When Design Fiction Meets Geospatial Sciences to Create a More Inclusive Smart City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Bases
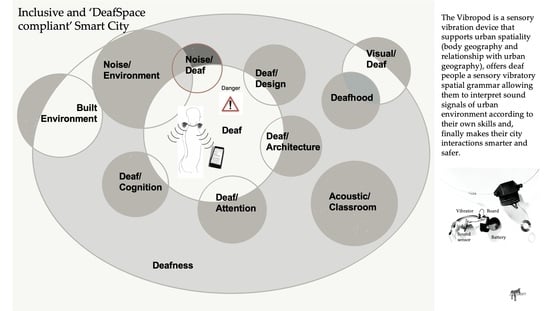
2.1. Inclusive Smart City
2.2. Deafness: Deaf Gain, Deafscape, and Cochlear Implants
- -
- Peripheral refers to the use of rhythmic, repetitive, and intuitive visual cues to support the deaf person’s peripheral vision;
- -
- Transparency refers to visual connections, openness, and of the degree of the enclosure;
- -
- Reflection refers to the extension of vision, allowing deaf people to see behind them, and to access depth and perspectives;
- -
- Vibration refers to the characteristics of the floor surfaces that allow to feel the presence of others and initiate contact;
- -
- Shared sensory reach refers to the interdependency of deaf individuals when they navigate their environment, as they strongly depend on one another to extend their spatial and orientation skills and spatial reasoning capabilities.
2.3. Spatial Skills, Spatiality
2.4. Design Fiction
- -
- “i. Design fiction suspends disbelief in change,
- -
- ii. It often examines the implications presented by potential design in the context of technological conflict,
- -
- iii. It enables discussion of social and political context,
