Peptidomic Fingerprints of Stored UHT Milk Inoculated with Protease Extracts from Different Pseudomonas Strains Relative to aprX Expression and Visible Spoilage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Preparation of Bacterial Extracellular Extracts
2.2. UHT Milk Preparation, Storage Experiment and Sampling
2.3. Determination of Physical Stability in Inoculated UHT Milk during Storage
2.4. Determination of Proteolytic Activity in Inoculated UHT Milk during Storage
2.5. Peptidomics of Inoculated UHT Milk from Storage Experiment
2.6. aprX mRNA Gene Expression
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
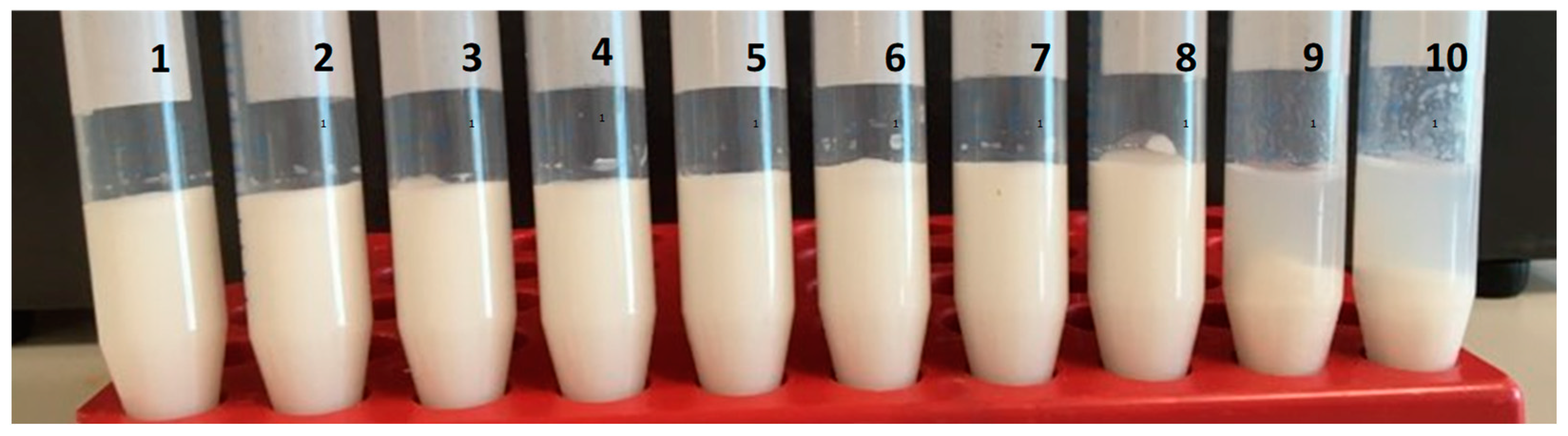
3.1. Physical Stability during Storage
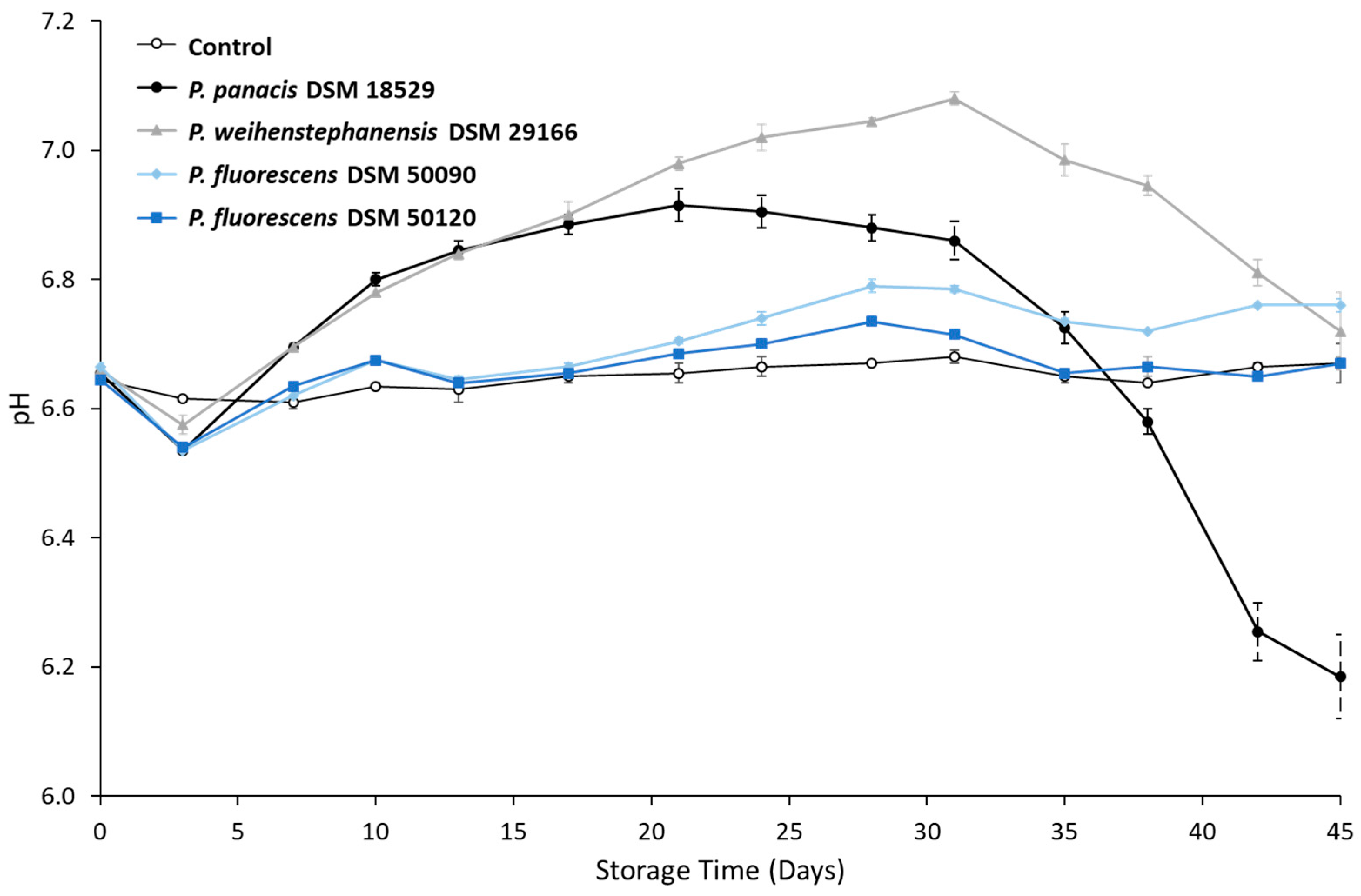
3.2. Development in pH during Storage
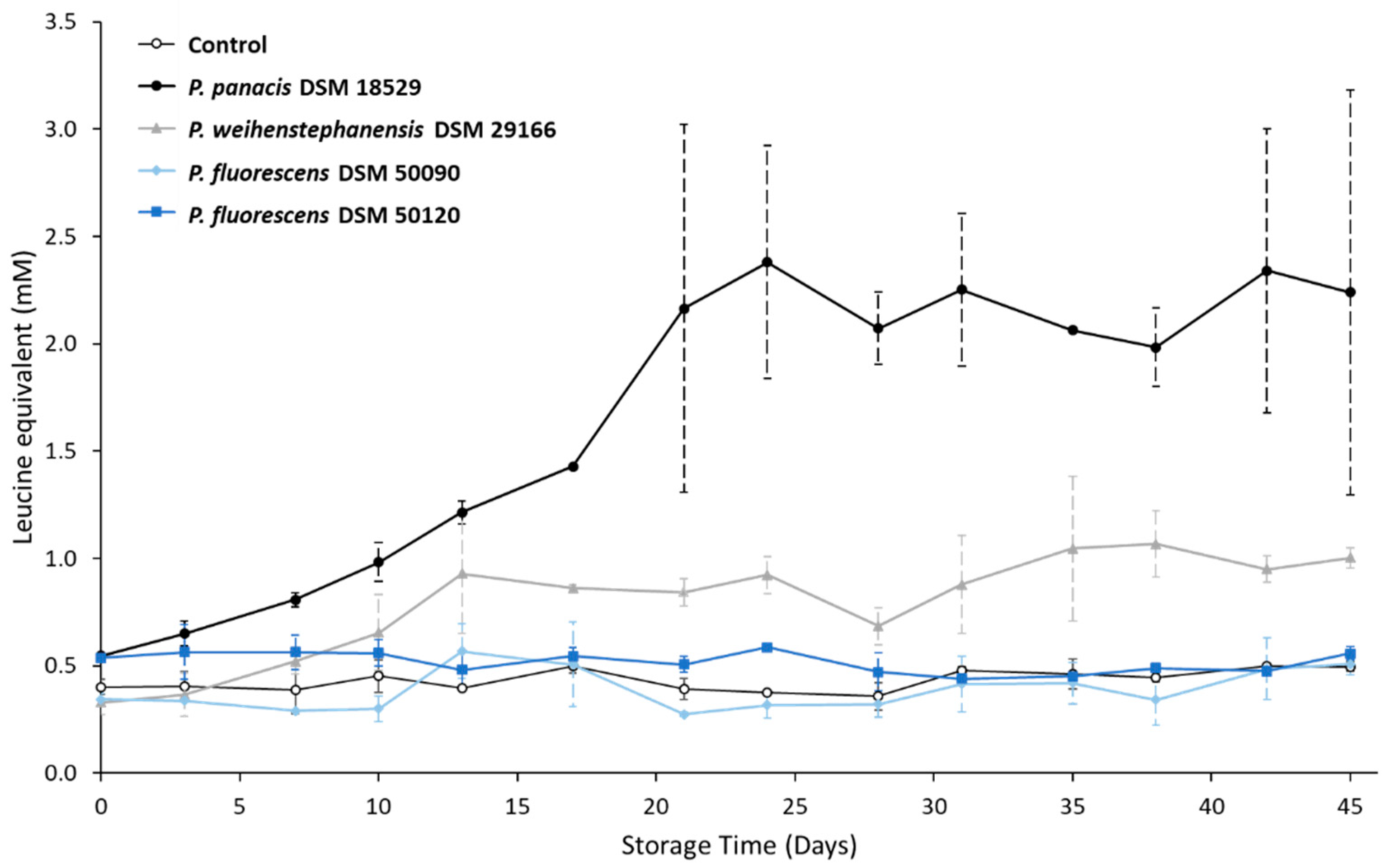
3.3. Development in Proteolysis Level during Storage
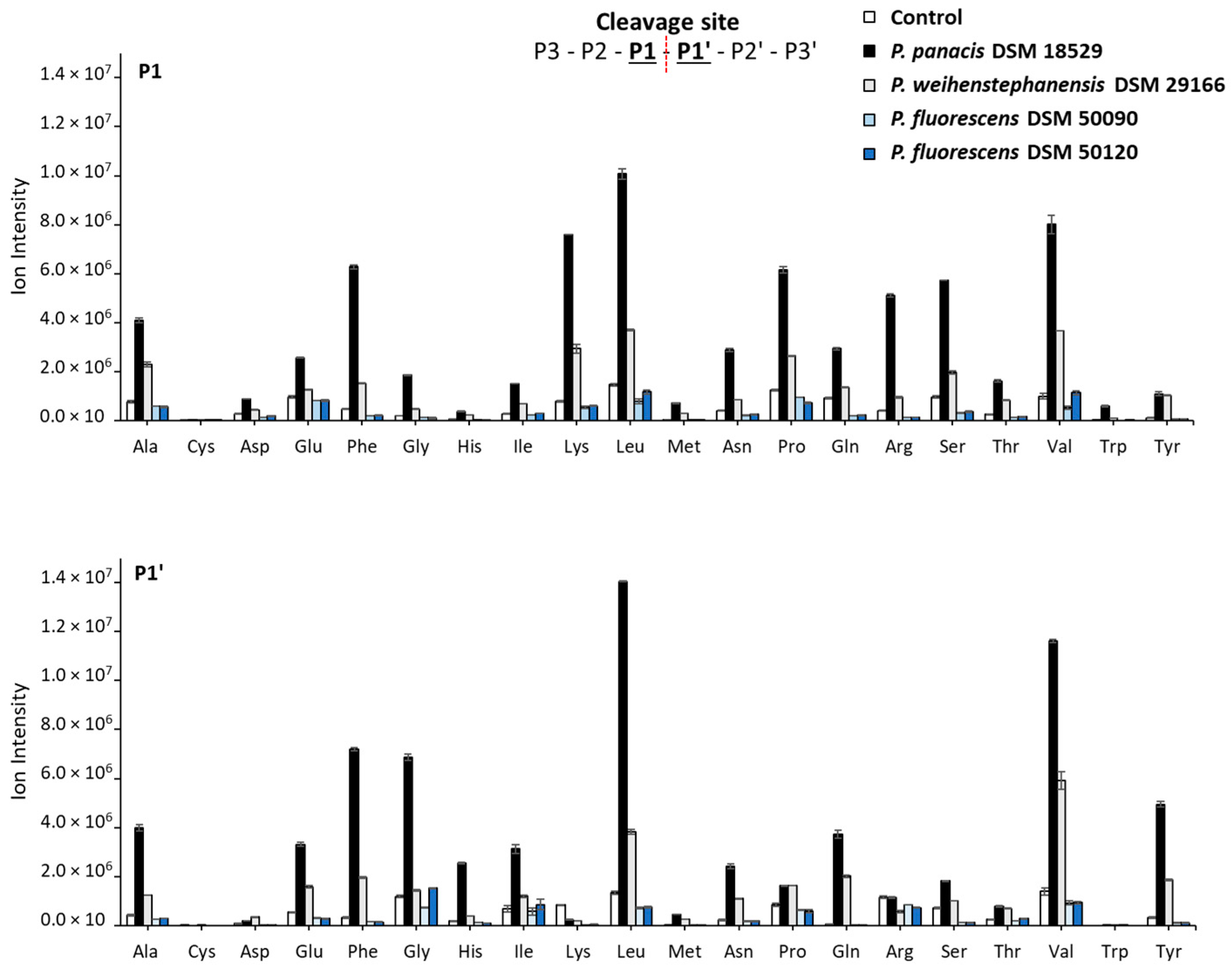
3.4. Generated Peptides and Sites Cleaved in the Major Milk Proteins by Peptidomic Analysis after 45 Days of Storage
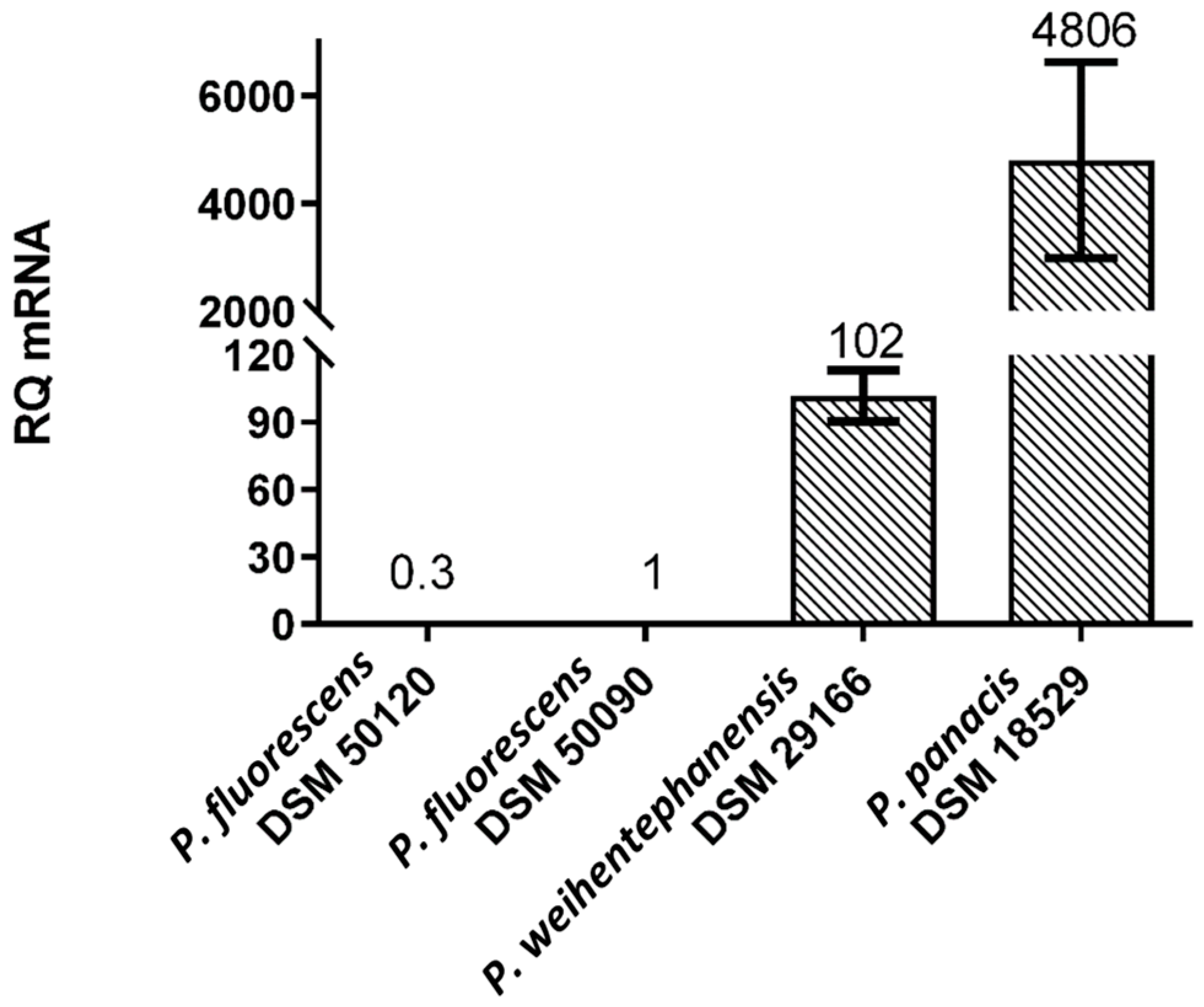
3.5. Expression Levels of aprX mRNA
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship between Spoilage Potential, Milk Proteolysis and aprX Expression
4.2. pH Changes and UHT Milk Spoilage during Storage
4.3. Peptidomics: Identified Peptides and Cleavage Sites
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beldman, A.; Junfei, B.; Binbin, C.; Zhijun, C.; Xiangming, F.; Wen, D.; Huiyuan, G.; Pei, G.; Beizhong, H.; Dinghuan, H.; et al. White Paper. China Dairy, 1 January 2014; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gooch, E.; Hoskin, R.; Law, J. China’s Dairy Supply and Demand. Livestock, Dairy, Poult. Outlook 2017, 282, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, C.; Rentschler, E.; Krewinkel, M.; Merz, M.; von Neubeck, M.; Wenning, M.; Scherer, S.; Stoeckel, M.; Hinrichs, J.; Stressler, T.; et al. Thermostability of peptidases secreted by microorganisms associated with raw milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 56, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.G.; Baglinière, F.; Marchand, S.; Van Coillie, E.; Vanetti, M.C.D.; De Block, J.; Heyndrickx, M. The Biodiversity of the Microbiota Producing Heat-Resistant Enzymes Responsible for Spoilage in Processed Bovine Milk and Dairy Products. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.; Torres-Frenzel, P.; Wiedmann, M. Invited review: Controlling dairy product spoilage to reduce food loss and waste. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Enzymology of Milk and Milk Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783319148915. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, S.; Vandriesche, G.; Coorevits, A.; Coudijzer, K.; De Jonghe, V.; Dewettinck, K.; De Vos, P.; Devreese, B.; Heyndrickx, M.; De Block, J. Heterogeneity of heat-resistant proteases from milk Pseudomonas species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 133, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, R.G.; Burger, M.; Beven, C.-A.; Beacham, I.R. The aprX–lipA operon of Pseudomonas fluorescens B52: A molecular analysis of metalloprotease and lipase production The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences reported in this paper are AF216700, AF216701 and AF216702. Microbiology 2001, 147, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, C.; Hofmann, K.; Huptas, C.; Scherer, S.; Wenning, M.; Lücking, G. Simultaneous quantification of the most common and proteolytic Pseudomonas species in raw milk by multiplex qPCR. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 1693–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bijl, E.; Svensson, B.; Hettinga, K. The Extracellular Protease AprX from Pseudomonas and its Spoilage Potential for UHT Milk: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 834–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinidou, S.; Peterson, D.G. Control of Maillard-Type Off-Flavor Development in Ultrahigh-Temperature-Processed Bovine Milk by Phenolic Chemistry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8023–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, D.; Nicodème, M.; Perrin, C.; Driou, A.; Brusseaux, E.; Humbert, G.; Gaillard, J.