Abstract
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles are a promising platform for drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, complement activation and immune recognition remain major barriers to their clinical translation. Previously, we reported that dextran-coated SPIO nanoworms (NWs) trigger potent complement activation and infusion reactions. Here, we systematically map the temporal sequence of immune events following SPIO NW administration, including C3 opsonization, granulocyte uptake, and cytokine release. In both in vitro and in vivo models, C3 deposition occurred rapidly, peaking at approximately 5 min post-incubation or post-injection. Higher Fe/plasma ratios led to reduced C3 deposition per particle, although the absolute amount of C3 bound was greater in vivo than in vitro. Notably, C3 dissociation from the particle surface exhibited a consistent half-life of ~14 min, independent of the NW injected dose and circulation time. Immune uptake by blood granulocytes was delayed relative to opsonization, becoming prominent only at 60 min post-injection. Further, cytokine release, measured by plasma IL-6 levels, displayed an even slower profile, with peak expression at 6 h post-injection. Together, these results reveal a distinct sequential immune response to SPIO NWs: rapid C3 opsonization, delayed cellular uptake, and late cytokine response. Understanding these dynamics provides a basis for developing strategies to inhibit complement activation and improve the hemocompatibility of SPIO-based theranostic agents.
1. Introduction
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles are widely used as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) due to their ability to shorten the transverse relaxation time (T2), resulting in strong negative contrast in T2-weighted images. SPIO nanoparticles are typically composed of magnetite (Fe3O4) or maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) crystals, whose surfaces are anionic owing to the formation of surface Fe–OH groups [1,2,3]. These hydroxyl groups enable hydrogen bonding with the hydroxyl groups of biopolymers such as dextran, carboxydextran, and chitosan, which are critical for imparting water solubility, biocompatibility, and colloidal stability to the nanoparticles in biological environments.
Clinically relevant SPIO formulations are predominantly synthesized using a one-pot coprecipitation method first described by Molday and MacKenzie [4], where ferrous (Fe2+) and ferric (Fe3+) salts are precipitated in the presence of a stabilizing biopolymer under alkaline conditions. This synthetic approach is highly valued for its simplicity, scalability, and the low cost and availability of raw materials.
Building upon this platform, we and others have previously developed and characterized dextran-coated SPIO nanoworms (NWs) [5,6]. These SPIO NWs consist of linear aggregates of multiple Fe3O4 crystals embedded within a 20 kDa dextran matrix, resulting in a worm-like morphology with a hydrodynamic diameter of approximately 60 nm. This unique architecture contributes to excellent transverse relaxivity (r2) and a high saturation magnetization of up to 140 emu/g, making SPIO NWs particularly promising for sensitive MR imaging. As a rule of thumb, transverse relaxivity and magnetic properties are increased by the clustering of Fe3O4 crystals, the exposure of magnetic crystals to water (e.g., PEGylation and inorganic shell decrease relaxivity), and an increase in the crystal size [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. All these factors likely contribute to the observed excellent contrast properties of SPIO NWs.
However, despite their imaging benefits, SPIO nanoparticles are associated with significant biological challenges. Prominently, SPIO nanoparticles can trigger immune-related adverse effects, including rapid clearance by monocytes and macrophages, as well as complement activation leading to hypersensitivity reactions [6,14,15,16]. Several SPIO-based contrast agents, such as Resovist and Feridex that have been withdrawn from the market, exhibit complement-mediated pseudoallergic reactions (CARPA, complement activation-related pseudoallergy). SPIO nanoparticles exhibit immune activation in preclinical models and thromboinflammation in human blood [17,18,19].
One potential alternative, ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxides (USPIOs) such as Feraheme (ferumoxytol), feature a reduced hydrodynamic size (15–30 nm), which contributes to decreased complement activation, extended blood circulation, and diminished immune cell recognition [2,11,12,13,14,16]. However, these improvements come at the expense of magnetic performance; USPIOs display lower r2 relaxivities due to smaller magnetic cores and relatively thick polymer coatings, limiting their contrast-enhancing abilities compared to larger SPIO NWs.
