Environmental Applications of Zeolites: Preparation and Screening of Cu-Modified Zeolites as Potential CO Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
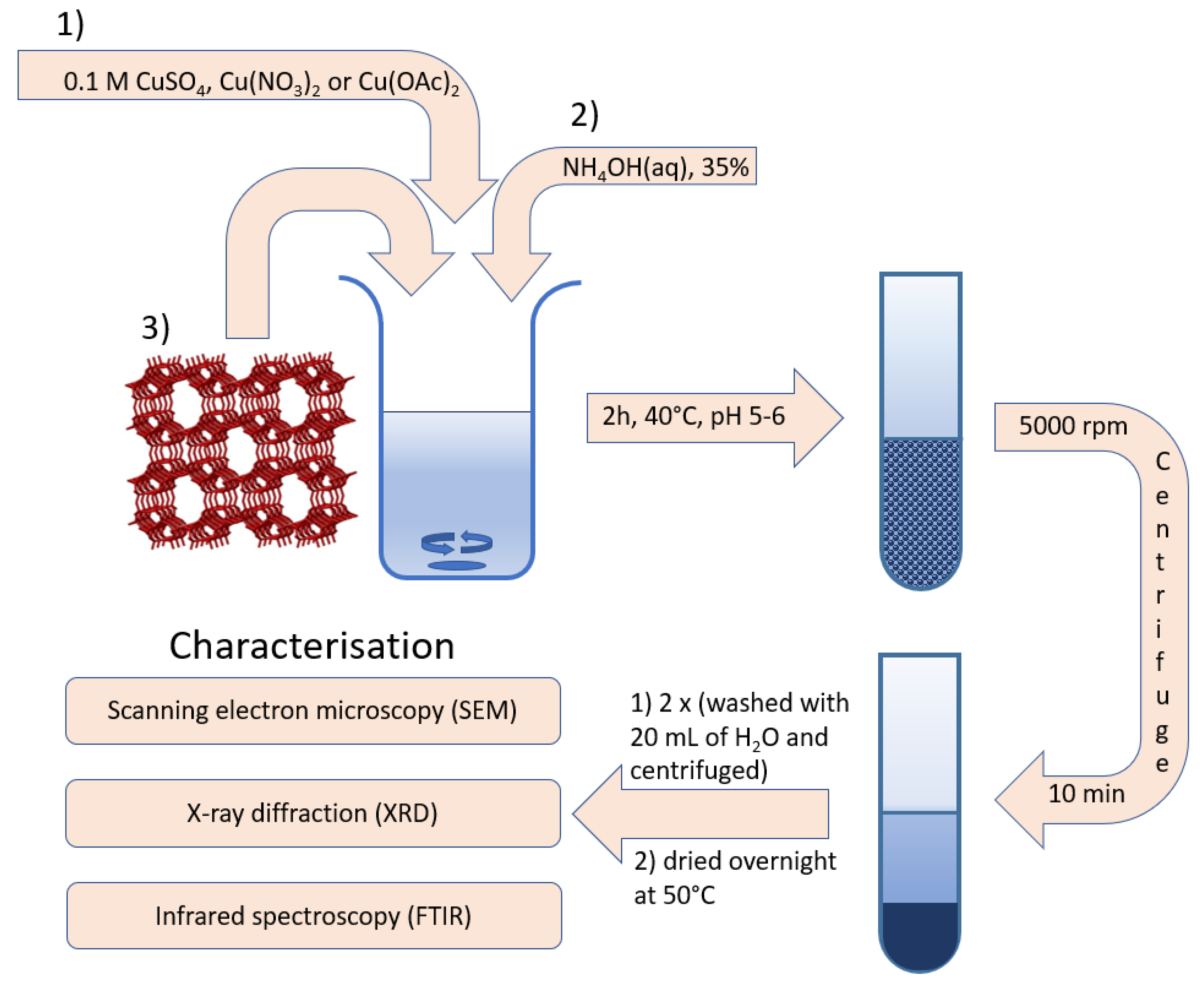
2.2. Sensor Preparation
2.3. Sensor Characterisation
2.4. Operando Gas Detection
3. Results and Discussion
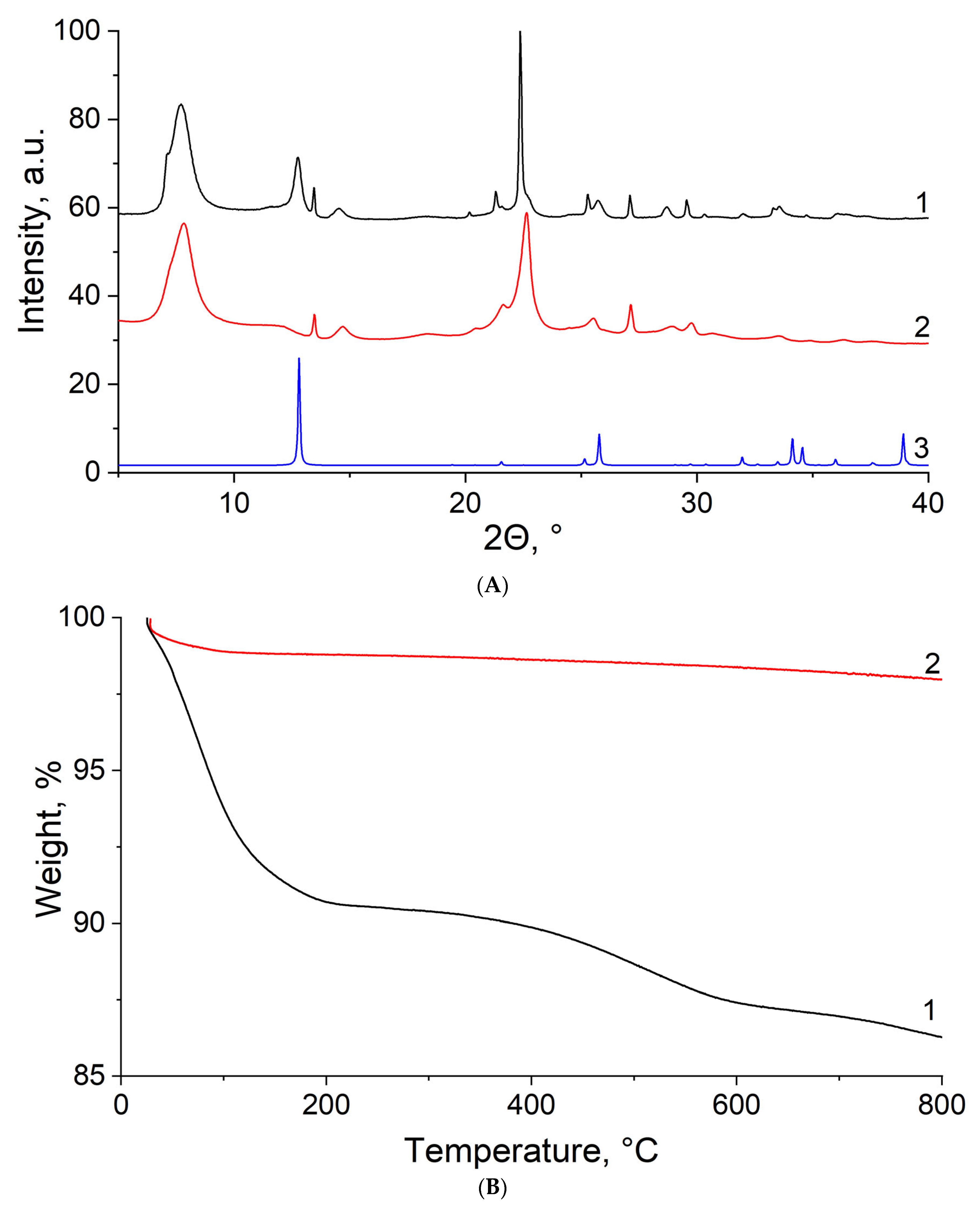
3.1. SEM-EDX
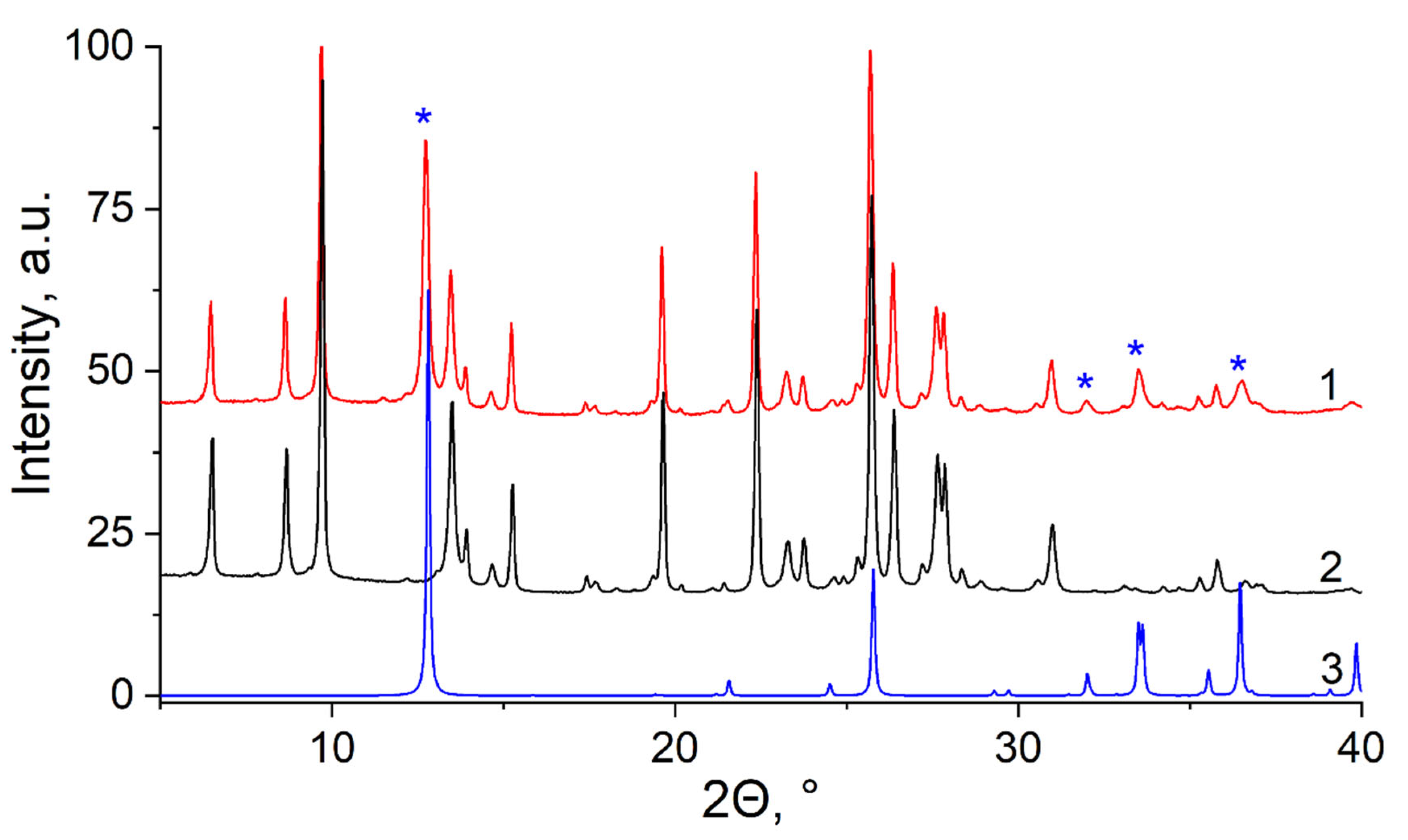
3.2. XRD
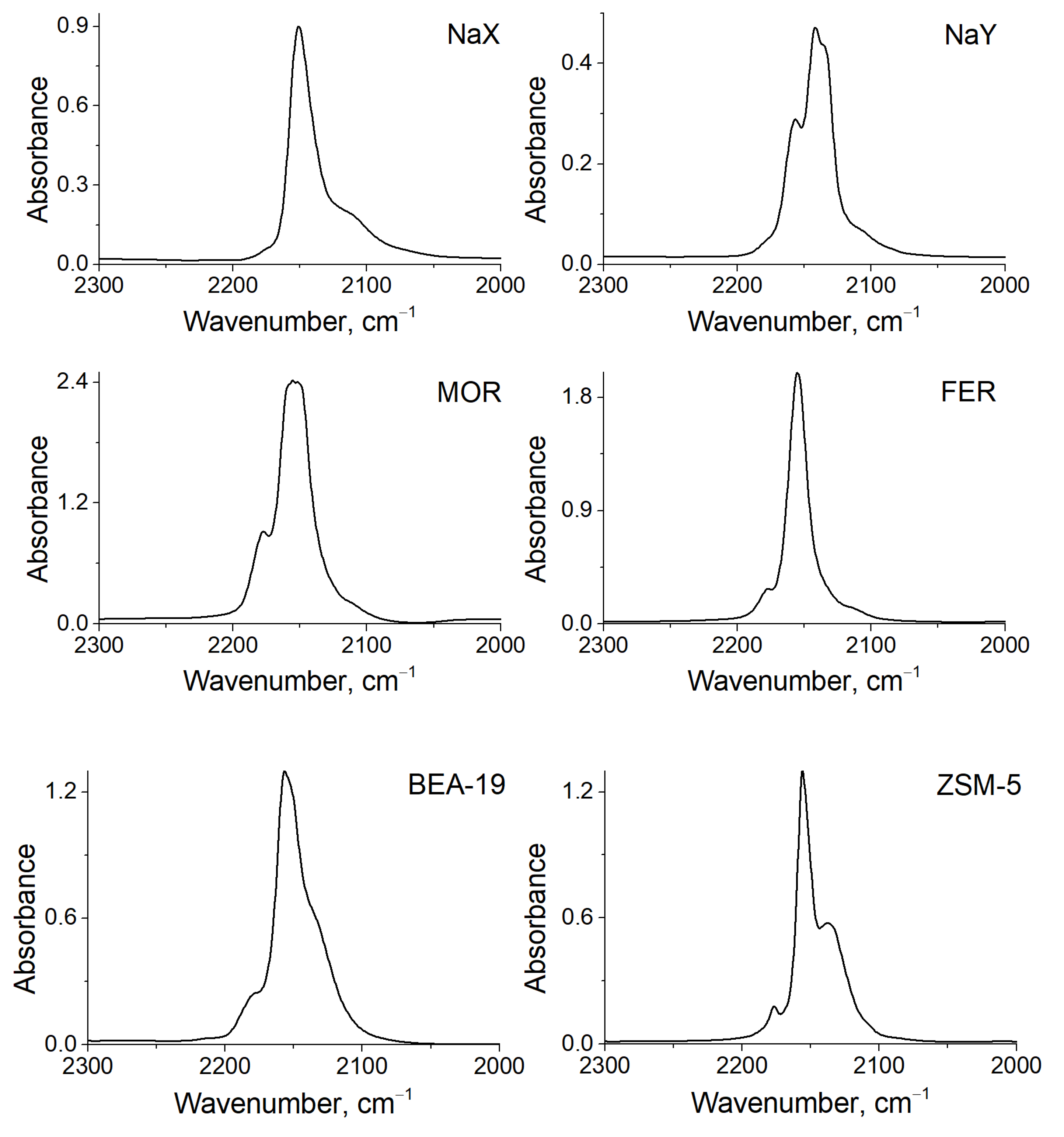
3.3. FTIR
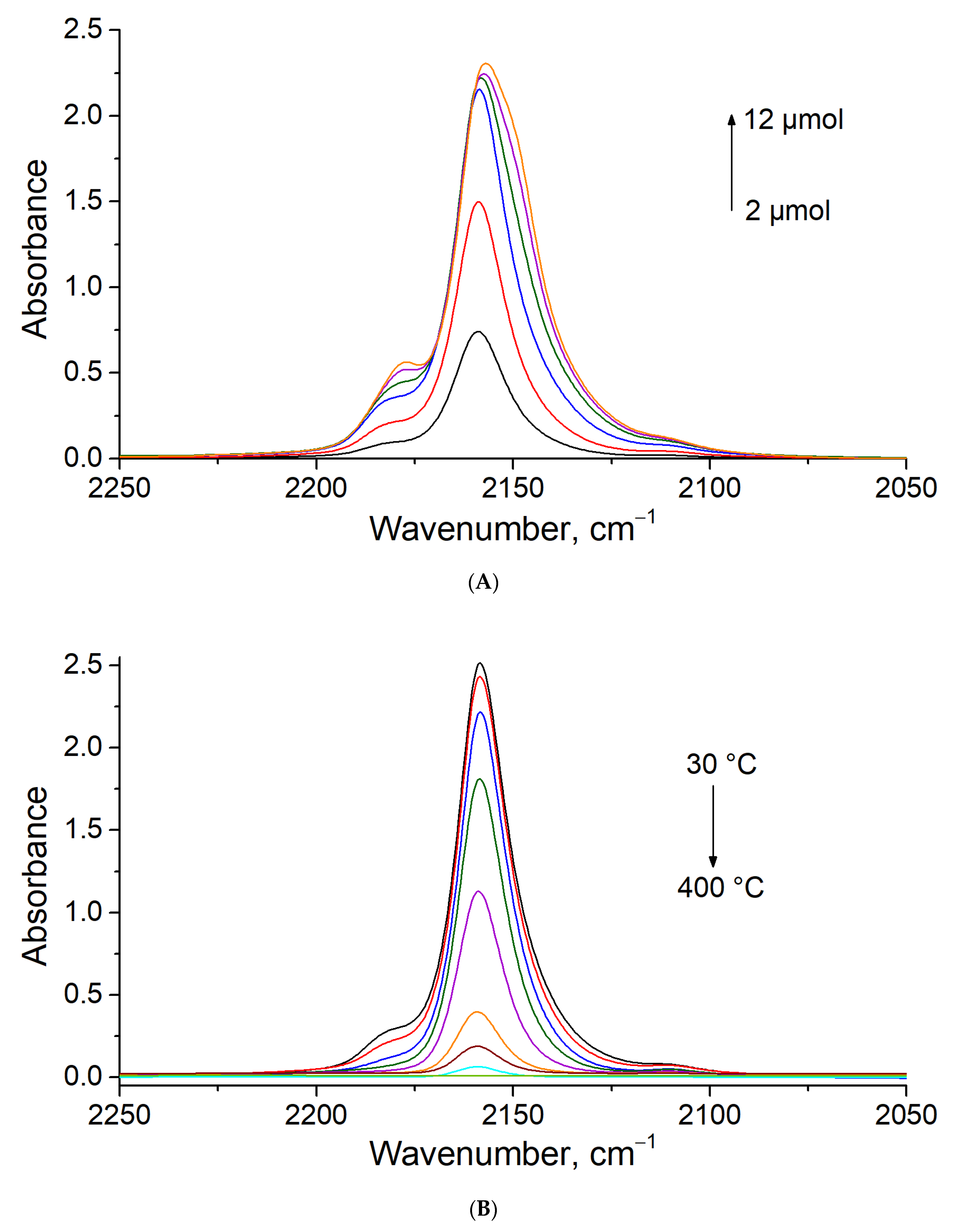
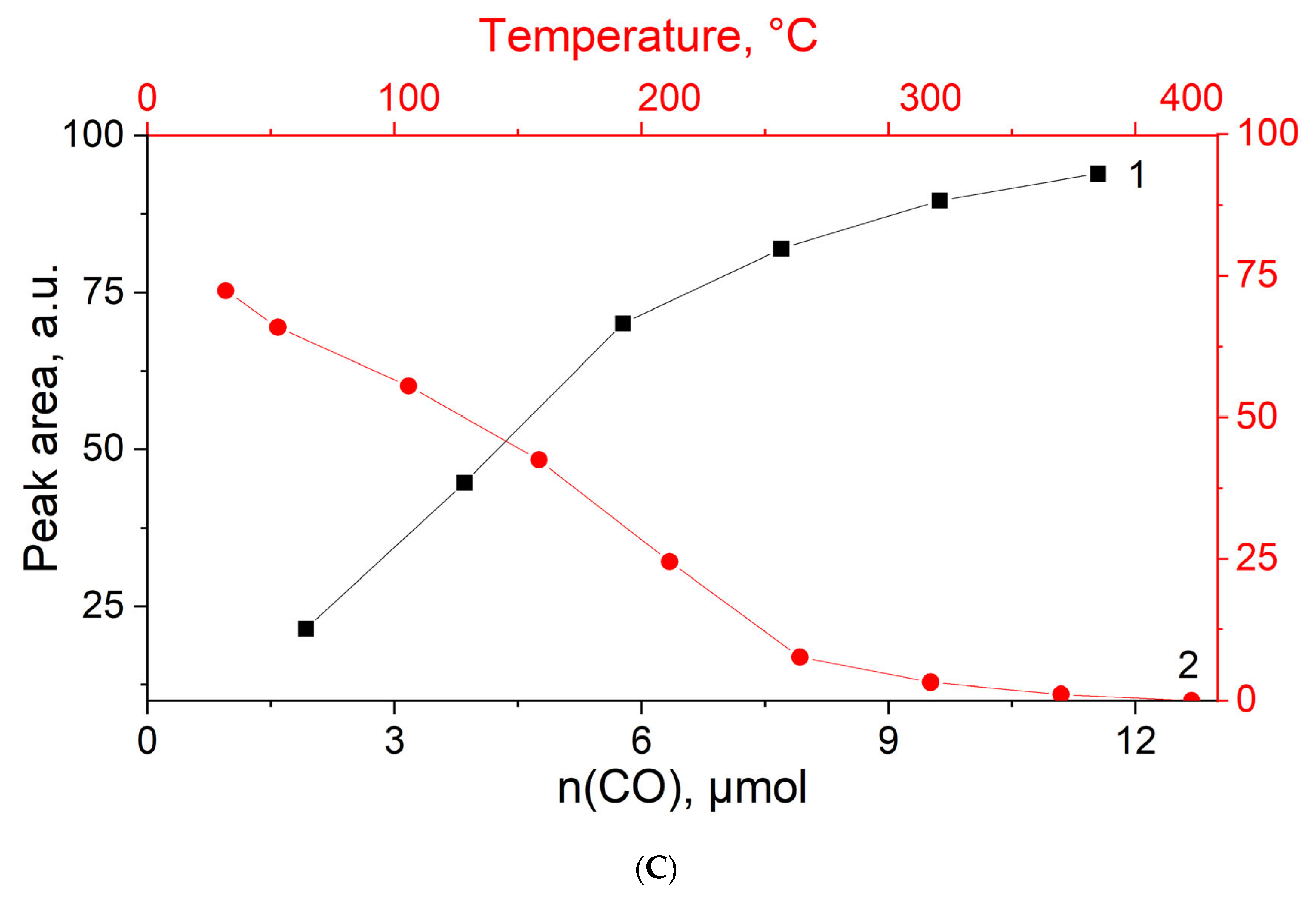
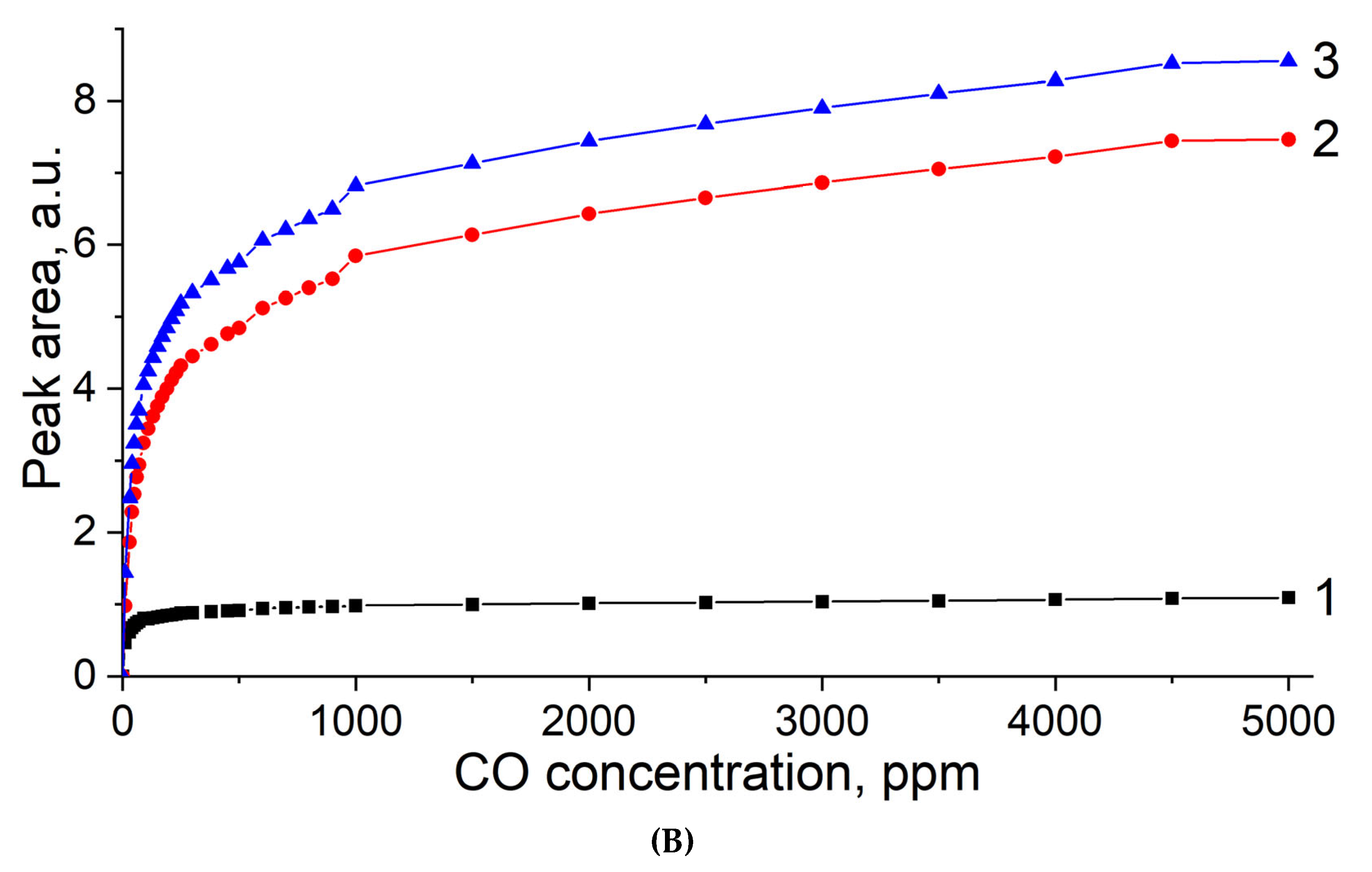
3.4. CO Titration and Stepwise Desorption at Different Temperatures on MOR-Cu(NO3)2
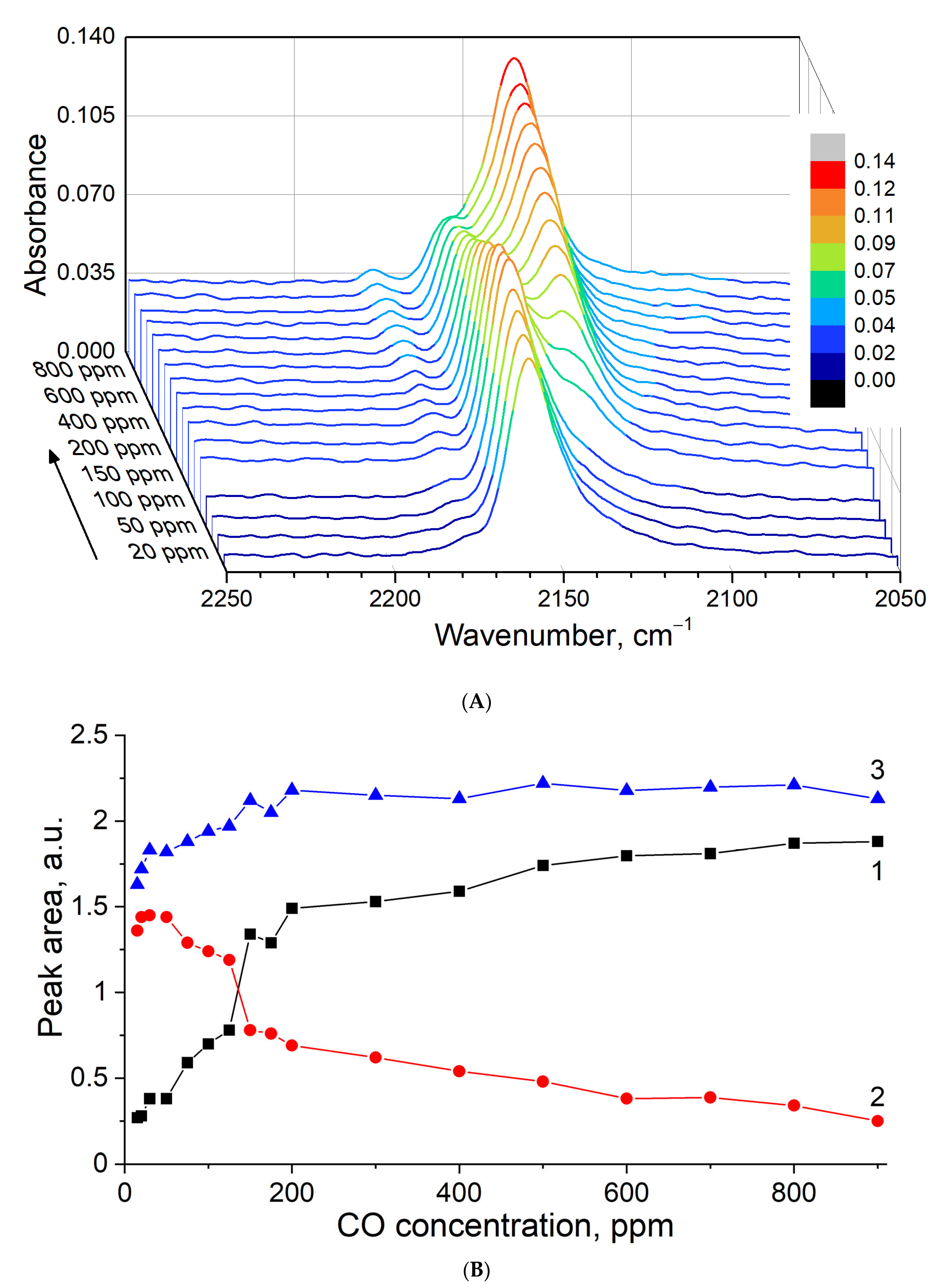
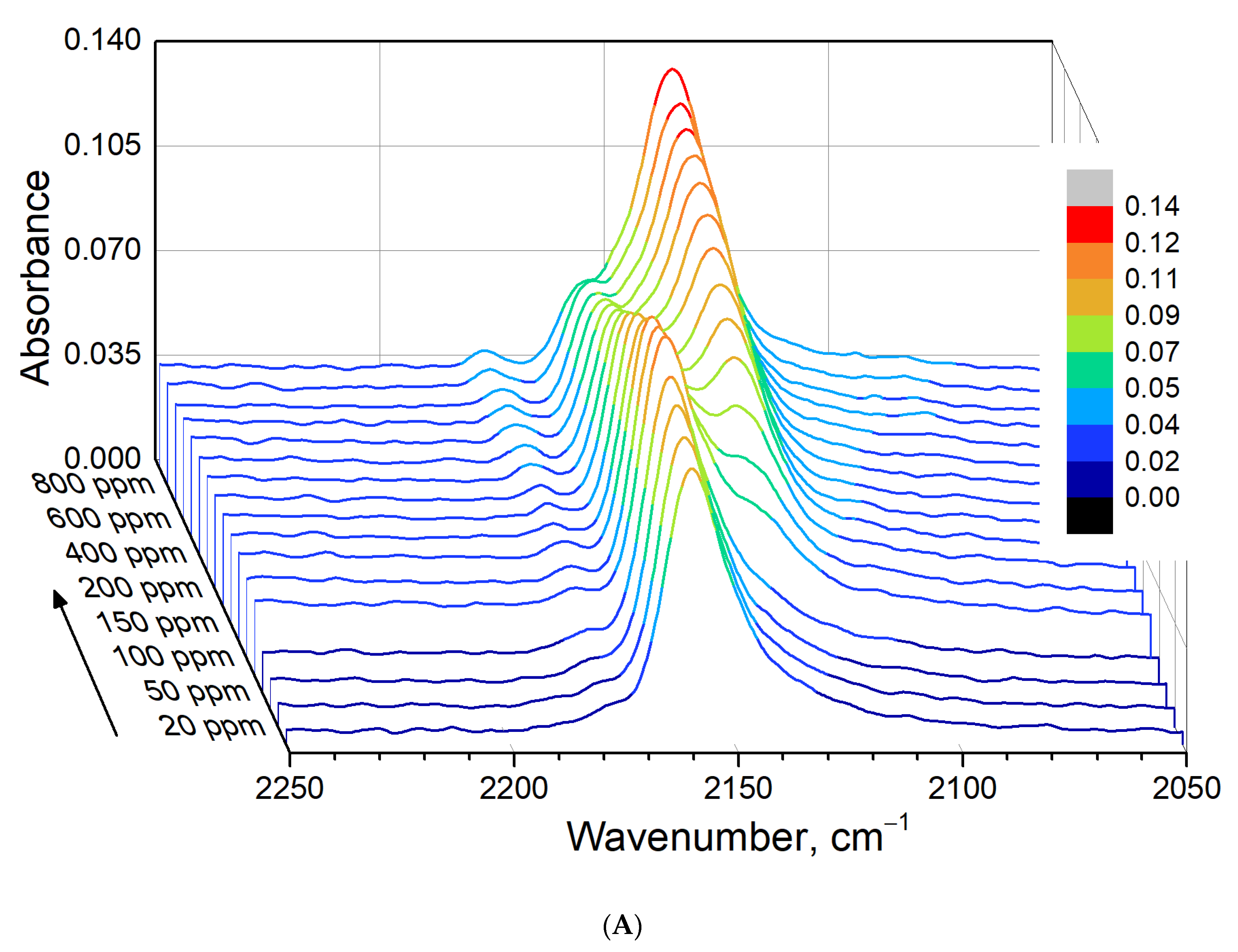
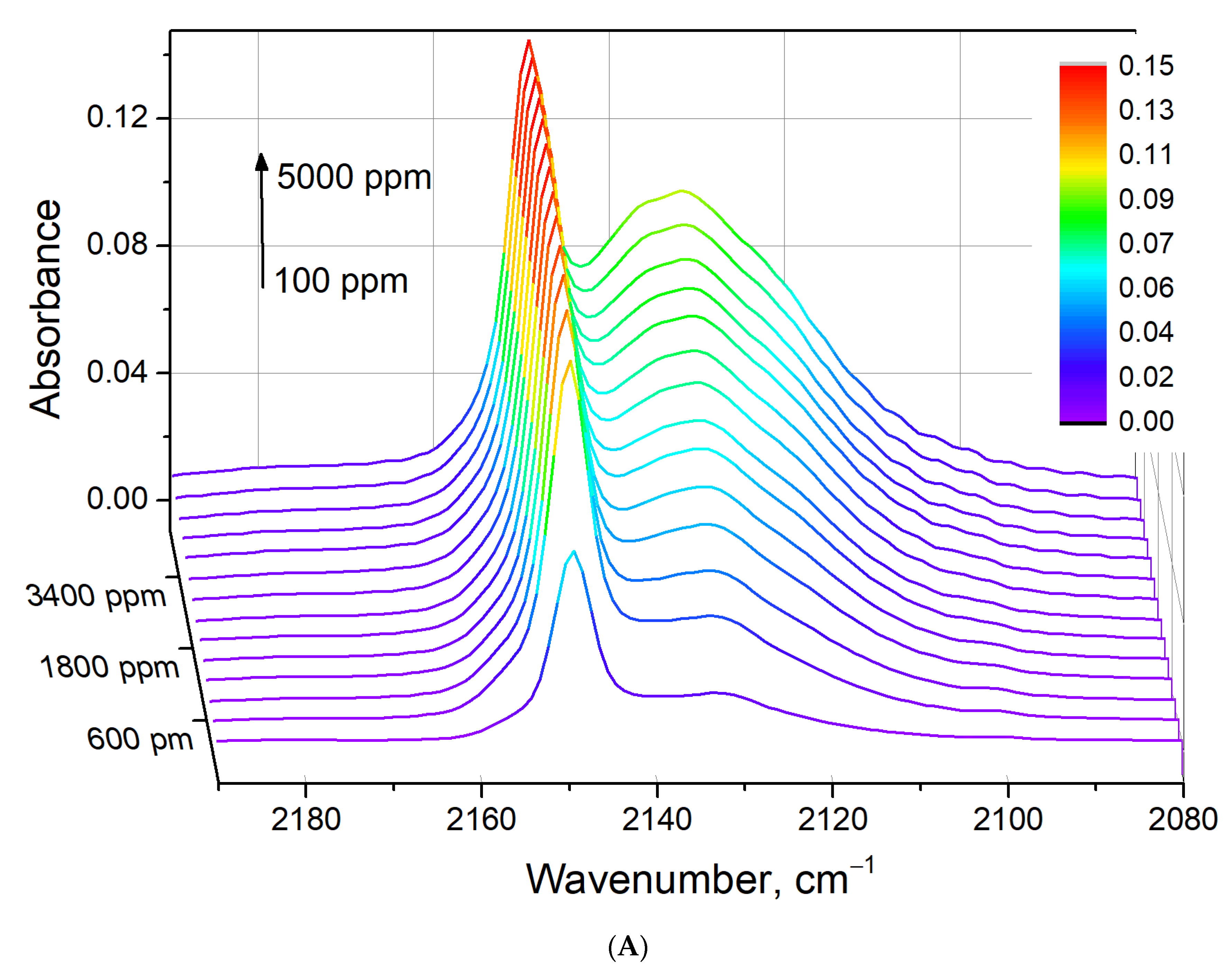
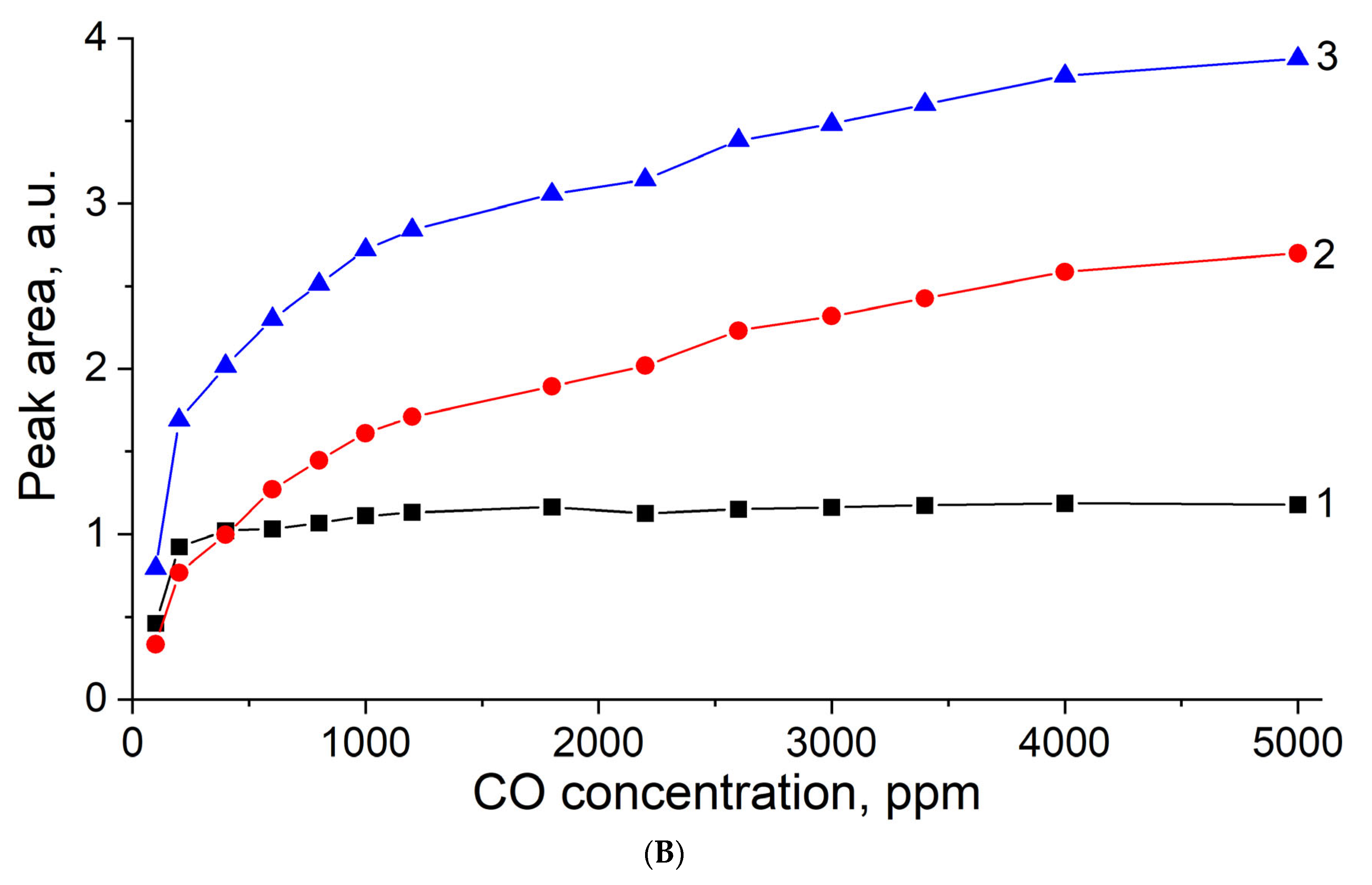
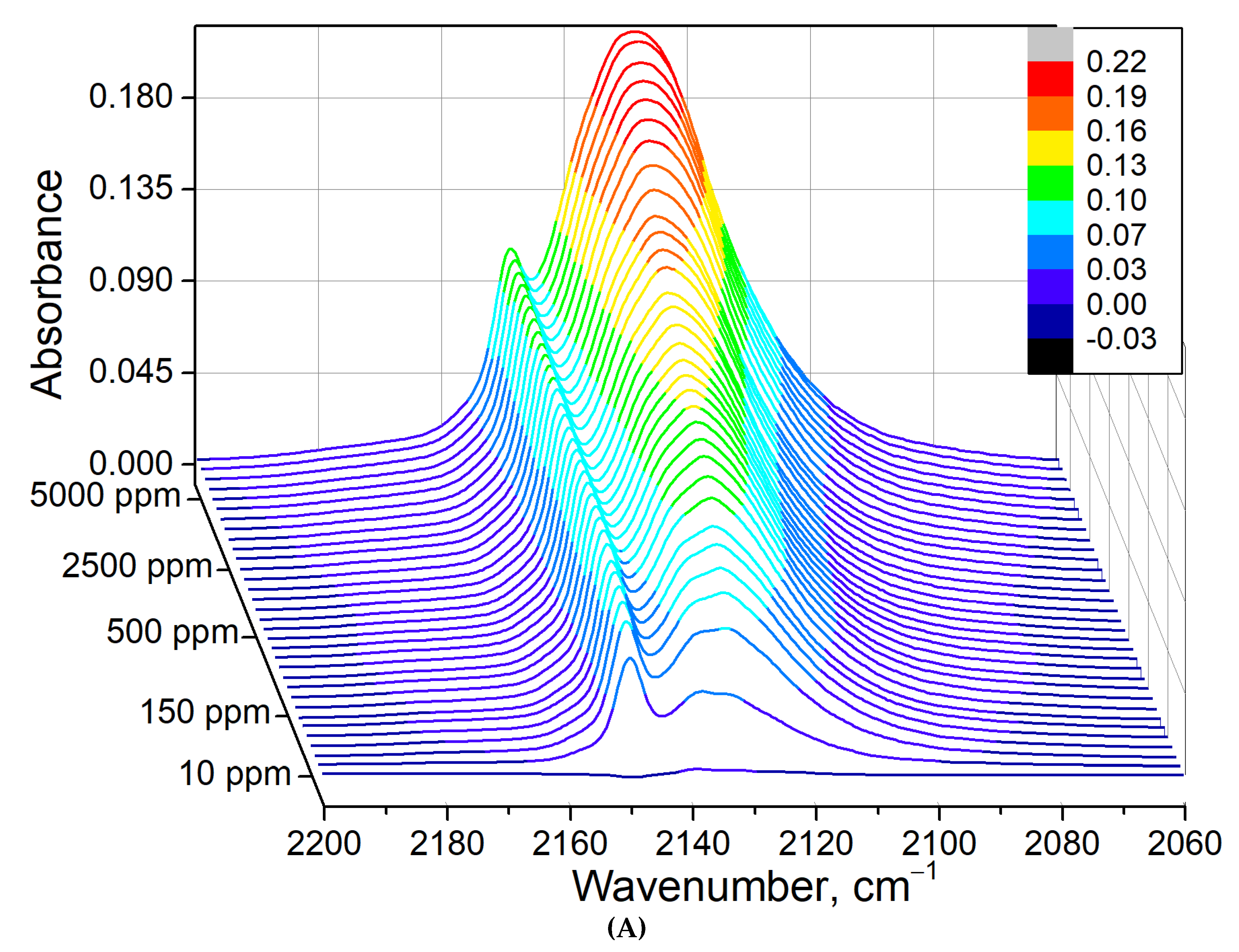
3.5. In Situ CO Adsorption on Cu(NO3)2-Impregnated MOR
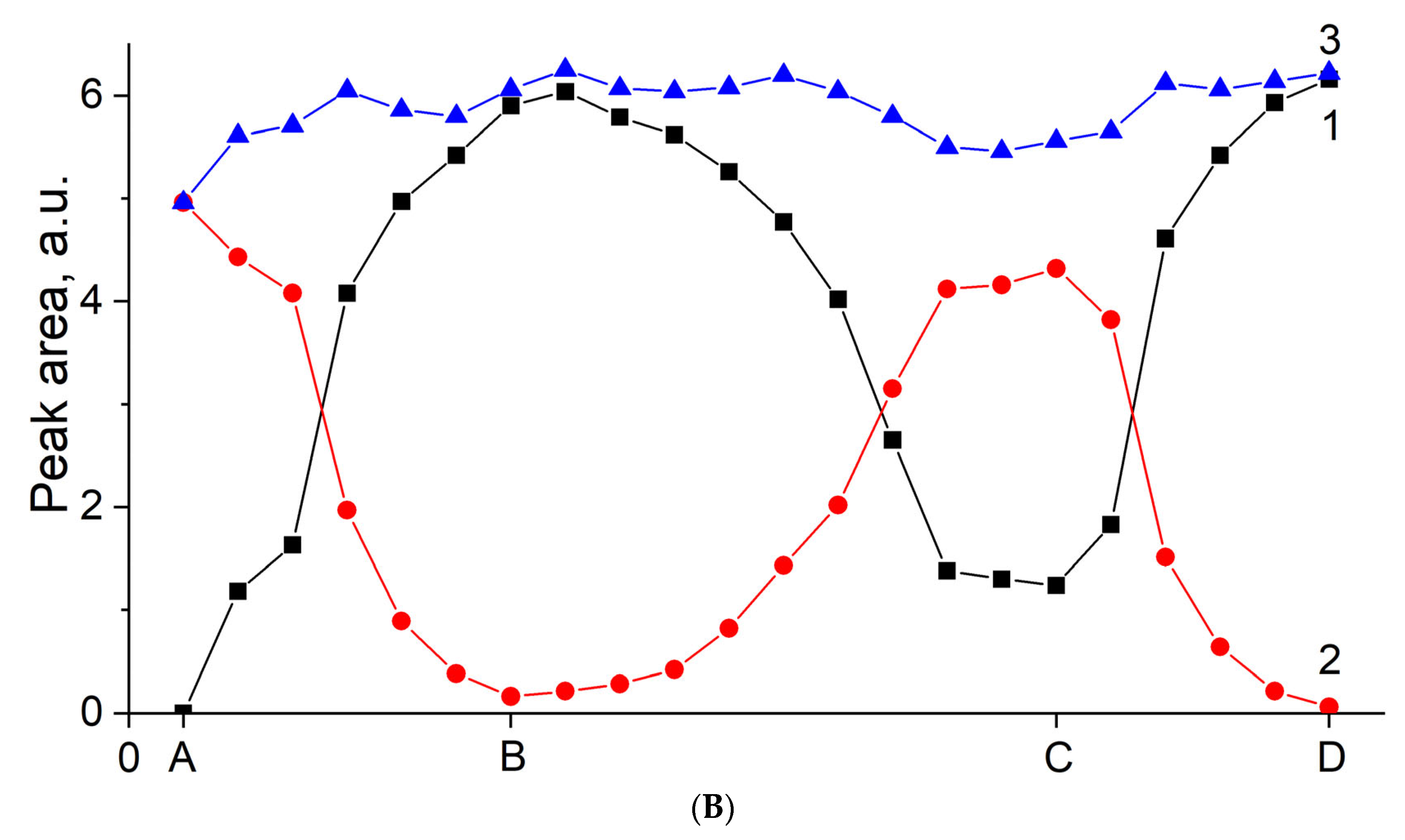
3.6. In Vacuo CO–H2O Coadsorption on Cu(NO3)2-MOR
3.7. Cu-Impregnated Sn-BEA
3.8. CO–H2O Co-Adsorption on CuSn-BEA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobb, N.; Etzel, R.A. Unintentional Carbon Monoxide—Related Deaths in the United States, 1979 Through 1988. JAMA 1991, 266, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, M. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. J. Emerg. Nurs. 2008, 34, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struttmann, T.; Scheerer, A.; Scott Prince, T.; Goldstein, L. Unintentional Carbon Monoxide Poisoning From an Unlikely Source. J. Am. Board Fam. Pract. 