Assessment of Raisins Byproducts for Environmentally Sustainable Use and Value Addition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
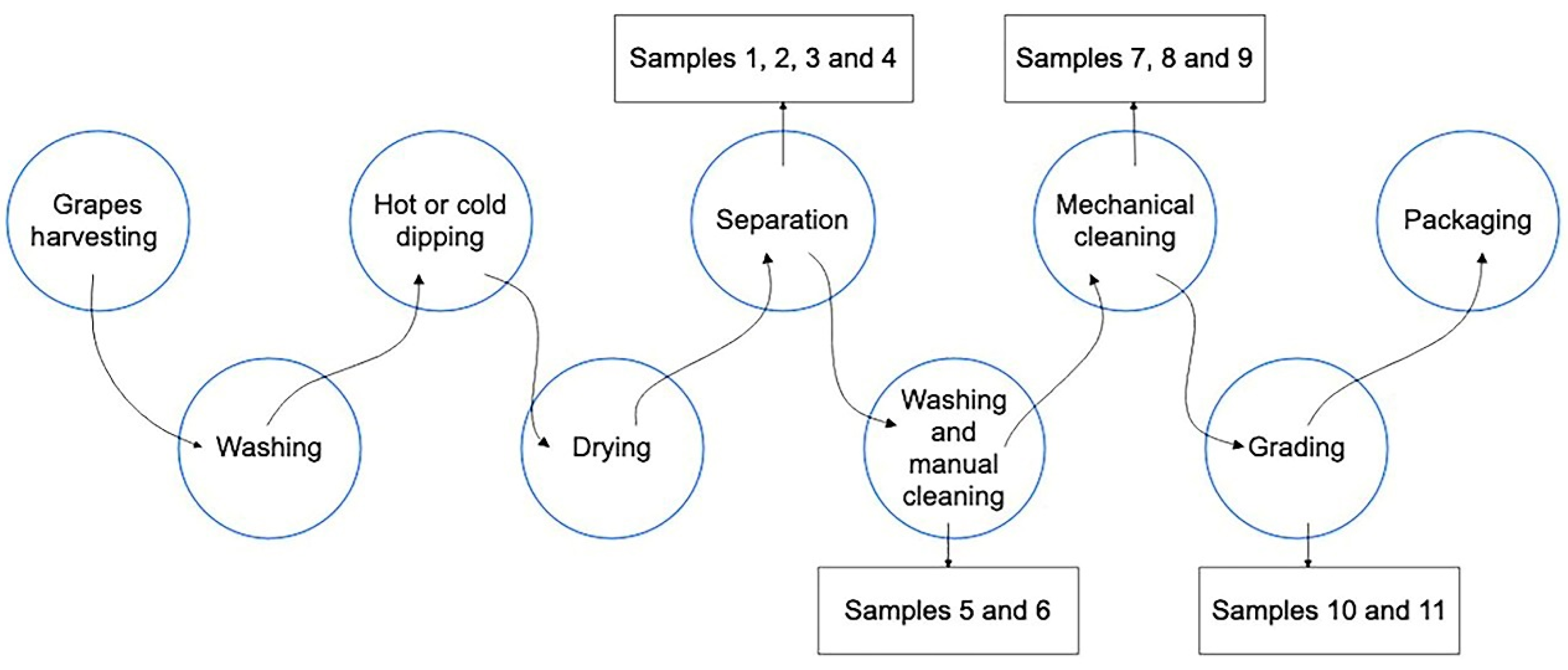
2.1. Preparation of Byproduct Samples
2.2. Ultimate Analysis and Heating Value
2.3. Chemical Composition
2.4. Lignocellulose Composition and Total Solids Concentrations
2.5. Biogas Production
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Data Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
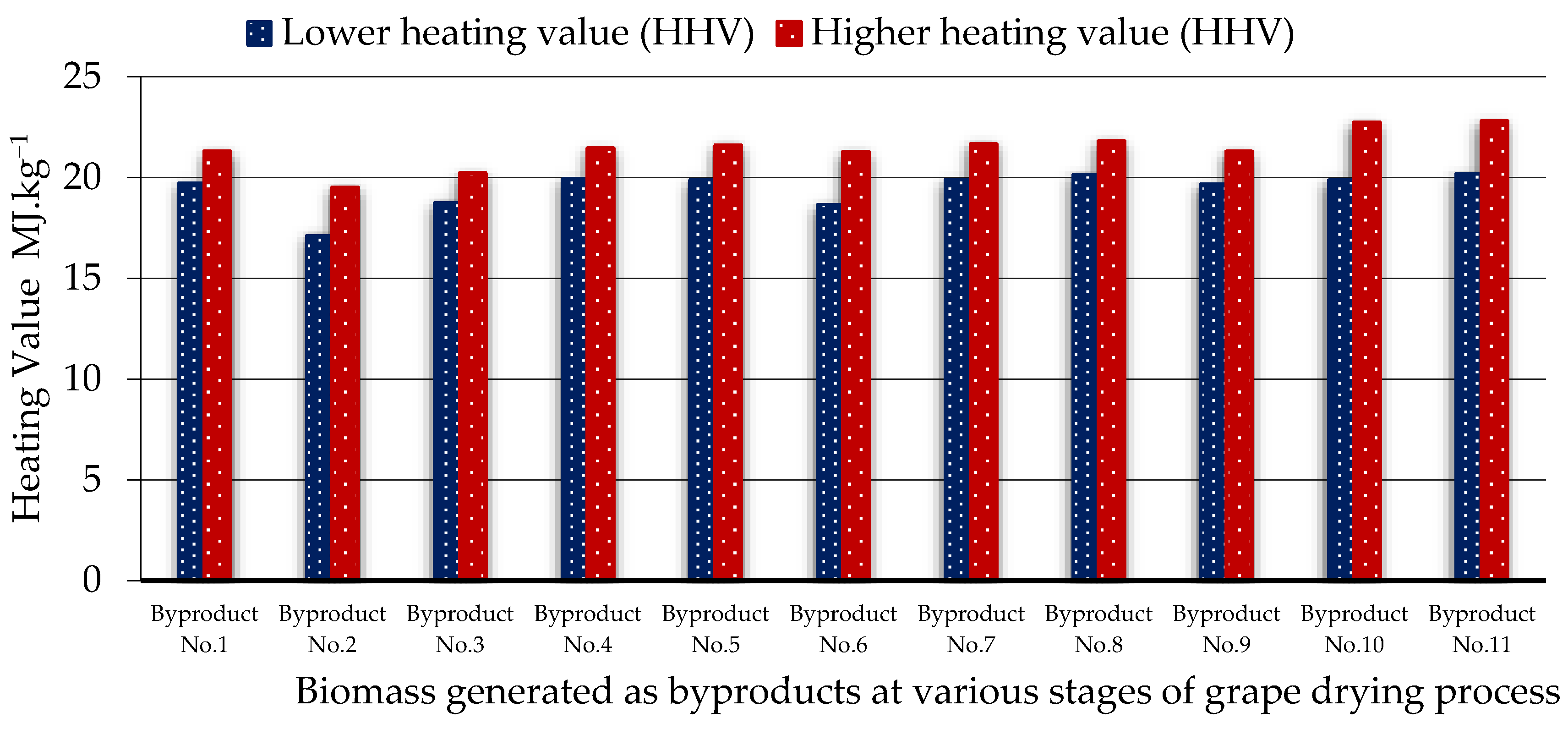
3.1. Ultimate Analysis and Heating Values
3.2. Chemical Compositions
3.3. Lignocellulose Composition of Byproduct Samples
3.4. Total Solids Concentrations
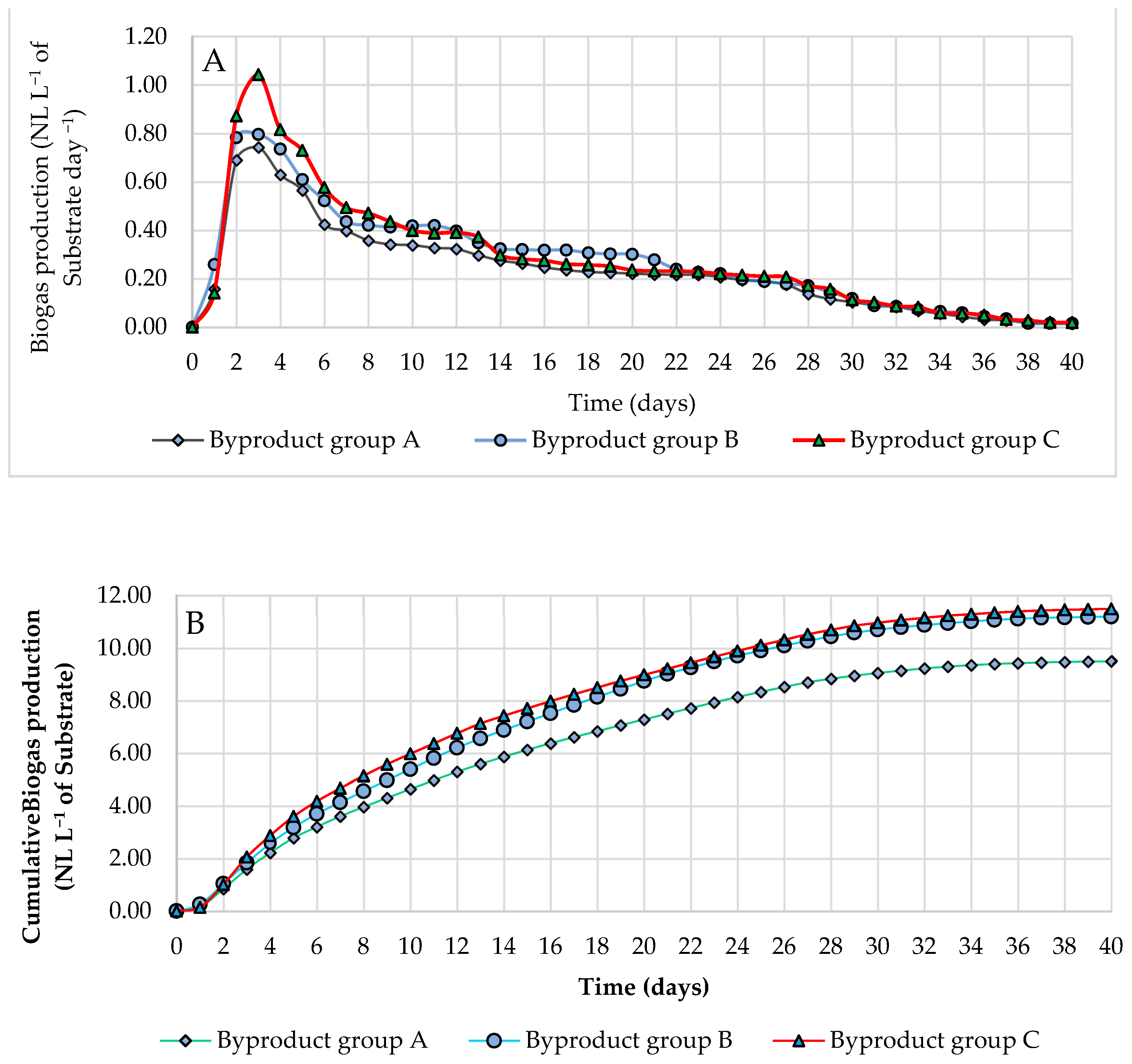
3.5. Biogas Production and Methane Percentages
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OIV, International Organization of Vine and Wine. 2019 Statistical Report on World Vitiviniculture. Available online: http://www.oiv.int/public/medias/6782/oiv-2019-statistical-report-on-world-vitiviniculture.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). Foreign Agricultural Service. Market and Trade Data for the Worldwide Production of Raisins. 2017–2019; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Teixeira, N.; Azevedo, J.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Proanthocyanidin screening by LC–ESI-MS of Portuguese red wines made with teinturier grapes. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiume, M.M.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W. Safety assessment of Vitis vinifera (Grape)-derived ingredients as used in cosmetics. Int. J. Toxic 2014, 33, 48S–83S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, T.P.; Lima, M.A.C.; Alves, R.; Gonçalves, A.L.D.S.; Souza, A.P.C. Chemical characterization of winemaking byproducts from grape varieties cultivated in Vale do São Francisco, Brazil. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-León, C.; Ramírez-Guzman, N.; Londoño-Hernandez, L.; Martinez-Medina, G.A.; Díaz-Herrera, R.; Navarro-Macias, V.; Alvarez-Pérez, O.B.; Picazo, B.; Villarreal-Vázquez, M.; Ascacio-Valdes, J. Food waste and byproducts: An opportunity to minimize malnutrition and hunger in developing countries. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Chen, X.; Cui, J.; Kaparaju, P.; Ellegaard, L. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of source-sorted organic fraction of household municipal solid waste: Start-up procedure for continuously stirred tank reactor. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, L.; Brosse, N.; Sannigrahi, P.; Ragauskas, A. Evaluation of grape stalks as a bioresource. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svinartchuk, T.; Hunziker, P.; Novello, V.; Tonni, M.; Corbet-Milward, J.; de la Fuente, M.; Costa, D. Methodological Recommendations for Accounting for GHG Balance in the Vitivinicultural Sector; OIV—International Organization of Vine and Win, 18 Rue d’Aguesseau: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dinuccio, E.; Balsari, P.; Gioelli, F.; Menardo, S. Evaluation of the biogas productivity potential of some Italian agro-industrial biomasses. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3780–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, G.; De la Torre, N.; Moldes, A.B.; Cruz, J.M.; Domínguez, J.M. Revalorization of hemicellulosic trimming vine shoots hydrolyzates trough continuous production of lactic acid and biosurfactants by L. pentosus. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriariyanun, M.; Gundupalli, M.P.; Phakeenuya, V.; Phusamtisampa, T.; Cheng, Y.; Venkatachalam, P. Biorefinery approaches for production of cellulosic ethanol fuel using recombinant engineered microorganisms. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2023, 27, 1985–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriariyanun, M.; Kitsubthawee, K. Trends in Lignocellulosic Biorefinery for Production of Value-added Biochemicals. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 13, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravindhan, R.; Rao, J.R.; Nair, B.U. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from marine macro-algal biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.H.; Jiang, Y.M.; Shi, J.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Datta, N.; Singanusong, R.; Chen, S.S. Flavonoids in food and their health benefits. Plant Foods Hum. Nut. 2004, 59, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, G.; Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J.; Zając, G.; Słowik, T.; Krzaczek, P.; Piekarski, W. Energy and emission characteristics of biowaste from the corn grain drying process. Energies 2019, 12, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, G.; Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J.; Gołębiowski, W.; Szczepanik, M. Chemical characteristics of biomass ashes. Energies 2018, 11, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Phenol sulfuric total sugar. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldsine, P.; Abeyta, C.; Andrews, W.H. AOAC INTERNATIONAL Methods Committee Guidelines for Validation of Qualitative and Quantitative Food Microbiological Official Methods of Analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 85, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory Methods of Soil and Plant Analysis: A Working Manual, 2nd ed.; Sacred Africa: Nairobi, Kenya, 2002; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nusstrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jančík, F.; Homolka, P.; Čermák, B.; Lád, F. Determination of indigestible neutral detergent fibre contents of grasses and its prediction from chemical composition. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 53, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists). Official Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sendaaza, C. Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Waste: A Kitchen Waste Case Study. Master’s Thesis, The American University, Mechanical Engineering Department, Cairo, Egypt, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Samah, E. Measuring Small-Scale Biogas Capacity and Production; International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA): Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2016; ISBN 978-92-95111-12-7. [Google Scholar]
- EGCSA, Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems Association 2012. A Practical Guide to Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems for the Maritime Industry. EGCSA Handbook 2012. Sustainable Maritime Solutions Ltd. PDF-Document. Available online: https://www.egcsa.com/wp-content/uploads/EGCSA-Handbook-2012-A5-size-.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- UNEP, United Nations Environment Programme 2019. Frontiers 2018/19 Emerging Issues of Environmental Concern, Nairobi. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/27543/Frontiers1819_ch4.