Starting Electroosmosis in a Fibrous Porous Medium with Arbitrary Electric Double-Layer Thickness
Abstract
1. Introduction
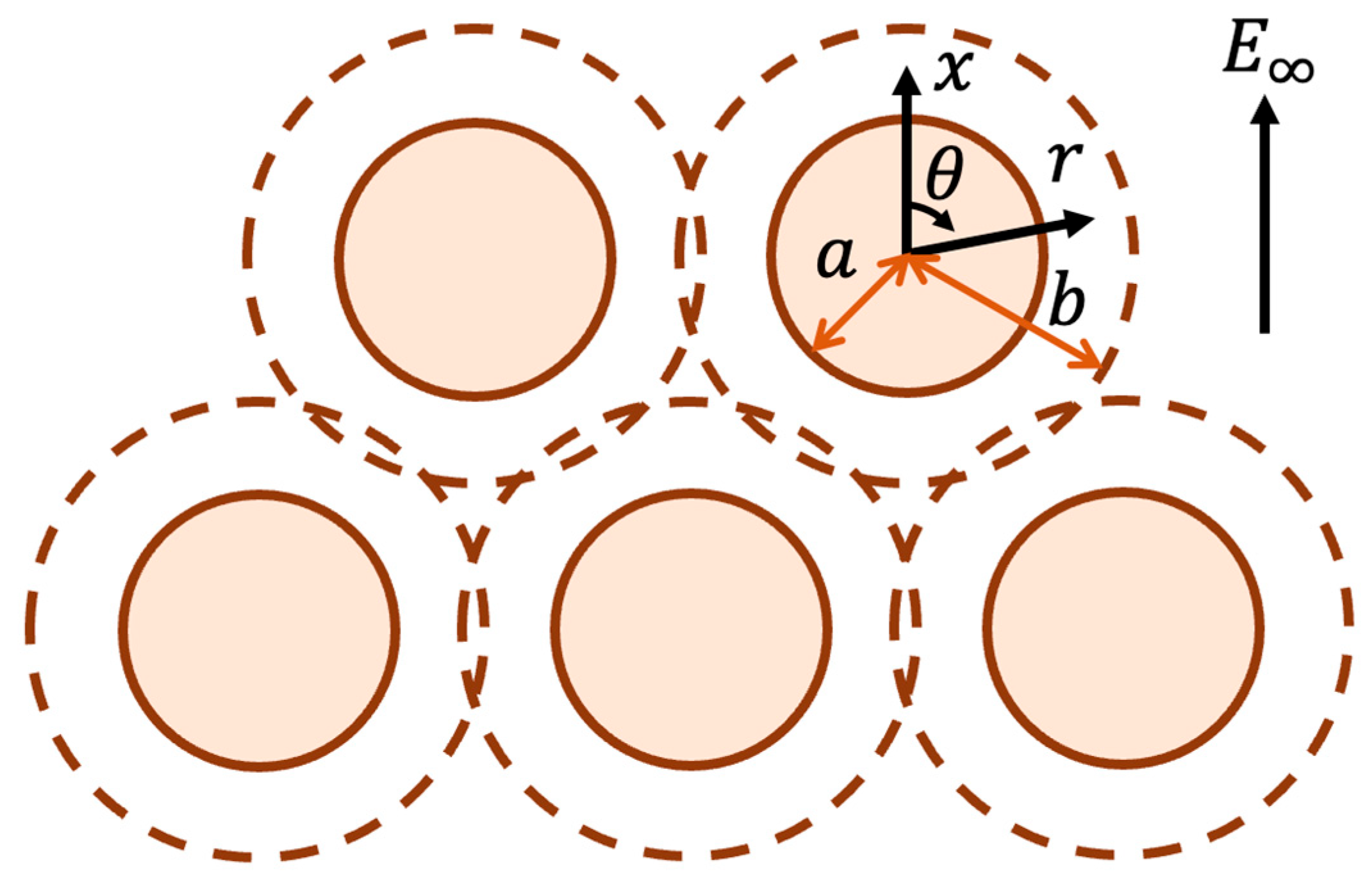
2. Analysis
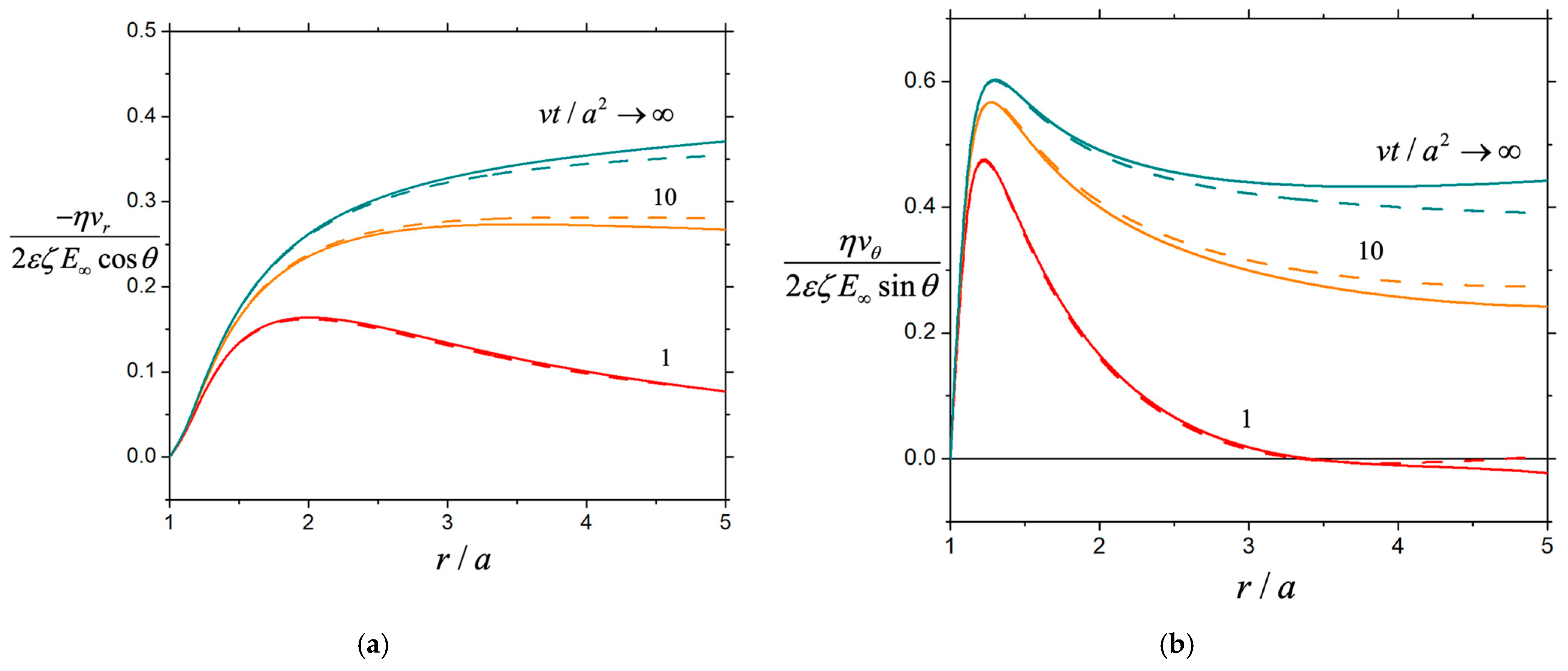
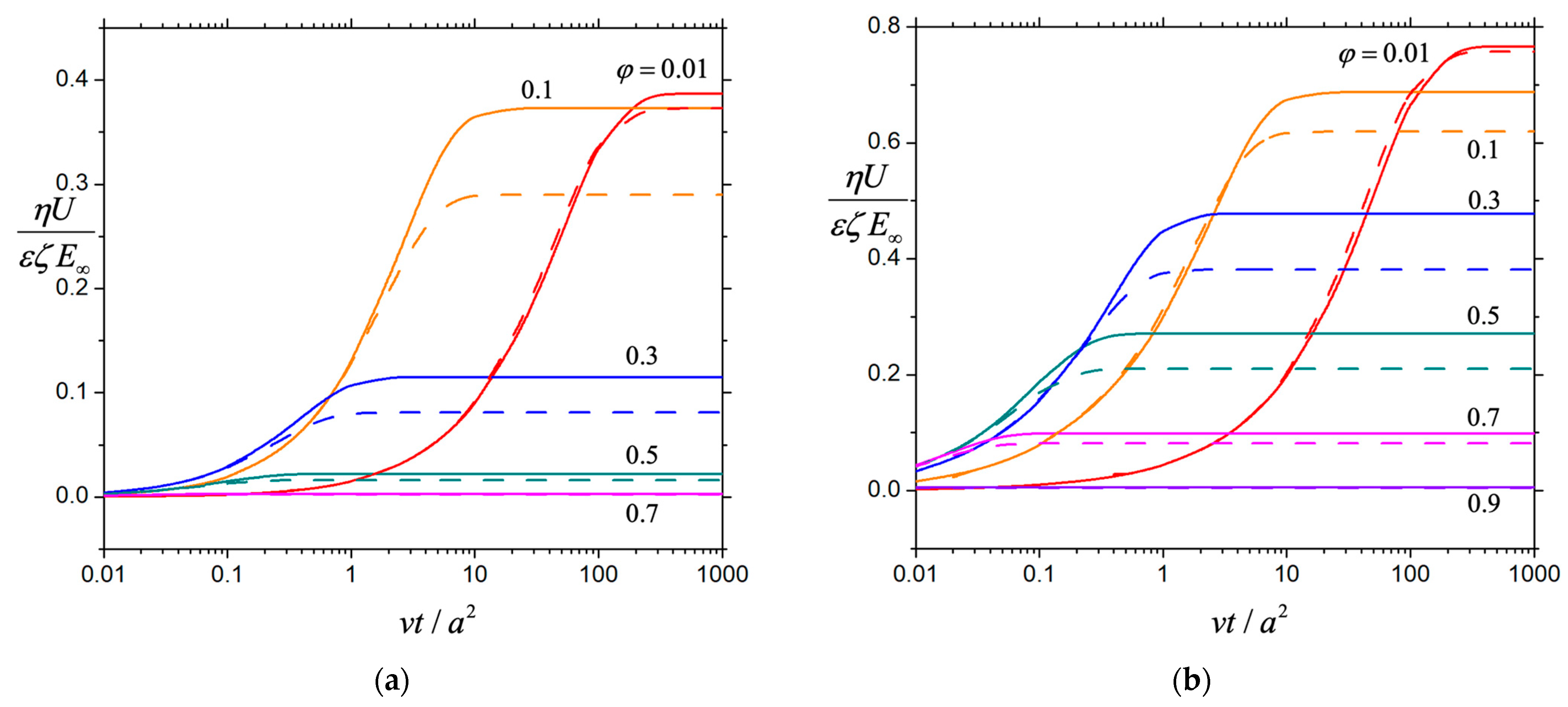
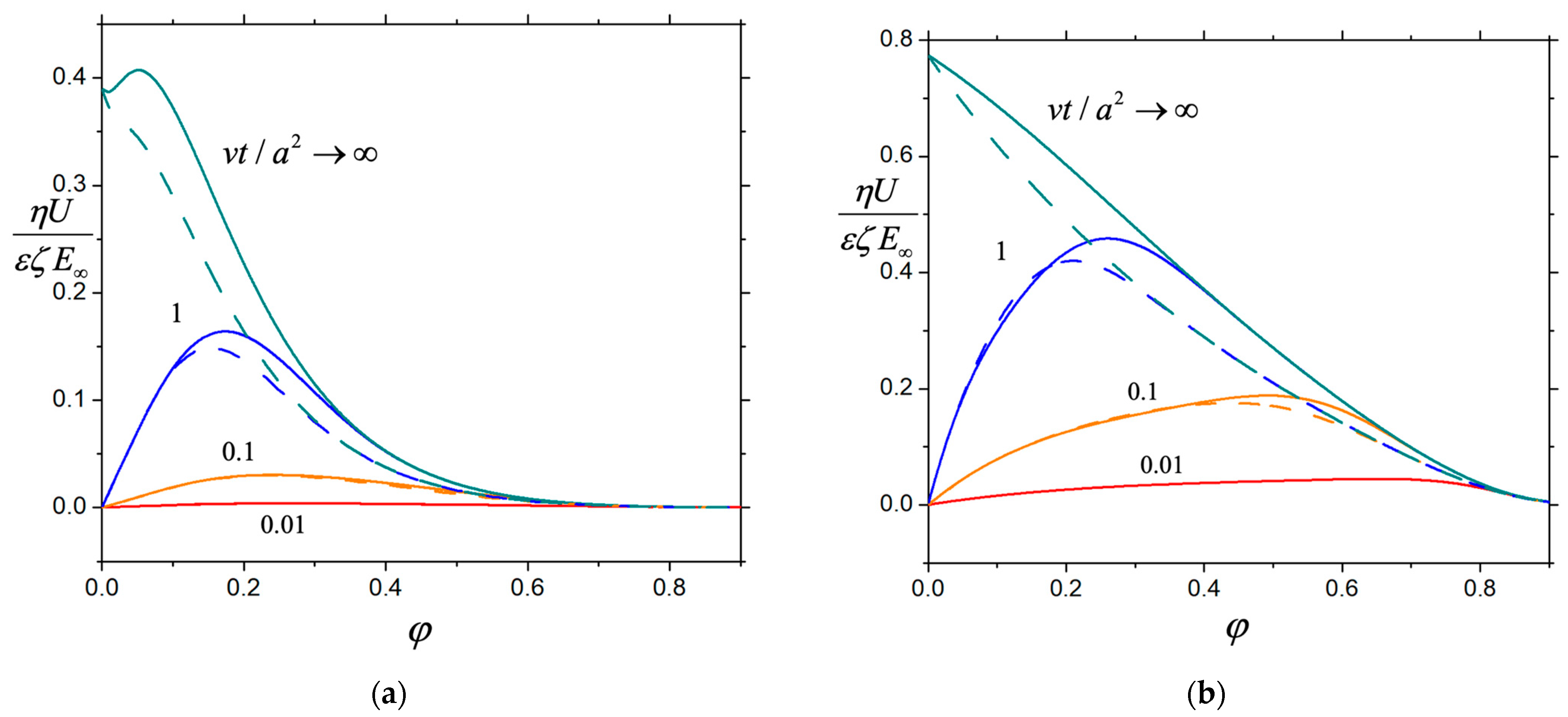
3. Results and Discussion
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Rice, C.L.; Whitehead, R. Electrokinetic flow in a narrow cylindrical capillary. J. Phys. Chem. 1965, 69, 4017–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, T.M.; Bazant, M.Z. Induced-charge electro-osmosis. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 509, 217–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Sherwood, J.D.; Ghosal, S. Electro-osmotic flow through a nanopore. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 749, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Muccio, G.; della Rocca, B.M.; Chinappi, M. Geometrically induced selectivity and unidirectional electroosmosis in uncharged nanopores. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 8716–8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, K.; Bai, J.; Wang, G. Asymmetric temporal variation of oscillating AC electroosmosis with a steady pressure-driven flow. Exp. Fluids 2020, 61, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhong, X.; Liu, B.; Shi, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, Y. Mixing mechanism of a straight channel micromixer based on light-actuated oscillating electroosmosis in low-frequency sinusoidal AC electric field. