Abstract
Detecting objects in digital images is challenging in computer vision, traditionally requiring manual threshold selection. However, object detection has improved significantly with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and other advanced algorithms, like region-based convolutional neural networks (R-CNNs) and you only look once (YOLO). Deep learning methods have various applications in agriculture, including detecting pests, diseases, and fruit quality. We propose a lightweight YOLOv4-Tiny-based object detection system with a circular bounding box to accurately determine chrysanthemum flower harvest time. The proposed network in this study uses a circular bounding box to accurately classify the degree of chrysanthemums blooming and detect circular objects effectively, showing better results than the network with the traditional rectangular bounding box. The proposed network has excellent scalability and can be applied to recognize general objects in a circular form.
1. Introduction
Finding or classifying the desired object in a digital image, such as a person, object, or scene, is a fundamental but challenging part of computer vision. The traditional approach to detecting objects in images is to manually select thresholds for features, such as the color, shape, and texture unique to the object, which an expert then catches. However, this approach needs more scalability and accuracy. The thresholds need to be redefined when the shooting conditions or the surrounding environment change, such as camera settings, brightness around the object, or shadows. However, since the advent of the convolutional neural network (CNN) developed by LeCun in the late 1990s, the accuracy and scalability of object detection have improved, which has had a major impact on modern object detection methods [1]. Afterward, region-based convolutional networks (R-CNNs) for accurate object detection and segmentation, which have further improved accuracy, find all expected objects by grouping them into image pixel units, dividing them into bounding boxes, and digitizing them to determine the exact location of objects, enabling more accurate object detection [2]. In addition, you only look once (YOLO), a unified, real-time object detection, which dramatically improves detection time by performing all object detection processes in a single network, predicts objects by dividing the input image into a minimum grid, and simultaneously detecting all objects. It is used in many fields to ensure faster processing time and accuracy [3]. Both algorithms use bounding boxes to increase the accuracy of object detection. The bounding box of an object is usually a rectangle, and a rectangular bounding box (rBBox) is convenient for detecting moving objects that cannot be stereotyped in an image. But a different bounding box type is needed for the fixed-shaped object.
Deep learning methods in agriculture can help solve many problems related to agricultural production. They can be usefully applied to places where pests, plant diseases, etc., are identified on farms, or where fruits are harvested or sorted [4,5,6,7,8,9], and they can also be applied to methods where varieties are identified by recognizing seeds or leaves of the crop [10,11]. Chrysanthemum, along with rose, is one of the four most popular cut flowers in the world. It is mainly used as an ornament for decoration, or as a raw material for functional food, such as tea and medicine, in Southeast Asian countries, represented by Korea, Japan, and China, as well as in European countries. It is cultivated in flower farms [12,13]. In harvesting chrysanthemums, it is essential to determine the appropriate degree of flowering, the appropriate size, and the presence of pests and diseases, and productivity is greatly affected by the expertise and skill of workers. If the product standards are not satisfied, it is often discarded, so it is essential to accurately determine the flowering degree of chrysanthemums. Still, few studies are related to this [14,15,16]. Recently, Chao [17] proposed a lightweight convolutional neural network called MC-LCNN to detect medicinal chrysanthemums in the bud stage, and confirmed that real-time detection is possible, even in an embedded environment. However, it is difficult to predict the flowering degree of the whole chrysanthemum by applying only the bud stage of medicinal chrysanthemums to the YOLO network. In addition, the rBBox is not optimized for detecting fruits or flowers in farming and flower farms. In agriculture, objects, such as a fruit or a flower, have a generalized circular shape. Therefore, in recognizing a generalized circular object, it is advantageous to use a circular bounding box (cBBox). Realistic images can be obtained from all angles, unlike general objects for most fruits or flowers. Therefore, the existing rBBox includes an unnecessary background image in a place where a circular object is recognized. These extraneous background image contents interfere with learning. Thus, when only a circular object is to be detected, detection performance can be improved by using a cBBox suitable for the object. In addition, when using a cBBox, the number of learning parameters is reduced compared to a rBBox, which is effective for network training time and optimization performance.
Experimental results indicate that a network with a cBBox is >2% better in mean average precision (mAP) than that with the conventional rBBox. In addition, compared with the latest research results, the proposed method confirmed a slight performance advantage, even though it is a more difficult classification problem. Therefore, a network with cBBox is highly effective and superior to a network with rBBox.
