Development and Evaluation of a Passive Mechanism for a Transfemoral Prosthetic Knee That Prevents Falls during Running Stance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of the Proposed Prosthetic Knee
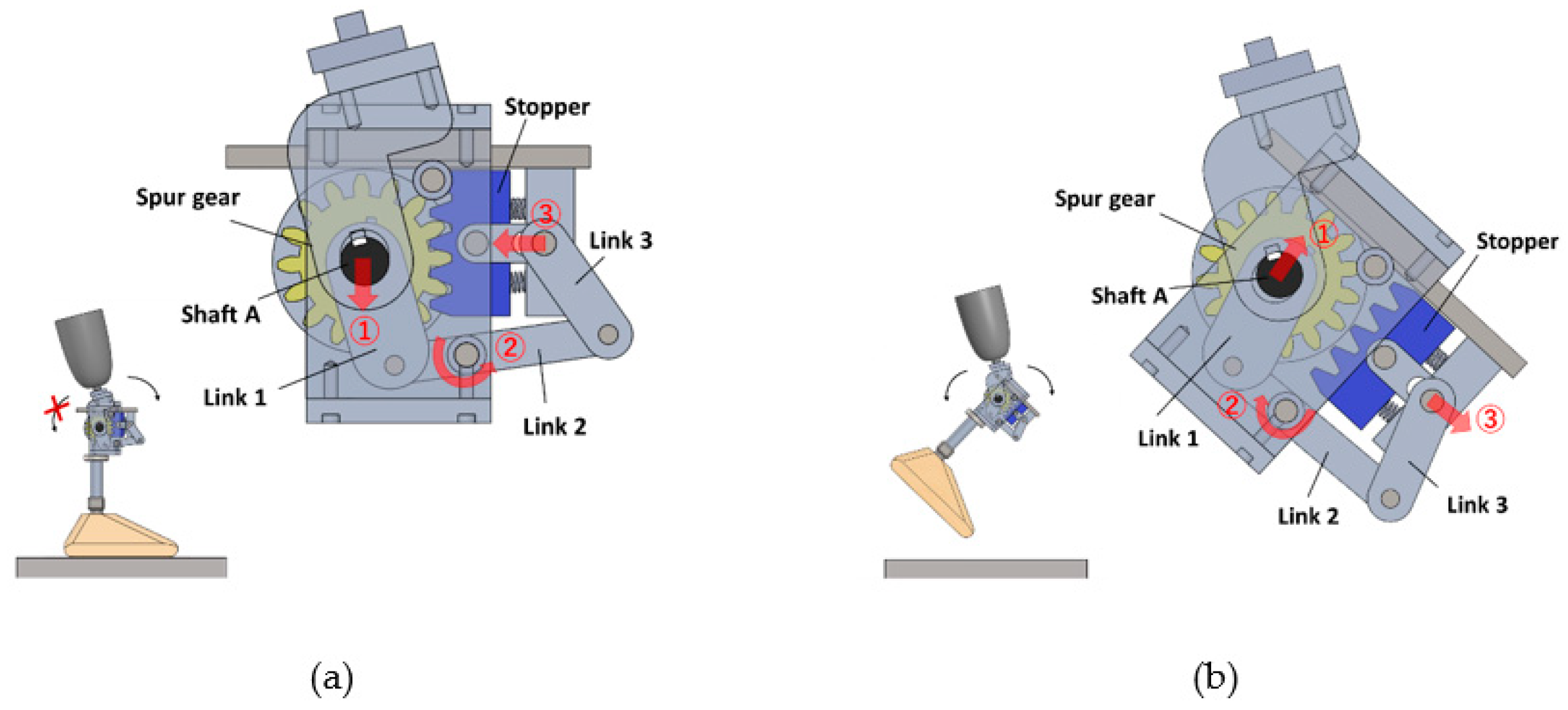
2.1. Structural Design
2.2. Flexion Lock Mechanism
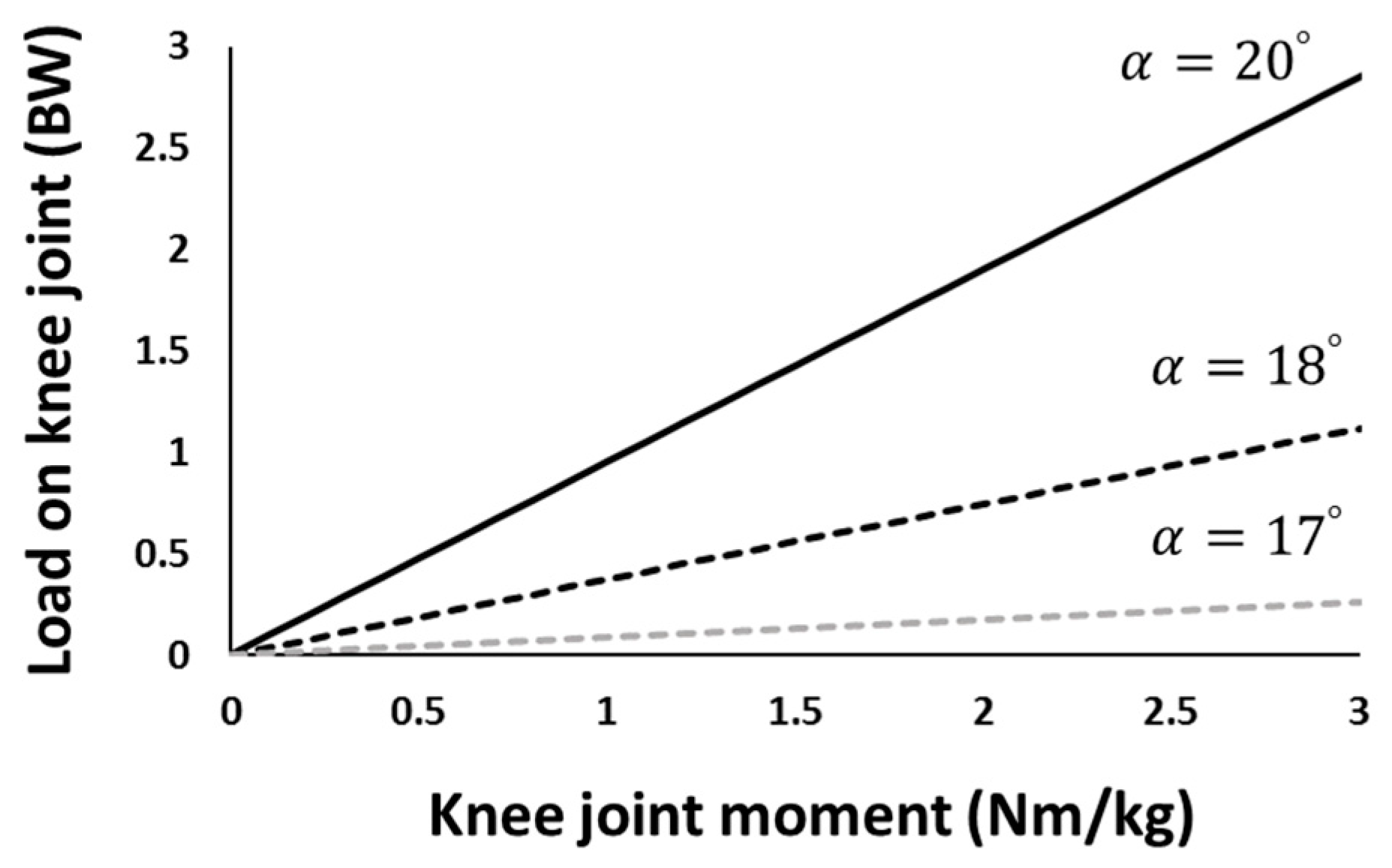
2.3. Mechanical Analysis
3. Evaluation Experiment
3.1. Methods
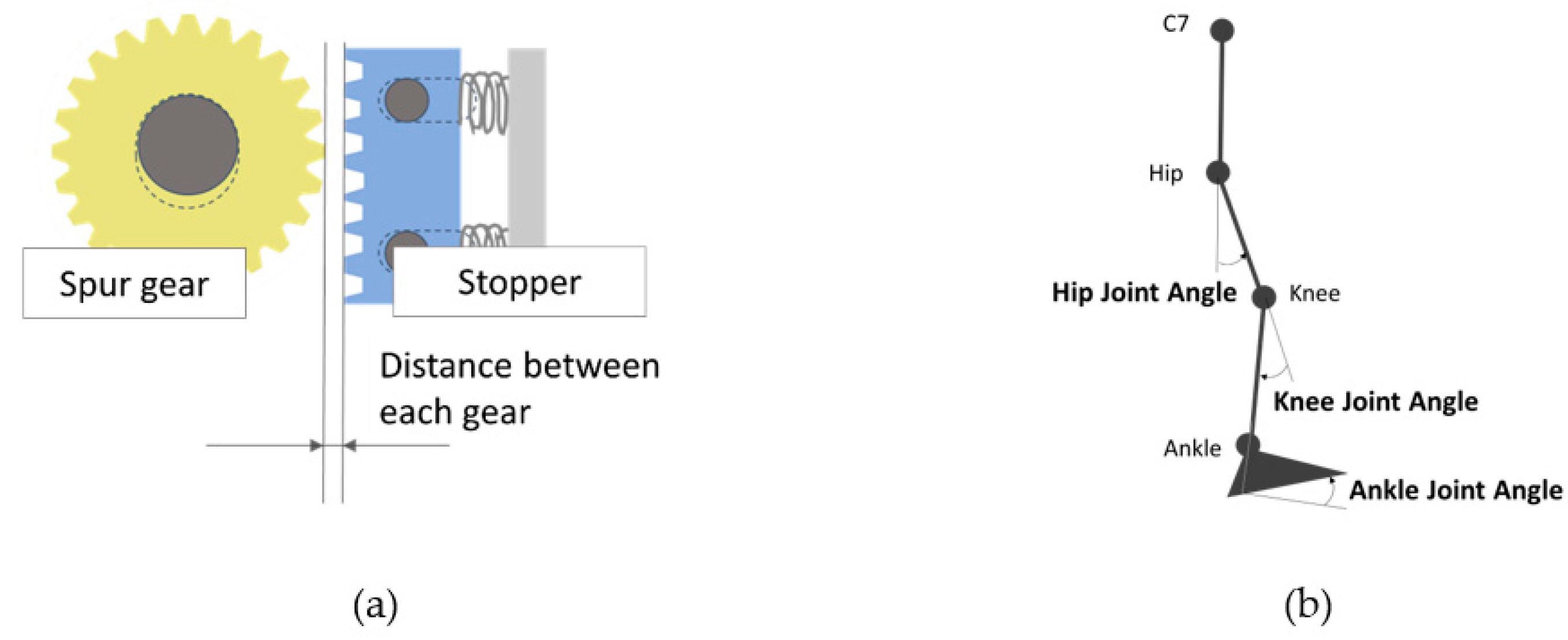
3.1.1. Experimental Procedure and Data Collection
3.1.2. Data Analysis
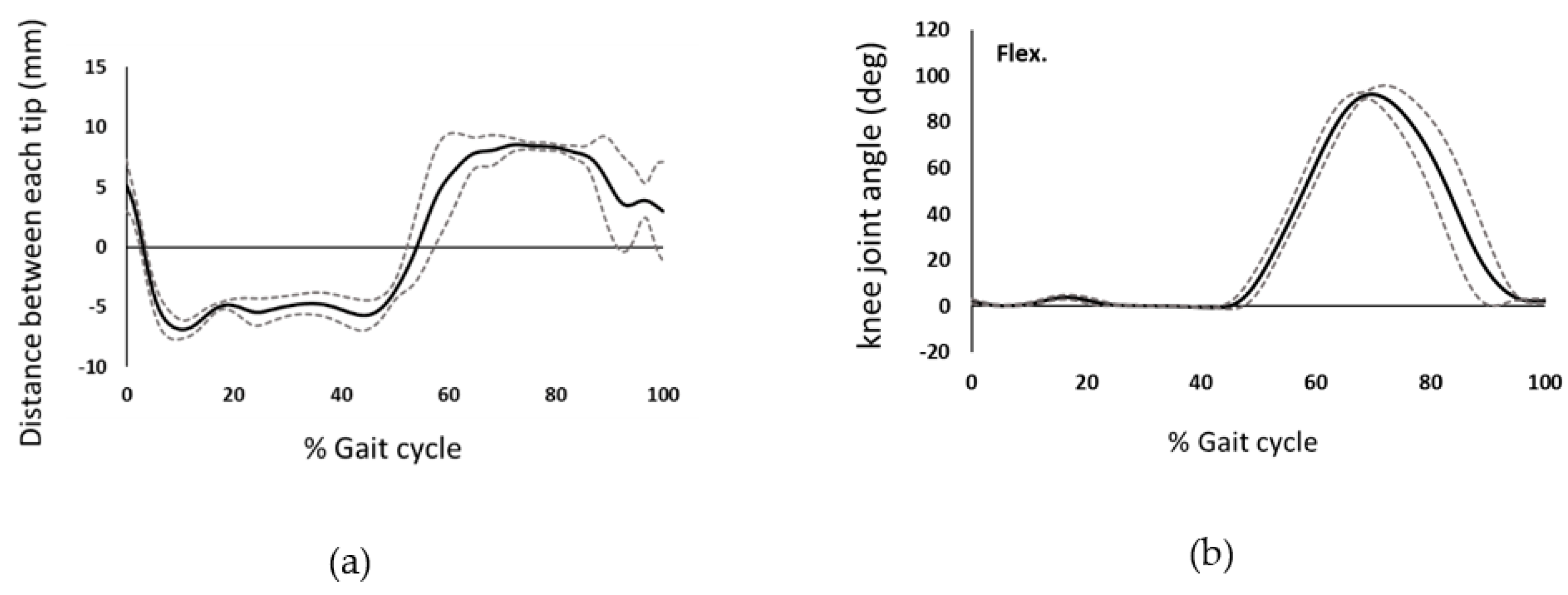
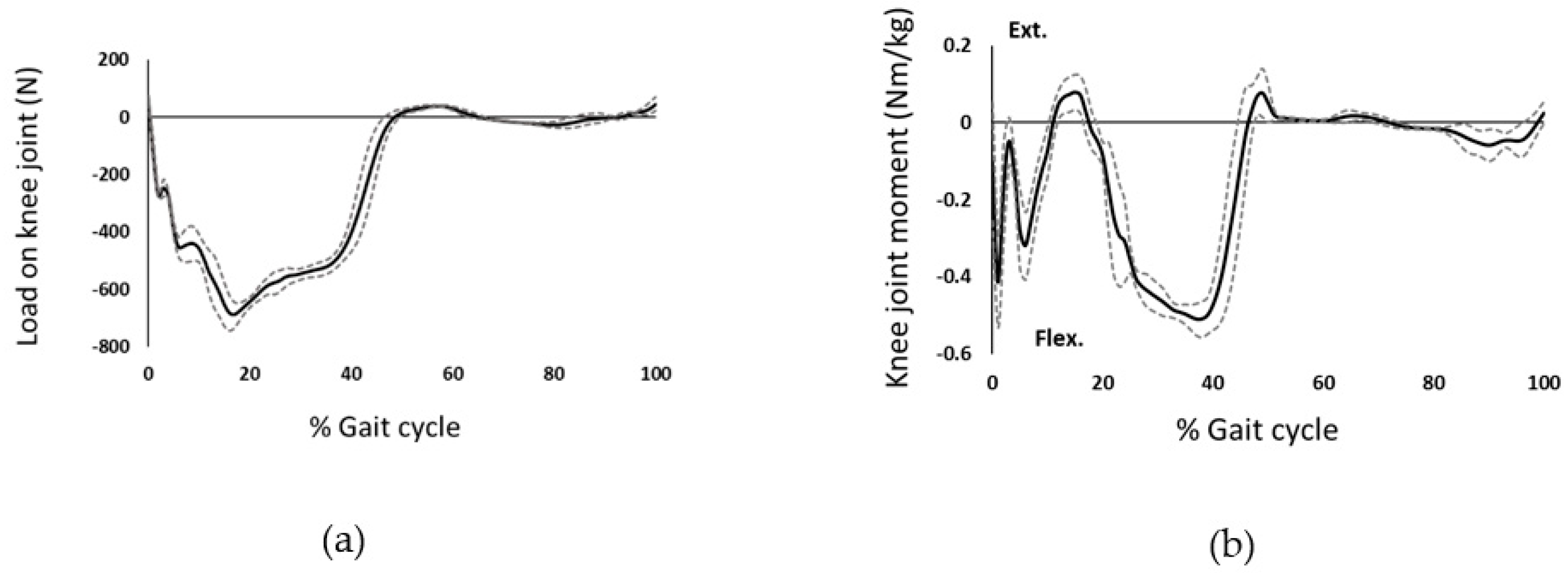
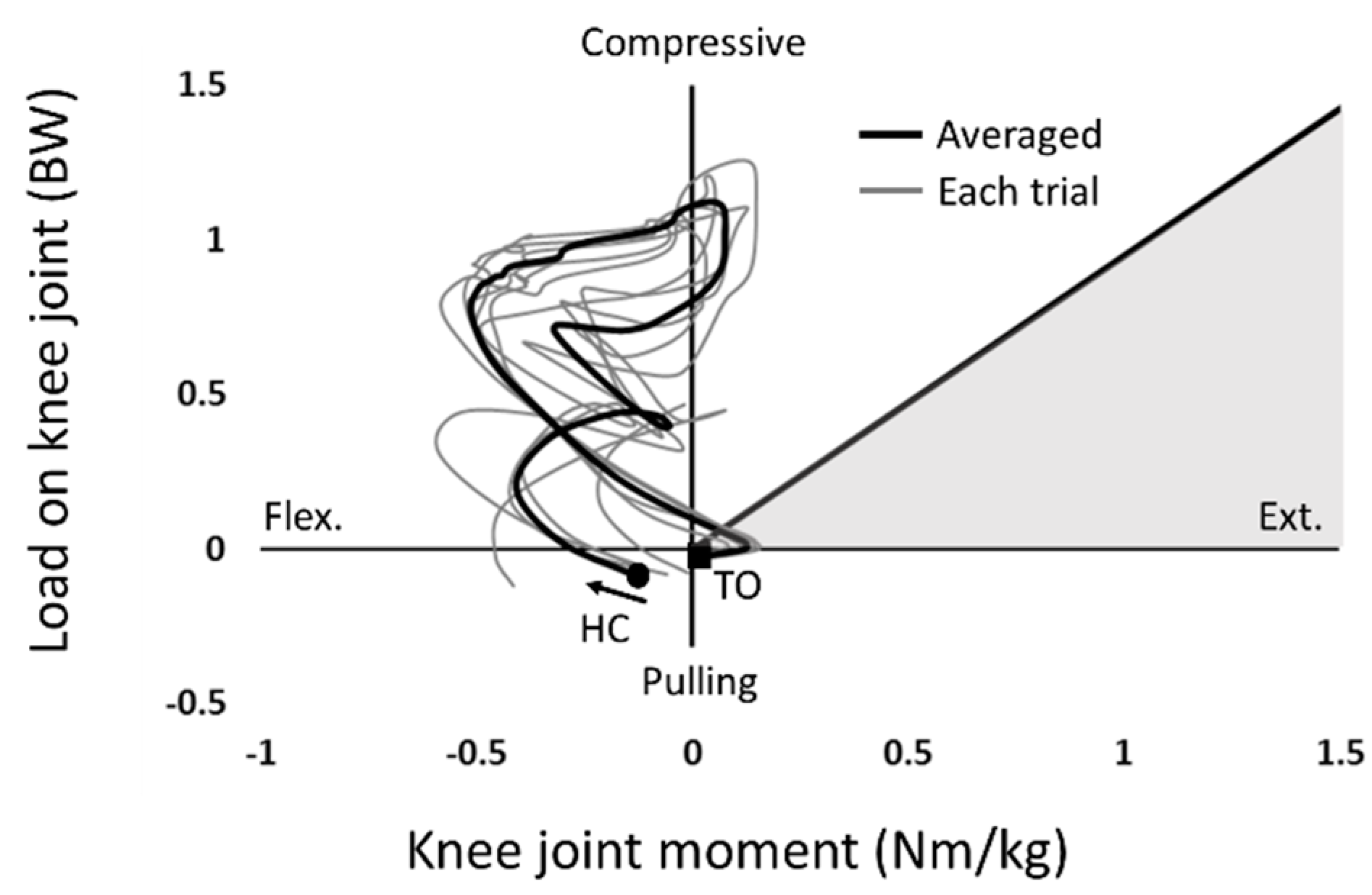
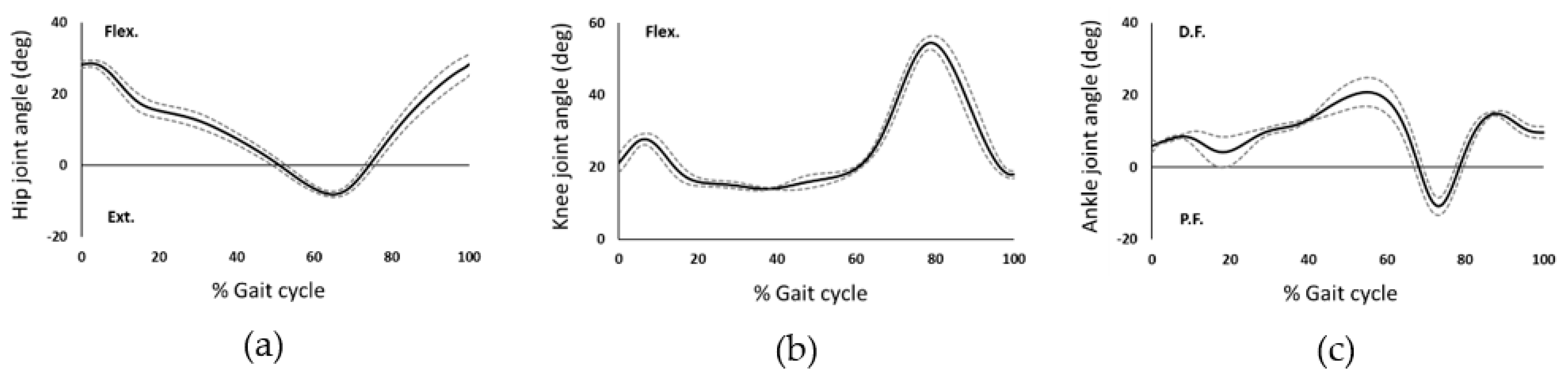
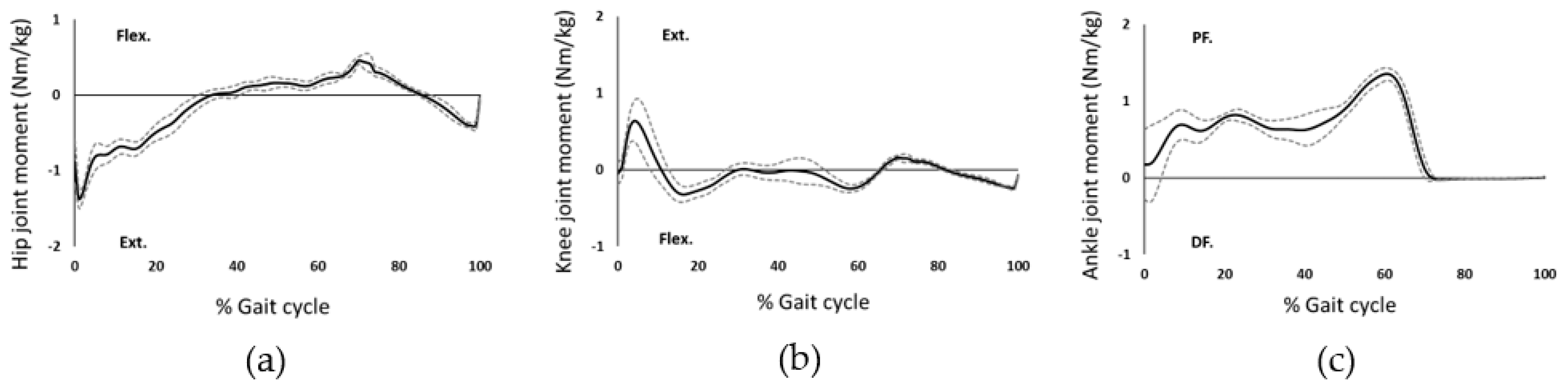
3.2. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hisano, G.; Kobayashi, Y.; Murai, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakashima, M.; Hobara, H. Factors associated with a risk of prosthetic knee buckling