Long-Term Marine Corrosion Under the Influence of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and Calcareous Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
3. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The rate of the long-term corrosion of steel in natural seawaters is inhibited in the presence of calcareous deposits on or within corrosion products, irrespective of the presence or otherwise of nutrients critical for microbial metabolism associated with microbiologically influenced corrosion.
- No experimental evidence was found that the reduction in corrosion loss by calcareous deposition is affected by environmental conditions such as depth of immersion, dissolved oxygen concentration and average seawater temperature. However, as previously established, these parameters do influence the rate of longer-term corrosion, including under microbiologically influenced corrosion conditions.
- The relative inhibiting effect of calcareous material, measured by the ratio of maximum corrosion rates under calcareous and non-calcareous conditions, is similar for the corrosion of steel in natural seawaters and steel in seawaters with elevated nutrient conditions.
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- LaQue, F.J. Marine Corrosion; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Lan, X.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Zhang, C.; Duan, J.; Hou, B. The interaction of biofoulants and calcareous deposits on corrosion performance of Q235 in seawater. Materials 2020, 13, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilbeik, S.; Tseung, A.C.C.; Mackay, A.L. The formation of calcareous deposits during the corrosion of mild steel in sea water. Corros. Sci. 1986, 26, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humble, R.A. The cathodic protection of steel piling in sea water. Corrosion 1949, 5, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdtfeger, W.J.; Manuele, R.J. Coatings formed on steel by cathodic protection and their evaluation by polarization measurements. Corrosion 1963, 19, 59t–68t. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackland, B.G.; Dylejko, K.P. Critical questions and answers about cathodic protection. Corr. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchler, M. On the mechanisms of cathodic protection and its implications on criteria including AC and DC interference conditions. Corrosion 2020, 76, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezennec, J.G. Cathodic protection and microbially induced corrosion. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 1994, 34, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, K.; van Haelst, S.; Chaves, I.A.; Luyckx, D.; Van Den Bergh, K.; Verbeken, K.; De Meyer, E.; Verhasselt, K.; Meskens, R.; Potters, G.; et al. The influence of concretion on the long-term corrosion rate of steel shipwrecks in the Belgian North Sea. Corros. Engi. Sci. Technol. 2025, 56, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSPAR. Third OSPAR Integrated Report on the Eutrophication Status of the OSPAR Maritime Area, 2006–2014. OSPAR. See Also Regional Quality Status Report II for the Greater North Sea, OSPAR Commission for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic, 2000. 2017. Available online: https://oap.ospar.org/en/ospar-assessments/intermediate-assessment-2017/pressures-human-activities/eutrophication/third-comp-summary-eutrophication/ (accessed on 29 June 2004).
- Melchers, R.E. Long-term immersion corrosion of steels in seawaters with elevated nutrient concentration. Corros. Sci. 2014, 81, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E. Long-term immersion corrosion of irons and steel in seawaters with calcareous deposition. Corrosion 2025, 77, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E.; Jeffrey, R. The transition from short- to long-term marine corrosion of carbon steels: 1. Experimental observations. Corrosion 2022, 78, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E.; Jeffrey, R. The transition from short- to long-term marine corrosion of carbon steels: 2. Parameterization and modeling. Corrosion 2022, 78, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.-M.; Jeannin, M.; Rémazeilles, C.; Sabot, R. Corrosion of carbon steel in marine environments: Role of the corrosion product layer. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Melchers, R.E. (Eds.) Condition Assessment of Aged Structures; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Little, B.J.; Lee, J.S. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Melchers, R.E. Modeling of marine immersion corrosion for mild and low alloy steels—Part 1: Phenomenological model. Corrosion 2003, 59, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E. Mathematical modelling of the diffusion controlled phase in marine immersion corrosion of mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E. A review of trends for corrosion loss and pit depth in longer-term exposures. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2018, 1, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M. (Ed.) Seawater Corrosion Handbook; Noyes Data Corporation: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, M.A.; Melchers, R.E.; Jeffrey, E. Long-Term Corrosion of Steel Chains on Pacific Ocean Beach Sand. In Proceeding of Corrosion & Prevention, 11–14 November, Adelaide, Australia; Australasian Corrosion Association: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Little, B.J.; Gerke, T.L.; Lee, J.S. Mini-review: The morphology, mineralogy and microbiology of accumulated iron corrosion products. Biofouling 2014, 30, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, B.J.; Lee, J.S.; Briggs, B.R.; Ray, R.; Sylvester, A. Examination of archived rusticles from World War II shipwrecks. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crolet, J.-L. From biology and corrosion to biocorrosion. In Microbial Corrosion; Sequeira, C.A., Tiller, A.K., Eds.; The Institute of Metals: London, UK, 1992; pp. 