Development and Evaluation of a Small-Scale Apple Sorting Machine Equipped with a Smart Vision System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Acquisition System
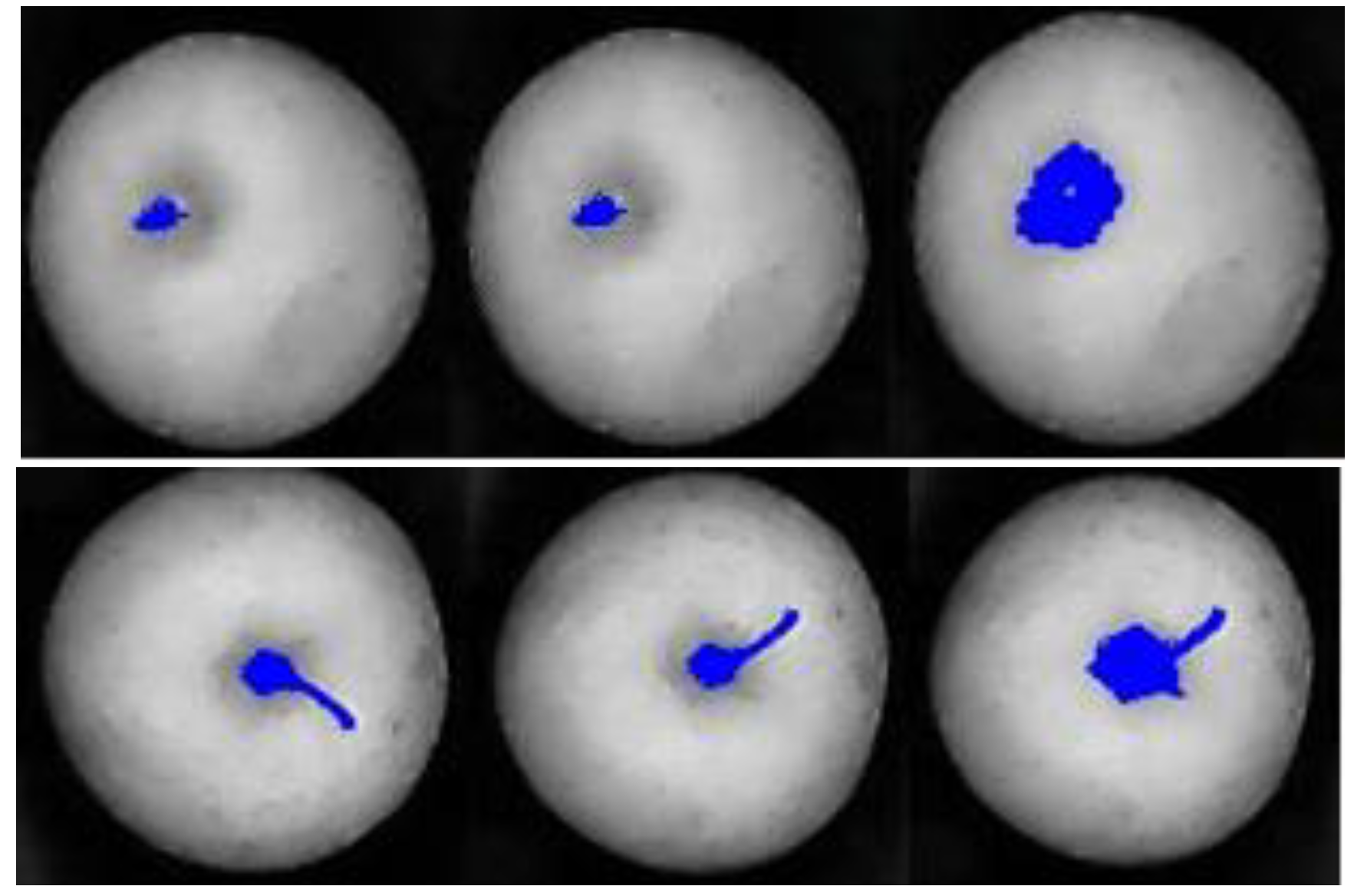
2.2. Stem and Calyx Recognition
2.3. Classification Method
2.4. Feature Extraction
2.5. Segmentation of Image by Niblack Thresholding
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Li, Y. Computer vision technology in agricultural automation—A review. Inf. Process. Agric. 2019, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.K.; Sengar, N.; Minhas, N.; Sarkar, B.; Goon, A.; Banerjee, K. Image processing based classification of grapes after pesticide exposure. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneh, N.M.; Navid, H.; Kafashan, J. Mechatronic components in apple sorting machines with computer vision. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1135–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, E.; Siche, R.; Castro, W.; Huaman, R.; Quevedo, R. Measurement parameter of color on yacon (Smallanthus sonchi-folius) slices using a computer vision system. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; Zhou, G.; He, M. Detection of Apple Defects Based on the FCM-NPGA and a Multivariate Image Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 38833–38845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennedsen, B.; Peterson, D.; Tabb, A. Identifying defects in images of rotating apples. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 48, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, J.; Aleixos, N.; Molto, E. Machine Vision System for Automatic Quality Grading of Fruit. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 85, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, Y.C.; Chen, C.H. Development of online apple bruise detection system. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 2017, 10, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throop, J.; Aneshansley, D.; Anger, W.; Peterson, D. Quality evaluation of apples based on surface defects: Development of an automated inspection system. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2005, 36, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Tao, Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Lou, Y. NIR-MIR dual sensor machine vision system for online apple stem end/calyx recog-nition. Trans. ASAE 2003, 46, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekramirad, N.; Khaled, A.Y.; Doyle, L.E.; Loeb, J.R.; Donohue, K.D.; Villanueva, R.T.; Adedeji, A.A. Nondestructive Detection of Codling Moth Infestation in Apples Using Pixel-Based NIR Hyperspectral Imaging with Machine Learning and Feature Selection. Foods 2021, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohana, S.H.; Prabhakar, C.J. Stem- calyx recognition of an apple using shape descriptors. Signal Image Process. Ternational J. 2014, 5, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Jancsók, P.; De Baerdemaeker, J. Stem-end/Calyx Identification on Apples using Contour Analysis in Multispectral Images. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 96, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, A.; Lu, R. A low-cost color vision system for automatic estimation of apple fruit orientation and maximum equatorial diameter. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 813–827. [Google Scholar]