In flower farmers, the timing of cut flowers must be determined based on flowering status and other parameters, such as storage period and remaining post-harvest conditions [18]. In this study, we propose an object detection system based on a YOLOv4-Tiny with cBBox that classifies the flowering degree of chrysanthemums into three categories to accurately determine the harvest time of chrysanthemums. The proposed network can classify the degree of flowering of chrysanthemums into three categories: full bloom, early bloom, and budding, and it can provide primary data for predicting the harvest time, aiding flower farmers. The proposed network with cBBox showed higher results in the average precision (AP) analysis than the general YOLO network with rBBox. The proposed network has excellent scalability that can be applied both to classifying the degree of blooming of chrysanthemums, and to recognizing general objects of circular form.
2. Related Work
In modern object detection systems, with the development of hardware technology capable of parallel computing, such as graphics processing units (GPUs) and tensor processing units (TPUs), the number of calculations that can be processed at one time has increased, and the processing time has also reduced. Therefore, high accuracy and real-time performances are shown, even in machine learning and deep learning-based systems that require much computation [19,20,21]. A general object detection system proceeds with selecting object candidate regions, extracting features from each candidate region, and applying a class to the candidate region through a classifier. Depending on the detection method, post-processing, such as bounding box regression, may be used to improve localization performance. Early object detection systems were designed by configuring the process of selecting object candidate regions as a separate network. But recently, some studies have improved detection performance by using a method of simultaneous detection by combining object feature extraction and classification networks. In particular, YOLO proposed by Redmon, is a regression method with a simple structure that estimates the bounding box coordinates of object candidates and object class probability values compared to the classifier-based CNN method. The network configuration is relatively simple, and the loss significantly affects detection performance. This is the most famous object detection deep learning algorithm, as real-time detection is possible by drastically reducing the detection time by directly learning the function [22,23,24,25]. Various YOLO network models have been developed in many studies. Among them, YOLOv4 became faster by applying optimization methods, such as weighted residual connections (WRCs), cross-stage partial connections (CSPs), and complete intersection over union (cIoU) loss in many CNN-related studies. YOLOv4 shows the accurate recognition rate [26]. Nevertheless, using a real-time object detection system is challenging due to network complexity in a low-cost embedded environment. YOLOv4-Tiny, introduced by Wang, is a more simplified model of the YOLOv4 network, and the network size is 10% of YOLOv4. While it has a slightly lower detection accuracy, it is used in many studies for real-time object detection due to its fast network learning and detection speed [27,28,29,30,31]. As the performance of this deep learning technique has been verified in various fields, it is also used in agriculture to diagnose and predict diseases and pests, detect fruit and determine ripeness, and predict yield, showing good performance [32,33,34,35,36]. Ramar [37] trained the Plantvillage dataset with a network modified from LeNet [1] to classify three diseases in maize leaves, achieving a high accuracy of over 97%. Inspired by the YOLO series, Koirala proposed the MangoYOLO [38] network to detect mangoes, which showed excellent real-time performance with an F1 score of 0.97. Fu [39] achieved high accuracy by applying the YOLOv4 network to accurately detect bananas of various sizes and shapes, even in poor surroundings, such as orchards. Zhang [32] proposed RTSD-Net by modifying the YOLOv4-Tiny network model with fewer convolutional layers to be applied to strawberry harvest, and achieved faster detection speed. Chao [17] proposed a lightweight convolutional neural network called MC-LCNN to detect medicinal chrysanthemums in real time, and used it to enable real-time detection, even in an embedded environment. Most of the deep learning algorithms applied in the agricultural field have focused on research to improve detection performance using existing known network structures, or to improve network structures for real-time processing. Even though fruits and flowers in general present a circular shape, the existing rBBox was used in object detection. Using a rBBox includes much unnecessary background content content that is not part of the objects, and learning this alongside the flowers negatively impacts both the learning time and accuracy.