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Melchers, R.E.; Lee, T. Analysis of field observations of severe MIC of FPSO mooring chains. In Failure Analysis of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion; Skovhus, T.L., Eckert, R.B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, R.; Unsal, T.; Xu, D.; Lekbach, Y.; Gu, T. Microbiologically influenced corrosion and current mitigation strategies: A state of the art review. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 2019, 137, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Xu, D. Microbially Influenced Corrosion of Steel in Marine Environments: A Review from Mechanisms to Prevention. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovhus, T.L.; Whitby, C. (Eds.) Oilfield Microbiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, N.J. Deterioration of Structures of Timber, Metal and Concrete Exposed to the Action of Seawater, 15th and 18th Reports; The Institution Civil Engineers: London, UK, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, O.U.; Canter, E.J.; Gillies, L.E.; Paisie, T.K.; Roberts, B.J. Mississippi River plume enriches microbial diversity in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuguchi, M.; Dulai, H.; Burnett, K.M.; Santos, I.R.; Sugimoto, R.; Stieglitz, T.; Kim, G.; Moosdorf, N.; Burnett, W.C. Submarine groundwater discharge: Updates on its measurement techniques, geophysical drivers, magnitudes, and effects. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdrup, H.U.; Johnson, M.W.; Fleming, R.H. The Oceans: Their Physics, Chemistry, and General Biology; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Bristow, L.A.; Mohr, W.; Ahmerkamp, S.; Kuypers, M.M.M. Nutrients that limit growth in the ocean. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R474–R478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khouri, A.; Pellegrino, C.; Cameron, J. Rusticle magnetotaxis elucidating Rustflower formations in RMS Titanic’s Turkish Baths. Deep.-Sea Res. Part 1 2023, 197, 104068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezak, R. Deep Sea Carbonates. In Deep Sea Sediments: Physical and Mechanical Properties; Inderbitzen, A.L., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Back, S.-H.; Hong, J.-W.; Kim, K.Y.; Teom, S.; Kwon, T.-H. X-ray computed microtomography imaging of abiotic carbonate precipitation in porous media from a supersaturated solution: Insights into the effect of CO2 mineral trapping on permeability. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 3835–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E.; Chernov, B.B. Corrosion loss of mild steel in high temperature hard freshwater. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Kirk, M.F. pH as a primary control in environmental microbiology: 1. Thermodynamic perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjones, D.A. Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Googan, C. Offshore pipelines: Do we need −900mV? In Proceedings of the European Corrosion Congress, Graz, Austria, 6–10 September 2015; Paper 100.
- Googan, C. The cathodic protection potential criteria: Evaluation of the evidence. Mater. Corros. 2025, 72, 446–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.; Wagner, P.; Duquette, D. Microbiologically induced increase in corrosion current density of stainless steel under cathodic protection. Corrosion 1988, 44, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanaga, K.; Terashi, R.; Kawai, H.; Unno, H.; Tanji, Y. Biocidal effect of cathodic protection on bacterial viability in biofilm attached to carbon steel. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 97, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.; Hamilton, W.A. Effect of cathodic protection on the activity of microbial biofilms. Ind. Corros. 1987, 5, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.D., III. Long-term corrosion processes of iron and steel shipwrecks in the marine environment: A review of current knowledge. J. Marit. Arch. 2015, 10, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, R.D. The Discovery of the Titanic; Warner Books: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Titanic Sub Dive Reveals Parts Are Being Lost to Sea. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-49420935 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.wrecksite.eu/wreck.aspx?10779 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L6EU3BV1sHQ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Available online: https://coastmonkey.ie/hms-audacious/ (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.wrecksite.eu/wreck.aspx?603 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E0hxkptfY58 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.hmshood.com/hoodtoday/2001expedition/index.htm (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.kbismarck.com/wreck.html (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.hmshood.com/hoodtoday/2001expidition/bismarck/bismarck1.htm (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Herdendorf, C.E.; Thompson, T.G.; Evans, R.D. Science on a deep-ocean shipwreck. Ohio J. Sci. 1995, 95, 4–224. [Google Scholar]