- Kafashan, J.; Tijskens, B.; Ramon, H. Shape modelling of fruit by image processing. Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2005, 70, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Lillywhite, K.D.; Lee, D.-J.; Tippetts, B.J. Automated apple stem end and calyx detection using evolution-constructed features. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, X.; Luo, Y.; Tao, Y. 3D structure reconstruction and analysis in automated apple stem-end/calyx identification. Trans. ASABE 2009, 52, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Tao, Y. Dual-camera NIR/MIR imaging system for stem-end/calyx identification in apple defect sorting. Trans. ASAE 2000, 43, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, D.W. Determination of stem and calyx location on apples using automatic visual inspection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2001, 33, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallem, P.; Serajoddin, A.; Pourghassem, H. Computer vision-based apple grading for golden delicious apples based on surface features. Inf. Process. Agric. 2017, 4, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofu, M.; Er, O.; Kayacan, M.; Cetişli, B. Design of an automatic apple sorting system using machine vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Wang, C.; Gong, L.; Zhao, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, D. Computer vision recognition of stem and calyx in apples using near-infrared linear-array structured light and 3D reconstruction. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 139, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Guo, Z. Automatic detection of defective apple using NIR coded and structured light and fast lightness correction. J. Food Eng. 2017, 203, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Ni, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, B.; Xu, L. A segmentation method of red apple image. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, L.; Ma, Z.; Yang, B. A segmentation method of bagged green apple image. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyaz, A. Harvest glove and LabView based mechanical damage determination on apples. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 228, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unay, D.; Gosselin, B. Stem and calyx recognition on ‘Jonagold’ apples by pattern recognition. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, L. Stem and Calyx Identification of 3D Apples Using Multi-Threshold Segmentation and 2D Convex Hull. Photonics 2022, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Efficient extraction of deep image features using convolutional neural network (CNN) for applica-tions in detecting and analysing complex food matrices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zhu, J.; Ren, T. Detection of apple defect using laser-induced light backscattering imaging and convolutional neural network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 81, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C.; Cui, Z.; Niu, C. A new lightweight deep neural network for surface scratch detection. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 123, 1999–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jia, X.; Huang, W.; He, X.; Li, L.; Fan, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, C. Real-Time Grading of Defect Apples Using Semantic Segmentation Combination with a Pruned YOLO V4 Network. Foods 2022, 11, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.; Guan, L.; Lim, K.; Karim, A. The applications of computer vision system and tomographic radar imaging for assessing physical properties of food. J. Food Eng. 2004, 61, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heiden, F.; Duin, R.; de Ridder, D.; Tax, D. Classification, Parameter Estimation, and State Estimation: An Engineering Approach Using MATLAB; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nirpjeet, K.E.; Rajpreet, K.E. A review on various methods of image thresholding. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 3, 3441–3443. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Gong, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, D. Computer vision detection of defective apples using automatic lightness correction and weighted RVM classifier. J. Food Eng. 2015, 146, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, I.; Alam, N.; Gwun, O. Calyx and Stem Discrimination for Apple Quality Control Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Int. Conf. Technol. Trends 2018, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Velastin, S.A.; Yin, F. Automatic grading of apples based on multi-features and weighted K-means clustering algorithm. Inf. Process. Agric. 2020, 7, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Bo, Z.; Jie-Wen, Z.; Yanxiao, L.; Holmes, M. In-line detection of apple defects using three color cameras system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2009, 70, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unay, D.; Gosselin, B.; Kleynen, O.; Leemans, V.; Destain, M.F.; Debeir, O. Automatic grading of bi-colored apples by mul-tispectral machine vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 75, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, P.; Mazurek, W.; Pastuszka-Woźniak, J.; Majewska, U. Detection of early bruises in apples using hyperspectral data and thermal imaging. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.R.; Jalal, A.S. Detection and Classification of Apple Fruit Diseases Using Complete Local Binary Patterns. In Proceedings of the 2012 Third International Conference on Computer and Communication Technology, Allahabad, India, 23–25 November 2012; pp. 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresha, M.; Shilpa, N.A.; Soumya, B. Apples grading based on SVM classifier. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 975, 8878. [Google Scholar]
