A Parametric Study on a Dental Implant Geometry Influence on Bone Remodelling through a Numerical Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
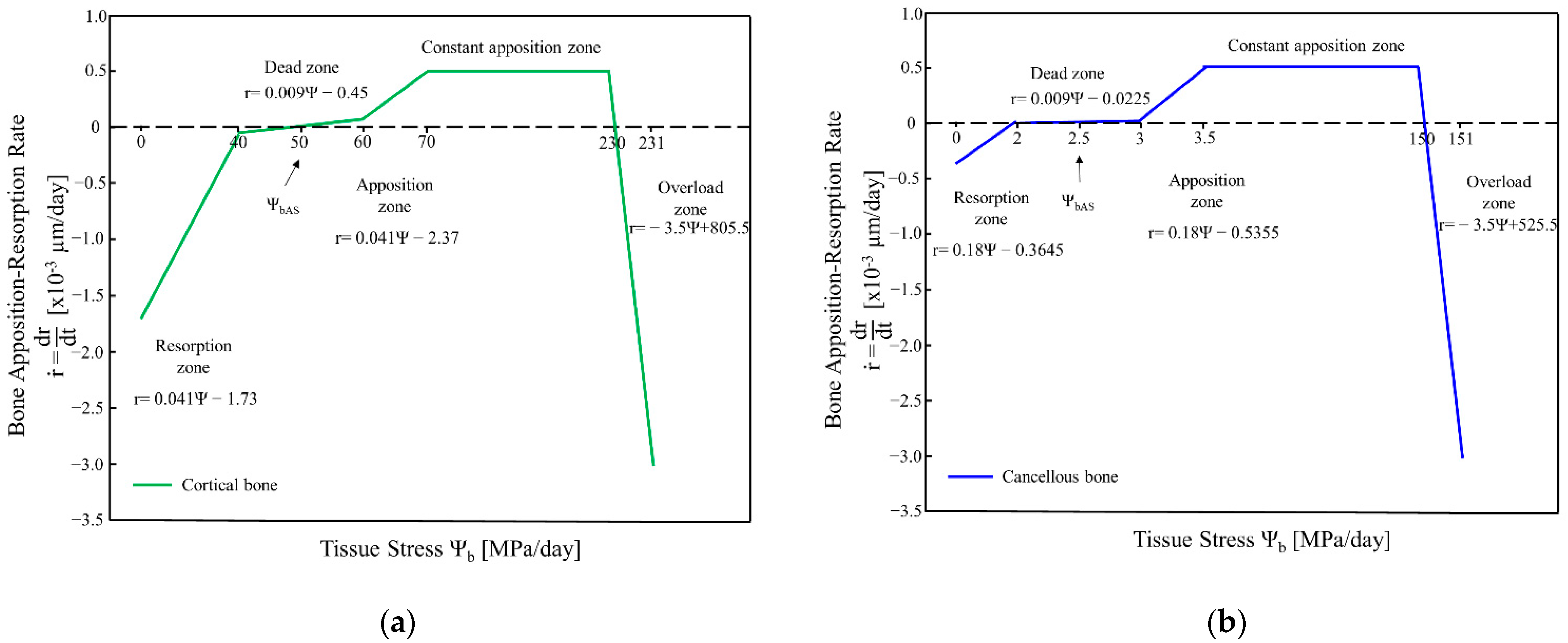
2. Bone Remodelling Algorithm
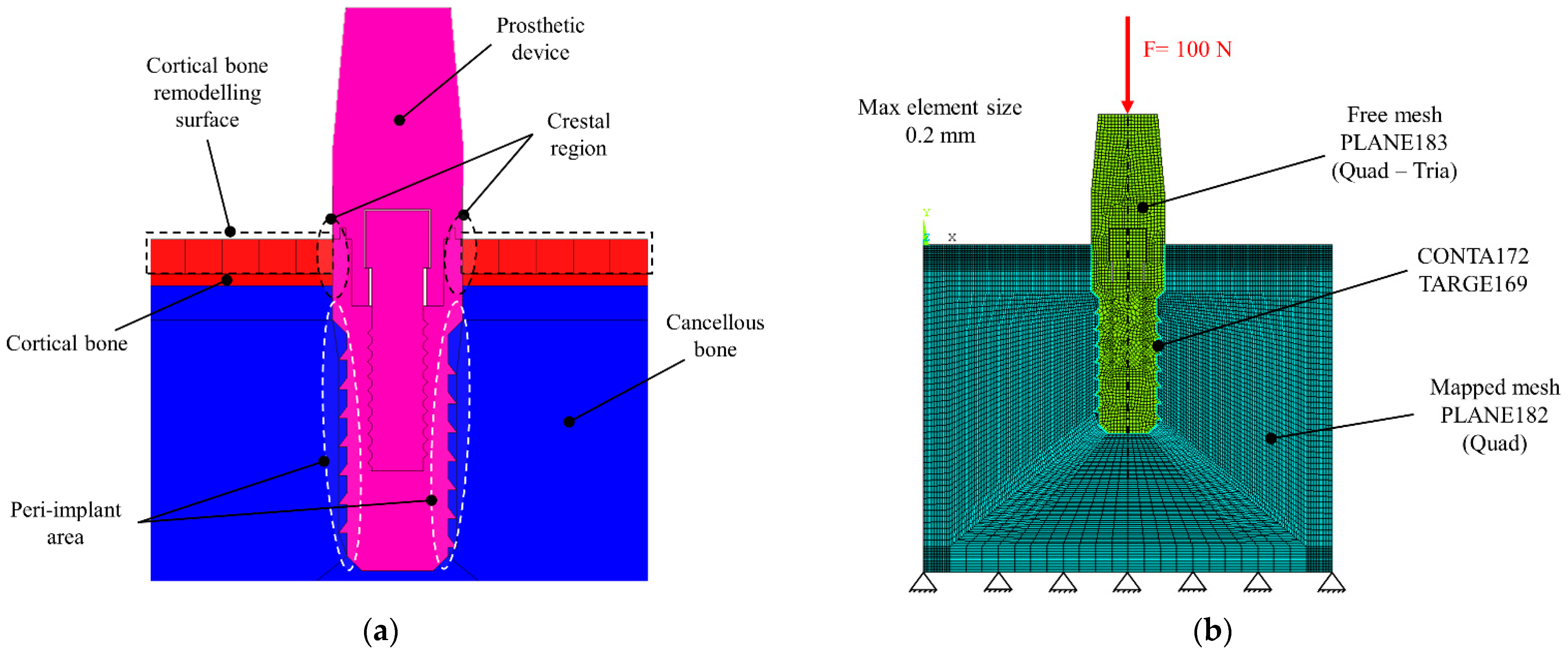
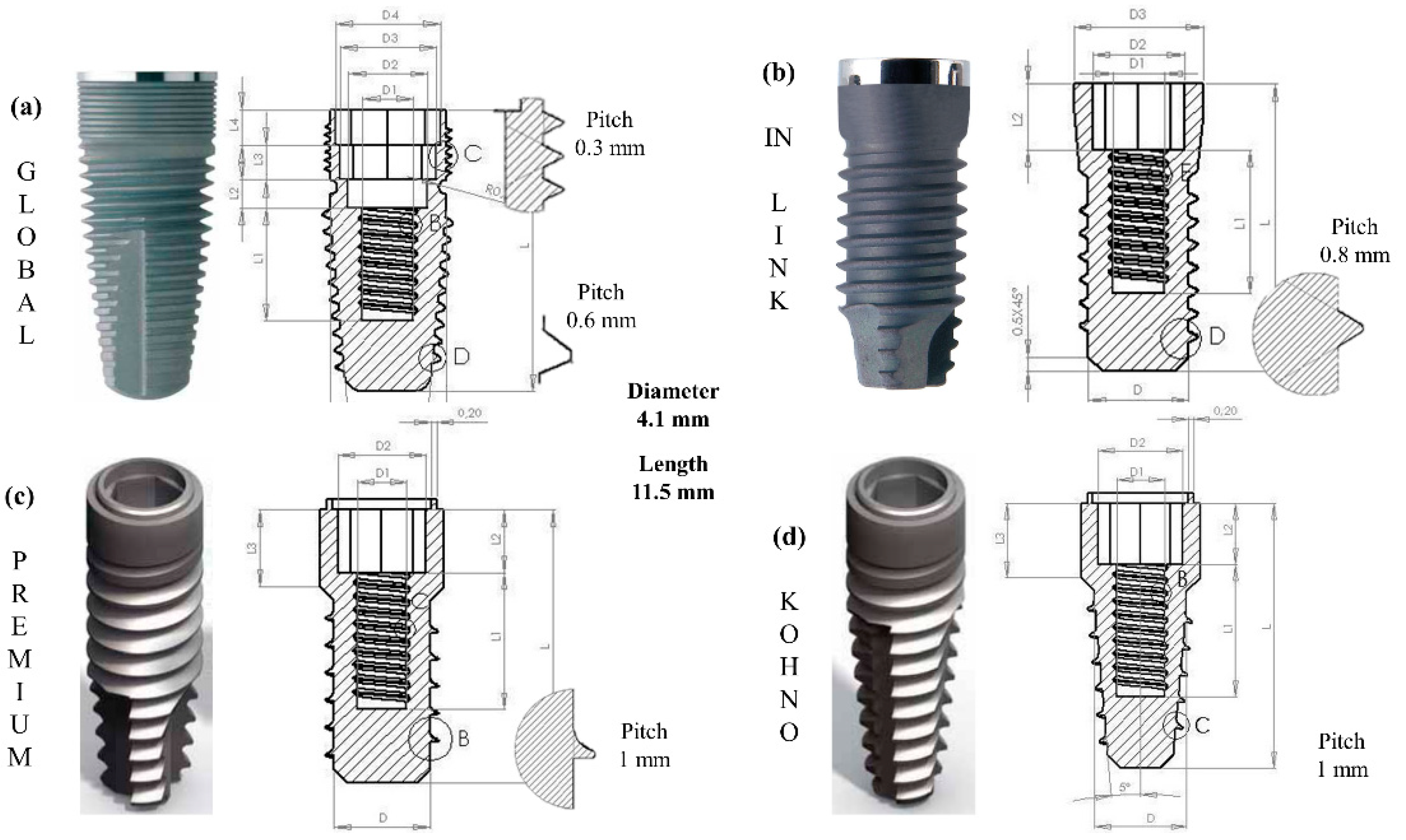
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
- Internal remodelling through a change of density in cancellous and cortical bone;
- External remodelling by moving the points on the external surface of cortical bone;
- Stresses on the peri-implant and crestal areas;
- Stability of the implants by vertical and horizontal micromovements.
