Pesticide-Free Robotic Control of Aphids as Crop Pests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
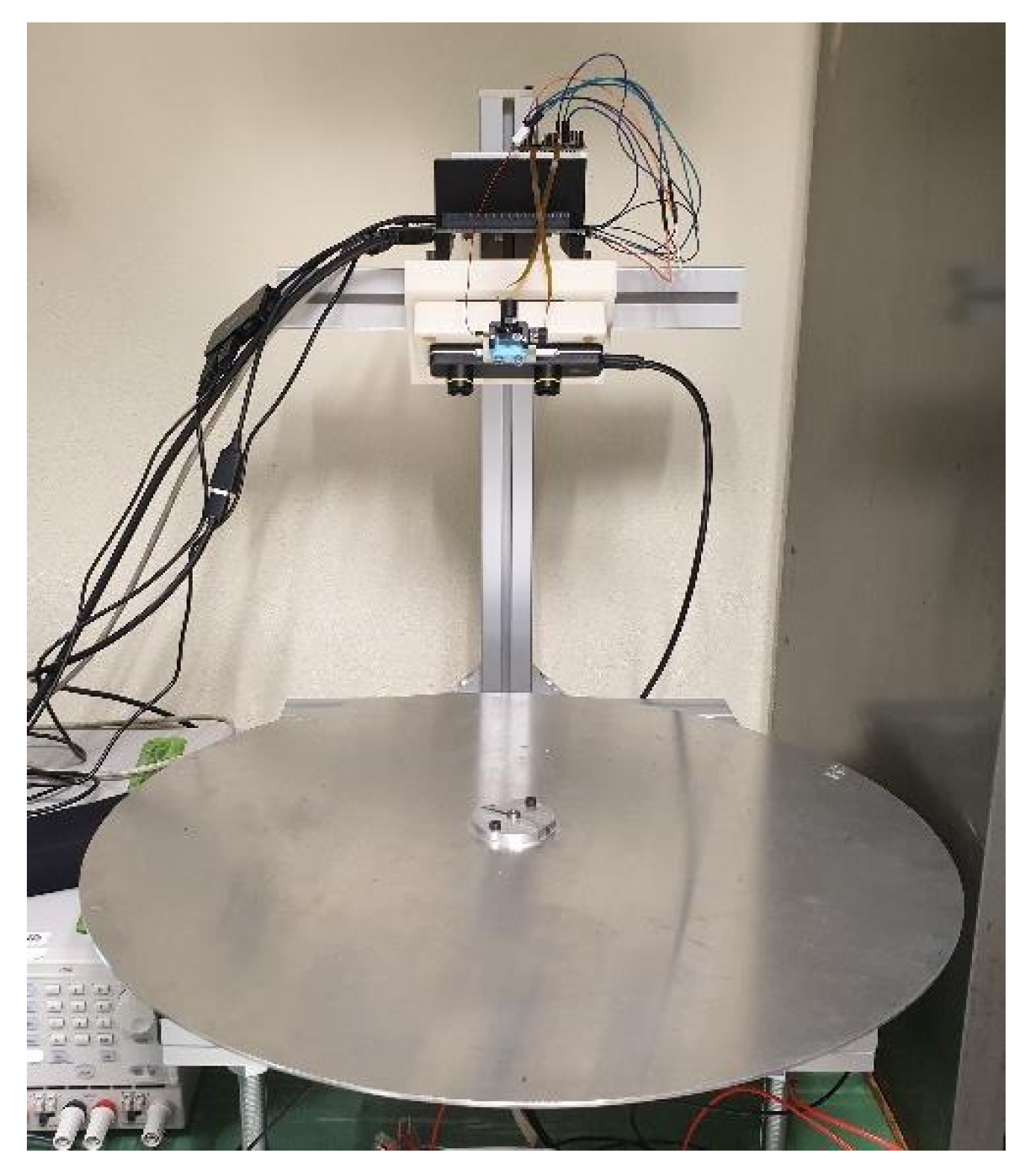
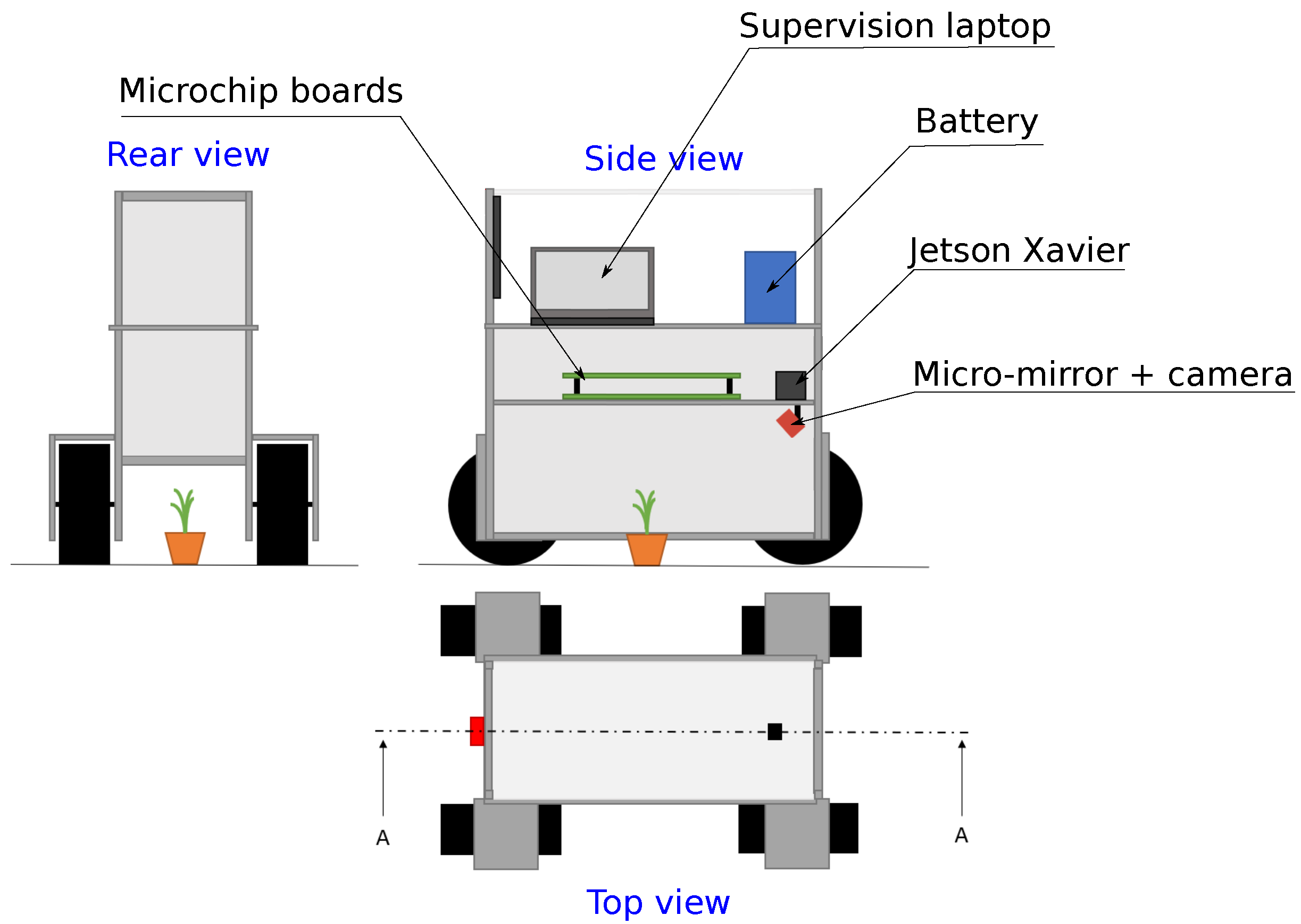
2.1. Prototype Robot Structure
2.2. Insects and Plants
2.3. Global Process
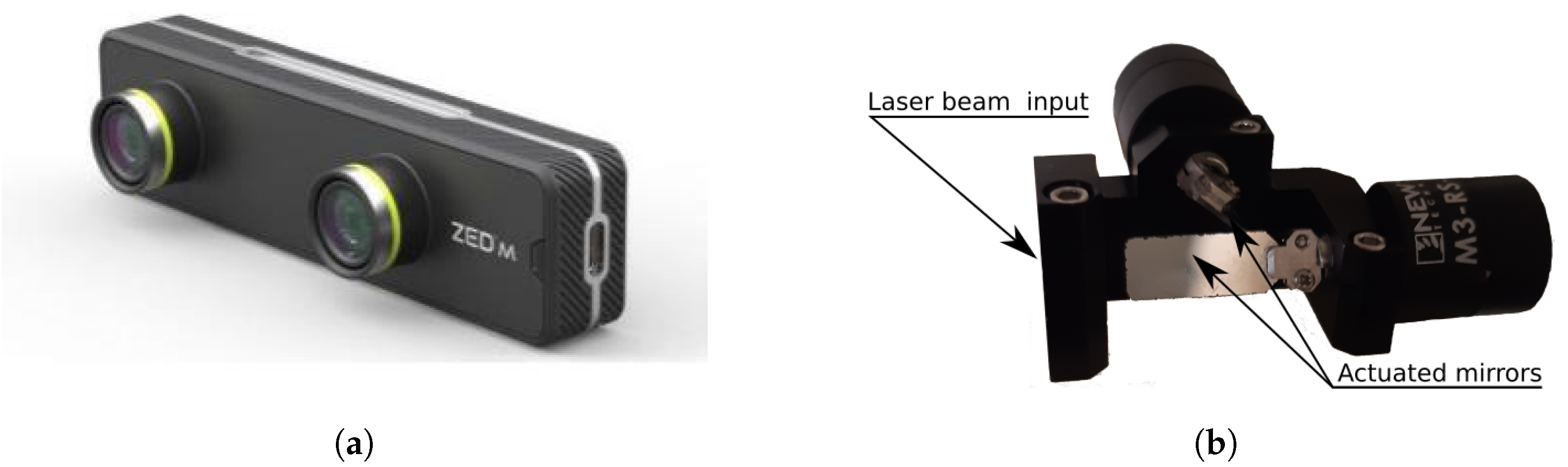
2.4. RGB-D Acquisition
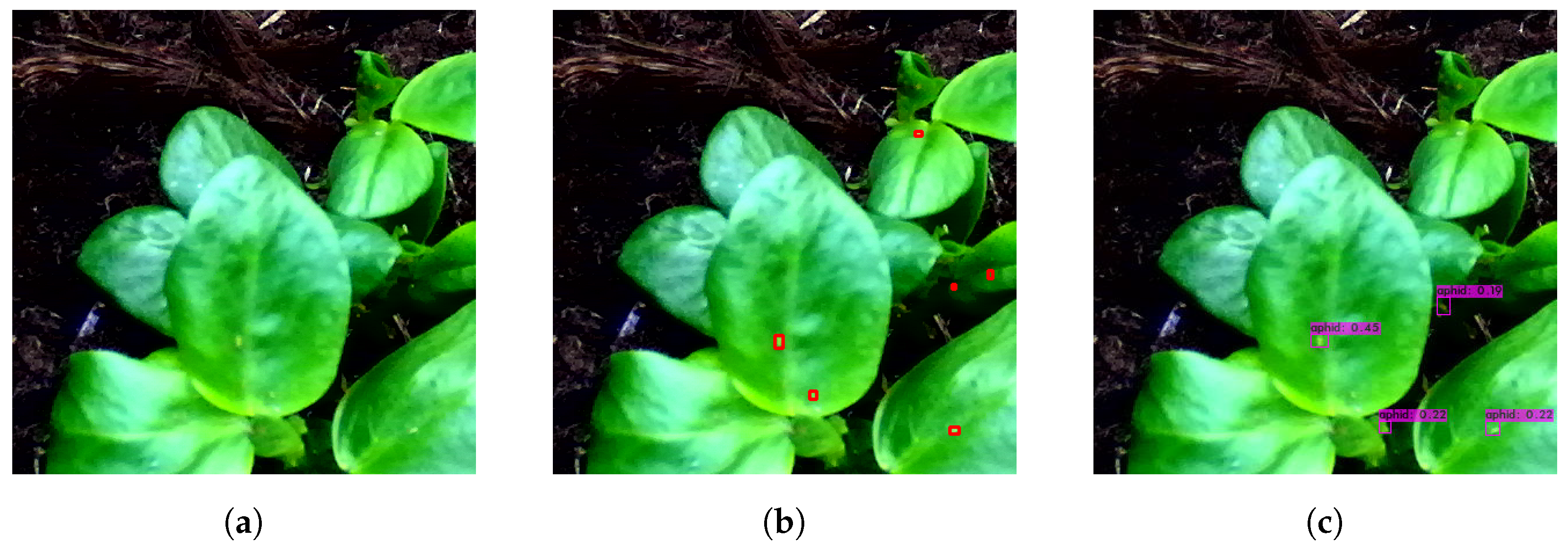
2.5. Detection and Localization
- Detection accuracy: a maximum error of 3 mm must exist between the center of detected aphids and their true location in the image so that the laser spot always overlaps a part of the targeted aphid;
- Detection sensitivity: at least 60% of aphids present in the image (this level has been set arbitrarily taking into account that natural predators should finish the work, but it requires experimental validation);
- Real-time operation: the entire program (detection algorithm + laser control) must run at a speed greater than 10 frames per second to permit the robot to cover a 1 ha crop field in 24 h (in the case of a field where rows are located every 40 cm, the robot will have to travel 25 km during 12 h, corresponding to a mean speed of 1 km/h or 29 cm/s).