- Mohana, S.H.; Prabhakar, C.J.; Praveen Kumar, P.U. Surface defect detection and grading of apples. In Proceedings of the International conference on MPCIT, Shimoga, India, 19–21 December 2013; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima, A.; Lu, R. An image segmentation method for apple sorting and grading using support vector machine and Otsu’s method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 94, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susnjak, T.; Barczak, A.; Reyes, N. A decomposition machine-learning strategy for automated fruit grading. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science, Vol II WCECS, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–25 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, F.; Lu, R.; Cen, H. Grading of apples based on firmness and soluble solids content using Vis/SWNIR spectroscopy and spectral scattering techniques. J. Food Eng. 2014, 125, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toylan, H.; Kuscu, H. A Real-Time Apple Grading System Using Multicolor Space. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 292681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadegaonkar, V.D.; Wagh, K.H. Automatic sorting using computer vision and image processing for improving apple quality. Int. J. Innov. Res. Dev. 2015, 4, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Fan, S.; Li, J.; Huang, W.; Zhao, C.; Qian, M.; Zheng, L. Detection of Early Rottenness on Apples by Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Spectral Analysis and Image Processing. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilian, K.A.; Massah, J. An apple grading system according to European fruit quality standard using Gabor filter and arti-ficial neural networks. Sci. Study Res. Chem. Chem. Eng. Biotechnol. Food Ind. 2016, 17, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Keresztes, J.C.; Goodarzi, M.; Saeys, W. Real-time pixel based early apple bruise detection using short wave infrared hyperspectral imaging in combination with calibration and glare correction techniques. Food Control 2016, 66, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W. On line detection of defective apples using computer vision system combined with deep learning methods. J. Food Eng. 2020, 286, 110102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henila, M.; Chithra, P. Segmentation using fuzzy cluster-based thresholding method for apple fruit sorting. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 4178–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurygin, B.; Smirnov, I.; Chilikin, A.; Khort, D.; Kutyrev, A.; Zhukovskaya, S.; Solovchenko, A. Mutual Augmentation of Spectral Sensing and Machine Learning for Non-Invasive Detection of Apple Fruit Damages. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Bai, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Huo, Y.; Min, R. Multi-Band-Image Based Detection of Apple Surface Defect Using Machine Vision and Deep Learning. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



