Mechanical, Structural, and Environmental Properties of Building Cements from Valorized Sewage Sludges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
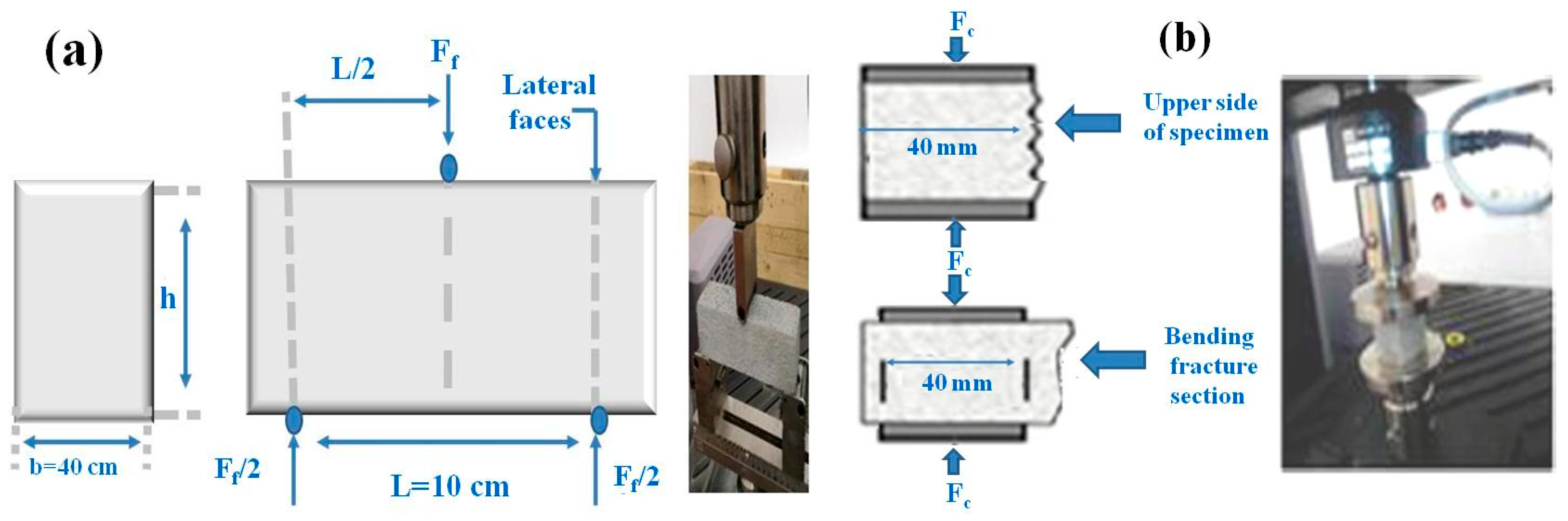
3. Methods
4. Results and Discussion
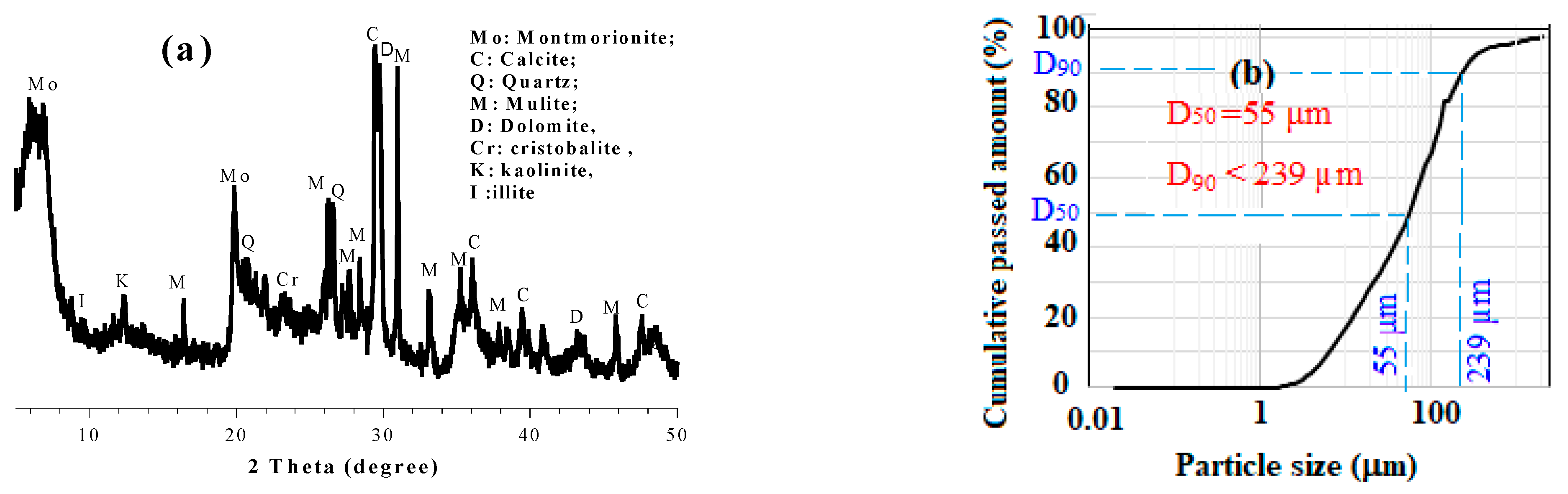
4.1. Characteristics of Sewage Sludge
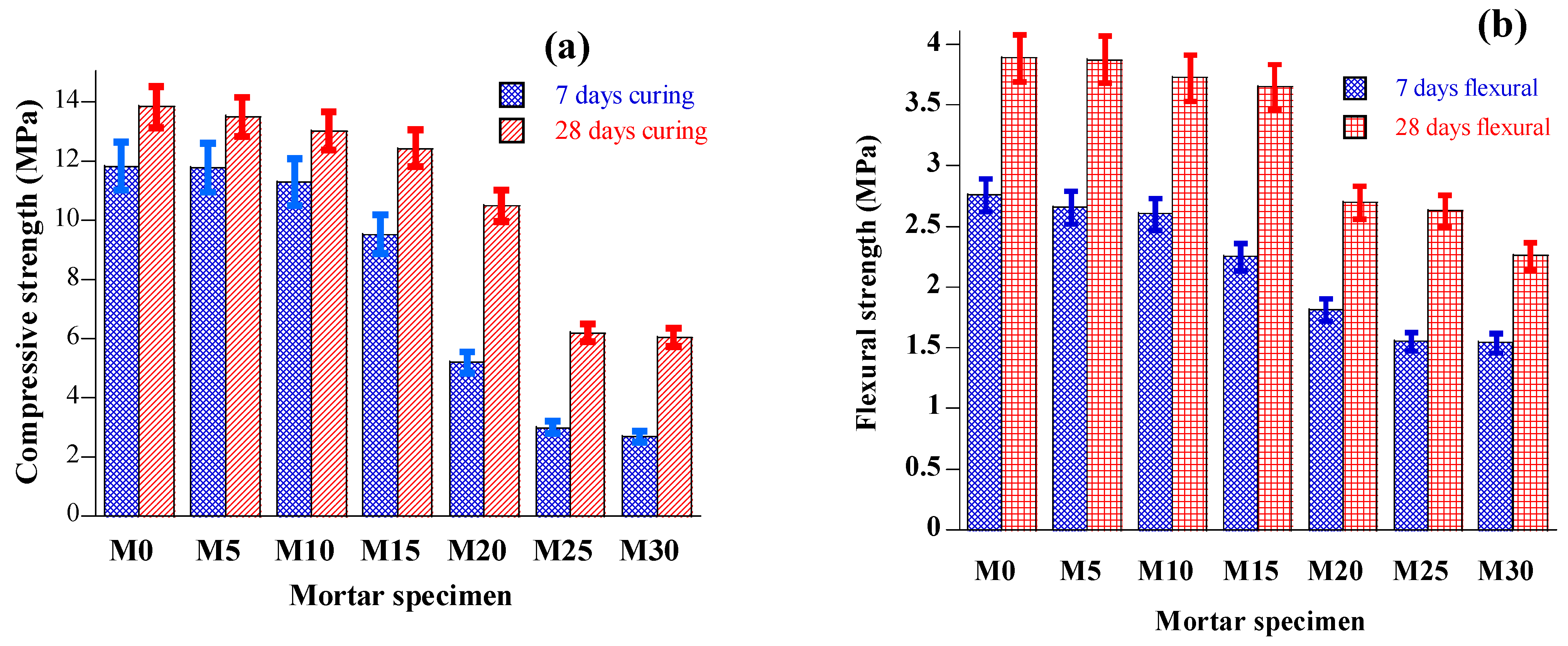
4.2. Mechanical Properties
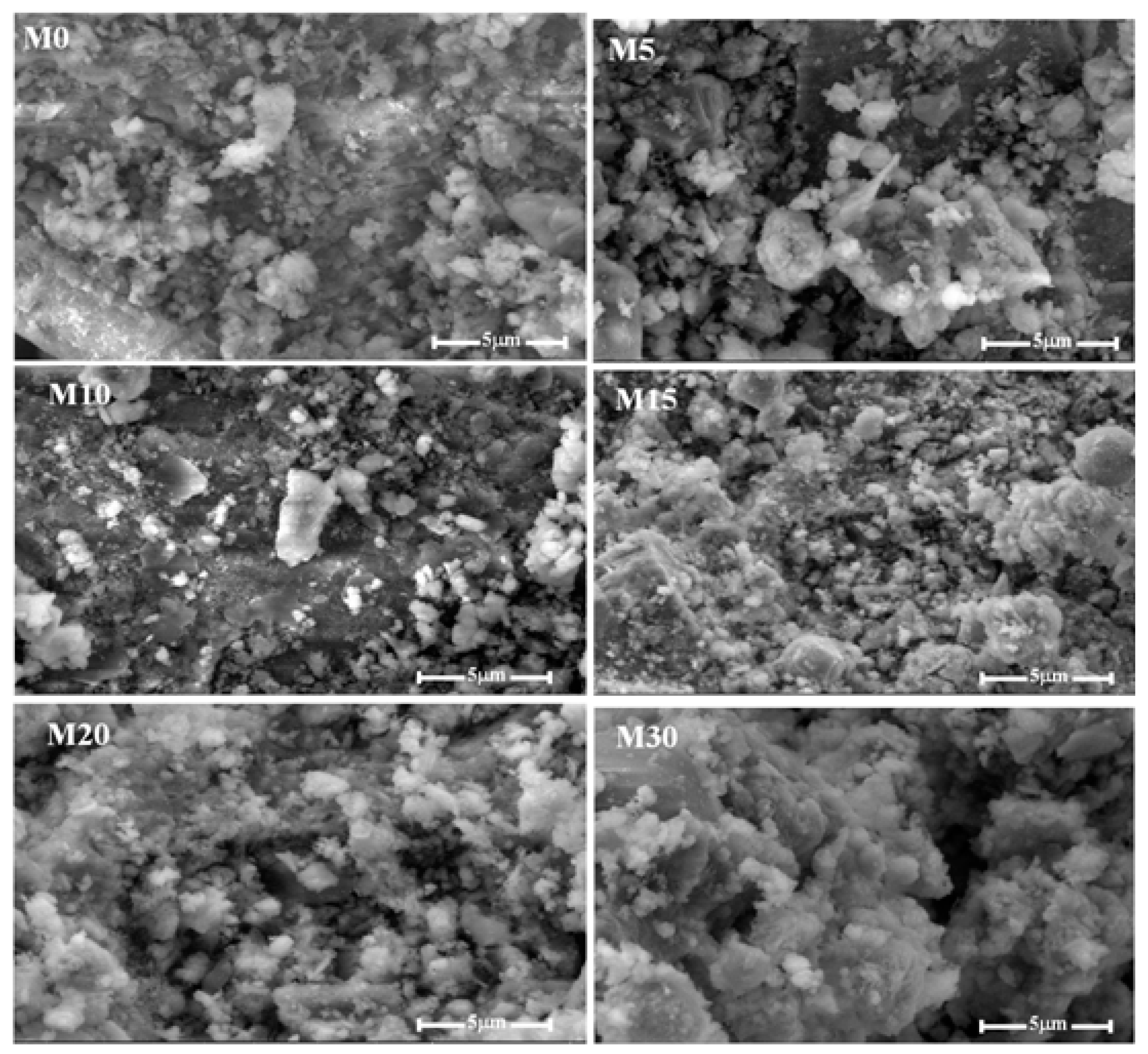
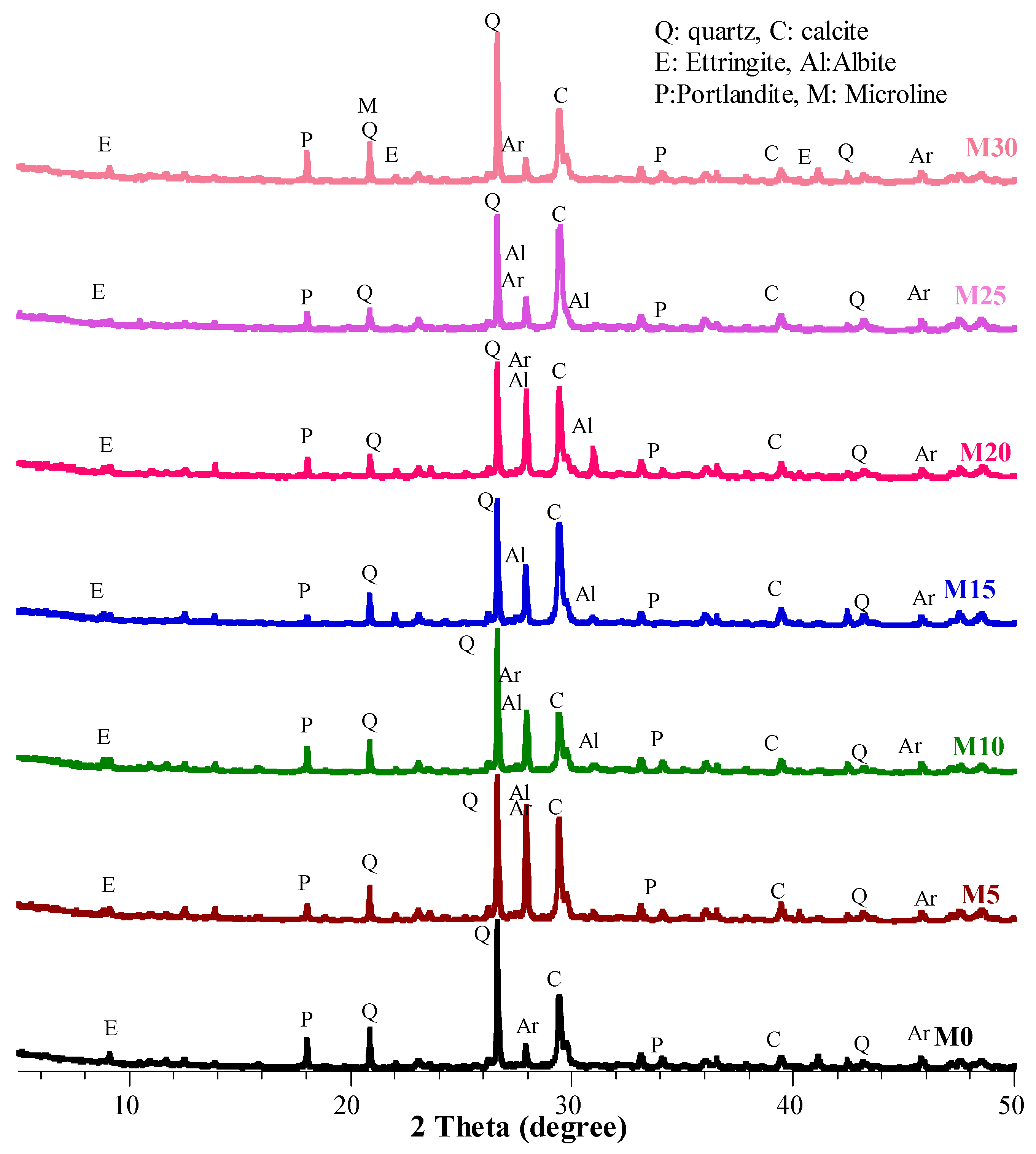
4.3. Microstructure Analysis of the Mortars
4.4. Environmental Assessment of Sludge-Amended Mortar
4.5. Radiological Assessment of Sludge-Amended Mortar
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quintaliani, C.; Merli, F.; Fiorini, C.V.; Corradi, M.; Speranzini, E.; Buratti, C. Vegetal Fiber Additives in Mortars: Experimental characterization of thermal and acoustic properties. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatello, S.; Cheeseman, C.R. Recycling and recovery routes for incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA): A review. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2328–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, C.J.; Dhir, R.K.; Ghataora, G.S.; West, R.P. Sewage sludge ash characteristics and potential for use in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, M.; Polaczyk, P.; Huang, B. Analytical investigation of phase assemblages of alkali-activated materials in CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 systems: The management of reaction products and designing of precursors. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Polaczyk, P.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Hu, W. Evaluation of glass powder-based geopolymer stabilized road bases containing recycled waste glass aggregate. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Biswas, S.; Pal, P.; Pal, A. Reduction of 4-nitrophenol using copper loaded surfactant-modified chitosan beads: An approach towards sludge management. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhair, A.; Belahbib, L.; Azkour, K.; Nebdi, H.; Benjelloun, M.; Nourreddine, A. Measurement of natural radioactivity and radon exhalation rate in coal ash samples from a Thermal Power Plant. World J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Ng, W.C.; Wong, B.S.E.; Teo, S.L.-M.; Sivananthan, G.D.; Baeg, G.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Wang, C.-H. Evaluation of sewage sludge incineration ash as a potential land reclamation material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherghel, A.; Teodosiu, C.; De Gisi, S. A review on wastewater sludge valorisation and its challenges in the context of circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zari, R.; Graich, A.; Mghiouini, R.; Monkade, M.; El Hadrami, A.; Brahmi, R.; Abdelouahdi, K.; Laghzizil, A. Treatment of tannery wastewater by infiltration/percolation process using natural clay combined solid wastes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 277, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, K.B.; Pacheco, E.; Guzmán, A.; Pereira, Y.A.; Cuadro, H.C.; Valencia, J.A.F. Use of sludge ash from drinking water treatment plant in hydraulic mortars. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwaeli, M.; Gołaszewski, J.; Niesler, M.; Pizoń, J.; Gołaszewska, M. Recycle option for metallurgical sludge waste as a partial replacement for natural sand in mortars containing CSA cement to save the environment and natural resources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Machi, A.; Mabroum, S.; Taha, Y.; Tagnit-Hamou, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Hakkou, R. Use of flint from phosphate mine waste rocks as an alternative aggregates for concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.