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2021, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.-C.; Lin, H.; Li, K.; Yi, F. Study on ethanol driven by alternating current electroosmosis in microchannels. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 351, 114174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Smith, K.; Palmer, X. Long-range ACEO phenomena in microfluidic channel. Surfaces 2023, 6, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yossifon, G.; Frankel, I.; Miloh, T. Macro-scale description of transient electro-kinetic phenomena over polarizable dielectric solids. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 620, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, W.T.; Osterle, J.F. Transient electro-osmosis in capillary tubes. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 49, 4062–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xiao, T. Transient two-layer electroosmotic flow and heat transfer of power-law nanofluids in a microchannel. Micromachines 2022, 13, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keh, H.J.; Tseng, H.C. Transient electrokinetic flow in fine capillaries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 24, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q. Time periodic electro-osmotic flows through a microannulus. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, J.-S.; Ri, N.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Hyon, S.-H. Impact of charged soft layers on electroosmosis of Maxwell fluids in soft nanochannels. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.; Neale, G.H. The prediction of electrokinetic phenomena within multiparticle systems I. Electrophoresis and electroosmosis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkikh, N.I.; Shilov, V.N. Theory of collective electrophoresis of spherical particles in the Henry approximation. Colloid J. USSR Engl. Transl. 1982, 43, 865–870. [Google Scholar]
- Kozak, M.W.; Davis, E.J. Electrokinetic phenomena in fibrous porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 112, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, H. Electroosmotic velocity in fibrous porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 210, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keh, H.J.; Wei, Y.K. Diffusioosmosis and electroosmosis of electrolyte solutions in fibrous porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 252, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zholkovskiy, E.K.; Masliyah, J.H.; Shilov, V.N.; Bhattacharjee, S. Electrokinetic phenomena in concentrated disperse systems: General problem formulation and spherical cell approach. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 134–135, 279–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahualli, S.; Jimenez, M.L.; Carrique, F.; Delgado, A.V. AC electrokinetics of concentrated suspensions of soft particles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 1986–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keh, H.J.; Wu, Y.Y. Electroosmotic velocity and electric conductivity in a fibrous