Study on Pressure Fluctuation Characteristics and Chaos Dynamic Characteristics of Two-Way Channel Irrigation Pumping Station Under the Ultra-Low Head Based on Wavelet Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Calculation Model and Method
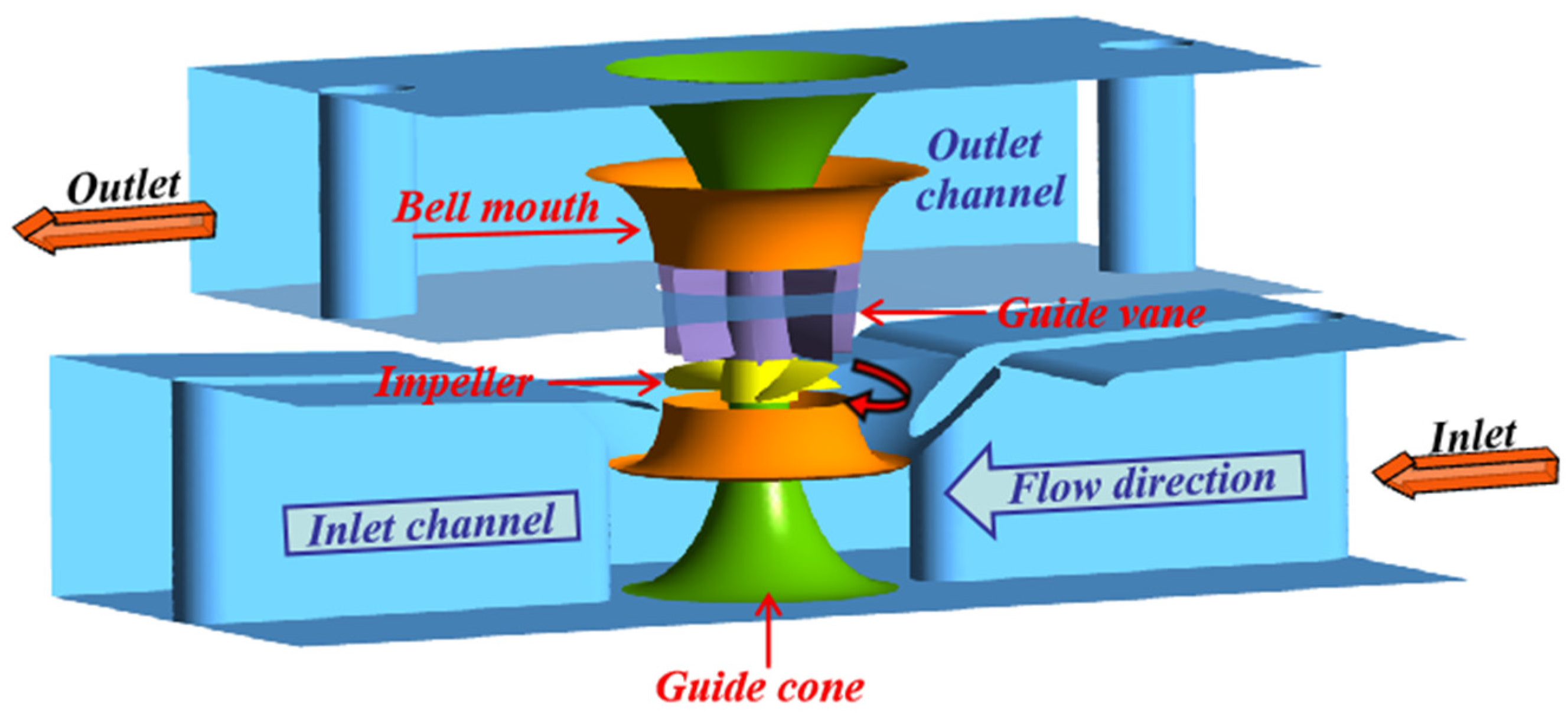
2.1. Calculation Model
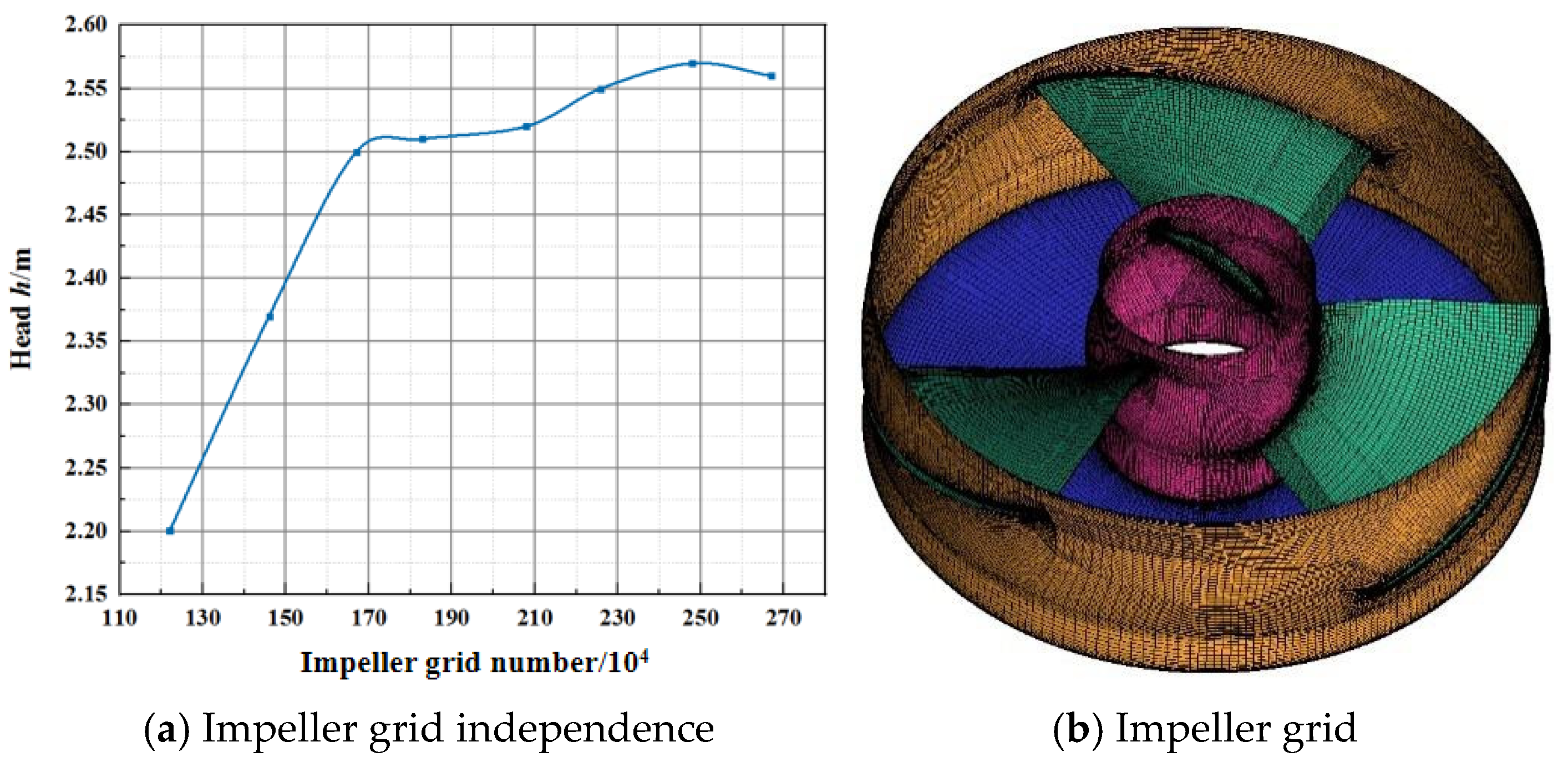
2.2. Calculation Method and Mesh Generation