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Vivin, P.; Castelan-Estrada, M.; Gaudillere, J.P. Seasonal changes in chemical composition and construction costs of grapevine tissues. VITIS-J. Grapevine Res. 2003, 42, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerini Filho, M.; Lumi, M.; Hasan, C.; Marder, M.; Leite, L.C.S.; Konrad, O. Energy recovery from wine sector wastes: A study about the biogas generation potential in a vineyard from Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 29, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, M.; García-Rojas, M.; Muñoz-Espinoza, C.; Carrasco-Valenzuela, T.; Defilippi, B.; González-Agüero, M.; Meneses, C.; Infante, R.; Hinrichsen, P. Transcriptomic study of pedicels from GA 3-treated table grape genotypes with different susceptibility to berry drop reveals responses elicited in cell wall yield, primary growth and phenylpropanoids synthesis. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burg, P.; Ludín, D.; Rutkowski, K.; Krakowiak-Bal, A.; Travnicek, P.; Zemánek, P.; Turan, J.; Visacki, V. Calorific evaluation and energy potential of grape pomace. Int. Agrophysics 2016, 30, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivkovic, M.; Urosevic, M.; Oljaca, S.; Oljaca, M.; Gligorevic, K.; Zlatanovic, I.; Koprivica, R. Aspects of using potential energy products of biomass after pruning fruit and grape plantations in the Republic of Serbia. Agric. For. 2013, 59, 167–182. [Google Scholar]
- Manzone, M.; Paravidino, E.; Bonifacino, G.; Balsari, P. Biomass availability and quality produced by vineyard management during a period of 15 years. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravalos, I.; Xyradakis, P.; Kateris, D.; Gialamas, T.; Bartzialis, D.; Giannoulis, K. An Experimental Determination of Gross Calorific Value of Different Agroforestry Species and Bio-Based Industry Residues. Nat. Resour. 2016, 7, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacan, C.Ö.; Olea, R.A. Mapping of compositional properties of coal using isometric log-ratio transformation and sequential Gaussian simulation–A comparative study for spatial ultimate analyses data. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 186, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, E.C.; Uchôa-Thomaz, A.M.A.; Carioca, J.O.B.; Morais, S.M.; Lima, A.; Martin, C.G.; Alexandrino, C.D.; Ferreira, P.A.T.; Rodrigues, A.L.M.; Rodrigues, S.P. Chemical composition and bioactive compounds of grape pomace (Vitis vinifera L.), Benitaka variety, grown in the semiarid region of Northeast Brazil. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobera, A.; Cañellas, J. Antioxidant activity and dietary fibre of Prensal Blanc white grape (Vitis vinifera) byproducts. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, C.J.K. Anaerobic co-digestion of fruit juice industry wastes with lignocellulosic biomass. Master’s Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Western Cape, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Prozil, S.O.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Lopes, L.P.C. Chemical composition of grape stalks of Vitis vinifera L. from red grape pomaces. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 35, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigno, G.; Maggi, L.; Amendola, D.; Dragoni, M.; De Faveri, D.M. Influence of cultivar on the lignocellulosic fractionation of grape stalks. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.H.; Yip, C.H.; Nie, W.L.S. A Case Study on the Anaerobic Treatment of Food Waste and Gas Formation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Construction and Building Technology (ICCBT), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 16–20 June 2008; pp. 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Deressa, L.; Libsu, S.; Chavan, R.B.; Manaye, D.; Dabassa, A. Production of biogas from fruit and vegetable wastes mixed with different wastes. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2015, 3, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomeda-De Mesa, R.A.P.; Soriano, A.N.; Marquez, A.R.D.; Adornado, A.P. Physical and Chemical Properties of Philippine Coal Blended with Torrefied Biomass from Rice (Oryza sativa) Straw. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, 2nd International Conference on Green Energy and Environment Engineering, Okinawa, Japan, 2–5 July 2019; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2019; p. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, R.; Takeuchi, H.; Hasegawa, T. Methane production from lignocellulosic agricultural crop wastes: A review in context to second generation of biofuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darimani, H.S.; Pant, D.C. Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Grass with Food Waste. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2019, 9, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olugbemide, A.D.; Likozar, B. Assessment of Liquid and Solid Digestates from Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Husk as Potential Biofertilizer and Nutrient Source for Microalgae Cultivation. Processes 2022, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Polo, C.; Cledera-Castro, M.D.M.; Soria, B.Y.M. Biogas Production from Vegetable and Fruit Markets Waste—Compositional and Batch Characterizations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, A.; Power, N. Modelling methane production kinetics of complex poultry slaughterhouse wastes using sigmoidal growth functions. Renew. Energy 2017, 104, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Byproduct | Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (%) ± SD | N (%) ± SD | H (%) ± SD | S (%) ± SD | O * (%) ± SD | Ash (%) ± SD | |
| Byproduct 1 | 40.82 ± 0.03 g | 1.82 ± 0.09 f | 5.60 ± 0.04 c | 0.12 ± 0.03 a | 43.85 ± 0.03 b | 7.79 ± 0.12 a |
| Byproduct 2 | 45.62 ± 0.02 ab | 1.98 ± 0.12 ef | 5.18 ± 0.04 e | 0.17 ± 0.05 a | 41.25 ± 0.16 e | 5.80 ± 0.07 c |
| Byproduct 3 | 44.17 ± 0.01 cd | 2.08 ± 0.11 de | 5.27 ± 0.05 de | 0.12 ± 0.04 a | 42.51 ± 0.06 cd | 5.85 ± 0.07 c |
| Byproduct 4 | 45.95 ± 0.03 a | 2.48 ± 0.05 b | 5.38 ± 0.03 d | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 39.31 ± 0.07 f | 6.78 ± 0.04 b |
| Byproduct 5 | 43.21 ± 0.01 e | 1.99 ± 0.04 ef | 5.89 ± 0.03 b | 0.10 ± 0.05 a | 43.70 ± 0.10 b | 5.11 ± 0.03 e |
| Byproduct 6 | 46.43 ± 0.01 a | 1.41 ± 0.06 g | 6.07 ± 0.05 a | 0.11 ± 0.03 a | 41.41 ± 0.07 e | 4.57 ± 0.06 g |
| Byproduct 7 | 44.93 ± 0.06 bc | 2.68 ± 0.03 a | 6.06 ± 0.05 a | 0.07 ± 0.03 a | 41.79 ± 0.09 de | 4.47 ± 0.04 g |
| Byproduct 8 | 43.65 ± 0.1 de | 1.99 ± 0.04 ef | 6.04 ± 0.06 a | 0.09 ± 0.03 a | 43.48 ± 0.10 b | 4.75 ± 0.05 f |
| Byproduct 9 | 43.16 ± 0.01 e | 2.36 ± 0.04 bc | 5.80 ± 0.02 b | 0.15 ± 0.03 a | 43.14 ± 0.06 bc | 5.40 ± 0.04 d |
| Byproduct 10 | 42.25 ± 0.03 f | 2.04 ± 0.04 e | 6.06 ± 0.02 a | 0.13 ± 0.05 a | 45.85 ± 0.14 a | 3.65 ± 0.06 i |
| Byproduct 11 | 43.67 ± 0.01 de | 2.28 ± 0.04 cd | 6.13 ± 0.03 a | 0.15 ± 0.04 a | 43.73 ± 0.02 b | 4.05 ± 0.05 h |
| Byproduct | Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content (%) ± SD | Total Sugar (%) ± SD | Total Carbohydrates (%) ± SD | Fiber (%) ± SD | Protein Content (%) ± SD | K (%) ± SD | |
| Byproduct 1 | 4.41 ± 0.3 h | 26.86 ± 0.06 d | 46.55 ± 0.03 e | 4.20 ± 0.02 b | 9.43 ± 0.28 f | 1.29 ± 0.2 b |