- -
- iv. It inspires discussion about desirable and preferable futures,
- -
- v. It helps to reveal potential user concerns and uncertainties, and
- -
- vi. It presents a disruptive space for emerging cultural artifacts.” [57]
3. Design Fiction Workshops
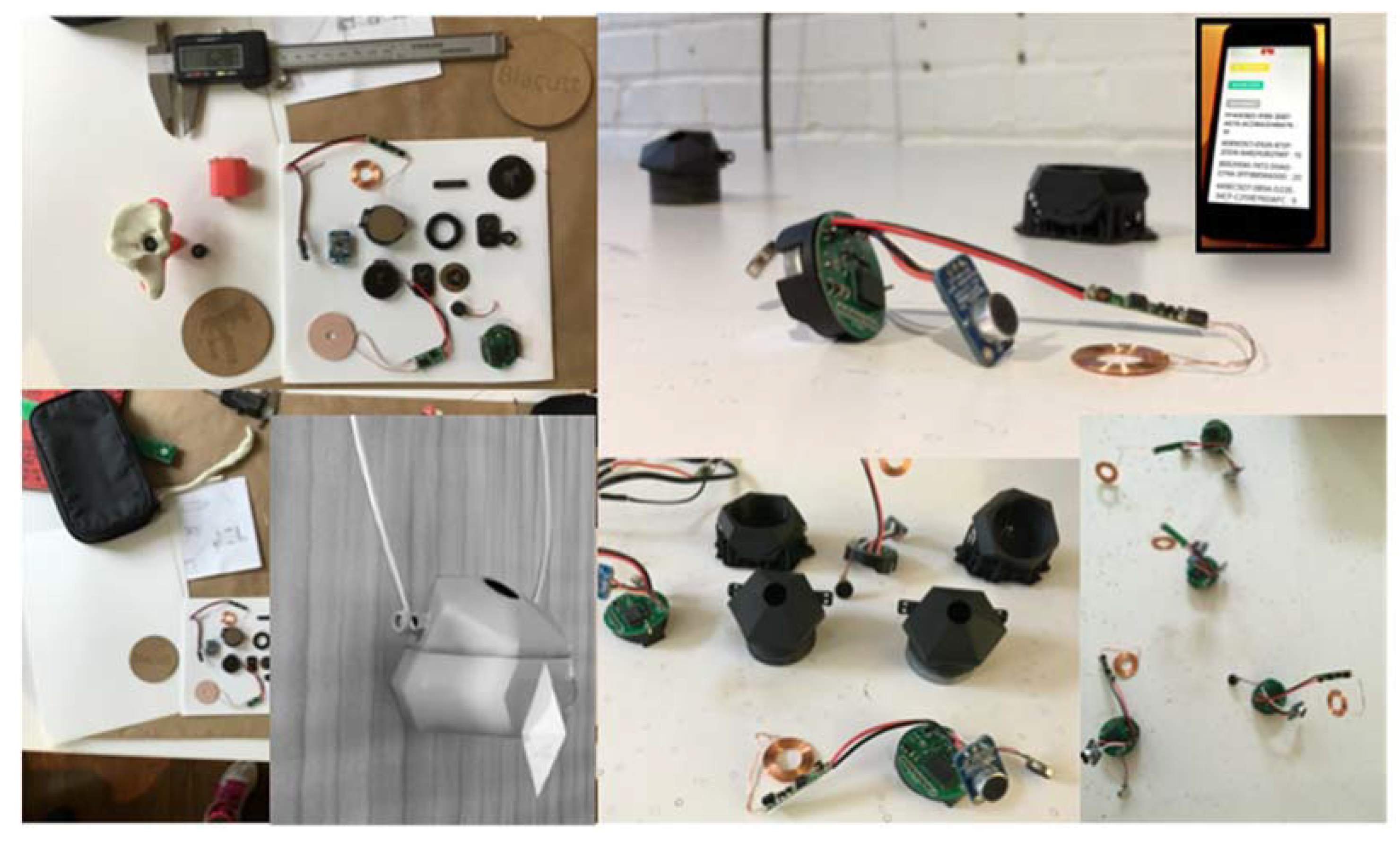
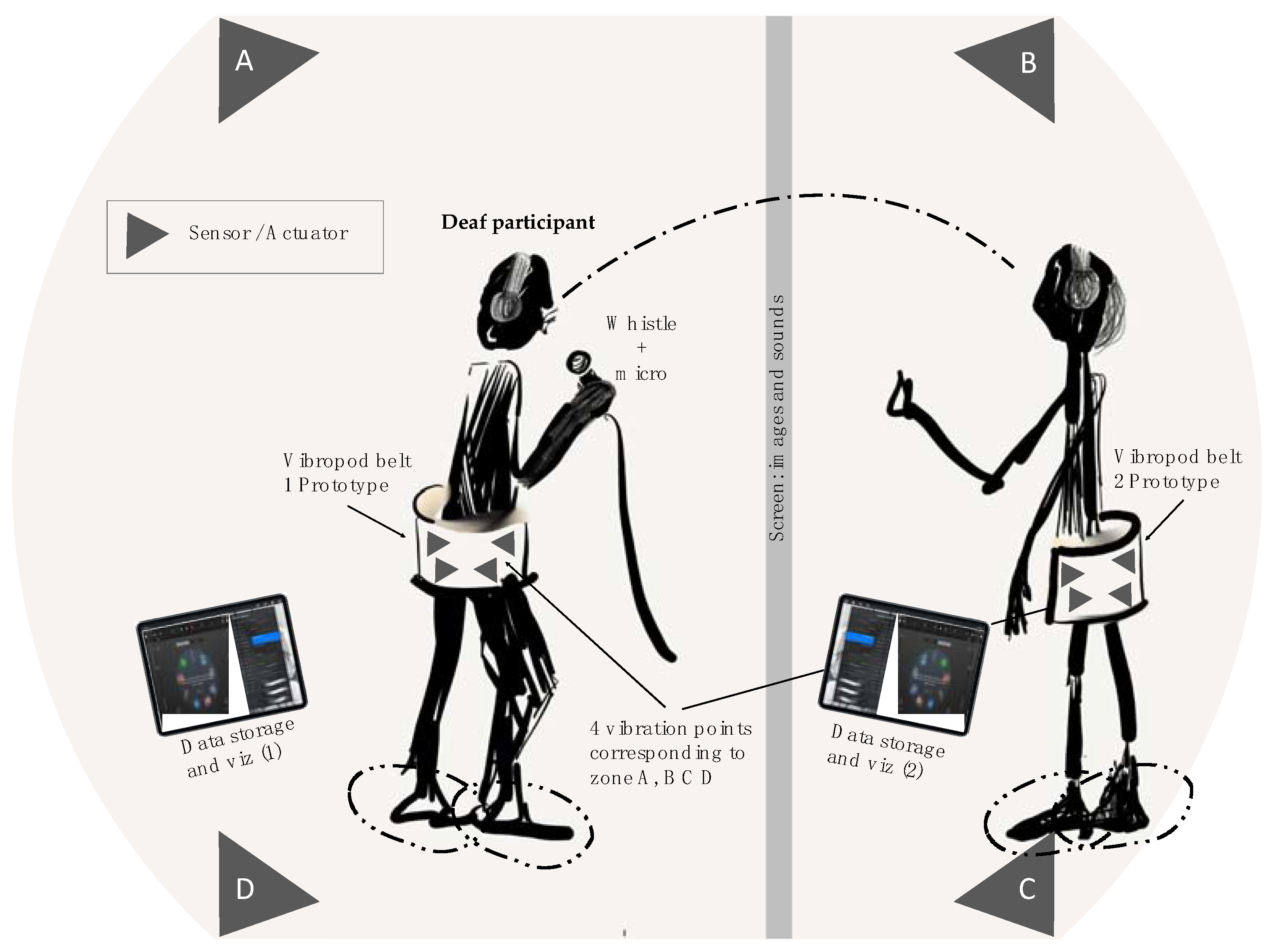
3.1. The Vibropod
3.1.1. The Vibropod Design
- -
- Segmentation (1): dividing the vibrations in independent as well as linked and scalable components, allowed us to proceed to a spatialization of body sounds;
- -
- Extraction (2) and total quality (3): extracting only the relevant parts and properties of meaningful “types of sound/vibration/body part” associations;
- -
- Asymmetry (4): replacing a symmetrical object by an asymmetrical one, as a way of locating participants in space (Figure 3);
- -
- Combination (5): spatial and temporal integration of homogeneous or contiguous modes of sound production;
- -
- Universality (6): designing a versatile device (in line with universal design), a device that can produce and sense different sound/vibration combinations;
- -
- Nesting (7): designing an object which can fully contain another object, and could be fully contained by another one (Russian dolls).