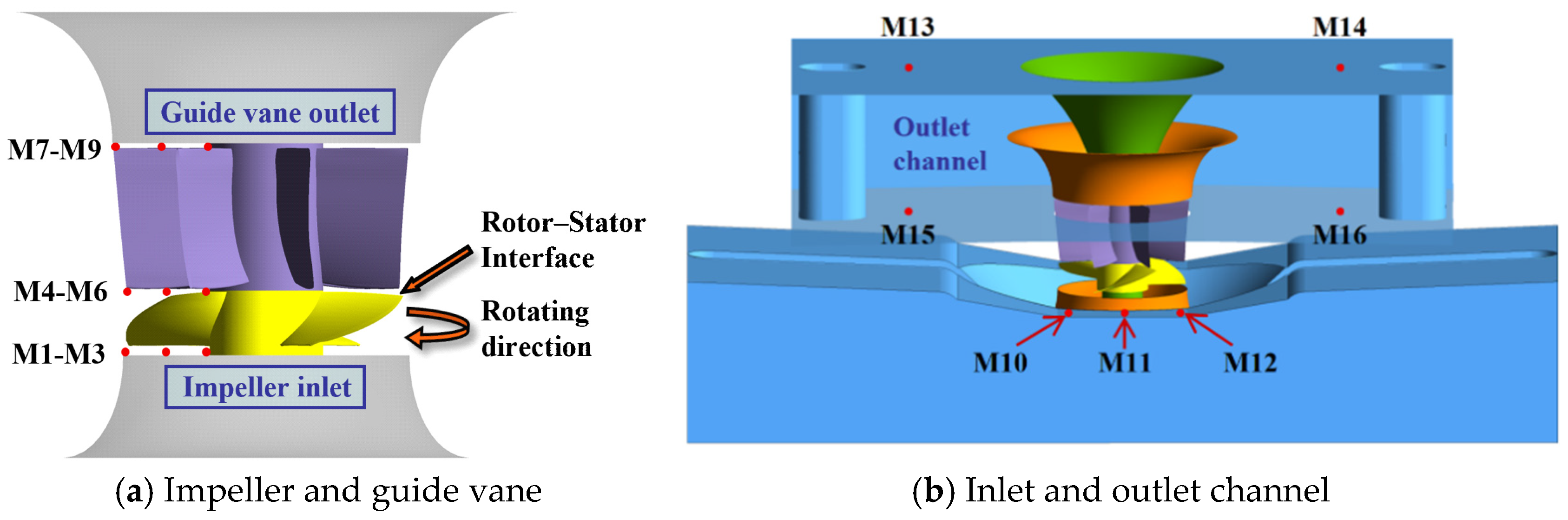
2.3. Calculation Parameters and Boundary Conditions
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Experimental Instrument
3.2. Uncertainty Analysis
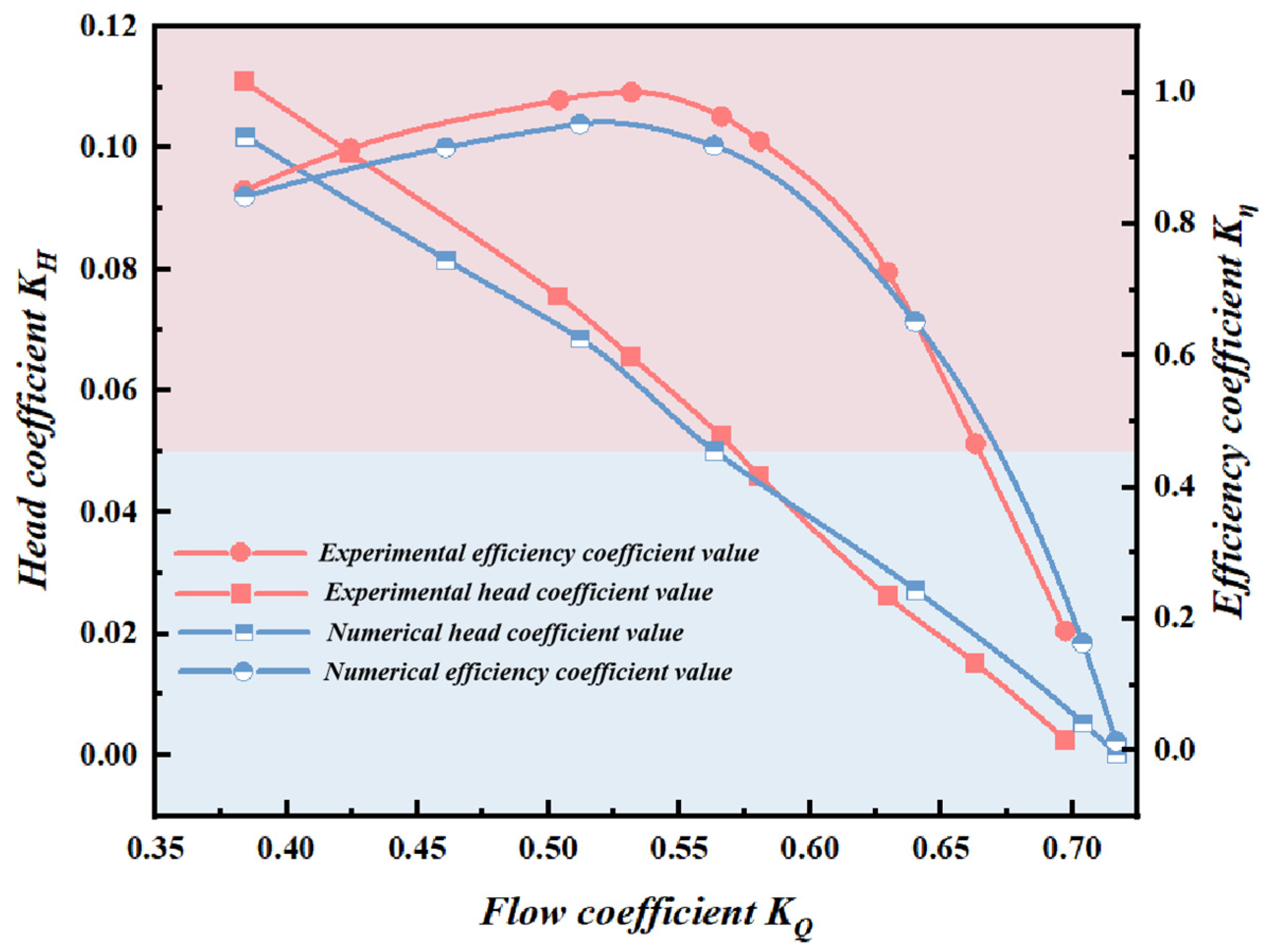
3.3. Experimental Verification
4. Calculation Results
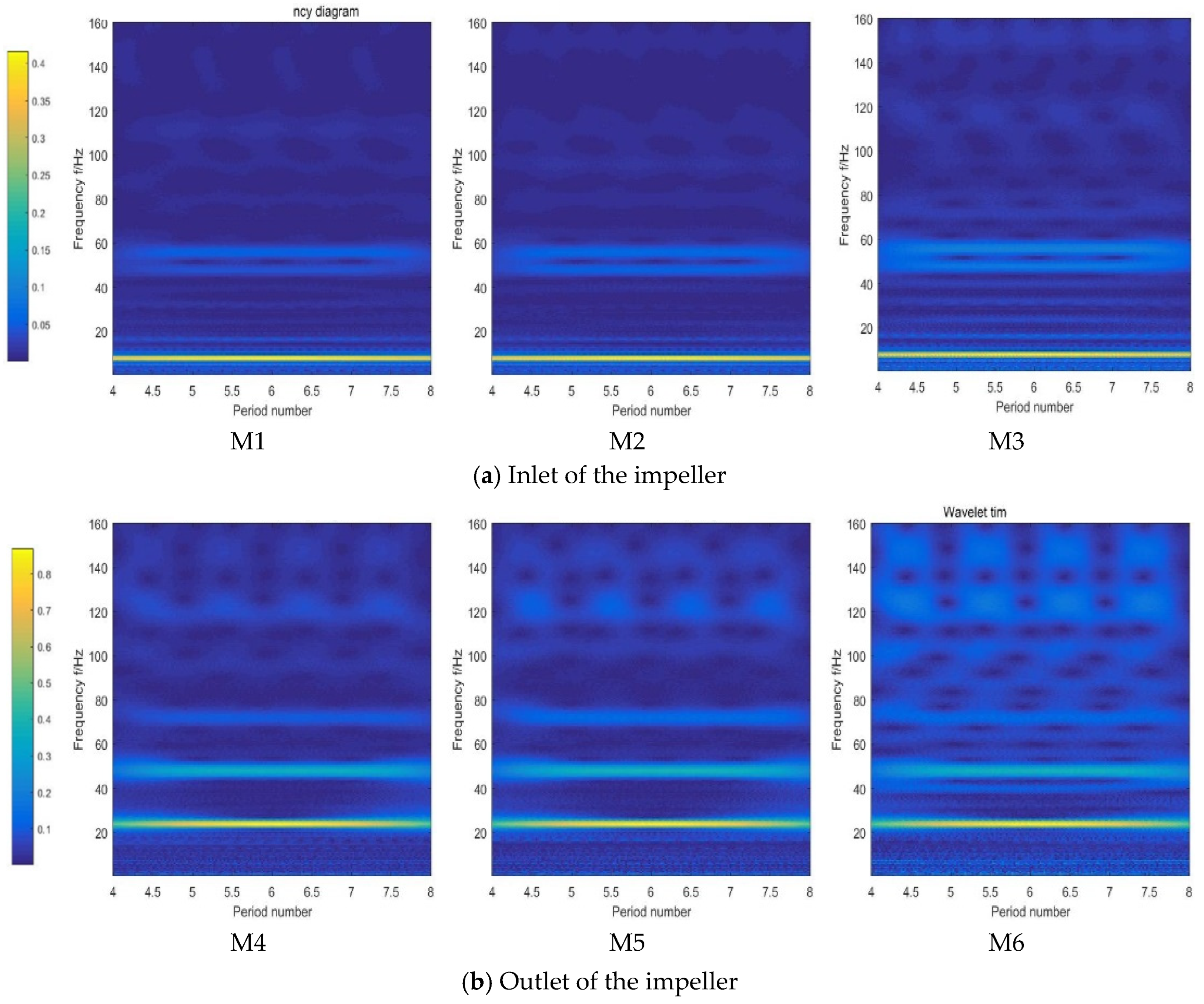
4.1. Pressure Fluctuation
4.2. Chaotic Dynamics
