Piplartine, a Bioactive Amide from Piper truncatum, Displays Potent Anthelmintic Activity Against the Zoonotic Nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Extraction and Isolation of Piplartine
2.4. Parasite and Animal Maintenance
2.5. Antiparasitic Activity Against A. cantonensis L1
2.6. Antiparasitic Activity Against A. cantonensis L3
2.7. Selectivity Assessment in C. elegans
2.8. Computational ADME Profiling
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Ethical Compliance
3. Results
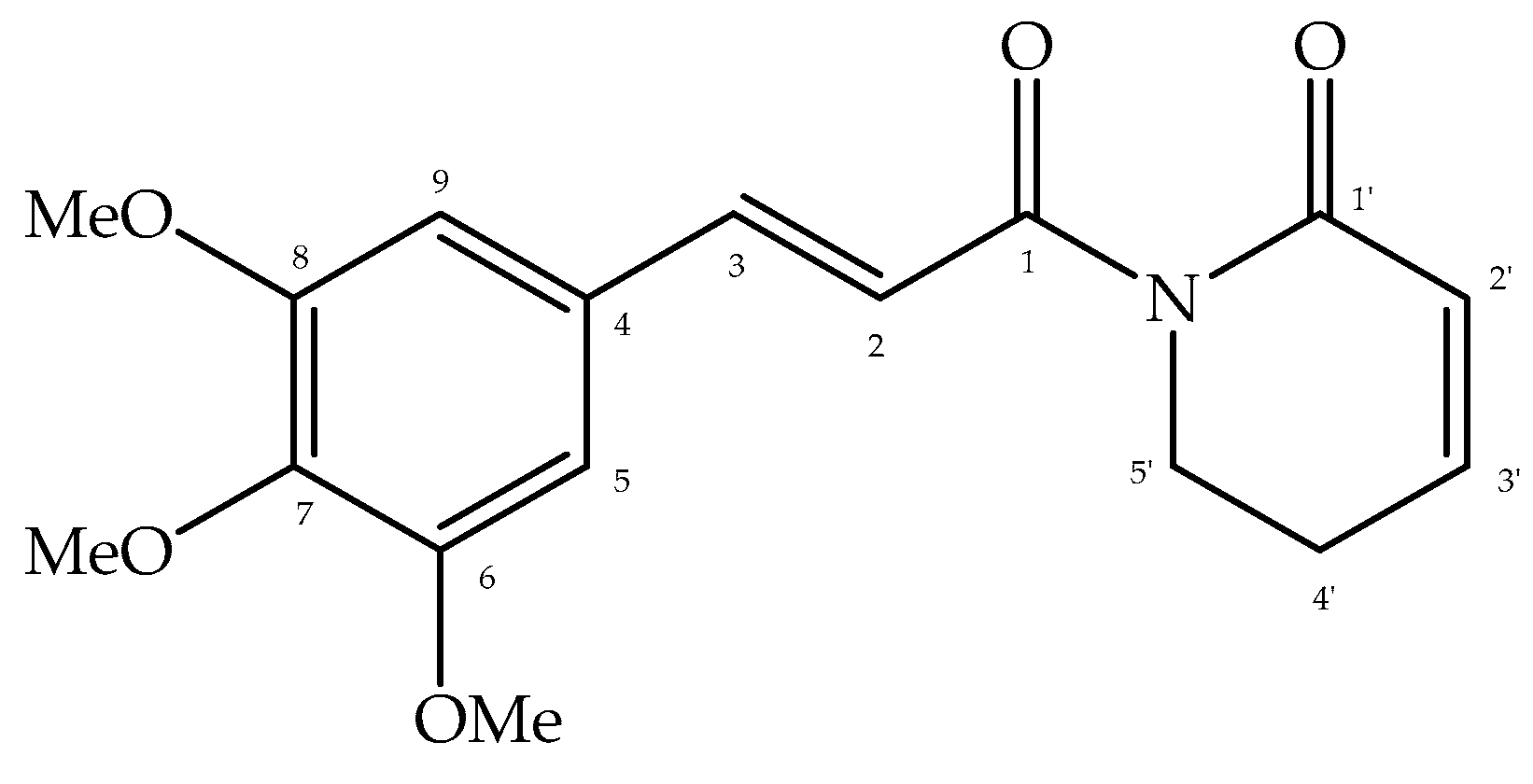
3.1. Chemical Characterization of Piplartine
3.2. Anthelmintic Activity Against A. cantonensis Larvae
3.3. Selectivity and Safety Profile
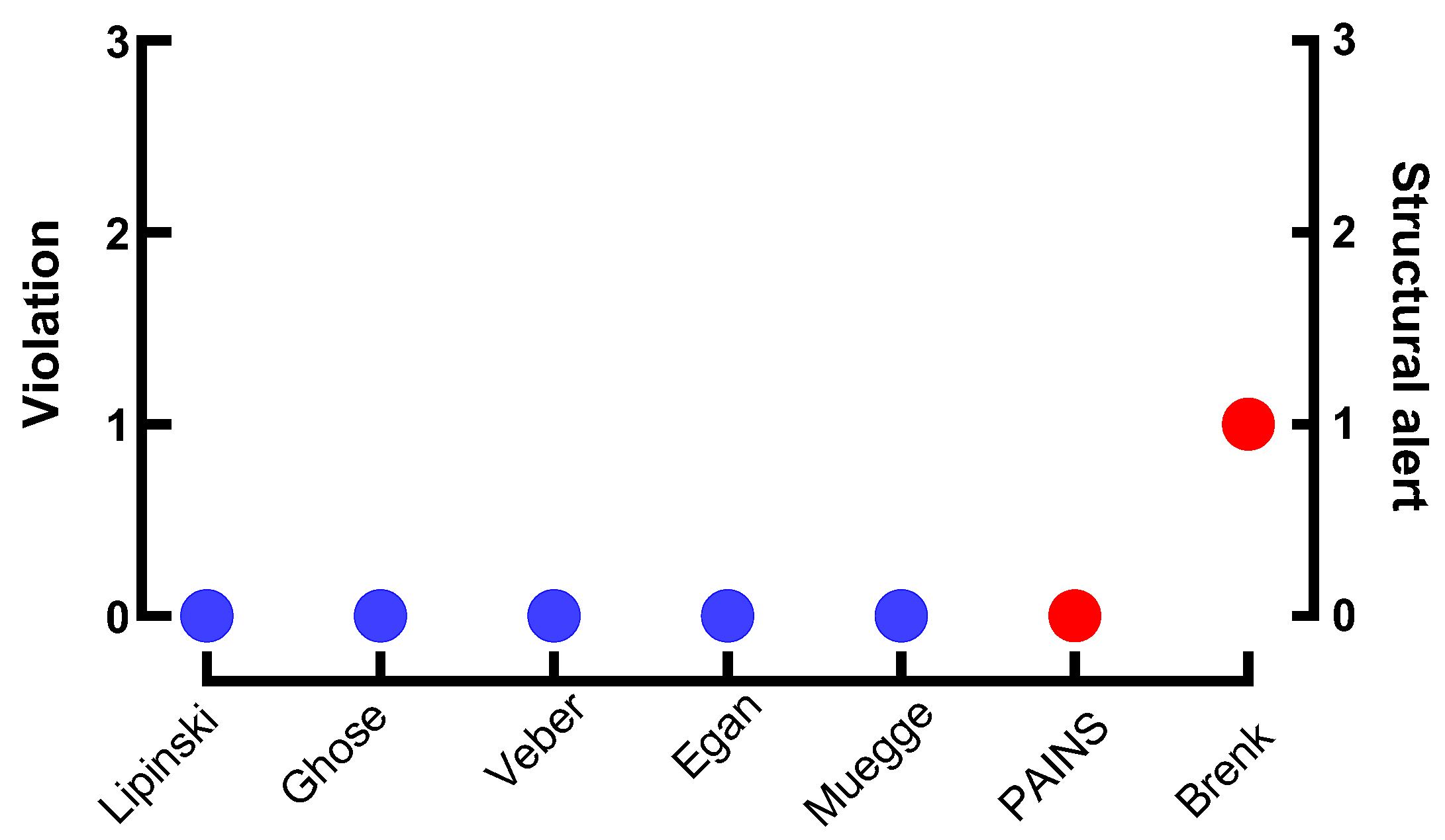
3.4. In Silico ADME and Drug-Likeness Profiling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CC | Column Chromatography |
| CDCl3 | Deuterated Chloroform |
| CONCEA | Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal/National Council for the Control of Animal Experimentation |
| d | Doublet |
| dd | Double-Doublet |
| ddt | Double-Double-Triplet |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| EC50 | Effective Concentration at 50% |
| EtOAc | Ethyl Acetate |
| GSK | GlaxoSmithKline |
| HIA | Passive Gastrointestinal Absorption |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| J | Coupling Constant |
| L1 | First-Stage Larvae |
| L3 | Infective Third-Stage Larvae |
| LD50 | Lethal Dose 50% |
| m | Multiplet |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MHz | Megahertz |
| mM | Micromolar |
| NGM | Nematode Growth Medium |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| PAINS | Pan-Assay Interference |
| PDA | Photodiode Array |
| P-gp | P-Glycoprotein |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute |
| s | Singlet |
| SISGEN | Sistema Nacional de Gestão do Patrimônio Genético e do Conhecimento Tradicional Associado/National System For The Management of Genetic Heritage and Associated Traditional Knowledge |
| SMILES | Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System |
| t | Triplet |
| TLC | Thin Layer Chromatography |
| TMS | Tetramethyl Silane |
| TPSA | Topological Polar Surface Area |
| WLOGP | Wildman Lipophilicity |
References