| Byproduct 2 | 5.11 ± 0.05 g | 27.18 ± 0.04 d | 46.12 ± 0.05 f | 3.81 ± 0.02 c | 10.51 ± 0.03 d | 1.20 ± 0.02 cd |
| Byproduct 3 | 4.54 ± 0.04 h | 24.42 ± 0.10 f | 46.24 ± 0.07 f | 4.22 ± 0.07 b | 9.40 ± 0.04 f | 1.27 ± 0.01 bc |
| Byproduct 4 | 6.19 ± 0.03 e | 24.35 ± 0.16 f | 46.27 ± 0.06 f | 4.60 ± 0.25 a | 9.90 ± 0.06 e | 1.10 ± 0.07 e |
| Byproduct 5 | 5.65 ± 0.04 f | 21.83 ± 0.60 g | 47.27 ± 0.04 d | 3.85 ± 0.02 c | 12.21 ± 0.03 b | 1.017 ± 0.01 f |
| Byproduct 6 | 5.65 ± 0.03 f | 25.27 ± 0.05 ef | 48.51 ± 0.04 c | 3.39 ± 0.02 e | 10.26 ± 0.09 d | 1.02 ± 0.01 f |
| Byproduct 7 | 7.90 ± 0.02 c | 28.14 ± 0.03 d | 49.27 ± 0.04 b | 2.60 ± 0.02 ef | 12.41 ± 0.12 b | 1.07 ± 0.01 ef |
| Byproduct 8 | 7.27 ± 0.02 d | 26.60 ± 0.07 de | 47.19 ± 0.04 d | 2.85 ± 0.06 e | 12.16 ± 0.01 b | 1.38 ± 0.02 a |
| Byproduct 9 | 8.88 ± 0.03 b | 29.55 ± 0.22 c | 48.52 ± 0.08 c | 2.50 ± 0.05 f | 11.80 ± 0.02 c | 1.18 ± 0.01 d |
| Byproduct 10 | 9.15 ± 0.02 ab | 39.28 ± 0.04 b | 49.79 ± 0.13 a | 1.80 ± 0.04 g | 13.77 ± 0.05 a | 1.09 ± 0.02 e |
| Byproduct 11 | 9.24 ± 0.03 a | 41.18 ± 0.03 a | 49.80 ± 0.06 a | 2.03 ± 0.03 g | 13.93 ± 0.05 a | 1.08 ± 0.01 ef |
| Byproduct | Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDF (% TS) ± SD | ADF (% TS) ± SD | ADL (% TS) ± SD | CE * (% TS) ± SD | HC * (% TS) ± SD | |
| Byproduct 1 | 61.62 ± 0.02 a | 46.24 ± 0.07 abc | 23.24 ± 0.07 cd | 22.10 ± 0.01 c | 15.56 ± 0.08 ab |
| Byproduct 2 | 61.80 ± 0.08 a | 46.43 ± 0.08 ab | 23.37 ± 0.04 bc | 23.06 ± 0.04 bc | 15.19 ± 0.15 bc |
| Byproduct 3 | 61.30 ± 0.07 ab | 46.78 ± 0.17 a | 23.26 ± 0.08 cd | 23.52 ± 0.18 ab | 14.52 ± 0.34 de |
| Byproduct 4 | 61.57 ± 0.18 a | 46.52 ± 0.09 ab | 23.55 ± 0.01 a | 22.98 ± 0.09 c | 15.05 ± 0.24 bcd |
| Byproduct 5 | 61.09 ± 0.58 ab | 45.17 ± 0.09 d | 22.38 ± 0.04 g | 22.79 ± 0.12 c | 15.92 ± 0.51 a |
| Byproduct 6 | 60.70 ± 0.05 b | 46.00 ± 0.55 bc | 22.37 ± 0.07 g | 23.63 ± 0.48 a | 14.70 ± 0.11 cd |
| Byproduct 7 | 58.32 ± 0.06 d | 45.83 ± 0.08 c | 22.79 ± 0.05 f | 23.05 ± 0.07 bc | 12.48 ± 0.09 f |
| Byproduct 8 | 58.29 ± 0.11 d | 44.33 ± 0.03 e | 22.96 ± 0.07 e | 21.37 ± 0.04 e | 13.96 ± 0.09 e |
| Byproduct 9 | 59.39 ± 0.06 c | 44.50 ± 0.20 e | 22.23 ± 0.07 g | 22.28 ± 0.13 d | 14.89 ± 0.26 cd |
| Byproduct 10 | 55.39 ± 0.92 e | 43.68 ± 0.03 f | 23.20 ± 0.05 d | 20.48 ± 0.02 f | 11.71 ± 0.08 g |