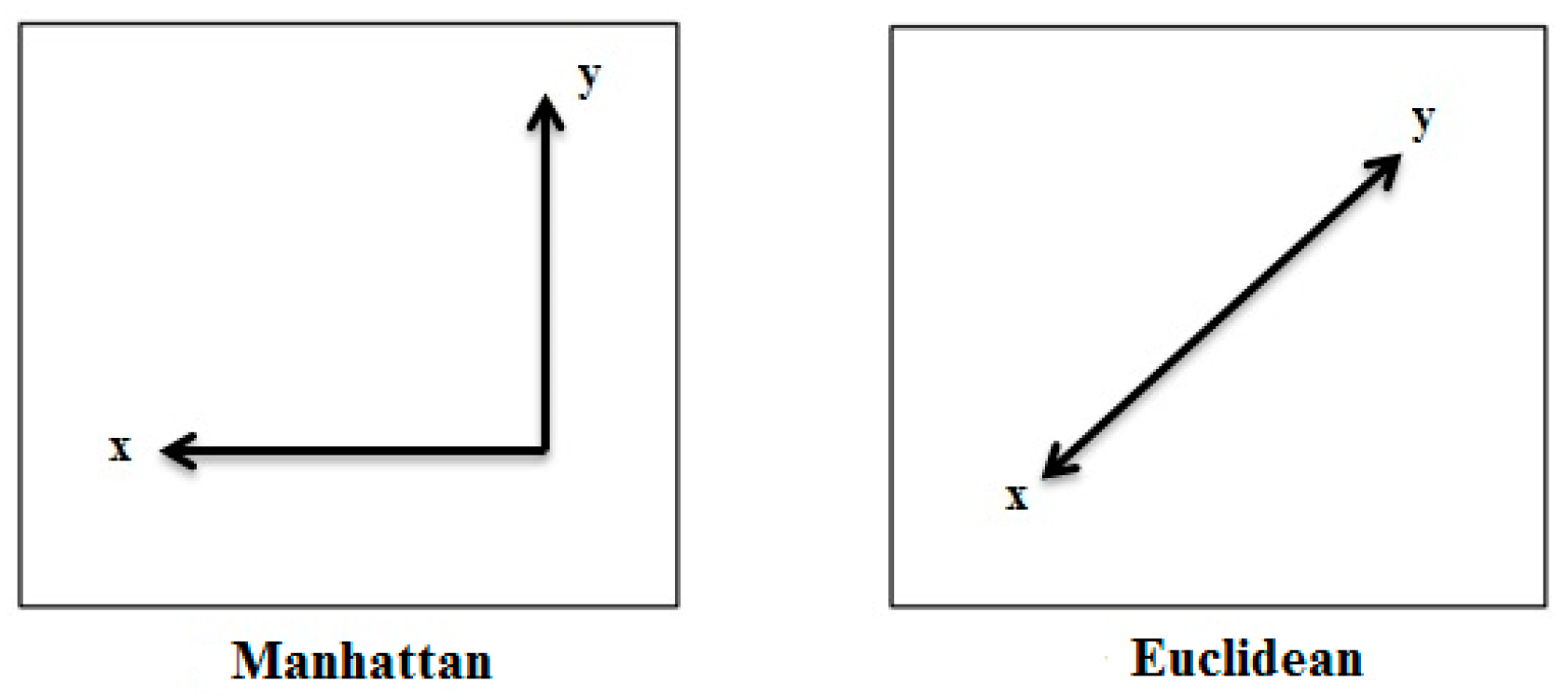


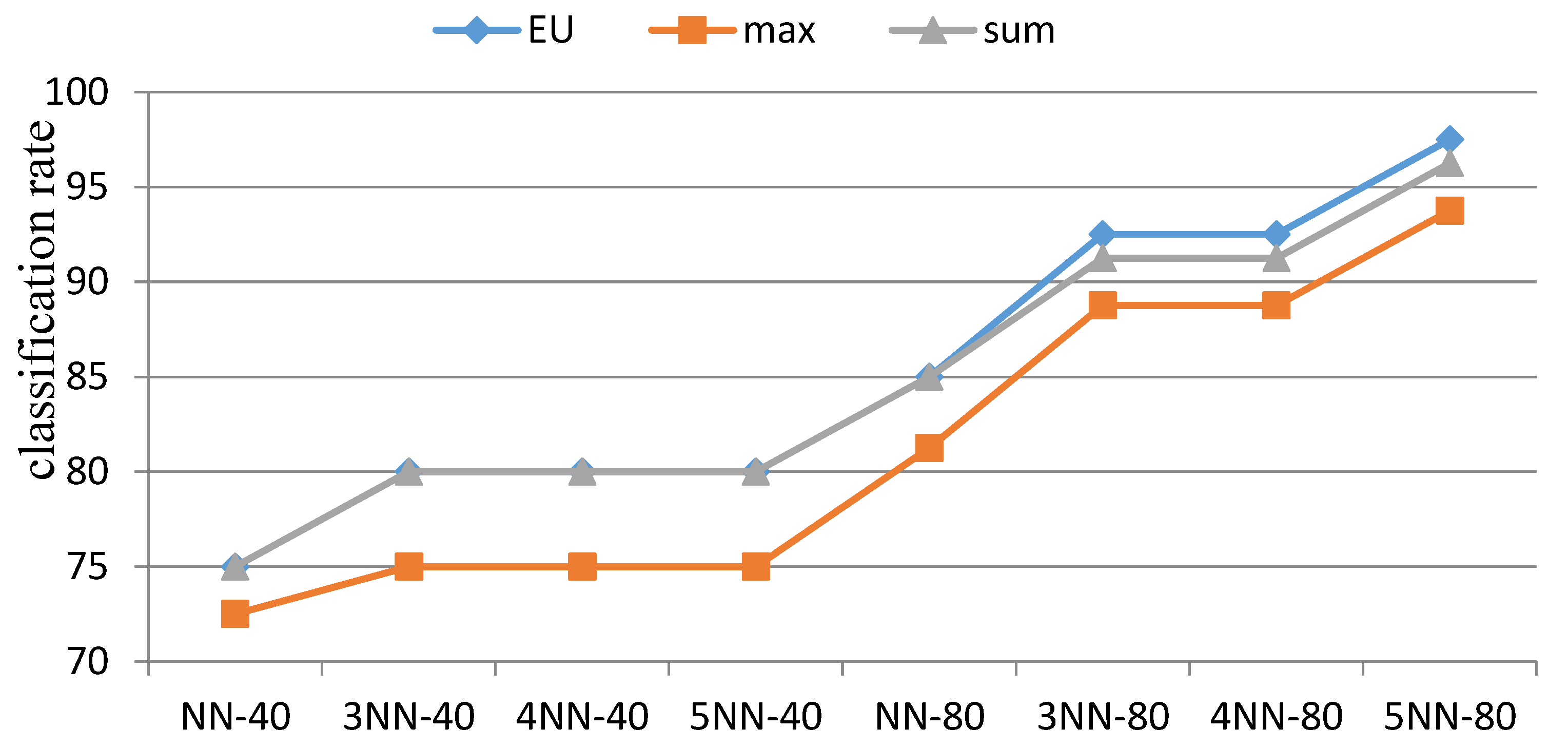
| Classification Method | Metric Distance | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Euclidean | Maximum | Sum | |||||
| Training set | 40 | 80 | 40 | 80 | 40 | 80 | |
| NN | stem | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| calyx | 75 | 85 | 72.5 | 81.25 | 75 | 85 | |
| 3-NN | stem | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| calyx | 80 | 92.5 | 75 | 88.75 | 80 | 91.25 | |
| 4-NN | stem | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| calyx | 80 | 92.5 | 75 | 88.75 | 80 | 91.25 | |
| 5-NN | stem | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| calyx | 80 | 97.5 | 75 | 93.75 | 80 | 96.25 | |
| Source | Type III Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | 224,748.909 | 3 | 74,916.303 | 2.438 | 0.021 |
| Number of training samples | 316,714.909 | 1 | 316,714.909 | 10.306 | 0.000 |
| Metric distances | 147,470.576 | 2 | 73,735.288 | 2.399 | 0.060 |
| Classification methods × training samples | 362,626.61 | 3 | 120,875.354 | 4.504 | 0.002 |
| Classification methods × metric distances | 420,985.857 | 6 | 70,164.309 | 2.615 | 0.013 |
| Training samples × metric distances | 159,939.660 | 2 | 79,969.830 | 2.980 | 0.053 |
| Classification methods × training samples × metric distances | 509,843.426 | 6 | 84,973.904 | 3.167 | 0.004 |
| Error(s) | 7,898,122.091 | 257 | 30,731.993 | ||
| Total | 1.034 × 108 | 264 | |||
| Corrected Total | 8,587,056.485 | 263 | |||
| a. R Squared = 0.961 (Adjusted R Squared = 0.957) | |||||
| Mean | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|
| Classification method | ||
| NN | 698.712 | 200.660 |
| 3-NN | 766.287 | 170.801 |
| 4-NN | 766.621 | 173.498 |
| 5-NN | 777.030 | 171.299 |
| Training sample size | ||
| 40 | 714.606 | 166.956 |
| 80 | 789.719 | 187.770 |
| Metric distance | ||
| Euclidean | 770.693 | 167.833 |
| Maximum | 718.806 | 200.560 |
| Sum | 766.988 | 165.513 |
| Authors | Year | Conveying Type | Imaging Type | Lighting Type | Pattern Recognition Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiaobo et al. [39] | 2010 | cone shape roller conveyor | three-color CCD cameras | N/A | N/A |
| Unay et al. [40] | 2011 | N/A | monochrome camera | N/A | N/A |
| Baranowski et al. [41] | 2012 | N/A | hyperspectral and thermal cameras | N/A | N/A |
| Shive Rame and Anand Singh [42] | 2012 | N/A | N/A | N/A | multiclass SVM |
| Suresha et al. [43] | 2012 | N/A | N/A | N/A | SVM |
| Mohana et al. [44] | 2013 | N/A | N/A | N/A | k-NN classifier |
| Mizushima and Lu [45] | 2013 | N/A | CCD color camera | eight LED lights | linear SVM and Otsu method |