- King, C.H. Helminthiasis Epidemiology and Control: Scoring Successes and Meeting the Remaining Challenges. Adv. Parasitol. 2019, 103, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Griffin, C.D.; Ezenwa, V.O.; Cowie, R.H. Insights into the Biology of the Rat Lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Parasites Vectors 2025, 18, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Chen, S.; Duan, L.; Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Lv, S. The Global Spread Pattern of Rat Lungworm Based on Mitochondrial Genetics. Pathogens 2023, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohal, R.J.; Gilotra, T.S.; Nguyen, A.D.; Lui, F. Angiostrongyliasis; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.; Steel, A.; Howe, K.; Jarvi, S. Management of Rat Lungworm Disease (Neuroangiostrongyliasis) Using Anthelmintics: Recent Updates and Recommendations. Pathogens 2022, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengarda, A.C.; Silva, T.C.; Silva, A.S.; Roquini, D.B.; Fernandes, J.P.S.; de Moraes, J. Toward Anthelmintic Drug Candidates for Toxocariasis: Challenges and Recent Developments. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 251, 115268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Dai, L.; Cao, X.; Ma, Y.; Gulnaz, I.; Miao, X.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Natural products in antiparasitic drug discovery: Advances, opportunities and challenges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.; Lago, J.H.G. Natural Products as Lead Compounds for Treatment of Neglected Tropical Diseases: Dream or Reality? Future Med. Chem. 2022, 14, 1607–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Gyawali, R.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Rajkovic, J.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Khan, T.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Ozleyen, A.; Turkdonmez, E.; et al. Piper Species: A Comprehensive Review on Their Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo-Vilges, K.M.; Oliveira, S.V.; Couto, S.C.P.; Fokoue, H.H.; Romero, G.A.S.; Kato, M.J.; Romeiro, L.A.S.; Leite, J.R.S.A.; Kuckelhaus, S.A.S. Effect of Piplartine and Cinnamides on Leishmania amazonensis, Plasmodium falciparum and on Peritoneal Cells of Swiss Mice. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticona, J.C.; Bilbao-Ramos, P.; Flores, N.; Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Bolás-Fernàndez, F.; Jiménez, I.A.; Bazzocchi, I.L. (E)-Piplartine Isolated from Piper pseudoarboreum, a Lead Compound Against Leishmaniasis. Foods 2020, 9, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, D.; Vanathi, P.; Gowri, P.M.; Rao, V.R.S.; Rao, J.M.; Sreedhar, A.S. Diferuloylmethane Augments the Cytotoxic Effects of Piplartine Isolated from Piper chaba. Toxicol. Vitr. 2009, 23, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodiwala, H.S.; Singh, G.; Singh, R.; Dey, C.S.; Sharma, S.S.; Bhutani, K.K.; Singh, I.P. Antileishmanial Amides and Lignans from Piper cubeba and Piper retrofractum. J. Nat. Med. 2007, 61, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Tyagi, A.K. Historical Spice as a Future Drug: Therapeutic Potential of Piperlongumine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4151–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, V.S.; Jain, S.C.; Bisht, K.S.; Jain, R.; Taneja, P.; Jha, A.; Tyagi, O.D.; Prasad, A.K.; Wengel, J.; Olesen, C.E.; et al. Phytochemistry of the genus Piper. Phytochemistry 1997, 46, 597–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.F.; Ramos, Y.J.; de Lima Moreira, D.; Alves, C.R.; Gonçalves-Oliveira, L.F. Potential of Piper spp. as a Source of New Compounds for the Leishmaniases Treatment. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 2731–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, J.; Keiser, J.; Ingram, K.; Nascimento, C.; Yamaguchi, L.F.; Bittencourt, C.R.; Bemquerer, M.P.; Leite, J.R.; Kato, M.J.; Nakano, E. In Vitro Synergistic Interaction between Amide Piplartine and Antimicrobial Peptide Dermaseptin against Schistosoma mansoni Schistosomula and Adult Worms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campelo, Y.D.M.; Mafud, A.C.; Véras, L.M.C.; Guimarães, M.A.; Yamaguchi, L.F.; Lima, D.F.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Kato, M.J.; Mendonça, R.Z.; Pinto, P.L.S.; et al. Synergistic Effects of In Vitro Combinations of Piplartine, Epiisopiloturine and Praziquantel against Schistosoma mansoni. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S. The Genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugai, E.; Mattos, T.; Brisola, A. Nova Técnica para Isolar Larvas de Nematóides das Fezes–Modificação do Método de Baermann. Rev. Inst. Adolfo Lutz 1954, 14, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquini, D.B.; Silva, G.L.; Ferreira, L.L.G.; Andricopulo, A.D.; Wilairatana, P.; de Moraes, J. Susceptibility of Angiostrongylus cantonensis Larvae to Anthelmintic Drugs. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 901459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquini, D.B.; Lemes, B.L.; Kreutz, A.L.B.; Spoladore, S.C.; Amaro, M.C.; Lopes, F.B.; Fernandes, J.P.S.; de Moraes, J. Antihistamines H1 as Potential Anthelmintic Agents against the Zoonotic Parasite Angiostrongylus cantonensis. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31159–31165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Mota, D.J.G.; de Melo, L.C.V.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Gava, R.; Pinto, P.L.S. First Record of Natural Infection by Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea) in Belocaulus willibaldoi and Rattus norvegicus in an Urban Area of São Paulo City, SP, Brazil. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, D.C.S.; Totini, C.H.; Cajás, R.A.; Teixeira, T.R.; Oliveira, E.A.; Cirino, M.E.; Souza, M.C.; Salvadori, M.C.; Teixeira, F.S.; de Moraes, J.; et al. In Vivo Antischistosomal Efficacy of Porcelia ponderosa γ-Lactones. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirino, M.E.; Teixeira, T.R.; Silva, A.M.H.; Borges, A.C.C.; Fukui-Silva, L.; Wagner, L.G.; Fernandes, C.; McCann, M.; Santos, A.L.S.; de Moraes, J. Anthelmintic Activity of 1,10-Phenanthroline-5,6-Dione-Based Metallodrugs. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, R.P.; Mengarda, A.C.; Silva, M.P.; Roquini, D.B.; Salvadori, M.C.; Teixeira, F.S.; Pinto, P.L.; Morais, T.R.; Ferreira, L.L.G.; Andricopulo, A.D.; et al. H1-antihistamines as antischistosomal drugs: In vitro and in vivo studies. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengarda, A.C.; Iles, B.; Longo, J.P.F.; de Moraes, J. Recent Trends in Praziquantel Nanoformulations for Helminthiasis Treatment. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, C.C.; Costa, P.S.; Laktin, G.T.; de Carvalho, P.H.; Geraldo, R.B.; de Moraes, J.; Pinto, P.L.; Couri, M.R.; Pinto, P.F.; Da Silva Filho, A.A. Cardamonin, a Schistosomicidal Chalcone from Piper aduncum L. (Piperaceae) That Inhibits Schistosoma mansoni ATP Diphosphohydrolase. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.A.; Campos, I.M.; Cajás, R.A.; Costa, D.S.; Carvalho, L.S.A.; Franklin, P.F.C.; de Nigro, N.P.D.; Pinto, P.F.; Capriles, P.S.Z.; de Moraes, J.; et al. In Vivo Efficacy of Uvangoletin from Piper aduncum (Piperaceae) against Schistosoma mansoni and In Silico Studies Targeting SmNTPDases. Exp. Parasitol. 2025, 269, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Sharma, A. Structural Insights and Pharmaceutical Relevance of Plumbagin in Parasitic Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Recent Adv. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2022, 17, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Imtiaz, M.; Al Nasr, I.; Koko, W.S.; Khan, T.A.; Jaremko, M.; Mahmood, S.; Fatmi, M.Q. Antiprotozoal Activity of Thymoquinone (2-Isopropyl-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone) for the Treatment of Leishmania major-Induced Leishmaniasis: In Silico and In Vitro Studies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.B.S.; Gomes, R.C.; Nunes, V.R.V.; Gonçalves, J.C.R.; Correia, C.A.; Dos Santos, A.Z.G.; de Sousa, D.P. The Antitumor Activity of Piplartine: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Min, X.; Zhuang, C.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Dong, G.; Yao, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological activity of piperlongumine derivatives as selective anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 82, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, M.; Shen, Y.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Fu, C.; Yan, Z.; Wu, Q.; Cao, J.; Sang, W.; Zeng, L.; et al. Piperlongumine selectively suppresses ABC-DLBCL through inhibition of NF-κB p65 subunit nuclear import. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2015, 462, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, D.P.; Pessoa, C.; de Moraes, M.O.; Saker-Neto, N.; Silveira, E.R.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Overview of the therapeutic potential of piplartine (piperlongumine). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.L.; Habenschus, M.D.; Barth, T.; Marques, L.M.; Pilon, A.C.; Bolzani, V.S.; Vessecchi, R.; Lopes, N.P.; Oliveira, A.R. Metabolic profile and safety of piperlongumine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33646. [Google Scholar]
