Full-Arch, Implant-Fixed Complete Dentures in Monolithic Zirconia and Titanium: A Digital Workflow to Maximize Cost Effectiveness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Technique
- The patient receives an immediate loaded, full-arch, implant-supported fixed provisional prosthesis, which makes her/him feel comfortable, both functionally and aesthetically.
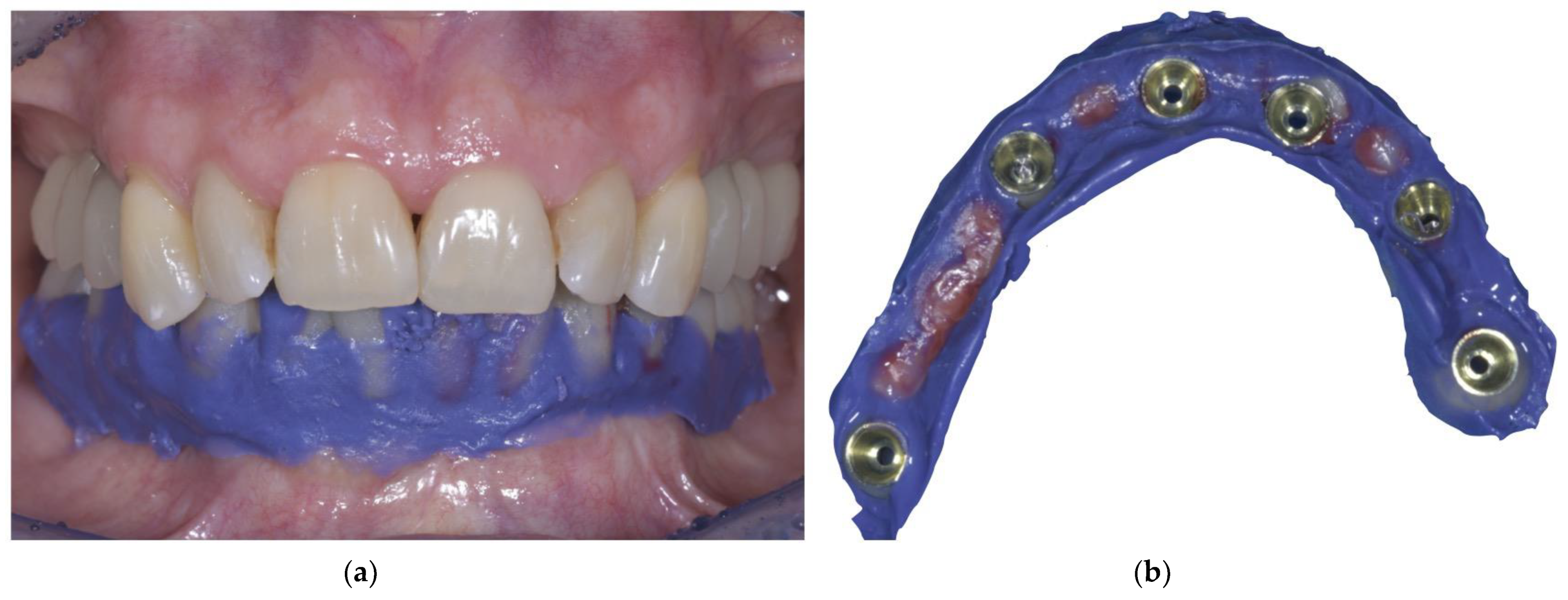
- When the implants reach osteointegration and the soft tissues are stable, an analogic impression is taken to cast a master model, and the provisional prosthesis is relined with the impression material to obtain a perfect impression of the soft tissues (Figure 1a,b).
