A Wearable Internet of Things Device for Noninvasive Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs Related to Heart Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
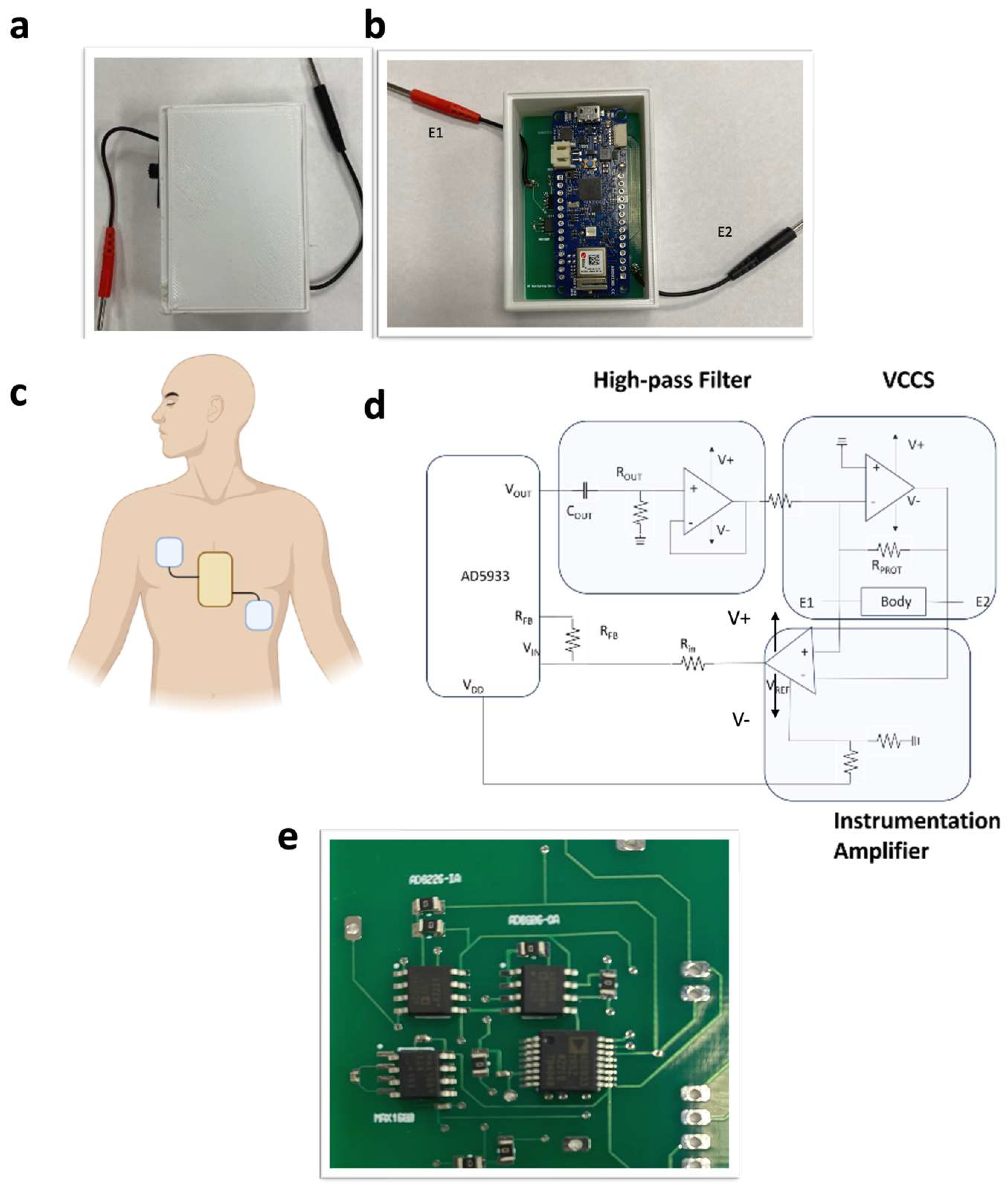
Sensor Development
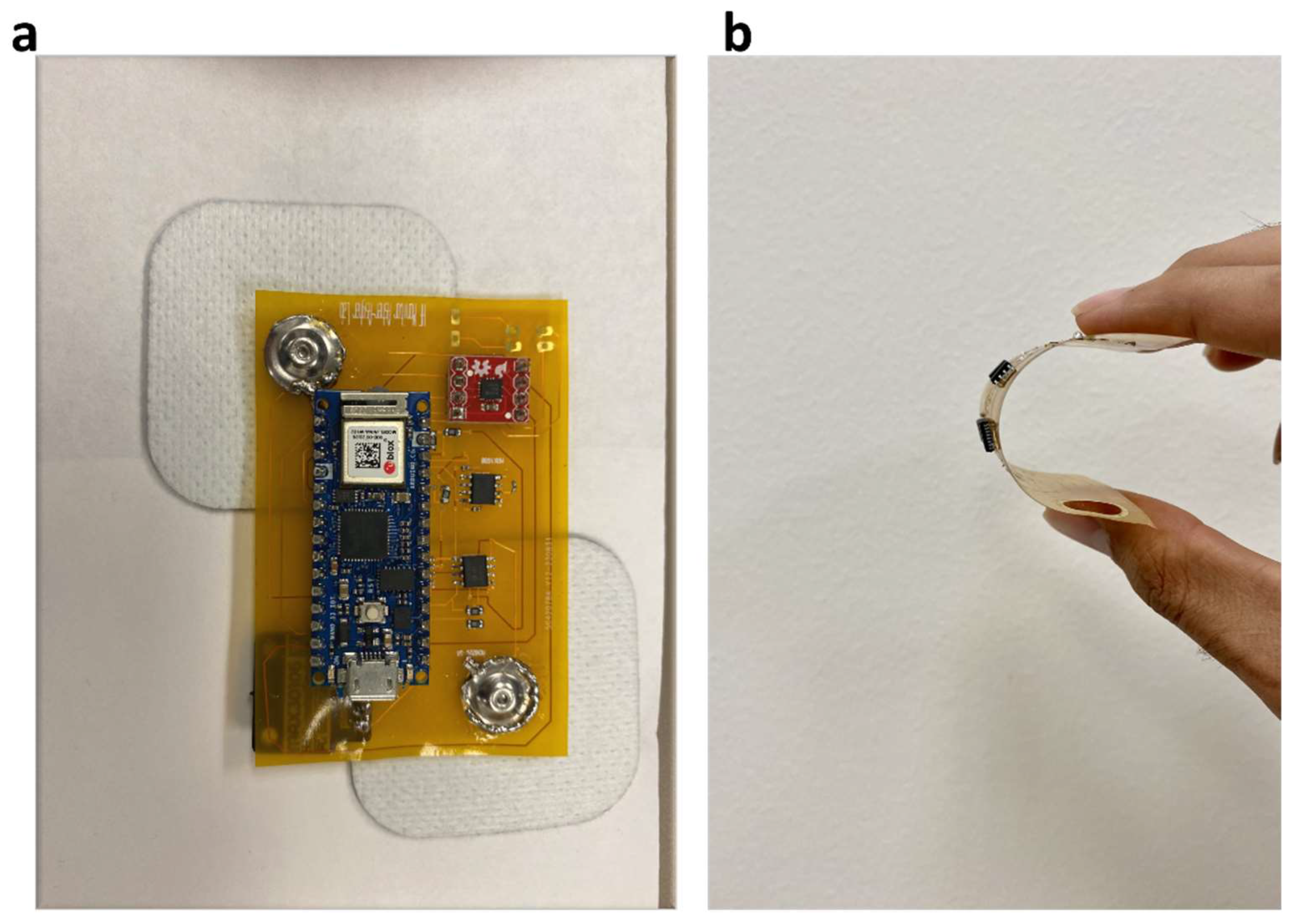
3. Skin Patch
4. Experimentation
4.1. Thoracic Impedance Sensor Calibration
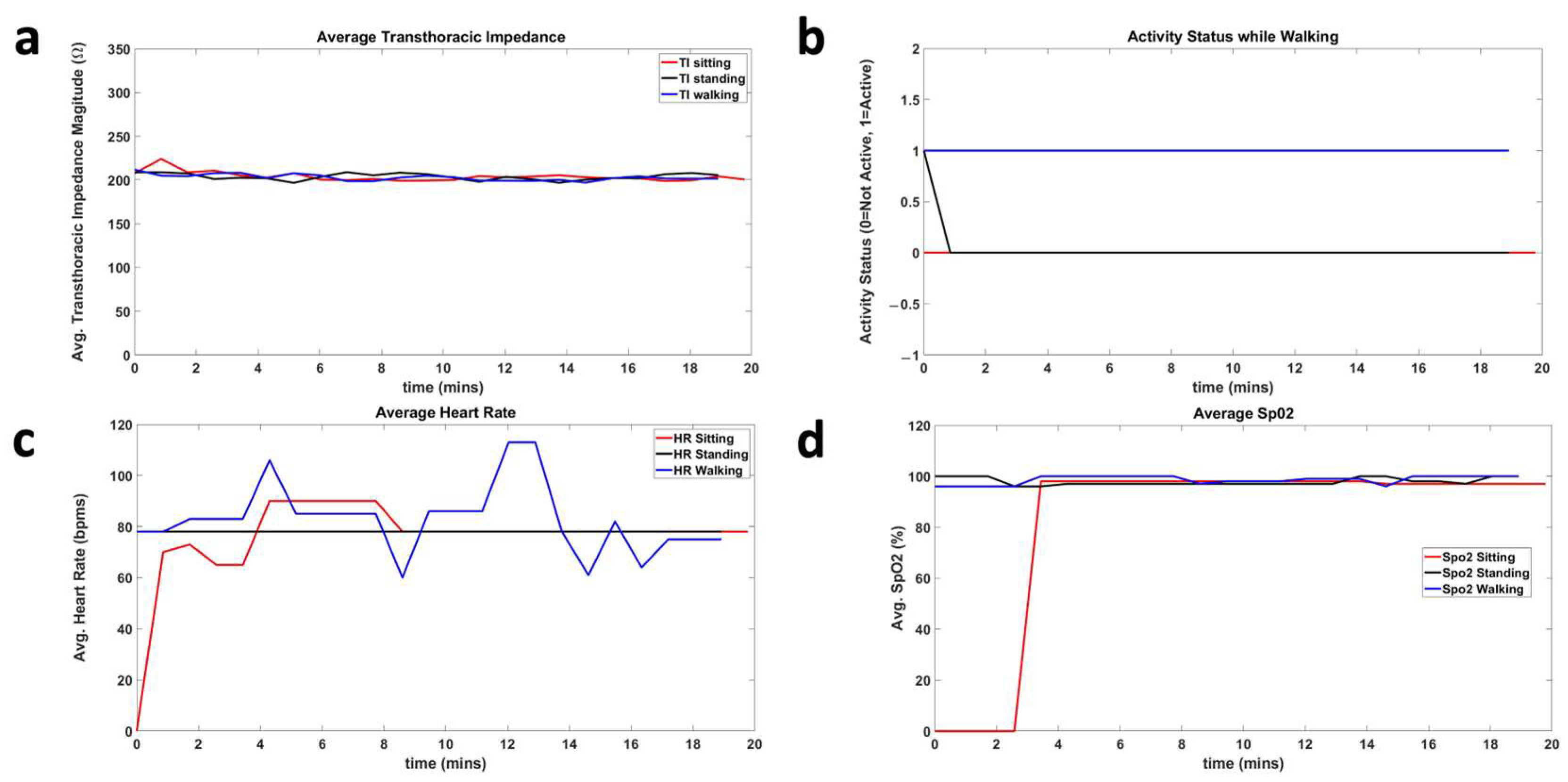
4.2. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NHS Inform. Cardiovascular Disease—Illnesses & Conditions. Available online: https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/heart-and-blood-vessels/conditions/cardiovascular-disease (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Heart Failure Facts & Information. Available online: https://hfsa.org/patient-hub/heart-failure-facts-information (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Yan, T.; Zhu, S.; Yin, X.; Xie, C.; Xue, J.; Zhu, M.; Weng, F.; Zhu, S.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, X.; et al. Burden, Trends, and Inequalities of Heart Failure Globally, 1990 to 2019: A Secondary Analysis Based on the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, 27852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo Clinic. Pulmonary Edema—Symptoms & Causes. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009 (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- American Heart Association. Types of Heart Failure. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-failure/what-is-heart-failure/types-of-heart-failure (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- American Heart Association. Devices That May Interfere with ICDs and Pacemakers. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/arrhythmia/prevention--treatment-of-arrhythmia/devices-that-may-interfere-with-icds-and-pacemakers (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Medtronic. Cardiac Monitors—Reveal LINQ ICM System. Available online: https://www.medtronic.com/us-en/healthcare-professionals/products/cardiac-rhythm/cardiac-monitors/reveal-linq-icm.html (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Medtronic. The CareLink