porous medium in the transverse direction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9168–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.W.; Keh, H.J. Electrokinetic flow of salt-free solutions in a fibrous porous medium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 9724–9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Keh, H.J. Electroosmosis and electric conduction of electrolyte solutions in charge-regulating fibrous porous media. Colloids Interfaces 2021, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Keh, H.J. Start-up of electrokinetic flow in a fibrous porous medium. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 2826–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.C.; Keh, H.J. Transient electroosmosis in the transverse direction of a fibrous porous medium. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 481, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Keh, H.J. Start-up electrophoresis of a cylindrical particle with arbitrary double layer thickness. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 9967–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Happel, J.; Brenner, H. Low Reynolds Number Hydrodynamics; Nijhoff: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, A. The accurate numerical inversion of Laplace transforms. IMA J. Appl. Math. 1979, 23, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murli, A.; Rizzardi, M. Talbot’s method for the Laplace inversion problem. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1990, 16, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaleta, A.; Sempere, C.; Gravelle, S.; Siria, A.; Fulcrand, R.; Ybert, C.; Bocquet, L. Sub-additive ionic transport across arrays of solid-state nanopores. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A.; Bondarenko, M.P. Interaction of potential sources in infinite 2D arrays: Diffusion through composite membranes, micro-electrochemistry, entrance resistance, and other examples. Adv. Theory Simul. 2021, 4, 2100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, M.; Di Muccio, G.; Viola, F.; Giacomello, A.; Cecconi, F.; Balme, S.; Chinappi, M. Performance of single nanopore and multi-pore membranes for blue energy. ChemPhysChem 2024, 25, e202400395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.Z.; Keh, H.J. Starting Electroosmosis in a Fibrous Porous Medium with Arbitrary Electric Double-Layer Thickness. Chemistry 2025, 7, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7010005
Chen WZ, Keh HJ. Starting Electroosmosis in a Fibrous Porous Medium with Arbitrary Electric Double-Layer Thickness. Chemistry. 2025; 7(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei Z., and Huan J. Keh. 2025. "Starting Electroosmosis in a Fibrous Porous Medium with Arbitrary Electric Double-Layer Thickness" Chemistry 7, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7010005
APA StyleChen, W. Z., & Keh, H. J. (2025). Starting Electroosmosis in a Fibrous Porous Medium with Arbitrary Electric Double-Layer Thickness. Chemistry, 7(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry7010005