- Herdendorf, C.E.; Robbins, E.I. Iron degradation on a deep-ocean shipwreck. Adv. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/German_submarine_U-155_(1941) (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KAavHyF_bzc (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Available online: https://sanctuaries.noaa.gov/shipwrecks/ituna/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.archaeology.org/issues/202-1601/trenches/3937-trenches-california-ituna-wreck (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_off_Samar (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=324d24jyoeM (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Dobson, N.C.; Gerth, E.; Winckler, J.L. The shipwreck of the SS Republic (1865). Experimental deep sea archaeology. Part 1: Fieldwork and site history, Odyssey Papers 5. In Oceans Odyssey: Deep-Sea Shipwrecks in the English Channel; Stemm, G., Kingsley, S., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BpLUe342g2c (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- MacLeod, I.D. In-situ corrosion measurements of WWII shipwrecks in Chuuk Lagoon, quantification of decay mechanisms and rates of deterioration. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HMS_Invincible_(1907) (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zgZ8JEiu_AQ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Church, R.; Warren, D.; Cullimore, R.; Johnston, L.; Schroeder, W.; Patterson, W.; Shirley, T.; Kilgour, M.; Morris, N.; Moore, J. Archaeological and Biological Analysis of World War II Shipwrecks in the Gulf of Mexico: Artificial Reef Effect in Deep Water; U.S. Department of the Interior, Minerals Management Service: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2007; 387p.
- Available online: https://www.boem.gov/environment/deepwater-shipwrecks (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Available online: https://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/explorations/19microbial-stowaways/logs/june26/june26.html (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Cook, C.D.; Peterson, C.E. Corrosion of submerged artifacts and the conservation of the USS Monitor. In Industrial Applications of the Mossbauer Effect; Gracia, M., Marco, J.F., Plazaola, F., Eds.; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-N6j6dGFoPo (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P7257ozFHkI (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Cvikel, D.; Mentovich, E.D.; Ashenazi, D.; Kahanov, Y. Casting techniques of cannonballs from the Akko 1 shipwreck: Archaeometallurgical investigation. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2013, 49, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M. An iron bastard minion drake extraordinary by John Browne from the pinnacle Swan (1641-53). Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2004, 33, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://trove.scot/actitivities/932320 (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Available online: https://www.historyscotland.com/features/resurrectingtheswan.html (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2790913/the-lost-ships-malin-head-divers-exploring-wrecks-warships-liners-sunk-world-wars-tanks-military-vehicles-gold-bars-missing.html (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W8cJYWUzx8E (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NtviTPqyRqE (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KjZ4Y-PBzCI (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://xray-mag.com/content/u89-exploring-u-boats-ireland (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YfyhuPAafro (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/German_submarine_U-352 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3sou8U5NJdY (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.johnchatterton.com/final-report-on-u869/ (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MfQlUjj20NE (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.livescience.com/50031-sunken-japanese-battleship-located.html (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s-c8Mh6mJZ0 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BQSdG91icCg (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5hNhQC7TGrg (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cj7-55VevmA (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/German_submarine_U-711 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j82Hv0XefqQ (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HhsnHi2d7Ws (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Russell, M.A.; Conlin, D.L.; Murphy, L.E.; Carr, J.D. A minimum impact method for measuring corrosion rate of steel-hulled shipwrecks in seawater. Int. J. Nav. Archaeol. 2006, 35, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.L.; Medlin, D.J.; Murphy, L.E.; Carr, J.D.; Conlin, D.L. Corrosion Rate Trajectories of Concreted Iron and Steel Shipwrecks and Structures in Seawater—The Weins Number. Corrosion 2011, 67, 125005-1–125005-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://en.wijipedia.org/wiki/USS_Arizona (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Church, R.A.; Warren, D.J.; Irion, J.B. Analysis of deepwater shipwrecks in the Gulf of Mexico: Artificial reef effect of six World War II shipwrecks. Oceanography 2009, 22, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://uboat.net/allies/merchants/ship/1679.html (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.wrecksite.eu/wreck.aspx?14875 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LXi9wouGSOI (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.chron.com/news/nation-world/article/Amazing-photos-detail-spectacular-WWII-wreck-in-5616006.php#photo-6587681 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://nautiluslive.org/video/2014/07/07/close-home-exploring-german-u-boat-sunk-us-coast (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://abcnews.go.com/International/awesome-photos-wwii-ship-wrecks-166-ss-robert/story?id=24559749 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LrxUjqsyQZ0 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: http://www.nautiluslive.org/video/2014/07/15/sunken-steamer-ss-alcoa-puritan (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C7pFd_SeY9E (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZEkR1Y9I9rk (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Karcher, D.B.; Roth, F.; Carvalho YCTilstra, A.; Kürten, B.; Struck, U.; Jones, B.H.; Wild, C. Nitrogen eutrophication particularly promotes turf algae in coral reefs of the central Red Sea. Peer J. 2020, 8, e8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sMDs82jQ8pY (accessed on 20 March 2025).
