Seasonal and Episodic Variation of Aseismic Creep Displacement Along the West Valley Fault, Philippines
Abstract
1. Introduction
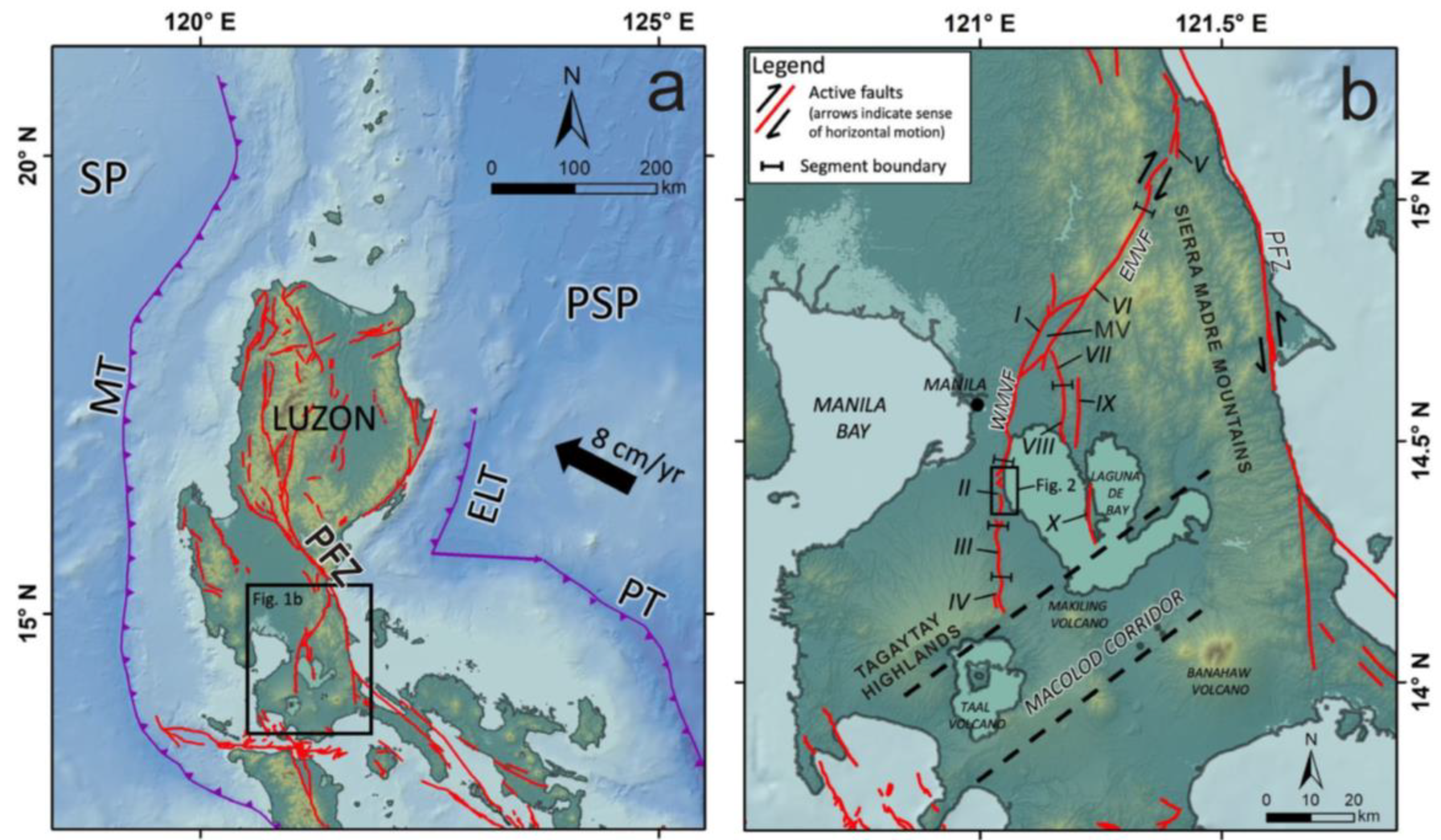
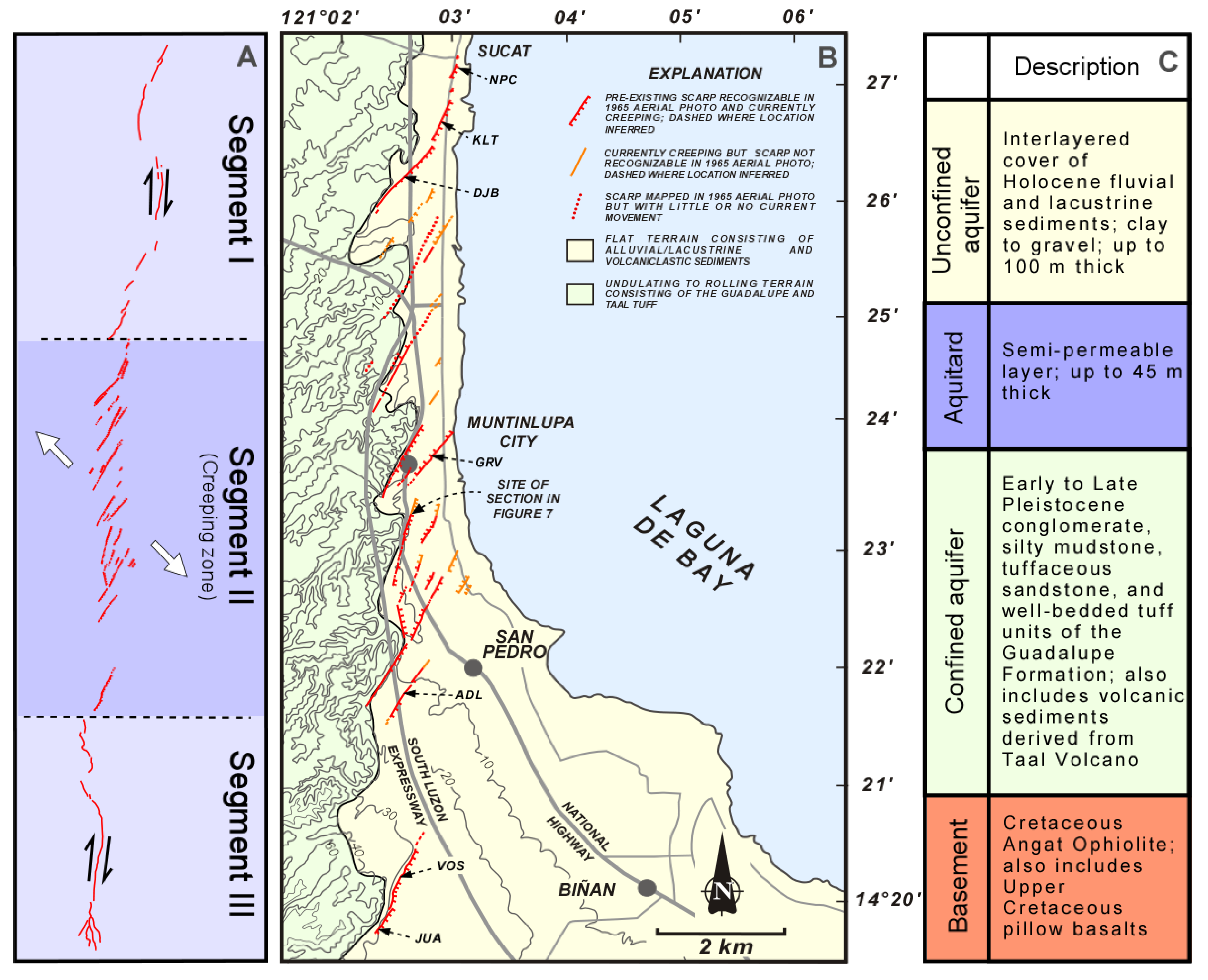
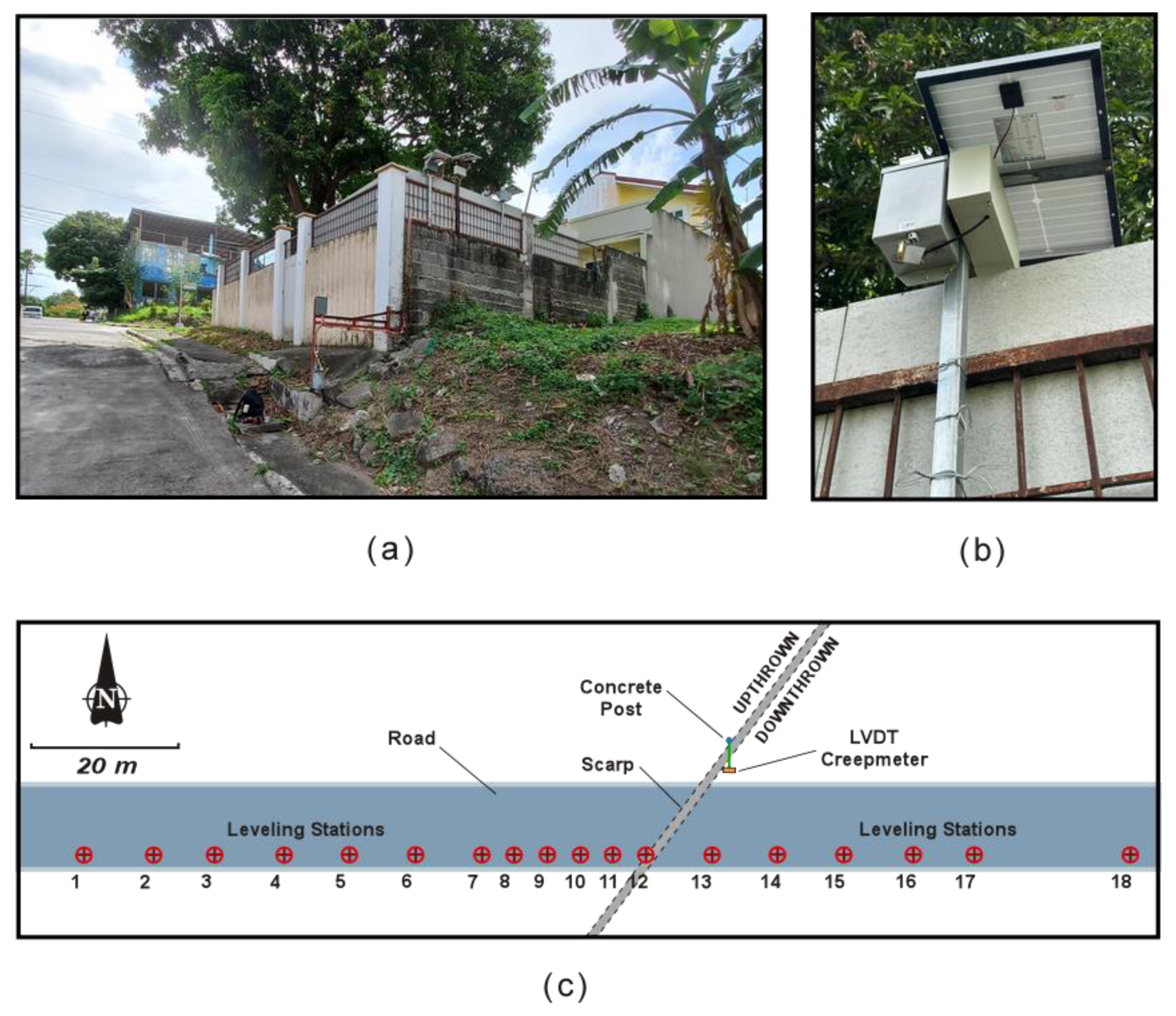
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
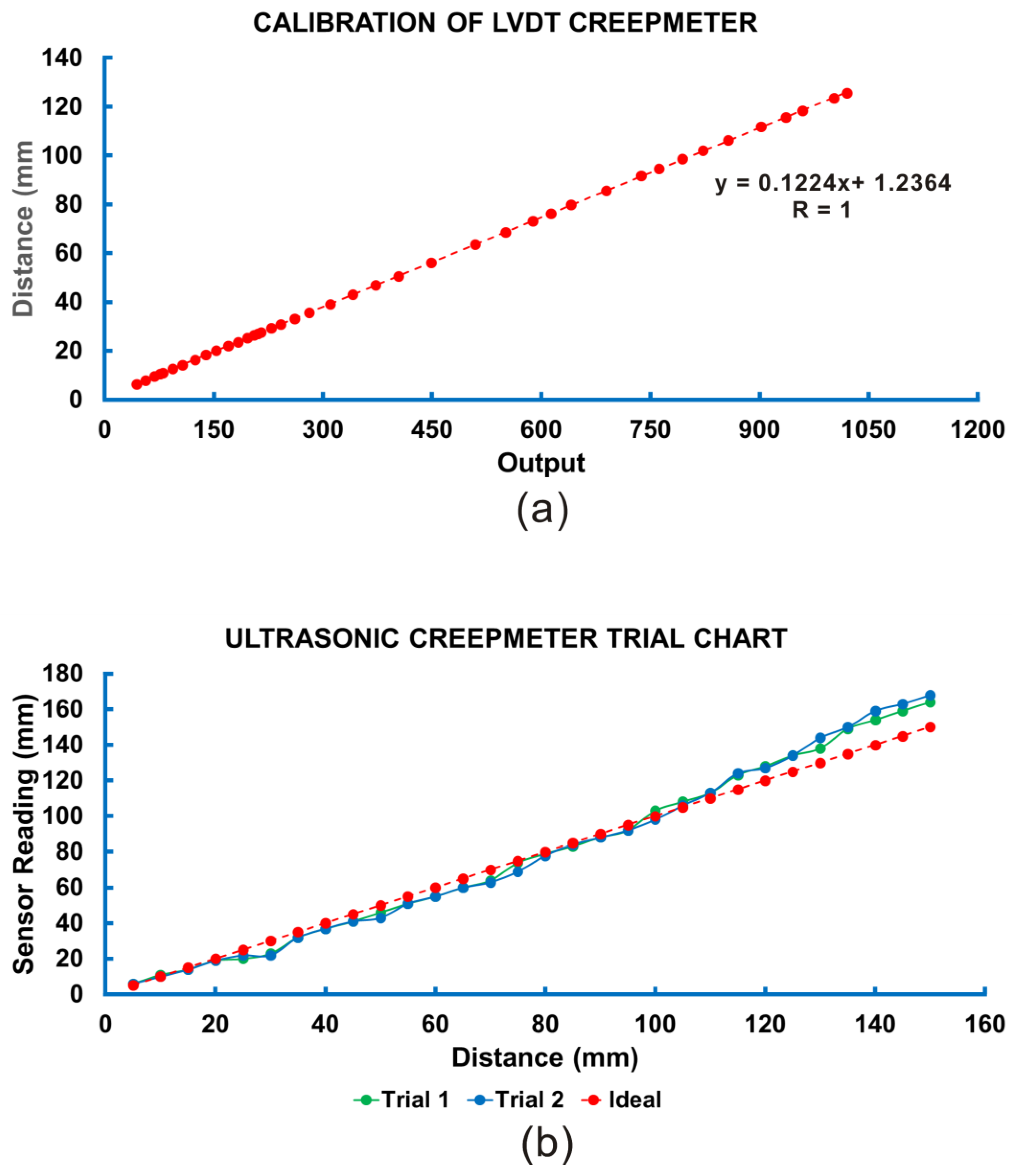
3.1. Testing of Creepmeters
3.2. Displacements Measured by the LVDT and Ultrasonic Creepmeters
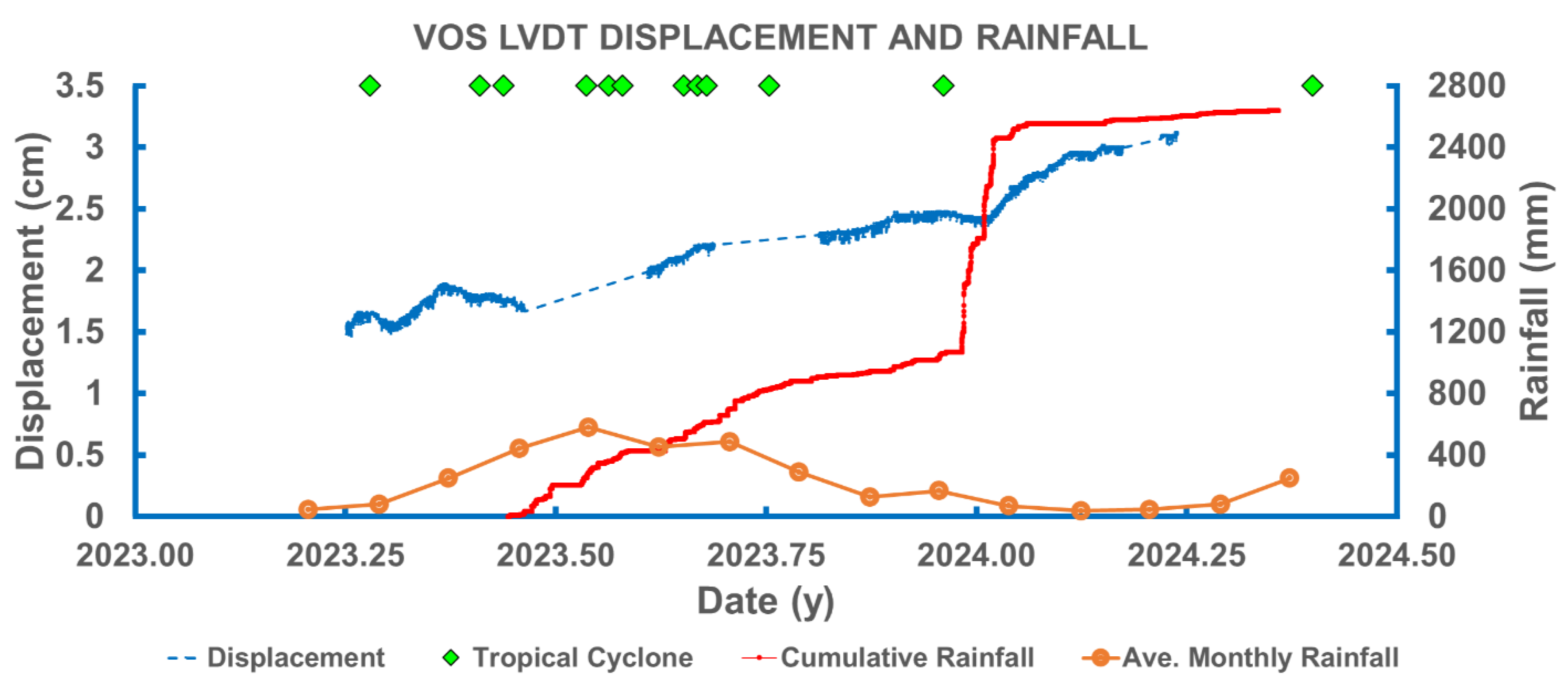

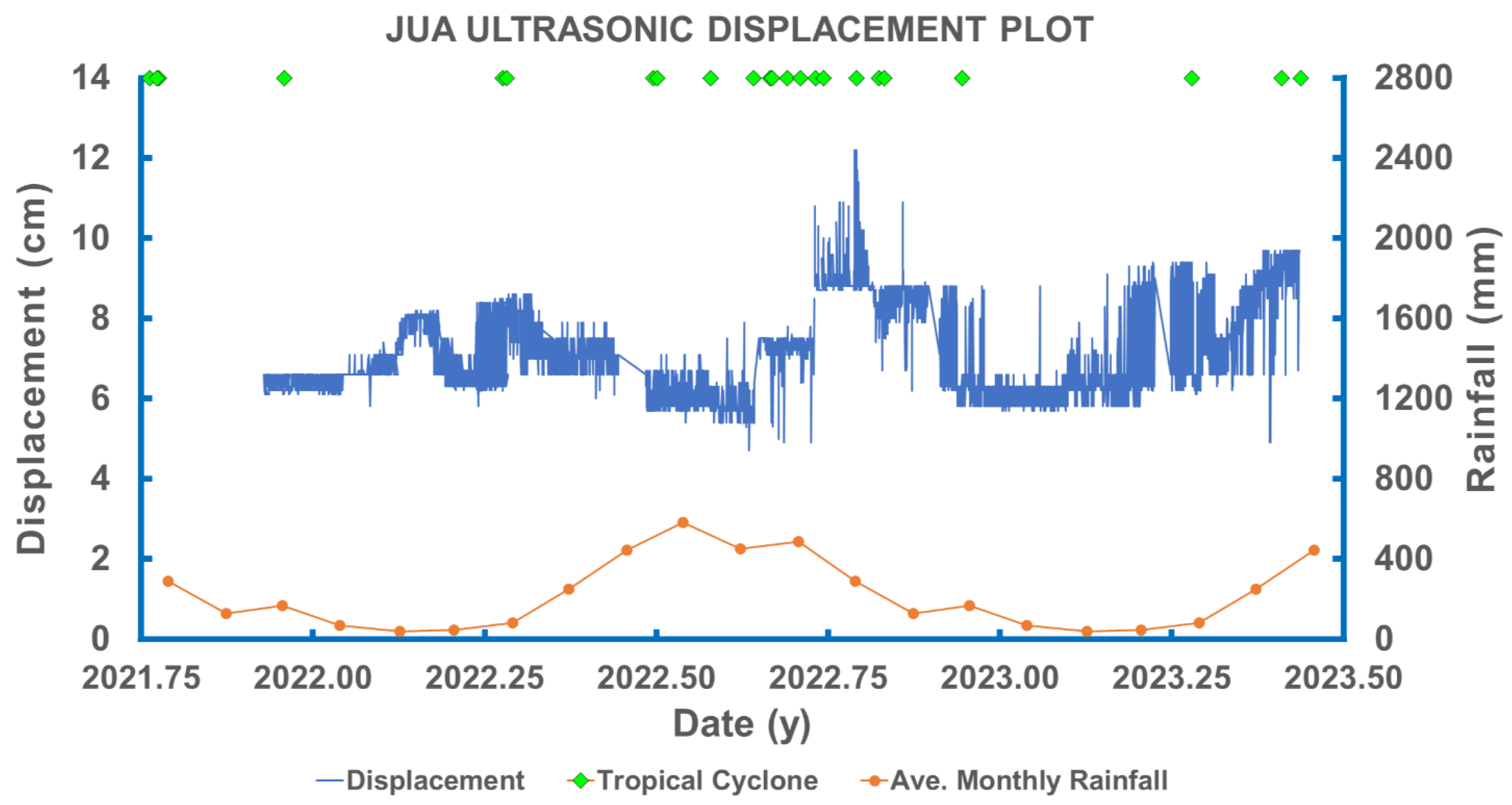
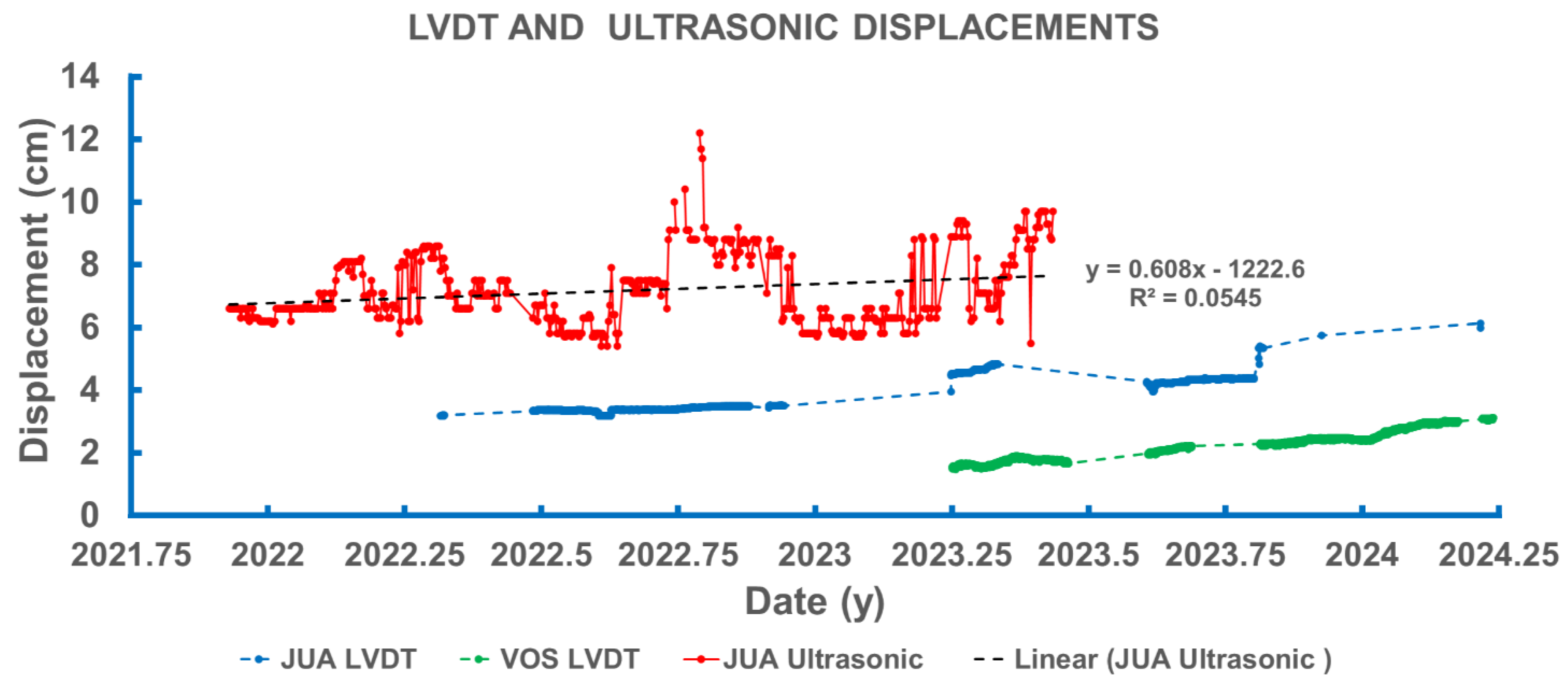
3.3. Comparison with Longer-Term Displacements from Precise Leveling

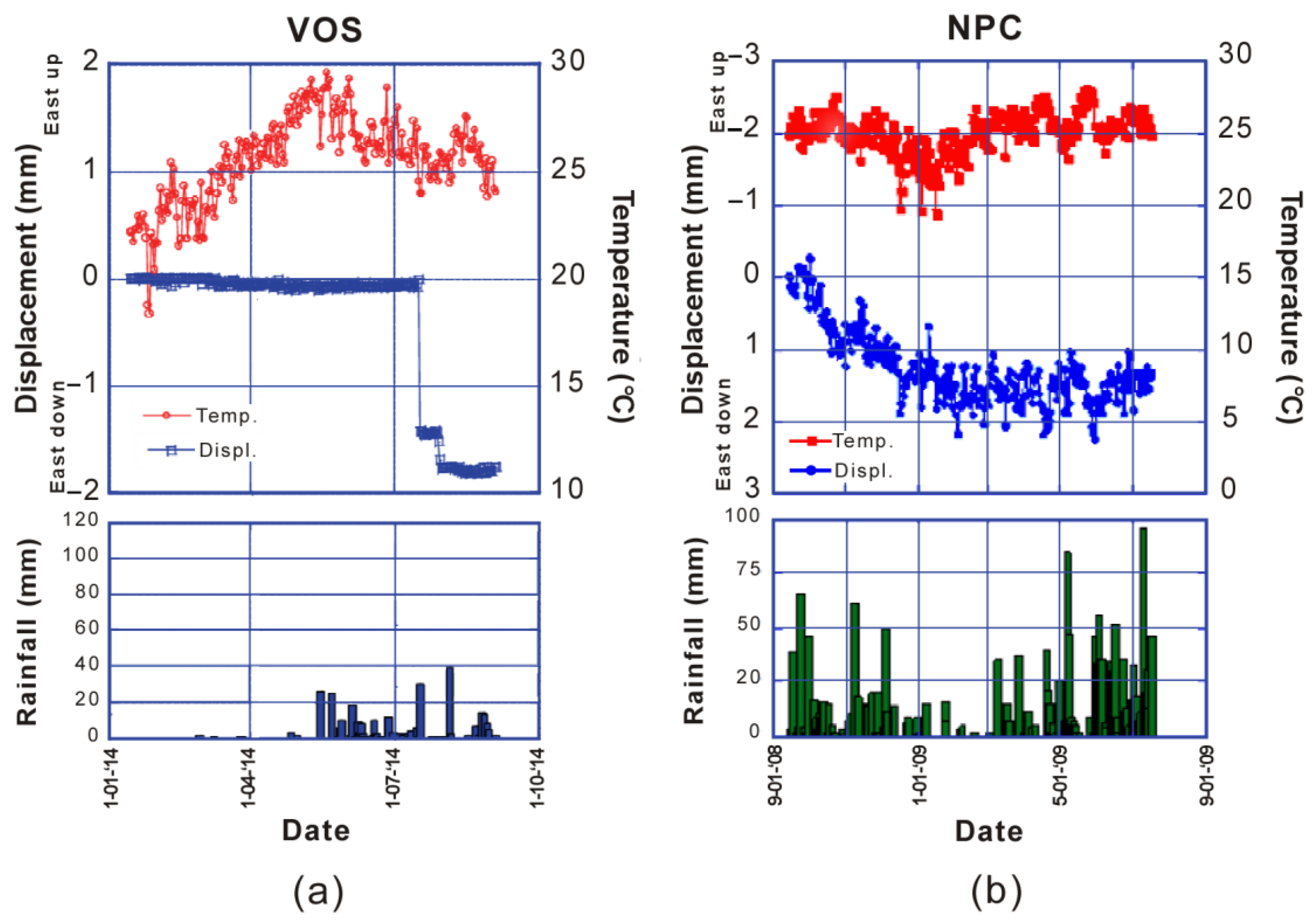
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rimando, R.E. Neotectonic and Paleoseismic Study of the Marikina Valley Fault System, Philippines. Ph.D. Thesis, State University of New York at Binghamton, Binghamton, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rimando, R.E.; Kurita, K.; Kinugasa, Y. Spatial and temporal variation of aseismic creep along the dilational jog of the West Valley Fault, Philippines: Hazard implications. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 935161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimando, R.E.; Knuepfer, P.L.K. Tectonic control of aseismic creep and potential for induced seismicity along the West Valley Fault in southeastern Metro Manila, Philippines. GeoHazards 2024, 5, 1172–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimando, R.E.; Knuepfer, P.L. Neotectonics of the Marikina Valley fault system (MVFS) and tectonic framework of structures in northern and central Luzon, Philippines. Tectonophysics 2006, 415, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcilla, C.A.; Ruelo, H.B.; Umbal, J. The Angat ophiolite, Luzon, Philippines: Lithology, structure, and problems in age interpretation. Tectonophysics 1989, 168, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seno, T.; Stein, S.; Gripp, A.E. A model for the motion of the Philppine Sea Plate consistent with NUVEL-1 and geological data. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 17941–17948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS). Available online: https://www.phivolcs.dost.gov.ph/ (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- National Mapping and Resource Information Authority (NAMRIA). Available online: https://www.namria.gov.ph/ (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO). Available online: https://www.gebco.net (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Holzer, T.L. Ground failure induced by ground-water withdrawal from unconsolidated sediment. In Man-Induced Land Subsidence; Holzer, T., Ed.; Reviews in Engineering Geology; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1984; Volume 6, pp. 67–105. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, J.P.; Bartlett, S.R. Land subsidence and earth fissuring on the Central Arizona Project, Arizona. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Land Subsidence, Houston, TX, USA, 12–17 May 1991; pp. 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, D.-Y.; Li, Z.-S. Ground fissure hazards in USA and China. Acta Seismol. 2000, 13, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; You, G.; Shi, B.; Qiu, Z.L.; Li, H.Y.; Tuck, M. Earth fissures in Jiangsu Province, China and geological investigation of Hetang earth fissure. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; You, G.G.; Shi, B.; Wu, S.L.; Wu, J.Q. Large differential land subsidence and earth fissures in Jiangyin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phien-wej, N.; Giao, P.H.; Nutalaya, P. Land subsidence in Bangkok, Thailand. Eng. Geol. 2006, 82, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambolati, G.; Frezze, R.A. Mathematical simulation of the subsidence of Venice: Theory. Water Resour. Res. 1973, 9, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, O.G.; Rudolph, D.L.; Cherry, J.A. The analysis of long-term land subsidence near Mexico City: Field investigations and predictive modeling. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3327–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.; Arzate, J.; Rojas, E.; Arroyo, M.; Yutsis, V.; Ochoa, G. Delimitation of ground failure zones due to land subsidence using gravity data and finite element modeling in the Querétaro valley, México. Eng. Geol. 2006, 84, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Reyes, J.; Nieto-Samaniego, A.F. Efectos geológicos de la tectónica reciente en la parte central de México. Rev. Mex. De Cienc. Geológicas 1990, 9, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rimando, R.E.; Knuepfer, P.L.K. Earthquake history and rupture extents from morphology of fault scarps along the Valley Fault System (Philippines). GeoHazards 2025, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Madrigal, V.M.; Muñiz-Jáuregui, J.A.