-Y.; Chou, P.-H.; Hua, C.-R.; Chien, K.-L.; Cheeseman, C. Lightweight bricks manufactured from water treatment sludge and rice husks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Long, G.; Zhou, J.L.; Ma, C. Valorization of sewage sludge in the fabrication of construction and building materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naamane, S.; Rais, Z.; Taleb, M. The effectiveness of the incineration of sewage sludge on the evolution of physicochemical and mechanical properties of Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Standard NF EN 196-1; Methods of Testing Cement. Part 1: Determination of Strength. AFNOR Editions: Paris, France, 2016. Available online: www.boutique.afnor.org/en-gb/standard/nf-en-1961/methods-of-testing-cement-part-1-determination-of-strength/fa184622/57803 (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Huseien, G.F.; Sam, A.R.M.; Shah, K.W.; Budiea, A.M.A.; Mirza, J. Utilizing spend garnets as sand replacement in alkali-activated mortars containing fly ash and GBFS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Blanc, D.; Gautier, M.; Mehu, J.; Gourdon, R. Environmental and technical assessments of the potential utilization of sewage sludge ashes (SSAs) as secondary raw materials in construction. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Alameda, A.; Giro-Paloma, J.; Rodríguez-Romero, A.; Serret, J.; Menargues, A.; Andrés, A.; Chimenos, J. Environmental potential assessment of MSWI bottom ash-based alkali-activated binders. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard NEN 7345; Leaching Characteristics of Solid Earthy and Stony Building and Waste Materials—Leaching tests—Determination of the Leaching of Inorganic Components from Buildings and Monolitic Waste Materials with the Diffusion Test. GlobalSpec: Albany, NY, USA, 1995.
