Combining the Sensitivity of LAMP and Simplicity of Primer Extension via a DNA-Modified Nucleotide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
General
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, L.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gamson, A.S.; Roembke, B.T.; Nakayama, S.; Sintim, H.O. Isothermal amplified detection of DNA and RNA. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 970–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, G.T.; Fraiser, M.S.; Schram, J.L.; Little, M.C.; Nadeau, J.G.; Malinowski, D.P. Strand displacement amplification—An isothermal, in vitro DNA amplification technique. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.Q. Rolling replication of short DNA circles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4641–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, M.; Xu, Y.; Kong, H. Helicase dependent isothermal DNA amplification. EMBO 2004, 5, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Notomi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tomita, N.; Kanda, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Principle, features, and future prospects. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quyen, T.L.; Ngo, T.A.; Bang, D.D.; Madsen, M.; Wolff, A. Classification of multiple DNA dyes based on inhibition effects on real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Prospect for point of care setting. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Nagamine, K.; Tomita, N.; Notomi, T. Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.H.; Evans, T.C. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. Biotechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, S.; Takabe, K.; Inagaki, M.; Funakoshi, N.; Suzuki, K. Detection of gene point mutation in paraffin sections using in situ loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Pathol. Int. 2007, 57, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Yonekawa, T.; Otsuka, K.; Suzuki, W.; Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Tatsumi, K.I.; Horigome, T.; Notomi, T.; Kanda, H. Validation of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping with whole blood. Genome Lett. 2003, 2, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Ma, L.; Ma, Y.-P.; Ding, Y.-Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Ma, L.-Q. Rapid pre-clinical detection of classical swine fever by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Mol. Cell. Probes 2009, 23, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.M.; Nakajima, C.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of Newcastle Disease Virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suleman, E.; Mtshali, M.S.; Lane, E. Investigation of false positives associated with loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for detection of Toxoplasma gondii in archived tissue samples of captive felids. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2016, 28, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagai, K.; Horita, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsukahara, T.; Nagakura, H.; Tashiro, K.; Shibata, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Nakashima, K.; Ushio, R.; et al. Diagnostic test accuracy of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, K.; Steck, A.L.; Strütt, S.; Baccaro, A.; Welte, W.; Diederichs, K.; Marx, A. Structures of KlenTaq DNA polymerase caught while incorporating C5-modified pyrimidine and C7-modified 7-deazapurine nucleoside triphosphates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11840–11843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganai, R.A.; Johansson, E. DNA Replication-A Matter of Fidelity. Mol. Cell. 2016, 62, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishino, S.; Ishino, Y. DNA polymerases as useful reagents for biotechnology—The history of developmental research in the field. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baccaro, A.; Steck, A.L.; Marx, A. Barcoded nucleotides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balintova, J.; Welter, M.; Marx, A. Antibody–nucleotide conjugate as a substrate for DNA polymerases. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7122–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agard, N.J.; Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. A strain-promoted [3 + 2] azide−alkyne cycloaddition for covalent modification of biomolecules in living systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15046–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, M.; Verga, D.; Marx, A. Sequence-specific incorporation of enzyme-nucleotide chimera by DNA polymerases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10131–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verga, D.; Welter, M.; Steck, A.L.; Marx, A. DNA polymerase-catalyzed incorporation of nucleotides modified with a G-quadruplex-derived DNAzyme. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7379–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verga, D.; Welter, M.; Marx, A. Sequence selective naked-eye detection of DNA harnessing extension of oligonucleotide-modified nucleotides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
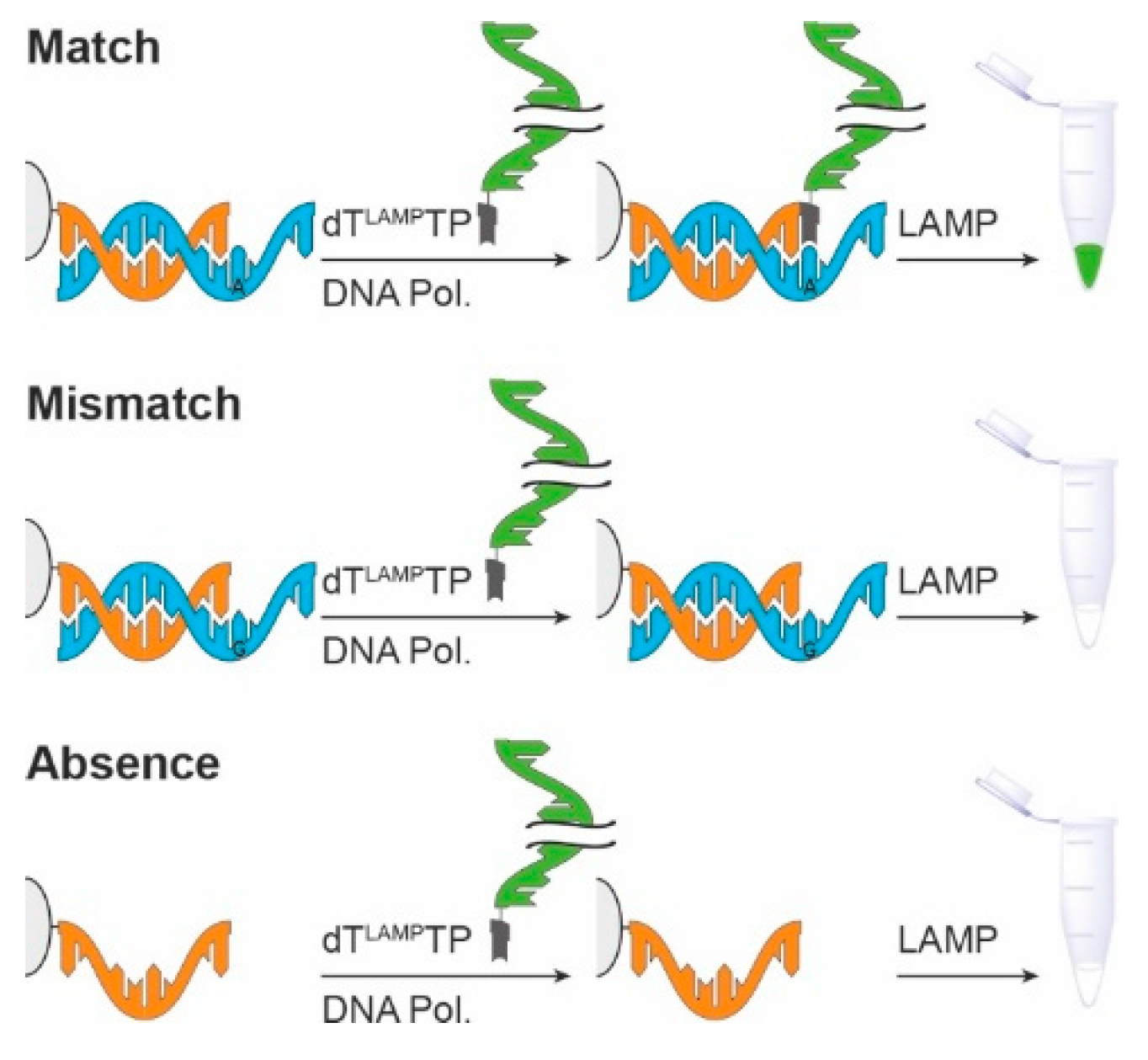
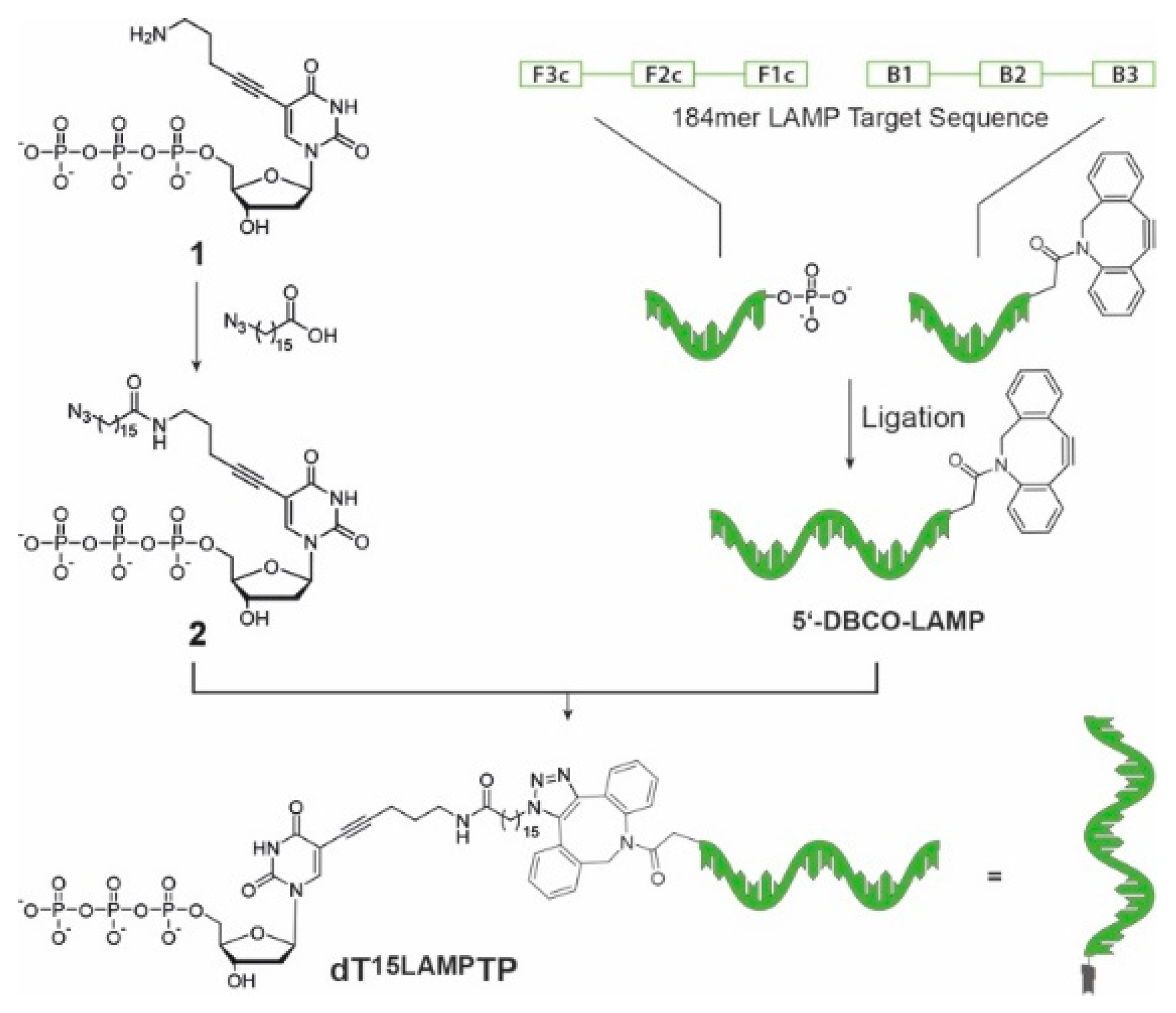
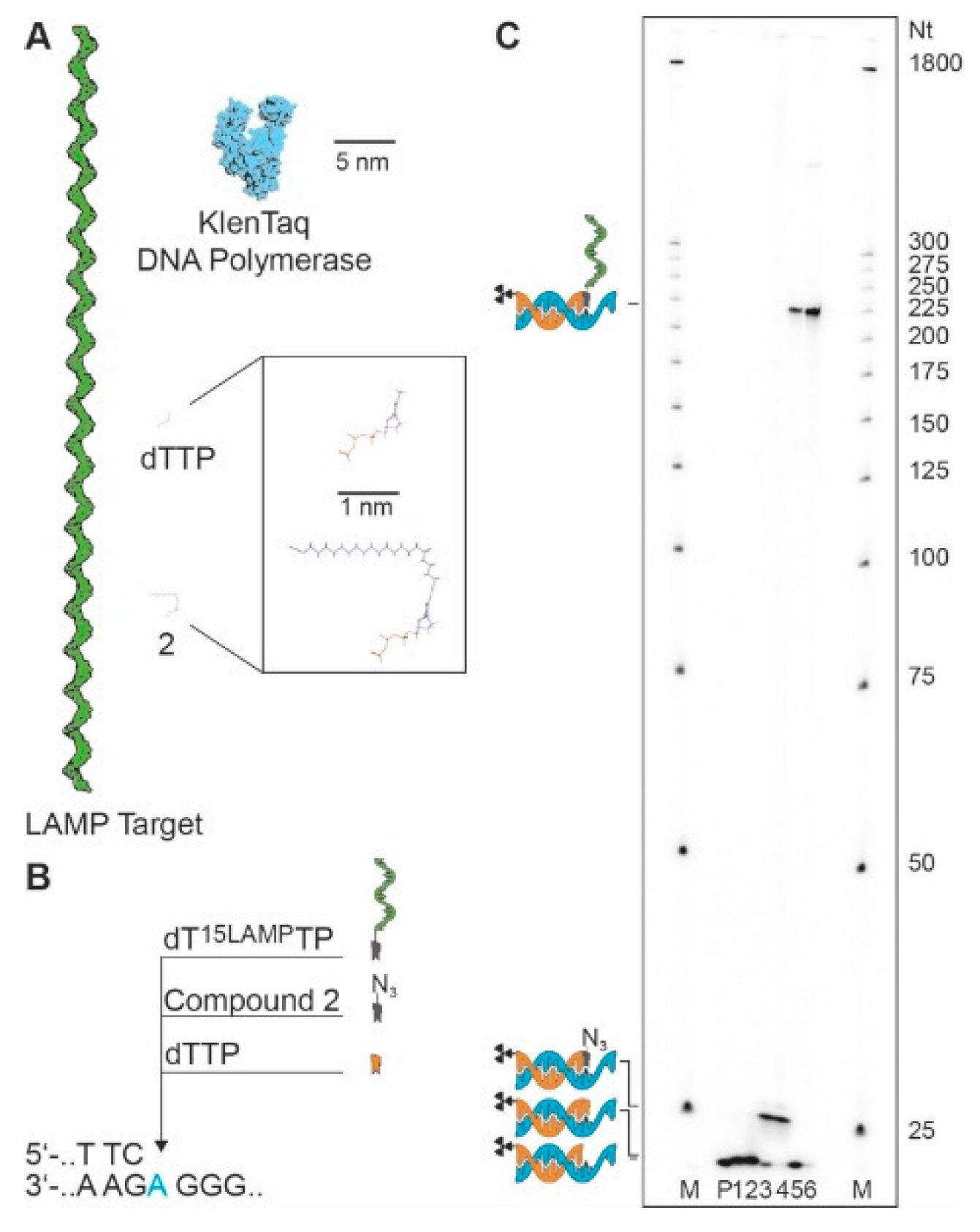

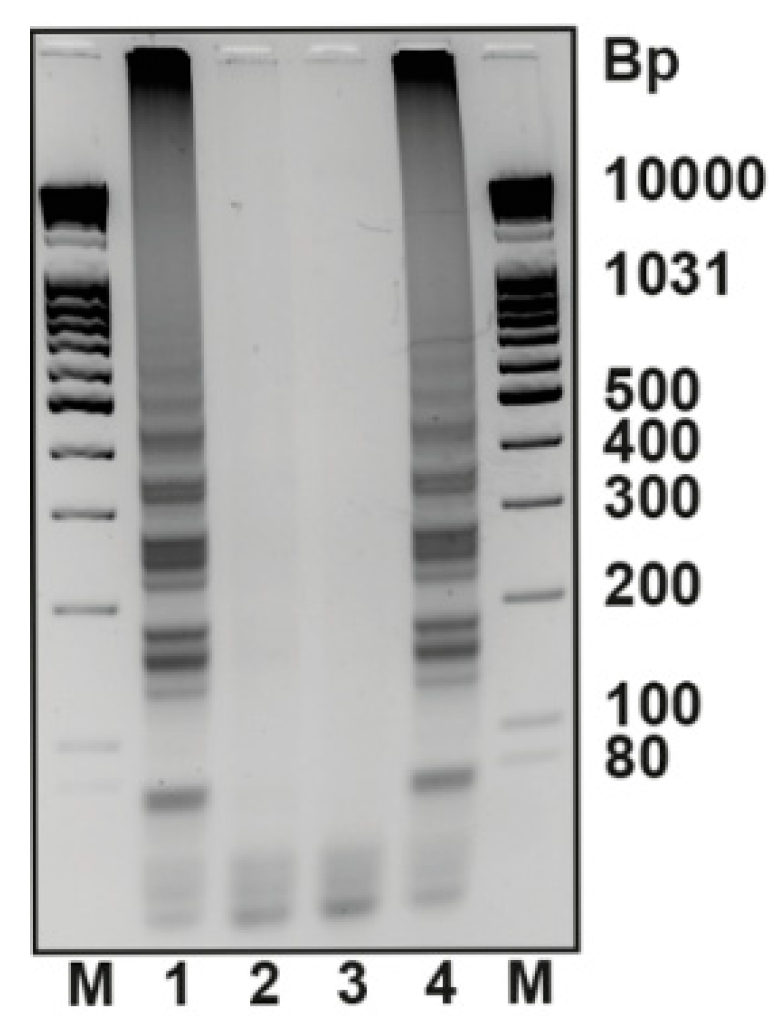
| LAMP Backward Inner Primer | 5′-d (GAG AGA ATT TGT ACC ACC TCC CAC CGG GCA CAT AGC AGT CCT AGG GAC AGT) |
| LAMP backward loop primer | 5′-d (ACC ATC TAT GAC TGT ACG CC) |
| LAMP backward outer primer | 5′-d (GGA CGT TTG TAA TGT CCG CTC C) |
| LAMP forward inner primer | 5′-d (CAG CCA GCC GCA GCA CGT TCG CTC ATA GGA GAT ATG GTA GAG CCG C) |
| LAMP forward loop primer | 5′-d (CTG CAT ACG ACG TGT CT) |
| LAMP forward outer primer | 5′-d (GGC TTG GCT CTG CTA ACA CGT T) |