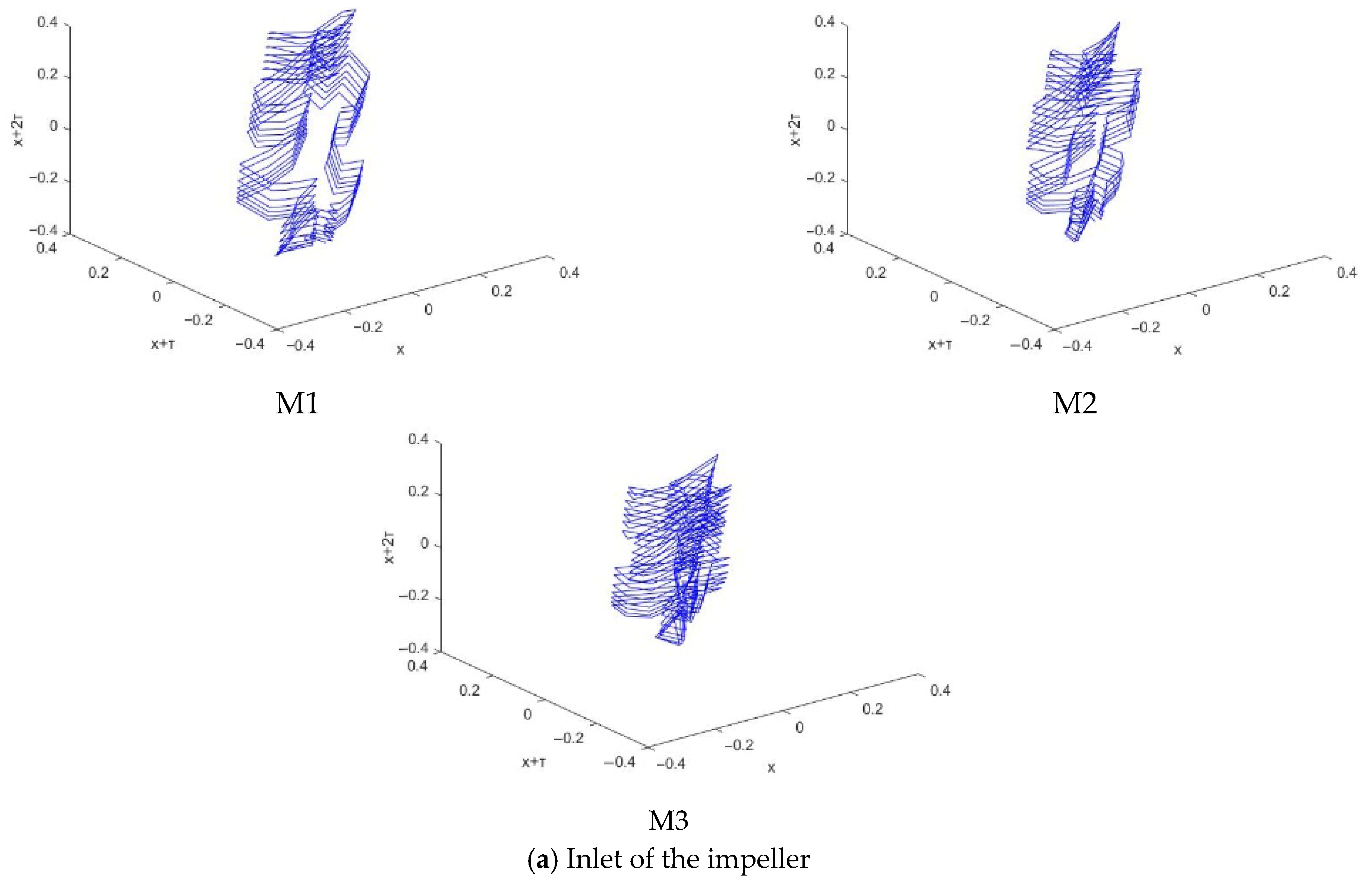
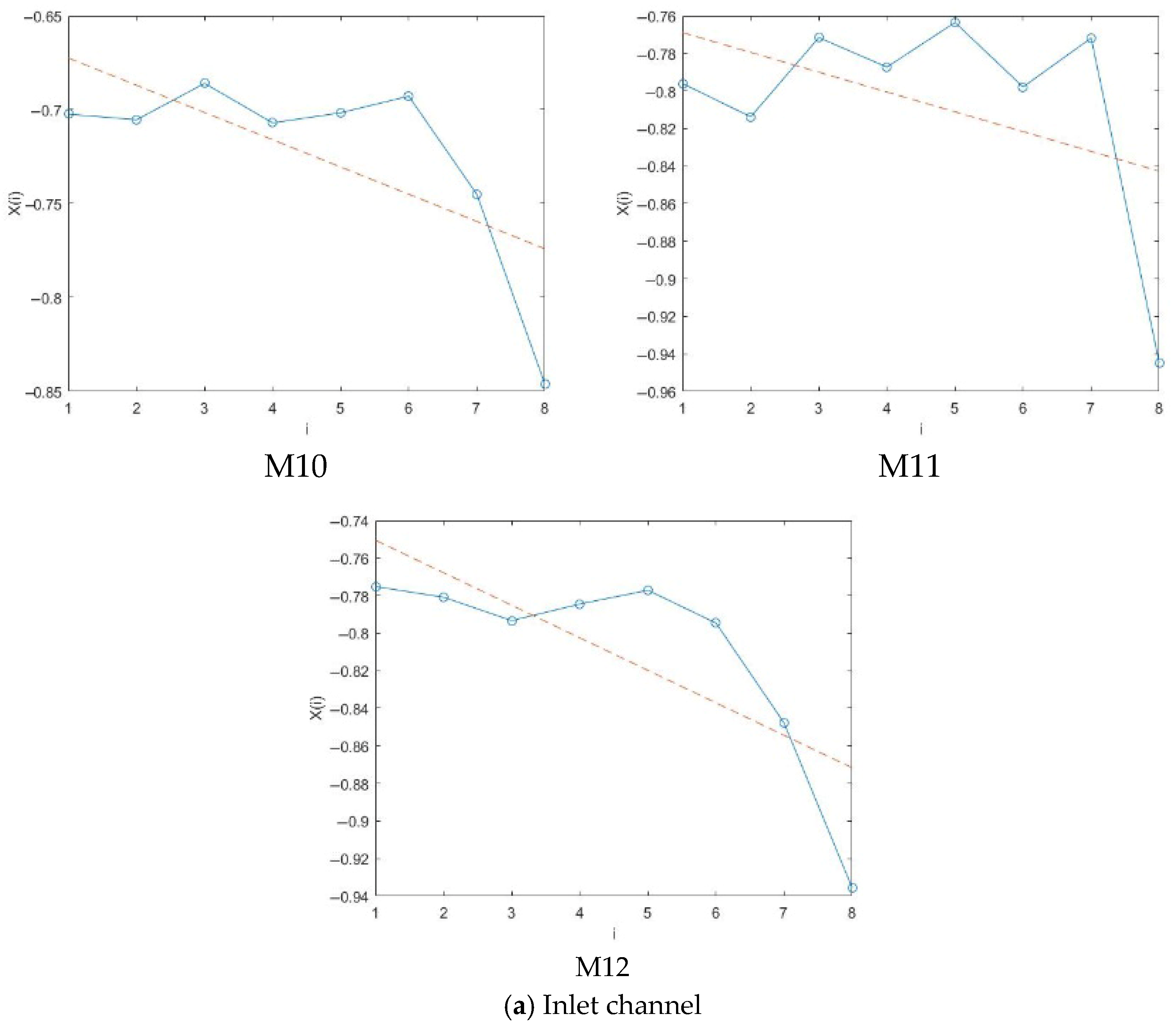
4.2.1. Phase Diagram Analysis
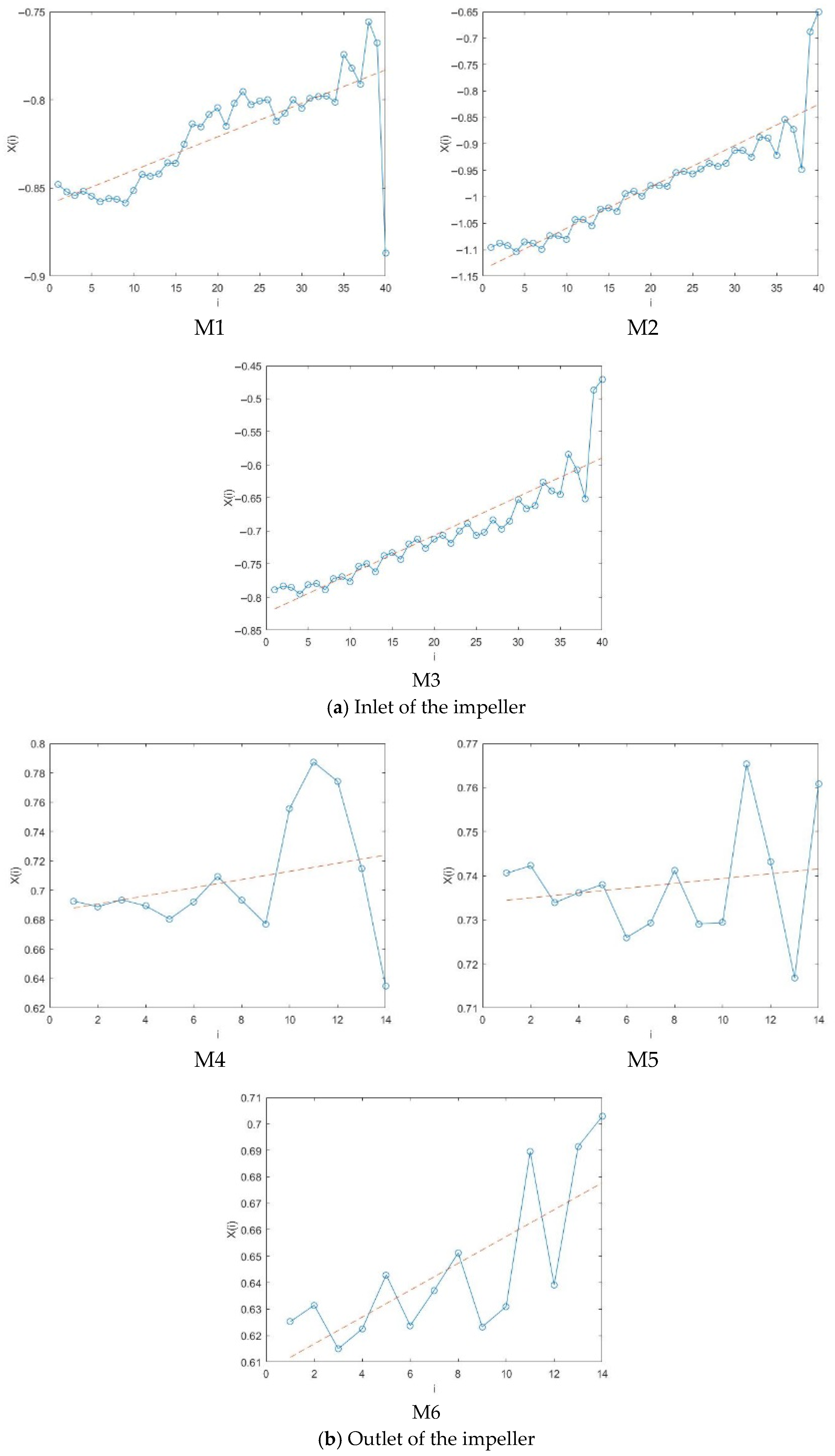
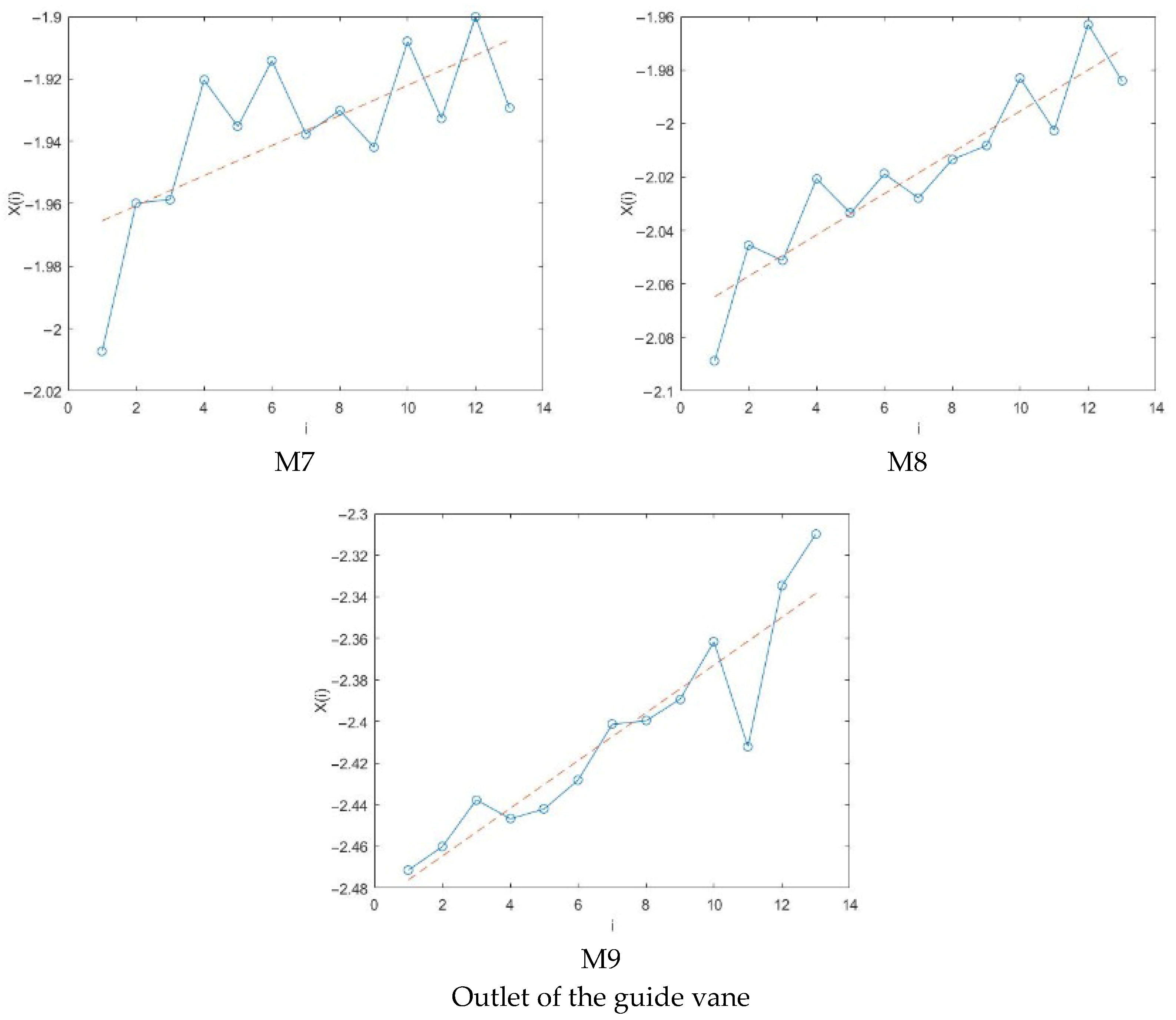
4.2.2. Maximum Lyapunov Exponent Analysis
- (1)
- The pressure fluctuation time series is denoted as , where N represents the endpoint of the time series.
- (2)
- The time delay τ is determined using the mutual information method.
- (3)
- The embedding dimension m was determined by comparing the results of the Cao method and the saturated correlation dimension (G-P) method.
- (4)
- (5)
- Assume that the initial point in the reconstructed phase space is , and its distance from the nearest neighbor is . The temporal evolution of these two points is then tracked. At time , if the separation becomes , where is a predefined threshold, the point is retained. A new neighboring point is then selected within the vicinity, satisfying , ensuring the angle between the vectors remains as small as possible. This process is repeated until all available data points in the time series are traversed. After a total iteration time of , the maximum Lyapunov exponent can be expressed as [51].