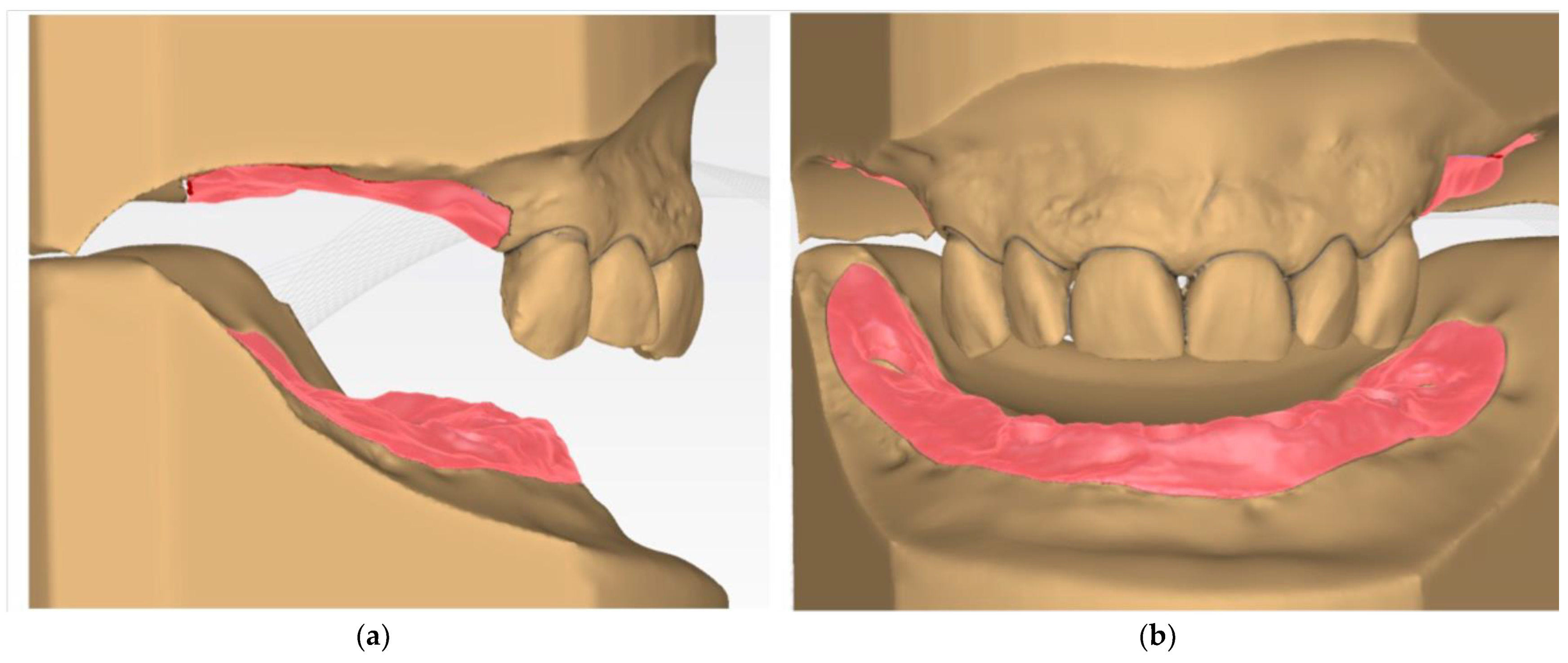
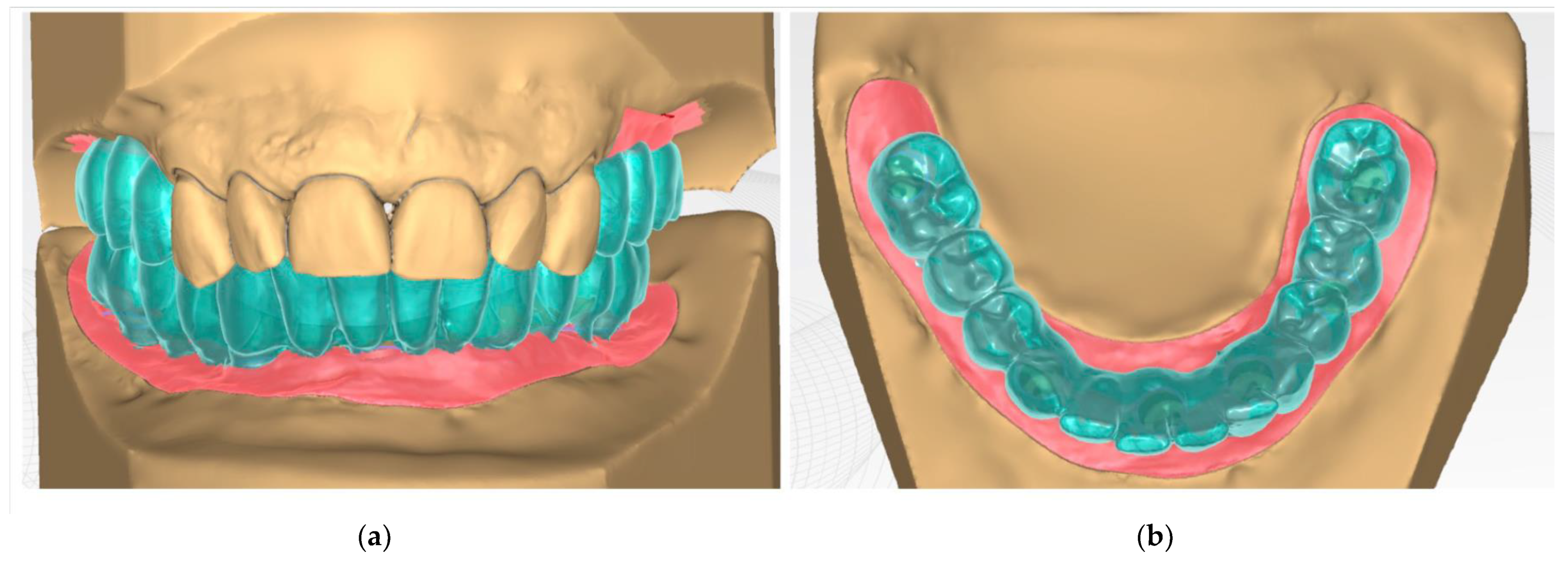
- Digital wax-up is performed with a CAD-CAM software (Figure 4a,b).
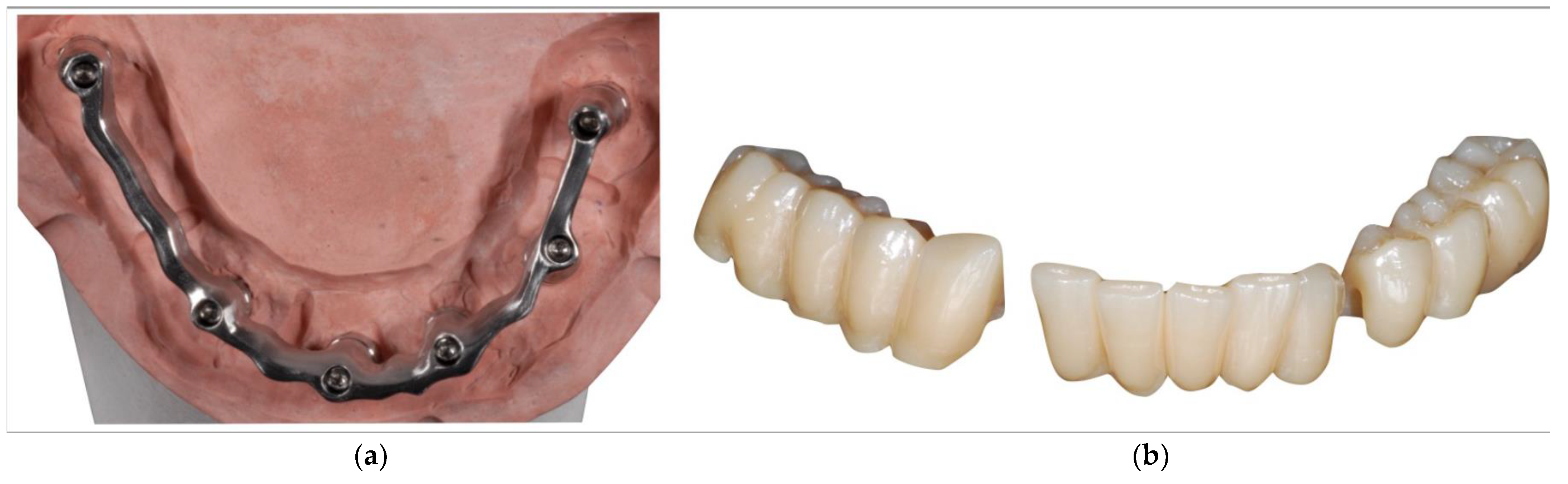
- After checking the projects, the components—a titanium bar and an aesthetic coating part in monolithic zirconia—are milled with a CAM milling machine. In the case shown as an example of zirconia, Katana STML (Kuraray Noritake, Japan) was used (Figure 5a,b).
