Design and Initial Testing of Acoustically Stimulated Anaerobic Digestion Coupled with Effluent Aeration for Agricultural Wastewater Remediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
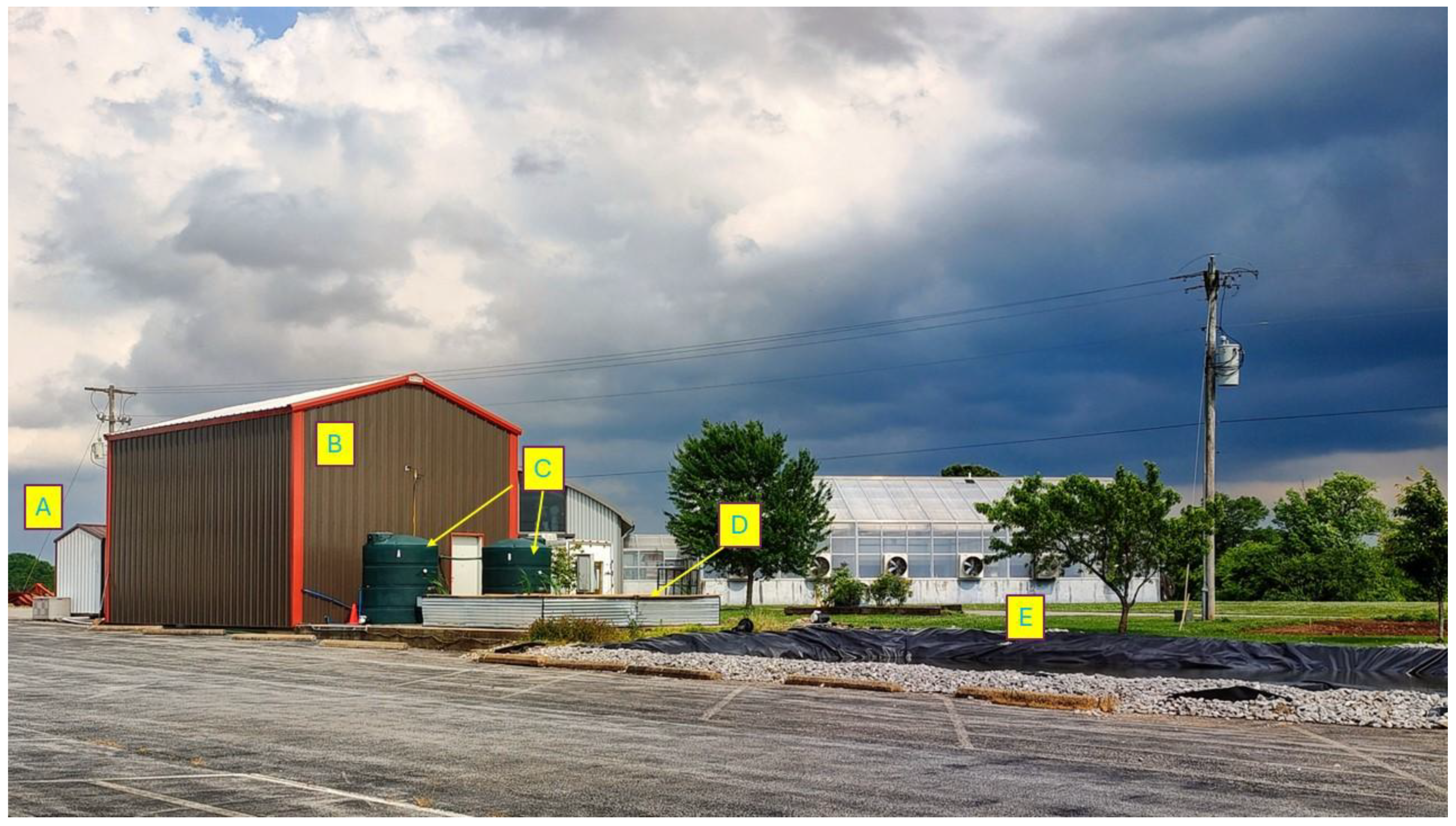
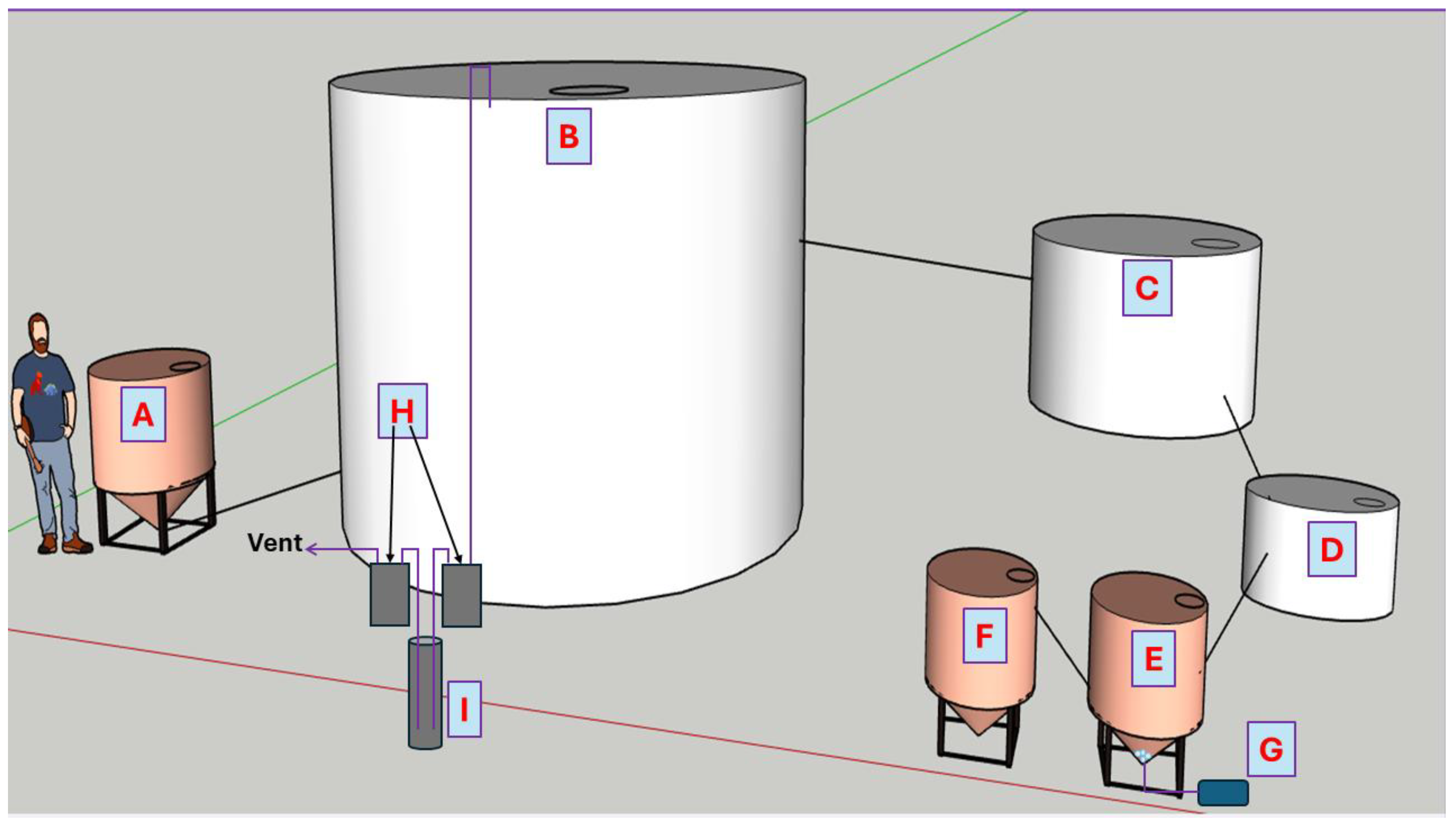
2.1. Waste Treatment System Description
2.2. Sound Systems
2.3. Wastewater Treatment System Operation
2.4. Sampling
3. Results and Discussion
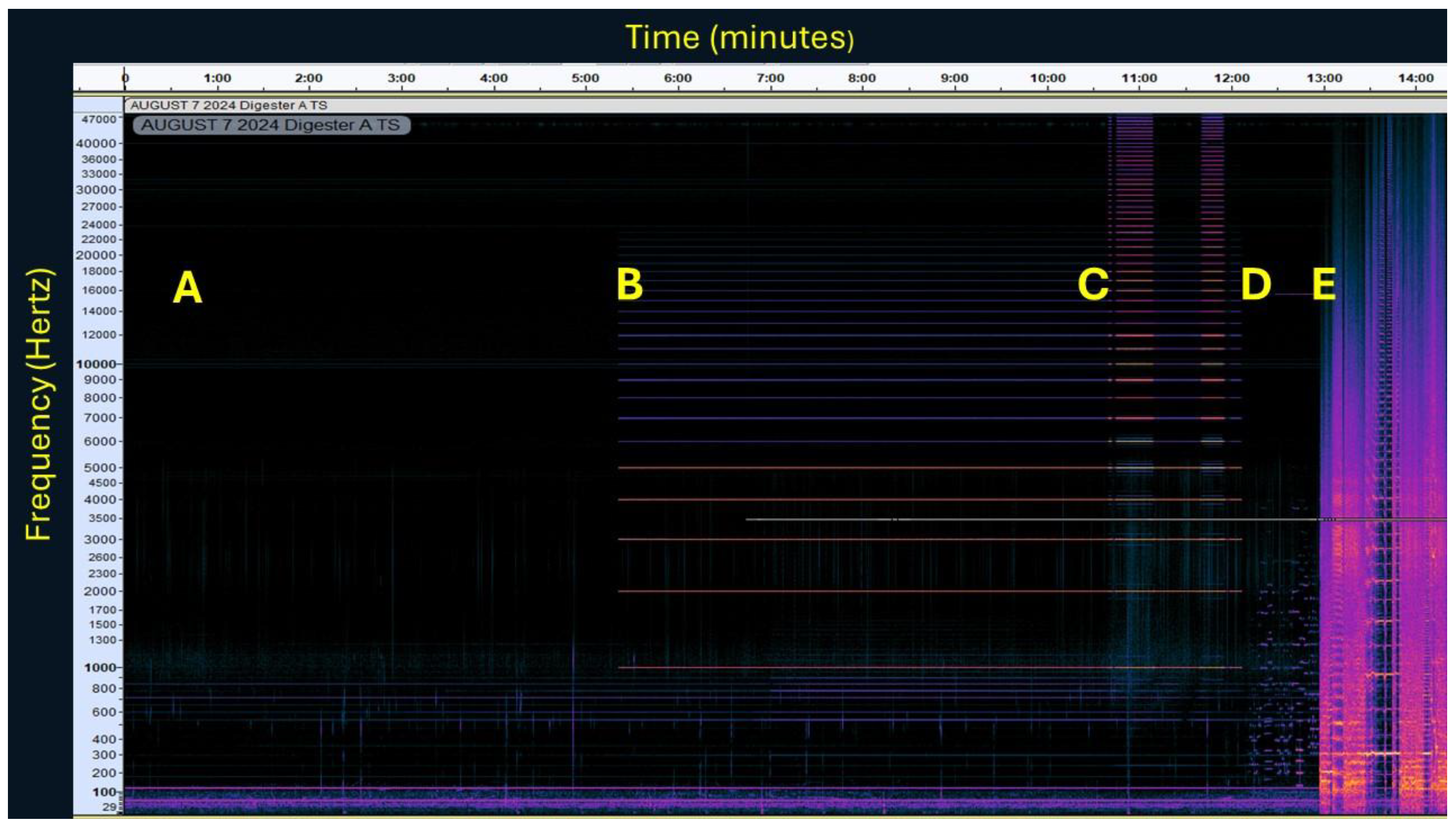
3.1. Sound Treatment of Digesters
3.2. Wastewater Quality
3.3. Biogas Production
3.4. Gas Emissions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilbert, P.M. From hogs to HABs: Impacts of industrial farming in the US on nitrogen and phosphorus and greenhouse gas pollution. Biogeochemistry 2020, 150, 139–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center, T.J. Governmental oversight of discharges from concentrated animal feeding operations. Environ. Manag. 2006, 37, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkholder, J.; Libra, B.; Weyer, P.; Heathcote, S.; Kolpin, D.; Thorne, P.S.; Wichman, M. Impacts of waste from concentrated animal feeding operations on water quality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.W.; Kourtchev, I.N.; Ndegwa, P.W.; Cumba, H.J.; Gioelli, F. Methane and carbon dioxide emissions from simulated anaerobic swine manure treatment lagoons under summer conditions. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooy, P.; Purvis-Roberts, K.L.; Silva, P.J.; Nee, M.J.; Cocker, D. Characterization of secondary products formed through oxidation of reduced sulfur compounds. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 256, 118148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooy, P.; Drover, R.; Cress, T.; Michael, C.; Purvis-Roberts, K.L.; Silva, P.J.; Nee, M.J.; Cocker, D. Methanesulfonic acid and sulfuric acid aerosol formed through oxidation of reduced sulfur compounds in a humid environment. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.J.; Kacarab, M.E.; Cocker, D.R.; Purvis-Roberts, K.L.; Silva, P.J. Effects of temperature on the formation of secondary organic aerosol from amine precursors. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 50, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboomian, V.J.; He, Q.; Montoya-Aguilera, J.; Ali, N.; Fleming, L.T.; Lin, P.; Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Rudich, Y.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Light absorption and scattering properties of indole secondary organic aerosol prepared under various oxidant and relative humidity conditions. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, A.; Vande Burgt, N.H.; Abram, F.; Barry, G.; Fenton, O.; Markey, B.K.; Nolan, S.; Richards, K.; Bolton, D.; De Waal, T.; et al. Agricultural anaerobic digestion power plants in Ireland and Germany: Policy and practice. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2017, 97, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altege, M.R.; Senol, H.; Djaafri, M.; Hansu, T.A.; Krisa, D.; Atabani, A.; Eskicioglu, C.; Muratçobaboğlu, H.; Unalan, S.; Kalloum, S.; et al. A critical overview of the state-of-the-art methods for biogas purification and utilization processes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Persson, T.; Hulteberg, C.; Tamm, D. Biogas upgrading—Technology overview, comparison and perspectives for the future. Biofpr 2013, 7, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, C.; Brorsen, B.W. Anaerobic digester production and cost functions. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 152, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Szamosi, Z.; Siménfalvi, Z. State of the art on mixing in an anaerobic digester: A review. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagegele, H.J.; Lemmer, A.; Oechsner, H.; Jungbluth, T. Electric energy consumption of the full scale research biogas plant ‘unterer lindenhof’: Results of longterm and full detail measurements. Energies 2012, 5, 5198–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyama, I.D.; Zhai, X.; Wu, B. Influence of mixing on anaerobic digestion efficiency in stirred tank digesters: A review. Water Res. 2018, 142, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, G.D.; Roš, M. Heat and energy requirements in thermophilic anaerobic sludge digestion. Renew. Energ. 2003, 28, 2255–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Du, L.; Tang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, X. Improving methane production during the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: CaO-ultrasonic pretreatment and using different seed sludges. Proc. Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J. Effect of different hydrolytic enzymes pretreatment for improving the hydrolysis and biodegradability of waste activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 2, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neis, U.; Nickel, K.; Lundén, A. Improving anaerobic and aerobic degradation by ultrasonic disintegration of biomass. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2008, 43, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilli, S.; Bhunia, P.; Yan, S.; LeBlanc, R.J.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrin, J.; Antle, S.W.; Sistani, K.; Lovanh, N. In situ acoustic treatment of anaerobic digesters to improve biogas yields. Environments 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelen, I.; Türker, M. Recovery of ammonia as struvite from anaerobic digester effluents. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2015, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jin, H.-F.; Lim, B.-R.; Park, K.-Y.; Lee, K. Ammonia removal from anaerobic digestion effluent of livestock waste using green alga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8649–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Bai, X.; Li, H.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Huang, Z. Nutrients removal and biomass production from anaerobic digested effluent by microalgae: A review. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, N.D.; Tuomisto, H.L.; McCulloch, M.D. Meta-Analysis of greenhouse gas emissions from anaerobic digestion processes in dairy farms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 39, 5211–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Schubert, B.A.; Jahren, A.H. A 23 m.y. record of low atmospheric CO2. Geology 2020, 48, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hadi, M.A. A simple apparatus for biogas quality determination. Misr. J. Ag. Eng. 2008, 25, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, E. H2S removal from biogas using bioreactors: A review. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2015, 6, 479–498. [Google Scholar]