1998, 11, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, G.F.; Cavanagh, L.M.; Afonja, A.; Binions, R. Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor Gas Sensors in Environmental Monitoring. Sensors 2010, 10, 5469–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandy, T.; Coutu, R.A.; Ababei, C. Carbon monoxide sensing technologies for next-generation cyber-physical systems. Sensors 2018, 18, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosterev, A.A.; Bakhirkin, Y.A.; Tittel, F.K. Ultrasensitive gas detection by quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy in the fundamental molecular absorption bands region. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2005, 80, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, F.; Wang, Y.; Cong, M.; Li, L.; An, Y.; Song, Z.; Guo, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, L. Design and characteristics of quantum cascade laser-based CO detection system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 142, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegleb, G.; Heitbaum, J. Semiconductor gas sensor for detecting NO and CO traces in ambient air of road traffic. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 17, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon Monoxide Detector Market—Forecasts from 2021 to 2026; Research and Markets: Dublin, Ireland, 2021.
- Mahajan, S.; Jagtap, S. Metal-oxide semiconductors for carbon monoxide (CO) gas sensing: A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.K.; Chauhan, P.S.; Awasthi, M.; Bhattacharya, S. α-Fe2O3 loaded rGO nanosheets based fast response/recovery CO gas sensor at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 465, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Cao, Y. Cobalt-doped indium oxide/molybdenum disulfide ternary nanocomposite toward carbon monoxide gas sensing. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introduction to Zeolite Science and Practice; Cejka, J., van Bekkum, H., Corma, A., Schuth, F., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C.; Bonino, F.; Travert, A.; Thibault-Starzyk, F. Probing zeolites by vibrational spectroscopies chemical society reviews probing zeolites by vibrational spectroscopies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7262–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjiivanov, K.I.; Vayssilov, G.N. Characterization of oxide surfaces and zeolites by carbon monoxide as an IR probe molecule. Adv. Catal. 2002, 47, 307–511. [Google Scholar]
- Nachtigallová, D.; Bludský, O.; Otero Aerán, C.; Bulánek, R.; Nachtigall, P. The vibrational dynamics of carbon monoxide in a confined space-CO in zeolites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 2006, 8, 4849–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharchenko, A.; Zholobenko, V.; Vicente, A.; Fernandez, C.; Vezin, H.; De Waele, V.; Mintova, S. Formation of copper nanoparticles in LTL nanosized zeolite: Spectroscopic characterization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 