A Note on the Sound Absorption Characteristics of Microperforated Panels with Non-Circular Holes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sound Absorption Characteristics of Non-Circular MPPs
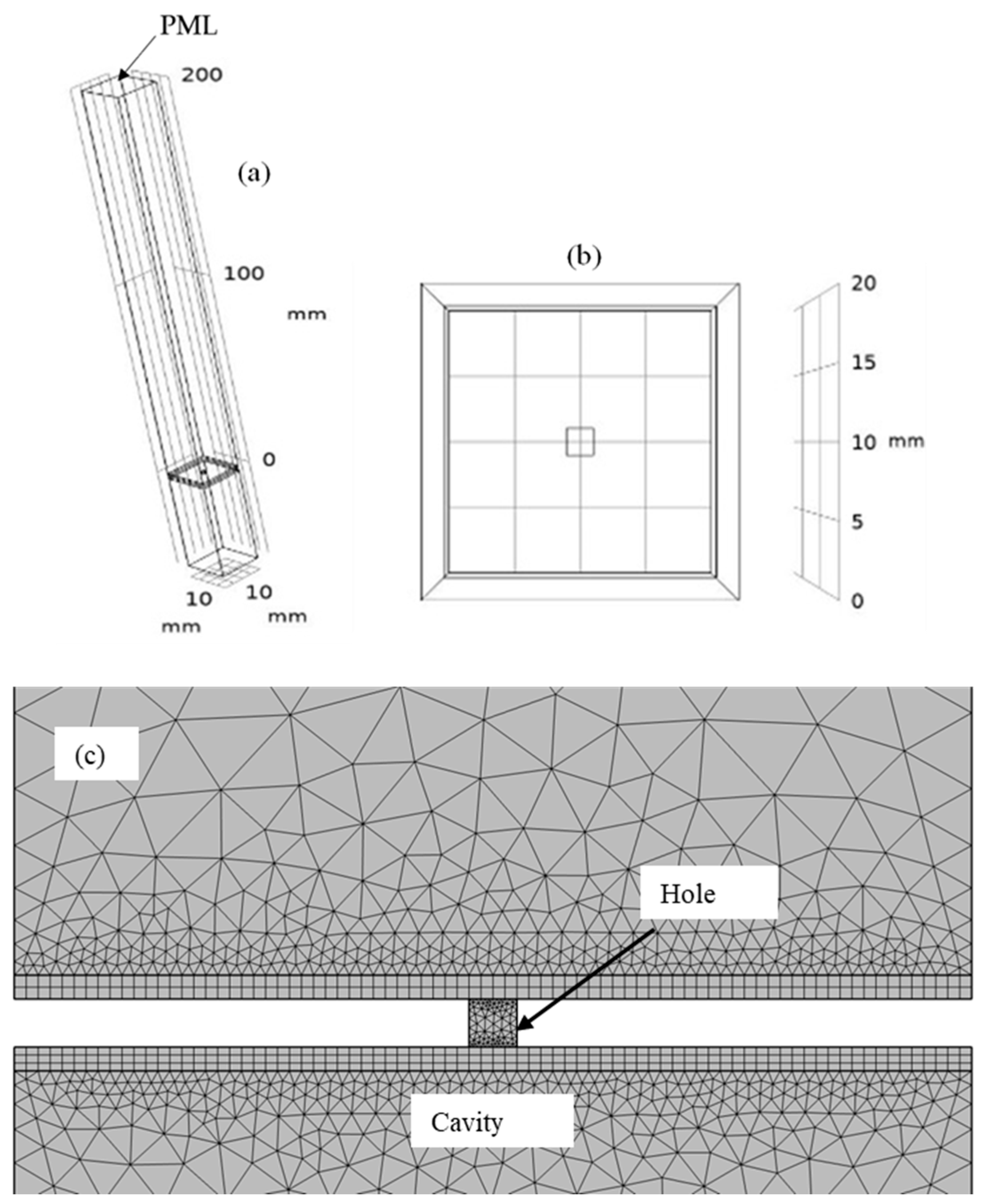