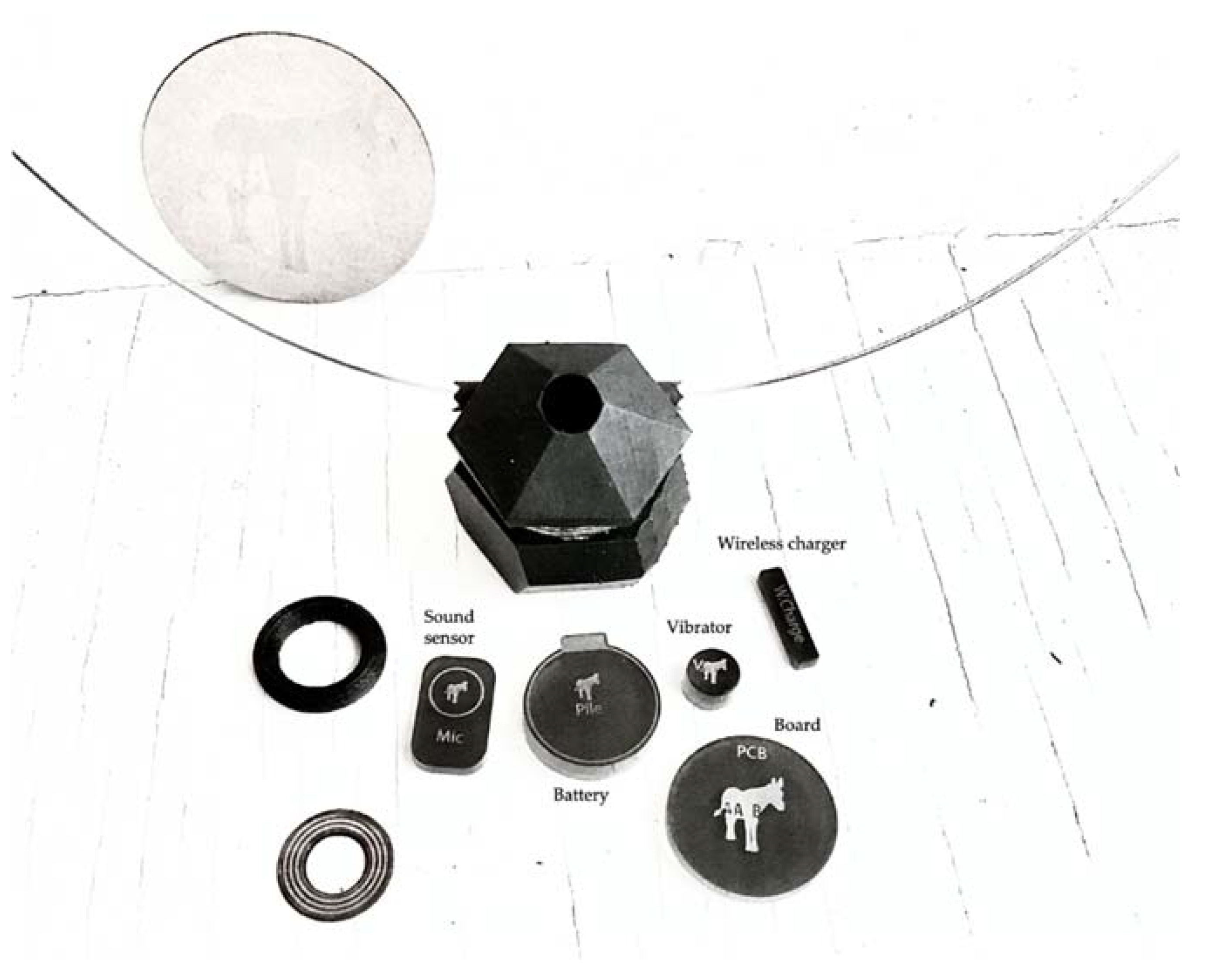
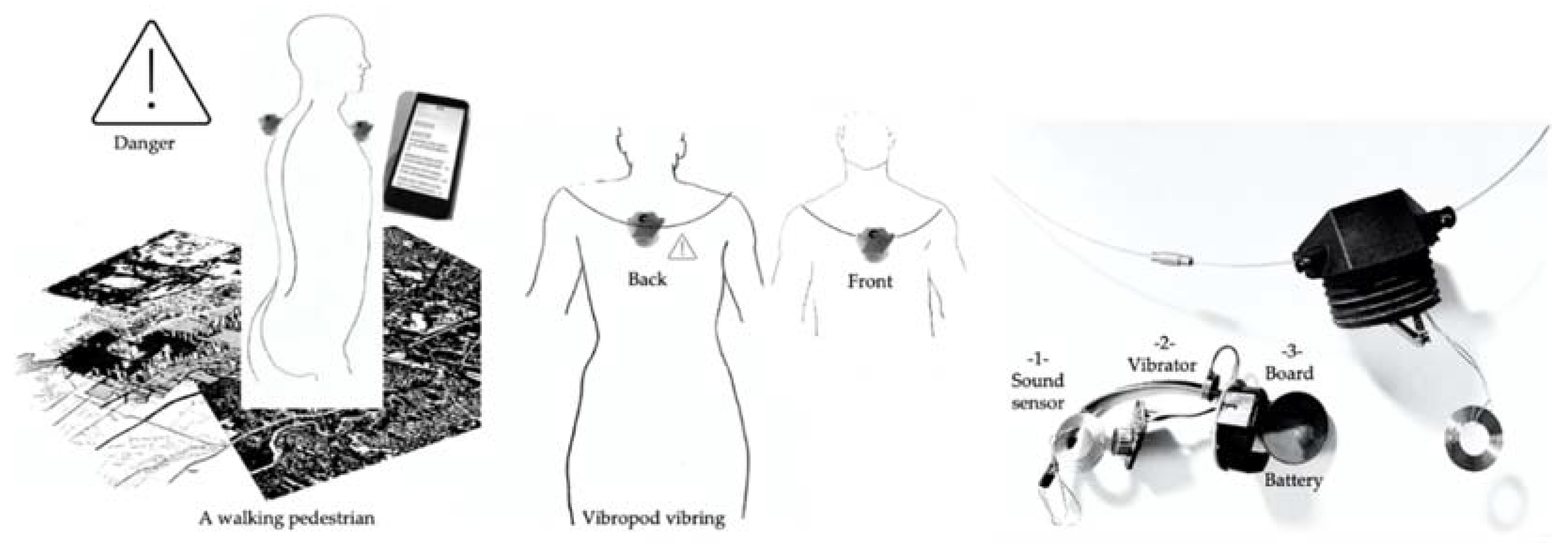
3.1.2. How Does the Vibropod Work on a Technical Level?
- -
- A circuit board control card (Simblee Bluetooth (BLE) Module—RFD77101: a small Arduino-programmable Bluetooth 4.0 (BLE) module allowing control of the IoT—Internet of Things) + RFduino—Simblee Starter Kit;
- -
- A sound sensor (VCC 2.4-5.5 V Adjustable Gain GY-MAX4466 20-20 KHz Electret Microphone Amplifier MAX4466 Adjustable Amplifier Sensor Module);
- -
- A vibrator (a VPM2 Vibrator: a Mini Motor generating a silent and intense vibration, in a metal case easy to put in place with the supplied adhesive);
- -
- A Custom Rechargeable Lithium Power battery LIR2450 (3.6 v, 120 ± 5 mah, 0.2c ma, 1c ma, 24.5 mm × 5.0 mm, 5.3 ± 0.2 g);
- -
- A Wireless Charging Module 5 V/300 mA (induction charger);
- -
- A chain allowing the user to wear the device around the neck.
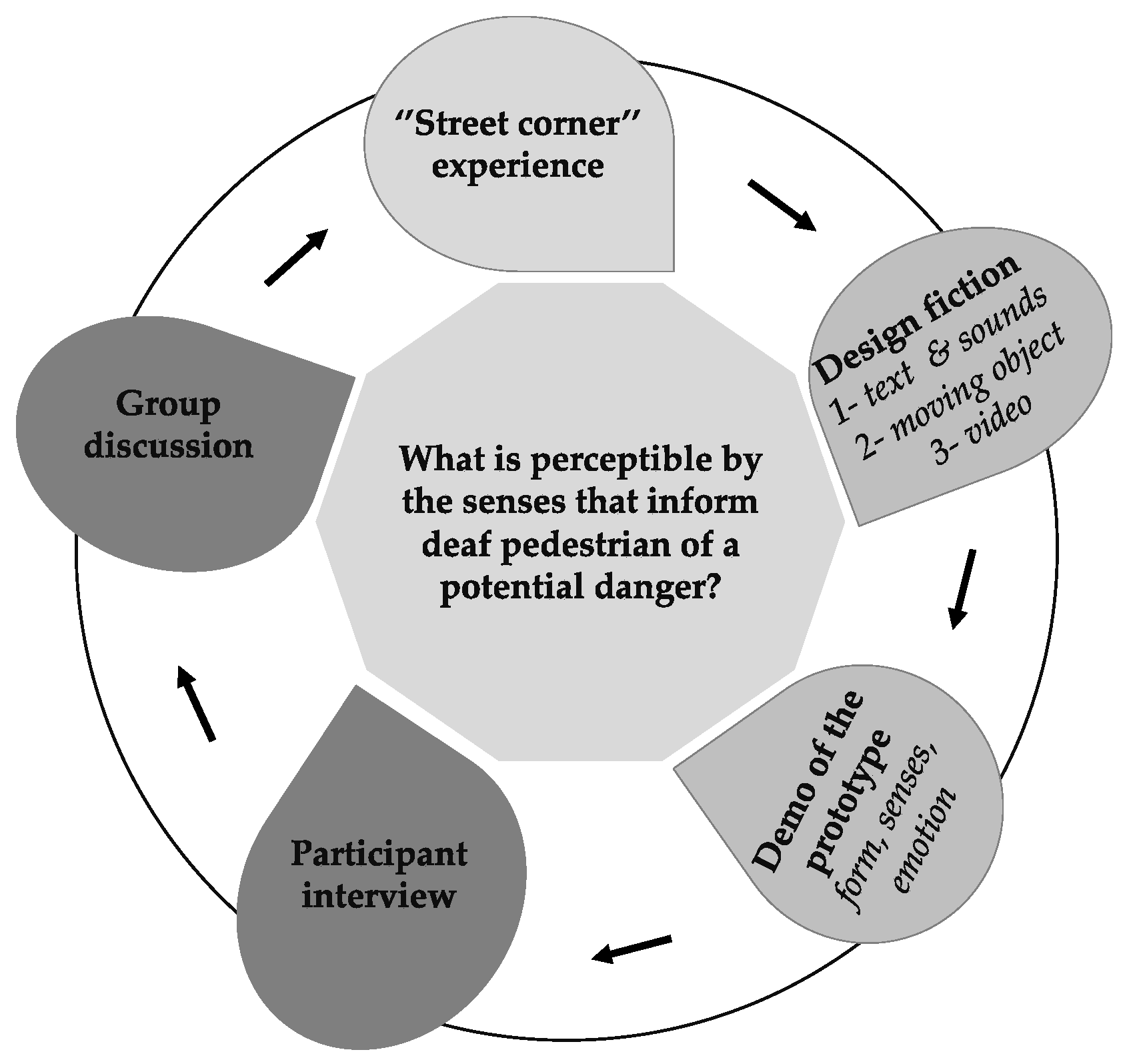
3.1.3. The Vibropod Design Fiction Workshop
- -
- Reading an excerpt from “The concept of nature” by Whitehead;
- -
- Followed by the movement of a red object in space (a billiard ball);
- -
- Then, finally, viewing a music video.
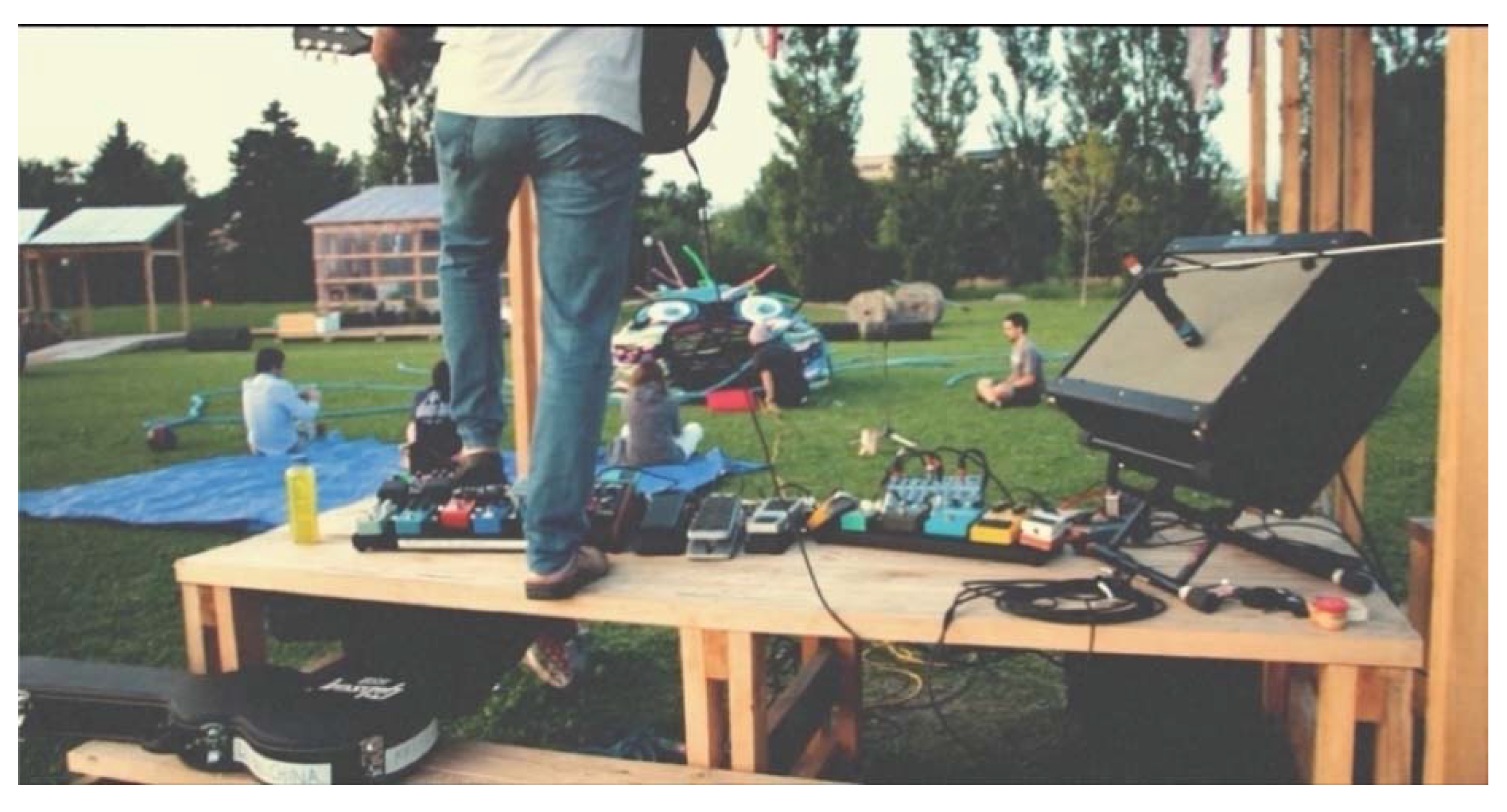
3.2. The “Pointe-aux-Lièvres” Urban Workshop
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodological Contributions
4.2. Spatial-Enablement of Hearing Impaired People
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batty, M. The New Science of Cities; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Caragliu, A.; Del Bo, C.; Nijkamp, P. Smart cities in Europe. J. Urban Technol. 2011, 18, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Pardo, T.A.; Aldama-Nalda, A. Smart cities and smart governments: Using information technologies to address urban challenges. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research, Quebec, QC, Canada, 17–20 June 2013; pp. 296–297. [Google Scholar]
- Selada, C. Smart Cities and the Quadruple Helix Innovation Systems Conceptual Framework: The Case of Portugal. In The Quadruple Innovation Helix Nexus. Palgrave Studies in Democracy, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship for Growth; De Oliveira Monteiro, S., Carayannis, E., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, V.; Berardi, U.; Dangelico, R.M. Smart cities: Definitions, dimensions, performance, and initiatives. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S. Geographic information science I: Why does a smart city need to be spatially enabled? Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2014, 38, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B. The 3 Generations of Smart Cities: Inside the Development of the Technology Driven City, 8 October 2015. Available online: https://www.fastcompany.com/3047795/the-3-generations-of-smart-cities (accessed on 13 August 2020).