2880–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, G.; Zecchina, A.; Bordiga, S.; Ricchiardi, G.; Martra, G.; Leofanti, G.; Petrini, G. Cu (I)-ZSM-5 zeolites prepared by reaction of H-ZSM-5 with gaseous CuCl: Spectroscopic characterization and reactivity towards carbon monoxide and nitric oxide. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1994, 3, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.W.; Cordon, M.J.; Di Iorio, J.R.; Vega-Vila, J.C.; Ribeiro, F.H.; Gounder, R. Titration and quantification of open and closed Lewis acid sites in Sn-Beta zeolites that catalyze glucose isomerization. J. Catal. 2016, 335, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobler, J.; Abrevaya, H.; Mintova, S.; Bein, T. High-Silica Zeolite-: From Stable Colloidal Suspensions to Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 14274–14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ani, A.; Haslam, J.J.C.; Mordvinova, N.E.; Lebedev, O.I.; Vicente, A.; Fernandez, C.; Zholobenko, V. Synthesis of nanostructured catalysts by surfactantlating of large-pore zeolites. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, C.; Mccusker, L.B.; Olson, D.H. Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C.; Geobaldo, F.; Zecchina, A.; Palomino, G.T.; Areán, C.O. Fourier-Transform Infrared Study of CO Adsorbed at 77 K on H-Mordenite and Alkali-Metal-Exchanged Mordenites. Langmuir 1995, 11, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, G.T.; Zecchina, A.; Giamello, E.; Fisicaro, P.; Berlier, G.