- Little, B.J.; Ray, R.I.; Pope, R.K. Relationship between corrosion and the biological sulfur cycle: A review. Corrosion 2000, 56, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likens, G.E.; Wright, R.F.; Galloway, J.N.; Butler, T.J. Acid Rain. SciAm 1979, 241, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bist, R.B.; Subedi, S.; Chai, L.; Yang, X. Ammonia emissions, impacts, and mitigation strategies for poultry production: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 116919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-K.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Liao, T.-L. Assessment of ammonium–N and nitrate–N contamination of shallow groundwater in a complex agricultural region, central western Taiwan. Water 2022, 14, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrin, J.H.; Antle, S.W.; Polk, J. A Gas Chromatographic Method for the Determination of Bicarbonate and Dissolved Gases. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.; Clesceri, L.; Greenberg, A.; Franson, M. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Loughrin, J.; Antle, S.; Simmons, J.; Sistani, K.; Lovanh, N. In Situ Sonification of Anaerobic Digestion: Extended Evaluation of Performance in a Temperate Climate. Energies 2020, 13, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennen, C.E. Cavitation and Bubble Dynamics, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 268. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, D. Chaotic sound synthesis. Comput. Music J. 1998, 22, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Chaotic oscillations of gas bubbles under dual-frequency acoustic excitation. Ultasonics Sonochem. 2018, 40(B), 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Acoustic streaming and its applications. Fluids 2018, 3, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobaraki, M.; Semken, R.S.; Mikkola, A.; Pyrhonen, J. Enhanced sludge dewatering based on the application of high-power ultrasonic vibration. Ultrasonics 2018, 84, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Shimizu, K.; Utsumi, Y.; Lee, D.