3. Network and Data Acquisition
3.1. YOLOv4-Tiny Detector
Figure 1 shows the schematic structure of YOLOv4-Tiny. The basic configuration of the network consists of a CNN-based neural network module as the backbone, an FPN module, and a YOLO-head module. The backbone extracts the main features of an object from the input image, and the FPN module improves feature extraction performance by merging functions of various layers. The YOLO-head module outputs object prediction results of multiple sizes. The CNN-based backbone is designed by repeating convolution-batch normalization-LeakyReLU (CBL) block and cross-stage partial (CSP) block. Still, compared to YOLOv4, the overall network is lightweight by reducing the number of iterations and compressing in block units. YOLOv4-Tiny simplifies the YOLOv4 network and greatly reduces the network size, resulting in slightly lower detection accuracy, but speedy learning and detection speed [25,26,27,28,29]. Therefore, if object detection accuracy can be improved, it can be used as a beneficial network.
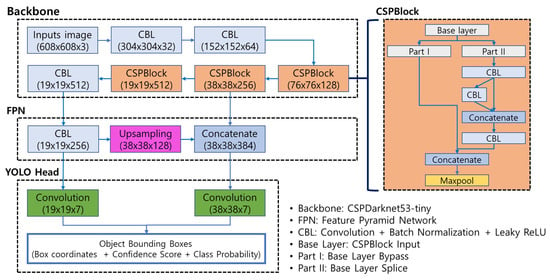
Figure 1.
YOLOv4-Tiny.
Figure 2 shows a schematic of the YOLOv4-Tiny detector detecting the degree of flowering of chrysanthemum flowers. When an image is an input to the YOLOv4-Tiny network, the location information of the chrysanthemum petal predicted through YOLOv4-Tiny is output, and the object overlap test and final class is output. The YOLOv4-Tiny network extracts object features through the backbone network and FPN (feature pyramid network). The predicted chrysanthemum flower information is output through the YOLO head. In this study, the input image size is (608 × 608) pxl, and the CSPdarnet53-Tiny model and FPN structure are applied as a network for feature extraction. The output structure of the YOLO head consists of the coordinates of the center point of the bounding box (A, B) representing the location and size of the cBBox, the circle radius (r), the confidence score, and the class probability. Non-maximum suppression (NMS) is applied to the same class to remove redundant detection among the values output by the YOLO head. If different classes are predicted, the class with the more significant confidence score is selected and determined as the final output.
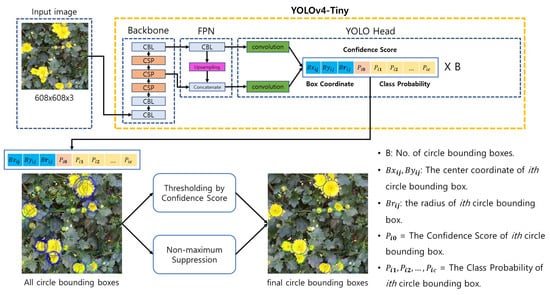
Figure 2.
YOLOv4-Tiny detection.
3.2. Circle Bounding Box
In most object detection systems, it is common to designate an object area with an rBBox to detect various objects. rBBoxes are very reasonable for recognizing moving objects that cannot be stereotyped in an image. However, for objects whose shapes do not change, a bounding box that is similar to the object’s shape is more beneficial. The cBBox is advantageous for learning to recognize circular objects, such as fruit or flowers. In the case of rBBox, it is not easy to train accurate object features because an unnecessary background image other than the object is included. In particular, more background image components are included in an object rotated at a certain angle, significantly affecting the learning efficiency and detection performance. However, if only a circular object needs to be detected, detection performance can be improved using cBBox suitable for the object. In addition, the number of learning parameters is small, which is advantageous in terms of learning time [40,41]. Therefore, in this study, the surrounding background image other than chrysanthemum flowers was minimized by applying cBBox suitable for detecting chrysanthemum flowers. To evaluate multiple bounding boxes in the YOLOv4-Tiny network, the circle intersection over union (cIoU) evaluation index is defined and applied as follows [40]:
Figure 3 shows two cBBoxes, A and B, of different sizes, where and are the radii of A and B, respectively. If the distance (d) between the center points of the two circles is , the two circles overlap. The overlapping area of the two cBBoxes is given by Equation (1):
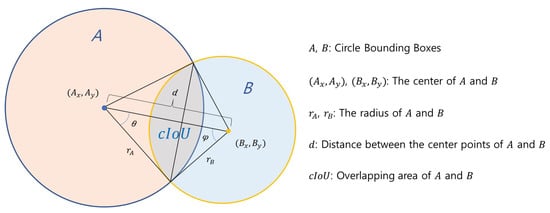
Figure 3.