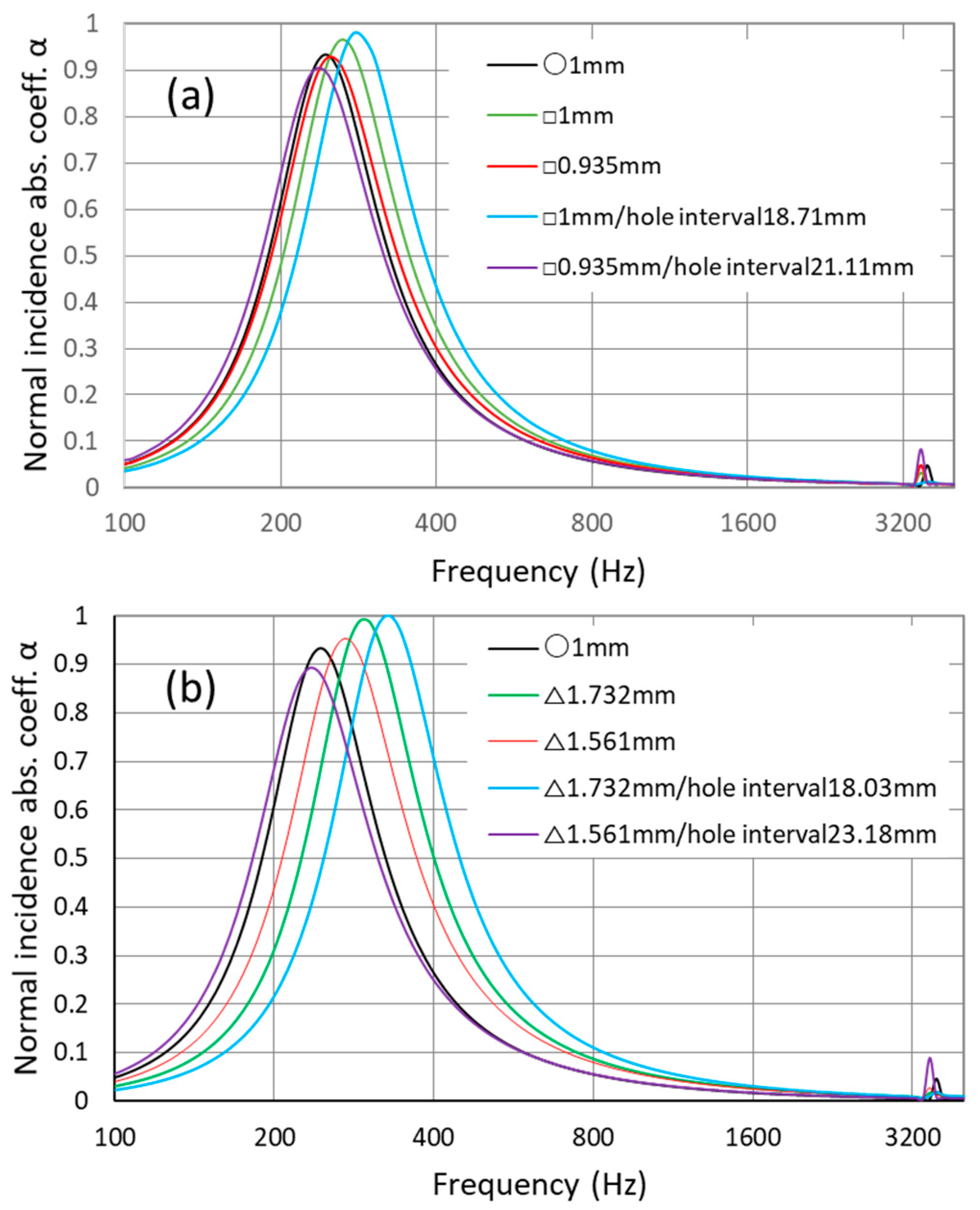
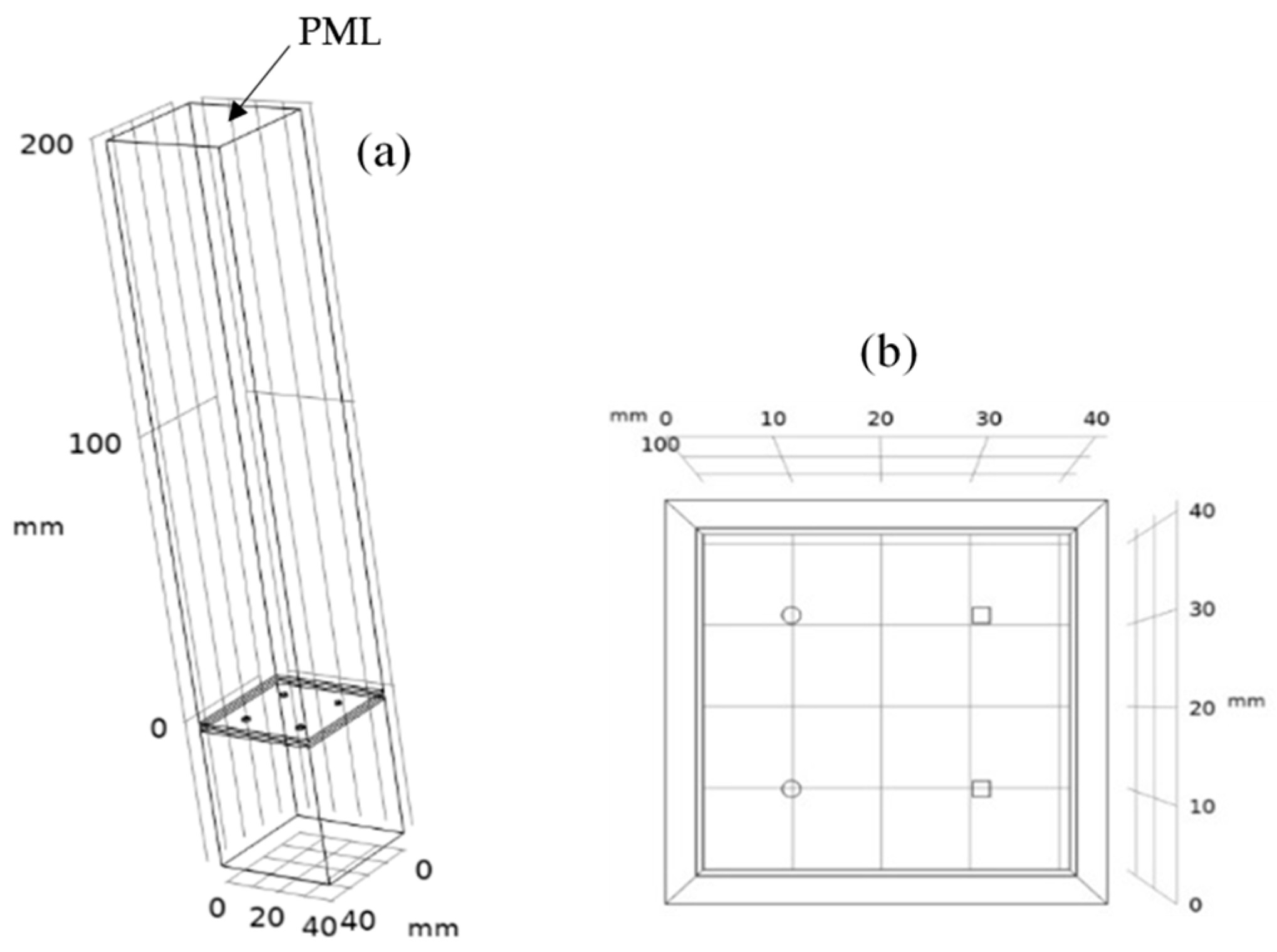
2.1. Model for Simulation (Single Hole Cases)
2.2. Evaluation Method
2.3. Degree of the Agreement of Sound Absorption Characteristics
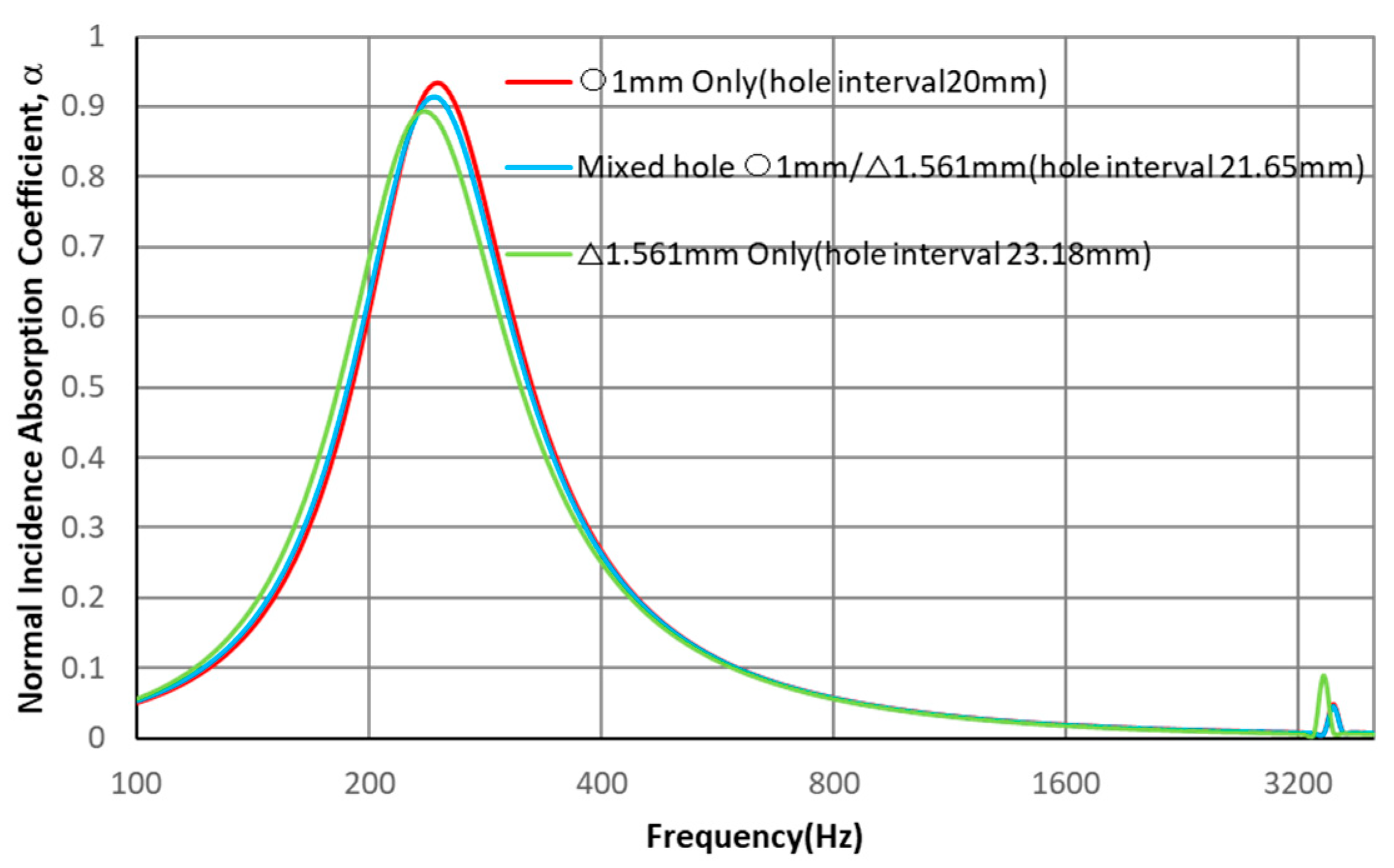
3. MPPs with a Mixture of Non-Circular and Circular Holes
- For MPPs with a mixture of circular and square holes, we consider two cases: 1 and 2.
- For MPPs with a mixture of circular and equilateral triangular holes, we consider case 1.
- When the non-circular holes are designed to match both the flow resistivity and perforation ratio of the circular-hole MPP.
- When the non-circular holes are designed to match only the flow resistivity of the circular-hole MPP.
