Ultrastructural Evidence of Interactions Between Eosinophils and Mast Cells in Gastric Cancer: Considerations in AllergoOncology Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinicopathological Findings
2.2. Light Microscopy
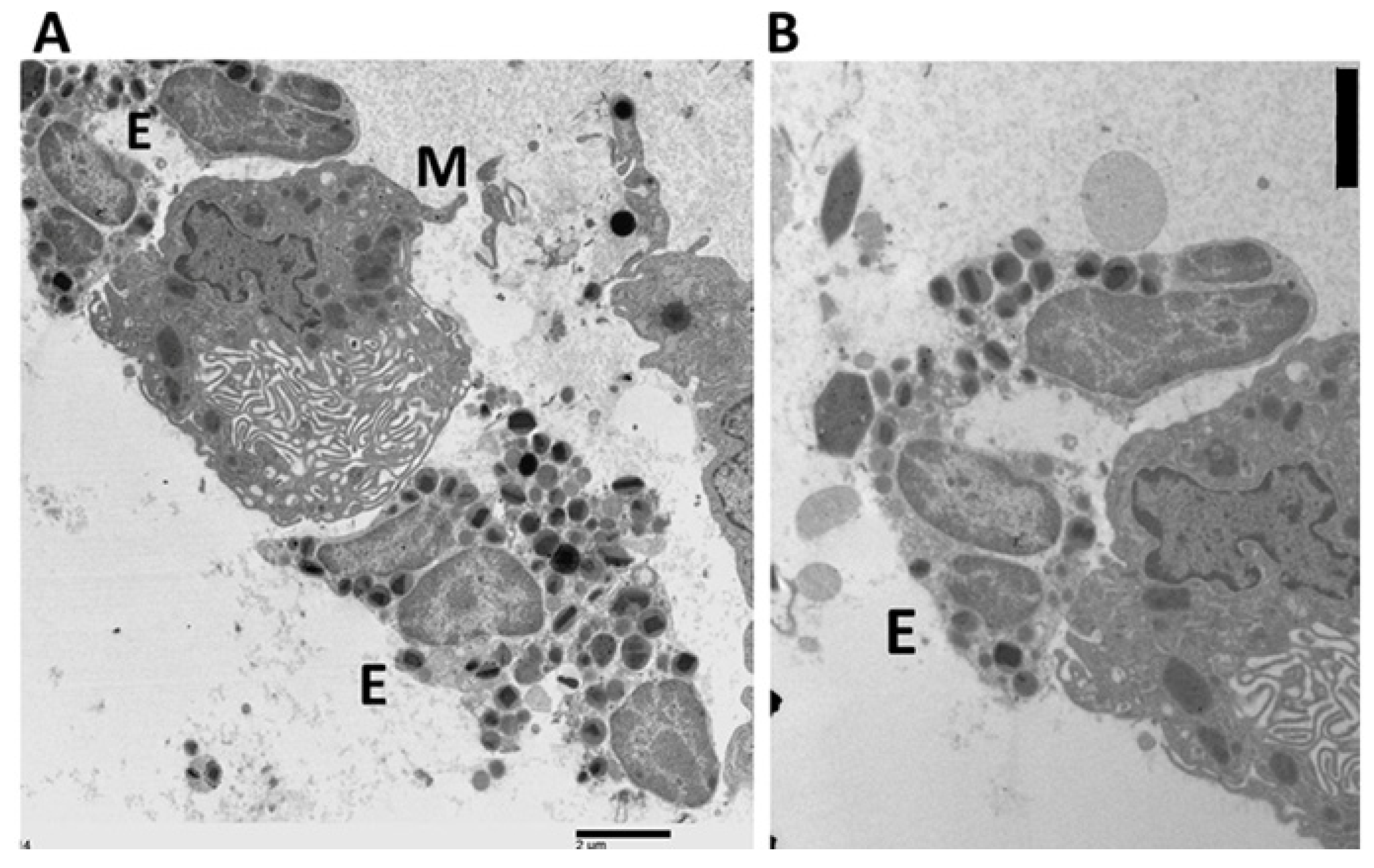
2.3. Electron Microscopy
2.4. Ultrastructural Evidence of Mast Cell–Eosinophil Interactions
2.5. Ultrastructural Pattern of Degranulation and Cytolysis
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Tissue Sample
4.2. Definition of TATEM
4.3. Ultrastructural Characteristics of Mast Cell Degranulation
4.4. Ultrastructural Characteristics of Eosinophil Degranulation
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FEGs | Free extracellular granules |
| ETosis | Extracellular trap cell death |
| TATEM | Tumor-associated tissue eosinophils and mast cells |
References
- Minai-Fleminger, Y.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Mast Cells and Eosinophils: The Two Key Effector Cells in Allergic Inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elishmereni, M.; Alenius, H.T.; Bradding, P.; Mizrahi, S.; Shikotra, A.; Minai-Fleminger, Y.; Mankuta, D.; Eliashar, R.; Zabucchi, G.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Physical Interactions between Mast Cells and Eosinophils: A Novel Mechanism Enhancing Eosinophil Survival In Vitro. Allergy 2011, 66, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minai-Fleminger, Y.; Elishmereni, M.; Vita, F.; Soranzo, M.R.; Mankuta, D.; Zabucchi, G.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Ultrastructural Evidence for Human Mast Cell-Eosinophil Interactions In Vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 341, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Eosinophils Interaction with Mast Cells: The Allergic Effector Unit. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1178, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahima, H.; Puzzovio, P.G.; Levi-Schaffer, F. 2B4 and CD48: A Powerful Couple of the Immune System. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 204, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Seaf, M.; Marone, G.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Marone, G. Bidirectional Mast Cell-Eosinophil Interactions in Inflammatory Disorders and Cancer. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Achatz, G.; Turner, M.C.; Karagiannis, S.; Legrand, F.; Capron, M.; Penichet, M.L.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Siccardi, A.G.; Vangelista, L.; et al. AllergoOncology: The Role of IgE-Mediated Allergy in Cancer. Allergy 2008, 63, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Valle, L.; Gatta, A.; Farinelli, A.; Scarano, G.; Lumaca, A.; Tinari, N.; Cipollone, F.; Paganelli, R.; Di Gioacchino, M. Allergooncology: An Expanding Research Area. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, M.; Bax, H.J.; Bergmann, C.; Bianchini, R.; Castells, M.; Chauhan, J.; De Las Vecillas, L.; Hartmann, K.; Álvarez, E.I.; Jappe, U.; et al. Granulocytes and Mast Cells in AllergoOncology—Bridging Allergy to Cancer: An EAACI Position Paper. Allergy 2024, 79, 2319–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, R.A.; Fedele, F.; Parisi, A.; Paparo, D.; Bonanno, A.; Finocchiaro, G.; Branca, G.; Scardigno, M.; Rigoli, L. Chronic Allergic-Like Inflammation in the Tumor Stroma of Human Gastric Carcinomas: An Ultrastructural Study. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2012, 36, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.C.N.; Dvorak, A.M.; Weller, P.F. Eosinophil Ultrastructure. In Atlas of Eosinophil Cell Biology and Pathology; Elsevier: London, UK, 2022; pp. 61–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ueki, S.; Melo, R.C.N.; Ghiran, I.; Spencer, L.A.; Dvorak, A.M.; Weller, P.F. Eosinophil Extracellular DNA Trap Cell Death Mediates Lytic Release of Free Secretion-Competent Eosinophil Granules in Humans. Blood 2013, 121, 2074–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauren, P. The Two Histological Main Types of Gastric Carcinoma: Diffuse and So-Called Intestinal-Type Carcinoma. An Attempt at a Histo-Clinical Classification. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1965, 64, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihlan, M.; Wissmann, S.; Gavrilov, A.; Kaltenbach, L.; Britz, M.; Franke, K.; Hummel, B.; Imle, A.; Suzuki, R.; Stecher, M.; et al. Neutrophil Trapping and Nexocytosis, Mast Cell-Mediated Processes for Inflammatory Signal Relay. Cell 2024, 187, 5316–5335.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, V.H.; Palazzi, C.; Bonjour, K.; Ueki, S.; Weller, P.F.; Melo, R.C.N. In Vivo ETosis of Human Eosinophils: The Ultrastructural Signature Captured by TEM in Eosinophilic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 938691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, V.H.; Palazzi, C.; Malta, K.K.; Bonjour, K.; Kneip, F.; Dias, F.F.; Neves, J.S.; Weller, P.F.; Melo, R.C.N. Extracellular Sombrero Vesicles Are Hallmarks of Eosinophilic Cytolytic Degranulation in Tissue Sites of Human Diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024, 116, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Tokunaga, T.; Melo, R.C.N.; Saito, H.; Honda, K.; Fukuchi, M.; Konno, Y.; Takeda, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirokawa, M.; et al. Charcot-Leyden Crystal Formation Is Closely Associated with Eosinophil Extracellular Trap Cell Death. Blood 2018, 132, 2183–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereydouni, M.; Ahani, E.; Desai, P.; Motaghed, M.; Dellinger, A.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Yin, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kafri, T.; Bhatt, A.P.; et al. Human Tumor Targeted Cytotoxic Mast Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 871390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.S.; Perez, S.A.; Spencer, L.A.; Melo, R.C.N.; Reynolds, L.; Ghiran, I.; Mahmudi-Azer, S.; Odemuyiwa, S.O.; Dvorak, A.M.; Moqbel, R.; et al. Eosinophil Granules Function Extracellularly as Receptor-Mediated Secretory Organelles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18478–18483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, V.S.; Baptista-Dos-Reis, R.; Neves, J.S. Functional Extracellular Eosinophil Granules: A Bomb Caught in a Trap. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 162, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.C.N.; Weller, P.F. Contemporary Understanding of the Secretory Granules in Human Eosinophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreone, S.; Spadaro, F.; Buccione, C.; Mancini, J.; Tinari, A.; Sestili, P.; Gambardella, A.R.; Lucarini, V.; Ziccheddu, G.; Parolini, I.; et al. IL-33 Promotes CD11b/CD18-Mediated Adhesion of Eosinophils to Cancer Cells and Synapse-Polarized Degranulation Leading to Tumor Cell Killing. Cancers 2019, 11, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, F.; Andreone, S.; Marone, G.; Gambardella, A.R.; Loffredo, S.; Varricchi, G.; Schiavoni, G. Eosinophils in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 273, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H.; Loegering, D.A.; Adolphson, C.R.; Gleich, G.J. Cytotoxic Properties of Eosinophil Granule Major Basic Protein for Tumor Cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 118, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.D.; Peterson, C.G.; Venge, P.; Cohn, Z.A. Mechanism of Membrane Damage Mediated by Human Eosinophil Cationic Protein. Nature 1986, 321, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, S.; Aleu, J.; Jiménez, M.; Boix, E.; Cuchillo, C.M.; Nogués, M.V. The Cytotoxicity of Eosinophil Cationic Protein/Ribonuclease 3 on Eukaryotic Cell Lines Takes Place through Its Aggregation on the Cell Membrane. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosti, J.M.; Altman, L.C.; Ayars, G.H.; Loegering, D.A.; Gleich, G.J.; Klebanoff, S.J. The Injurious Effect of Eosinophil Peroxidase, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Halides on Pneumocytes In Vitro. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987, 79, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Peng, K.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Y. Histones: The Critical Players in Innate Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1030610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, A.; Hirahara, K.; Kiuchi, M.; Nakayama, T. Eosinophils: Cells Known for Over 140 Years with Broad and New Functions. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson-Souza, G.A.; Vasconcelos, C.R.I.; Neves, J.S. Eosinophils: Focus on DNA Extracellular Traps. Life Sci. 2022, 311, 121191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, A.M. Ultrastructural Studies of Human Basophils and Mast Cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2005, 53, 1043–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, A.M.; Tepper, R.I.; Weller, P.F.; Morgan, E.S.; Estrella, P.; Monahan-Earley, R.A.; Galli, S.J. Piecemeal Degranulation of Mast Cells in the Inflammatory Eyelid Lesions of Interleukin-4 Transgenic Mice. Blood 1994, 83, 3600–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, C.K.; Mori, M.; Bjermer, L.; Löfdahl, C.G.; Erjefält, J.S. Alterations in Lung Mast Cell Populations in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumors Editorial Board. Tumors of the Stomach. In WHO Classification of Tumors: Digestive System Tumors, 5th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2019; pp. 59–110. [Google Scholar]









| Patients | Patients with TATEM n = 9 (%) | Patients without TATEM n = 63 (%) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median) | 65 (50–78) | 70 (41–83) | 0.39 |
| Tumor size (median) | 5 cm (3–8) | 5 cm (2–9) | 0.43 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 6 (67) | 37 (59) | |
| Female | 3 (33) | 26 (41) | 0.73 |
| Location | |||
| Upper + Middle third | 3 (33) | 33 (52) | |
| Lower third | 6 (67) | 30 (48) | 0.47 |
| Depth of invasion | |||
| T1–T2 | 3 (33) | 23 (37) | |
| T3–T4 | 6 (67) | 40 (63) | 1.00 |
| Lauren classification | |||
| Intestinal | 6 (67) | 44 (70) | |
| Diffuse | 3 (33) | 19 (30) | 1.00 |
| Lymph node metastasis | |||
| Negative | 4 (44) | 18 (29) | |
| Positive | 5 (56) | 45 (71) | 0.44 |
| Stage of disease | |||
| I–II | 8 (89) | 33 (52) | |
| III–IV | 1 (11) | 30 (48) | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caruso, R.; Caruso, V.; Rigoli, L. Ultrastructural Evidence of Interactions Between Eosinophils and Mast Cells in Gastric Cancer: Considerations in AllergoOncology Research. Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030041
Caruso R, Caruso V, Rigoli L. Ultrastructural Evidence of Interactions Between Eosinophils and Mast Cells in Gastric Cancer: Considerations in AllergoOncology Research. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2025; 7(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaruso, Rosario, Valerio Caruso, and Luciana Rigoli. 2025. "Ultrastructural Evidence of Interactions Between Eosinophils and Mast Cells in Gastric Cancer: Considerations in AllergoOncology Research" Gastrointestinal Disorders 7, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030041
APA StyleCaruso, R., Caruso, V., & Rigoli, L. (2025). Ultrastructural Evidence of Interactions Between Eosinophils and Mast Cells in Gastric Cancer: Considerations in AllergoOncology Research. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 7(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030041






