LLM-Driven Offloading Decisions for Edge Object Detection in Smart City Deployments
Abstract
Highlights
- We introduce an LLM-driven framework that auto-generates and refines DRL reward functions from natural language objectives for edge offloading in object detection.
- On a real-world dataset, policies trained with LLM-generated rewards achieve higher throughput and lower process latency than expert-designed rewards.
- DRL policies can be retargeted across objectives (e.g., latency, energy, and accuracy) using prompts only, eliminating manual reward redesign.
- Engineering overhead is reduced while accelerating the adaptation of edge AI services when goals or conditions change.
- The robustness of offloading and scheduling improves under heterogeneous workloads, fluctuating bandwidths, and dynamic device capabilities.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- LLM-driven DRL retargeting framework: We present a novel framework that leverages LLMs to directly retarget DRL scheduling policies for edge-based object detection from natural language instructions, removing the need for manual reward engineering.
- Automatic reward generation and refinement: The proposed approach converts optimization objectives into an executable, environment-compliant reward function code and iteratively improves it using simulation feedback.
- Adaptability to dynamic optimization goals: Our method supports rapid adaptation of DRL policies to evolving service requirements, sustaining high performance under shifting priorities in latency, accuracy, and energy consumption.
- Comprehensive experimental validation: Extensive simulations on real-world datasets verify that LLM-generated rewards enable DRL schedulers to outperform human expert-crafted rewards, even when optimization objectives change dynamically.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Edge-Based Object Detection in Smart Cities
2.2. Intelligent Offloading and Scheduling Strategies for Edge Object Detection
2.3. Large Language Models for Decision Making
3. Materials and Methods
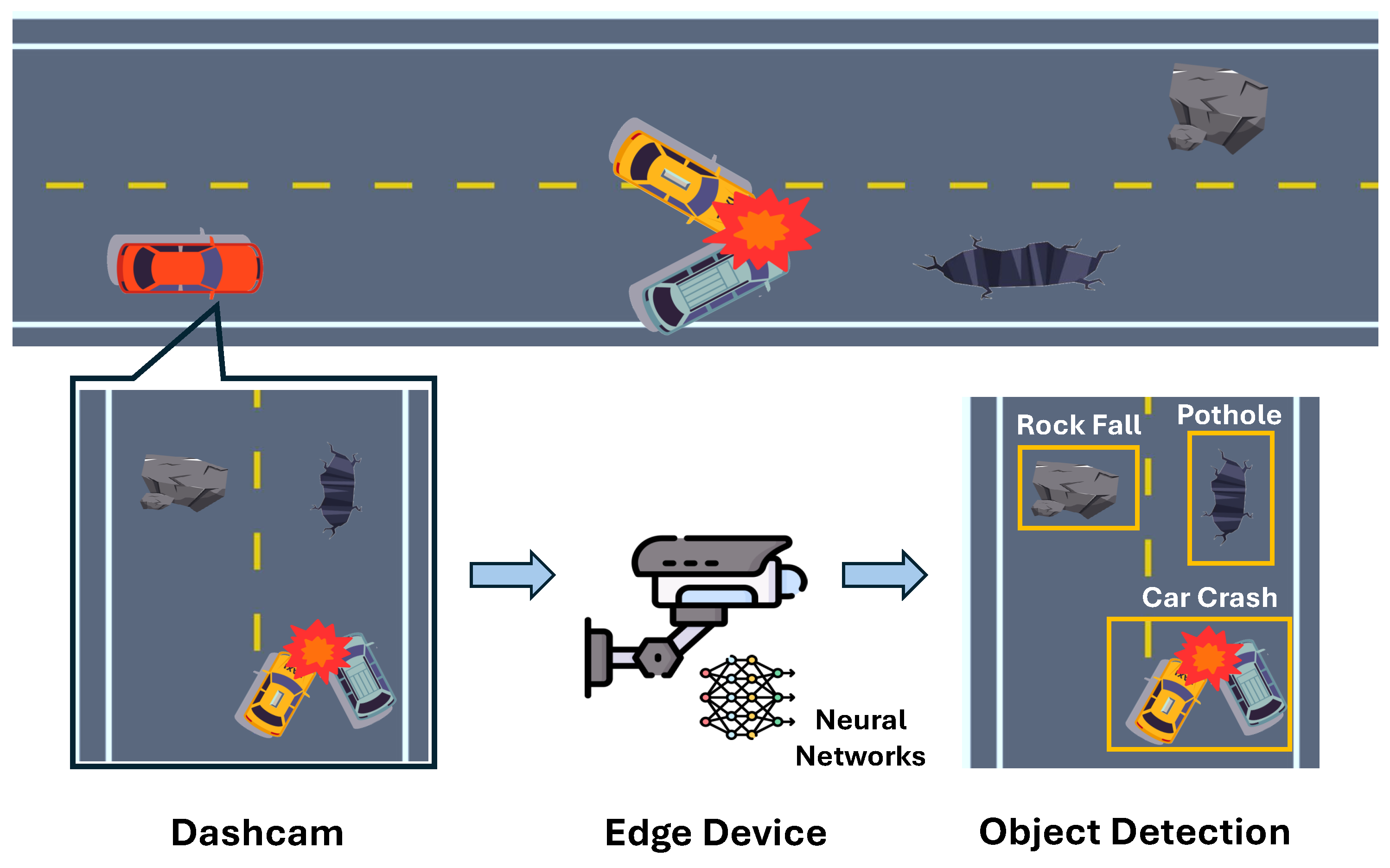
3.1. Task Offloading Actions in Edge-Based Object Detection
3.2. Preference-Driven Utility Modeling
3.3. MDP Formulation and DQN-Based Learning Framework
3.4. LLM-Driven Reward Function Integration and Policy Training
| Algorithm 1: LLM-Guided Reward Design and DQNTraining for Edge Offloading |
 |
4. Results
4.1. Overhead of LLM-Based Reward Function Generation
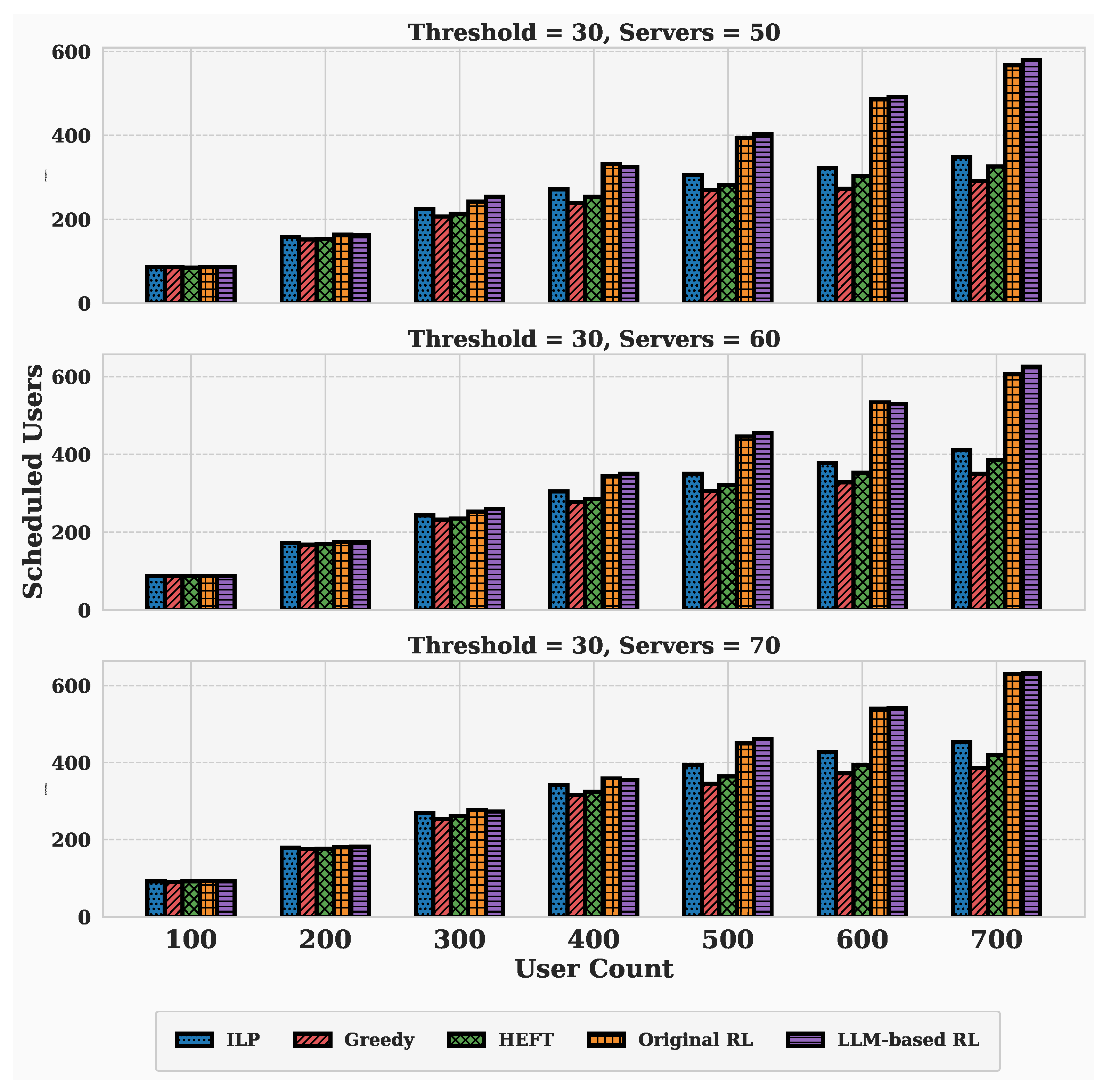
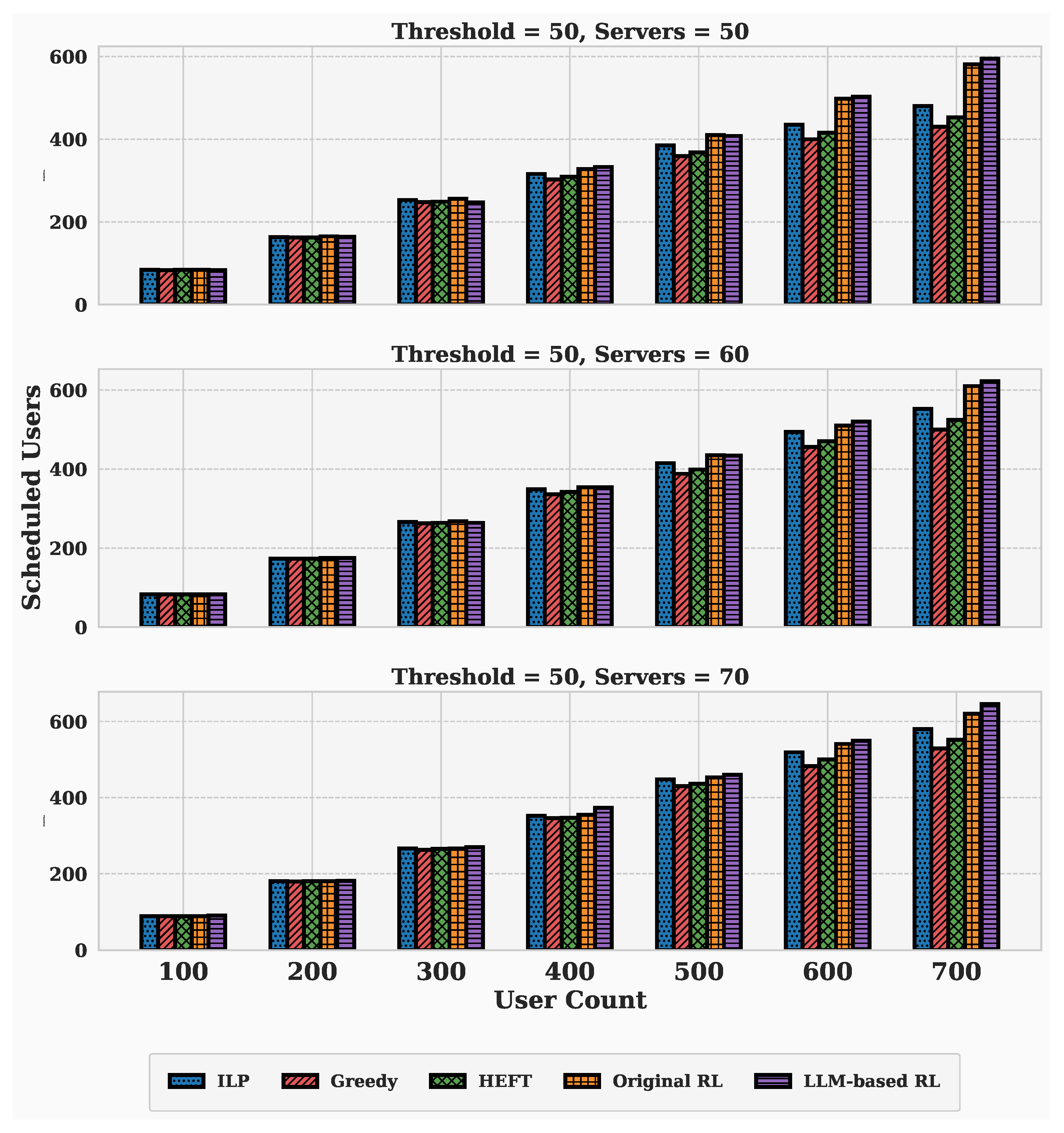
4.2. Performance Evaluation Under Varying Server and User Scales