Overlap of two cBBoxes.
3.3. Image Data Collection
There is no open dataset for chrysanthemum petals, so images obtained by direct filming were used. The images of chrysanthemums used in this study were extracted from videos taken with a tablet (Samsung S8 Ultra: Samsung Electronics in Korea) with a built-in camera at the Jinju Chrysanthemum Exhibition in November 2022. The video was filmed at FHD (1920 × 1080 pixels) at 30 fps under natural light conditions, the same chrysanthemum species were selected, and images were extracted considering different brightness and environmental conditions. Training and test images were collected. The extracted images were cut at a resolution suitable for learning (608 × 608 pixels) to create 117 training and test images. We randomly selected 82 images for learning and 35 as test data for the performance evaluation. Figure 4 shows a part of the extracted image. For the fairness of network performance evaluation, the images were composed of images with different brightness and sharpness. Figure 4a,b are images taken under natural light conditions, but Figure 4b is a very defocused image. Figure 4c is a very dark image taken in the shade, and Figure 4d–f are images taken under backlight conditions.
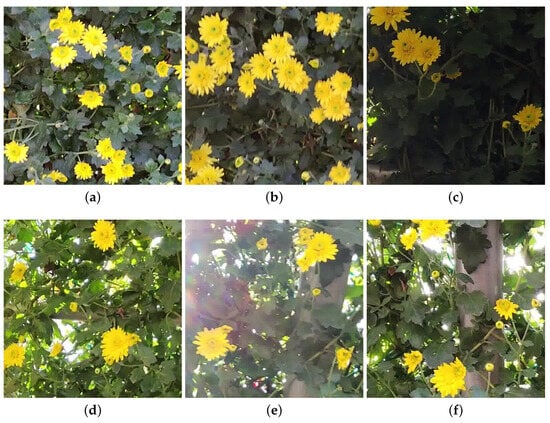

Figure 4.
Examples of training and test images. (a) Focused image under natural light conditions; (b) defocused image under natural light conditions; (c) dark image under natural light conditions; (d) focused image under backlight conditions; (e) defocused image under backlight conditions; (f) dark image under backlight conditions.
To classify the degree of flowering of chrysanthemums required for this study, the state of chrysanthemum petals is divided into , , and , with the naked eye, and labeled. is a fully bloomed state in which the petals are wide open, and the pistil in the center of the flower is visible. is a state in which petals are not visible, compared to , and buds start sprouting in lumps. Other flowers in the progress of flowering whose petals were not completely unfolded were labeled as . The number of , , and objects in the training image are 581, 675, and 117, respectively. Table 1 shows the definition of the flowering stage of chrysanthemum and the labeling results for sample images. In the sample image, when the chrysanthemum petal is located at the edge, only when the center of the chrysanthemum petal exists in the image is it recognized as an object and labeled. The three flowering states are beneficial flowering classifications that can inform the exact harvest time of cut flowers and differentiation in flower farmers. The labeled cBBox is defined in Equation (6), and it is one less than the parameter of the rBBox.
where i is the cBBox number, j is the label index, is the center coordinate of the cBBox, and is the radius of the cBBox.

Table 1.
Data label.
3.4. Data Augmentation
Eighty-two training images for YOLO network learning are insufficient for training data, and overfitting may occur during network learning. Therefore, data augmentation is required for improved detection performance and practical training. Most flower objects in the image are circular and have a consistent object image with a change in angle. Therefore, the images of the prepared data were applied to increase the number of data while maintaining the object characteristics in the image through inversion and rotation. In the case of rotation transformation, the data augmentation effect was maximized by converting only the object’s size and position while maintaining the object’s characteristics by setting it to not deviate from the 608 × 608 input image size using a scale factor. In other words, rotation alone has the effect of changing the sizes and characteristics of an object. For image rotation, 82 image data were expanded to 11,808 by rotating and converting the original image and the inverted image to degrees at intervals of degrees. Figure 5 shows the data augmentation process.

Figure 5.
Data augmentation.
Table 2 shows the number of original training data and augmented training data. The 82 original training images contain 581, 675, and 117 data labeled A, B, and C, respectively. These were increased to 83,664, 97,200, and 16,848, respectively, through data augmentation. for the performance evaluation, 35 test images were not used for training, and there were 271, 295, and 53 labeled data in the test images, respectively.

