Classification of Pear Leaf Diseases Based on Ensemble Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Dataset
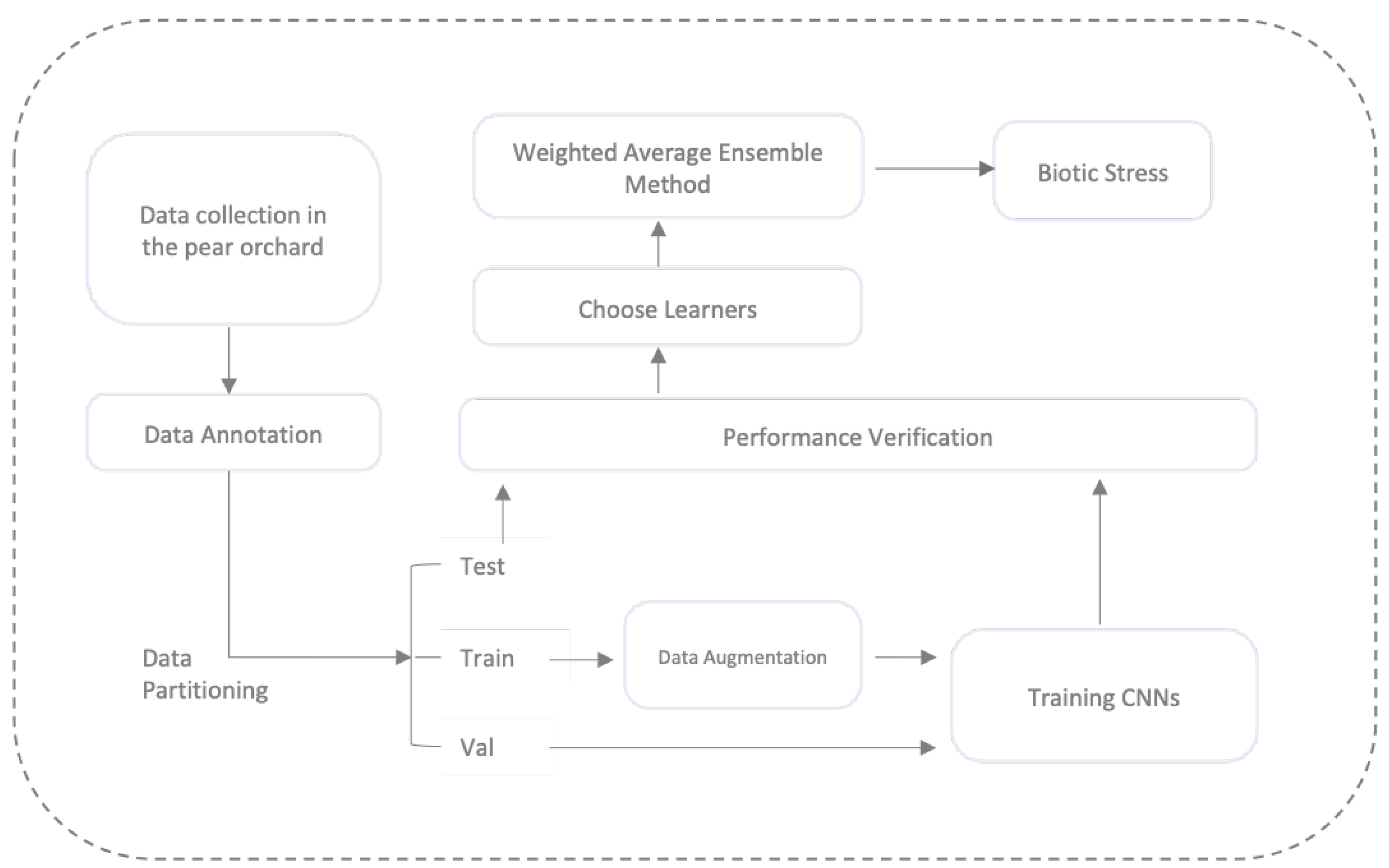
2.2. Experimental Approach
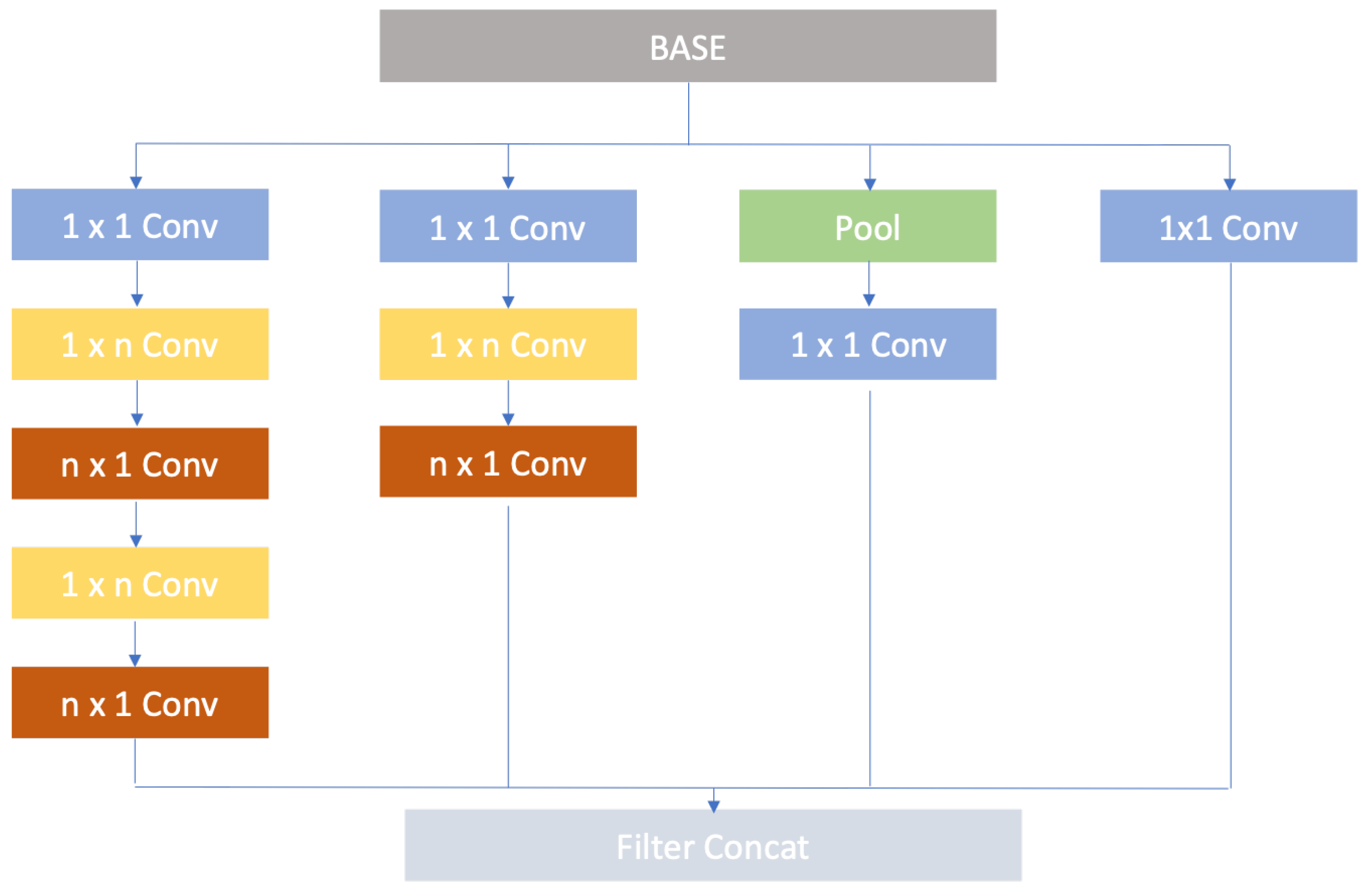
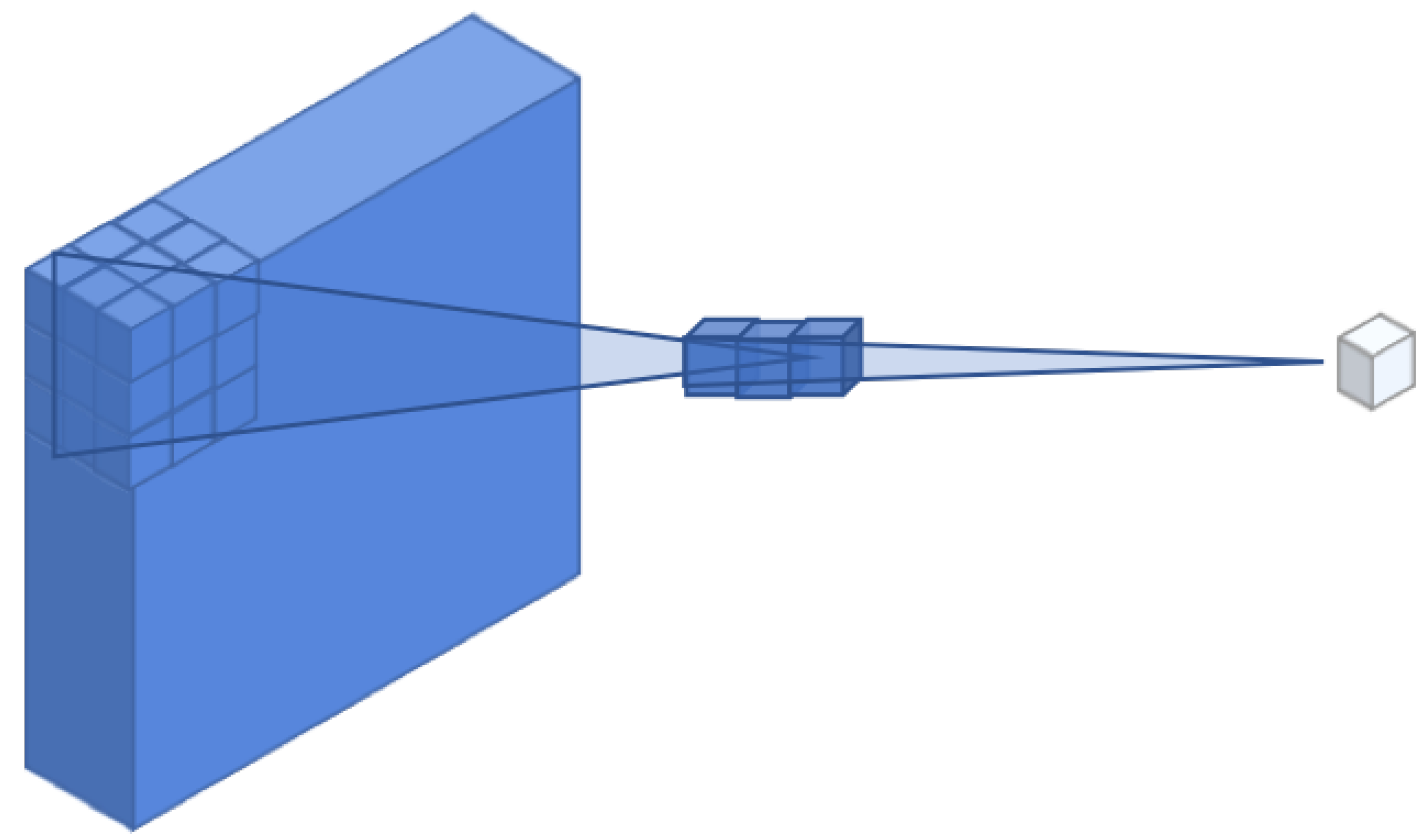
2.3. Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
2.4. Transfer Learning
2.5. Data Augmentation
2.6. Proposed Ensemble Convolutional Neural Network
| Algorithm 1: The detailed illustration of the algorithm. |
Input : Leaf Images using dataset D Output: Class prediction 1 Step 1: D is divided into training set () (60%), validation set ()(20%), test set () (20%) 2 Step 2: Pre-processing: 3 The input images are resized to 224 × 224 × 3 4 The input images are normalized 5 The data augmentation techniques are applied 6 Step 3: Training 7 foreach 8 l = 0.001 9 for epochs = 1 to 100 do 10 Update the parameters of the model n 11 foreach mini batch () ∈ () do 12 if the test accuracy is not improving for 10 epochs then 13 l = l × 0.2 14 end 15 end 16 end 17 end 18 Step 4: 19 foreach do 20 ensemble the output of all networks 21 end |
2.7. Evaluation Metrics
- Accuracy is defined as ;
- Precision is defined as ;
- Recall is defined as ;
- F1 score is defined as ;
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| DSS | Decision Support System |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| ECNN | Ensemble convolutional neural network |
| RF | Random Forest |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
References