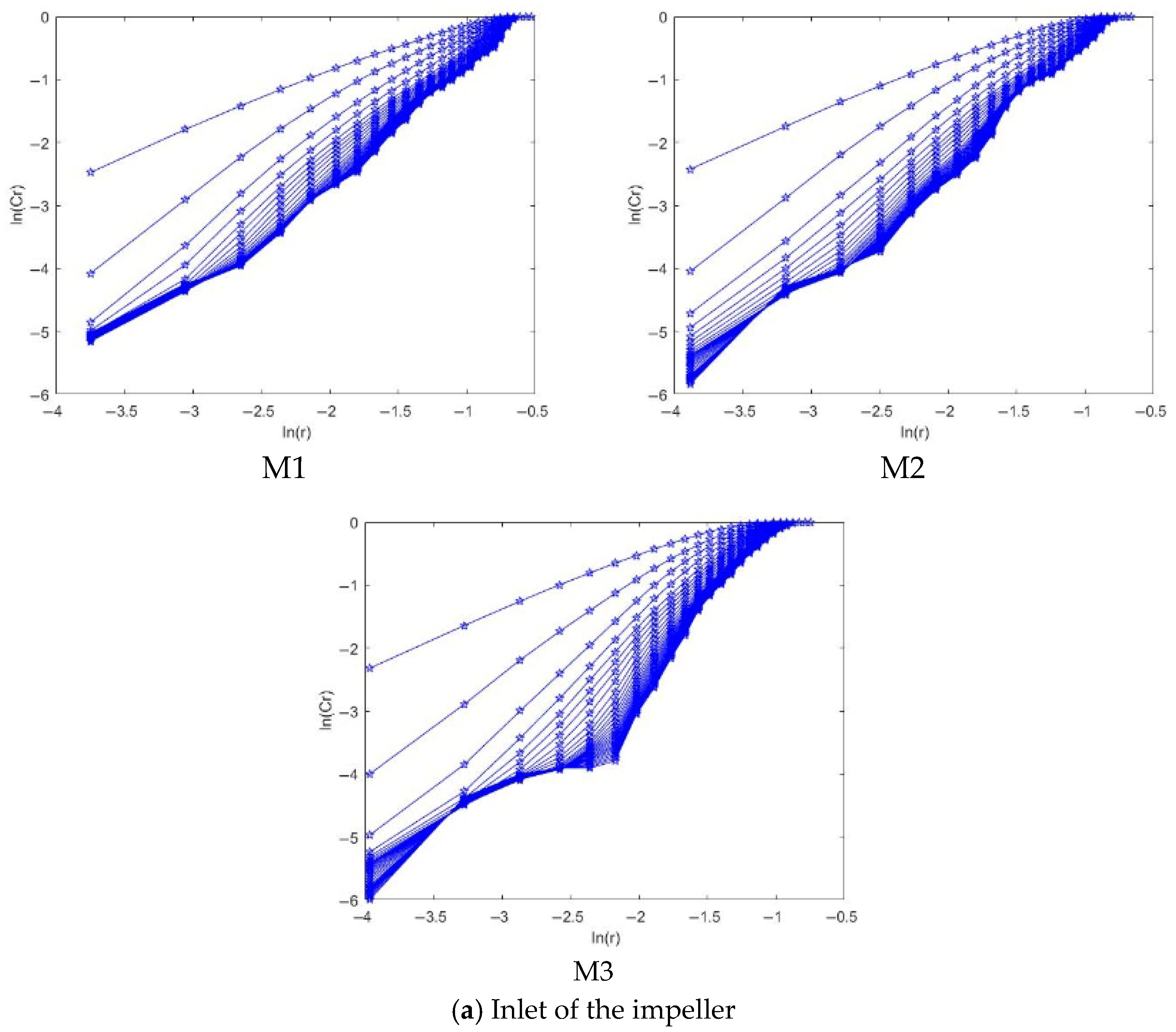
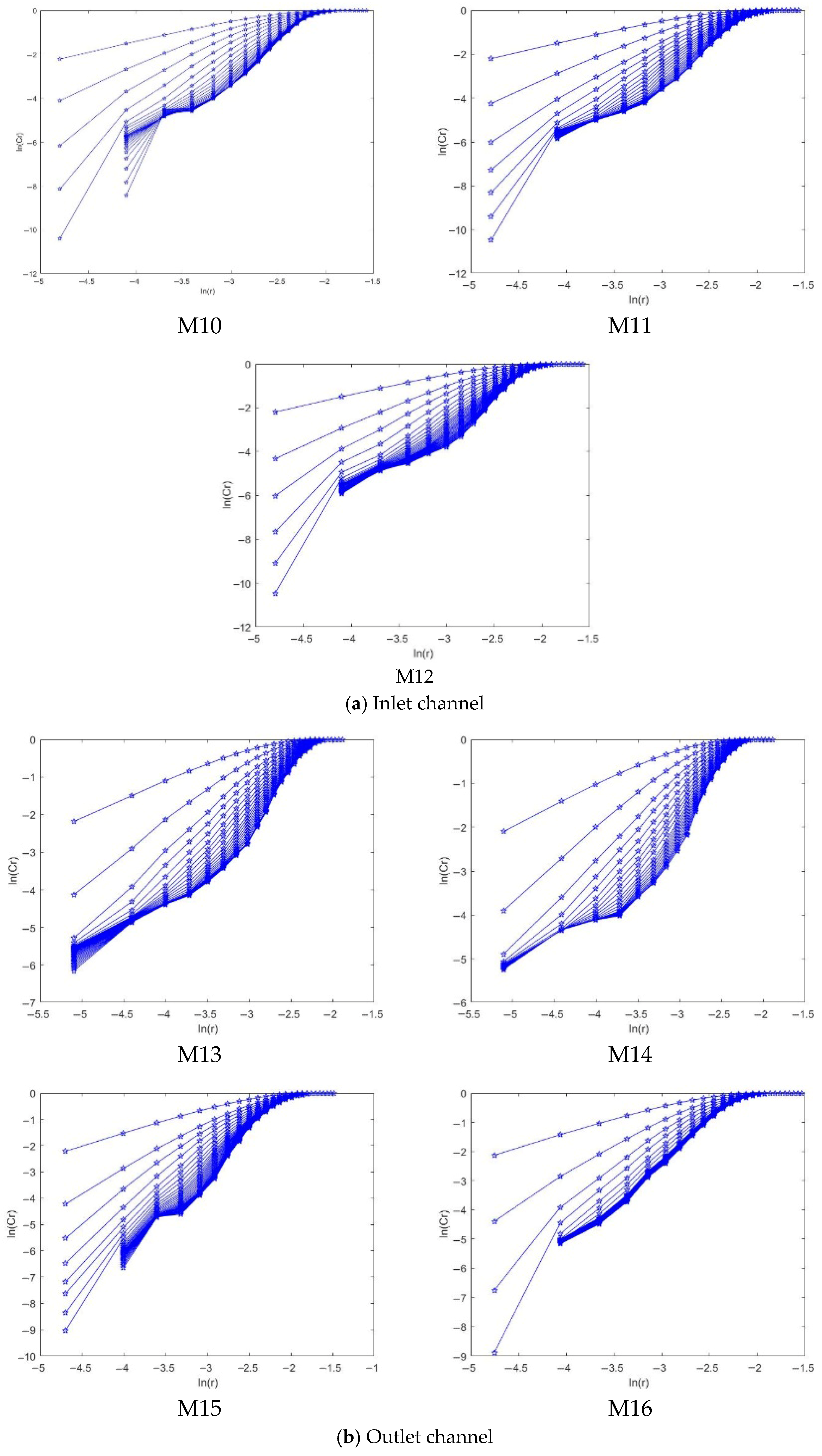
4.2.3. Correlation Dimension Analysis
5. Comparative Analysis and Future Work
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The pressure fluctuation at the inlet of the impeller and the outlet of the guide vane is mainly low frequency, and the proportion of high frequency at the outlet of the impeller is slightly increased. At the same time, there are fluctuation signals that change with time, and the amplitude at the rim is larger than at the hub.