| Byproduct 11 | 55.24 ± 0.07 e | 43.66 ± 0.10 f | 23.49 ± 0.07 ab | 20.17 ± 0.12 f | 11.58 ± 0.03 g |
| Byproduct | Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS (%) Byproduct | VS (% TS) Byproduct | TS (%) Inoculum | VS (% TS) Inoculum | pH Inoculum | |
| Byproduct 1 | 31.70 ± 0.04 d | 93.82 ± 0.06 a | 7.66 ± 0.02 f | 81.37 ± 0.06 a | 7.64 ± 0.01 c |
| Byproduct 2 | 31.30 ± 0.04 d | 93.30 ± 0.07 bc | 7.58 ± 0.01 cd | 81.23 ± 0.05 a | 7.58 ± 0.01 d |
| Byproduct 3 | 31.22 ± 0.06 d | 93.18 ± 0.07 c | 7.62 ± 0.01 bcd | 80.77 ± 0.27 b | 7.72 ± 0.01 b |
| Byproduct 4 | 31.37 ± 0.04 d | 93.49 ± 0.06 b | 7.72 ± 0.01 a | 81.22 ± 0.06 a | 7.35 ± 0.01 e |
| Byproduct 5 | 34.53 ± 0.05 c | 92.78 ± 0.11 d | 7.65 ± 0.03 abc | 79.37 ± 0.04 c | 7.77 ± 0.01 a |
| Byproduct 6 | 34.61 ± 0.07 c | 92.84 ± 0.09 d | 7.56 ± 0.04 d | 79.23 ± 0.07 c | 7.12 ± 0.02 f |
| Byproduct 7 | 34.88 ± 0.04 bc | 92.67 ± 0.04 d | 7.43 ± 0.01 e | 79.32 ± 0.07 b | 7.36 ± 0.01 e |
| Byproduct 8 | 34.84 ± 0.54 bc | 92.08 ± 0.18 e | 7.40 ± 0.03 e | 80.63 ± 0.02 d | 6.81 ± 0.01 g |
| Byproduct 9 | 34.61 ± 0.06 c | 92.25 ± 0.08 e | 7.31 ± 0.03 f | 78.69 ± 0.02 d | 6.48 ± 0.02 i |
| Byproduct 10 | 35.20 ± 0.04 ab | 91.29 ± 0.05 g | 7.32 ± 0.03 f | 78.59 ± 0.05 d | 6.90 ± 0.01 g |
| Byproduct 11 | 35.46 ± 0.05 a | 91.54 ± 0.07 f | 7.29 ± 0.06 f | 79.36 ± 0.02 c | 6.74 ± 0.01 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okasha, M.; Hegazy, R.; Kamel, R.M. Assessment of Raisins Byproducts for Environmentally Sustainable Use and Value Addition. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 1469-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5030091
Okasha M, Hegazy R, Kamel RM. Assessment of Raisins Byproducts for Environmentally Sustainable Use and Value Addition. AgriEngineering. 2023; 5(3):1469-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5030091
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkasha, Mahmoud, Rashad Hegazy, and Reham M. Kamel. 2023. "Assessment of Raisins Byproducts for Environmentally Sustainable Use and Value Addition" AgriEngineering 5, no. 3: 1469-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5030091
APA StyleOkasha, M., Hegazy, R., & Kamel, R. M. (2023). Assessment of Raisins Byproducts for Environmentally Sustainable Use and Value Addition. AgriEngineering, 5(3), 1469-1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5030091








