Towards Evaluation the Cornerstone of Smart City Development: Case Study in Dalat City, Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Smart City
2.2. Motivating Factors and Benefits
3. Methodology
4. Case Study
4.1. City Vision and Transformation—Strengths
4.1.1. Well Defined and Realistic Goals
4.1.2. Technological Innovation
4.2. City Vision and Transformation—Weakness
4.2.1. Managerial and Organizational
4.2.2. Citizen’s Awareness and Involvement
4.3. City Vision and Transformation—Opportunities
4.3.1. Institutional Interactions
4.3.2. Citizen-Centric, Innovation and Entrepreneurship
4.4. City Vision and Transformation—Threats
4.4.1. Economic Uncertainty
4.4.2. Lack of Universal Standardized and Interoperability Issues
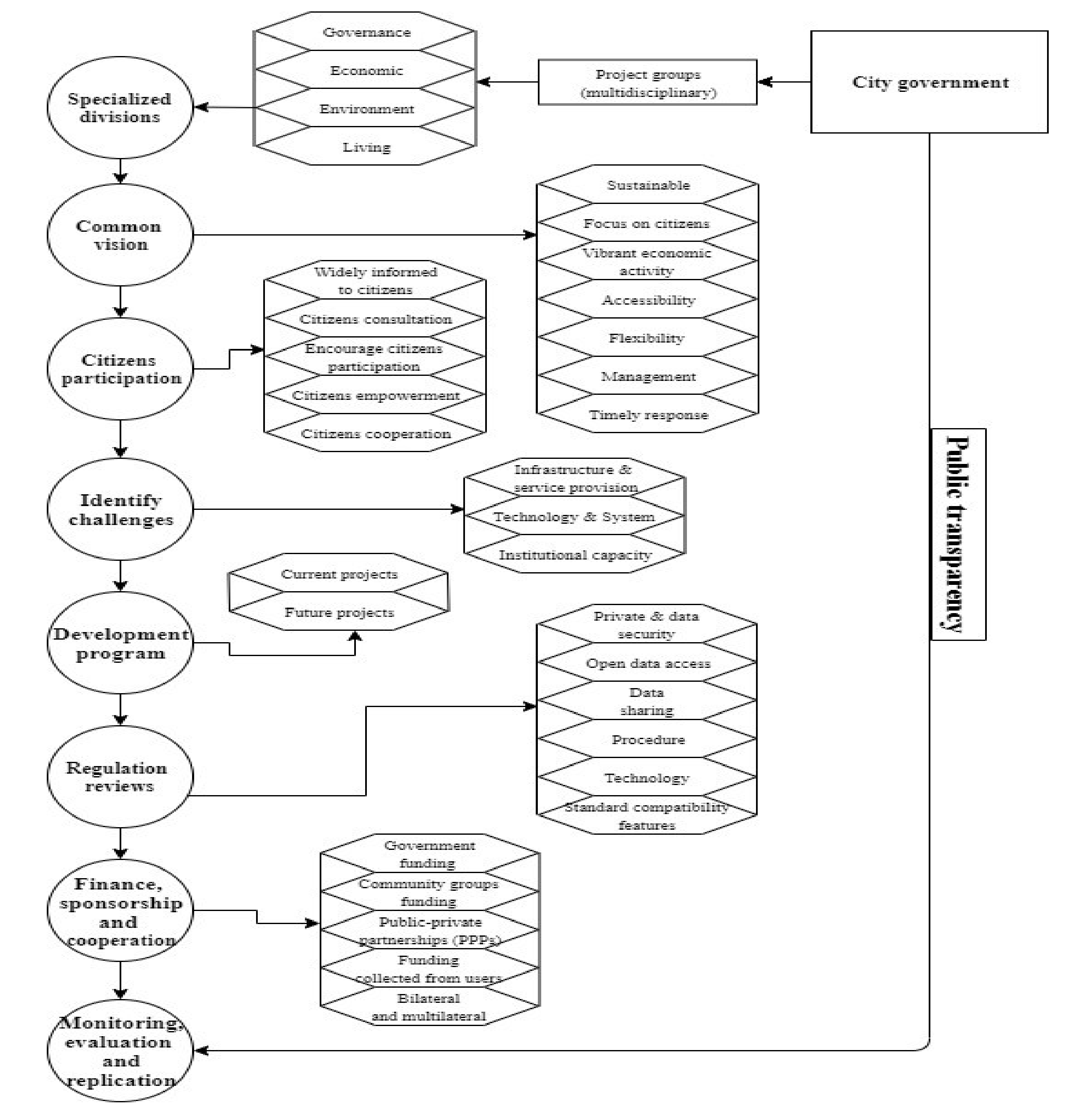
4.5. Suitable Strategies Framework for the Development of a Smart City in Dalat
4.5.1. Specialized Divisions
4.5.2. Common Vision
4.5.3. Citizens Participation
4.5.4. Identify Challenges
4.5.5. Development Programs
4.5.6. Regulation Reviews
4.5.7. Finance, Sponsorship and Cooperation
4.5.8. Monitoring, Evaluation and Replication
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN DESA. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; United Nations: Department of Economic and Social Affairs/Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, B. Urbanization in developing countries: Current trends, future projections, and key challenges for sustainability. J. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, A.; Paddison, R. New Challenges for Urban Governance. Urban Stud. 2000, 37, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutemeri, N.; Callaghan, C.; Hermanus, M. Good Practice Note Public Infrastructure and Mining; University of the Witwatersrand: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tallman, S.; Fladmoe-Lindquist, K. Internationalization, Globalization, and Capability-Based Strategy. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2002, 45, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choongik, C.; Chun-il, K. The 4th Industrial Revolution, Smart Cities, and Sustainable Urban Regeneration: A Perspective Study. J. Environ. Policy Admin. 2017, 25, 61–91. [Google Scholar]
- PWC. Global Industry 4.0 Survey, Industry 4.0: Building the Digital Enterprise. Available online: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/industries/industries-4.0/landing-page/industry-4.0-building-your-digital-enterprise-april-2016.pdf (accessed on 3 September 2019).
- IHS Technology. Smart Cities to Rise Fourfold in Number from 2013 to 2025. Available online: https://news.ihsmarkit.com/press-release/design-supply-chain-media/smart-cities-rise-fourfold-number-2013–2025 (accessed on 6 September 2019).
- Mulligan, C.E.A.; Olsson, M. Architectural implications of smart city business models: An evolutionary perspective. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2013, 51, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameri, R.P.; Rosenthal-Sabroux, C. Smart City. In Smart City and Value Creation; Dameri, R.P., Rosenthal-Sabroux, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank, MPI. Vietnam 2035: Toward Prosperity, Creativity, Equity, and Democracy; The World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hieu, N.N. Urban boundary and growth management in the peri-urban area. Vietnam. Archit. 