3.1. Model for Simulation
3.2. Results and Discussion
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Comparison of the Results Using the Thermoviscous Boundary Layer Impedance and Those Using the Thermoviscous Acoustics Interfaces
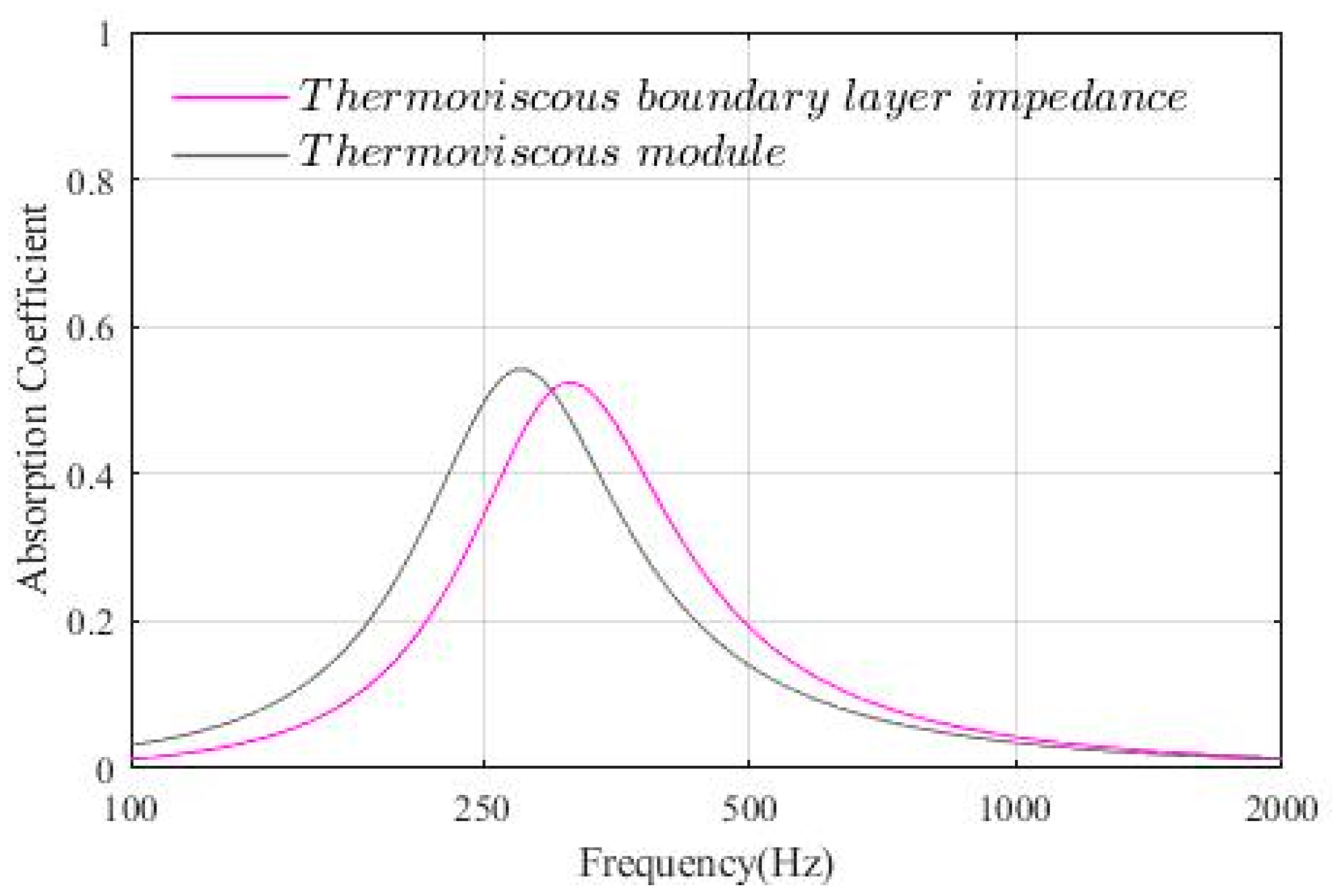
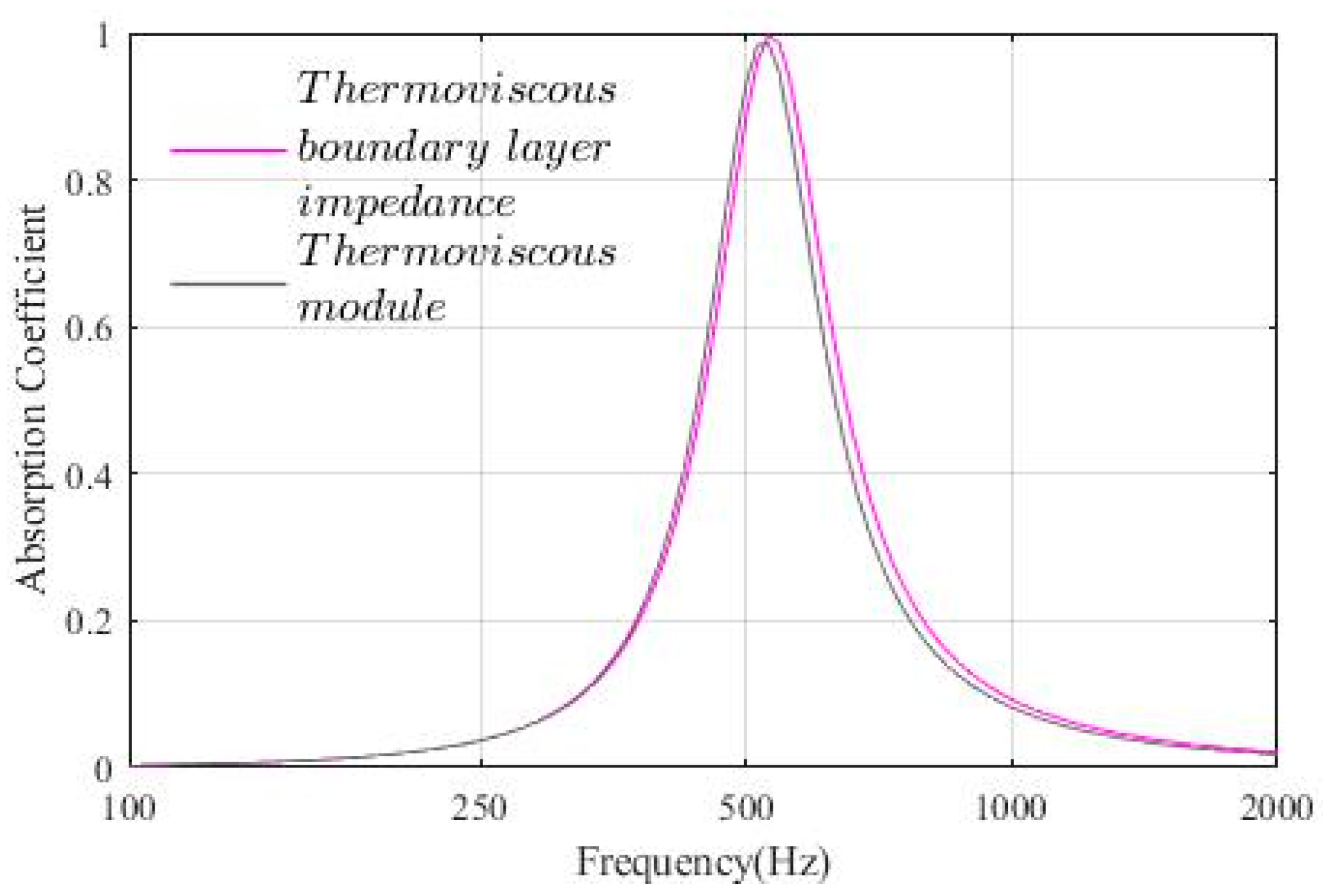
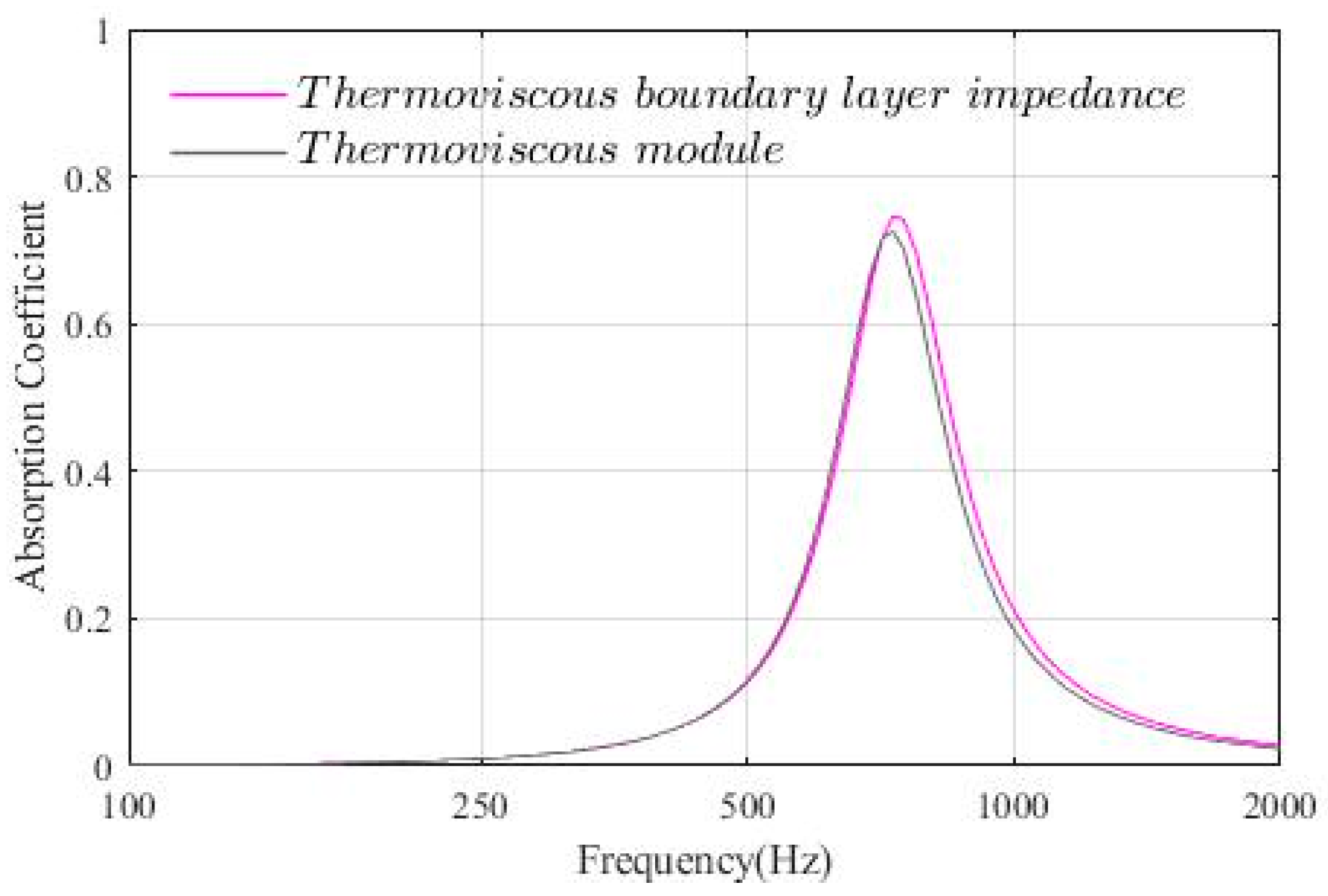
References
- Adams, T. Sound Materials: A Compendium of Sound Absorbing Materials for Architecture and Design; Frame Pub: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2017; pp. 214–231. [Google Scholar]
- Herrin, D.; Liu, J.; Seybert, A. Properties and applications of microperforated panels. Sound Vib. 2011, 45, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Maa, D.-Y. Theory and design of microperforated panel sound-absorbing constructions. Sci. Sin. 1975, 17, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Maa, D.-Y. Microperforated-panel wideband absorbers. Noise Control Eng. J. 1987, 29, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, D.-Y. Potential of microperforated panel absorber. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, D.-Y. Practical single MPP absorber. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2007, 12, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Fuchs, H.V. Predicting absorption of open weave textiles and micro-perforated membranes backed by an air space. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 220, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, H.V.; Zha, X. Acrylic-glass sound absorbers in the plenum of the Deutscher Bundestag. Appl. Acoust. 1997, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, H.V.; Zha, X.; Zhou, X.; Drotleff, H. Creating low-noise environments in communication rooms. Appl. Acoust. 2001, 62, 1375–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.; Fuchs, H.V.; Drotleff, H. Improving the acoustic working conditions for musicians in small spaces. Appl. Acoust. 2002, 63, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, K.; Morimoto, M.; Koike, W. A numerical study of double-leaf microperforated panel absorbers. Appl. Acoust. 