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H.; Flores-Lázaro, N.; Figueroa-Miranda, S. Depreciation factor equation to evaluate the economic losses from ground failure due to subsidence related to groundwater withdrawal. Nat. Sci. 2014, 6, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Mines and Geosciences. Geology and Mineral Resources of the Philippines, 1st ed.; Bureau of Mines and Geosciences: Manila, Philippines, 1981; pp. 152–153. [Google Scholar]
- Cest, Inc. Water Resources assessment for prioritized critical areas (Phase 1): Final report; submitted to the National Water Resources Board, Unpublished work; Cest, Inc.: Metro Manila, Philippines, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, R.S.; Abracosa, R.P.; David, C.C.; Inocencio, A.B.; Tabios, G.Q. Metro Manila and Metro Cebu Groundwater Assessment; PIDS Discussion Paper Series, No. 2001-05; Philippine Institute for Development Studies: Makati City, Philippines, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zanoria, E. The Depositional and Volcanological Origin of the Diliman Volcaniclastic Formation, Southwestern Luzon, Philippines. Master’s Thesis, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Punongbayan, R.S.; Rimando, R.E. Detailed mapping of active faults in the Fort Bonifacio area and vicinity: Project Terminal Report. Metro Manila, Philippines. submitted to the Department of Science and Technology, Unpublished work. 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rimando, R.E.; Panol, M.D.; Daligdig, J.A.; Lanuza, L.; Besana, G.M.; Takezono, M. Aseismic slip of the Marikina fault in Metro Manila, Philippines (abstract). EOS 2000, 81, WP147. [Google Scholar]