2015, 12, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Vietnam Urbanization Review—Technical Assistance Report Vietnam; The World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Habitat. Vietnam Housing Sector Profile; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, C.T.T. Environmental Pollution in Vietnam: Challenges in Management and Protection. J. Viet. Env. 2018, 9, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Government Portal. Decision No. 950/QD-TTG Dated 01/08/2018. Available online: http://vanban.chinhphu.vn/portal/page/portal/chinhphu/hethongvanban?class_id=2&_page=1&mode=detail&document_id=194337 (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- MIC. Vietnam ICT Index Anual Report 2017; Vietnam government, Ministry of Information and Communications: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2017.
- Araya, D. Smart Cities and the Network Society: Toward Commons-Driven Governance. In Smart Cities as Democratic Ecologies; Araya, D., Ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: Houndmills, UK; ASC: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.M. E-democracy for Smart Cities. In Advances in 21st Century Human Settlements; Kumar, T.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Hu, F. Big data and cloud computing: Innovation opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 10, 13–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komninos, N. Intelligent cities: Towards interactive and global innovation environments. Int. J. Innov. Reg. Dev. 2009, 1, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramers, A.; Höjer, M.; Lövehagen, N.; Wangel, J. Smart sustainable cities–exploring ICT solutions for reduced energy use in cities. Environ. Model Softw. 2014, 56, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neirotti, P.; De Marco, A.; Cagliano, A.C.; Mangano, G.; Scorrano, F. Current trends in smart city initiatives: Some stylised facts. Cities 2014, 38, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niaros, V.; Kostakis, V.; Drechsler, W. Making in the smart city: The emergence of makerspaces. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, M. Deconstructing Smart Cities: An Intertextual Reading of Concepts and Practices for Integrated Urban and ICT Development. In Proceedings of the Real Corp 2012: Re-Mixing the City—Towards Sustainability and Resilience, Aachen, Germany, 14–16 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giffinger, R.; Fertner, C.; Kramar, H.; Kalasek, R.; Pichler-Milanovic, N.; Meijers, E. Smart Cities: Ranking of European Medium-Sized Cities. Available online: http://www.smart-cities.eu/download/smart_cities_final_report.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Pelley, J. Building smart-growth communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, A.; Bolívar, M.P.R. Governing the smart city: A review of the literature on smart urban governance. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2016, 82, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, A.; Peter, N. Redefining the Smart City: Culture, Metabolism and Governance. Smart Cities 2018, 1, 4–25. [Google Scholar]
- ITU. What is a smart Sustainable City? Available online: http://itunews.itu.int/en/5215-what-is-a-smart-sustainable-city.note.aspx (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Zygiaris, S. Smart city reference model: Assisting planners to conceptualize the building of smart city innovation ecosystems. J. Knowl. Econ. 2012, 4, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietnam Ministry of Construction. Smart City Vision in Vietnam. Available online: http://www.moc.gov.vn/vi/thong-tin-tu-lieu/-/tin-chi-tiet/ek4I/86/447727/tam-nhin-do-thithong-minh-tai-viet-nam.html (accessed on 16 September 2019).