Given the clinical importance of balancing immune compatibility with strong MR contrast, there is a clear need to better understand the biological interactions of SPIO NWs. In particular, detailed studies on how nanoparticle surface properties and dosing influence complement activation, immune cell uptake, and systemic inflammatory responses are lacking. Improved mechanistic insights could inform the rational design of SPIO-based theranostics that maintain high imaging performance while minimizing immunogenicity.
In this study, we investigate the dynamics of complement activation and downstream immune responses following the intravenous injection of 60 nm SPIO NWs. Using both in vitro and in vivo models, we map the temporal sequence from early complement activation to blood granulocyte uptake and cytokine induction. These findings provide guidelines for designing next-generation MRI contrast agents with optimized safety profiles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of SPIO NWs
SPIO NWs were prepared as described previously [20] by precipitation of FeCl2 and FeCl3 salts( Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) with T-20 dextran (Pharmacosmos, Holbæk, Denmark). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed using a Tecnai G2 Biotwin TEM (Thermo Fisher) at 80 kV, with samples imaged using an AMT low-mount NS15B sCMOS camera (AMT Imaging, Woburn, MA, USA).
2.2. C3 Dot Blot Assay
The experiments to detect the amount of deposited complement component C3 were performed as described [21]. Briefly, SPIO NWs were incubated with BALB/c mouse serum (male) at various Fe/serum ratios for 30 min at 37 °C in a water bath. Following incubation, the samples were washed three times with PBS by ultracentrifugation. C3 deposition on particles was assessed using a quantitative dot blot assay as previously described [21].
2.3. In Vivo Administration and Sample Collection
SPIO NWs were intravenously administered to BALB/c male mice at doses of either 10 mg Fe/kg or 50 mg Fe/kg in 100 µL volume. Blood samples were collected at designated time points via retro-orbital sinus puncture using tubes containing EDTA (final concentration of 20 mM). Plasma was separated by centrifugation and used to isolate nanoparticles for C3 quantification and half-life analysis as described in [22]. For the assessment of leukocyte uptake, fresh whole blood was passed through a MACS column (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) to isolate magnetic leukocytes containing internalized nanoparticles. The purity of the cells was validated by staining nuclei and imaging with fluorescent microscopy. Cell suspensions were subsequently analyzed by a Guava EasyCyte HT flow cytometer (Luminex, Austin, TX, USA). Forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) parameters were used to gate and quantify leukocyte subpopulations (granulocytes) as described in [22].
2.4. Cytokine Analysis in Mouse Plasma
IL-6 concentrations were quantified in mouse plasma using the Mouse IL-6 ELISA Kit—Quantikine (Bio-Techne, catalog number M6000B-1, Minneapolis, MN, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Results
We used 60 nm dextran SPIO NWs, as described extensively in our previous studies [20] (Figure 1).
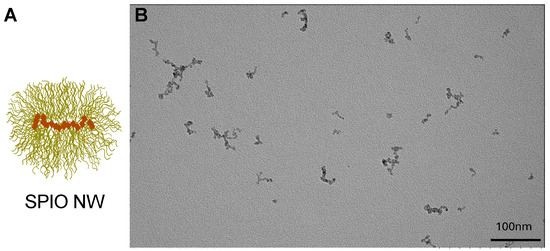
Figure 1.
Dextran-coated SPIO NWs. (A) Schematic illustration of SPIO NWs, showing aggregates of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocrystals (brown) embedded in a 20 kDa dextran coating (yellow). (B) TEM image of SPIO NWs, exhibiting a characteristic worm-like morphology of superparamagnetic crystals. Only the core is visible on TEM, but not the coating. Scale bar: 100 nm.