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S. Polycarbonylic and polynitrosylic species in Cu I-exchanged ZSM-5, β, Mordenite and Y zeolites: Comparison with homogeneous complexes. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2000, 130, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar]
- Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Zecchina, A.; Salvalaggio, M.; Geobaldoc, F.; Otero, C. XANES, EXAFS and FTIR characterization of copper-exchanged mordenite. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnes Palomino, G.; Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C.; Zecchina, A.; Otero Areán, C. Vibrational and optical spectroscopic studies on copper-exchanged ferrierite. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2002, 1142, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Giordanino, F.; Vennestrøm, P.N.R.; Lundegaard, L.F.; Stappen, F.N.; Mossin, S.; Beato, P.; Bordiga, S.; Lamberti, C. Characterization of Cu-exchanged SSZ-13: A comparative FTIR, UV-Vis, and EPR study with Cu-ZSM-5 and Cu-β with similar Si/Al and Cu/Al ratios. Dalt. Trans 2013, 42, 12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Salvalaggio, M.; Spoto, G.; Zecchina, A.; Geobaldo, F.; Vlaic, G.; Bellatreccia, M. XAFS, IR, and UV−Vis Study of the CuI Environment in CuI-ZSM-5. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholobenko, V.; Freitas, C.; Jendrlin, M.; Bazin, P.; Travert, A.; Thibault-Starzyk, F. Probing the acid sites of zeolites with pyridine: Quantitative AGIR measurements of the molar absorption coefficients. J. Catal. 