- The precision of the components on the analogic models is verified, paying specific attention to the passivity of the titanium bar on the implants.
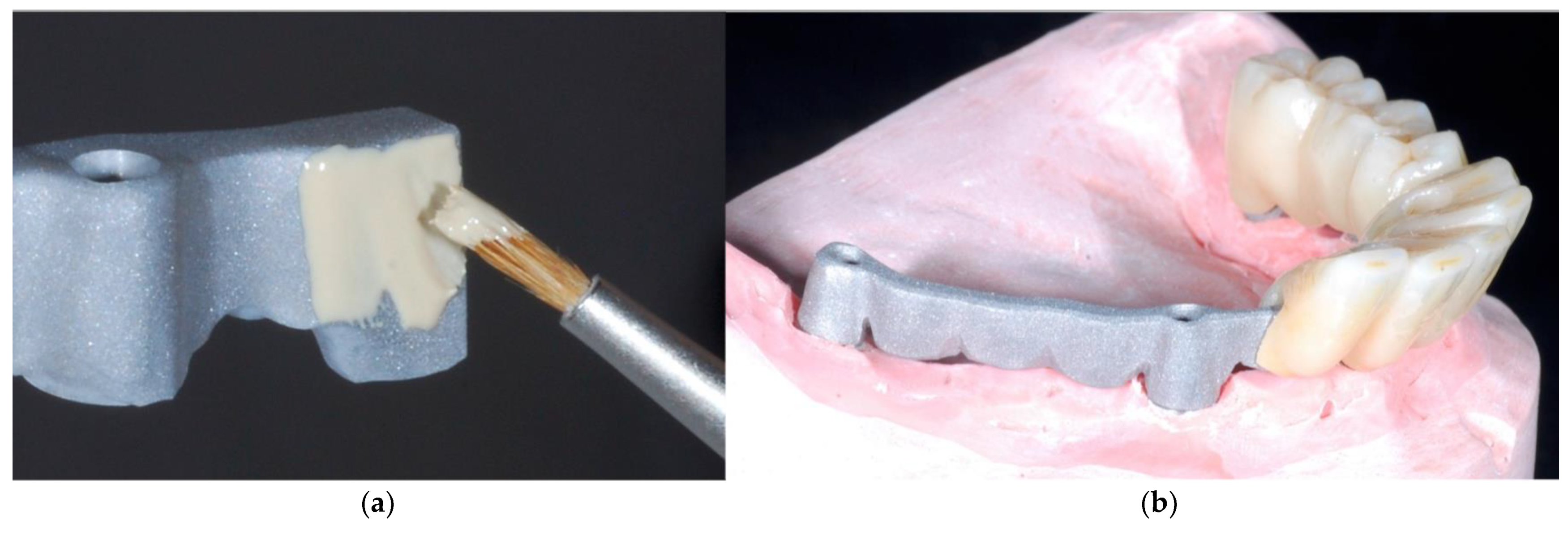
- Stains and glaze are applied to the aesthetic component (Figure 6a,b).