- Ambraseys, N.N. Some characteristic features of the Anatolian fault zone. Tectonophysics 1970, 9, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.C.; Prescott, W.H.; Lisowski, M.; King, N. Geodolite measurements of deformation near Hollister, California, 1971–1978. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 7599–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, R.O.; Harsh, P.W. Slip on the San Andreas fault in central California from alinement array surveys. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1980, 70, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.B.; Liu, C.C. Fault creep on the central segment of the Longitudinal Valley fault, eastern Taiwan. Proc. Geol. Soc. China 1989, 32, 209–231. [Google Scholar]
- Lienkaemper, J.J.; Borchardt, G.; Lisowski, M. Historic creep rate and potential for seismic slip along the Hayward fault, California. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 18261–18283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelson, K.I.; Simpson, G.D.; Lettis, W.R.; Haraden, C.C. Holocene slip rate and earthquake recurrence of the northern Calaveras fault at Leyden Creek, northern California. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 5961–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenner, H.D.; Ueta, K. Looking for evidence of large surface rupturing events on the rapidly creeping Southern Calaveras fault, California. In Proceeding of the Hokudan International Symposium and School on Active Faulting, Hokudan-cho, Awaji Island, Japan, 18–26 January 2000; pp. 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, K.; Kinugasa, Y.; Rimando, R.E.; Papiona, K. Continuous monitoring of the fault creeping on Marikina Valley fault system (MVFS), Metro Manila, Philippines. Res. Rep. Tokyo Metrop. Coll. Ind. Technol. 2011, 5, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, K.; Kinugasa, Y.; Deguchi, T.; Rimando, R.E. Monitoring of ground deformation in southern part of Metro Manila, Philippines. In Advances in Civil Engineering and Building Materials; Chang, S., Al Bahar, S., Zhao, J., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012; pp. 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K.; Kinugasa, Y.; Deguchi, T.; Rimando, R. Monitoring of active fault in south-east part of Metro Manila, Philippines. Res. Rep. Tokyo Metrop. Coll. Ind. Technol. 2015, 9, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, K.; Kinugasa, Y.; Deguchi, T.; Rimando, R.E.; Watanabe, M. Monitoring aseismic surface creep along the Western Valley (Marikina) Fault. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Seismic Microzoning and Risk Reduction, Granada, Spain, 22–24 October 2016; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333891626_Monitoring_Aseismic_Surface_Creep_along_the_Western_Valley_Marikina_Fault (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Kurita, K.; Kinugasa, Y.; Rimando, R.E.; Garduque, J.R. Monitoring of ground deformation along the Marikina Valley fault system, Manila, Philippines. In Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Seismic Microzoning and Risk Reduction, Lima, Peru, 5–8 September 2018; Kanagawa University: Yokohama, Japan, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Foulger, G.R.; Wilson, M.P.; Gluyas, J.G.; Julian, B.R.; Davies, R.J. Global review of human-induced earthquakes. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 178, 438–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.P.; Foulger, G.R.; Gluyas, J.G.; Davies, R.J.; Julian, B.R. HiQuake: The human-induced earthquake database. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2017, 88, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. A review of unloading-induced fault instability. Undergr. Space 2021, 6, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, W.D.; Davis, S.D.; Carlson, S.M.; Dupree, J.; Ewing, T.E. The evolution of seismic barriers and asperities caused by the depressuring of fault planes in oil and gas fields of South Texas. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1986, 76, 939–948. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolau, V.; Miholca, C.; Andrei, M. Fuzzy rules of sound speed influence on ultrasonic sensing in outdoor environments. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Soft Computing Applications, Szeged-Arad, Romania, 29 July–1 August 2009; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, G.; Agrawal, D.; Nshimiyimana, A.; Hossain, A. Effects of environment on accuracy of ultrasonic sensor operates in millimetre range. Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, D.A. Environmental effects on the speed of sound. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1988, 36, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- World Weather Online. Available online: https://www.worldweatheronline.com/binan-weather-averages/laguna/ph.aspx (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Available online: https://www.pagasa.dost.gov.ph/climate/tropical-cyclone-associated-rainfall (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- National Water Resources Board (Resolution No. 001-0904: Policy Recommendations for Metro Manila Critical Areas). Available online: https://nwrb.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/BR_001-0904.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Gonzalez, E.B. Tropical cyclones and storm surges. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Natural Disaster Mitigation in the Philippines, Quezon City, Philippines, 19–20 October 1994; Punongbayan, R.S., Ed.; Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology: Quezon City, Philippines, 1994; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Roeloffs, E. Creep rate changes at Parkfield, California 1966–1999: Seasonal, precipitation induced, and tectonic. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 16525–16547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, Y.; Cappa, F.; Avouac, J.P.; Henry, P.; Elsworth, D. Seismicity triggered by fluid injection-induced aseismic slip. Science 2015, 348, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, T.L.; Davis, S.N.; Lofgren, B.E. Faulting caused by groundwater extraction in southcentral Arizona. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P. Earthquakes triggered by fluid extraction. Geology 1989, 17, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P. Stress and subsidence resulting from subsurface fluid withdrawal in the epicentral region of the 1983 Coalinga earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 6801–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P. Induced stresses due to fluid extraction from axisymmetric reservoirs. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1992, 139, 535–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Burford, R.O.; Mavko, B. Influence of Seismicity and Rainfall on Episodic Creep on the San Andreas Fault System in Central California. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 7475–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Angelier, J.; Chu, H.T.; Hu, J.C.; Jeng, F.S. Continuous monitoring of an active fault in a plate suture zone: A creepmeter study of the Chihshang Fault, eastern Taiwan. Tectonophysics 2001, 333, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Angelier, J.; Chu, H.T.; Hu, J.C.; Jeng, F.S. Monitoring active fault creep as a tool in seismic hazard mitigation: Insights from creepmeter study at Chihshang, Taiwan. Tectonophysics 2005, 337, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Vissa, N.K.; Gahalaut, V.K. Influence of anthropogenic groundwater unloading in Indo-Gangetic plains on the 25 April 2015 Mw 7.8 Gorkha, Nepal earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10607–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Vissa, N.K.; Gahalaut, K.; Gahalaut, V.K.; Panda, D.; Malik, K. Influence of anthropogenic groundwater pumping on the 2017 November 12 M7.3 Iran-Iraq border earthquake. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.K.; Jha, B.; Kundu, B.; Gahalaut, V.K.; Vissa, N.K. Groundwater extraction-induced seismicity around Delhi region, India. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, S.K.Y.; Huang, Y.; Young, R.P. The role of fluid pressure-induced aseismic slip in earthquake cycle modulation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.J.; Tiampo, K.F.; Palano, M.; Cannavo, F.; Fernandez, J. The 2011 Lorca earthquake slip distribution controlled by groundwater crustal unloading. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, C.B.; Audet, P.; Hammond, W.C.; Bürgmann, R.; Johanson, I.A.; Blewitt, G. Uplift and seismicity driven by groundwater depletion in central California. Nature 2014, 509, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.; Engelder, J.T. The role of asperity indentation and ploughing in rock friction. I. Asperity creep and stick slip. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1976, 13, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aki, K. Characterization of barriers on an earthquake fault. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 6140–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, T.; Kanamori, H.; Ruff, L. The asperity model and the nature of large subduction zone earthquakes. Earthq. Predict. Res. 1982, 1, 3–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sibson, R.H. Rupture interaction with fault jogs. In Earthquake Source Mechanics; Das, S., Boatwright, J., Scholz, C.H., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume 37, pp. 