- Fenu, G.; Malloci, F.M. Using Multi-Output Learning to Diagnose Plant Disease and Stress Severity. Complexity 2021, 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenu, G.; Malloci, F.M. Forecasting Plant and Crop Disease: An Explorative Study on Current Algorithms. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2021, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Tan, L.; Jiang, H. Review on convolutional neural network (CNN) applied to plant leaf disease classification. Agriculture 2021, 11, 707. [Google Scholar]
- Fenu, G.; Malloci, F.M. An Application of Machine Learning Technique in Forecasting Crop Disease. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Big Data Research, Cergy-Pontoise, France, 20–22 November 2019; pp. 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahimi, M.; Boukhalfa, K.; Moussaoui, A. Deep learning for tomato diseases: Classification and symptoms visualization. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 31, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. Deep learning in agriculture: A survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Dang, L.M.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Moon, H. Crop pest recognition in natural scenes using convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereciartua-Pérez, A.; Gómez, L.; Picón, A.; Navarra-Mestre, R.; Klukas, C.; Eggers, T. Insect counting through deep learning-based density maps estimation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, W.; Wei, X. A review on weed detection using ground-based machine vision and image processing techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 158, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevavuori, P.; Narra, N.; Lipping, T. Crop yield prediction with deep convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 163, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarrak, K.; Gulzar, Y.; Hamid, Y.; Mehmood, A.; Soomro, A.B. A Deep Learning-Based Model for Date Fruit Classification. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.; Wani, S.; Soomro, A.B.; Alwan, A.A.; Gulzar, Y. Smart Seed Classification System based on MobileNetV2 Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Computing and Information Technology (ICCIT), Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, 25–27 January 2022; pp. 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladojevic, S.; Arsenovic, M.; Anderla, A.; Culibrk, D.; Stefanovic, D. Deep neural networks based recognition of plant diseases by leaf image classification. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 3289801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yi, S.; Zeng, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Identification of rice diseases using deep convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing 2017, 267, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, D.; Li, Y. Identification of apple leaf diseases based on deep convolutional neural networks. Symmetry 2017, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferentinos, K.P. Deep learning models for plant disease detection and diagnosis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, E.C.; Yujian, L.; Njuki, S.; Yingchun, L. A comparative study of fine-tuning deep learning models for plant disease identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 161, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Hassanien, A.E.; Pandey, H.M. An optimized dense convolutional neural network model for disease recognition and classification in corn leaf. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramcharan, A.; McCloskey, P.; Baranowski, K.; Mbilinyi, N.; Mrisho, L.; Ndalahwa, M.; Legg, J.; Hughes, D.P. A mobile-based deep learning model for cassava disease diagnosis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 2019, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javierto, D.P.P.; Martin, J.D.Z.; Villaverde, J.F. Robusta Coffee Leaf Detection based on YOLOv3- MobileNetv2 model. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 13th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment, and Management (HNICEM), Manila, Philippines, 28–30 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.M.; Maji, A.K.; Jasiński, M.; Leonowicz, Z.; Jasińska, E. Identification of plant-leaf diseases using CNN and transfer-learning approach. Electronics 2021, 10, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Guo, S.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, X. A survey on deploying mobile deep learning applications: A systemic and technical perspective. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenu, G.; Malloci, F.M. DiaMOS plant: A dataset for diagnosis and monitoring plant disease. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenu, G.; Malloci, F.M. Evaluating impacts between laboratory and field-collected datasets for plant disease classification. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Hamid, M.; Yousaf, S.; Shah, S.T.; Ahmad, M.O. Optimizing Pretrained Convolutional Neural Networks for Tomato Leaf Disease Detection. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8812019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Sistla, V.; Kolli, V.K.K. Transfer learning-based deep ensemble neural network for plant leaf disease detection. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2022, 129, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutaji, D.; Yıldız, O. LEMOXINET: Lite ensemble MobileNetV2 and Xception models to predict plant disease. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N. Plant leaf disease detection using ensemble classification and feature extraction. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. (TURCOMAT) 2021, 12, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zeb, A.; Nanehkaran, Y.; Zhang, D. Stacking ensemble model of deep learning for plant disease recognition. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
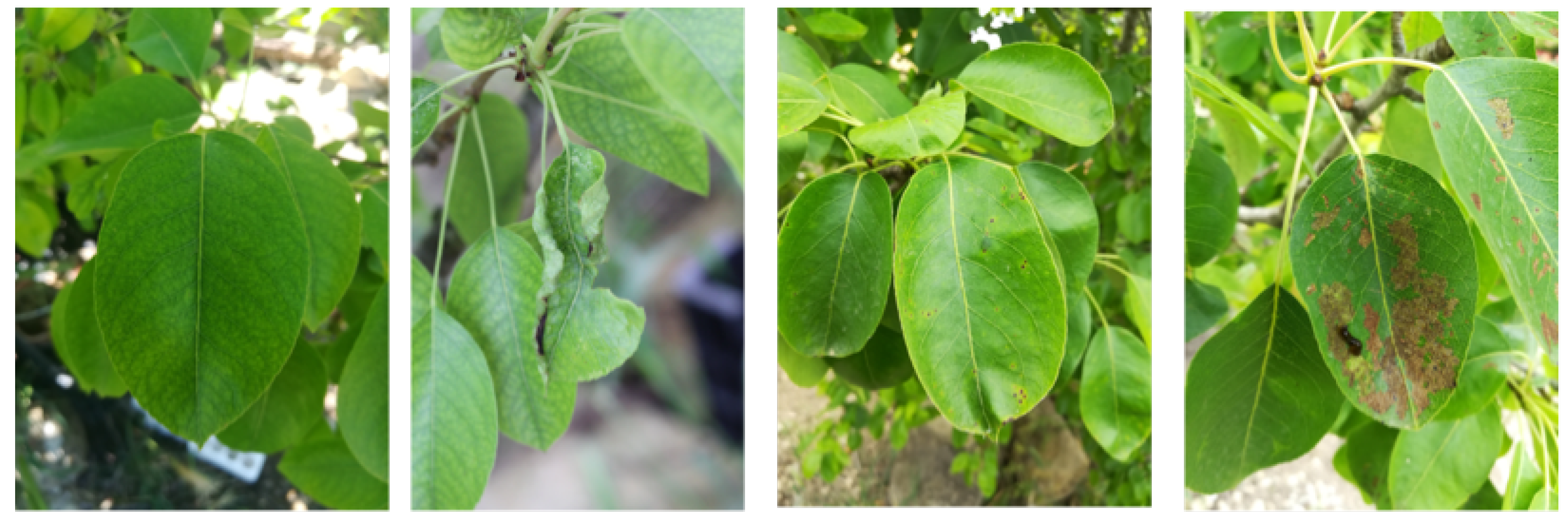

| DiaMOS Plant Dataset [23] | |
|---|---|
| Plant | Pear |
| Cultivar | Septoria Piricola |
| Type of data | RGB Images |
| ROI (Region of Interest) captured | leaf, fruit |
| Total size | 3505 images (3006 leaves images + 499 fruit images) |
| Data Accessibility | https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5557313 Date: 16 January 2023 |
| Application | The images are suitable for different machine and |
| deep learning tasks such as images detection | |
| and classification. | |
| Smartphone Camera | DSRL Camera | |
|---|---|---|
| Image size | 2976 × 3968 | 3456 × 5184 |
| Model device | Honor 6× | Canon EOS 60D |
| Focal length | 3.83 mm | 50 mm |
| Focal ratio | f/2.2 | f/4.5 |
| Color space | RGB | RGB |
| Leaf Disease | Size |
|---|---|
| Healthy | 43 |
| Spot | 884 |
| Curl | 54 |
| Slug | 2025 |
| Total | 3006 |
| Accuracy (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | Optimizer | Train | Validation | Test |
| EfficientNetB0 | RMSprop | 81.13 | 82.82 | 83.38 |
| Adam | 89.02 | 86.33 | 86.05 | |
| InceptionV3 | RMSprop | 81.96 | 79.66 | 82.72 |
| Adam | 84.44 | 80.29 | 83.39 | |
| MobileNetV2 | RMSprop | 85.38 | 81.12 | 83.06 |