Table 2.
The original training and augmented data numbers.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experiment Environment and Setup
The YOLOv4-Tiny network model provided by Matlab® [42] was used for network training. The image input layer and YOLO head output layer were changed to match the dataset and output structure, and the SGDM (stochastic gradient descent with momentum) optimization algorithm was used. Learning was performed by applying an initial learning rate of 0.0001, a maximum epoch of 200, and a mini-batch size of 16. The hardware used in the experiment was an Intel i9-9900K CPU and NVIDIA RTX2090 GPU. The YOLOv4-Tiny network can quickly and accurately detect objects with various aspect ratios and scales using predefined anchor boxes of a specific size. Since this study uses a cBBox, a circular anchor box is also required. A circular anchor box has an aspect ratio of 1, so anchor boxes with different aspect ratios are unnecessary; only size considerations are needed. In this study, the average cIoU of the circular anchor boxes was confirmed through K-means clustering, and the number of circular anchor boxes with an average cIoU of 0.8083 was selected as 4. The loss function used in training the YOLOv4-Tiny network was calculated on the object classification loss , the object reliability loss using the binary cross entropy function, and the position error of the bounding box using the root mean square error (RMSE). The overall loss function reflecting these settings is shown in Equation (7).
where are the scale factors set to in this study.
4.2. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Circular Bounding Box
The average mask detection ratio (MDT) [40] for object detection results was measured to evaluate the efficiency of the cBBox applied in this study. A high mask detection rate means that many object elements to be detected are included in the bounding box. The mask detection ratio was compared by calculating the ratio occupied by each bounding box of chrysanthemum petals in pixel units when the bounding box was selected as a circle or a rectangle from 30 randomly selected object images. Figure 6 shows the MDT calculation and results for rBBox and cBBox. The cBBox has an average MDT of , and the rectangular bounding box has an average MDT of , about higher than the cBBox. This result is expected because the shapes of the chrysanthemum petals are close to circular. The cBBox is more useful in learning because it contains more object characteristics than the rBBox.
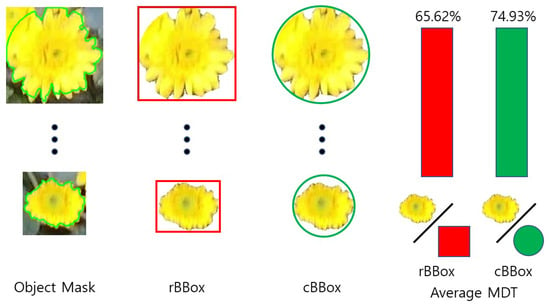
Figure 6.
Average MDT according to the bounding box shapes.
4.3. Object Detection Performance Evaluation
After training the network for 200 epochs, the final overall loss is 0.1832. The test dataset uses 35 images that have not been used for network training. For the performance evaluation, 35 images included 271 objects for , 295 objects for , and 53 objects for , depending on the flowering degree of the chrysanthemum. For the performance evaluation of detection results, we define average precision (AP) as in Equation (8) and introduce a series of evaluation indicators based on AP, including , , , , and for a detailed evaluation. indicates that the cIoU of the classification truth value and prediction result is 0.5 or more, and is 0.7 or more. When the cIoU is 0.5 or 0.7 or more, to detect the overall classification performance, is evaluated, as shown in Equation (9).
where N is the total number of test images, , and is the change value between the and image and .
where is the of class i, and n is the number of classes.
Table 3 shows the results of learning YOLOv4-Tiny networks with cBBox and rBBox by applying the same data and learning rules. Regarding the object class classification results, both networks’ and object detection performances are relatively high compared to . Objects and have large bounding boxes characterized by petals. However, in the case of small objects, such as , the object detection performance is slightly degraded. This includes the difficulty in detecting small objects, which is a drawback of YOLO networks. In addition, the learning images of objects and are more than five times larger than the learning images of object , so it is judged that authentic learning has been achieved. In addition, it is difficult for humans to distinguish and objects accurately, so incorrect data labeling for building training data is also judged to cause the error. Then, and are compared and analyzed for the performance analysis of the two networks. In the case of , the network to which the cBBox is applied has and higher and object detection performances, respectively. The cBBox has a relatively high MDT compared to the rBBox and contains fewer images of the surrounding environment, except for petals. This is advantageous for accurately learning the characteristics of an object. But for , a rBBox is marginally better at . Overall, for , the network with a cBBox is better. Also, in the case of , the network to which the cBBox was applied showed and higher performances in detecting and objects, respectively, but lower results by in detecting objects. For a small-sized object, such as , regardless of the shape of the bounding box, the effect of the background around the object appears small. Overall, also shows a higher performance in the network to which the cBBox is applied. Therefore, in terms of network performance, a network with cBBox is very effective and superior to a network with rBBox.