-J. A novel anaerobic digestion system coupling biogas recirculation with MgCl2 addition for multipurpose sewage sludge treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Li, B.; Patel, K.; Wang, L.B. A review of the processes, parameters, and optimization of anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katuwal, S.; Rafsan, N.A.S.; Ashworth, A.J.; Kolar, P. Poultry litter physiochemical characterization based on production conditions for circular systems. BioResouces 2023, 18, 3961–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilderer, P.A.; Jones, W.L.; Dau, U. Competition in denitrification systems affecting reduction rate and accumulation of nitrite. Water Res. 1987, 21, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Gao, B. Recovery of phosphorus from wastewater: A review based on current phosphorous removal technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 53, 1148–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Treatment Stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Digester | Effluent Storage Tank | Aeration Tank | Wetland |
| Temperature (°C) | 27.1 ± 1.0 b | 29.2 ± 1.9 b | 27.3 ± 1.4 a | 24.6 ± 1.9 c |
| pH | 6.7 ± 0.3 d | 7.2± 0.2 c | 7.9 ± 0.4 a | 7.6 ± 0.2 b |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg L−1) | 1.3 ± 0.5 b | 1.4 ± 0.9 b | 2.5 ± 1.3 a | 1.0 ± 0.7 b |
| Oxidation–Reduction Potential (mV) | −271 ± 23.2 b | −263 ± 20.8 b | −151 ± 83.1 a | −158 ± 59.9 a |
| Conductivity (µS cm−1) | 3390 ± 1120 a | 2910 ± 801 ab | 2520 ± 723 b | 982 ± 384 c |
| Concentration (mg L−1) | ||||
| Ammonium | 148 ± 93.1 a | 161 ± 4.5 a | 103 ± 80.7 b | 16.7 ± 20.7 c |
| Nitrite | 67.8 ± 190 a | 11.3 ± 27.2 a | 10.0 ± 14.4 a | 16.9 ± 19.3 a |
| Nitrate | 2.04 ± 3.08 a | 1.16 ± 1.79 a | 9.33 ± 12.1 a | 0.82 ± 0.48 a |
| Phosphate | 254 ± 228 a | 177 ± 134 ab | 95.7 ± 81.3 bc | 20.2 ± 24.8 c |
| Sulfate | 22.1 ± 23.5 ab | 16.8 ± 12.9 bc | 38.1 ± 17.6 a | 3.60 ± 2.94 c |
| Sodium | 99.0 ± 47.3 ab | 104 ± 39.2 a | 80.4 ± 41.4 b | 40.9 ± 25.4 c |
| Potassium | 316 ± 168 a | 301 ± 133 a | 221 ± 130 b | 89.0 ± 59.9 c |
| Calcium | 106 ± 36.7 a | 89.0 ± 30.0 a | 59.1 ± 27.2 b | 45.8 ± 9.36 b |
| Magnesium | 47.3 ± 18.3 a | 42.9 ± 15.3 ab | 33.9 ± 5.63 ab | 27.4 ± 8.20 b |
| Sampling Period a | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Before Sound Treatment | During Sound Treatment |
| Carbon dioxide, µg L−1 | 326,000 ± 65,200 | 341,000 ± 74,400 |
| Methane, µg L−1 | 508,000 ± 99,300 | 485,000 ± 97,600 |
