato, R.; Dam, H.; DioGiovanni, R.; Elphick, C.; Frisk, M.; Gobler, C.; Hice, L.; et al. Biology and ecology of Long Island Sound. In Long Island Sound: Prospects for the Urban Sea; Latimer, J.S., Tedesco, M.A., Swanson, R.L., Yarish, C., Stacey, P.E., Garza, C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 583. [Google Scholar]
- Pederson, J.; Byllock, R.; Carlton, J.; Dijkstra, J.; Dobroski, N.; Dyrynda, P.; Fisher, R.; Harris, L.; Hobbs, N.; Lambert, G.; et al. Marine Invaders in the Northeast: Rapid Assessment Survey of Non-Native and Native Marine Species of Floating Dock Communities; MIT Sea Grant College Program: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pederson, J.; Carlton, J.; Bastidas, C.; David, A.; Grady, S.; Green-Gavrielidis, L.; Hobbs, N.V.; Kennedy, C.; Knack, J.; McCuller, M.; et al. 2019 Rapid Assessment Survey of marine bioinvasions of southern New England and New York, USA, with an overview of new records and range expansions. Bioinvasions Rec. 2021, 10, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Lacheur, E.A.; Sammons, J.C. Tides and Currents in Long Island and Block Island Sounds; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1932; Volume 174.
- Parker, C.A.; O’Reilly, J.E. Oxygen deplietion in Long Island Sound: A historical perspective. Estuaries 1991, 14, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, M.M.; Vlahos, P. Reducing Hypoxia in an Urban Estuary Despite Climate Warming. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.-C. Sea level variability in Long Island Sound. Estuaries 1990, 13, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, A.M.; Heer, A.K.; Rice, S.S.; Buonaiuto, F.; Tommaso, D.M.; Bocamazo, L.M.; Couch, S.A.; McDonald, J.M. South Shore of Long Island, New York Regional Sediment Management Investigation: An Overview of Challenges and Opportunities; US Army Corps of Engineers, Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, L.W. A Practical Guide to the Marine Animals of Northeastern North America; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, H.M.; Bennett, D.; May, P.; Churchill, L.; Venti, C. Marine Animals of Southern New England and New York: Identification Keys to Common Nearshore and Shallow Water Macrofauna. In State Geological and Natural History Survey of Connecticut; Department of Environmental Protection: Hartford, CT, USA, 1995; p. 349. [Google Scholar]
- Board, W.E. World Register of Marine Species. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Villalobos-Guerrero, T.F.; Bakken, T. Revision of the Alitta virens species complex (Annelida: Nereididae) from the North Pacific Ocean. Zootaxa 2018, 4483, 201–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight-Jones, P.; Perkins, T.H. A revision of Sabella, Bispira and Stylomma (Polychaeta: Sabellidae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 123, 385–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnich, R.; Fiege, D. Revision of the genus Harmothoe Kinberg, 1856 (Polychaeta: Polynoidae) in the Northeast Atlantic. Zootaxa 2009, 2014, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida-Zavala, J.R.; ten Hove, H.A. Revision of Hydroides Gunnerus, 1768 (Polychaeta: Serpulidae) from the Western Atlantic Region. Beaufortia 2002, 52, 103–178. [Google Scholar]
- Mackie, A.S.Y.; Pleijel, F. A review of the Melinna cristata-species group (Polychaeta: Ampharetidae) in the northeastern Atlantic. Mitteilungen Aus Dem Hambg. Zool. Mus. Und Inst. 1995, 92, 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, K. The polychaete worms, definitions and keys to the orders, families and genera. Nat. Hist. Mus. Los Angeles Cty. Sci. Ser. 1977, 28, 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbig, B. Family Nereididae Johnston, 1845. In Taxonomic Atlas of the Benthic Fauna of the Santa Maria Basin and Western Santa Barbara Channel. 4—The Annelida Part 1. Oligochaeta and Polychaeta: Phyllodocida (Phyllodocidae to Paralacydoniidae); Blake, J.A., Hilbig, B., Eds.; Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 301–327. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; Harris, L.H. Parasabella Bush, 1905, replacement name for the polychaete genus Demonax Kinberg, 1867 (Annelida, Polychaeta, Sabellidae). Zookeys 2010, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meissner, K.; Bick, A.; Götting, M. Arctic Pholoe (Polychaeta: Pholoidae): When integrative taxonomy helps to sort out barcodes. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 179, 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Verrill, A.E.; Smith, S.I. Report Upon the Invertebrate Animals of Vineyard Sound and the Adjacent Waters, with an Account of the Physical Characters of the Region; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1873; pp. 295–778.