2020, 385, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Nemeth, L.T.; Renz, M.; Valencia, S. Sn-zeolite beta as a heterogeneous chemoselective catalyst for Baeyer-Villiger oxidations. Nature 2001, 412, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendrlin, M.; Grand, J.; Lakiss, L.; Dubray, F.; Bazin, P.; El Fallah, J.; Mintova, S.; Zholobenko, V. Environmental applications of zeolites: Hydrophobic Sn-BEA as a selective gas sensor for exhaust fumes. Submitt. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar]

| Zeolite | Si (at.%) | Al (at.%) | Cu (at.%) | Si/Al | Cu/Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOR-CuSO4 | 76.6 | 8.2 | 12.6 | 9.3 | 1.5 |
| MOR-Cu(NO3)2 | 78.4 | 8.4 | 13.2 | 9.4 | 1.6 |
| MOR-Cu(OAc)2 | 80.5 | 8.1 | 11.4 | 9.9 | 1.4 |
| MOR-Cu(NO3)2-IE * | 89.4 | 8.3 | 2.3 | 10.7 | 0.3 |
| BEA-12-CuSO4 | 78.8 | 6.3 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 1.8 |
| BEA-12-Cu(NO3)2 | 63.7 | 5.2 | 13.5 | 12.2 | 2.6 |
| BEA-12-Cu(OAc)2 | 84.2 | 6.6 | 9.2 | 12.8 | 1.4 |
| BEA-19-CuSO4 | 80.1 | 4.2 | 12.5 | 19.0 | 3.0 |
| BEA-19-Cu(NO3)2 | 80.0 | 4.5 | 15.5 | 17.9 | 3.5 |
| BEA-19-Cu(OAc)2 | 87.2 | 4.5 | 8.4 | 19.5 | 1.9 |
| ZSM-5-CuSO4 | 84.1 | 2.4 | 10.8 | 35.2 | 4.5 |
| ZSM-5-Cu(NO3)2 | 68.5 | 2.0 | 13.4 | 33.7 | 6.6 |
| ZSM-5-Cu(OAc)2 | 87.1 | 2.4 | 10.5 | 36.1 | 4.4 |
| NaX-CuSO4 | 39.9 | 30.4 | 11.7 | 1.3 | 0.4 |
| NaX-Cu(NO3)2 | 42.1 | 31.6 | 11.0 | 1.3 | 0.4 |
| NaX-Cu(OAc)2 | 44.9 | 31.7 | 8.6 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| NaY-CuSO4 | 54.5 | 20.3 | 12.6 | 2.7 | 0.6 |
| NaY-Cu(NO3)2 | 55.4 | 20.4 | 15.3 | 2.7 | 0.7 |