| Adam | 87.70 | 83.83 | 84.05 | |
| VGG19 | RMSprop | 72.42 | 71.68 | 73.75 |
| Adam | 76.66 | 76.53 | 75.75 | |
| CNN | Optimizer | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetB0 | RMSprop | 81.14 | 83.38 | 82.23 |
| Adam | 84.42 | 86.04 | 85.03 | |
| InceptionV3 | RMSprop | 80.21 | 82.72 | 81.45 |
| Adam | 81.14 | 83.38 | 82.23 | |
| MobileNetV2 | RMSprop | 81.35 | 83.05 | 82.07 |
| Adam | 82.37 | 84.05 | 83.06 | |
| VGG19 | RMSprop | 70.47 | 73.75 | 71.76 |
| Adam | 72.71 | 75.74 | 74.05 |
| Test Accuracy—Weighted Average | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensemble CNNS | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) |
| EfficientNetB0 + InceptionV3 | 91.14 | 89.84 | 90.02 | 89.93 |
| EfficientNetB0 + MobileNetV2 | 86.21 | 84.13 | 85.51 | 84.82 |
| InceptionV3 + MobileNetV2 | 85.35 | 83.02 | 85.14 | 84.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fenu, G.; Malloci, F.M. Classification of Pear Leaf Diseases Based on Ensemble Convolutional Neural Networks. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010009
Fenu G, Malloci FM. Classification of Pear Leaf Diseases Based on Ensemble Convolutional Neural Networks. AgriEngineering. 2023; 5(1):141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleFenu, Gianni, and Francesca Maridina Malloci. 2023. "Classification of Pear Leaf Diseases Based on Ensemble Convolutional Neural Networks" AgriEngineering 5, no. 1: 141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010009
APA StyleFenu, G., & Malloci, F. M. (2023). Classification of Pear Leaf Diseases Based on Ensemble Convolutional Neural Networks. AgriEngineering, 5(1), 141-152. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010009