Table 3.
Comparison of APs according to the IoU.
Next, the object’s size was set to three ranges, and the for the fixed ranges was evaluated. The IoU of the classification truth value and prediction result is selected as 0.5 or more. In the case of a cBBox, indicates an object with a size less than pixels, greater than pixels and less than pixels, and greater than pixels. For an rBBox, it is defined as the square of the pixel length equal to the pixel area of the cBBox. We set to less than pixels, to more than pixels and less than pixels, and to more than pixels. The difference in the reference areas of , , and is due to pixel unit calculation errors. Table 4 shows the performance evaluation results according to the bounding box size of the two networks. The network with a cBBox offers more than performance regardless of the size of the bounding box, and the performance is superior to the network with a rBBox. In Table 3, the for the object is , but in the case of , the performance is improved by including and small . A series of test results confirm that a network with a cBBox is advantageous for learning and excellent in performance evaluation because it includes fewer background images than a network with a rBBox.

Table 4.
Comparison of APs according to the bounding box size.
So far, there are few research results regarding detecting chrysanthemum petals. Recently, Chao [15] reported several research results on chrysanthemum petal detection. In this study, we compare Chao’s performance evaluation results. Chao’s study achieved excellent detection performance by applying the YOLO network to detect young shoots with high medicinal value for the harvest of medicinal chrysanthemums. In this study, it is different from the chrysanthemum species used by Chao, and it is not easy to directly compare the performance because the degree of flowering of chrysanthemum petals is detected in three states. However, since this study recently detected chrysanthemum objects using a similar YOLO network, it is selected for comparison.
Table 5 shows the results of Chao’s YOLO networks and the proposed network (TC-YOLO) among several network experiments. The detection result of Chao represents for one type of young shoot state and in this study. It was confirmed that the method proposed in this study is slightly better than TC-YOLO. The proposed method detects the flowering degree of chrysanthemum petals in three states, so it is a more complex problem than the TC-YOLO classification. Nevertheless, a slight performance advantage was confirmed.

Table 5.
Performance comparison with other models.
Figure 7 is the test detection result of the proposed network. The cBBox is displayed by classifying colors by class and overlapping them on the image. From the results in Figure 7a–c, flowers with different flowering degrees were detected at the correct location and size, even when the flowers overlap. In the case of Figure 7d, it was confirmed that was well detected, even when leaves covered it among the overlapping flowers at the top of the image. In Figure 7e,f, the part marked with a pink box is the result of over-predicting an object that does not even exist in the truth value of the test data. In the case of Figure 7e, the object is out of the center of the image, and it is difficult to distinguish it from the naked eye under difficult conditions, such as backlighting. In the case of Figure 7f, it is difficult for humans to judge, because the flowers are unclear. Nevertheless, the proposed network can accurately detect objects. Figure 7g,h show the result of not detecting the flowers correctly, and the truth value of the test data is displayed in a red box. Both objects do not have a clear boundary between blooming flowers, and the object is difficult to see because chrysanthemum leaves cover it. Figure 7h is a case where the direction of the flower is distorted and covered by the chrysanthemum leaf, and it is an object shape that does not exist in the training data. Figure 7i shows an example of incorrectly detecting as . The detected object is a case where an error occurs because some flowers are similar to the characteristics of . From the above results, the lack of training data and inaccurate labeling are identified as problems when an object is not detected or detected incorrectly. Therefore, performance improvement is expected if extensive training data and accurate class classification are preceded.