| NaY-Cu(OAc)2 | 59.9 | 21.6 | 9.1 | 2.8 | 0.4 |
| FER-CuSO4 | 81.3 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 9.7 | 1.0 |
| FER-Cu(NO3)2 | 74.3 | 7.4 | 11.4 | 10.1 | 1.5 |
| FER-Cu(OAc)2 | 82.6 | 8.7 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 1.0 |
| Zeolite | Cu+-CO *, cm−1 | Cu+-(CO)2 *, cm−1 | Cu+-CO, cm−1 | Cu+-(CO)2, cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaX | 2153 | 2176, 2113 | - | - |
| NaY | 2148 | 2157, 2108 | 2143 [24] | 2168, 2135 [24] |
| MOR | 2156 | 2178, 2108 | 2159 [25] | 2180, 2152 [25] |
| FER | 2155 | 2177, 2115 | 2157 [26] | 2178, 2142 [26] |
| BEA-12 | 2154 | 2180, 2130 | 2157 [24] 2158 [27] | 2180, 2152 [24] 2180, 2152 [27] |
| BEA-19 | 2157 | 2179, 2132 | - | - |
| ZSM-5 | 2156 | 2176, 2133 | 2158 [24] 2157 [28] | 2178, 2150 [24] 2178, 2151 [28] |
| Zeolite | Area CO | μmol CO/g of zeolite # | μmol Cu/g of zeolite, total † | Cu+/Cu ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOR-CuSO4 | 74.3 | 672 | 1227 | 0.55 |
| MOR-Cu(NO3)2 | 88.7 | 801 | 1101 | 0.73 |
| MOR-Cu(OAc)2 | 60.8 | 549 | 899 | 0.61 |
| MOR-Cu(NO3)2 * | 26.2 | 237 | 229 | 1.03 |
| BEA-12-CuSO4 | 18.1 | 164 | 1545 | 0.11 |
| BEA-12-Cu(NO3)2 | 40.9 | 370 | 1279 | 0.29 |
| BEA-12-Cu(OAc)2 | 54.7 | 495 | 1192 | 0.42 |
| BEA-19-CuSO4 | 20.1 | 181 | 1190 | 0.15 |
| BEA-19-Cu(NO3)2 | 46.1 | 417 | 1126 | 0.37 |
| BEA-19-Cu(OAc)2 | 69.5 | 628 | 735 | 0.86 |
| ZSM-5-CuSO4 | 11.3 | 102 | 1498 | 0.07 |
| ZSM-5-Cu(NO3)2 | 34.0 | 307 | 1315 | 0.23 |
| ZSM-5-Cu(OAc)2 | 32.3 | 292 | 797 | 0.37 |