Network—Information Systems. Available online: https://www.medtronic.com/us-en/healthcare-professionals/products/cardiac-rhythm/managing-patients/information-systems/carelink-network.html (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Medtronic. Patient Management—Cardiac Device CareLink Network. Available online: https://www.medtronic.com/ca-en/healthcare-professionals/products/cardiac-rhythm/patient-management-carelink/medtronic-carelink-network-cardiac-device-patients.html (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Abbott. How the CardioMEMS HF System and Merlin.net PCN Works. Available online: https://www.cardiovascular.abbott/us/en/hcp/products/heart-failure/pulmonary-pressure-monitors/cardiomems/about/how-it-works.html?gclid=CjwKCAjwh8mlBhB_EiwAsztdBCTDS73LGEUvOYK6ae3FRJe_THVaSifd5ab6Zyq8_H1gszp4H2Lu0hoCH9EQAvD_BwE (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- DAIC. ICD Manufacturers Must Increase Battery Life to Cut Costs, Improve Care. Available online: https://www.dicardiology.com/article/icd-manufacturers-must-increase-battery-life-cut-costs-improve-care (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Schmier, J.K.; Ong, K.L.; Fonarow, G.C. Cost-Effectiveness of Remote Cardiac Monitoring With the CardioMEMS Heart Failure System. Clin. Cardiol. 2017, 40, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.M.A.; Mahgoub, I.; Du, E.; Leavitt, M.A.; Asghar, W. Advances in healthcare wearable devices. npj Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, P. Advances in wearable technology and its medical applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Stehlik, J.; Schmalfuss, C.; Bozkurt, B.; Nativi-Nicolau, J.; Wohlfahrt, P.; Wegerich, S.; Rose, K.; Ray, R.; Schofield, R.; Deswal, A.; et al. Continuous wearable monitoring analytics predict heart failure hospitalization: The link-hf multicenter study. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020, 13, e006513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- What Is the Internet of Things (IoT)? Available online: https://www.oracle.com/internet-of-things/what-is-iot/ (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- IEEE Pulse. IoMT (Internet of Medical Things): Reducing Cost While Improving Patient Care. Available online: https://www.embs.org/pulse/articles/iomt-internet-of-medical-things-reducing-cost-while-improving-patient-care/ (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Haghi Kashani, M.; Madanipour, M.; Nikravan, M.; Asghari, P.; Mahdipour, E. A systematic review of IoT in healthcare: Applications, techniques, and trends. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 192, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bi, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Gu, J. Skin-inspired antibacterial conductive hydrogels customized for wireless flexible sensor and collaborative wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2023, 11, 14096–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Wen, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, H. Mechanically Strong, Wet Adhesive, and Self-Healing Polyurethane Ionogel Enhanced with a Semi-interpenetrating Network for Underwater Motion Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 54203–54214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Liang, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Tian, Y. Skin-Inspired Ultra-Tough Supramolecular Multifunctional Hydrogel Electronic Skin for Human–Machine Interaction. Nanomicro Lett. 2023, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, S.; Jin, K.; Li, D.; Fu, Z.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Aloe Inspired Special Structure Hydrogel Pressure Sensor for Real-Time Human-Computer Interaction and Muscle Rehabilitation System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2308175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovancescu, S.; Saczynski, J.S.; Darling, C.E.; Riistama, J.; Kuniyoshi, F.S.; Meyer, T.; Goldberg, R.; McManus, D.D. Detecting Heart Failure Decompensation by Measuring Transthoracic Bioimpedance in the Outpatient Setting: Rationale and Design of the SENTINEL-HF Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2015, 4, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemotag. Rapid Vitals for Monitoring Structural Heart Health. Available online: https://hemotag.com/ (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- PubMed. A Usability Study of a Mobile Monitoring System for Congestive Heart Failure Patients. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25160241/ (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Masip, J.; Gayà, M.; Páez, J.; Betbesé, A.; Vecilla, F.; Manresa, R.; Ruíz, P. Pulse Oximetry in the Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure. Rev. Española Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2012, 65, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MN Department of Health. Oxygen Levels, Pulse Oximeters, and COVID-19. Available online: https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/coronavirus/pulseoximeter.html (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Penn Medicine. Exercise & Activity for Patients with Heart Failure. Available online: https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/heart-and-vascular-blog/2015/july/5-tips-for-exercise-with-heart-failure (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- SparkFun. Photodetector Breakout—MAX30101 (Qwiic)—SEN-16474—SparkFun Electronics. Available online: https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16474 (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Devices, A. Micropower, 3-Axis, ±2 g/±4 g/±8 g Digital Output MEMS Accelerometer ADXL362. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/adxl362.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Basics of the I2C Communication Protocol. Available online: https://www.circuitbasics.com/basics-of-the-i2c-communication-protocol (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Basics of the SPI Communication Protocol. Available online: https://www.circuitbasics.com/basics-of-the-spi-communication-protocol (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Devices A. MSPS, 12-Bit Impedance Converter, Network Analyzer AD5933. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD5933.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Arduino Online Shop. Arduino MKR WiFi 1010. Available online: https://store-usa.arduino.cc/products/arduino-mkr-wifi-1010 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Firebase. Available online: https://firebase.google.com/?gad=1&gclid=CjwKCAjw9pGjBhB-EiwAa5jl3KycMFGWjGE_t6A8_G_ZhAsbRyKNtocDcqUWhCkMU_PUO_ioOCFfAhoCefwQAvD_BwE&gclsrc=aw.ds (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Iqbal, S.M.A.; Mahgoub, I.; Du, E.; Leavitt, M.A.; Asghar, W. Development of a wearable belt with integrated sensors for measuring multiple physiological parameters related to heart failure. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqueveque, P.; Gómez, B.; Monsalve, E.; Germany, E.; Ortega-Bastidas, P.; Dubo, S.; Pino, E.J. Simple Wireless Impedance Pneumography System for Unobtrusive Sensing of Respiration. Sensors 2020, 20, 5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TestEquity. Keysight E4980AL/032 Precision LCR Meter—300 kHz. Available online: https://www.testequity.com/product/22137-1-E4980AL-032?gclid=Cj0KCQjwzdOlBhCNARIsAPMwjby6wZYxrFeHvnX4rxsLX3PTZpulMSzP5S6WtuB07ixiKrFLxPqdtgYaAtr2EALw_wcB (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- MATLAB. Empirical Mode Decomposition. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/discovery/empirical-mode-decomposition.html (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Jarchi, D.; Salvi, D.; Tarassenko, L.; Clifton, D.A. Validation of Instantaneous Respiratory Rate Using Reflectance PPG from Different Body Positions. Sensors 2018, 18, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physics LibreTexts. 9.4: Resistivity and Resistance. Available online: https://phys.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/University_Physics/Book%3A_University_Physics_(OpenStax)/Book%3A_University_Physics_II_-_Thermodynamics_Electricity_and_Magnetism_(OpenStax)/09%3A_Current_and_Resistance/9.04%3A_Resistivity_and_Resistance (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- PubMed. Transthoracic Impedance: Differences between Men and Women with Implications for Impedance Cardiography. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7159339/ (accessed on 13 May 2023).