-L.; Dary, A. Molecular typing of industrial strains of Pseudomonas spp. isolated from milk and genetical and biochemical characterization of an extracellular protease produced by one of them. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, N.; Deeth, H. Age Gelation of UHT Milk—A Review. Food Bioprod. Process. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. Part C 2001, 79, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, I.; Tanguy, G.; Fauquant, J.; Jardin, J.; Rousseau, F.; Robert, B.; Madec, M.-N.; Gaucheron, F. Proteolysis of casein micelles by Pseudomonas fluorescens CNRZ 798 contributes to the destabilisation of UHT milk during its storage. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2011, 91, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, N.; Kelly, A. The Role of Proteases in the Stability of UHT-Treated Milk. In Agents of Change; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 311–347. ISBN 9783030554828. [Google Scholar]
- Matéos, A.; Guyard-Nicodème, M.; Baglinière, F.; Jardin, J.; Gaucheron, F.; Dary, A.; Humbert, G.; Gaillard, J.-L. Proteolysis of milk proteins by AprX, an extracellular protease identified in Pseudomonas LBSA1 isolated from bulk raw milk, and implications for the stability of UHT milk. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 49, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Poojary, M.M.; Rauh, V.M.; Ray, C.A.; Olsen, K.; Lund, M.N. Quantitation of α-Dicarbonyls and Advanced Glycation Endproducts in Conventional and Lactose-Hydrolyzed Ultrahigh Temperature Milk during 1 Year of Storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12863–12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglinière, F.; Tanguy, G.; Jardin, J.; Matéos, A.; Briard, V.; Rousseau, F.; Robert, B.; Beaucher, E.; Humbert, G.; Dary, A.; et al. Quantitative and qualitative variability of the caseinolytic potential of different strains of Pseudomonas fluorescens: Implications for the stability of casein micelles of UHT milks during their storage. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, C.; Krewinkel, M.; Kutzli, I.; Kranz, B.; von Neubeck, M.; Huptas, C.; Wenning, M.; Scherer, S.; Stoeckel, M.; Hinrichs, J.; et al. Isolation and characterisation of a heat-resistant peptidase from Pseudomonas panacis withstanding general UHT processes. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 49, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, M.; Lidolt, M.; Achberger, V.; Glück, C.; Krewinkel, M.; Stressler, T.; von Neubeck, M.; Wenning, M.; Scherer, S.; Fischer, L.; et al. Growth of Pseudomonas weihenstephanensis, Pseudomonas proteolytica and Pseudomonas sp. in raw milk: Impact of residual heat-stable enzyme activity on stability of UHT milk during shelf-life. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 59, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bijl, E.; Hettinga, K. Destabilization of UHT milk by protease AprX from Pseudomonas fluorescens and plasmin. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.; Huptas, C.; Von Neubeck, M.; Scherer, S.; Wenning, M.; Lücking, G. Genetic Organization of the aprX-lipA2 Operon Affects the Proteolytic Potential of Pseudomonas Species in Milk. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, V.; Schalk, J.; Anema, S.G. Sedimentation in UHT milk. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 78, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, M.; Johansen, L.B.; Rauh, V.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B. Contribution of casein micelle size and proteolysis on protein distribution and sediment formation in UHT milk during storage. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, T.; Clausen, M.R.; Sundekilde, U.K.; Eggers, N.; Nyegaard, S.; Larsen, L.B.; Ray, C.; Sundgren, A.; Andersen, H.J.; Bertram, H.C. Lactose-Hydrolyzed Milk Is More Prone to Chemical Changes during Storage than Conventional Ultra-High-Temperature (UHT) Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7886–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Jakobsen, L.M.; Geiker, N.R.; Bertram, H.C. Chemically acidified, live and heat-inactivated fermented dairy yoghurt show distinct bioactive peptides, free amino acids and small compounds profiles. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Beverly, R.L.; Dallas, D.C. Milk Proteins Are Predigested Within the Human Mammary Gland. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2017, 22, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, U.M.; Costa, E.D.; Mantovani, H.C.; Vanetti, M. The proteolytic activity of Pseudomonas fluorescens 07A isolated from milk is not regulated by quorum sensing signals. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matselis, E.; Roussis, I. Proteinase and lipase production by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Proteolysis and lipolysis in thermized ewe’s milk. Food Control 1998, 9, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Pinto, U.; Riedel, K.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Milk-deteriorating exoenzymes from Pseudomonas fluorescens 041 isolated from refrigerated raw milk. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunsell, B.; Adams, C.; O’Gara, F. Complex regulation of AprA metalloprotease in Pseudomonas fluorescens M114: Evidence for the involvement of iron, the ECF sigma factor, PbrA and pseudobactin M114 siderophore. Microbiology 2006, 152, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G. Age Gelation, Sedimentation, and Creaming in UHT Milk: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 18, 140–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, J.M.S.; Deeth, H.C. Cross-Linking of Proteins and Other Changes in UHT Milk during Storage at Different Temperatures. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 2008, 63, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ranvir, S.; Sharma, R.; Gandhi, K.; Nikam, P.; Mann, B. Physico-chemical changes during processing and storage of UHT milk. Indian J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 74, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, M.; Johansen, L.B.; Rauh, V.; Sørensen, J.; Larsen, L.B.; Poulsen, N.A. Relationship between casein micelle size, protein composition and stability of UHT milk. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 112, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. Physicochemical changes and age gelation in stored UHT milk: Seasonal variations. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 118, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, J.M.; Gennari, A.; Monteiro, B.W.; Lehn, D.N.; Souza, C.F.V. Effects of Pasteurization and Ultra-High Temperature Processes on Proximate Composition and Fatty Acid Profile in Bovine Milk. Am. J. Food Technol. 2015, 10, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglinière, F.; Matéos, A.; Tanguy, G.; Jardin, J.; Briard-Bion, V.; Rousseau, F.; Robert, B.; Beaucher, E.; Gaillard, J.L.; Amiel, C.; et al. Proteolysis of ultra high temperature-treated casein micelles by AprX enzyme from Pseudomonas fluorescens F induces their destabilisation. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 31, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuknytė, M.; Decimo, M.; Colzani, M.; Silvetti, T.; Brasca, M.; Cattaneo, S.; Aldini, G.; De Noni, I. Extracellular thermostable proteolytic activity of the milk spoilage bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens PS19 on bovine caseins. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4188–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, I.; García-Risco, M.R.; Ramos, M.; López-Fandiño, R. Characterization of peptides produced by the action of psychrotrophic proteinases on κ-casein. J. Dairy Res. 2000, 67, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.R.; Coolbear, T.; Ayers, J.S.; Coolbear, K.P. The action of chymosin on κ-casein and its macropeptide: Effect of pH and analysis of products of secondary hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; García-Risco, M.R.; López-Fandiño, R. Proteolysis, protein distribution and stability of UHT milk during storage at room temperature. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo-Lira, C.; Oria, M.; Hayes, K.; Nielsen, S. Effect of Psychrotrophic Bacteria and of an Isolated Protease from Pseudomonas fluorescens M3/6 on the Plasmin System of Fresh Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2190–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohbieter, K.; Ismail, B.; Nielsen, S.; Hayes, K. Effects of Pseudomonas fluorescens M3/6 Bacterial Protease on Plasmin System and Plasminogen Activation. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3392–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target Gene and Strains | Sequence (5′–3′) | Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| rpoB (Universal) | F: 5′-CAGCCGYTGGGTGGTAA-3′ R: 5′-CCGTTCACATCGTCCGA-3′ | 130 | [9] |
| aprX P. panacis DSM 18529 | F: 5′-AAATCGATAGCTTCAGCC-3′ R: 5′-GAGGTCAGGAAGGTGTAG-3′ P: 5′-Fam-ACGGTGTAGGAGGGTTTGC-BHQ-1-3′ | 169 | This study |
| aprX P. weihenstephanensis DSM 29166 | F: 5′-TGTGCAAAAGCTGTATGG-3′ R: 5′-GTGAGGTTGATTTTCTGG T -3′ P: 5′-Fam-CGAGGTGGCGCTATAGAAGT-BHQ-1-3′ | 195 | This study |
| aprX P. fluorescens DSM 50090 | F: 5′-TAAAGGGACAGCAGGACTAG-3′ R: 5′-GAGCAACACCAACCAGAA-3′ P: 5′-Fam-CCACCGTCCCATACCGAAAACA-BHQ-1-3′ | 248 | This study |
| aprX P. fluorescens DSM 50120 | F: 5′-ATCTTACCTACACCTTCC-3′ R: 5′-CCACTTGTGTTGTACTTC-3′ P: 5′-Fam-TCAGCCAGTTCAGCAACC-BHQ-1-3′ | 265 | This study |
| Control | P. panacis DSM 18529 | P. weihenstephanensis DSM 29166 | P. fluorescens DSM 50090 | P. fluorescens DSM 50120 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative number of peptide distribution (%) | β-casein | 45 | 50 | 47 | 45 | 48 |
| αs1-casein | 23 | 25 | 22 | 25 | 25 | |
| αs2-casein | 12 | 10 | 13 | 13 | 12 | |