2006, 67, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, K.; Okuzono, T. Some considerations on the use of space sound absorbers with next-generation materials reflecting COVID situations in Japan: Additional sound absorption for post-pandemic challenges in indoor acoustic environments. UCL Open Environ. 2020, 2, e012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.P.; Kumar, S.; Aow, J.W. Proof-of-concept design for MPP acoustic absorbers with element of art. Designs 2021, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajo, J.; Ramis, I.; Godinho, L.; Amado-Mendes, P. Assessment of methods to study the acoustic properties of heterogeneous perforated panel absorbers. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, M.; Sakagami, K.; Okuzono, T. A basic study on the absorption properties and their prediction of heterogeneous micro-perforated panels; A case study of micro-perforated panels with heterogeneous hole size and perforation ratio. Acoustics 2021, 3, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, K.; Kusaka, M.; Okuzono, T. A basic study on the design of dotted-art heterogeneous MPP sound absorbers. Acoustics 2022, 4, 588–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, K.; Kusaka, M.; Okuzono, T.; Nakanishi, S. The effect of deviation due to the manufacturing accuracy in the parameters of an MPP on its acoustic properties: Trial production of MPPs of different hole shapes using 3D printing. Acoustics 2020, 2, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miasa, I.M.; Okuma, M.; Kishimoto, G.; Nakahara, T. An experimental study of a multi-size microperforated panel absorber. J. Sys. Des. Dynam. 2007, 1, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.F.; Ren, S.W.; Zhao, G.P. Acoustic properties of micro-perforated panel absorber having arbitrary cross-sectional perforations. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 111, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, W.; Peng, X.; Xian, F.; Lu, T.J. Sound absorption theory for micro-perforated panel with petal-shaped perforations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, J.F.; Atalla, N. Propagation of Sound in Porous Media: Modelling Sound Absorbing Materials, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Son, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- COMSOL Documentation. Acoustics Module User’s Guide Ver. 6.3; COMSOL: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.H. COMSOL Blog, Theory of Thermoviscous Acoustics: Thermal and Viscous Losses. 2016. Available online: https://www.comsol.com/blogs/theory-of-thermoviscous-acoustics-thermal-and-viscous-losses (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Pierce, A.D. Acoustics: An Introduction to Its Physical Principles and Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1981; (rpt. 1989, Acoust. Soc. Am., NY, USA). [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, S. Elements of Acoustics; Acoustical Society of America: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, P.M.; Ingard, K.U. Theoretical Acoustics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristic Parameters to Match the Circular-Hole MPP | Parameters of the Non-Circular-Hole MPP to be Operated | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydraulic radius | Hole dimension |
| 2 | Hole flow resistivity | Hole dimension |
| 3 | Hydraulic radius and panel flow resistivity | Hole dimension and interval |
| 4 | Hole flow resistivity and perforation ratio | Hole dimension and interval |
| Characteristic Parameter to Be Fixed | fdifference (%) | αdifference (%) | RMS Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic radius | +10.42 | +3.806 | 0.050672 |
| Hole flow resistivity | +4.167 | −0.043 | 0.024892 |
| Hydraulic radius and panel flow resistivity | +16.67 | +5.581 | 0.083242 |
| Hole flow resistivity and perforation ratio | −1.667 | −2.581 | 0.004727 |