4.1. Internal Remodelling
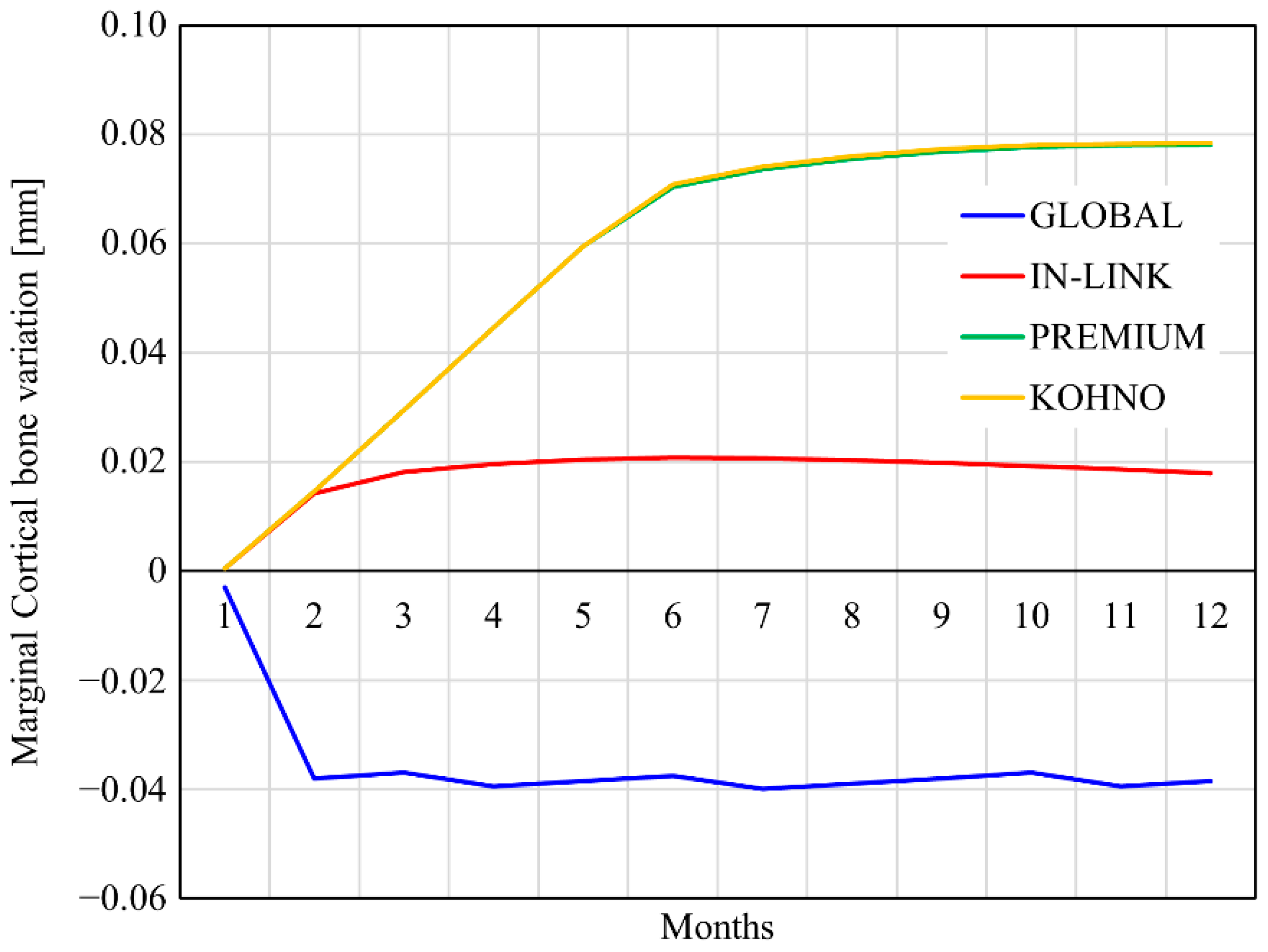
4.2. External Remodelling
4.3. Stress on the Peri-Implant Area
4.4. Stability of the Implants
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schenk, R.K.; Buser, D. Osseointegration: A reality. Periodontology 2000 1998, 17, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, H.-A.; Albrektsson, T.; Brȧnemark, P.-I. Structural aspects of the interface between tissue and titanium implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukhil, I. Biology of wound healing. Periodontology 2000 2000, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A.R. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.A. Current interpretations of the osseointegrated response: Clinical significance. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1993, 6, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsson, T.; Chrcanovic, B.; Östman, P.-O.; Sennerby, L. Initial and long-term crestal bone responses to modern dental implants. Periodontology 2000 2016, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, I.; Lekholm, U.; Holm, S.; Kultje, C. Evaluation of patient and implant characteristics as potential prognostic factors for oral implant failures. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2005, 20, 220–230. [Google Scholar]
- Marquezan, M.; Osório, A.; Sant’Anna, E.; Souza, M.M.; Maia, L. Does bone mineral density influence the primary stability of dental implants? A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 23, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.-I.; Kim, S.-G.; Oh, J.-S.; Jeong, M.-A. Consideration of Various Bone Quality Evaluation Methods. Implant. Dent. 2013, 22, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Rotta, R.F.; De Oliveira, R.C.G.; Dias, D.R.; Lindh, C.; Leles, C.R. Bone tissue microarchitectural characteristics at dental implant sites part 2: Correlation with bone classification and primary stability. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 25, e47–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froum, S.J.; Rosen, P.S.; Clem, D.S., III. Response to ‘on crestal/marginal bone loss around dental implants’. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 407–409. [Google Scholar]
- Hof, M.; Pommer, B.; Zukic, N.; Vasak, C.; Lorenzoni, M.; Zechner, W. Influence of Prosthetic Parameters on Peri-Implant Bone Resorption in the First Year of Loading: A Multi-Factorial Analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 17, e183–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J. The Law of Bone Remodeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Brunski, J.B. In Vivo Bone Response to Biomechanical Loading at the Bone/Dental-Implant Interface. Adv. Dent. Res. 1999, 13, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, S.; Werke, M. The implant thread as a retention element in cortical bone: The effect of thread size and thread profile: A finite element study. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormianer, Z.; Matalon, S.; Block, J.; Kohen, J. Dental Implant Thread Design and the Consequences on Long-Term Marginal Bone Loss. Implant. Dent. 2016, 25, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, B.C.; Bateli, M.; Ben Rahal, G.; Christmann, M.; Vach, K.; Kohal, R. Does Oral Implant Design Affect Marginal Bone Loss? Results of a Parallel-Group Randomized Controlled Equivalence Trial. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andrade, C.L.; Carvalho, M.A.; Bordin, D.; da Silva, W.J.; Del Bel Cury, A.A.; Sotto-Maior, B.S. Biomechanical Behavior of the Dental Implant Macrodesign. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.R.; Desai, M.S.; Katti, G.; Karthikeyan, I. Evaluation of design parameters of eight dental implant designs: A two-dimensional finite element analysis. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2012, 15, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, I.N.; Dhanasekar, B.; Lingeshwar, D.; Gupta, L. Implant crest module: A review of biomechanical considerations. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2012, 23, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.W.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, Y.; Oh, Y.A.; Lee, J.H.; You, H.K. Implant fracture failure rate and potential associated risk indicators: An up to 12-year retrospective study of implants in 5124 patients. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñarrocha, M.; Palomar, M.; Sanchis, J.M.; Guarinos, J.; Balaguer, J. Radiologic study of marginal bone loss around 108 dental implants and its relationship to smoking, implant location, and morphology. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 861–867. [Google Scholar]
- Prosper, L.; Redaelli, S.; Pasi, M.; Zarone, F.; Radaelli, G.; Gherlone, E.F. A randomized prospective multicenter trial evaluating the platform-switching technique for the prevention of postrestorative crestal bone loss. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Cicciù, M.; Cervino, G.; Terranova, A.; Risitano, G.; Raffaele, M.; Cucinotta, F.; Santonocito, D.; Fiorillo, L. Prosthetic and Mechanical Parameters of the Facial Bone under the Load of Different Dental Implant Shapes: A Parametric Study. Prosthesis 2019, 1, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkaya, D.; Muftu, S.; Muftu, A. Evaluation of load transfer characteristics of five different implants in compact bone at different load levels by finite elements analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramanti, E.; Cervino, G.; Lauritano, F.; Fiorillo, L.; D’Amico, C.; Sambataro, S.; Denaro, D.; Famà, F.; Ierardo, G.; Polimeni, A.; et al. FEM and Von Mises Analysis on Prosthetic Crowns Structural Elements: Evaluation of Different Applied Materials. Sci. World J. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, G.; Romeo, U.; Lauritano, F.; Bramanti, E.; Fiorillo, L.; D’Amico, C.; Milone, D.; Laino, L.; Campolongo, F.; Rapisarda, S.; et al. Fem and Von Mises Analysis of OSSTEM® Dental Implant Structural Components: Evaluation of Different Direction Dynamic Loads. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicciù, M.; Cervino, G.; Milone, D.; Risitano, G. FEM Analysis of Dental Implant-Abutment Interface Overdenture Components and Parametric Evaluation of Equator® and Locator® Prosthodontics Attachments. Materials 2019, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicciu, M.; Bramanti, E.; Matacena, G.; Guglielmino, E.; Risitano, G. FEM evaluation of cemented-retained versus screw-retained dental implant single-tooth crown prosthesis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 817–825. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, L.; Prendergast, P.J. Bone remodelling algorithms incorporating both strain and microdamage stimuli. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, E.; Ortiz-Hernández, M.; Perez, R.A.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Cerrolaza, M.; Gil, F.J. Crestal module design optimization of dental implants: Finite element analysis and in vivo studies. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, T.; Ayukawa, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sakai, N.; Matsuzaki, M.; Masuzaki, T.; Haraguchi, T.; Ogino, Y.; Koyano, K. Effect of post-osseointegration loading magnitude on the dynamics of peri-implant bone: A finite element analysis and in vivo study. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 63, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C. Effect of Integration Patterns Around Implant Neck on Stress Distribution in Peri-Implant Bone: A Finite Element Analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2016, 26, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qing, L.; Colin, M.; Yubo, F. Numerical simulation of dental bone remodeling induced by implant-supported fixed partial denture with or without cantilever extension. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2013, 29, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotto-Maior, B.S.; Mercuri, E.G.F.; Senna, P.M.; Assis, N.M.S.P.; Francischone, C.E.; Cury, A.A.D.B. Evaluation of bone remodeling around single dental implants of different lengths: A mechanobiological numerical simulation and validation using clinical data. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuţu, E. Role of initial density distribution in simulations of bone remodeling around dental implants. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2018, 20, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Beaupre, G.S.; Orr, T.E.; Carter, D.R. An approach for time-dependent bone modeling and remodeling-theoretical development. J. Orthop. Res. 1990, 8, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishijima, M.; Rittling, S.R.; Yamashita, T.; Tsuji, K.; Kurosawa, H.; Nifuji, A.; Denhardt, D.T.; Noda, M. Enhancement of osteoclastic bone resorption and suppression of osteoblastic bone formation in response to reduced mechanical stress do not occur in the absence of osteopontin. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D.; Halloran, B.P. The response of bone to unloading. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 1999, 17, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, H.; Zander, H.A. Tooth contact patterns in mastication. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1963, 13, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaupre, G.S.; Orr, T.E. An approach for time-dependent bone modeling and remodeling—Application: A preliminary remodeling simulation. J. Orthop. Res. 1990, 8, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, R.; Carter, D.; Steele, C. Influence of physical activity on the regulation of bone density. J. Biomech. 1988, 21, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Wagner, J.; Wasnich, R.; Heilbrun, L. The effect of long-distance running upon appendicular bone mineral content. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1984, 16, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Duckmanton, N.; Swain, M. Mandibular bone remodeling induced by dental implant. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Swain, M. Bone remodeling induced by dental implants of functionally graded materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 92, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Swain, M. Dental implant induced bone remodeling and associated algorithms. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 2, 410–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirynen, M.; Naert, I.; Van Steenberghe, D.; Teerlinck, J.; DeKeyser, C.; Theuniers, G. Periodontal aspects of osseointegrated fixtures supporting an overdenture. A 4-year retrospective study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1991, 18, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirynen, M.; Naert, I.; Van Steenberghe, D. Fixture design and overload influence marginal bone loss and future success in the Brånemark® system. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1992, 3, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirynen, M.; Naert, I.; van Steenberghe, D.; Dekeyser, C.; Callens, A. Periodontal aspects of osseointegrated fixtures supporting a partial bridge: An up to 6-years retrospective study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1992, 19, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Guglielmino, E.; La Rosa, G.; Sloten, J.V.; Van Oosterwyck, H. Numerical analysis of bone adaptation around an oral implant due to overload stress. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2004, 218, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D. Bone maintenance and remodeling: A control system based on fatigue damage. J. Orthop. Res. 1997, 15, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.; Prendergast, P.J. A model for fatigue crack propagation and remodelling in compact bone. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 1997, 211, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowin, S.C.; Moss-Salentijn, L.; Moss, M.L. Candidates for the Mechanosensory System in Bone. J. Biomech. Eng. 1991, 113, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.B. Porosity and specific surface of bone. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng 1984, 10, 179–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kwon, T.-G. Density of the alveolar and basal bones of the maxilla and the mandible. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.; Meunier, A. The elastic anisotropy of bone. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, D.T.; Burstein, A.H. The elastic and ultimate properties of compact bone tissue. J. Biomech. 1975, 8, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R. Adaptive bone-remodeling analysis. Chir. Organi Mov. 1992, 77, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reilly, D.T.; Burstein, A.H.; Frankel, V.H. The elastic modulus for bone. J. Biomech. 1974, 7, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Ferguson, A.B. Mechanical Property Distributions in the Cancellous Bone of the Human Proximal Femur. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1980, 51, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, M.; Van Audekercke, R.; Delport, P.; De Meester, P.; Mulier, J. The mechanical characteristics of cancellous bone at the upper femoral region. J. Biomech. 1983, 16, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlmann, A.; Mößner, U.; Bergmann, G.; Hees, G.; Kölbel, R. Die Beanspruchung des Femur nach Hüftgelenkersatz. Z. Orthopädie Ihre Grenzgeb. 1983, 121, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, A.M.; Williams, J.L.; Katz, J.O.; Spencer, P. Anisotropic elastic properties of cancellous bone from a human edentulous mandible. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2000, 11, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, L.A. Biomechanics of Growth, Remodeling, and Morphogenesis. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1995, 48, 487–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.R.; Simo, J.C.; Beaupré, G.S.; Cartert, D.R. Adaptive bone remodeling incorporating simultaneous density and anisotropy considerations. J. Biomech. 