| Liters of biogas wk−1 | 5760 ± 688 | 5580 ± 1580 |
| Wastewater Treatment Stage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digester | Effluent Holding Tank | Aeration Tank | Wetland | |
| Aqueous Phase Concentration | ||||
| CO2 (mM) a | 3.16 ± 0.14 | 0.74 ± 0.049 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.011 |
| CH4 (mM) a | 25.0 ± 2.32 | 26.4 ± 3.69 | 0.81 ± 0.14 | 0.98 ± 0.13 |
| NH4+ (mM) a | 11.0 ± 10.2 | 7.91 ± 2.56 | 6.72 ± 4.86 | 0.58 ± 1.75 |
| N2O (pM) a | 225 ± 35.1 | 213 ± 39.7 | 184 ± 39.1 | 188 ± 33.1 |
| Atmospheric Concentration (ppm) | ||||
| CO2 | 64,400 ± 61,500 | 2830 ± 1200 | 911 ± 156 | 2230 ± 3890 |
| CH4 | 37,700 ± 34,700 | 716 ± 350 | 45.7 ± 11.0 | 708 ± 3.310 |
| NH3 | 12.8 ± 17.9 | 6.51 ± 4.22 | 9.87 ± 1.33 | 7.58 ± 5.41 |
| N2O (ppb) | 26.9 ± 17.9 | 16.6 ± 8.22 | 1.26 ± 0.24 | 0.96 ± 0.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loughrin, J.H.; Silva, P.J.; Antle, S.W.; Lovanh, N.; Vanotti, M.B.; Sistani, K.R. Design and Initial Testing of Acoustically Stimulated Anaerobic Digestion Coupled with Effluent Aeration for Agricultural Wastewater Remediation. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050136
Loughrin JH, Silva PJ, Antle SW, Lovanh N, Vanotti MB, Sistani KR. Design and Initial Testing of Acoustically Stimulated Anaerobic Digestion Coupled with Effluent Aeration for Agricultural Wastewater Remediation. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(5):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050136
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoughrin, John H., Philip J. Silva, Stacy W. Antle, Nanh Lovanh, Matias B. Vanotti, and Karamat R. Sistani. 2025. "Design and Initial Testing of Acoustically Stimulated Anaerobic Digestion Coupled with Effluent Aeration for Agricultural Wastewater Remediation" AgriEngineering 7, no. 5: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050136
APA StyleLoughrin, J. H., Silva, P. J., Antle, S. W., Lovanh, N., Vanotti, M. B., & Sistani, K. R. (2025). Design and Initial Testing of Acoustically Stimulated Anaerobic Digestion Coupled with Effluent Aeration for Agricultural Wastewater Remediation. AgriEngineering, 7(5), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050136