- The monolithic zirconia component is cemented onto the titanium bar using a dual-curing luting composite (Figure 7a,b).
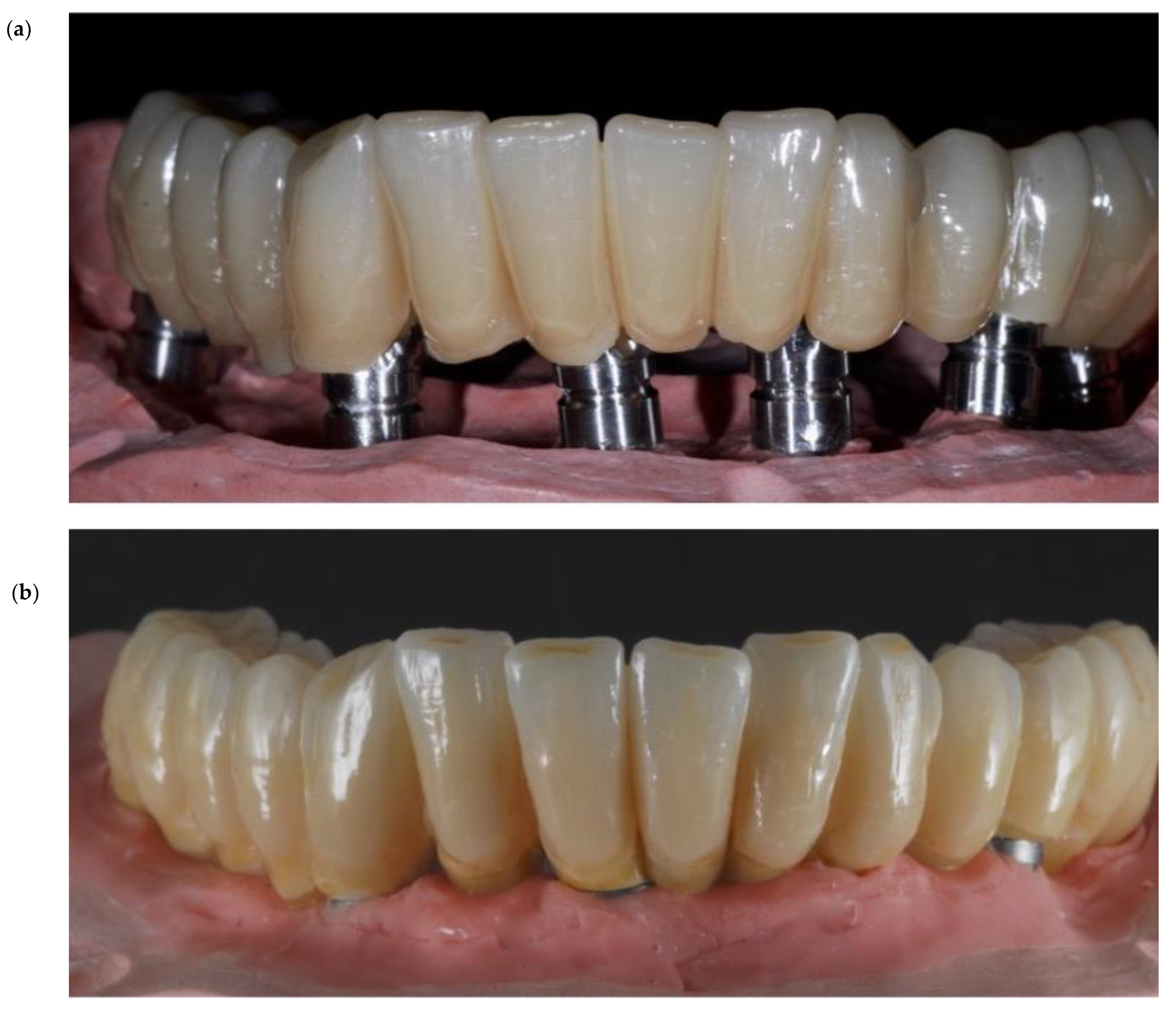
- The prosthesis in the patient’s mouth is checked by fixing it on the implants (Figure 8a,b).