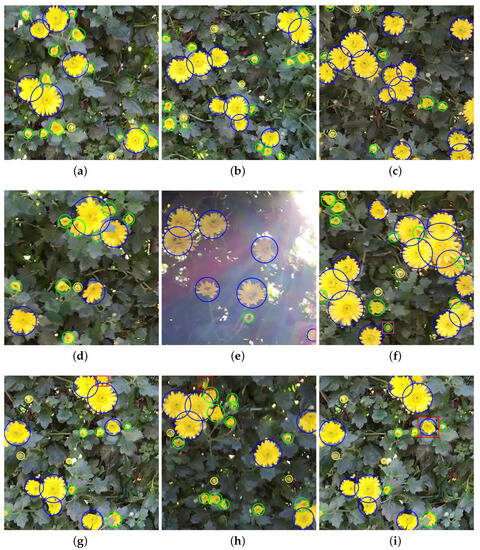

Figure 7.
Test results (blue: , Green: , yellow: ). (a) Example 1 of accurate detection; (b) Example 2 of accurate detection; (c) Example 3 of accurate detection; (d) Example 4 of accurate detection; (e) Example 5 of accurate over-predicting detection; (f) Example 6 of accurate over-predicting detection; (g) Example 7 of missing detection; (h) Example 8 of missing detection; (i) Example 9 of inaccurate detection.
The proposed network can classify the degree of flowering of chrysanthemums into three categories: full bloom, early bloom, and budding, and it can provide flower farmers with data to predict harvest time. From the consumer’s point of view, the blooming state of the chrysanthemum differs according to the time and place of purchase. Therefore, in flower farmers, the timing of cut flowers must be determined based on the flowering status and other parameters, such as the storage period and remaining post-harvest conditions. Therefore, the proposed network provides primary data for predicting the harvest time, aiding flower farmers. In addition, the proposed network is faster than other deep learning networks and it uses little memory, so the system device design is easy. These advantages can be easily applied to large-scale flower farms or small-scale farms.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we propose a lightweight YOLOv4-Tiny-based object detection system with cBBox that classifies the flowering degree of chrysanthemums into three categories to determine the harvest time of chrysanthemums accurately. Object recognition in agriculture exploits a circular shape, such as a fruit or flower, and it is advantageous to recognize a circular object in cBBox. The existing rBBox includes unnecessary background content in addition to circular objects. This unnecessary background content interferes with training. Therefore, when only a specific circular object needs to be detected, detection performance is improved by using the cBBox suitable for the object. In addition, the number of learning parameters is reduced, which is effective for the network learning time and optimization performance. The proposed network showed high performance in the AP analysis compared to general YOLO networks with rectangular bounding boxes. It can classify the degree of flowering of chrysanthemums into three categories: full bloom, early bloom, and budding, and provide flower farmers with data to predict harvest time. In addition, the proposed network has excellent scalability that can be applied to classify the degree of blooming of chrysanthemum flowers and the field of recognizing circular objects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-H.P.; methodology, H.-M.P. and J.-H.P.; software, H.-M.P.; validation, H.-M.P. and J.-H.P.; formal analysis, H.-M.P. and J.-H.P.; data curation, H.-M.P.; writing—review and editing, H.-M.P. and J.-H.P.; supervision, J.-H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Upon reasonable request, the datasets of this study can be available from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Cao, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Wu, X. A review of deep learning in multiscale agricultural sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguettaya, A.; Zarzour, H.; Kechida, A.; Taberkit, A. Deep learning techniques to classify agricultural crops through UAV imagery: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9511–9536. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Tan, L.; Jiang, H. Review on convolutional neural network (CNN) applied to plant leaf disease classification. Agriculture 2021, 11, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F. Deep learning in agriculture: A survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar]
- Mota-Delfin, C.; López-Canteñs, G.d.J.; López-Cruz, I.L.; Romantchik-Kriuchkova, E.; Olguín-Rojas, J.C. Detection and Counting of Corn Plants in the Presence of Weeds with Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4892. [Google Scholar]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F. A review of the use of convolutional neural networks in agriculture. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 156, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, T.-G.; Amin, N.; Dimitrios, F.; Soodabeh, F.; Mahmoud, O.; Nikolaos, N. Automated In Situ Seed Variety Identification via Deep Learning: A Case Study in Chickpea. Plants 2021, 10, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.; Amin, T.-G.; Dimitrios, F.; Yu-Dong, Z.; Nikolaos, N. Automated Grapevine Cultivar Identification via Leaf Imaging and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks: A Proof-of-Concept Study Employing Primary Iranian Varieties. Plants 2021, 10, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, W.; Gao, B.; Kimura, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Rapid identification of chrysanthemum teas by computer vision and deep learning. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Nyalala, I.; Chen, K. Detecting the early flowering stage of tea chrysanthemum using the F-YOLO model. Agronomy 2021, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, Y. Realization of Chrysanthemum Harvesting Recognition System based on CNN. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning & International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications (CVIDL & ICCEA), Changchun, China, 20–22 May 2022; pp. 