| κ-casein | 13 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 11 | |
| β-lactoglobulin | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 5 | |
| Relative ion intensity distribution (%) | β-casein | 65 | 67 | 67 | 61 | 62 |
| αs1-casein | 14 | 26 | 17 | 18 | 15 | |
| αs2-casein | 8 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 9 | |
| κ-casein | 7 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 8 | |
| β-lactoglobulin | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilera-Toro, M.; Nielsen, S.D.-H.; Kragh, M.L.; Xiao, Y.; Hansen, L.T.; Rauh, V.; Wiking, L.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B. Peptidomic Fingerprints of Stored UHT Milk Inoculated with Protease Extracts from Different Pseudomonas Strains Relative to aprX Expression and Visible Spoilage. Dairy 2023, 4, 83-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010005
Aguilera-Toro M, Nielsen SD-H, Kragh ML, Xiao Y, Hansen LT, Rauh V, Wiking L, Poulsen NA, Larsen LB. Peptidomic Fingerprints of Stored UHT Milk Inoculated with Protease Extracts from Different Pseudomonas Strains Relative to aprX Expression and Visible Spoilage. Dairy. 2023; 4(1):83-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilera-Toro, Miguel, Søren Drud-Heydary Nielsen, Martin Laage Kragh, Yinghua Xiao, Lisbeth Truelstrup Hansen, Valentin Rauh, Lars Wiking, Nina Aagaard Poulsen, and Lotte Bach Larsen. 2023. "Peptidomic Fingerprints of Stored UHT Milk Inoculated with Protease Extracts from Different Pseudomonas Strains Relative to aprX Expression and Visible Spoilage" Dairy 4, no. 1: 83-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010005
APA StyleAguilera-Toro, M., Nielsen, S. D.-H., Kragh, M. L., Xiao, Y., Hansen, L. T., Rauh, V., Wiking, L., Poulsen, N. A., & Larsen, L. B. (2023). Peptidomic Fingerprints of Stored UHT Milk Inoculated with Protease Extracts from Different Pseudomonas Strains Relative to aprX Expression and Visible Spoilage. Dairy, 4(1), 83-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dairy4010005