| LAMP_Splint | 5′-d (GGC TGG CTG TCC AGT GAG AGA ATT TGT ACC) |
| LAMP_Target_A | 5′-DBCO-d (GGA CGT TTG TAA TGT CCG CTC CGG CAC ATA GCA GTC CTA GGG ACA GTG GCG TAC AGT CAT AGAT GGT CGG TGG GAG GTG GTA CAA ATT CTC TC) |
| LAMP_Target_B | 5′-P-d (ACT GGA CAG CCA GCC GCA GCA CGT TCC TGC ATA CGA CGT GTC TGC GGC TCT ACC ATA TCT CCT ATG AGC AAC GTG TTA GCA GAG CCA AGC C) |
| 5′-biotin BRAF primer | 5′-biotin-d (TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TGA CCC ACT CCA TCG AGA TTT C) |
| BRAF template (DNA) | 5′-d (TGC CTG GTG TTT GGG AGA AAT CTC GAT GGA GTG GGT C) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Welter, M.; Marx, A. Combining the Sensitivity of LAMP and Simplicity of Primer Extension via a DNA-Modified Nucleotide. Chemistry 2020, 2, 490-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2020029
Welter M, Marx A. Combining the Sensitivity of LAMP and Simplicity of Primer Extension via a DNA-Modified Nucleotide. Chemistry. 2020; 2(2):490-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleWelter, Moritz, and Andreas Marx. 2020. "Combining the Sensitivity of LAMP and Simplicity of Primer Extension via a DNA-Modified Nucleotide" Chemistry 2, no. 2: 490-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2020029
APA StyleWelter, M., & Marx, A. (2020). Combining the Sensitivity of LAMP and Simplicity of Primer Extension via a DNA-Modified Nucleotide. Chemistry, 2(2), 490-498. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry2020029