To understand the dynamics of complement activation, we incubated SPIO NWs in mouse serum at various Fe/serum ratios for 5, 15, or 30 min. Complement activation was halted with 20 mM EDTA, followed by washing the particles through ultracentrifugation, and detecting NW-bound complement component C3 by the dot blot immunoassay (Figure 2A). We found that C3 opsonization reached a plateau within 5 min at low Fe/serum ratios (0.1–0.25 mg/mL), while at higher Fe/serum ratios (0.5–1.25 mg/mL), it took 15–30 min to plateau. Notably, the level of C3 deposition was approximately 2.5-fold higher at low Fe/serum ratios compared to high Fe/serum ratios, likely due to an excess of complement factors at lower NW concentrations.
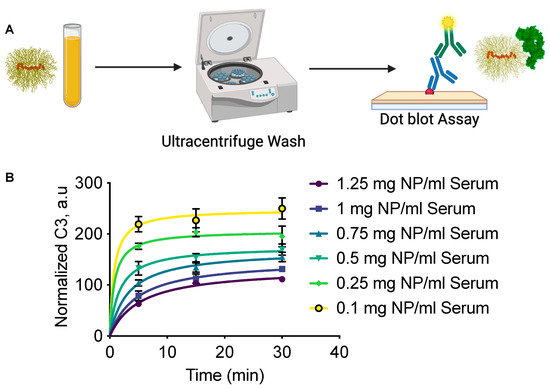
Figure 2.
In vitro kinetics of C3 opsonization on SPIO NWs at varying Fe/serum ratios. (A) Schematic representation of the in vitro workflow for the C3 opsonization assay. SPIO NWs were incubated with mouse serum at 37 °C across a range of Fe/serum ratios and time points, followed by ultracentrifugation and dot blot analysis using anti-C3 antibodies. (B) Quantification of C3 deposition at Fe/serum concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 1.25 mg/mL at various time points (5 min, 15 min, 30 min). The amount of C3 was normalized to the Fe concentration to enable comparison.
To measure in vivo opsonization kinetics as a function of NW dose, BALB/c mice were injected with either 10 mg/kg or 50 mg/kg SPIO NWs, and their blood clearance profiles were measured (Figure 3A). A significant difference in half-life was noted: nanoparticles administered at 10 mg/kg demonstrated a half-life of 37 min, while those at 50 mg/kg exhibited a prolonged half-life of 305 min. C3 levels measured over time (Figure 3B) indicated that C3 opsonization was approximately five-fold lower at the higher dose than at the lower dose, mirroring the trend observed in vitro. Notably, peak C3 opsonization occurred at ~5 min post-injection, after which the amount of C3 per NW decreased in a monoexponential decay. The kinetics of C3 opsonization were comparable between doses, with half-lives of 14.4 min and 14.6 min for 10 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg, respectively. These findings imply that although the extent of C3 opsonization is dose-dependent, the kinetics of complement binding are independent of the nanoparticle clearance rate.
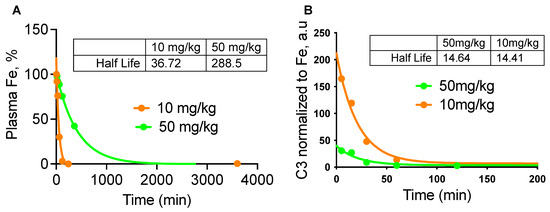
Figure 3.
In vivo kinetics of complement C3 opsonization of SPIO NWs. (A) Plasma levels of Fe show different half-lives as a function of the injected dose; (B) levels of C3 normalized to F levels show that C3 is lost from NWs with a half-life of ~14 min, regardless of the injected dose and NW circulation time. n = 3 mice per group.
Given that C3 opsonization promotes immune uptake, we analyzed the uptake of SPIO NWs by measuring the number of magnetic blood leukocytes recovered in vivo at 5, 30, and 60 min post-injection using flow cytometry (Figure 4). Minimal uptake was observed at 5 and 30 min, while measurable uptake occurred by 60 min (Figure 4A). Plotting the levels of magnetic leukocytes and gated granulocytes shows the increase at 60 min. These data suggest that blood immune cell uptake is considerably slower than complement opsonization.
