Envisioning the Future of Machine Learning in the Early Detection of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders via Speech and Language Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Current Landscape
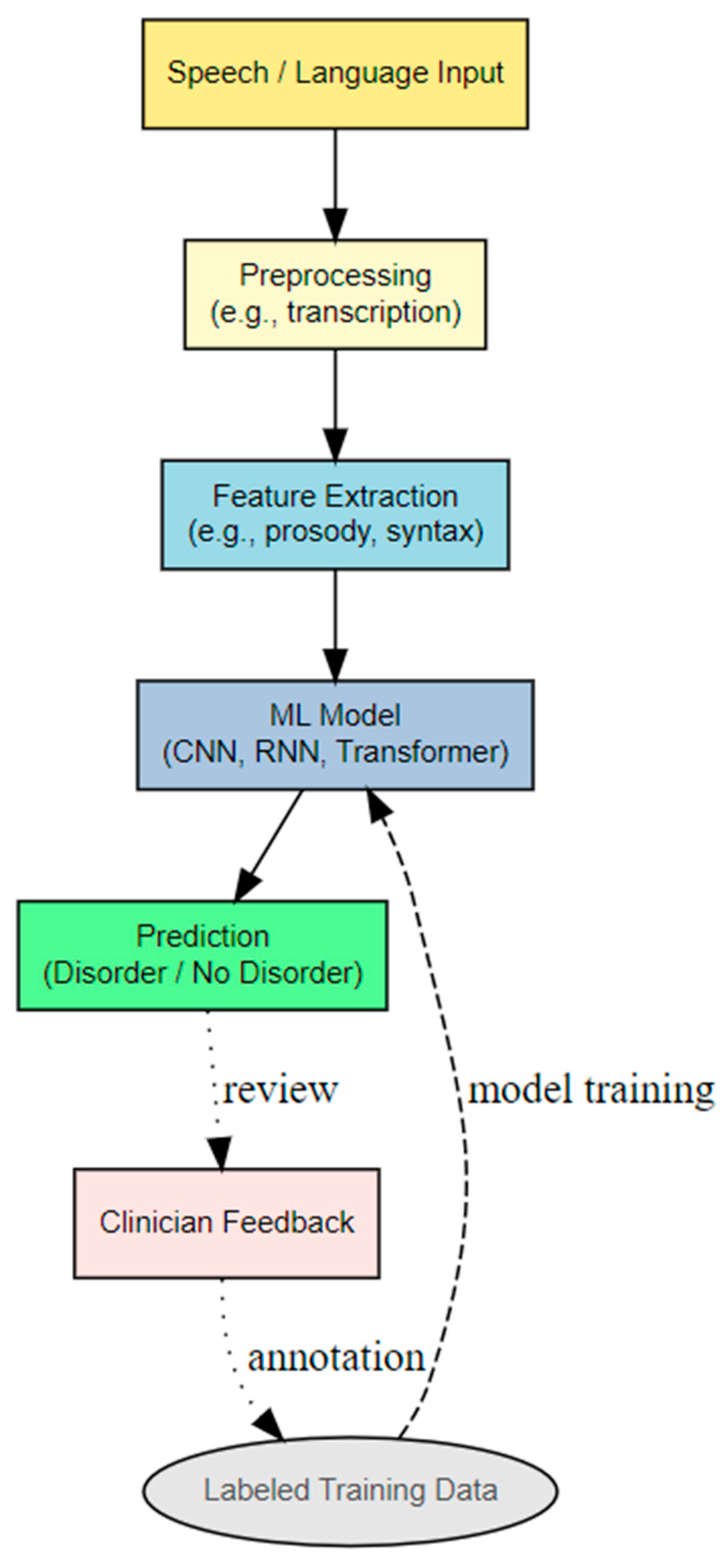
2.1. Overview of Current Machine Learning Techniques
2.2. Review of Current Applications
2.3. Datasets Used in Previous Work
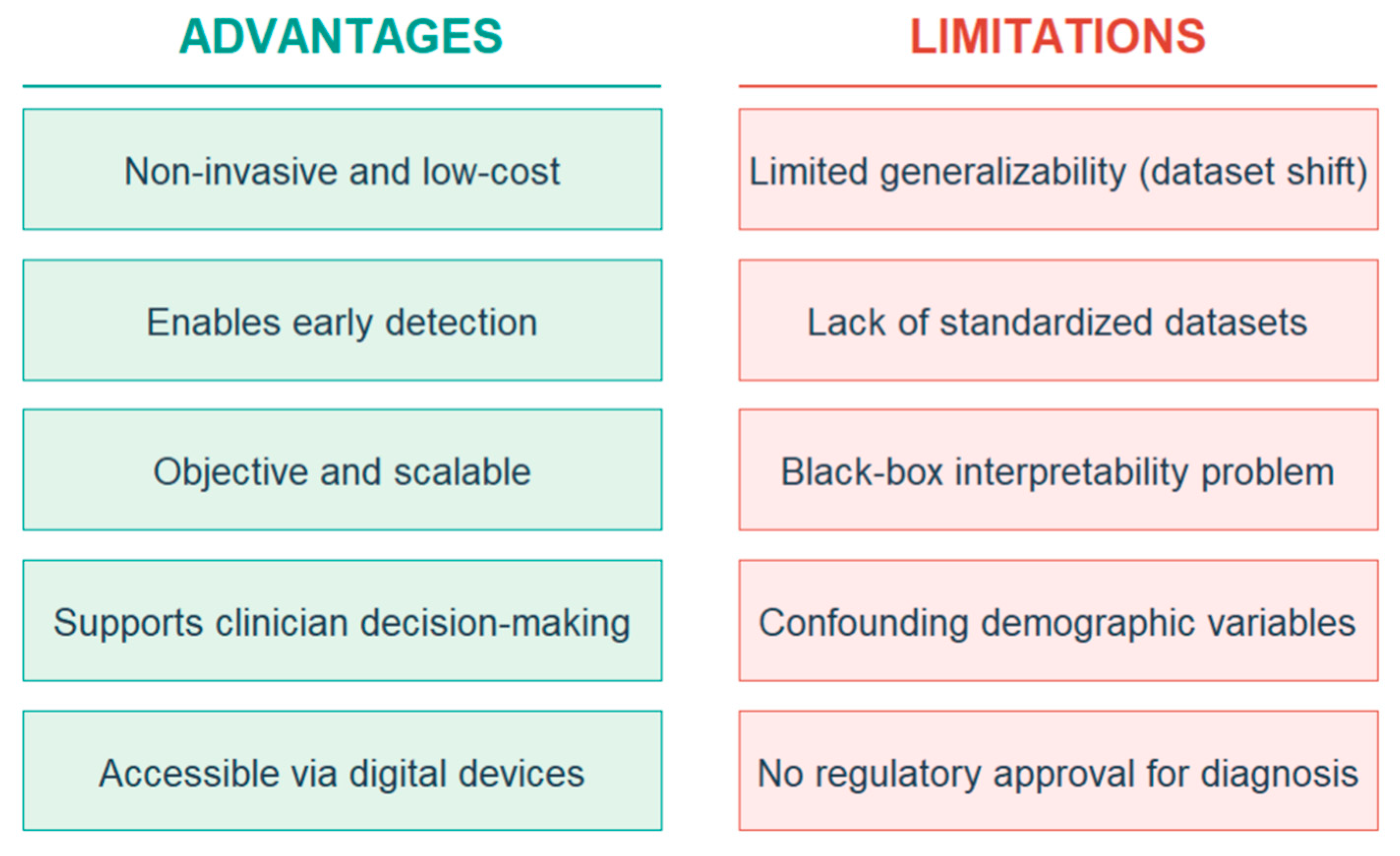
2.4. Advantages and Limitations
3. Future Trends and Scenarios
3.1. Data Availability and Quality
3.2. Model Evolution
3.3. Multilingual and Cross-Cultural Models
3.4. Regulatory and Clinical Translation
3.5. Hybrid Systems and Human-AI Collaboration
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Kang, D.; Fang, W.; Chen, F. Global, regional, and national burden and attributable risk factors of neurological disorders: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2019. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 952161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Autism Spectrum Disorders (Fact Sheet). 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/autism-spectrum-disorders (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Santomauro, D.F.; Erskine, H.E.; Herrera, A.M.M.; Miller, P.A.; Shadid, J.; Hagins, H.; Addo, I.Y.; Adnani, Q.E.S.; Ahinkorah, B.O.; Ahmed, A.; et al. The Global Epidemiology and Health Burden of the Autism Spectrum: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Psychiatry 2025, 12, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. Dementia Statistics (Facts & Figures); Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2020; Available online: https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/dementia-statistics/ (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. Numbers of People with Dementia Worldwide: An Update to the Estimates in the World Alzheimer Report 2015; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2020; Available online: https://www.alzint.org/resource/numbers-of-people-with-dementia-worldwide/ (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Parkinson Disease—Fact Sheet; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/parkinson-disease (accessed on 9 October 2025).