- (2)
- Compared with the impeller and guide vane, the proportion of high-frequency fluctuation signals at the intake bell mouth and outlet channel is significantly increased. There is a fluctuating signal with time sinusoidal variation at the high frequency of the monitoring point in the outlet channel.
- (3)
- The pressure fluctuation phase trajectory of the monitoring points at the impeller and guide vane has obvious regularity, showing a contraction trend from the hub to the rim, and the corresponding pressure fluctuation signal is weakened.
- (4)
- The positive maximum Lyapunov exponents at the impeller and guide vane indicate chaotic pressure fluctuations under high flow conditions. At the same time, the negative values at the inlet bell mouth and outlet channel suggest non-chaotic behavior. Moreover, the saturated correlation dimension is associated with both the chaotic characteristics and the amplitude variation in the signal—larger amplitude fluctuations correspond to higher correlation dimensions.
- (5)
- This study reveals the key mechanisms of pressure pulsations and chaotic characteristics in ultra-low-head two-way channel pump stations, confirming the presence of significant chaotic behavior in the impeller and guide vane regions. Optimization strategies for the impeller leading edge and guide vane arrangement are proposed to enhance operational stability and performance under extreme conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Cui, S.; Wu, M.; Huang, X.; Cao, X. Unravelling resources use efficiency and its drivers for water transfer and grain production processes in pumping irrigation system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, R.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Yuan, J. Day-ahead scheduling model for agricultural microgrid with pumped-storage hydro plants considering irrigation uncertainty. J. Energy Storage 2024, 95, 112468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogie, R.I.; Dunn, S.; Holderness, T.; Turpin, E. Assessing the vulnerability of pumping stations to trash blockage in coastal mega-cities of developing nations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, L.; Tang, F.; Duan, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z. Analysis of inlet flow passage conditions and their influence on the performance of an axial-flow pump. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2021, 235, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; Meng, F.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X. Research on the Influence of Tip Clearance of Axial-Flow Pump on Energy Characteristics under Pump and Turbine Conditions. Machines 2022, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y. Numerical and experimental investigation of internal flow characteristics and pressure fluctuation in inlet passage of axial flow pump under deflection flow conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, J.; Tang, F.; Wang, C. Multi-disciplinary optimization design of axial-flow pump impellers based on the approximation model. Energies 2020, 13, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Gui, J.; Deng, Z.D.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, A.; Yang, C. Development of an ultra-low head siphon hydro turbine using computational fluid dynamics. Energy 2019, 181, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yuan, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, L. The effect of bell mouth height on the hydraulic characteristics of the two-way pumping station based on the parameter design. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2022, 236, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Cheng, L.; Pan, W.; Li, S.; Jiao, W. Dynamic Response Analysis of Dual-Flow Channel Pump Station Structure under Water Pressure Pulsation. Energies 2022, 15, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tao, W.; Zhou, H.B.; Tang, X.C. Optimal Design of Outlet Conical Pipe for Open Dual-Directional Pumping System. South--North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 164–166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Hydraulic performance improvement of a two-way pumping station through bell mouth shape design. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 035119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. Numerical and experimental assessment of the water discharge segment in a pumped-storage power station. Energy 2023, 265, 126375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhu, B.; Jiang, B. Comprehensive assessment and analysis of cavitation scale effects on energy conversion and stability in pumped hydro energy storage units. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 325, 119370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, F.; Guo, J.; Jian, H.; Sun, S.; Jin, X. Leakage flow characteristics in blade tip of shaft tubular pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Gu, Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, Z.; Cao, B. Investigation and optimization into flow dynamics for an axial flow pump as turbine (PAT) with ultra-low water head. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 314, 118684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Cheng, L.; Sheng, W. Study of energy dissipation mechanisms and pressure pulsation spectrums in a vertical axial flow pump station on the ultra-low head condition based on multiple analysis methods. Energy 2025, 320, 135227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Chen, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Y. Energy loss and pressure fluctuation characteristics of coastal two-way channel pump stations under the ultra-low head condition. Energy 2023, 278, 127953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D. & Maxime, B. Energy loss mechanisms of transition from pump mode to turbine mode of an axial-flow pump under bidirectional conditions. Energy 2022, 257, 124630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xue, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, Z. CFD-based hydraulic-mechanical-electrical coupled simulation method for variable-speed pumped storage units. Energy 2025, 329, 136701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Bian, J.; Wang, Q.; Stephen, C.; Liu, B.; Cheng, L. Energy performance and pressure fluctuation in multi-stage centrifugal pump with floating impellers under various axial oscillation frequencies. Energy 2024, 307, 132691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Towards the integration of new-type power systems: Hydraulic stability analysis of pumped storage units in the S-characteristic region based on experimental and CFD studies. Energy 2025, 329, 136755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Li, C.; Li, D. A prospective assessment of scale effects of energy conversion in ultra-low-head pumped hydro energy storage units. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 315, 118798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, G.; Zou, Y.; Xiao, Z. Optimization of geometric parameters of hydraulic turbine runner in turbine mode based on the orthogonal test method and CFD. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 14476–14487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hua, H. Numerical investigation of tip clearance effects on propulsion performance and pressure fluctuation of a pump-jet propulsor. Ocean Eng. 2019, 192, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, A.R. Analysis of the effect of various impeller blade angles on characteristic of the axial pump with pressure fluctuations based on time-and frequency-domain investigations. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2021, 45, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, L. Experimental Study on the Internal Pressure Pulsation Characteristics of a Bidirectional Axial Flow Pump Operating in Forward and Reverse Directions. Machines 2022, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Li, N.; Xie, R.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Z. Analysis of Timing Effect on Flow Field and Pulsation in Vertical Axial Flow Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, F. Investigation on hydrodynamic characteristics of coastal axial flow pump system model under full working condition of forward rotation based on experiment and CFD method. Ocean Eng. 2022, 253, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Qiu, R.