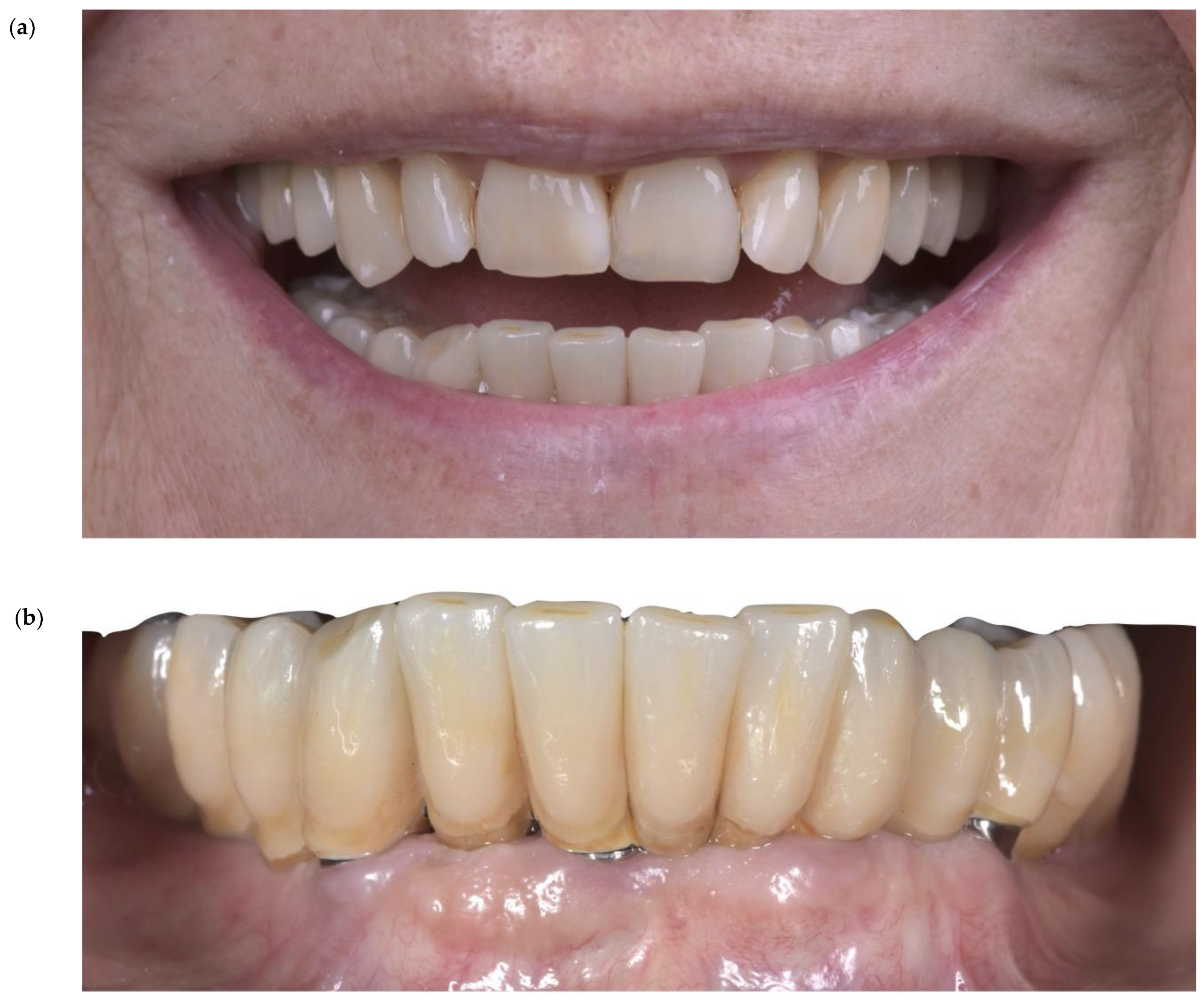
- The screw access hole is closed with Teflon and composite.