- Bhidayasiri, R.; Sringean, J.; Phumphid, S.; Anan, C.; Thanawattano, C.; Deoisres, S.; Panyakaew, P.; Phokaewvarangkul, O.; Maytharakcheep, S.; Buranasrikul, V.; et al. The Rise of Parkinson’s Disease Is a Global Challenge, but Efforts to Tackle This Must Begin at a National Level: A Protocol for National Digital Screening and “Eat, Move, Sleep” Lifestyle Interventions to Prevent or Slow the Rise of Non-Communicable Diseases in Thailand. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1386608. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, G.M.; First, M.B.; Kogan, C.S.; Hyman, S.E.; Gureje, O.; Gaebel, W.; Maj, M.; Stein, D.J.; Maercker, A.; Tyrer, P.; et al. Innovations and Changes in the ICD-11 Classification of Mental, Behavioural and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. World Psychiatry 2019, 18, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Requirements for ICD-11 Mental, Behavioural and Neurodevelopmental Disorders; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, A.K.; Stanton, J.; Hans, S.; Grabrucker, A. Autism Spectrum Disorders: Etiology and Pathology; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2021; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a Biological Definition of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised Criteria for Diagnosis and Staging of Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Rosa-Neto, P. Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers: Amyloid, Tau, Neurodegeneration (ATN)—Where Do We Go from Here? Pract. Neurol. 2019, 88, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, B.; Michelini, G.; Asherson, P.; Banaschewski, T.; Bilbow, A.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Cormand, B.; Faraone, S.V.; Ginsberg, Y.; Haavik, J.; et al. Live Fast, Die Young? A Review on the Developmental Trajectories of ADHD across the Lifespan. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 28, 1059–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaigenbaum, L.; Bauman, M.L.; Choueiri, R.; Kasari, C.; Carter, A.; Granpeesheh, D.; Mailloux, Z.; Smith Roley, S.; Wagner, S.; Fein, D.; et al. Early intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder under 3 years of age: Recommendations for practice and research. Pediatrics 2015, 136 (Suppl. 1), S60–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibing, A. The Earlier the Better: Alzheimer’s Prevention, Early Detection, and the Quest for Pharmacological Interventions. Cult. Med. Psychiatry 2014, 38, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, C.; Lee, W.H.; Carson, A.; Stone, J. Iatrogenic harm in functional neurological disorder. Brain 2025, 148, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Wittens, M.M.J.; Engelborghs, S.; van Herwijnen, M.H.; Tsamou, M.; Roggen, E.; Smeets, B.; Krauskopf, J.; Briedé, J.J. Beyond CSF and neuroimaging assessment: Evaluating plasma miR-145-5p as a potential biomarker for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Vogel, A.P.; Gharahkhani, P.; Renteria, M.E. Speech and language biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease prediction, early diagnosis and progression. NPJ Parkinson’s Dis. 2025, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, G.P.; Theodorou, E. Abilities of children with developmental language disorders in perceiving phonological, grammatical, and semantic structures. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 53, 4483–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszczynska, M.A.; Ojamies, P.N.; Lacoste, A.M.; Neil, D.; Saffari, A.; Mead, R.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Holbrook, J.D.; Ferraiuolo, L. Applications of machine learning to diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro-Velazquez, L.; Gomez-Garcia, J.A.; Arias-Londoño, J.D.; Dehak, N.; Godino-Llorente, J.I. Advances in Parkinson’s disease detection and assessment using voice and speech: A review of the articulatory and phonatory aspects. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 66, 102418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaye, G.E. Random Forest for High-Dimensional Data. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, TX, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Vásquez-Correa, J.C.; Arias-Vergara, T.; Orozco-Arroyave, J.R.; Eskofier, B.; Klucken, J.; Nöth, E. Multimodal assessment of Parkinson’s disease: A deep learning approach. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 1618–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weede, P.; Smietana, P.D.; Kuhlenbäumer, G.; Deuschl, G.; Schmidt, G. Two-stage convolutional neural network for classification of movement patterns in tremor patients. Information 2024, 15, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, N. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Baevski, A.; Zhou, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Auli, M. Wav2vec 2.0: A framework for self-supervised learning of speech representations. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 12449–12460. [Google Scholar]