| Sasnjak et al. [46] | 2013 | roller conveyor | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Zhang et al. [16] | 2013 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ECO features and GA |
| Mendoza et al. [47] | 2014 | N/A | N/A | quartz tungsten halogen light source | N/A |
| Toylan and Kuscu. [48] | 2014 | roller conveyor | complementary metal oxide semiconductor color camera | four fluorescent lamps | a method based on multicolor space |
| Zhang et al. [36] | 2015 | N/A | multispectral vision system | two pairs of visible LED light sources and NIR LED light sources | RVM classifier |
| Sadegaonkar and Wagh [49] | 2015 | roller conveyor | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Zhang et al. [50] | 2015 | N/A | hyperspectral monochrome CCD camera | N/A | SPA and a binary PLS-DA |
| Vakilian and Massaah [51] | 2016 | shielded conveyor belt | CCD color camera | N/A | Gabor filter and NN classifier |
| Sofu et al. [21] | 2016 | two channels roller conveyor | two CCD video cameras | N/A | N/A |
| Keresztes et al. [52] | 2016 | conveyor belt | infrared line scan camera | four 20 W DC tungsten halogen spots | N/A |
| Chio and Chen [8] | 2017 | revolving tray | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Wu et al. [30] | 2020 | N/A | laser-induced backscattering imaging system | semiconductor laser | convolutional neural networks (CNN) |
| Fan et al. [53] | 2020 | black fruit cup conveyor | two commercial RGB cameras | two light- emitting diode (LED) strips | convolutional neural networks (CNN) |
| Henila and Chithra [54] | 2020 | N/A | CCD camera | N/A | fuzzy cluster-based thresholding (FCBT) method |
| Shurygin et al. [55] | 2022 | table with rubber roller | hyperspectrometer BaySpec OCI-F | tungsten- halogen lamps | random forest (RF) classifiers |
| Tang et al. [56] | 2022 | N/A | near-infrared industrial camera | adjustable ring light source | U-Net |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baneh, N.M.; Navid, H.; Kafashan, J.; Fouladi, H.; Gonzales-Barrón, U. Development and Evaluation of a Small-Scale Apple Sorting Machine Equipped with a Smart Vision System. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 473-487. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010031
Baneh NM, Navid H, Kafashan J, Fouladi H, Gonzales-Barrón U. Development and Evaluation of a Small-Scale Apple Sorting Machine Equipped with a Smart Vision System. AgriEngineering. 2023; 5(1):473-487. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaneh, Nesar Mohammadi, Hossein Navid, Jalal Kafashan, Hatef Fouladi, and Ursula Gonzales-Barrón. 2023. "Development and Evaluation of a Small-Scale Apple Sorting Machine Equipped with a Smart Vision System" AgriEngineering 5, no. 1: 473-487. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010031
APA StyleBaneh, N. M., Navid, H., Kafashan, J., Fouladi, H., & Gonzales-Barrón, U. (2023). Development and Evaluation of a Small-Scale Apple Sorting Machine Equipped with a Smart Vision System. AgriEngineering, 5(1), 473-487. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering5010031