| Characteristic Parameter to Be Fixed | fdifference (%) | αdifference (%) | RMS Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic radius | +22.92 | +6.559 | 0.104885 |
| Hole flow resistivity | +13.33 | +2.516 | 0.067118 |
| Hydraulic radius and panel flow resistivity | +35.42 | +7.484 | 0.149535 |
| Hole flow resistivity and perforation ratio | −1.667 | −3.968 | 0.007807 |
| Subject for Calculating Deviation | fdifference (%) | αdifference (%) | RMS Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular-hole MPP and mixed-hole MPP | −0.627 | +2.903 | 0.00477 |
| Circular-hole MPP and square-hole MPP | −3.639 | +5.737 | 0.00701 |
| Subject for Calculating Deviation | fdifference (%) | αdifference (%) | RMS Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular-hole MPP and mixed-hole MPP | −1.413 | +1.205 | 0.00631 |
| Circular-hole MPP and equilateral triangular hole MPP | −4.860 | +6.121 | 0.01110 |
| Subject for Calculating Deviation | fdifference (%) | αdifference (%) | RMS Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular-hole MPP and mixed-hole MPP | −2.368 | −1.835 | 0.00879 |
| Circular-hole MPP and square-hole MPP | +1.715 | +1.342 | 0.01690 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakagami, K.; Abe, S. A Note on the Sound Absorption Characteristics of Microperforated Panels with Non-Circular Holes. Acoustics 2025, 7, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030057
Sakagami K, Abe S. A Note on the Sound Absorption Characteristics of Microperforated Panels with Non-Circular Holes. Acoustics. 2025; 7(3):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030057
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakagami, Kimihiro, and Sakurako Abe. 2025. "A Note on the Sound Absorption Characteristics of Microperforated Panels with Non-Circular Holes" Acoustics 7, no. 3: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030057
APA StyleSakagami, K., & Abe, S. (2025). A Note on the Sound Absorption Characteristics of Microperforated Panels with Non-Circular Holes. Acoustics, 7(3), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics7030057