| NaX-CuSO4 | 16.4 | 148 | 1173 | 0.13 |
| NaX-Cu(NO3)2 | 26.1 | 236 | 1096 | 0.21 |
| NaX-Cu(OAc)2 | 47.8 | 432 | 858 | 0.50 |
| NaY-CuSO4 | 5.8 | 52 | 1228 | 0.04 |
| NaY-Cu(NO3)2 | 16.0 | 144 | 1432 | 0.10 |
| NaY-Cu(OAc)2 | 13.4 | 121 | 829 | 0.15 |
| FER-CuSO4 | 29.3 | 265 | 820 | 0.32 |
| FER-Cu(NO3)2 | 46.7 | 422 | 1135 | 0.37 |
| FER-Cu(OAc)2 | 44.5 | 402 | 877 | 0.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jendrlin, M.; Grand, J.; Lakiss, L.; Bazin, P.; Mintova, S.; Zholobenko, V. Environmental Applications of Zeolites: Preparation and Screening of Cu-Modified Zeolites as Potential CO Sensors. Chemistry 2023, 5, 314-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010024
Jendrlin M, Grand J, Lakiss L, Bazin P, Mintova S, Zholobenko V. Environmental Applications of Zeolites: Preparation and Screening of Cu-Modified Zeolites as Potential CO Sensors. Chemistry. 2023; 5(1):314-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleJendrlin, Martin, Julien Grand, Louwanda Lakiss, Philippe Bazin, Svetlana Mintova, and Vladimir Zholobenko. 2023. "Environmental Applications of Zeolites: Preparation and Screening of Cu-Modified Zeolites as Potential CO Sensors" Chemistry 5, no. 1: 314-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010024
APA StyleJendrlin, M., Grand, J., Lakiss, L., Bazin, P., Mintova, S., & Zholobenko, V. (2023). Environmental Applications of Zeolites: Preparation and Screening of Cu-Modified Zeolites as Potential CO Sensors. Chemistry, 5(1), 314-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry5010024