- Pawłowska, M.; Mila-Kierzenkowska, C.; Szczegielniak, J.; Woźniak, A. Oxidative Stress in Parasitic Diseases—Reactive Oxygen Species as Mediators of Interactions between the Host and the Parasites. Antioxidants 2023, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.B.; Stone, S.A.; Koury, E.J.; Paredes, A.G.; Shao, F.; Lovato, C.; Chen, M.; Shi, R.; Li, A.Y.; Candal, I.; et al. Quantitative tests of albendazole resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans beta-tubulin mutants. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2024, 25, 100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
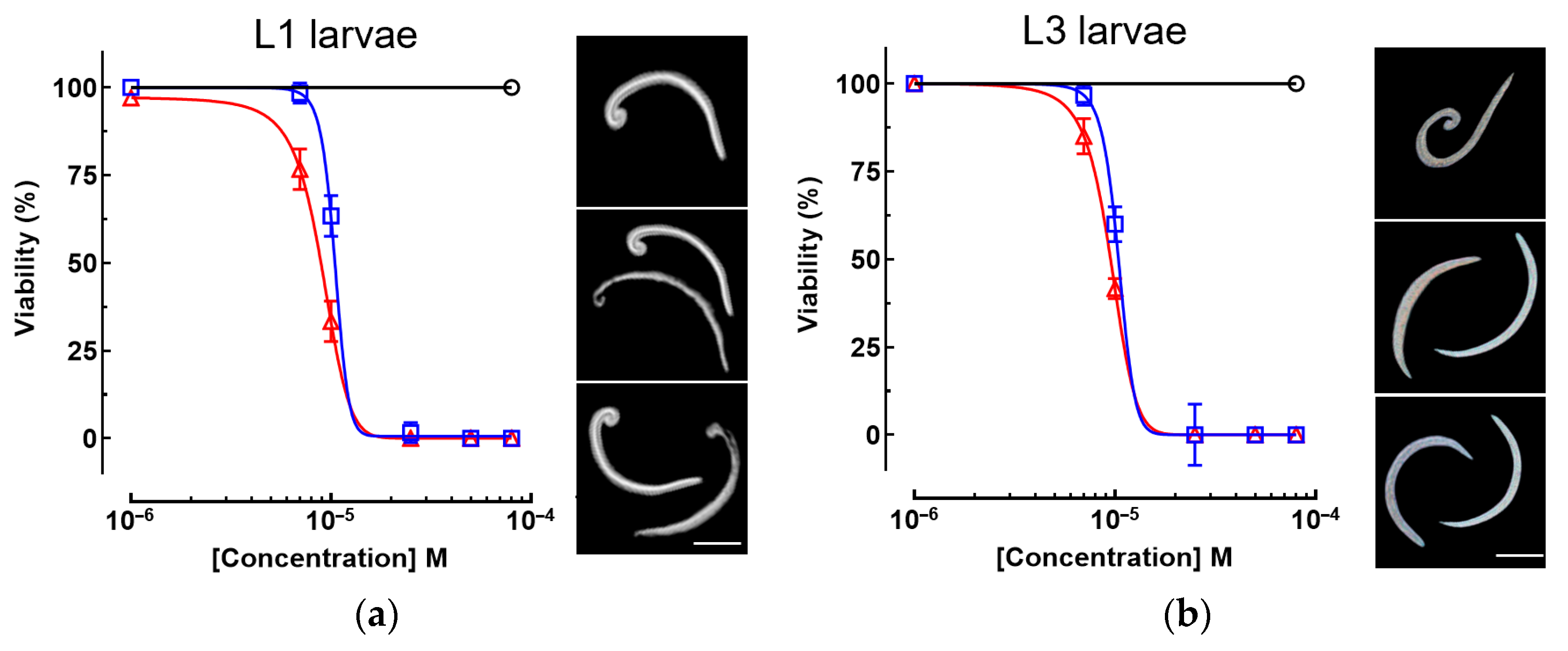

| Compound | A. cantonensis EC50 (µM) | C. elegans LD50 (µM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L3 | ||
| piplartine | 8.3 ± 0.9 * | 10.4 ± 0.7 * | > 500 |
| albendazole | 14.2 ± 1.1 | 15.6 ± 1.2 | 14.8 ± 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukui-Silva, L.; Spoladore, S.C.; Lemes, B.L.; Amorim, C.S.; Gonçalves, M.M.; Lago, J.H.G.; de Moraes, J. Piplartine, a Bioactive Amide from Piper truncatum, Displays Potent Anthelmintic Activity Against the Zoonotic Nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Chemistry 2025, 7, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040105
Fukui-Silva L, Spoladore SC, Lemes BL, Amorim CS, Gonçalves MM, Lago JHG, de Moraes J. Piplartine, a Bioactive Amide from Piper truncatum, Displays Potent Anthelmintic Activity Against the Zoonotic Nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Chemistry. 2025; 7(4):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040105
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukui-Silva, Lucas, Sophia C. Spoladore, Bruna L. Lemes, Camila S. Amorim, Marina M. Gonçalves, João Henrique G. Lago, and Josué de Moraes. 2025. "Piplartine, a Bioactive Amide from Piper truncatum, Displays Potent Anthelmintic Activity Against the Zoonotic Nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis" Chemistry 7, no. 4: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040105
APA StyleFukui-Silva, L., Spoladore, S. C., Lemes, B. L., Amorim, C. S., Gonçalves, M. M., Lago, J. H. G., & de Moraes, J. (2025). Piplartine, a Bioactive Amide from Piper truncatum, Displays Potent Anthelmintic Activity Against the Zoonotic Nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Chemistry, 7(4), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7040105