1997, 30, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashman, R.B.; Corint, J.D.; Turnerj, C.H. Elastic properties of cancellous bone: Measurement by an ultrasonic technique. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lin, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Swain, M.; Li, Q. Role of Mechanical Stimuli in Oral Implantation. J. Biosci. Med. 2014, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Isidor, F. Influence of forces on peri-implant bone. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Koak, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Rhyu, I.-C.; Ku, Y.; Heo, S.-J.; Han, C.-H. A Long-Term Prospective Evaluation of Marginal Bone Level Change Around Different Implant Systems. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brunski, J.B.; Puleo, D.A.; Nanci, A. Biomaterials and biomechanics of oral and maxillofacial implants: Current status and future developments. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Joos, U.; Wiesmann, H.; Szuwart, T.; Meyer, U. Mineralization at the interface of implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalakis, K.X.; Calvani, P.; Hirayama, H. Biomechanical considerations on tooth-implant supported fixed partial dentures. J. Dent. Biomech. 2012, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.E.; Turley, P.K.; Brezniak, N.; Fielder, P.J. Implants: Bone physiology and metabolism. CDA J. 1987, 15, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Norton, M.R.; Gamble, C. Bone classification: An objective scale of bone density using the computerized tomography scan. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraslan, O.; Inan, Ö. The effect of thread design on stress distribution in a solid screw implant: A 3D finite element analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2009, 14, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, S. The implant neck: Smooth or provided with retention elements—A biomechanical approach. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1999, 10, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickenig, H.-J.; Wichmann, M.; Schlegel, K.A.; Nkenke, E.; Eitner, S. Radiographic evaluation of marginal bone levels adjacent to parallel-screw cylinder machined-neck implants and rough-surfaced microthreaded implants using digitized panoramic radiographs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yue, X. Marginal Bone Loss around Machined Smooth Neck Implants Compared to Rough Threaded Neck Implants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, M.; Martinez, H.; Tecucianu, J.F.; Alcoforado, G.; Etienne, D.; Celletti, R. The self-tapping and ICE 3i implants: A prospective 3-year multicenter evaluation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2001, 16, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-W.; Choi, Y.-S.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, C.-S.; Moon, I.-S. Effect of microthread on the maintenance of marginal bone level: A 3-year prospective study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemezzi, P.; Ferrini, F.; Pantaleo, G.; Gherlone, E.; Capparè, P. Dental Implants with Different Neck Design: A Prospective Clinical Comparative Study with 2-Year Follow-Up. Materials 2020, 13, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messias, A.; Nicolau, P.; Guerra, F. Titanium dental implants with different collar design and surface modifications: A systematic review on survival rates and marginal bone levels. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 20–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggi, L.; Cappelloni, I.; Di Girolamo, M.; Maceri, F.; Vairo, G. The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comuzzi, L.; Tumedei, M.; Pontes, A.E.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Primary Stability of Dental Implants in Low-Density (10 and 20 pcf) Polyurethane Foam Blocks: Conical vs Cylindrical Implants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovatto, S.T.; Bassani, R.; Sarkis-Onofre, R.; dos Santos, M.B.F. Influence of Different Implant Geometry in Clinical Longevity and Maintenance of Marginal Bone: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, e713–e721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairo, F.; Barbato, L.; Tonelli, P.; Batalocco, G.; Pagavino, G.; Nieri, M. Xenogeneic collagen matrix versus connective tissue graft for buccal soft tissue augmentation at implant site. A randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufley, S.; Scott, J.E.; Ramirez-Yanez, G. The effect of the physical consistency of the diet on the bone quality of the mandibular condyle in rats. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 77, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; Parsa, A.; Hassan, B.; van der Stelt, P.; Rahmat, R.A.; Ismail, S.M.; Aartman, I.H.A. Comparison of anterior and posterior trabecular bone microstructure of human mandible using cone-beam CT and micro CT. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’andrea, D.; Cucinotta, F.; Farroni, F.; Risitano, G.; Santonocito, D.; Scappaticci, L. Development of machine learning algorithms for the determination of the centre of mass. Symmetry 2021, 13, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentia, M.; Abasolo, M.; Coria, I.; Albizuri, J. Fatigue Design of Dental Implant Assemblies: A Nominal Stress Approach. Metals 2020, 10, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

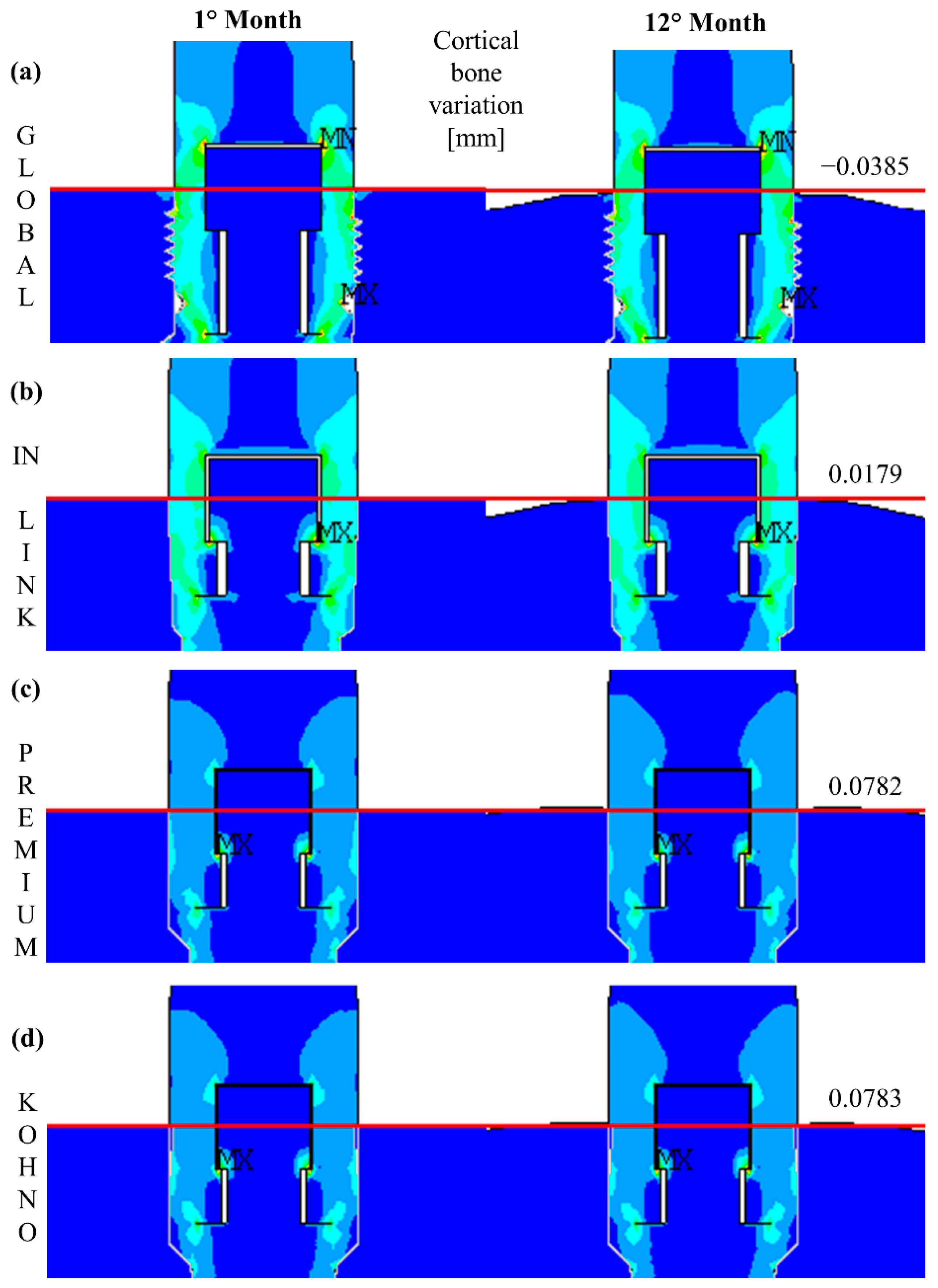
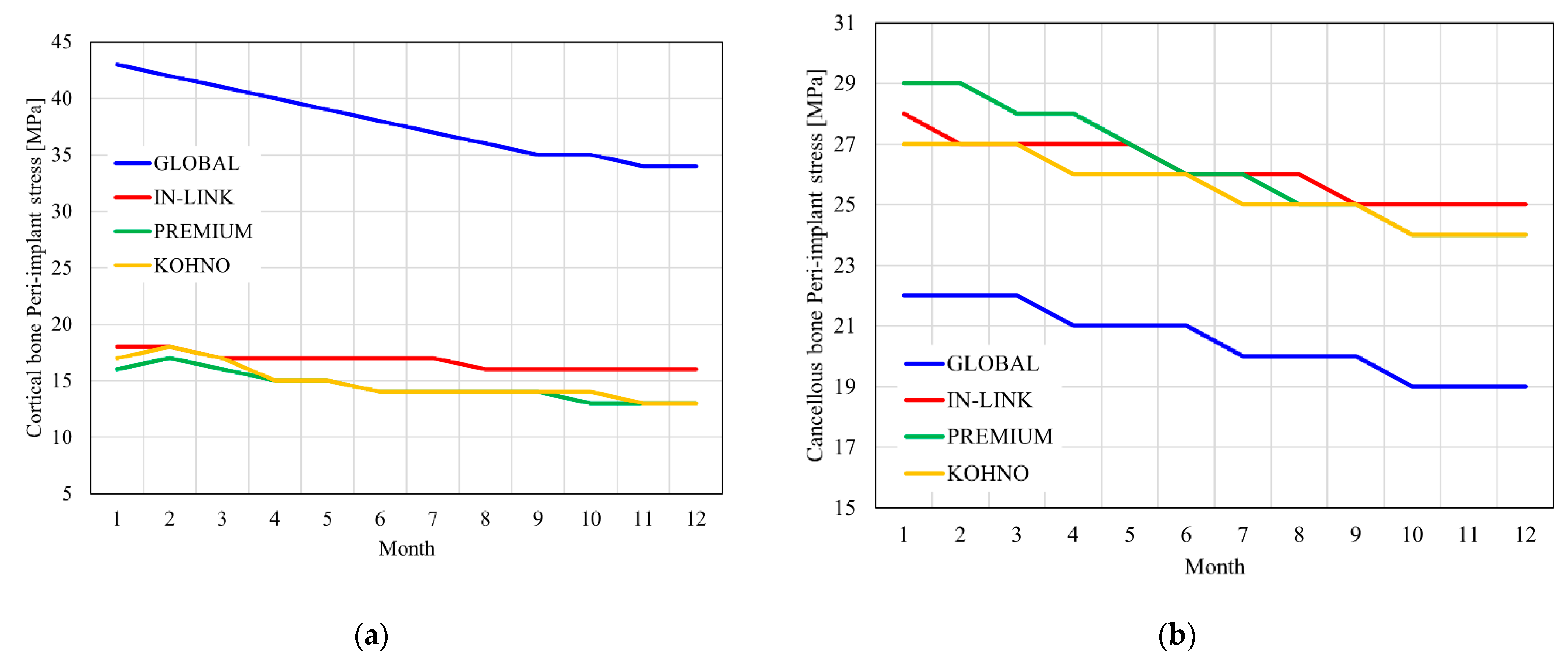

| Properties | Cortical Bone | Cancellous Bone | Titanium Grade IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density [g/cm3] | 1.74 | 0.9 | 4.51 |
| Exx [GPa] | 19.4 | 1.87 | 110 |
| Eyy [GPa] | 10.8 | ||
| Ezz [GPa] | 13.3 | ||
| νxx | 0.445 | 0.12 | 0.33 |
| νyy | 0.309 | ||
| νzz | 0.224 | ||
| Gxx [GPa] | 4.12 | ||
| Gyy [GPa] | 3.81 | ||
| Gzz [GPa] | 4.63 |
| Global | In-Link | Kohno | Premium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elements | 20,187 | 19,065 | 17,848 | 17,930 |
| Nodes | 21,086 | 20,389 | 18,892 | 19,146 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santonocito, D.; Nicita, F.; Risitano, G. A Parametric Study on a Dental Implant Geometry Influence on Bone Remodelling through a Numerical Algorithm. Prosthesis 2021, 3, 157-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis3020016
Santonocito D, Nicita F, Risitano G. A Parametric Study on a Dental Implant Geometry Influence on Bone Remodelling through a Numerical Algorithm. Prosthesis. 2021; 3(2):157-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis3020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantonocito, Dario, Fabiana Nicita, and Giacomo Risitano. 2021. "A Parametric Study on a Dental Implant Geometry Influence on Bone Remodelling through a Numerical Algorithm" Prosthesis 3, no. 2: 157-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis3020016
APA StyleSantonocito, D., Nicita, F., & Risitano, G. (2021). A Parametric Study on a Dental Implant Geometry Influence on Bone Remodelling through a Numerical Algorithm. Prosthesis, 3(2), 157-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis3020016