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, R.H. Effects of fault heterogeneity on rupture propagation. In Directions in Paleoseismology, Proceedings of Conference XXXIX, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 22–25 April 1987; Crone, A., Omdahl, E., Eds.; United States Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, A.R.; Personius, S.F.; Rimando, R.E.; Punongbayan, R.S.; Tungol, N.; Mirabueno, H.; Rasdas, A. Multiple large earthquakes in the past 1500 years on a fault in metropolitan Manila, the Philippines. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2000, 90, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.M. Contagious fault rupture, probabilistic hazard, and contagion observability. In Directions in Paleoseismology, Proceedings of Conference XXXIX, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 22–25 April 1987; Crone, A.J., Omdahl, E.M., Eds.; United States Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 1987; pp. 428–439. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1987/0673/report.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rimando, R.E.; Llamas, D.C.E.; Marfito, B.J.; Garduque, R.J. Seasonal and Episodic Variation of Aseismic Creep Displacement Along the West Valley Fault, Philippines. GeoHazards 2025, 6, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6030055
Rimando RE, Llamas DCE, Marfito BJ, Garduque RJ. Seasonal and Episodic Variation of Aseismic Creep Displacement Along the West Valley Fault, Philippines. GeoHazards. 2025; 6(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRimando, Rolly E., Deo Carlo E. Llamas, Bryan J. Marfito, and Renato J. Garduque. 2025. "Seasonal and Episodic Variation of Aseismic Creep Displacement Along the West Valley Fault, Philippines" GeoHazards 6, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6030055
APA StyleRimando, R. E., Llamas, D. C. E., Marfito, B. J., & Garduque, R. J. (2025). Seasonal and Episodic Variation of Aseismic Creep Displacement Along the West Valley Fault, Philippines. GeoHazards, 6(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/geohazards6030055