- Garau, C.; Desogus, G.; Zamperlin, P. Governing Technology-based Urbanism: Technocratic Governance or Progressive Planning? In The Routledge Companion to Smart Cities; Willis, K.S., Aurigi, A., Eds.; Rootledge: Abingdon, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kamolov, S.; Kandalintseva, Y. The Study on the Readiness of Russian Municipalities for Implementation of the “Smart City” Concept. In Ecological-Socio-Economic Systems: Models of Competition and Cooperation (ESES 2019), Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2020; Volume 392, pp. 256–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin, R. The ethics of smart cities and urban science. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Neto, J.S.; Kofuji, S.T. Inclusive Smart City: An Exploratory Study. In Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction. Interaction Techniques and Environments. UAHCI 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Antona, M., Stephanidis, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, K. Who Is the Assumed User in the Smart City? In Designing, Developing, and Facilitating Smart Cities: Urban Design to IoT Solutions; Angelakis, V., Tragos, E., Pöhls, H.C., Kapovits, A., Bassi, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rode, P.; Floater, G.; Thomopoulos, N.; Docherty, J.; Schwinger, P.; Mahendra, M.; Fang, W. Accessibility in Cities: Transport and Urban Form. In Disrupting Mobility; Meyer, G., Shaheen, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mobility; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauna, T.; Fung, B.C.M.; Iqbal, F.; Shahb, B. Security and privacy challenges in smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, M.F. Maximizing usability: The principles of universal design. Assist. Technol. 1998, 10, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kbar, G.; Mian, S.H.; Abidi, M.H. Unified Interface for People with Disabilities (UI-PWD) at Smart City (Design and Implementation). In Information Innovation Technology in Smart Cities; Ismail, L., Zhang, L., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougeyrollas, F.; Boucher, N.; Edwards, G.; Grenier, Y.; Noreau, L. The Disability Creation Process Model: A Comprehensive Explanation of Disabling Situations as a Guide to Developing Policy and Service Programs. Scand. J. Dis. Res. 2019, 21, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, H. DeafSpace. In The Senses: Design Beyong Vision; Ellen, L., Lipps, A., Eds.; Princeton Architectural Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, J.; Marangos, N.; Ziegler, N. Reliability of cochlear implants. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S.; Nabian, N.; Kloeckl, K.; Ratti, C. Are ‘smart cities’ smart enough? In Spatially Enabling Government, Industry and Citizens: Research Development and Perspectives; Rajabifard, A., Coleman, D., Eds.; GSDI Association Press: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 2012; pp. 215–236. [Google Scholar]
- Roche, S. Geographic information science III: Geographic information science III: Spatial thinking, interfaces and algorithmic urban places–Toward smart cities. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2016, 41, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattern, S. A City is Not a Computer. Places J. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L. How Can a Smart City Make Life Easier for People with Disabilities? Available online: https://www.inclusivecitymaker.com/how-can-a-smart-city-make-life-easier-for-people-with-disabilities/ (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Gharebaghi, A.; Mostafavi, M.-A.; Chavoshi, S.H.; Edwards, G.; Fougeyrollas, P. The Role of Social Factors in the Accessibility of Urban Areas for People with Motor Disabilities. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2018, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain, R.; Melià-Segui, J.; Pous, R.; Peig, E. Using Augmented Reality and Internet of Things to improve accessibility of people with motor disabilities in the context of Smart Cities. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 76, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D. The Rise of Data Poverty in America”, Report published by the Center for Data Innovation. Available online: http://www2.datainnovation.org/2014-data-poverty.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Graham, S. Bridging Urban Digital Divides? Urban Polarisation and Information and Communications Technologies (ICTs). Urban Stud. 2002, 39, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, H.; Gilart-Iglesias, V.; Pérez-Delhoyo, R.; Andújar-Montoya, M.D.; Compañ Gabucio, H.J. Interactive cloud system for the analysis of accessibility in smart cities. Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodyn. 2016, 11, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siny, J.; Vinod, N. Auxiliary Location-Based Services for Persons with Disabilities: What do City Planners and Non-Profit Agencies Think? In Proceedings of the ASSETS ’19: 21st International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 28–30 October 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart City for All. Available online: https://smartcities4all.org/ (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- mobiliSIG. Available online: http://mobilisig.scg.ulaval.ca/ (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Mostafavi, M.A.; Noreau, L. MobiliSIG: An Adaptive Mobile Geospatial Technology for the Mobility of People with Disabilities. In Embedded Systems and Assistive Technology for Last Mile Mobility; Magoulès, F., Monacelli, E., Noreau, L., Eds.; Institute of Computer Sciences Press (ICS): London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Wenbi, R.; da Silva, A.L.; Nadher, M.; Mudhish, M. Health and emergency-care platform for elderly and disabled people in Smart City. J. Syst. Softw. 2015, 110, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago Pineda, V.; Corburn, J. Disability, Urban Health Equity, and the Coronavirus Pandemic: Promoting Cities for All. J. Urban Health 2020, 97, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebernik, N.; Szajczyk, M.; Bahillo, A.; Goličnik Marušić, B. Measuring Disability Inclusion Performance in Cities Using Disability Inclusion Evaluation Tool (DIETool). Sustainability 2020, 12, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, N.W.; Baker, P.M.A.; Goughnour, K. Designing wearable technologies for users with disabilities: Accessibility, usability, and connectivity factors. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.S.; Takeo Kofuji, N.S.; Bourda, Y. People with Disabilities’ Needs in Urban Spaces as Challenges towards a More Inclusive Smart City. In Information Technology and Systems; Rocha, Á., Ferrás, C., Montenegro Marin, C., Medina García, V., Eds.; ICITS 2020, Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, M.; Feki, M.A. User Needs and Usage Analysis in a Smart Environment for People Requiring Assistance. Top. Geriatr. Rehabil. 2007, 23, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S. Geographic information science II: Less space, more places in smart cities. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2015, 40, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, J.; Larsson, S.; Östergren, P.O. The right to assistive technology: For whom, for what, and by whom? Dis. Soc. 2009, 26, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, H. DeafSpace: An Architechture toward a More Livable and Sustainable World. In Deaf Gain: Raising the Stakes for Human Diversity; Bauman, H.-L., Ed.; University of Minnesota Press: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2014; pp. 375–401. [Google Scholar]