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Gao, J.; Pearson, S.; Harman, H.; Chen, K.; Shu, L. Tea chrysanthemum detection under unstructured environments using the TC-YOLO model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 193, 116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Gao, J.; Chen, K.; Shu, L.; Pearson, S. Tea Chrysanthemum Detection by Leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks and Edge Computing. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 850606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Chang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Ben, Z.; Chen, K. Medicinal Chrysanthemum Detection under Complex Environments Using the MC-LCNN Model. Plants 2022, 11, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoumeh, A.-M.; Sadegh, M.-F.; Abdolhossein Rezaei, N.; Dimitrios, F. Nano-Selenium in the holding solution promotes rose and carnation vase life by improving both water relations and antioxidant status. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 98, 246–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.; Chen, K.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J. Object detection in 20 years: A survey. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 257–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.E.; Wei, G.-Y.; Brooks, D. Benchmarking TPU, GPU, and CPU platforms for deep learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.10701. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, J.D.; Houston, M.; Luebke, D.; Green, S.; Stone, J.E.; Phillips, J.C. GPU computing. Proc. IEEE 2008, 96, 879–899. [Google Scholar]
- Chandana, R.K.; Ramachandra, A.C. Real Time Object Detection System with YOLO and CNN Models: A Review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.00773. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J. Understanding of object detection based on CNN family and YOLO. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 104, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Yang, S.; Li, L.; Feng, Z.; Qu, R. A survey of deep learning-based object detection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128837–128868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Fruit detection and positioning technology for a Camellia oleifera C. Abel orchard based on improved YOLOv4-tiny model and binocular stereo vision. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 211, 118573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponara, S.; Elhanashi, A.; Zheng, Q. Developing a real-time social distancing detection system based on YOLOv4-tiny and bird-eye view for COVID-19. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2022, 19, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, K.; Chu, A.; Wang, G.; Wang, L. An improved light-weight traffic sign recognition algorithm based on YOLOv4-tiny. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 124963–124971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Scaled-yolov4: Scaling cross stage partial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2021, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13029–13038. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.; Jia, Y. Real-time object detection method based on improved YOLOv4-tiny. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.04244. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, W.; He, Y. Real-time strawberry detection using deep neural networks on embedded system (rtsd-net): An edge AI application. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugrul, B.; Elfatimi, E.; Eryigit, R. Convolutional Neural Networks in Detection of Plant Leaf Diseases: A Review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibabaei, K.; Gaspar, P.D.; Lima, T.M.; Campos, R.M.; Girão, I.; Monteiro, J.; Lopes, C.M. A Review of the Challenges of Using Deep Learning Algorithms to Support Decision-Making in Agricultural Activities. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, M.O. Tomato detection based on modified YOLOv3 framework. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, M.; Albogamy, F.; Elgibreen, H.; Algabri, M.; Alqershi, F.A. Deep learning and computer vision for estimating date fruits type, maturity level, and weight. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 206770–206782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahila, P.R.; Arivazhagan, S.; Arun, M.; Mirnalini, A. Maize leaf disease classification using deep convolutional neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 8887–8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, A.; Walsh, K.B.; Wang, Z.; McCarthy, C. Deep learning for real-time fruit detection and orchard fruit load estimation: Benchmarking of ‘MangoYOLO’. Precis. Agric. 2019, 20, 1107–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Duan, J.; Zou, X.; Lin, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Z. Fast and accurate detection of banana fruits in complex background orchards. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 196835–196846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Deng, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Roland, J.T.; Lu, L.; Landman, B.A.; Fogo, A.B.; Huo, Y. Circlenet: Anchor-free detection with circle representation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.02474. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Nouaze, J.C.; Touko, M.P.L.; Kim, J.H. YOLO-tomato: A robust algorithm for tomato detection based on YOLOv3. Sensors 2020, 20, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks Inc. Deep Learning Toolbox Version: 14.5; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