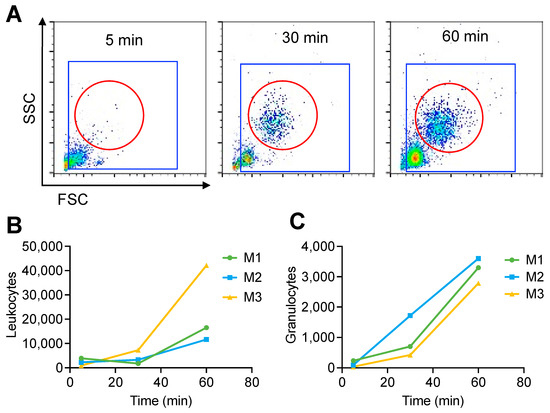
Figure 4.
Flow cytometry analysis of SPIO NW uptake by circulating leukocytes. (A) Representative flow cytometry data of magnetic leukocytes isolated from individual mice at 5, 30, and 60 min post-intravenous injection of SPIO NW. Blue ROI indicates total magnetic leukocytes; red ROI indicates total magnetic granulocytes. (B) Quantification of total magnetic leukocytes at each time point for individual mice. (C) Quantification of total magnetic granulocytes at each time point for individual mice (M, mouse; n = 3).
Finally, we assessed systemic inflammatory responses by measuring in vivo levels of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6, a reliable marker of macrophage activation. IL-6 was shown to be significantly elevated after incubation of IONPs in whole human blood [23]. IL-6 levels remained at baseline at early time points (5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, and 2 h), but increased at 6 h post-injection before returning to baseline at 24 h (Figure 5). This pattern indicates that although complement activation occurs rapidly, downstream inflammatory responses are delayed and transient.
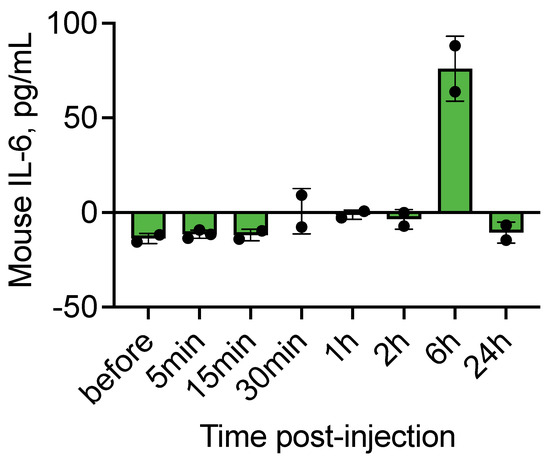
Figure 5.
Plasma interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels at multiple time points following intravenous injection of SPIO NWs. IL-6 concentrations were measured in plasma samples collected at 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 6 h, and 24 h after SPIO NW administration (n = 2–3 mice per time point).
4. Discussion
The complement represents an important component of the protein corona of iron oxide nanoparticles, leading to a variety of immunological responses [24,25]. This study explores the temporal dynamics of complement recognition and immune response following systemic administration of dextran-coated iron oxide SPIO nanoworms (NWs). A key finding is the rapidity and dose-dependent nature of C3 opsonization, followed by a lagging yet robust innate immune cascade involving granulocyte uptake and cytokine release. Both in vitro and in vivo, we observed that C3 deposition occurred within minutes, plateauing within 5–10 min of exposure. Interestingly, increasing NW concentrations led to lower C3 deposition per particle. This inverse relationship may be due to a surface-area-driven saturation, where higher NW concentrations outpace the capacity of available complement components, resulting in incomplete and competitive opsonization. In vivo, these effects were amplified, suggesting that the plasma milieu, rich in regulatory proteins, proteases, and cellular sinks, modulates the efficiency and persistence of C3 binding.