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, A.; Felton, D.A.; Jemt, T.; Koka, S. Rehabilitation of Edentulism and Mortality: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polzer, I.; Schimmel, M.; Biffar, R. Edentulism as part of the general health problems of elderly adults. Int. J. Dent. 2010, 60, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Att, W.; Stappert, C. Implant therapy to improve quality of life. Quintessence Int. 2003, 34, 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum, T.R.; Guichet, D.L.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Wadhwani, C.P.K. Clinician preferences for complete-arch fixed implant-supported prostheses: A survey of the membership of the Pacific Coast Society for Prosthodontics. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 669–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbush, C.A.; Kanawati, A.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Hinrichs, J.E. Patient-related and financial outcomes analysis of conventional full-arch rehabilitation versus the all-on-4 concept: A cohort study. Implant Dent. 2014, 23, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Noort, R. The future of dental devices is digital. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Ferrari, M.; Gallucci, G.O.; Wittneben, J.-G.; Brägger, U. Digital technology in fixed implant prosthodontics. Periodontology 2017, 73, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barootchi, S.; Askar, H.; Ravidà, A.; Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Travan, S.; Wang, H.L. Long-term clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness of full-arch implant-supported zirconia-based and metal-acrylic fixed dental prostheses: A retrospective analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2020, 35, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Chochlidakis, K.; Kang, K.; Chen, Y.W.; Alghfeli, A.; Kudara, Y.; Weber, H.P. Digital Workflow for Implant Rehabilitation with Double Full-Arch Monolithic Zirconia Prostheses. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontonasaki, E.; Rigos, A.E.; Ilia, C.; Istantsos, T. Monolithic zirconia: An update to current knowledge. Optical properties, wear, and clinical performance. Dent. J. 2017, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.S.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, Y.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Shin, S.W.; Huh, J.B. A study on the in-vitro wear of the natural tooth structure by opposing zirconia or dental porcelain. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2010, 2, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarano, A.; Stoppaccioli, M.; Casolino, T. Zirconia crowns cemented on titanium bars using CAD/CAM: A five-year follow-up prospective clinical study of 9 patients. BMC Oral Heal. 2019, 19, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noè, G.; Toffoli, A.; Bonfiglioli, R.; Macaluso, G.M.; Manfredi, E. Full-Arch, Implant-Fixed Complete Dentures in Monolithic Zirconia and Titanium: A Digital Workflow to Maximize Cost Effectiveness. Prosthesis 2022, 4, 73-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4010008
Noè G, Toffoli A, Bonfiglioli R, Macaluso GM, Manfredi E. Full-Arch, Implant-Fixed Complete Dentures in Monolithic Zirconia and Titanium: A Digital Workflow to Maximize Cost Effectiveness. Prosthesis. 2022; 4(1):73-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoè, Gaetano, Andrea Toffoli, Roberto Bonfiglioli, Guido Maria Macaluso, and Edoardo Manfredi. 2022. "Full-Arch, Implant-Fixed Complete Dentures in Monolithic Zirconia and Titanium: A Digital Workflow to Maximize Cost Effectiveness" Prosthesis 4, no. 1: 73-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4010008
APA StyleNoè, G., Toffoli, A., Bonfiglioli, R., Macaluso, G. M., & Manfredi, E. (2022). Full-Arch, Implant-Fixed Complete Dentures in Monolithic Zirconia and Titanium: A Digital Workflow to Maximize Cost Effectiveness. Prosthesis, 4(1), 73-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis4010008