during walking in unilateral transfemoral amputees. Gait Posture 2020, 77, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.C.; Speechley, M.; Deathe, B. The Prevalence and Risk Factors of Falling and Fear of Falling Among Lower Extremity Amputees. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, A.D.; Orendurff, M.S.; Klute, G.K.; McDowell, M.L.; Pecoraro, J.A.; Shofer, J.; Czerniecki, J.M. Kinematic and kinetic comparisons of transfemoral amputee gait using C-Leg and Mauch SNS prosthetic knees. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2006, 43, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, J.G. Sprint knematics of athletes with lower-limb amputations. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, K.R.; Levine, J.A.; Brey, R.H.; Iverson, B.K.; McCrady, S.K.; Padgett, D.J.; Joyner, M.J. Gait and balance of transfemoral amputees using passive mechanical and microprocessor-controlled prosthetic knees. Gait Posture 2007, 26, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, Y.; Hashizume, S.; Murai, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takemura, H.; Hobara, H. Joint moments during sprinting in unilateral transfemoral amputees wearing running-specific prostheses. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio039206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulea, T.C.; Kobetic, R.; To, C.S.; Audu, M.L.; Schnellenberger, J.R.; Triolo, R.J.A. Variable Impedance Knee Mechanism for Controlled Stance Flexion During Pathological Gait. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highsmith, M.J.; Kahle, J.T.; Miro, R.M.; Mengelkoch, L.J. Bioenergetic differences during walking and running in transfemoral amputee runners using articulating and non-articulating knee prostheses. Technol. Innov. 2016, 18, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murabayashi, M.; Inoue, K. Development of a passive mechanism of transfemoral prosthetic knee preventing falls during running. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 23–26 September 2020; pp. 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobara, H.; Sakata, H.; Amma, R.; Hisano, G.; Hashizume, S.; Baum, B.S.; Usui, F. Loading rates in unilateral transfemoral amputees with running-specific prostheses across a range of speeds. Clin. Biomech. 2020, 75, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, M.; Schmalz, T.; Blumentritt, S. Comparative biomechanical analysis of current microprocessor-controlled prosthetic knee joints. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willwacher, S.; Herrmann, V.; Heinrich, K.; Funken, J.; Strutzenberger, G.; Goldmann, J.-P.; Braunstein, B.; Brazil, A.; Irwin, G.; Potthast, W.; et al. Sprint Start Kinetics of Amputee and Non-Amputee Sprinters. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, T.; Bellmann, M.; Sottong, J.; Altenburg, B. Advantages and Limitations of New Sports Prosthetic Components Developed for Running in Lower Limb Amputees. Sports Med. Rehabil. J. 2017, 2, 1018. [Google Scholar]
- Harandi, V.J.; Ackland, D.C.; Haddara, R.; Lizama, L.E.C.; Graf, M.; Galea, M.P.; Lee, P.V.S. Gait compensatory mechanisms in unilateral transfemoral amputees. Med. Eng. Phys. 2020, 77, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, K.R.; Frittoli, S.; Frigo, C.A. Gait Asymmetry of Transfemoral Amputees Using Mechanical and Microprocessor-Controlled Prosthetic Knees. Clin. Biomech. (Bristol Avon) 2012, 27, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkett, B.; Smeathers, T.; Barker, T. Walking and running inter-limb asymmetry for Paralympic trans-femoral amputees, a biomechanical analysis. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2003, 27, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mâaref, K.; Martinet, N.; Grumillier, C.; Ghannouchi, S.; André, J.M.; Paysant, J. Kinematics in the terminal swing phase of unilateral transfemoral amputees: Microprocessor-controlled versus swing-phase control prosthetic knees. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damsgaard, M.; Rasmussen, J.; Christensen, S.T.; Surma, E.; Zee, M. Analysis of musculoskeletal systems in the AnyBody Modeling System. Simul. Modeling Pract. Theory 2006, 14, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, V.; Fluita, R.; Pellikaana, P.; Krogt, M.M.; Janssen, D.; Damsgaard, M.; Vigneron, L.; Feilkas, T.; Koopman, H.F.J.M.; Verdonschot, N. TLEM 2.0–A comprehensive musculoskeletal geometry dataset for subject-specific modeling of lower extremity. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentink, E.C.; Koopman, H.F.J.M.; Stramigioli, S.; Rietman, J.S.; Veltink, P.H. Variable stiffness actuated prosthetic knee to restore knee buckling during stance: A model study. Medical. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gard, S.A. Use of Quantitative Gait Analysis for the Evaluation of Prosthetic Walking Performance. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2006, 18, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, F.; Rezaeian, T.; Narimani, R.; Dinan, P.H. Kinematic and Dynamic Analysis of the Gait Cycle of Above-Knee Amputees. Sci. Iran. 2006, 13, 261–271. [Google Scholar]




| Muscles | Muscle Group |
|---|---|
| Gluteus maximus | GMAX |
| Gluteus medius | GMED |
| Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembraneous | HAM |
| Iliacus, Psoas | IL |
| Vastus lateralis, Vastus medialis, Vastus intermedius | VAS |
| Rectus femoris | RF |
| Soleus | SOL |
| Gastrocnemius | GAS |
| Tibialis anterior | TA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murabayashi, M.; Mitani, T.; Inoue, K. Development and Evaluation of a Passive Mechanism for a Transfemoral Prosthetic Knee That Prevents Falls during Running Stance. Prosthesis 2022, 4, 172-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4020018
Murabayashi M, Mitani T, Inoue K. Development and Evaluation of a Passive Mechanism for a Transfemoral Prosthetic Knee That Prevents Falls during Running Stance. Prosthesis. 2022; 4(2):172-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurabayashi, Mai, Takuya Mitani, and Koh Inoue. 2022. "Development and Evaluation of a Passive Mechanism for a Transfemoral Prosthetic Knee That Prevents Falls during Running Stance" Prosthesis 4, no. 2: 172-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4020018
APA StyleMurabayashi, M., Mitani, T., & Inoue, K. (2022). Development and Evaluation of a Passive Mechanism for a Transfemoral Prosthetic Knee That Prevents Falls during Running Stance. Prosthesis, 4(2), 172-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4020018





