Non-Volatile Particle Number Emission Measurements with Catalytic Strippers: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
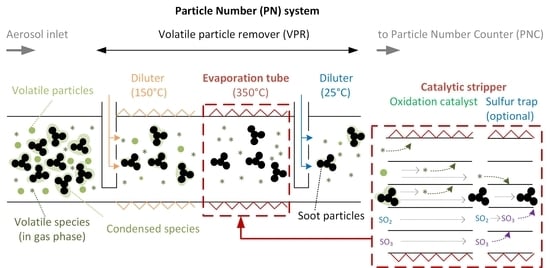
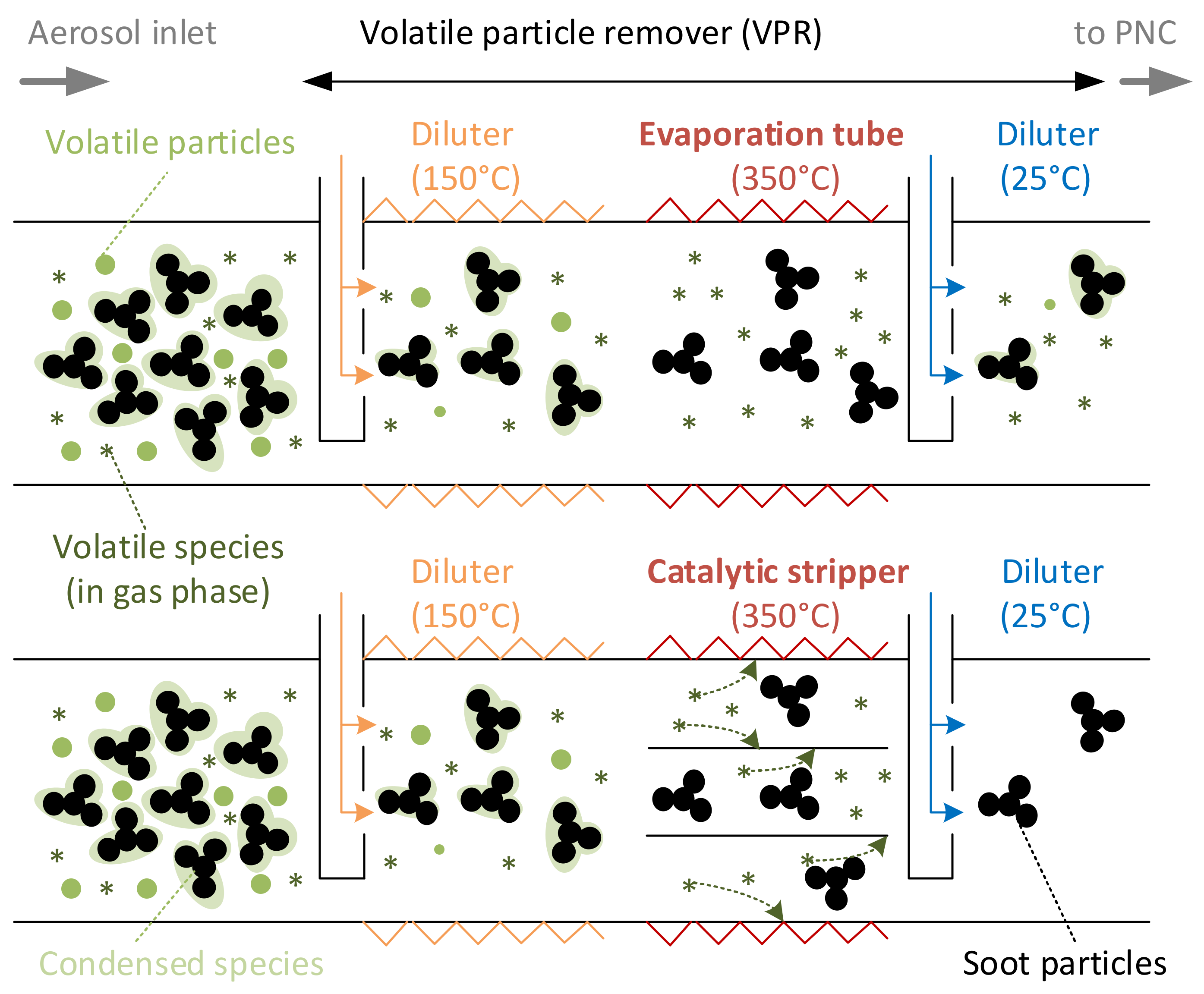
3.1. Volatile Particle Remover
3.1.1. Evaporation Tube-Based Systems
3.1.2. Catalytic Stripper-Based Systems
- Only oxidation catalyst;
- Sulfur trap and oxidation catalyst (in this order);
- Oxidation catalyst and sulfur trap.
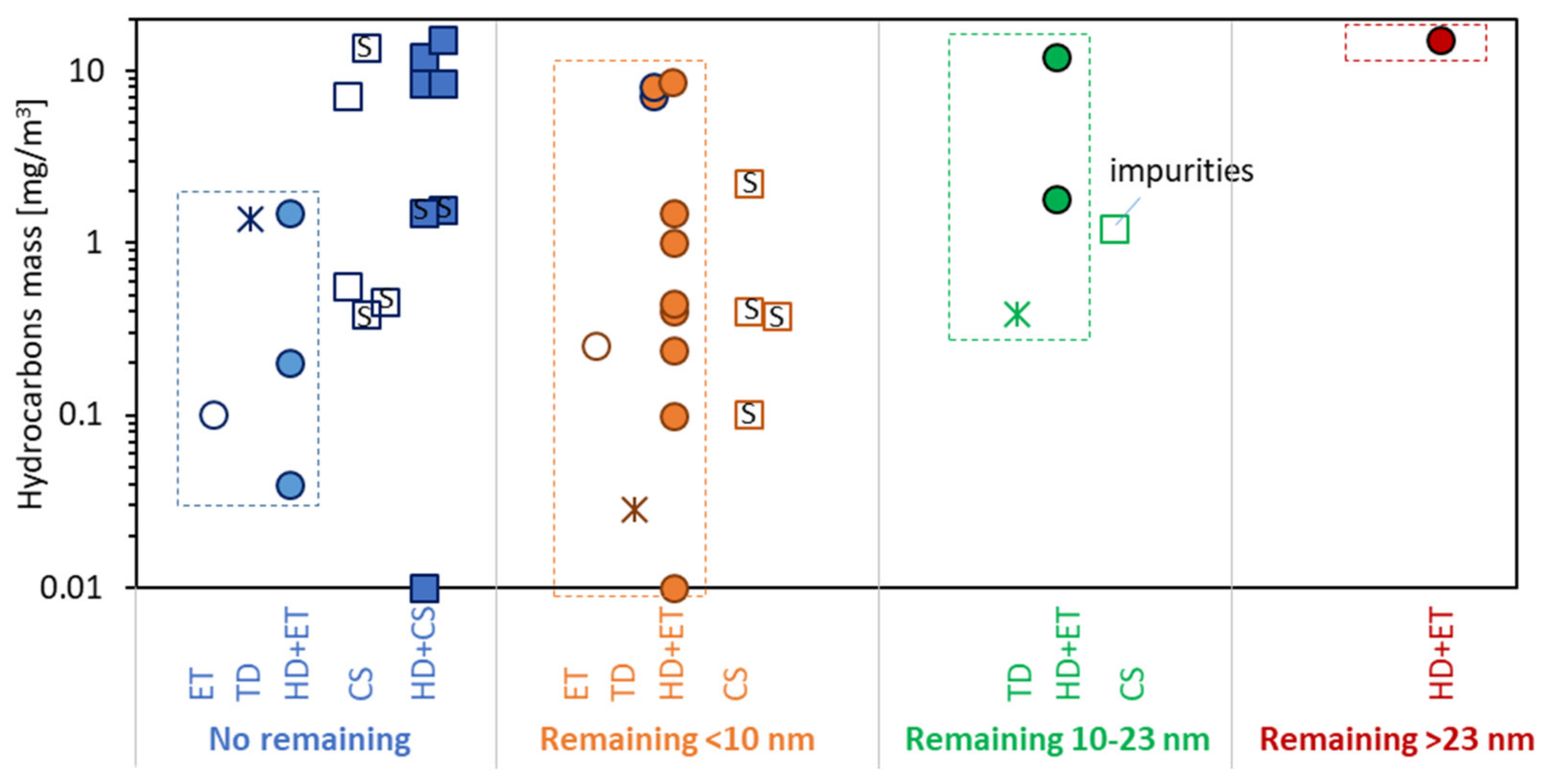
3.2. Hydrocarbons
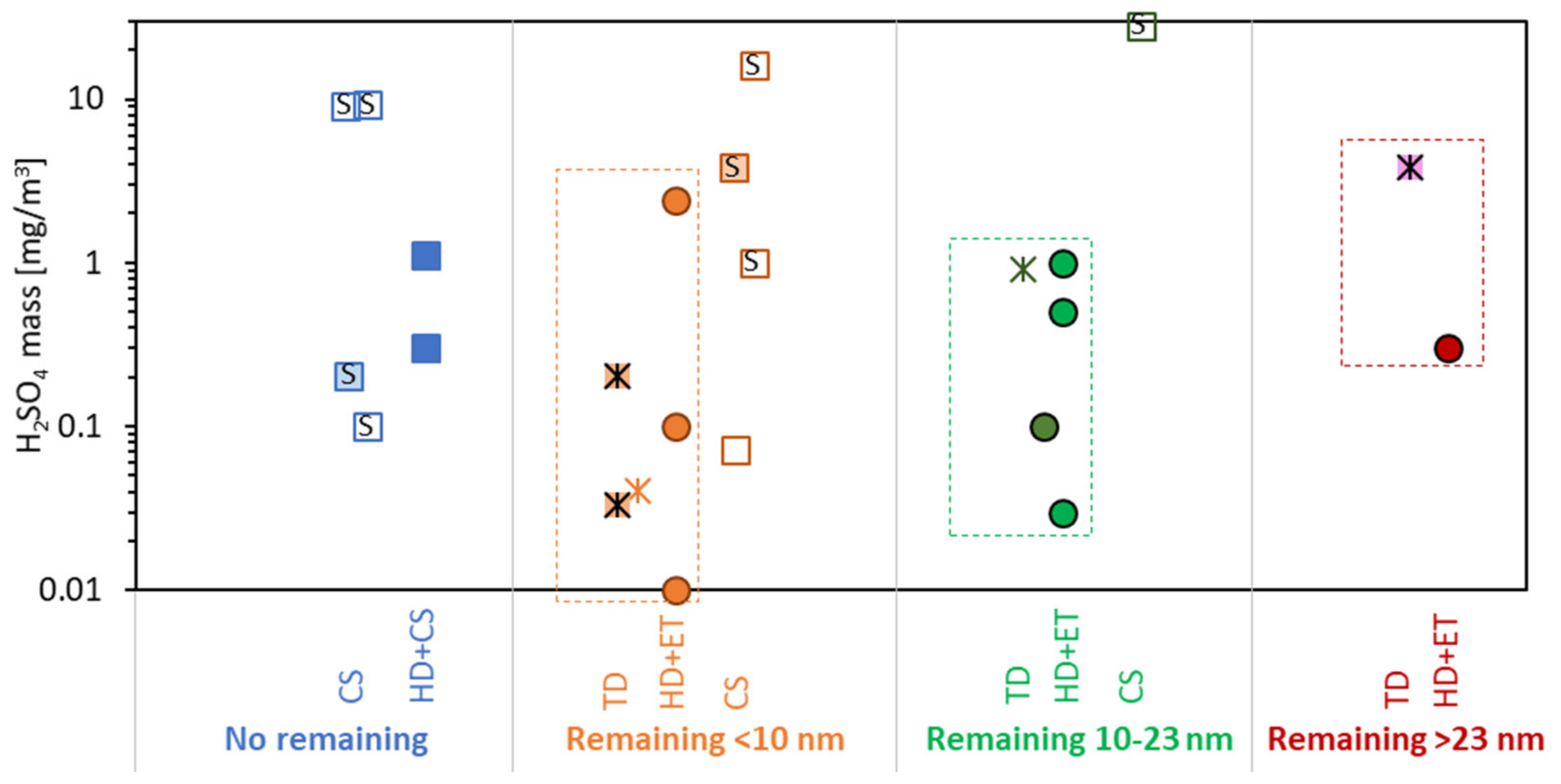
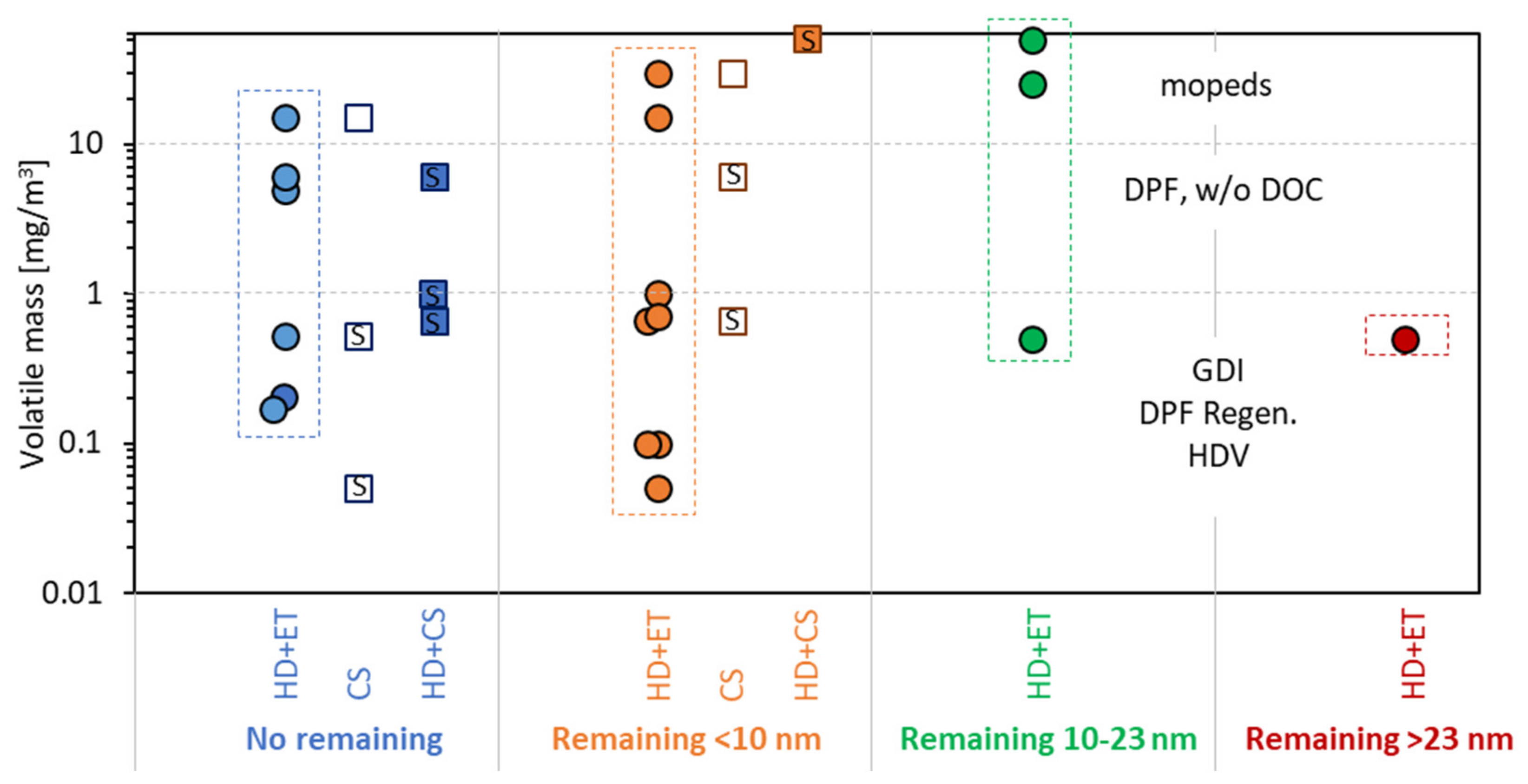
- No particles remained downstream of the system under evaluation (blue color). Note that typically the lower detection size of these studies was around 3–6 nm.
- Particles with sizes lower than 10 nm were detected downstream of the system under evaluation (orange color). These cases are of low risk for the future >10 nm regulation but could have artefacts with low cut-off counters.
- Particles in the size region 10–23 nm remained (green color). These cases are risky for the future >10 nm regulation and indicate hydrocarbons mass levels that could lead to “volatile” artefacts.
- Particles larger than 23 nm were detected (red color). These cases would affect also the results of the current >23 nm regulation.
- Standalone evaporation tubes (ET) (open circles).
- Thermodenuders (TD) (asterisks).
- Hot dilution (typically 10:1) plus evaporation tubes (HD + ET) (solid circles).
- Standalone catalytic strippers (CS) (open squares).
- Hot dilution plus catalytic strippers (HD + CS) (solid squares).
3.3. H2SO4
3.4. Ammonium Sulfate
3.5. Vehicles’ Exhaust
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaporation Tube
4.2. Catalytic Stripper
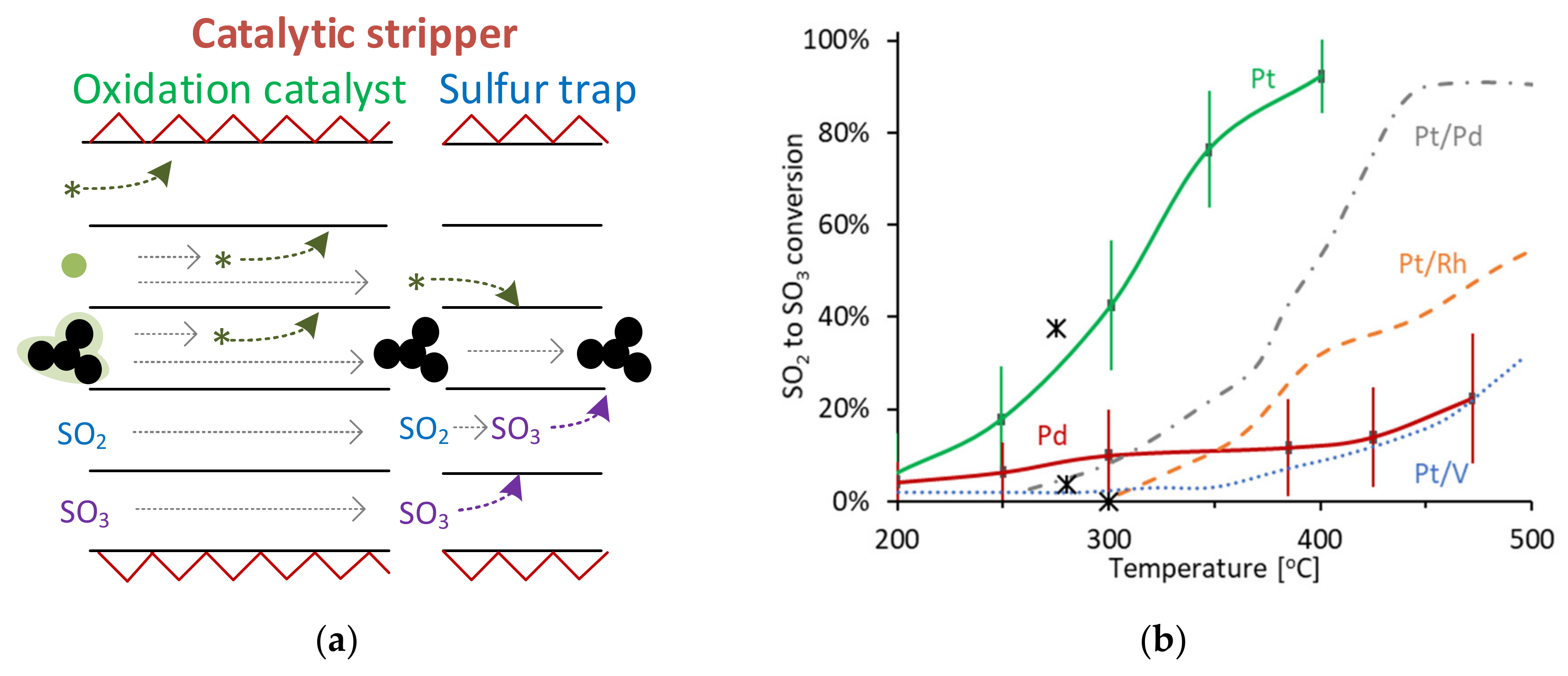
4.2.1. Oxidation and Sulfur Trap Parts
4.2.2. SO2 to SO3 Conversion
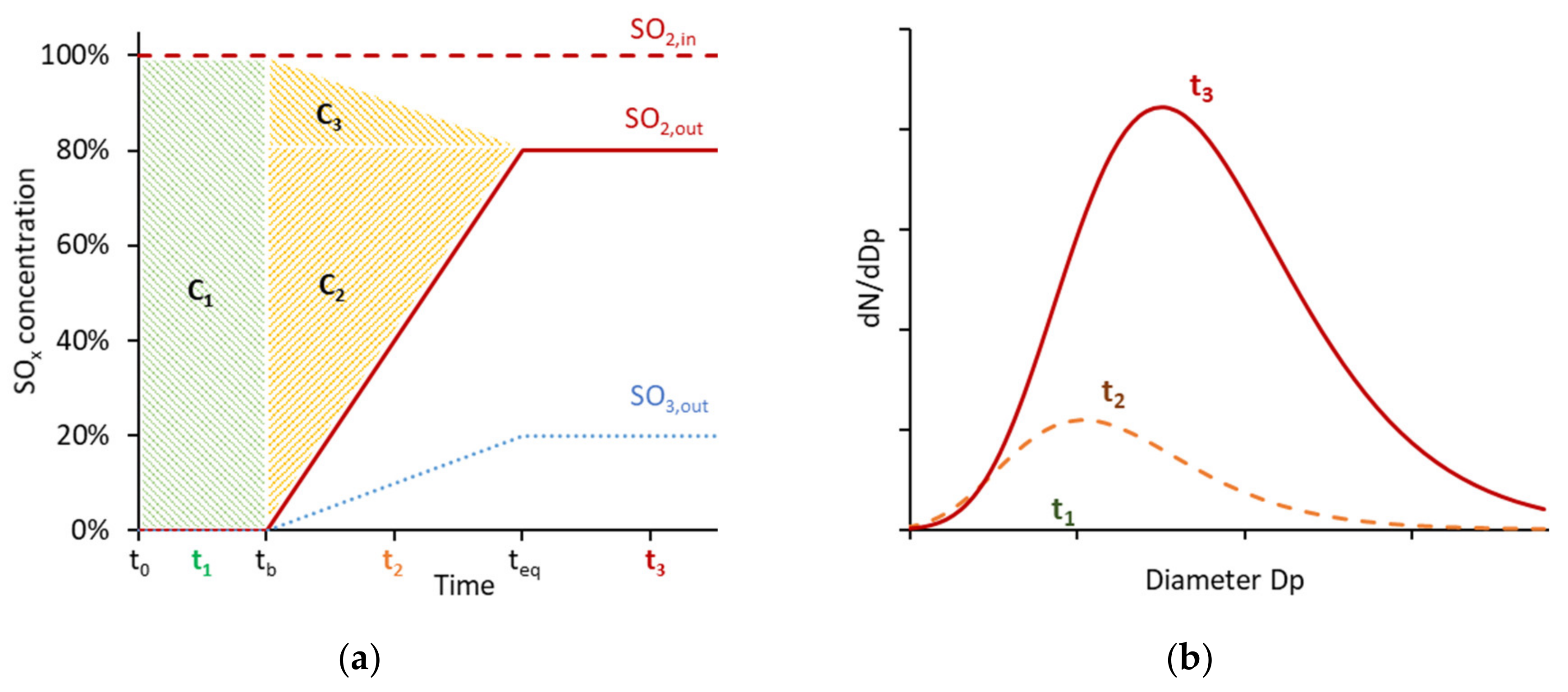
4.2.3. Storage Capacity
4.2.4. Position of Sulfur Trap
4.3. Open Issues
4.3.1. Particle Losses
4.3.2. SO3 Conversion Risks
4.3.3. Vehicles’ Volatile Aerosol
4.3.4. Catalytic Stripper Technical Requirements
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giechaskiel, B.; Maricq, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dardiotis, C.; Wang, X.; Axmann, H.; Bergmann, A.; Schindler, W. Review of motor vehicle particulate emissions sampling and measurement: From smoke and filter mass to particle number. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 67, 48–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Mamakos, A.; Andersson, J.; Dilara, P.; Martini, G.; Schindler, W.; Bergmann, A. Measurement of automotive nonvolatile particle number emissions within the European legislative framework: A review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 719–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Clairotte, M.; Grigoratos, T.; Zardini, A.; Perujo, A.; Martini, G. Particle number measurements in the European legislation and future JRC activities. Combust. Engines 2018, 174, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Joshi, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dilara, P. European regulatory framework and particulate matter emissions of gasoline light-duty vehicles: A review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Drossinos, Y. Theoretical investigation of volatile removal efficiency of particle number measurement systems. SAE Int. J. Engines 2010, 3, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H. Physical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 896–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Bonnel, P.; Perujo, A.; Dilara, P. Solid particle number (SPN) portable emissions measurement systems (PEMS) in the European legislation: A review. IJERPH 2019, 16, 4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Vanhanen, J.; Väkevä, M.; Martini, G. Investigation of vehicle exhaust sub-23 nm particle emissions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.C.; Durbin, T.D.; Jung, H.; Chaudhary, A.; Cocker, D.R.; Herner, J.D.; Robertson, W.H.; Huai, T.; Ayala, A.; Kittelson, D. Evaluation of the European PMP methodologies during on-road and chassis dynamometer testing for dpf equipped heavy-duty diesel vehicles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Manfredi, U.; Martini, G. Engine exhaust solid sub-23 nm particles: I. literature survey. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönkkö, T.; Virtanen, A.; Kannosto, J.; Keskinen, J.; Lappi, M.; Pirjola, L. Nucleation mode particles with a nonvolatile core in the exhaust of a heavy duty diesel vehicle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6384–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B. Solid particle number emission factors of Euro VI heavy-duty vehicles on the road and in the laboratory. IJERPH 2018, 15, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.; Czerwinski, J.; Kasper, M.; Ulrich, A.; Mooney, J.J. Metal Oxide Particle Emissions from Diesel and Petrol Engines; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Martini, G. Engine exhaust solid sub-23 nm particles: II feasibility study for particle number measurement systems. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Mamakos, A.; Woodburn, J.; Szczotka, A.; Bielaczyc, P. Evaluation of a 10 nm particle number portable emissions measurement system (PEMS). Sensors 2019, 19, 5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Gandi, S.; Keller, S.; Kreutziger, P.; Mamakos, A. Assessment of 10-nm particle number (PN) portable emissions measurement systems (PEMS) for future regulations. IJERPH 2020, 17, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Khalek, I.S.; Kittelson, D.B. Real time measurement of volatile and solid exhaust particles using a catalytic stripper. SAE Trans. 1995, 104, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigg, M.V. Catalytic control of emissions from cars. Catal. Today 2011, 163, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Baiker, A. NOx storage–reduction catalysis: From mechanism and materials properties to storage–reduction performance. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4054–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, P.-X. A review of NOx storage/reduction catalysts: Mechanism, materials and degradation studies. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 552–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Chen, L.; Stone, R. Effects of a catalytic volatile particle remover (VPR) on the particulate matter emissions from a direct injection spark ignition engine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9036–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, P.; Durdina, L.; Brem, B.T.; Crayford, A.P.; Johnson, M.P.; Smallwood, G.J.; Siegerist, F.; Williams, P.I.; Black, E.A.; Llamedo, A.; et al. Comparison of standardized sampling and measurement reference systems for aircraft engine non-volatile particulate matter emissions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2020, 145, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Bahreini, R.; Zimmerman, S.; Fofie, E.A.; Asa-Awuku, A.; Park, K.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N.; Jung, H.S. Investigation of ambient aerosol effective density with and without using a catalytic stripper. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H.; Baltensperger, U.; Bukowiecki, N.; Cohn, P.; Hüglin, C.; Mohr, M.; Matter, U.; Nyeki, S.; Schmatloch, V.; Streit, N.; et al. Separation of volatile and non-volatile aerosol fractions by thermodesorption: Instrumental development and applications. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, J.A.; Ziemann, P.J.; Jayne, J.T.; Worsnop, D.R.; Jimenez, J.L. Development and characterization of a fast-stepping/scanning thermodenuder for chemically-resolved aerosol volatility measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, N.M.; Kroll, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Robinson, A.L. A two-dimensional volatility basis set—Part 2: Diagnostics of organic-aerosol evolution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, M.M. Chemical characterization of particulate emissions from diesel engines: A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 1079–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Myung, C.L.; Park, S. Review on characterization of nano-particle emissions and PM morphology from internal combustion engines: Part 2. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2014, 15, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalek, I.A. Sampling system for solid and volatile exhaust particle size, number, and mass emissions. SAE Trans. 2007, 116, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalek, I.A.; Bougher, T. Development of a solid exhaust particle number measurement system using a catalytic stripper technology. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelson, D.B.; Stenitzer, M. A new catalytic stripper for removal of volatile particles. In Proceedings of the 7th ETH Conference on Combustion Generated Nanoparticles, Zurich, Switzerland, 18–20 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, J.; Kittelson, D. Evaluation of thermal denuder and catalytic stripper methods for solid particle measurements. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Katsaounis, D.; Samaras, Z.; Bergmann, A. Evaluation of an oxidation catalyst (“catalytic stripper”) in eliminating volatile material from combustion aerosol. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 57, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Zardini, A.; Martini, G. Particle emission measurements from L-category vehicles. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 8, 2322–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Karjalainen, P.; Saukko, E.; Simonen, P.; Kuittinen, N.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Timonen, H.; Rönkkö, T.; Keskinen, J. Comparative performance of a thermal denuder and a catalytic stripper in sampling laboratory and marine exhaust aerosols. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melas, A.D.; Koidi, V.; Deloglou, D.; Daskalos, E.; Zarvalis, D.; Papaioannou, E.; Konstandopoulos, A.G. Development and evaluation of a catalytic stripper for the measurement of solid ultrafine particle emissions from internal combustion engines. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Riccobono, F.; Bonnel, P. Feasibility Study on the Extension of the Real-Driving Emissions (RDE) Procedure to Particle Number (PN): Chassis Dynamometer Evaluation of Portable Emission Measurement Systems (PEMS) to Measure Particle Number (PN) Concentration: Phase II; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2015; ISBN 978-92-79-51003-8. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki, Y.; Tochino, S.; Kondo, K.; Haruta, K. Portable Emissions Measurement System for Solid Particle Number Including Nanoparticles Smaller than 23 nm; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki, Y.; Takeda, K.; Haruta, K.; Mori, N. A Solid Particle Number Measurement System Including Nanoparticles Smaller than 23 Nanometers; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kiwull, B.; Wolf, J.C.; Niessner, R. Evaluation of Volatile Particle Remover Devices for Exhaust Particle Quantification; Technische Universität München: Munich, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Johnson, K.C.; Liu, Z.; Durbin, T.D.; Hu, S.; Huai, T.; Kittelson, D.B.; Jung, H.S. Investigation of Solid Particle Number Measurement: Existence and Nature of Sub-23nm Particles Under PMP Methodology. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, M. Characterisation of the Second Generation PMP “Golden Instrument”; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Carriero, M.; Martini, G.; Krasenbrink, A.; Scheder, D. Calibration and validation of various commercial particle number measurement systems. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2009, 2, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, J.; Kittelson, D.; Giechaskiel, B.; Bergmann, A.; Twigg, M. A miniature catalytic stripper for particles less than 23 nanometers. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2013, 6, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery Oil Removal Efficiency. Available online: http://catalytic-instruments.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Application-note0007.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Crayford, A.P.; Johnson, M.; Marsh, R.; Sevcenco, Y.; Walters, D.; Williams, P.; Christie, S.; Chung, W.; Petzold, A.; Ibrahim, A.; et al. SAMPLE III (SC01): Contribution to Aircraft Engine PM Certification Requirement and Standard First Specific Contract—Final Report; EASA: Cologne, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kondo, K.; Otsuki, Y.; Haruta, K. A New On-Board PN Analyzer for Monitoring the Real-Driving Condition; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Kournikakis, B.; Gunning, A.; Fildes, J. Submicron aerosol characterization of water by a differential mobility particle sizer. J. Aerosol Sci. 1988, 19, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Chirico, R.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Clairotte, M.; Adam, T.; Martini, G.; Heringa, M.F.; Richter, R.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U. Evaluation of the particle measurement programme (PMP) protocol to remove the vehicles’ exhaust aerosol volatile phase. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5106–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B. Differences between tailpipe and dilution tunnel sub-23 nm nonvolatile (solid) particle number measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamakos, A.; Martini, G.; Marotta, A.; Manfredi, U. Assessment of different technical options in reducing particle emissions from gasoline direct injection vehicles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 63, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Amanatidis, S.; Samaras, Z.; Giechaskiel, B.; Bergmann, A. Use of a catalytic stripper as an alternative to the original PMP measurement protocol. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2013, 6, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamakos, A.; Martini, G.; Manfredi, U. Assessment of the legislated particle number measurement procedure for a Euro 5 and a Euro 6 compliant diesel passenger cars under regulated and unregulated conditions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 55, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Riccobono, F.; Mendoza-Villafuerte, P.; Grigoratos, T. Particle Number (PN)—Portable Emissions Measurement Systems (PEMS) Heavy Duty Vehicles Evaluation Phase at the Joint Research Centre (JRC); Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Durbin, T.D.; Karavalakis, G.; Johnson, K.C.; Chaudhary, A.; Cocker, D.R.; Herner, J.D.; Robertson, W.H.; Huai, T.; Ayala, A.; et al. Nature of sub-23-nm particles downstream of the European particle measurement programme (PMP)-compliant system: A real-time data perspective. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Pistikopoulos, P.; Samaras, Z. Comparative Assessment of Two Different Sampling Systems for Particle Emission Type-Approval Measurements; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B. Particle number emissions of a diesel vehicle during and between regeneration events. Catalysts 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F. Effect of ammonia on new particle formation: A kinetic H2SO4-H2O-NH3 nucleation model constrained by laboratory measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmetty, M.; Vehkamäki, H.; Virtanen, A.; Kulmala, M.; Keskinen, J. Homogeneous ternary H2SO4–NH3–H2O nucleation and diesel exhaust: A classical approach. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2007, 7, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.R.; Yu, J.H.; Markovich, A.; Lee, S.-H. Ternary homogeneous nucleation of H2SO4, NH3, and H2O under conditions relevant to the lower troposphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4755–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Pechout, M.; Vojtíšek, M.; Astorga, C. Regulated and non-regulated emissions from Euro 6 diesel, gasoline and CNG vehicles under real-world driving conditions. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, J.; Zimmerli, Y.; Mayer, A.; Heeb, N.; Lemaire, J.; D’Urbano, G.; Bunge, R. Testing of Combined DPF+SCR Systems for HD-Retrofitting—VERTdePN; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sipila, M.; Berndt, T.; Petaja, T.; Brus, D.; Vanhanen, J.; Stratmann, F.; Patokoski, J.; Mauldin, R.L.; Hyvarinen, A.-P.; Lihavainen, H.; et al. The role of sulfuric acid in atmospheric nucleation. Science 2010, 327, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrner, U.; von Löwis, S.; Vehkamäki, H.; Wehner, B.; Bräsel, S.; Hermann, M.; Stratmann, F.; Kulmala, M.; Wiedensohler, A. Dilution and aerosol dynamics within a diesel car exhaust plume—CFD simulations of on-road measurement conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7440–7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, M.; Alanen, J.; Palmroth, M.R.T.; Rönkkö, T.; Dal Maso, M. Inversely modeling homogeneous H2SO4—H2O nucleation rate in exhaust-related conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6367–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, P.; Rönkkö, T.; Pirjola, L.; Heikkilä, J.; Happonen, M.; Arnold, F.; Rothe, D.; Bielaczyc, P.; Keskinen, J. Sulfur driven nucleation mode formation in diesel exhaust under transient driving conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 2336–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yu, F. Nanoparticle formation in the exhaust of vehicles running on ultra-low sulfur fuel. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4729–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaaraslahti, K.; Keskinen, J.; Giechaskiel, B.; Solla, A.; Murtonen, T.; Vesala, H. Effect of lubricant on the formation of heavy-duty diesel exhaust nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8497–8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmetty, M.; Rönkkö, T.; Virtanen, A.; Keskinen, J.; Pirjola, L. The effect of sulphur in diesel exhaust aerosol: Models compared with measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalek, I.A.; Kittelson, D.B.; Brear, F. Nanoparticle Growth During Dilution and Cooling of Diesel Exhaust: Experimental Investigation and Theoretical Assessment; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, F.; Pirjola, L.; Rönkkö, T.; Reichl, U.; Schlager, H.; Lähde, T.; Heikkilä, J.; Keskinen, J. First online measurements of sulfuric acid gas in modern heavy-duty diesel engine exhaust: Implications for nanoparticle formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11227–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouitsis, E.