- Horizontal or vertical image flip;
- Rotation of 10° in the positive or negative direction;
- Brightness modification;
- Hue and saturation modification;
- Contrast modification;
- Grayscale modification.
2.6. Laser-Based Targeting
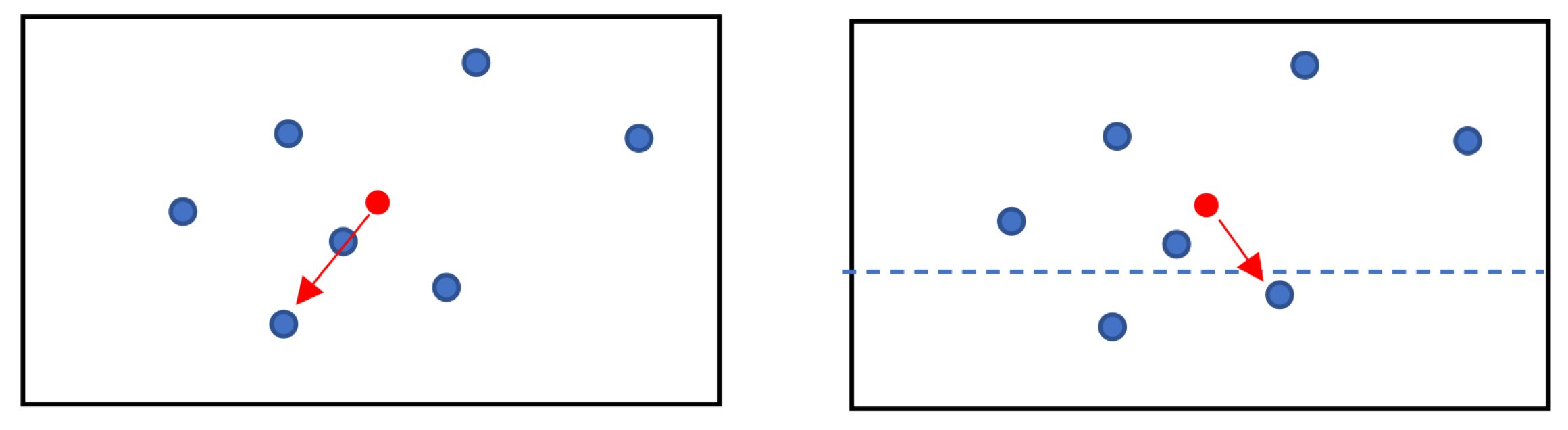
2.7. Multiple Target Optimization
2.8. Laser Choice and Dimensioning
3. Results
3.1. Aphid Detection and Localization
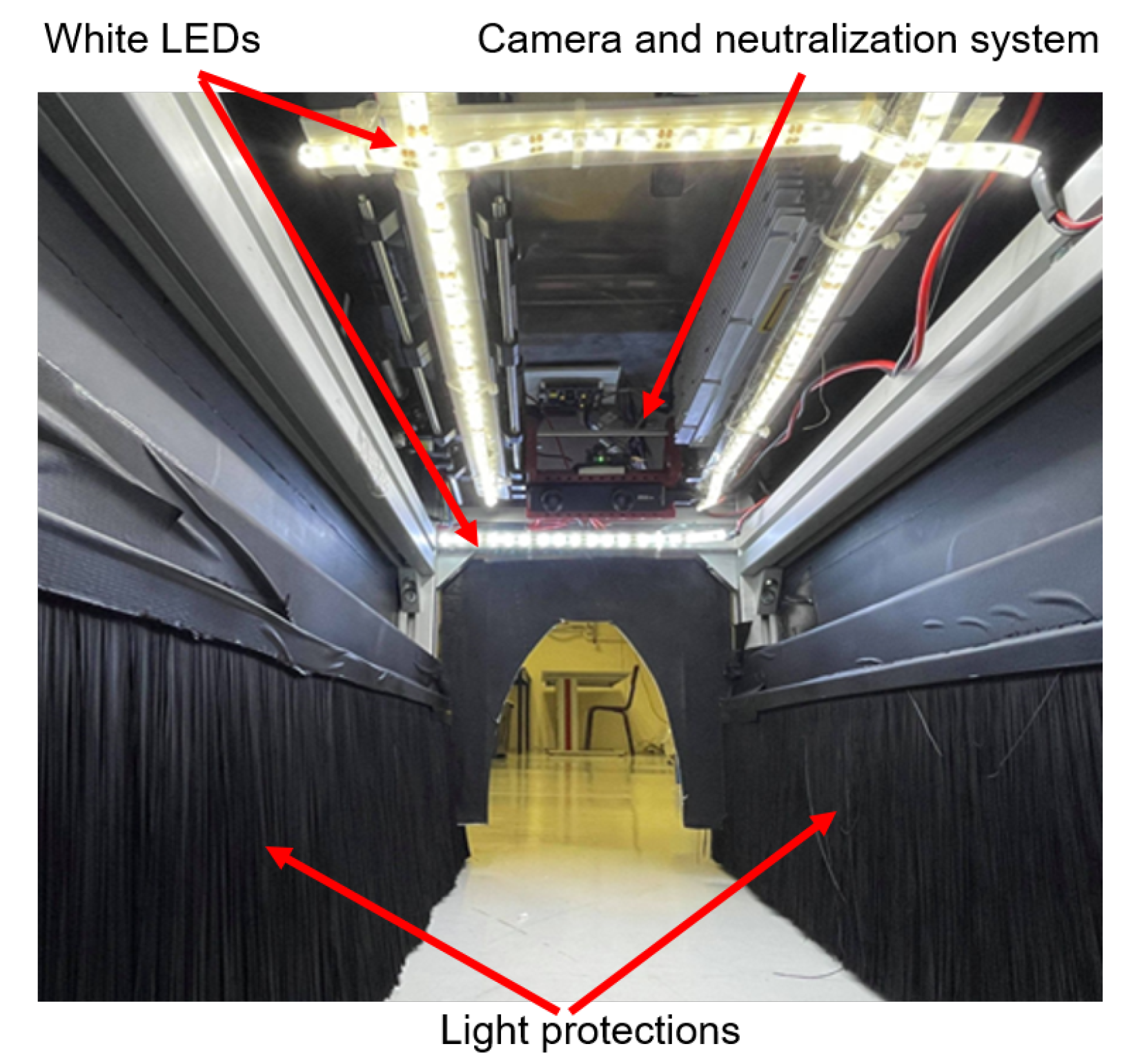
3.1.1. Lighting Conditions
3.1.2. Localization Performance
3.2. Laser-Based Neutralization
3.2.1. Pest Neutralization
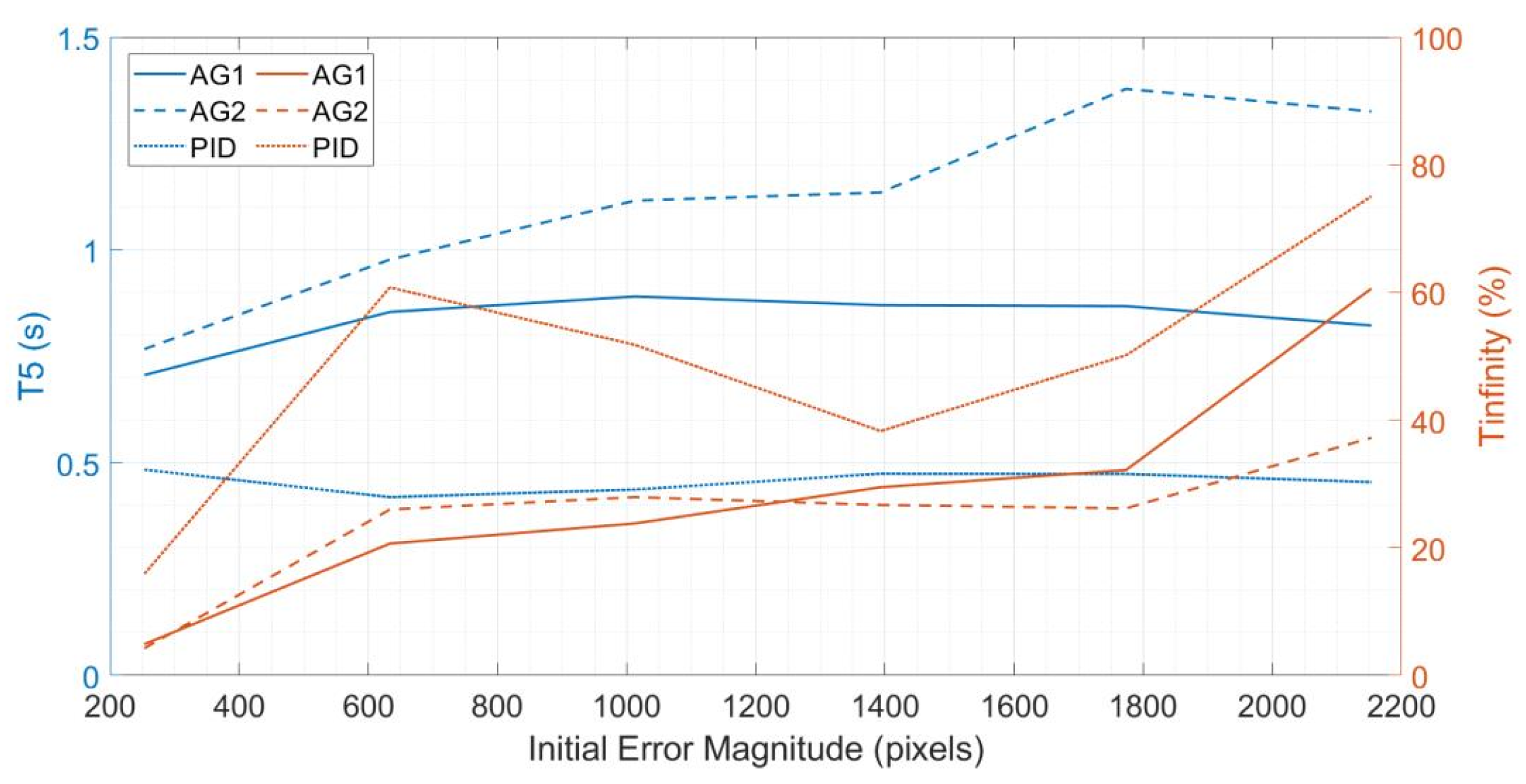
3.2.2. Targeting
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNM | detection-neutralisation module |
| FP16 | 16-bit floating point format |
| FPS | Frames per Second |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| IBVS | Image-Based Visual Servo |
| INT8 | Integer coded with 8 bits |
| LD | Lethal Dose |
| LWIR | Long Wavelength Infra-Red |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| RGB | Red Green Blue |
| RGB-D | Red Green Blue and Depth |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| SWIR | Short Wavelength Infra-Red |
| TSP | Traveling Salesman Problem |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- RISE Foundation. Crop Protection & the EU Food System: Where Are They Going, 1st ed.; RISE Foundation: Brüssel, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pesticide Action Network Europe. Endocrine Disrupting Pesticides in European Food; Pesticide Action Network Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.H.M.; Lenzen, M.; McBratney, A.; Maggi, F. Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, C.; Park, K.J.; Whitehorn, P.; David, A.; Goulson, D. The Neonicotinoid Insecticide Thiacloprid Impacts upon Bumblebee Colony Development under Field Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiz-Rubio, V.; Rovira-Más, F. From Smart Farming towards Agriculture 5.0: A Review on Crop Data Management. Agronomy 2020, 10, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phasinam, K.; Kassanuk, T.; Shabaz, M. Applicability of internet of things in smart farming. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2022, 7692922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vougioukas, S.G. Agricultural Robotics. Annu. Rev. Control. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 2, 365–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridou, E.; Vrochidou, E.; Papakostas, G.A.; Pachidis, T.; Kaburlasos, V.G. Machine Vision Systems in Precision Agriculture for Crop Farming. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meshram, A.T.; Vanalkar, A.V.; Kalambe, K.B.; Badar, A.M. Pesticide spraying robot for precision agriculture: A categorical literature review and future trends. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žibrat, U.; Knapič, M.; Urek, G. Plant pests and disease detection using optical sensors/Daljinsko zaznavanje rastlinskih bolezni in škodljivcev. Folia Biol. Geol. 2019, 60, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.K.; Kuska, M.T.; Behmann, J.; Polder, G.; Walter, A. Hyperspectral sensors and imaging technologies in phytopathology: State of the art. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacotte, V.; Peignier, S.; Raynal, M.; Demeaux, I.; Delmotte, F.; da Silva, P. Spatial–Spectral Analysis of Hyperspectral Images Reveals Early Detection of Downy Mildew on Grapevine Leaves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haff, R.P.; Saranwong, S.; Thanapase, W.; Janhiran, A.; Kasemsumran, S.; Kawano, S. Automatic image analysis and spot classification for detection of fruit fly infestation in hyperspectral images of mangoes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 86, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B.; Naiker, M. Seeing red: A review of the use of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in entomology. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2020, 55, 810–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.; Leandro, M.E.; Pereira, L.; Valero, C.; Gonçalves Bazzo, C. Automatic Detection and Monitoring of Insect Pests—A Review. Agriculture 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, M.; Conte, D.; Raveaux, R.; Arnault, I.; Munier, D.; Venturini, G. A survey on image-based insect classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 65, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Shao, Y.; He, Y. Different algorithms for detection of malondialdehyde content in eggplant leaves stressed by grey mold based on hyperspectral imaging technique. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2015, 21, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, R.; Xie, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, W. A coarse-to-fine network for aphid recognition and detection in the field. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 187, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.A.; Khoshtaghaza, M.H.; Minaei, S.; Jamshidi, B. Vision-based pest detection based on SVM classification method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 137, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefpour Vakilian, K.; Massah, J. Performance evaluation of a machine vision system for insect pests identification of field crops using artificial neural networks. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2013, 46, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupanagudi, S.R.; Ranjani, B.S.; Nagaraj, P.; Bhat, V.G.; Thippeswamy, G. A novel cloud computing based smart farming system for early detection of borer insects in tomatoes. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Communication, Information & Computing Technology (ICCICT), Mumbai, India, 15–17 January 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuphab, A.; Silapachote, P.; Tantratorn, W.; Krakornkul, P.; Darote, P. Insect Detection on an Unmanned Ground Rover. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2018—2018 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Jeju, Korea, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 0954–0959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, C.; Lee, J. Vision-based pest detection and automatic spray of greenhouse plant. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Seoul, Korea, 5–8 July 2009; pp. 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibhute, A.S.; Tate Deshmukh, K.R.; Hindule, R.S.; Sonawane, S.M. Pest Management System Using Agriculture Robot. In Techno-Societal 2020; Pawar, P.M., Balasubramaniam, R., Ronge, B.P., Salunkhe, S.B., Vibhute, A.S., Melinamath, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 829–837. [CrossRef]
- Drees, B.M.; Leroy, T.R. Evaluation of alternative methods for suppression of crape myrtle aphids. In Upper Coast 1990–1991 Entomological Result Demonstration Handbook; Texas A & M University System Edition; Texas Agricultural Extension Service: Tamu, TX, USA, 1991; pp. 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kusakari, S.i.; Okada, K.; Shibao, M.; Toyoda, H. High Voltage Electric Fields Have Potential to Create New Physical Pest Control Systems. Insects 2020, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.D.; Leahy, D.J.; Norton, B.J.; Johanson, T.; Mullen, E.R.; Marvit, M.; Makagon, A. Laser induced mortality of Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obasekore, H.; Fanni, M.; Ahmed, S.M. Insect Killing Robot for Agricultural Purposes. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Hong Kong, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Aravecchia, S.; Lottes, P.; Stachniss, C.; Pradalier, C. Robotic weed control using automated weed and crop classification. J. Field Robot. 2020, 37, 322–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaierle, S.; Marx, C.; Rath, T.; Hustedt, M. Find and Irradiate—Lasers Used for Weed Control. Laser Tech. J. 2013, 10, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, K.; Mahore, A.; Malkani, P.; Singh, A.K. Robotics-automation and sensor-based approaches in weed detection and control: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 542–550. [Google Scholar]
- Fuad, M.T.H.; Fime, A.A.; Sikder, D.; Iftee, M.A.R.; Rabbi, J.; Al-Rakhami, M.S.; Gumaei, A.; Sen, O.; Fuad, M.; Islam, M.N. Recent Advances in Deep Learning Techniques for Face Recognition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 99112–99142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minks, A.K.; Harrewijn, P. Aphids: Their Biology, Natural Enemies, and Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Simonet, P.; Duport, G.; Gaget, K.; Weiss-Gayet, M.; Colella, S.; Febvay, G.; Charles, H.; Viñuelas, J.; Heddi, A.; Calevro, F. Direct flow cytometry measurements reveal a fine-tuning of symbiotic cell dynamics according to the host developmental needs in aphid symbiosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quigley, M.; Conley, K.; Gerkey, B.; Faust, J.; Foote, T.; Leibs, J.; Berger, E.; Wheeler, R.; Ng, A.Y. ROS: An open-source Robot Operating System. In ICRA Workshop on Open Source Software; IEEE: Kobe, Japan, 2009; Volume 3, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ribera, J.; Güera, D.; Chen, Y.; Delp, E.J. Locating Objects Without Bounding Boxes. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. A Study on the Damage and Economic Threshold of the Soybean Aphid at the Seedling Stage. Plant Prot. 1994, 20, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Showers, W.B.; Von Kaster, L.; Mulder, P.G. Corn Seedling Growth Stage and Black Cutworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Damage 1. Environ. Entomol. 1983, 12, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurej, M.; Werf, W.V.D. The influence of black bean aphid, Aphis fabae Scop., and its honeydew on leaf growth and dry matter production of sugar beet. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1993, 122, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Yeh, I.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W. CSPNet: A New Backbone that can Enhance Learning Capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, S.; Hager, G.; Corke, P. A tutorial on visual servo control. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 651–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreff, N.; Tamadazte, B. Laser steering using virtual trifocal visual servoing. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 672–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudryavtsev, A.V.; Chikhaoui, M.T.; Liadov, A.; Rougeot, P.; Spindler, F.; Rabenorosoa, K.; Burgner-Kahrs, J.; Tamadazte, B.; Andreff, N. Eye-in-Hand Visual Servoing of Concentric Tube Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, M.D.; Norton, B.J.; Farrar, D.J.; Rutschman, P.; Marvit, M.; Makagon, A. Optical tracking and laser-induced mortality of insects during flight. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagadic Team. ViSP Tutorial: How to Boost Your Visual Servo Control Law. 2021. Available online: https://visp-doc.inria.fr/doxygen/visp-2.9.0/tutorial-boost-vs.html (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Helvig, C.S.; Robins, G.; Zelikovsky, A. Moving-Target TSP and Related Problems. In Algorithms—ESA’ 98; Bilardi, G., Italiano, G.F., Pietracaprina, A., Pucci, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 453–464. [Google Scholar]
- Gaetani, R.; Lacotte, V.; Dufour, V.; Clavel, A.; Duport, G.; Gaget, K.; Calevro, F.; Da Silva, P.; Heddi, A.; Vincent, D.; et al. Sustainable laser-based technology for insect pest control. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Shibuya, K.; Sato, M.; Saito, Y. Lethal effects of short-wavelength visible light on insects. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Parameters | Values | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | HD1080 (1920 × 1080) | A 2K resolution would consume a lot of resources and therefore would slow down the detection algorithm. |