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W. Space-time frequency spectra analyses of the unsteady cavitating vortical flows inside a mixed-flow pump. Ocean Eng. 2021, 238, 109758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, F.; Cheng, L.; Pan, W.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Ge, Y. Numerical Simulation of Internal Flow Characteristics and Pressure Fluctuation in Deceleration Process of Bulb Tubular Pump. Water 2022, 14, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Li, W.; Shi, W.; Zhou, L.; Agarwal, R. Experimental study of pressure pulsation in a mixed-flow pump with different tip clearances based on wavelet analysis. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 9041686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yao, Z.; Li, D.; Xiao, R.; Wang, F.; He, C. Experimental investigation of transient characteristics of a double suction centrifugal pump system during starting period. Energies 2019, 12, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Xu, Z. Arc fault diagnosis method based on chaos and fractal theories. Electr. Mach. Control 2021, 25, 125–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Hou, P.; Yan, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C. Chaotic characteristic analysis and feature recognition of mechanical failure of high voltage reactor winding and iron core. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2022, 42, 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.T.; Li, X.B.; Lan, C.F.; An, S.; Wang, J.-S.; Li, F.-C. Chaotic dynamic characteristics of pressure fluctuation signals in hydro-turbine. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 5009–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, N. Cavitation fault diagnosis of centrifugal pump based on wavelet multi-scale chaotic characteristic parameters. J. Vib. Shock 2021, 40, 106–112+134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, X.-C.; Hu, D. Investigating the hydrodynamics of airlift pumps by wavelet packet transform and the recurrence plot. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 92, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Song, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. Wavelet and improved Hilbert–Huang transform method are used to study the spectrum distribution and energy of turbine pressure pulsation. Eng. Rep. 2022, 4, e12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Gui, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xiao, R.; Tao, R. Pressure pulsation of pump turbine at runaway condition based on Hilbert Huang transform. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1344676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tai, G.; Shen, J.; Pei, J.; Yuan, S. Experimental investigation on pressure fluctuation characteristics of a mixed-flow pump as turbine at turbine and runaway conditions. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Cheng, L.; Jia, S.; Jiao, W.; Zhang, B.; Yang, A. Numerical simulation and experimental study on hydraulic instability of pump as turbine devices induced by thoma number based on scale-averaged wavelet spectrum. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2025, 19, 2454297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Jin, N.D. Research on flow pattern classification method of two phase flow based on chaotic attractor morphological characteristic. Acta Phys. Sin. 2007, 56, 5149–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Luo, X.; Arndt, R.E.; Wu, Y. Numerical simulation of three dimensional cavitation shedding dynamics with special emphasis on cavitation–vortex interaction. Ocean Eng. 2014, 87, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.S.; Bin, C.H.E.N. Unsteady flow analysis and experimental investigation of axial-flow pump. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2010, 22, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. RNG k-ε pump turbine working condition of numerical simulation and optimization of the model. In International Conference on Intelligent Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 684–693. [Google Scholar]
- Roberson, J.A.; Chaudhry, M.H. Hydraulic Engineering, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, S.; Cheng, L.; Sheng, W. Study on power losses and pressure fluctuations of diffuser mixed flow pump as turbine on different power generation speeds based on energy power models. Renew. Energy 2024, 237, 121771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T. Chaotic Time Series Analysis Research and Application; Harbin Engineering University: Harbin, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein, M.T.; Collins, J.J.; De Luca, C.J. A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1993, 65, 117–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z. The calculating method of the average period of chaotic time series. Syst. Eng. 2010, 28, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1983, 9, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Duan, L. Study of fault characteristic extraction method of reciprocating pump based on chaotic theory. China Pet. Mach. 2009, 37, 56–59+91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Shen, W.; Liu, H.; Tang, F.; Yan, B. Study on pressure field characteristics of high specific speed axial flow pump under full working conditions based on wavelet transform. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 025207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chang, P.; Hu, W.; Mao, B.; Liu, C.; Li, Z. Numerical study on pressure pulsation in a slanted axial-flow pump device under partial loads. Processes 2021, 9, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Shi, W.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Q. Numerical analysis of unsteady internal flow characteristics in a bidirectional axial flow pump. Sustainability 2024, 16, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Design flow rate of single unit (m3/s) | 20 |
| Design net head of drainage condition (m) | 2.61 |
| Design net head of diversion condition (m) | 1.89 |
| Impeller diameter (m) | 2.50 |
| Impeller blades number | 3 |
| Guide vane number | 7 |
| Rotating speed (r/min) | 150 |
| Single-machine power of synchronous motor (kW) | 1000 |
| Characteristic Head | Drainage Condition | Irrigation Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum head (m) | 4.09 | 2.60 |
| Design head (m) | 2.61 | 1.89 |
| Average head (m) | 2.06 | 1.57 |
| Minimum head (m) | −0.1 | −0.3 |
| Equipment | Type | Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic flowmeter | MF | 0–600 (L/s) | ±0.2% |
| Difference pressure transmitter | EJA110A | 0–2 (bar) | ±0.10% |
| Torque-speed sensor | JC | 0–500 (N · m) | ±0.15% |
| Digital torque and speed indicators algorithmic indicator | TS-3200B | 0–4000 (rpm) | ±0.05% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, W.; Xi, X.; Fan, H.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Dou, J.; Jia, X. Study on Pressure Fluctuation Characteristics and Chaos Dynamic Characteristics of Two-Way Channel Irrigation Pumping Station Under the Ultra-Low Head Based on Wavelet Analysis. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090270
Jiao W, Xi X, Fan H, Chen Y, Shen J, Dou J, Jia X. Study on Pressure Fluctuation Characteristics and Chaos Dynamic Characteristics of Two-Way Channel Irrigation Pumping Station Under the Ultra-Low Head Based on Wavelet Analysis. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(9):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090270
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Weixuan, Xiaoyuan Xi, Haotian Fan, Yang Chen, Jiantao Shen, Jinling Dou, and Xuanwen Jia. 2025. "Study on Pressure Fluctuation Characteristics and Chaos Dynamic Characteristics of Two-Way Channel Irrigation Pumping Station Under the Ultra-Low Head Based on Wavelet Analysis" AgriEngineering 7, no. 9: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090270
APA StyleJiao, W., Xi, X., Fan, H., Chen, Y., Shen, J., Dou, J., & Jia, X. (2025). Study on Pressure Fluctuation Characteristics and Chaos Dynamic Characteristics of Two-Way Channel Irrigation Pumping Station Under the Ultra-Low Head Based on Wavelet Analysis. AgriEngineering, 7(9), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7090270