- Gitlow, L.; Flecky, K. (Eds.) Assistive Technologies and Environmental Interventions in Healthcare: An Integrated Approach; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.; Harold, G. DeafSpace and the principles of universal design. Dis. Rehabil. 2014, 36, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirdre, D.; Layton, N.; Bentley, J.; Boot, F.H.; Borg, J.; Dhungana, B.M.; Gallagher, P.; Gitlow, L.; Gowran, R.J.; Groce, N.; et al. Assistive technology and people: A position paper from the first global research, innovation and education on assistive technology (GREAT) summit. Dis. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2018, 13, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lid Inger, M. Universal Design and disability: An interdisciplinary perspective. Dis. Rehabil. 2013, 36, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fougeyrollas, P. Quebec model of disability creation process. In Encyclopedia of Disability; Albrecht, G.L., Ed.; SAGE Publications: Chicago, IL, USA, 2006; Volume III, pp. 1325–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Contrera, K.J.; Choi, J.S.; Blake, C.R.; Betz, J.F.; Niparko, J.K.; Lin, F.R. Rates of Long-Term Cochlear Implant Use in Children. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 2035, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.T. Cochlear Implants in Congenitally Deaf Children: A Discussion Built on Rights-Based Arguments. Am. Ann. Deaf 2020, 164, 46–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, A.A.; Nazarian, R.; Telischi, F.F.; Rajguru, S.M.; Truy, E.; Gupta, S.M. The cochlear implant: Historical aspects and future prospects. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouard, C.-H. Entendre sans Oreille; Robert Laffont: Paris, France, 1978; 210p. [Google Scholar]
- Bennette, R.J.; Jayakody, D.M.P.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Taljaard, D.S.; Atlas, M.D. A prospective study evaluating cochlear implant management skills: Development and validation of the Cochlear Implant Management Skills. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2016, 41, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, W.F. Cochlear Implants. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1976, 85, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussault, M. Compétences de Spatialité, EspacesTemps.net. 2014. Available online: https://www.espacestemps.net/articles/competences-de-spatialite/ (accessed on 23 August 2020).