- Beke, A.; Szaszák, G. Unsupervised clustering of prosodic patterns in spontaneous speech. In Proceedings of the Text, Speech and Dialogue, TSD 2012, Brno, Czech Republic, 3–7 September 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 648–655. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.; Li, S.; Xiao, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Ma, X. Computer aided Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by an unsupervised deep learning technology. Neurocomputing 2020, 392, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlett-Pelleriti, C.M.; Stevens, E.; Dixon, D.; Linstead, E.J. Applications of unsupervised machine learning in autism spectrum disorder research: A review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2023, 10, 406–421. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Rani, S.; Sharma, S.; Min, H. Multimodality fusion aspects of medical diagnosis: A comprehensive review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.F.; Shaker, S.H. Review of autistic detection using eye tracking and vocalization based on deep learning. J. Algebr. Stat. 2022, 13, 286–297. [Google Scholar]
- Oller, D.K.; Niyogi, P.; Gray, S.; Richards, J.A.; Gilkerson, J.; Xu, D.; Yapanel, U.; Warren, S.F. Automated vocal analysis of naturalistic recordings from children with autism, language delay, and typical development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13354–13359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijper, S.J.; Hartman, C.A.; Bogaerds-Hazenberg, S.; Hendriks, P. Narrative production in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Similarities and differences. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2017, 126, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Spielman, J.; Ramig, L.O. Novel speech signal processing algorithms for high-accuracy classification of Parkinson’s disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, F.; Gewald, H. Language characteristics supporting early Alzheimer’s diagnosis through machine learning—A literature review. Health Inform. Int. J. 2021, 10, 10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, S.; Haider, F.; de la Fuente Garcia, S.; Fromm, D.; MacWhinney, B. Alzheimer’s dementia recognition through spontaneous speech. Front. Comput. Sci. 2021, 3, 780169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratch, J.; Artstein, R.; Lucas, G.M.; Stratou, G.; Scherer, S.; Nazarian, A.; Wood, R.; Boberg, J.; DeVault, D.; Marsella, S.; et al. The Distress Analysis Interview Corpus of human and computer interviews. In Proceedings of the LREC, Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; pp. 3123–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Krishnan, P.; Kumar, R.; Ramoji, S.; Chetupalli, S.R.; Ghosh, P.K.; Ganapathy, S. Coswara—A database of breathing, cough, and voice sounds for COVID-19 diagnosis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.10548. [Google Scholar]
- MacWhinney, B. The CHILDES Project: Tools for Analyzing Talk. Volume I: Transcription Format and Programs; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brahmi, Z.; Mahyoob, M.; Al-Sarem, M.; Algaraady, J.; Bousselmi, K.; Alblwi, A. Exploring the role of machine learning in diagnosing and treating speech disorders: A systematic literature review. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2024, 2205–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potla, R.T. Scalable Machine Learning Algorithms for Big Data Analytics: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 2, 124–141. [Google Scholar]
- Quiñonero-Candela, J.; Sugiyama, M.; Schwaighofer, A.; Lawrence, N.D. Dataset Shift in Machine Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Washington, P.; Wall, D.P. A review of and roadmap for data science and machine learning for the neuropsychiatric phenotype of autism. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2023, 6, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Care Service Corporation (HCSC). Digital Health Technologies: Diagnostic Applications; Policy No. PSY301.024; Effective 15 December 2024; Health Care Service Corporation (HCSC): Chicago, IL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.; Shinn-Cunningham, B.; Tager-Flusberg, H. Meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature characterizing auditory mismatch negativity in individuals with autism. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 87, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, J.; Oranje, B.; Vestergaard, M.; Foldager, M.; Kjær, T.W.; Arnfred, S.; Aggernæs, B. Reduced mismatch negativity in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder is associated with their impaired adaptive functioning. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, H.; Hillman, R.E.; Mehta, D.D. Toward generalizable machine learning models in speech, language, and hearing sciences: Estimating sample size and reducing overfitting. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2024, 67, 753–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Deep learning for medical image-based cancer diagnosis. Cancers 2023, 15, 3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanarayanan, V.; Lammert, A.C.; Rowe, H.P.; Quatieri, T.F.; Green, J.R. Speech as a biomarker: Opportunities, interpretability, and challenges. Perspect. ASHA Spec. Interest Groups 2022, 7, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premera Blue Cross. Prescription Digital Health Diagnostic Aid for Autism Spectrum Disorder (Medical Policy 3.03.01); Premera Blue Cross: Spokane, WA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kleine, A.K.; Kokje, E.; Hummelsberger, P.; Lermer, E.; Gaube, S. AI-enabled clinical decision support tools for mental healthcare: A product review. OSF Preprints 2023. Available online: https://osf.io/ez43g (accessed on 3 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, H.; Howe, C.L.; Armstrong, D.G.; Subbian, V. Leveraging mobile health applications for biomedical research and citizen science: A scoping review. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Mondal, T.; Deen, M.J. Wearable sensors for remote health monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Li, W.; Milletari, F.; Roth, H.R.; Albarqouni, S.; Bakas, S.; Galtier, M.N.; Landman, B.A.; Maier-Hein, K.; et al. The future of digital health with federated learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Xu, T.; Brockman, G.; McLeavey, C.; Sutskever, I. Robust speech recognition via large-scale weak supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; PMLR: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2023; pp. 28492–28518. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Ahuja, C.; Morency, L.P. Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, T.; Cai, P.; Mondal, S.K.; Sahoo, J.P. A comprehensive survey of few-shot learning: Evolution, applications, challenges, and opportunities. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, R. Inclusivity of AI Speech in Healthcare: A Decade Look Back. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.M.; Sarro, F.; Harman, M. A comprehensive empirical study of bias mitigation methods for machine learning classifiers. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2023, 32, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Lee, H.Y.; Borgholt, L.; Havtorn, J.D.; Edin, J.; Igel, C.; Kirchhoff, K.; Li, S.-W.; Livescu, K.; Maaløe, L.; et al. Self-supervised speech representation learning: A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 1179–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Wang, C.; Tjandra, A.; Lakhotia, K.; Xu, Q.; Goyal, N.; Singh, K.; von Platen, P.; Saraf, Y.; Pino, J.; et al. XLS-R: Self-supervised cross-lingual speech representation learning at scale. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.09296. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, D.; Stefik, M.; Choi, J.; Miller, T.; Stumpf, S.; Yang, G.Z. XAI—Explainable artificial intelligence. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaay7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Soejima, H.; Nakashima, N. Explanation of Machine Learning Models Using Shapley Additive Explanation and Application for Real Data in Hospital. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 214, 106584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.R.; Khan, N. Deterministic Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations for Stable Explainability. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2021, 3, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: The convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-software-medical-device (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Reflection Paper on the Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Lifecycle of Medicinal Products; EMA: London, UK, 2024; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/reflection-paper-use-artificial-intelligence-ai-medicinal-product-lifecycle_en.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Talitckii, A.; Kovalenko, E.; Anikina, A.; Zimniakova, O.; Semenov, M.; Bril, E.; Shcherbak, A.; Dylov, D.V.; Somov, A. Avoiding misdiagnosis of Parkinson’s disease with the use of wearable sensors and artificial intelligence. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Holmes, S.B.; Zou, L.; Patel, M.; Coulthard, P. Diagnosis of pathological speech with streamlined features for long short-term memory learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Chauhan, J.; Bozorgpour, A.; Huang, B.; Azad, R.; Merhof, D. Continual learning in medical image analysis: A comprehensive review of recent advancements and future prospects. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Akaila, D.; Arjemandi, M.; Papineni, V.; Yaqub, M. MINDSETS: Multi-omics integration with neuroimaging for dementia subtyping and effective temporal study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhonde, S.B.; Prasad, J.R. Machine learning approach to revolutionize use of holistic health records for personalized healthcare. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 313–321. [Google Scholar]
| Domain | Future Developments |
|---|---|
| Data availability & quality |
|
| Model evolution |
|
| Multilingual & cross-cultural models |
|
| Regulatory & clinical translation |
|
| Hybrid systems & human–AI collaboration |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgiou, G.P. Envisioning the Future of Machine Learning in the Early Detection of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders via Speech and Language Biomarkers. Acoustics 2025, 7, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040072
Georgiou GP. Envisioning the Future of Machine Learning in the Early Detection of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders via Speech and Language Biomarkers. Acoustics. 2025; 7(4):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040072
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgiou, Georgios P. 2025. "Envisioning the Future of Machine Learning in the Early Detection of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders via Speech and Language Biomarkers" Acoustics 7, no. 4: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040072
APA StyleGeorgiou, G. P. (2025). Envisioning the Future of Machine Learning in the Early Detection of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders via Speech and Language Biomarkers. Acoustics, 7(4), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7040072