- Juel, M.A.I.; Mizan, A.; Ahmed, T. Sustainable use of tannery sludge in brick manufacturing in Bangladesh. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Vollpracht, A. Leaching of monolithic geopolymer mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 136, 106161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatungimana, D.; Taşköprü, C.; İçhedef, M.; Saç, M.M.; Yazıcı, Ş. Compressive strength, water absorption, water sorptivity and surface radon exhalation rate of silica fume and fly ash based mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 23, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuccetelli, C.; Leonardi, F.; Trevisi, R. Building material radon emanation and exhalation rate: Need of a shared measurement protocol from the european database analysis. J. Environ. Radioact. 2020, 225, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Mahur, A.K.; Yadav, M.; Sonkawade, R.G.; Sharma, A.C.; Ramola, R.C.; Prasad, R. Measurement of natural radioactivity, radon exhalation rate and radiation hazard assessment in indian cement samples. Phys. Procedia 2015, 80, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rati, V.; Mahur, A.; Sonkawade, R.; Suhail, M.; Azam, A.; Prasad, R. Evaluation and analysis of 226Ra, 232Th, 40K and radon exhalation rate in various grey cements. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2010, 48, 473. [Google Scholar]
- Shoeib, M.; Thabayneh, K. Assessment of natural radiation exposure and radon exhalation rate in various samples of Egyptian building materials. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhao, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z. Study on mechanical properties and pore structure characteristics of alkali activation sludge-cement composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulthana Begum, B.S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T.; Nidheesh, P.V. Utilization of textile effluent wastewater treatment plant sludge as brick material. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2013, 15, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Siddique, R.; Jha, S.; Sharma, D. Utilization of textile sludge in cement mortar and paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchorab, Z.; Barnat-Hunek, D.; Franus, M.; Łagód, G. Mechanical and physical properties of hydrophobized lightweight aggregate concrete with sewage sludge. Materials 2016, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, R.; Chaudhary, R. Leaching behavior and immobilization of heavy metals in solidified/stabilized products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.C.; Lin, J.D.; Tsai, C.C.; Wang, K.S. Study on cement mortar and concrete made with sewage sludge ash. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 1689–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Exposure to Radiation from the Natural Radioactivity in Building Materials; Report by a Group of experts of the OECD; Nuclear Energy Agency: Paris, France, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Vespa, M.; Dähn, R.; Wieland, E. Competition behaviour of metal uptake in cementitious systems: An XRD and EXAFS investigation of Nd- and Zn-loaded 11Å tobermorite. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2014, 70–71, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, D. Applications of sewage sludge ash and nano-SiO2 to manufacture tile as construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3312–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurda, R.; Silvestre, J.D.; de Brito, J. Toxicity and environmental and economic performance of fly ash and recycled concrete aggregates use in concrete: A review. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Pillai, G.S.; Venkatraman, B. Assessment of heavy metals and radionuclides (238U, 232Th and 40K) concentration of beach sands collected from East Coast of Tamilnadu, India with multivariate statistical approach. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 3996–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRP, International Commission on Radiological Protection. Protection against Rn-222 at Home and at Work. In Annals of the ICRP 65; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]

| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | SO3 | TiO2 | MgO | LOI * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 17.77 | 6.00 | 3.00 | 1.23 | 63.00 | 3.35 | - | 2.65 | 11.90 |
| Sand | 42.53 | 2.76 | 1.65 | 0.44 | 25.01 | - | 0.29 | 1.79 | 4.60 |
| Initial setting time | 180 min |
| Final setting time | 210 min |
| Specific gravity | 3.15 t/m3 |
| Blaine fineness | 304 m2/Kg |
| Compressive strength | 7 days under 30 MPa—28 days under 40 MPa |
| M0 | M5 | M10 | M15 | M20 | M25 | M30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement (g) | 450.0 | 427.5 | 405 | 382.5 | 360.0 | 337.5 | 315.0 |
| Sludge (g) | 0.00 | 22.5 | 45.0 | 67.5 | 90.0 | 112.5 | 135.0 |
| Sludge % | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Mortars | M0 | M5 | M10 | M15 | M20 | M25 | M30 | Leaching Limits NEN 7345 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | U2 | ||||||||
| As | <LD * | <LD | <LD | <LD | <LD | <LD | <LD | 40 | 300 |
| Cr | <LD | 0.012 | 0.198 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 150 | 950 |