- Williamson, I.; Rajabifard, A.; Holland, P. Spatially Enabled Society. In Proceedings of the FIG Congress 2010, Facing the Challenges—Building the Capacity, Sydney. Available online: www.fig.net/pub/fig2010/papers/inv03%5Cinv03_williamson_rajabifard_et_al_4134.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2015).
- Lévy, J. Capital spatial. In Dictionnaire de la Géographie et de L’espace des Sociétés; Lévis, J., Lussault, M., Eds.; Editions Belin: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sanford, J.A.; Story, M.F.; Ringholz, D. Consumer participation to inform universal design. Technol. Dis. 1998, 9, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, N.; Pedell, S.; Mayasari, A.; Beh, J. Co-creating and Assessing Future Wellbeing Technology Using Design Fiction. She Ji J. Des. Econ. Innov. 2019, 5, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candy, S.; Dunagan, J. Designing an experiential scenario: The people who vanished. Futures 2017, 86, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, T.; Garry, T.; Belk, R. Design fiction diegetic prototyping: A research framework for visualizing service innovations. J. Serv. Mark. 2019, 34, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.R.; Ashby, S.R. From Design Fiction to Future Models of Community Building and Civic Engagement. In Proceedings of the 9th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–27 October 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyckvi, S.L.; Roto, V.; Buie, E.A.; Wu, Y. The role of design fiction in participatory design processes. In Proceedings of the NordiCHI ’18: 10th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Oslo, Norway, 1–3 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nägele, L.V.; Ryöppy, M.; Wilde, D. PDFi: Participatory Design Fiction with Vulnerable Users. In Proceedings of the 10th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Oslo, Norway, 29 September–3 October 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, D. Design Fictions an Introduction and Provisional Taxonomy. Digit. Creat. 2013, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, M. Research through Design Fiction: Narrative in Real and Imaginary Abstracts. In Proceedings of the CHI ’14: SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Toronto, ON, Canada, 26 April–1 May 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altshuller, G.S.; Clarke, D.W.; Fedoseev, U.; Rodman, S.; Shulyak, L.; Lerner, L. 40 Principles: TRIZ Keys to Innovation; Extended Edition; Technical Innovation Center Inc.: Worcester, MA, USA, 2005; 144p. [Google Scholar]
- Savransky, S. Engineering of Creativity: Introduction to TRIZ Methodology of Inventive Problem Solving; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; 394p. [Google Scholar]
- Louafa, T.; Perret, F.-L. Créativité & innovation: L’intelligence collective au service du management de projet, coll. In Créativité et Innovation; Presses Polytechniques et Universitaires Romandes: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2008; 351p. [Google Scholar]
- Meylan, C. Système TRIZ de Stimulation de la Créativité et D’aide à L’innovation Méthodes Pratiques Pour la Résolution de Problèmes Techniques et la Recherche de Nouvelles Opportunités D’affaires; CH-CM Consulting Édition: Peseux, Suisse, 2007; 105p. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, P. L’onto-logique de l’événement chez Whitehead. Les Études Philos. 2002, 4, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| La Chambre Blanche (Artists Center) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tasks | Participants | Duration | Recruitment Participants | Interaction Tools | Deliverables |
| Design, conception, production of the Vibropod | First author, a 3D printing technician, partners | One year | Vibropod prototype - 3D printing - choice and testing of materials and components | ||
| Design fiction evening workshop | 10 (general public, students) | Two hours - 60 min presentations - 60 min discussion | - Communication and call for participations in social media, - Contacts list (center), | - Art performance, - Face-to-face survey, - Video projection, | - Survey questionnaire - Discussion verbatim |
| La Pointe-aux-Lièvres (urban place) | |||||
| Design of the soundtrack to “dress up” the urban space | First author, music composer, filmmaker | One week | |||
| Design fiction evening workshop | 10 (general public) | Two hours | - Communication and call for participations in social media - Contact list (Quebec City and “Pépinière Espace Collectif”) | - Sound experimentation, - Discussion - Capture of the event by a filmmaker | - Documentary film - Verbatim of discussion |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blacutt, A.-A.; Roche, S. When Design Fiction Meets Geospatial Sciences to Create a More Inclusive Smart City. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1334-1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3040064
Blacutt A-A, Roche S. When Design Fiction Meets Geospatial Sciences to Create a More Inclusive Smart City. Smart Cities. 2020; 3(4):1334-1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlacutt, Andrée-Anne, and Stéphane Roche. 2020. "When Design Fiction Meets Geospatial Sciences to Create a More Inclusive Smart City" Smart Cities 3, no. 4: 1334-1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3040064
APA StyleBlacutt, A.-A., & Roche, S. (2020). When Design Fiction Meets Geospatial Sciences to Create a More Inclusive Smart City. Smart Cities, 3(4), 1334-1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3040064