- CDC-DNPAO. Calculating BMI using the English System—BMI for Age Training Course. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpao/growthcharts/training/bmiage/page5_2.html (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Iqbal, S.M.A.; Leavitt, M.A.; Pedilus, G.; Mahgoub, I.; Asghar. A wearable telehealth system for the monitoring of parameters related to heart failure. Heliyon. 2024, 4, e26841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmann, D.; Nägele, H.; Schauerte, P.; Wiegand, U.; Butter, C.; Zanotto, G.; Quesada, A.; Guthmann, A.; Hill, M.R.S.; Lamp, B. Clinical utility of intrathoracic impedance monitoring to alert patients with an implanted device of deteriorating chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.M.; Wang, L.; Chau, E.; Chan, R.H.W.; Kong, S.L.; Tang, M.O.; Christensen, J.; Stadler, R.W.; Lau, C.P. Intrathoracic impedance monitoring in patients with heart failure: Correlation with fluid status and feasibility of early warning preceding hospitalization. Circulation 2005, 112, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyllensten, I.C.; Bonomi, A.G.; Goode, K.M.; Reiter, H.; Habetha, J.; Amft, O.; Cleland, J.G.F. Early Indication of Decompensated Heart Failure in Patients on Home-Telemonitoring: A Comparison of Prediction Algorithms Based on Daily Weight and Noninvasive Transthoracic Bio-impedance. JMIR Med. Inform. 2016, 4, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, J.E.; Ramos-Tuarez, F.; Nieves, J.; Sabates, A.; Sehatbakhsh, S.; Pradeep, D.; Torres, P.; Chomko, T.A.; Abdallah, A.; Al Abbasi, B.; et al. Safety And Efficacy of The HemotagTm Recording Device To Detect Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2020, 26, S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Conditions | Duration (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Thoracic Impedance Activity Status HR SPO2 | Sitting | 20 |
| Thoracic Impedance Activity Status HR SPO2 | Standing | 20 |
| Thoracic Impedance Activity Status HR SPO2 | Walking | 20 |
| Subject | Gender | Age | Height (cm) | Weight (lb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 29 | 165.1 | 137 |
| 2 | M | 28 | 168 | 120 |
| 3 | M | 31 | 168 | 130 |
| 4 | M | 32 | 167.64 | 176 |
| 5 | F | 29 | 161.5 | 92.59 |
| 6 | F | 31 | 164 | 110.231 |
| 7 | F | 30 | 156 | 117 |
| 8 | F | 31 | 171 | 171.9 |
| 9 | F | 29 | 158 | 112 |
| 10 | F | 24 | 160 | 105 |
| Avg TI | SPO2 | Avg HR | Activity Status | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sitting | Standing | Walking | Sitting | Standing | Walking | Sitting | Standing | Walking | Sitting | Standing | Walking |
| 269.9 | 277.6 | 284.5 | 98.9 | 99.3 | 99 | 69.9 | 67.3 | 70.4 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 218.3 | 231.3 | 236.6 | 98.3 | 97.9 | 99.1 | 68.8 | 79.7 | 105.0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 223.1 | 216.0 | 220.7 | 99.6 | 98.4 | 98.7 | 70.0 | 64.9 | 89.2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 287.1 | 295.6 | 291.3 | 98.8 | 99.5 | 97.5 | 66.5 | 74.9 | 71.3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 190.1 | 195.9 | 196.3 | 97.7 | 97.1 | 98.5 | 76.9 | 81.5 | 86.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 221.2 | 229.6 | 231.6 | 98.7 | 98.4 | 97.8 | 61.9 | 67.2 | 75.4 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 210.1 | 217.4 | 218.1 | 97.1 | 97.3 | 98.5 | 67.1 | 65.4 | 74.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 268.8 | 280.2 | 291.1 | 99.1 | 99.7 | 98.3 | 65.9 | 64.7 | 82.8 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 242.6 | 245.2 | 239.9 | 98.6 | 98.9 | 97.7 | 66.9 | 62.7 | 78.9 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 226.4 | 228.9 | 230.8 | 99.5 | 97.1 | 98.6 | 77.3 | 75.7 | 73.0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, S.M.A.; Leavitt, M.A.; Mahgoub, I.; Asghar, W. A Wearable Internet of Things Device for Noninvasive Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs Related to Heart Failure. IoT 2024, 5, 155-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010008
Iqbal SMA, Leavitt MA, Mahgoub I, Asghar W. A Wearable Internet of Things Device for Noninvasive Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs Related to Heart Failure. IoT. 2024; 5(1):155-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Sheikh Muhammad Asher, Mary Ann Leavitt, Imadeldin Mahgoub, and Waseem Asghar. 2024. "A Wearable Internet of Things Device for Noninvasive Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs Related to Heart Failure" IoT 5, no. 1: 155-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010008
APA StyleIqbal, S. M. A., Leavitt, M. A., Mahgoub, I., & Asghar, W. (2024). A Wearable Internet of Things Device for Noninvasive Remote Monitoring of Vital Signs Related to Heart Failure. IoT, 5(1), 155-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/iot5010008