| Cu | 0.002 | 0.0038 | 0.0034 | 0.004 | 0.0046 | 0.0054 | 0.0054 | 50 | 350 |
| Ni | 0.00562 | 0.02 | 0.034 | 0.032 | 0.0134 | 0.014 | 0.0138 | 50 | 350 |
| Zn | 0.0078 | 0.058 | 0.054 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.5 | 200 | 1500 |
| Samples | AV (mBq m−3) | ES (mBq m−1 h−1) | EM (mBq kg−1 h−1) | Annual Dose E (mSv/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sludge | 624 | 489 | 28 | 16 |
| M0 | 168 | 132 | 7 | 4 |
| M5 | 182 | 143 | 8 | 5 |
| M10 | 250 | 196 | 11 | 6 |
| M15 | 312 | 244 | 14 | 8 |
| M20 | 354 | 301 | 17 | 9 |
| M25 | 418 | 328 | 19 | 10 |
| M30 | 418 | 328 | 19 | 11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zari, R.; Graich, A.; Abdelouahdi, K.; Monkade, M.; Laghzizil, A.; Nunzi, J.-M. Mechanical, Structural, and Environmental Properties of Building Cements from Valorized Sewage Sludges. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1227-1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030059
Zari R, Graich A, Abdelouahdi K, Monkade M, Laghzizil A, Nunzi J-M. Mechanical, Structural, and Environmental Properties of Building Cements from Valorized Sewage Sludges. Smart Cities. 2023; 6(3):1227-1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleZari, Rkia, Abderrazzak Graich, Karima Abdelouahdi, Mohamed Monkade, Abdelaziz Laghzizil, and Jean-Michel Nunzi. 2023. "Mechanical, Structural, and Environmental Properties of Building Cements from Valorized Sewage Sludges" Smart Cities 6, no. 3: 1227-1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030059
APA StyleZari, R., Graich, A., Abdelouahdi, K., Monkade, M., Laghzizil, A., & Nunzi, J.-M. (2023). Mechanical, Structural, and Environmental Properties of Building Cements from Valorized Sewage Sludges. Smart Cities, 6(3), 1227-1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities6030059