- PRB. An Overview of Population and Development in Vietnam. Available online: https://www.prb.org/anoverviewofpopulationanddevelopmentinvietnam/ (accessed on 16 September 2019).
- Fraser, C. E-government: The Canadian experience. Dalhousie J. Interdiscip. Manage. 2009, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mattoni, B.; Gugliermetti, F.; Bisegna, F. A multilevel method to assess and design the renovation and integration of smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 15, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, L. From e-government to we-government: Defining a typology for citizen coproduction in the age of social media. Gov. Inform. Q. 2012, 29, 446–454. [Google Scholar]
- Maria, L.M.L.; Joan, C.L.; Joaquim, M.F. Lessons in urban monitoring taken from sustainable and livable cities to better address the Smart Cities initiative. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2015, 90, 611–622. [Google Scholar]
- Kehua, S.; Jie, L.; Hongbo, F. Smart city and the applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electronics, Ningbo, China, 9–11 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eleonora, R.S.; Raffaella, R.S.; Valentina, V.; Ina, M.; Enrico, A. Smart Cities: Case Studies. In Smart Cities Atlas; Eleonora, R.S., Raffaella, R.S., Valentina, V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 47–140. [Google Scholar]
- Coman, A.; Ronen, B. Focused SWOT: Diagnosing critical strengths and weaknesses. In. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 47, 5677–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, G.; Lenie, K.; Vanhoof, K. A knowledge-based SWOT-analysis system as an instrument for strategic planning in small and medium sized enterprises. Decis. Support Syst. 1999, 26, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, K. Strategic Management Dynamics; Warren, K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, J.F. How Politically Correct Is Political Correctness? A SWOT Analysis of This Phenomenon. Bus. Soc. 2009, 48, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.; Wright, A. How to conduct a SWOT analysis. Br. J. Manag. 2009, 24, 10–34. [Google Scholar]
- Helms, M.M. Exploring SWOT analysis—where are we now?: A review of academic research from the last decade. J. Strat. Manag. 2010, 3, 215–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Williams, W. Strategic tools: An empirical investigation into strategy in practice in the UK. Strateg. Chang. 2007, 16, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. Why strategy teaching should be theory based. J. Manag. Inq. 2008, 17, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibis, B.J.; Corabian, P.; Meiesaar, K.; Koppel, A.; Jacobs, P. Application of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats analysis in the development of a health technology assessment program. Health Policy 2001, 58, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, M.J.; Passerini, K.; Parhankangas, A.; Casal, J. Using mind maps to study how business school students and faculty organize and apply general business knowledge. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2014, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.S.; Bush, K.L.; McCleish, J.M. Mind-mapped care plans: Integrating an innovative educational tool as an alternative to traditional care plans. J. Nurs. Educ. 2006, 45, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamdong Government. Resolution No. 03-NQ/TW Dated 13/09/2016. Available online: http://www.lamdong.gov.vn/vi-VN/a/vankiendang/Lists/VB%20QPPL/Attachments/99/nqs03.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2019).
- Khoa, H.V.B.; Sung-Kyun, K. Developing Smart City: Based on the Assessment of Smart Projects in Medium-Size Cities, Vietnam. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 56, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Glasmeier, A.; Christopherson, S. Thinking about Smart Cities. Camb. J. Regions. Econ. Soc. 2015, 8, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaroiu, G.C.; Roscia, M. Definition methodology for the smart cities model. Energy 2012, 47, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurman, D.; Baccarne, B.; De Marez, L. Mechant, Smart ideas for smart cities: Investigating crowdsourcing for generating and selecting ideas for ICT innovation in a city context. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2012, 7, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamdong Government. Implementation of the Project Building Dalat City Become a Smart City Period 2018—2025; Department of Information and Communication: Dalat, Vietnam, 2019.
- DalatCity People’s Committee. Implementation of Dalat-Online Application; Dalat Government: Dalat, Vietnam, 2019.