- Hartman, O. Polychaetous annelids. Part VI. Paraonidae, Magelonidae, Longosomidae, Ctenodrilidae, and Sabellariidae. Allan Hancock Pac. Exped. 1944, 10, 311–389. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaud, M.R. Species of Spiochaetopterus (Polychaeta, Chaetopteridae) in the Atlantic-Mediterranean biogeographic area. SARSIA 1998, 83, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, J.L.; Karaman, G.S. The families and genera of marine gammaridean Amphipoda (except marine gammaroids). Part 1. Rec. Aust. Mus. Suppl. 1991, 13, 1–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.A.; Lowry, J.K. A phylogeny and a new classification of the Corophiidea Leach, 1814 (Amphipoda). J. Crustacean Biol. 2003, 23, 443–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitombo, F.B. Phylogenetic analysis of the Balanidae (Cirripedia, Balanomorpha). Zool. Scr. 2004, 33, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.B. Occurrence and distribution of the tanaid crustacean Leptochelia savignyi on the calcareous hydrozoan Millepora complanata. B. Mar. Sci. 1998, 63, 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Wethey, D.S. Biogeography, competition, and microclimate:: The barnacle Chthamalus fragilis in New England. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusca, R.C. Phylogeny, evolution and biogeography of the marine isopod subfamily Idoteinae (Crustacea: Isopoda: Idoteidae). Trans. San Diego Soc. Nat. Hist 1984, 20, 99–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.B. Shrimps, Lobsters, and Crabs of the Atlantic Coast of the Eastern United States, Maine to Florida; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; p. 550. [Google Scholar]
- Ryland, J.S.; Porter, J.S. The identity of Alcyonidium gelatinosum (Linnaeus, 1761) (Bryozoa: Ctenostomatida). J. Nat. Hist. 2003, 37, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryland, J.S.; Hayward, P.J. Marine Flora and Fauna of the Northeast United States: Erect Bryozoa; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 1–48.
- Waeschenbach, A.; Vieira, L.M.; Reverter-Gil, O.; Souto-Derungs, J.; Nascimento, K.B.; Fehlauer-Ale, K.H. A phylogeny of Vesiculariidae (Bryozoa, Ctenostomata) supports synonymization of three genera and reveals possible cryptic diversity. Zool. Scr. 2015, 44, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, P. World List of Bryozoa. Biflustra tenuis (Desor, 1848). Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=878544 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Bock, P. World List of Bryozoa. Callopora craticula (Alder, 1856). Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=111193 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Bock, P. World List of Bryozoa. Cryptosula pallasiana (Moll, 1803). Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=111343 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Bock, P. World List of Bryozoa. Einhornia crustulenta (Pallas, 1766). Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=467577 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Winston, J.E.; Hayward, P.J. The Marine Bryozoans of the Northeast Coast of the United States: Maine to Virginia. Va. Mus. Nat. Hist. Mem. 2012, 11, 1–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D.P.; Taylor, P.D.; Bigey, F.P. Phylum Bryozoa: Moss animals, sea mats, lace corals. In New Zealand Inventory of Biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia; Gordon, D.P., Ed.; Canterbury University Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2009; pp. 271–297. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Mukai, H.; Watanabe, H. Studies on Japanese styelid ascidians II. A new species of the genus Botrylloides and redescription of B. violaceus Oka. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1981, 26, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hargitt, C.W. New and little known hydroids of Woods Hole. Biol. Bull. 1909, 17, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.E. New species, new records and redescriptions of Thecate hydroids (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa: Leptothecata) from Southern Australia. Zootaxa 2011, 3122, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, S.D.; Gershwin, L.; Brook, F.J.; Pugh, P.; Dawson, E.W.; Ocaña, O.V.; Vervoort, W.; Williams, G.; Watson, J.E.; Opresko, D.M.; et al. Phylum Cnidaria: Corals, medusae, hydroids, myxozoans. In New Zealand Inventory of Biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia; Gordon, D.P., Ed.; Canterbury University Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2009; pp. 59–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon, J.; Boero, F. Synopsis of the families and genera of the Hydromedusae of the world, with a list of the worldwide species. Thalass. Salent 2000, 24, 47–296. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, R. Calyptraeidae from the northeast Pacific (Gastropoda: Caenogastropoda). Zoosymposia 2019, 13, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, T.J. Cobscook Bay inventory: A historical checklist of marine invertebrates spanning 162 years. Northeast. Nat. 2004, 11, 261–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.G. The comparative morphology, phylogeny and evolution of the gastropod family Littorinidae. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1989, 324, 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, R.; Buchsbaum, R.; Roman, C.; Chandler, M. Inventory of intertidal marine habitats, Boston Harbor Islands national park area. Northeast. Nat. 2005, 12, 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, W.D. Natural History of the Marine Sponges of Southern New England. B. Peabody Mus. Nat. Hi. 1958, 12, 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieson, A.C.; Dawes, C.J. Seaweeds of the Northwest Atlantic; University of Massachusetts Press: Amherst, MA, USA, 2017; p. 798. [Google Scholar]
- Carlton, J.T. Biological invasions and cryptogenic species. Ecology 1996, 77, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pociecha, A.; Solarz, W.; Najberek, K.; Wilk-Wozniak, E. Native, alien, cosmopolitan, or cryptogenic? A framework for clarifying the origin status of rotifers. Aquat. Biol. 2015, 24, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBIF. The Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Available online: http://www.gbif.org (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Fofonoff, P.W.; Ruiz, G.M.; Steves, B.; Simkanin, C.; Carlton, J.T. National Exotic Marine and Estuarine Species Information System. Available online: http://invasions.si.edu/nemesis (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Carlton, J.T. A Checklist of the Introduced Marine and Estuarine Organisms on the Coast of Maine, U.S.A.; Williams College: Mystic, CT, USA, 2004; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Team, R. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. RStudio. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-7. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Gorley, R.N. Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: Similarity profiles and biota-environment linkage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, D.; Christman, M. Significant Cluster Analysis (clustsig). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/src/contrib/Archive/clustsig/clustsig_1.1.tar.gz (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–260. [Google Scholar]
- Neuwirth, E. RColorBrewer: ColorBrewer Palettes. R Package Version 1.1-2. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RColorBrewer (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Wickham, H. tidyr: Tidy Messy Data. R Package Version 1.1.3. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tidyr (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Bullard, S.G.; Davis, C.V.; Shumway, S.E. Seasonal patterns of ascidian settlement at an aquaculture facility in the damariscotta river, maine. J. Shellfish. Res. 2013, 32, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, J.F.; Whitlatch, R.B.; Osman, R.W. Effects of temperature on the recruitment phenology and niche overlap of shallow epifaunal assemblages in southern New England. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 489, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bowden, D.A. Seasonality of recruitment in Antarctic sessile marine benthos. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 297, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Broitman, B.R.; Blanchette, C.A.; Menge, B.A.; Lubchenco, J.; Krenz, C.; Foley, M.; Raimondi, P.T.; Lohse, D.; Gaines, S.D. Spatial and temporal patterns of invertebrate recruitment along the West Coast of the United States. Ecol. Monogr. 2008, 78, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, K.C.; Corlett, R.T. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in ecology and conservation: Opportunities, challenges and prospects. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, M.; Knowlton, N. DNA barcoding and metabarcoding of standardized samples reveal patterns of marine benthic diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).