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. Modelling of diesel exhaust aerosol during laboratory sampling. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouitsis, E.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. Theoretical investigation of the nucleation mode formation downstream of diesel after-treatment devices. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2008, 8, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Funato, K.; Sakurai, H. Application of the PMP methodology to the measurement of sub-23 nm solid particles: Calibration procedures, experimental uncertainties, and data correction methods. J. Aerosol Sci. 2015, 88, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Martini, G. JRC sub-23 nm update. In Proceedings of the 37th PMP meeting, Brussels, Belgium, 7 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- AVL Comments on GTR15 Ammendment. Available online: https://wiki.unece.org/display/trans/PMP+Web+Conference+02+April (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Neyestanaki, A.K.; Klingstedt, F.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y. Deactivation of postcombustion catalysts, a review. Fuel 2004, 83, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z.; Casati, R.; Scheer, V.; Vogt, R. Effect of Speed and Speed-Transition on the Formation of Nucleation Mode Particles from a Light Duty Diesel Vehicle; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, B.J.; Thoss, J.E. Role of NO in diesel particulate emission control. SAE Trans. 1989, 98, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröcher, O.; Widmer, M.; Elsener, M.; Rothe, D. Adsorption and desorption of SOx on diesel oxidation catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 9847–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; King, D.L. Method for determining performance of sulfur oxide adsorbents for diesel emission control using online measurements of SO2 and SO3 in the effluent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 4452–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsopoulos, S.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Eriksen, K.M.; Fehrmann, R. The role of support and promoter on the oxidation of sulfur dioxide using platinum based catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 306, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, E.; Seshan, K.; van Ommen, J.G.; Ross, J.R.H. Catalytic control of diesel engine particulate emission: Studies on model reactions over a EuroPt-1 (Pt/SiO2) catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1993, 2, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, M.; Manning, W.A.; Roth, S.A.; D’Aniello, M.J.; Andersson, E.S.; Fredholm, S.C.G. The design of flow-through diesel oxidation catalysts. SAE Trans. 1993, 102, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, M.; Saito, K.; Ichihara, S. The effects of flow-through type oxidation catalysts on the particulate reduction of 1990’s diesel engines. SAE Trans. 1990, 99, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzehlouyan, T.; Sampara, C.; Li, J.; Kumar, A.; Epling, W. Experimental and kinetic study of SO2 oxidation on a Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 152, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltsakis, G. Catalytic automotive exhaust aftertreatment. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1997, 23, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, Y.; Tzanis, L.; Soulard, M.; Patarin, J.; Vierling, M.; Molière, M. Adsorption of SOx by oxide materials: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 114, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedler, G.; Ahlström, G.; Fredholm, S.; Frost, J.; Lööf, P.; Marsh, P.; Walker, A.; Winterborn, D. High Performance Diesel Catalysts for Europe Beyond 1996; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Henk, M.G.; Williamson, W.B.; Silver, R.G. Diesel Catalysts for Low Particulate and Low Sulfate Emissions; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, J.; Kazi, M.; Farrauto, R. Palladium catalyst performance for methane emissions abatement from lean burn natural gas vehicles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1997, 14, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärkkäinen, M.; Honkanen, M.; Viitanen, V.; Kolli, T.; Valtanen, A.; Huuhtanen, M.; Kallinen, K.; Vippola, M.; Lepistö, T.; Lahtinen, J.; et al. Deactivation of diesel oxidation catalysts by sulphur in laboratory and engine-bench scale aging. Top Catal. 