- Nam, T.; Pardo, T.A. The changing face of a city government: A case study of Philly311. Gov. Inf. Q. 2014, 31, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamdong Government. Project of Building Dalat to Become a Smart City in the Period of 2017–2020; Office of Lamdong Provincial People’s Committee: Dalat, Vietnam, 2017.
- Irfan, A.H.; Anwar, A.S.; Muhammad, A.U.; Bhawani, S.C.; Tahir, R. Multi-criteria assessment of smart city transformation based on SWOT analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 5th National Symposium on Information Technology: Towards New Smart World (NSITNSW), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 17–19 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- King, S.; Cotterill, S. Transformational government? The role of information technology in delivering citizen-centric local public services. Local Gov. Stud. 2007, 33, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H. Developing and validating a citizen-centric typology for smart city services. Gov. Inf. Q. 2014, 31, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P. Creative cities and economic development. Urban Stud. 2000, 37, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.; Brunn, S.D.; Devriendt, L. Cyber Infrastructures and “Smart” World Cities: Physical, Human, and Soft Infrastructures. In International Handbook of Globalization and World Cities; Taylor, P., Derudder, B., Hoyler, M., Witlox, F., Eds.; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffers, H.; Komninos, N.; Pallot, M. Smart Cities as Innovation Ecosystems Sustained by the Future Internet. Available online: https://www.urenio.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/2012-FIREBALL-White-Paper-Final.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Nam, T.; Pardo, T. Conceptualizing smart city with dimensions of technology, people, and institutions. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Digital Government on Research Conference on Digital Government Innovation in Challenging Times, College Park, MD, USA, 12–15 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Hancock, M.G.; Hu, M.C. Towards an effective framework for building smart cities: Lessons from Seoul and San Francisco. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 89, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Phaal, R.; Lee, S.H. An integrated service-device-technology roadmap for smart city development. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2013, 80, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsbergen, D.J.; Wolken, G., Jr. Realizing the promise: Government information systems and the fourth generation of information technology. Public. Admin. Rev. 2001, 61, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumaya, B.L. How to strategize smart cities: Revealing the SMART model. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.S.; Darema, F.; Chang, V. Distributed behavior model orchestration in cognitive internet of things solution. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2017, 12, 414–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisi, F.; Ping, P. A discussion on smart city management based on meta-synthesis method. Manag. Sci. 2014, 8, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Allwinkle, S.; Cruickshank, P. Creating smarter cities: An overview. J. Urban Technol. 2011, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprotti, F.; Cowley, R. Interrogating Urban Experiments. Urban Geogr. 2017, 38, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dupont, L.; Morel, L.; Guidat, C. Innovative public-private partnership to support Smart City: The case of “Chaire REVES”. J. Strateg. Manag. 2015, 8, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotný, R.; Kuchta, R.; Kadlec, J. Smart city concept, applications and services. J. Telecommun. Syst. Manag. 2014, 3, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Dahiya, B. Cities in Asia 2012: Demographics, economics, poverty, environment and governance. Cites 2012, 29, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulu, M. Upgrading a city via technology. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 89, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abastante, F.; Lami, I.M.; Lombardi, P. An Integrated Participative Spatial Decision Support System for Smart Energy Urban Scenarios: A Financial and Economic Approach. Buildings 2017, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinawy, S.; El-Diraby, T.; Konomi, H. Customizing information delivery to project stakeholders in the smart city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orłowski, C.; Ziółkowski, A.; Orłowski, A.; Kapłański., P.; Sitek, T.; Pokrzywnicki, W. Designing Aggregate KPIs as a Method of Implementing Decision-Making Processes in the Management of Smart Cities. In Transactions on Computational Collective Intelligence XXV—Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Nguyen, N., Kowalczyk, R., Orłowski, C., Ziółkowski, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, 2016; Volume 9990. [Google Scholar]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoang Viet Bach, K.; Kim, S.-K. Towards Evaluation the Cornerstone of Smart City Development: Case Study in Dalat City, Vietnam. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010001
Hoang Viet Bach K, Kim S-K. Towards Evaluation the Cornerstone of Smart City Development: Case Study in Dalat City, Vietnam. Smart Cities. 2020; 3(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoang Viet Bach, Khoa, and Sung-Kyun Kim. 2020. "Towards Evaluation the Cornerstone of Smart City Development: Case Study in Dalat City, Vietnam" Smart Cities 3, no. 1: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010001
APA StyleHoang Viet Bach, K., & Kim, S.-K. (2020). Towards Evaluation the Cornerstone of Smart City Development: Case Study in Dalat City, Vietnam. Smart Cities, 3(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010001