| Capture Speed | 30 FPS | Maximum available in the HD1080 mode. |
| Brightness | 1 | Low brightness to limit light reflections on the surface of the leaves. |
| Contrast | 6 | High contrast makes it easier to detect pink aphids on green leaves. |
| Hue | 0 | Default value that matches the colors perceived by human eyes. |
| Saturation | 8 | Maximized to let the aphids appear on green leaves. |
| Gamma | 2 | A low gamma level limits the white light in the picture. |
| Acuity | 4 | Average value as high values generate noise on the back plane. |
| White Balance | auto | To adapt it taking into account fixed other color parameters (hue, saturation). |
| Exposition | 75% | Set to keep the brightness at an acceptable level. |
| Gain | 10 | Adjusted to keep the consistency between the other settings with minimal add noise addition. |
| YOLOv4 | U-Net-HD | |
|---|---|---|
| FPS (Nvidia Quadro 400) | 10-11 | 2-3 |
| True Positive (TP) | 238 | 278 |
| False Positive (FP) | 490 | 997 |
| False Negative (FN) | 1371 | 1349 |
| Precision | 0.37 | 0.15 |
| Recall | 0.21 | 0.17 |
| Network Input Size | Input Image Size | FPS (Quadro 400) | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Python API | C++ | ||||
| 640 × 640 | 2208 × 1242 | 10–11 | 16 | 0.35 | 0.49 |
| 512 × 512 | 2208 × 1242 | 13–14 | 21 | 0.34 | 0.46 |
| 512 × 512 | 800 × 600 | 13–14 | 21 | 0.4 | 0.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacotte, V.; NGuyen, T.; Sempere, J.D.; Novales, V.; Dufour, V.; Moreau, R.; Pham, M.T.; Rabenorosoa, K.; Peignier, S.; Feugier, F.G.; et al. Pesticide-Free Robotic Control of Aphids as Crop Pests. AgriEngineering 2022, 4, 903-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040058
Lacotte V, NGuyen T, Sempere JD, Novales V, Dufour V, Moreau R, Pham MT, Rabenorosoa K, Peignier S, Feugier FG, et al. Pesticide-Free Robotic Control of Aphids as Crop Pests. AgriEngineering. 2022; 4(4):903-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040058
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacotte, Virginie, Toan NGuyen, Javier Diaz Sempere, Vivien Novales, Vincent Dufour, Richard Moreau, Minh Tu Pham, Kanty Rabenorosoa, Sergio Peignier, François G. Feugier, and et al. 2022. "Pesticide-Free Robotic Control of Aphids as Crop Pests" AgriEngineering 4, no. 4: 903-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040058
APA StyleLacotte, V., NGuyen, T., Sempere, J. D., Novales, V., Dufour, V., Moreau, R., Pham, M. T., Rabenorosoa, K., Peignier, S., Feugier, F. G., Gaetani, R., Grenier, T., Masenelli, B., da Silva, P., Heddi, A., & Lelevé, A. (2022). Pesticide-Free Robotic Control of Aphids as Crop Pests. AgriEngineering, 4(4), 903-921. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040058