Furthermore, we found that C3 dissociation from the NW surface in vivo was remarkably consistent, with a half-life of approximately 14 min, independent of nanoparticle dose and circulation time. This implies that once formed, the opsonin–NW complexes are inherently transient and undergo spontaneous or protease-mediated disassembly [26]. The consistent off-rate suggests a potential kinetic bottleneck that could be exploited in therapeutic designs. Modifying surface chemistry to further destabilize C3 binding could mitigate downstream immune recognition without compromising initial nanoparticle functionality. Despite initial C3 opsonization, significant granulocyte engagement was delayed until 30–60 min post-injection. This delay suggests a threshold model of immune cell activation, where cumulative or sustained opsonization may be necessary to trigger effective phagocytic engagement. Alternatively, it could reflect trafficking dynamics, where granulocytes require time to interact with opsonized NWs in specific vascular compartments or after hepatic or splenic filtration.
Systemic inflammatory signaling, as measured by plasma IL-6 levels, exhibited an even slower response, peaking at 6 h post-injection. This indicates that complement activation and initial particle recognition are insufficient in isolation to drive an acute inflammatory cytokine response. Instead, the cytokine surge likely requires a convergence of multiple signals, including phagocytic uptake, endosomal processing, and inflammasome activation [27]. This delayed systemic response presents a critical temporal window during which interventions could be deployed to dampen inflammation without compromising nanoparticle efficacy.
In summary, our results support a model in which the immune system rapidly flags SPIO NWs but evolves a sequential response. This has important implications for nanoparticle design: improving hemocompatibility may not necessitate full complement evasion but rather delaying or destabilizing opsonin binding to fall below cellular activation thresholds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and D.S.; methodology, Y.L.; validation, Y.L.; formal analysis, Y.L. and D.S.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, Y.L. and D.S.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.L.; visualization, Y.L.; supervision, D.S.; project administration, D.S.; funding acquisition, D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by the NIH grant R01AI154959 to D.S.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The University of Colorado Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUC) approved the animal experiments (protocols 00108, approved 7 January 2023).
Data Availability Statement
Original data are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used Grammarly for the purposes of proofreading the manuscript. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Boehm, H. Acidic and Basic Properties of Hydroxylated Metal Oxide Surfaces. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1971, 52, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, M.C.; Bomati-Miguel, O.; Morales, M.D.; Serna, C.J.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S. Surface Characterisation of Dextran-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Pyrolysis and Coprecipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.W. Surface Properties of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Mr Contrast Agents: Ferumoxides, Ferumoxtran, Ferumoxsil. Magn. Reason. Imaging 1995, 13, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molday, R.S.; MacKenzie, D. Immunospecific Ferromagnetic Iron-Dextran Reagents for the Labeling and Magnetic Separation of Cells. J. Immunol. Methods 1982, 52, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Gu, L.; von Maltzahn, G.; Ruoslahti, E.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Biodegradable Luminescent Porous Silicon Nanoparticles for in Vivo Applications. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberg, D.; Park, J.H.; Karmali, P.P.; Zhang, W.M.; Merkulov, S.; McCrae, K.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.; Ruoslahti, E. Differential Proteomics Analysis of the Surface Heterogeneity of Dextran Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and the Implications for Their in Vivo Clearance. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3926–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Sun, X.M.; Suzuki, Y.; Mann, D.; Liu, Z.; Terashima, M.; Yang, P.C.; McConnell, M.V.; Nishimura, D.G.; et al. Feco/Graphitic-Shell Nanocrystals as Advanced Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging and near-Infrared Agents. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaConte, L.E.; Nitin, N.; Zurkiya, O.; Caruntu, D.; O’Connor, C.J.; Hu, X.; Bao, G. Coating Thickness of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Affects R2 Relaxivity. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2007, 26, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Hou, S.J.; Zheng, Z.L.; Zhou, J.; Bao, G. Coating Optimization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for High T-2 Relaxivity. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4607–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, E.S.G.; Tang, X.S.; Sheng, Y.; Shuter, B.; Xue, J.M. Controlled Loading of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles in Fluorescent Nanogels as Effective T-2-Weighted Mri Contrast Agents. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.J.; Lee, H.; Shao, H.; Hilderbrand, S.A.; Weissleder, R. Multicore Assemblies Potentiate Magnetic Properties of Biomagnetic Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4793–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, M.; Moon, W.K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T. Water-Dispersible Ferrimagnetic Iron Oxide Nanocubes with Extremely High R(2) Relaxivity for Highly Sensitive In Vivo Mri of Tumors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poselt, E.; Kloust, H.; Tromsdorf, U.; Janschel, M.; Hahn, C.; Masslo, C.; Weller, H. Relaxivity Optimization of a Pegylated Iron-Oxide-Based Negative Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agent for T(2)-Weighted Spin-Echo Imaging. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynal, I.; Prigent, P.; Peyramaure, S.; Najid, A.; Rebuzzi, C.; Corot, C. Macrophage Endocytosis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Mechanisms and Comparison of Ferumoxides and Ferumoxtran-10. Investig. Radiol. 2004, 39, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulte, J.W.; Kraitchman, D.L. Iron Oxide Mr Contrast Agents for Molecular and Cellular Imaging. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Weissleder, R.; Bogdanov, A., Jr. Uptake of Dextran-Coated Monocrystalline Iron Oxides in Tumor Cells and Macrophages. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 1997, 7, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampton, D.; Folkersen, J.; Fishbane, S.; Hedenus, M.; Howaldt, S.; Locatelli, F.; Patni, S.; Szebeni, J.; Weiss, G. Hypersensitivity Reactions to Intravenous Iron: Guidance for Risk Minimization and Management. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, T.; Nemes, R.; Meszaros, T.; Urbanics, R.; Kok, R.J.; Jackman, J.A.; Cho, N.J.; Storm, G.; Szebeni, J. Complement Activation In Vitro and Reactogenicity of Low-Molecular Weight Dextran-Coated Spions in the Pig Carpa Model: Correlation with Physicochemical Features and Clinical Information. J. Control Release 2018, 270, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerogianni, A.; Bal, M.; Mohlin, C.; Woodruff, T.M.; Lambris, J.D.; Mollnes, T.E.; Sjostrom, D.J.; Nilsson, P.H. In Vitro Evaluation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Induced Thromboinflammatory Response Using a Combined Human Whole Blood and Endothelial Cell Model. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benasutti, H.; Wang, G.; Vu, V.P.; Scheinman, R.; Groman, E.; Saba, L.; Simberg, D. Variability of Complement Response toward Preclinical and Clinical Nanocarriers in the General Population. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Monte, A.; Dylla, L.; Moghimi, S.M.; Simberg, D. Validation of Dot Blot Immunoassay for Measurement of Complement Opsonization of Nanoparticles. J. Immunol. Methods 2024, 528, 113668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jacques, S.; Gaikwad, H.; Wang, G.; Banda, N.K.; Holers, V.M.; Scheinman, R.I.; Tomlinson, S.; Moghimi, S.M.; Simberg, D. Inhibition of Acute Complement Responses Towards Bolus-Injected Nanoparticles Using Targeted Short-Circulating Regulatory Proteins. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf-Grosse, S.; Rokstad, A.M.; Ali, S.; Lambris, J.D.; Mollnes, T.E.; Nilsen, A.M.; Stenvik, J. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Cytokine Secretion in a Complement-Dependent Manner in a Human Whole Blood Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3927–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Ren, P.; Xi, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Specific Surface-Modified Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Trigger Complement-Dependent Innate and Adaptive Antileukaemia Immunity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; Fan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, R.; Ge, J.; Cao, X.; Qi, H.; Wang, N.; et al. Splenic Response to Protein Corona of Nanoparticles in Vivo. Nano Today 2025, 62, 102676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, G.; Griffin, J.I.; Brenneman, B.; Banda, N.K.; Holers, V.M.; Backos, D.S.; Wu, L.; Moghimi, S.M.; Simberg, D. Complement Proteins Bind to Nanoparticle Protein Corona and Undergo Dynamic Exchange In Vivo. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Nuñez, G. Sterile Inflammation: Sensing and Reacting to Damage. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).