2013, 56, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.C. Sulfur storage on automotive catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1976, 15, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Chung, J.S.; Guo, Z. Sulfur poisoning and regeneration of NOx storage–reduction Cu/K2Ti2O5 catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 7330–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Qi, G. Enhanced SO2 capture performance of MnO2 by doping with alkali metal ions for diesel emission control. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; King, D.L. High-capacity sulfur dioxide absorbents for diesel emissions control. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, M.; Saito, K.; Ichihara, S. Sulfur Storage and Discharge Behavior on Flow-Through Type Oxidation Catalysts; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Centi, G.; Passarini, N.; Perathoner, S.; Riva, A. Combined DeSOx/DeNOx reactions on a copper on alumina sorbent-catalyst. 1. Mechanism of sulfur dioxide oxidation-adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limousy, L.; Mahzoul, H.; Brilhac, J.F.; Gilot, P.; Garin, F.; Maire, G. SO2 sorption on fresh and aged SOx traps. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 42, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawody, J.; Skoglundh, M.; Olsson, L.; Fridell, E. Sulfur deactivation of Pt/SiO2, Pt/BaO/Al2O3, and BaO/Al2O3 NOx storage catalysts: Influence of SO2 exposure conditions. J. Catal. 2005, 234, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawody, J.; Skoglundh, M.; Olsson, L.; Fridell, E. Kinetic modelling of sulfur deactivation of Pt/BaO/Al2O3 and BaO/Al2O3 NOx storage catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 70, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylhammar, L.; Carlsson, P.-A.; Ingelsten, H.H.; Grönbeck, H.; Skoglundh, M. Regenerable ceria-based SOx traps for sulfur removal in lean exhausts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzehlouyan, T.; Sampara, C.S.; Li, J.; Kumar, A.; Epling, W.S. Kinetic study of adsorption and desorption of SO2 over γ-Al2O3 and Pt/γ-Al2O3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Asanuma, T.; Nishioka, H.; Hayashi, K.; Hirota, S. Development of NOx Reduction System for Diesel Aftertreatment with Sulfur Trap Catalyst; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Englund, J.; Xie, K.; Dahlin, S.; Schaefer, A.; Jing, D.; Shwan, S.; Andersson, L.; Carlsson, P.-A.; Pettersson, L.J.; Skoglundh, M. Deactivation of a Pd/Pt bimetallic oxidation catalyst used in a biogas-powered Euro VI heavy-duty engine installation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyle, M.; Bartholomew, C. Heterogeneous catalyst deactivation and regeneration: A review. Catalysts 2015, 5, 145–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasapidis, L.; Melas, A.D.; Tsakis, A.; Zarvalis, D.; Konstandopoulos, A. A Sampling and Conditioning Particle System for Solid Particle Measurements Down to 10 nm; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.; Jin, L. Global Progress toward Soot-Free Diesel Vehicles; International Council Clean Transportation (ICCT) Report; ICCT: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Inomata, S.; Tanimoto, H. Mechanisms of increased particle and VOC emissions during DPF active regeneration and practical emissions considering regeneration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasar, A.; Haider, R.; Tabinda, A.B.; Kausar, F.; Khan, M. A comparison of engine emissions from heavy, medium, and light vehicles for CNG, diesel, and gasoline fuels. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, J.R.; Sthel, M.S.; Campos, L.S.; Rocha, M.V.; Lima, G.R.; da Silva, M.G.; Vargas, H. Evaluation of pollutant gases emitted by ethanol and gasoline powered vehicles. Proc. Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gentner, D.R.; Worton, D.R.; Isaacman, G.; Davis, L.C.; Dallmann, T.R.; Wood, E.C.; Herndon, S.C.; Goldstein, A.H.; Harley, R.A. Chemical composition of gas-phase organic carbon emissions from motor vehicles and implications for ozone production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11837–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, H.J.; Beving, D.E.; Ziemann, P.J.; Sakurai, H.; Zuk, M.; McMurry, P.H.; Zarling, D.; Waytulonis, R.; Kittelson, D.B. Chemical analysis of diesel engine nanoparticles using a nano-DMA/thermal desorption particle beam mass spectrometer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, H.; Tobias, H.J.; Park, K.; Zarling, D.; Docherty, K.S.; Kittelson, D.B.; McMurry, P.H.; Ziemann, P.J. On-line measurements of diesel nanoparticle composition and volatility. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, J.J.; Kittelson, D.B.; Watts, W.F.; Gladis, D.D.; Twigg, M.V. Influence of storage and release on particle emissions from new and used CRTs. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3998–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Hock, N.; Weimer, S.; Borrmann, S.; Kirchner, U.; Vogt, R.; Scheer, V. Nucleation particles in diesel exhaust: Composition inferred from in situ mass spectrometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6153–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavalakis, G.; Gysel, N.; Schmitz, D.A.; Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C.; Schauer, J.J.; Cocker, D.R.; Durbin, T.D. Impact of biodiesel on regulated and unregulated emissions, and redox and proinflammatory properties of PM emitted from heavy-duty vehicles. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A.; Lopes, D.J.; Calvo, A.I.; Evtyugina, M.; Rocha, S.; Nunes, T. Emissions from light-duty diesel and gasoline in-use vehicles measured on chassis dynamometer test cycles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-H.; Huang, P.-H.; Chiang, H.-L. Air pollutants and toxic emissions of various mileage motorcycles for ECE driving cycles. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Vonk, W.A.; Papadopoulos, G.; van Mensch, P.; Geivanidis, S.; Mellios, G.; Papadimitriou, G.; Steven, H.; Elstgeest, M.; Ligterink, N.E.; et al. Effect Study of the Environmental Step Euro 5 for L-Category Vehicles; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; ISBN 978-92-79-70203-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kontses, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Zardini, A.A.; Papadopoulos, G.; Giechaskiel, B. Particulate emissions from L-Category vehicles towards Euro 5. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, M.A.; Murena, F.; Prati, M.V. Exhaust emissions of volatile organic compounds of powered two-wheelers: Effect of cold start and vehicle speed. Contribution to greenhouse effect and tropospheric ozone formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, B.; Fu, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Ma, Z.; Feng, R. The effect of air/fuel composition on the HC emissions for a twin-spark motorcycle gasoline engine: A wide condition range study. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymlet, N.; Lijewski, P.; Sokolnicka, B.; Siedlecki, M.; Domowicz, A. Analysis of research method, results and regulations regarding the exhaust emissions from two-wheeled vehicles under actual operating conditions. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kašpar, J.; Fornasiero, P.; Hickey, N. Automotive catalytic converters: Current status and some perspectives. Catal. Today 2003, 77, 419–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, A.; Mądziel, M.; Lejda, K. Creating an emission model based on portable emission measurement system for the purpose of a roundabout. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21641–21654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; Fu, J.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, H. Experimental study on combustion and emission characteristics of turbocharged gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine under cold start new European driving cycle (NEDC). Fuel 2018, 215, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Martinet, S.; Zhang, Y.; Andre, M.; Mao, H. Real-world gaseous emission characteristics of Euro 6b light-duty gasoline- and diesel-fueled vehicles. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 78, 102215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Fang, X.; Wei, N.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Yang, L. Transient characterization of automotive exhaust emission from different vehicle types based on on-road measurements. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonen, P.; Kalliokoski, J.; Karjalainen, P.; Rönkkö, T.; Timonen, H.; Saarikoski, S.; Aurela, M.; Bloss, M.; Triantafyllopoulos, G.; Kontses, A.; et al. Characterization of laboratory and real driving emissions of individual Euro 6 light-duty vehicles—Fresh particles and secondary aerosol formation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Son, J.; Myung, C.-L.; Park, S. Comparative study on low ambient temperature regulated/unregulated emissions characteristics of idling light-duty diesel vehicles at cold start and hot restart. Fuel 2018, 233, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikas, G.; Zervas, E. Regulated and non-regulated pollutants emitted during the regeneration of a diesel particulate filter. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Jeon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Characterization of particulate matter from diesel passenger cars tested on chassis dynamometers. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R’Mili, B.; Boréave, A.; Meme, A.; Vernoux, P.; Leblanc, M.; Noël, L.; Raux, S.; D’Anna, B. Physico-chemical characterization of fine and ultrafine particles emitted during diesel particulate filter active regeneration of Euro 5 diesel vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3312–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruehl, C.; Smith, J.D.; Ma, Y.; Shields, J.E.; Burnitzki, M.; Sobieralski, W.; Ianni, R.; Chernich, D.J.; Chang, M.-C.O.; Collins, J.F.; et al. Emissions during and real-world frequency of heavy-duty diesel particulate filter regeneration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5868–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Gioria, R.; Carriero, M.; Lähde, T.; Forloni, F.; Perujo, A.; Martini, G.; Bissi, L.M.; Terenghi, R. Emission factors of a Euro VI heavy-duty diesel refuse collection vehicle. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doozandegan, M.; Hosseini, V.; Ehteram, M.A. Solid nanoparticle and gaseous emissions of a diesel engine with a diesel particulate filter and use of a high-sulphur diesel fuel and a medium-sulphur diesel fuel. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. D J. Automob. Eng. 2017, 231, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, D.; Knauer, M.; Emmerling, G.; Deyerling, D.; Niessner, R. Emissions during active regeneration of a diesel particulate filter on a heavy duty diesel engine: Stationary tests. J. Aerosol Sci. 2015, 90, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.D.; Ruehl, C.; Burnitzki, M.; Sobieralski, W.; Ianni, R.; Quiros, D.; Hu, S.; Chernich, D.; Collins, J.; Huai, T.; et al. Real-time particulate emissions rates from active and passive heavy-duty diesel particulate filter regeneration. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 680, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| System | Laboratory HCs | Laboratory H2SO4 | Vehicles’ Aerosol |
|---|---|---|---|
| ET | 13 | 6 | 14 |
| CS | 15 (9) | 7 (5) | 8 (7) |
| CS vs. ET or TD | 10 (6) | 6 (4) | 8 (7) |
| Technology | Period | NM [mg/m3] | Gas HCs [ppm] | SO2 [ppm] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moped | Cold start | >10 | >50,000 | 60 | [8,34,49] |
| Motorcycle | Cold start | 10,000–35,000 | 12–20 | [120,121,122] | |
| Motorcycle | Cycle | 0.4 | 300–5000 | 9–20 | [123,124] |
| LD Gasoline | Cold start | 5 | 12,000 | 10 | [125,126,127,128,129,130] |
| LD Diesel | Cold start | low | 350 | 10 | [128,131] |
| LD Diesel | Regeneration | 1 | 200 | 25 | [57,132,133,134] |
| HD Diesel | Regeneration | 1–12 | 250 | 150 | [109,115,135,136,137,138,139] |
| Test | Comment | Example | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle losses | As required in the regulation | [33,36] | |
| Wall temperature | As required in the regulation | 300 °C to 350 °C | Regulation |
| SO2 to SO3 conversion | To be declared | % | [33,36] |
| Sulfur storage capacity | Based on SO2 | mg | [33,36] |
| VRE H2SO4 | Feasibility to be assessed | >99.9%; >1 mg/m3 | [39,44] |
| VRE gaseous HCs | Long term efficiency C3H8 | >99.9%; >10,000 ppm | [33] |
| VRE particle HCs | Tetracontane particles | >99.9%; >1 mg/m3 | [30,33,36] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giechaskiel, B.; Melas, A.D.; Lähde, T.; Martini, G. Non-Volatile Particle Number Emission Measurements with Catalytic Strippers: A Review. Vehicles 2020, 2, 342-364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles2020019
Giechaskiel B, Melas AD, Lähde T, Martini G. Non-Volatile Particle Number Emission Measurements with Catalytic Strippers: A Review. Vehicles. 2020; 2(2):342-364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles2020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiechaskiel, Barouch, Anastasios D. Melas, Tero Lähde, and Giorgio Martini. 2020. "Non-Volatile Particle Number Emission Measurements with Catalytic Strippers: A Review" Vehicles 2, no. 2: 342-364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles2020019
APA StyleGiechaskiel, B., Melas, A. D., Lähde, T., & Martini, G. (2020). Non-Volatile Particle Number Emission Measurements with Catalytic Strippers: A Review. Vehicles, 2(2), 342-364. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles2020019