4.3. Latency-Minimization Scheduling with Prompt-Driven Objective Changing
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Example of Prompt Design for LLM-Based Reward Function Generation


Appendix B. Example of Iterative Prompt for Reward Function Refinement



Appendix C. Differences in RULE Constraints Between GPT-4o-mini and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
Appendix C.1. GPT-4o-mini RULES

Appendix C.2. Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct RULES


References
- Syed, A.S.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Kumar, A.; Elmaghraby, A. IoT in smart cities: A survey of technologies, practices and challenges. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 429–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Puryear, N.; Abdelwahed, S.; Zohrabi, N. A review of IoT-based smart city development and management. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 1462–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.h.; Ramos, C.; Mohammed, S. Smart city and IoT. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 76, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, E.; Soylu, T. A performance comparison of YOLOv8 models for traffic sign detection in the Robotaxi-full scale autonomous vehicle competition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 25005–25035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D. Revolutionizing target detection in intelligent traffic systems: Yolov8-snakevision. Electronics 2023, 12, 4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tao, Q. Improving real-time object detection in Internet-of-Things smart city traffic with YOLOv8-DSAF method. SCient. Rep. 2024, 14, 17235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Song, S.; Qin, R.; Tang, Y. Remote sensing object detection in the deep learning era—A review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegun, A.A.; Fonou-Dombeu, J.V.; Viriri, S.; Odindi, J. Ontology-Based Deep Learning Model for Object Detection and Image Classification in Smart City Concepts. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 2182–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wu, H.; Zhen, L.; Hua, Q.; Garg, S.; Kaddoum, G.; Hassan, M.M.; Yu, K. Edge YOLO: Real-time intelligent object detection system based on edge-cloud cooperation in autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 25345–25360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Mehta, K.; Mishra, S.; AlMutawa, M. A Dynamic Distributed Scheduler for Computing on the Edge. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Symposium on Parallel Computing and Distributed Systems (PCDS), Singapore, 21–22 September 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, H.; Chen, S.; Feng, X. Energy efficient task scheduling for heterogeneous multicore processors in edge computing. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, T.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, X. A DRL-driven intelligent optimization strategy for resource allocation in cloud-edge-end cooperation environments. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, M.S.; Patan, R.; Gandomi, A.H.; Park, J.H.; Jung, H.Y. A DRL based 4-r Computation Model for Object Detection on RSU using LiDAR in IloT. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Orlando, FL, USA, 5–7 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Sun, J.; Lv, H.; Cui, H. A deep reinforcement learning assisted task offloading and resource allocation approach towards self-driving object detection. J. Cloud Comput. 2023, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumaran, K.; Deisenroth, M.P.; Brundage, M.; Bharath, A.A. Deep reinforcement learning: A brief survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalakou, A.; Troullinos, D.; Chalkiadakis, G.; Papageorgiou, M. Deep reinforcement learning reward function design for autonomous driving in lane-free traffic. Systems 2023, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegaro, D.; Levorato, M.; Restuccia, F. Smartdet: Context-aware dynamic control of edge task offloading for mobile object detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM), Belfast, UK, 14–17 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Li, M.; Cai, X.; Chen, J. Edge computing service deployment and task offloading based on multi-task high-dimensional multi-objective optimization. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.04101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Lee, J.; Baek, H. Real-time scheduling for multi-object tracking tasks in regions with different criticalities. J. Syst. Archit. 2025, 160, 103349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, X.; Dong, S. Multi-objective task offloading for highly dynamic heterogeneous Vehicular Edge Computing: An efficient reinforcement learning approach. Comput. Commun. 2024, 225, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Shim, B.; Yang, H.J. Adaptive resource allocation optimization using large language models in dynamic wireless environments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Cui, S.; Wang, F. Netllm: Adapting large language models for networking. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2024 Conference, Sydney, Australia, 4–8 August 2024; pp. 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Pompili, D. LLM-Based Multi-Agent Decision-Making: Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 5681–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behari, N.; Zhang, E.; Zhao, Y.; Taneja, A.; Nagaraj, D.; Tambe, M. A decision-language model (DLM) for dynamic restless multi-armed bandit tasks in public health. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 3964–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Liang, W.; Wang, G.; Huang, D.A.; Bastani, O.; Jayaraman, D.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, L.; Anandkumar, A. Eureka: Human-level reward design via coding large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuzhnaya, A.; Mityagin, S.; Lutsenko, E.; Getmanov, A.; Aksenkin, Y.; Fatkhiev, K.; Fedorin, K.; Nikitin, N.O.; Chichkova, N.; Vorona, V.; et al. LLM Agents for Smart City Management: Enhancing Decision Support Through Multi-Agent AI Systems. Smart Cities 2025, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misbah, S.; Shahid, M.F.; Siddiqui, S.; Khanzada, T.J.S.; Ashari, R.B.; Ullah, Z.; Jamjoom, M. Generative AI-Driven Smart Contract Optimization for Secure and Scalable Smart City Services. Smart Cities 2025, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Ni, Q. IoT-driven automated object detection algorithm for urban surveillance systems in smart cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 5, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubaei, F.S.; Al-Wesabi, F.N.; Hilal, A.M. Deep learning-based small object detection and classification model for garbage waste management in smart cities and iot environment. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Nazir, S.; Khan, H.U. Smart Object Detection and Home Appliances Control System in Smart Cities. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 67, 895–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Yang, S. Ec2detect: Real-time online video object detection in edge-cloud collaborative iot. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20382–20392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudasaini, D.; Abhari, A. Edge-based video analytic for smart cities. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Pang, S.; Ji, X.; Wang, M.; Qiao, S.; Yu, S. Intelligent driving task scheduling service in vehicle-edge collaborative networks based on deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 21, 4357–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.P.; Banerjee, A.; Bhattacharya, A. User allocation in mobile edge computing: A deep reinforcement learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, W. Energy-efficient task scheduling based on traffic mapping in heterogeneous mobile-edge computing: A green IoT perspective. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 7, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhong, L.; Bao, W.; Si, H.; Djahel, S.; Wu, C. Behavior Cloning with Fuzzy Logic for Accelerating Early-Stage DRL in Edge Offloading. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Hurst, A.; Lerer, A.; Goucher, A.P.; Perelman, A.; Ramesh, A.; Clark, A.; Ostrow, A.; Welihinda, A.; Hayes, A.; Radford, A.; et al. Gpt-4o system card. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.21276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Jauhri, A.; Pandey, A.; Kadian, A.; Al-Dahle, A.; Letman, A.; Mathur, A.; Schelten, A.; Yang, A.; Fan, A.; et al. The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.21783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.; He, Q.; Abdelrazek, M.; Chen, F.; Hosking, J.; Grundy, J.; Yang, Y. Optimal edge user allocation in edge computing with variable sized vector bin packing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing, Hangzhou, China, 12–15 November 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcuoglu, H.; Hariri, S.; Wu, M.Y. Performance-effective and low-complexity task scheduling for heterogeneous computing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2002, 13, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Token Usage | Latency (s) | Cost (USD) | Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT Original | ||||
| Llama Original | 0 | |||
| GPT Iteration | ||||
| Llama Iteration | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, X.; Li, H. LLM-Driven Offloading Decisions for Edge Object Detection in Smart City Deployments. Smart Cities 2025, 8, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050169
Yuan X, Li H. LLM-Driven Offloading Decisions for Edge Object Detection in Smart City Deployments. Smart Cities. 2025; 8(5):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050169
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Xingyu, and He Li. 2025. "LLM-Driven Offloading Decisions for Edge Object Detection in Smart City Deployments" Smart Cities 8, no. 5: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050169
APA StyleYuan, X., & Li, H. (2025). LLM-Driven Offloading Decisions for Edge Object Detection in Smart City Deployments. Smart Cities, 8(5), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities8050169