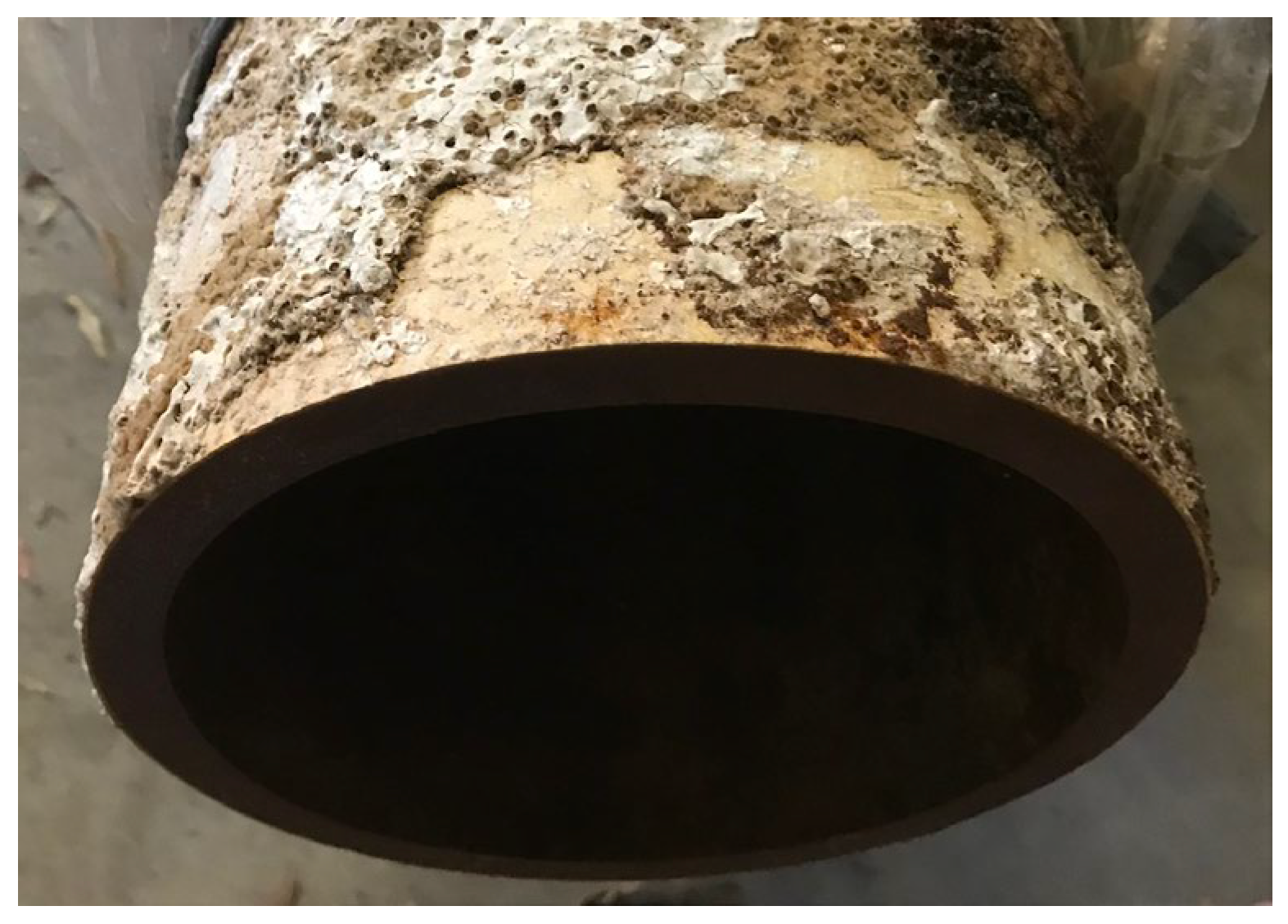

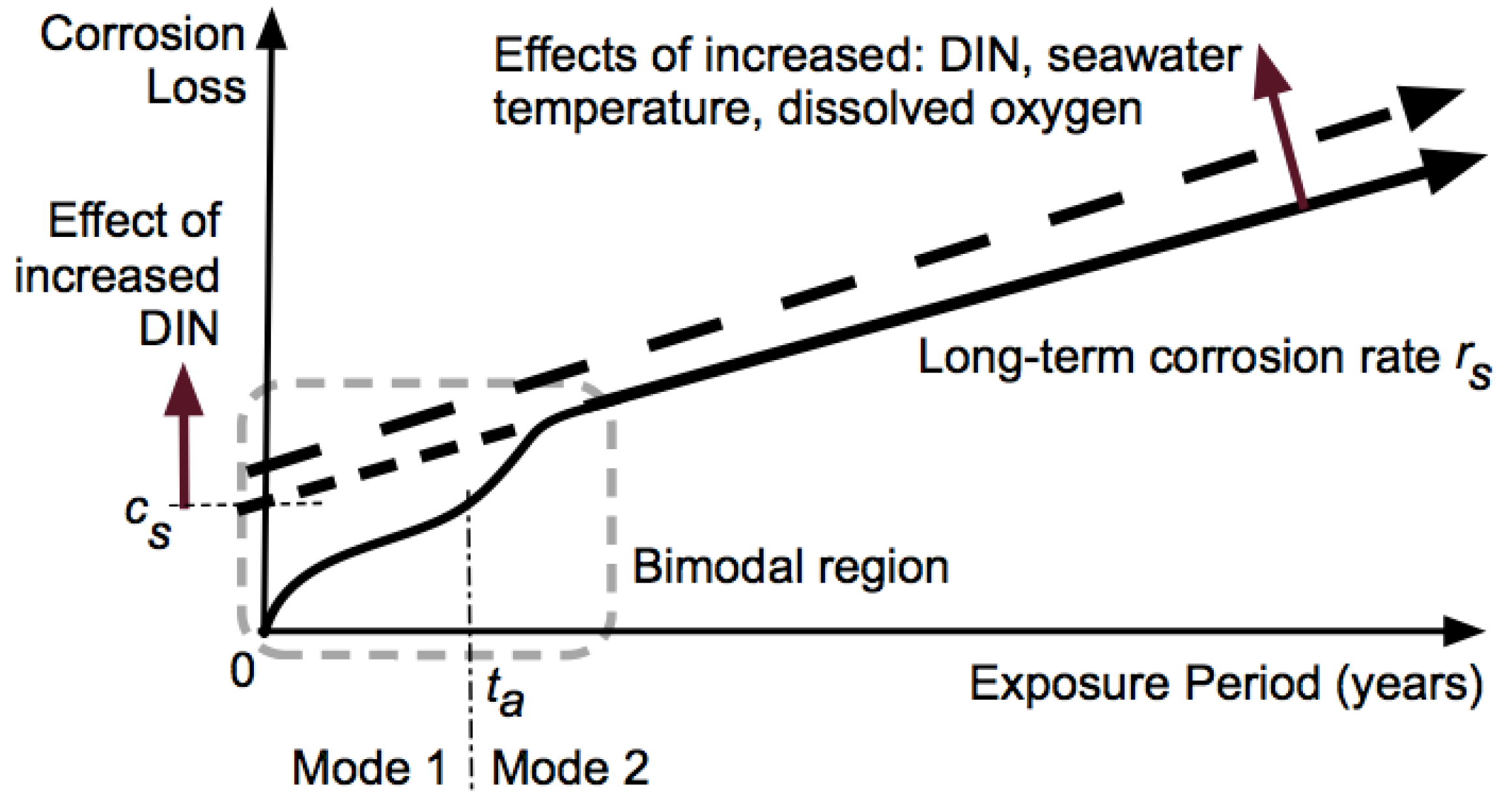
| 1 | Calcareous deposition | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| 2 | Seawater nutrient quality | Natural | Elevated DIN | Natural | Elevated DIN |
| 3 | Case numbers (total number) | 1–13 (13) | 14–22 (9) | 23–35 (13) | 36–46 (11) |
| 4 | Inferred corrosion severity (from observed rust) | Typical | Heavy | Little or none | Some |
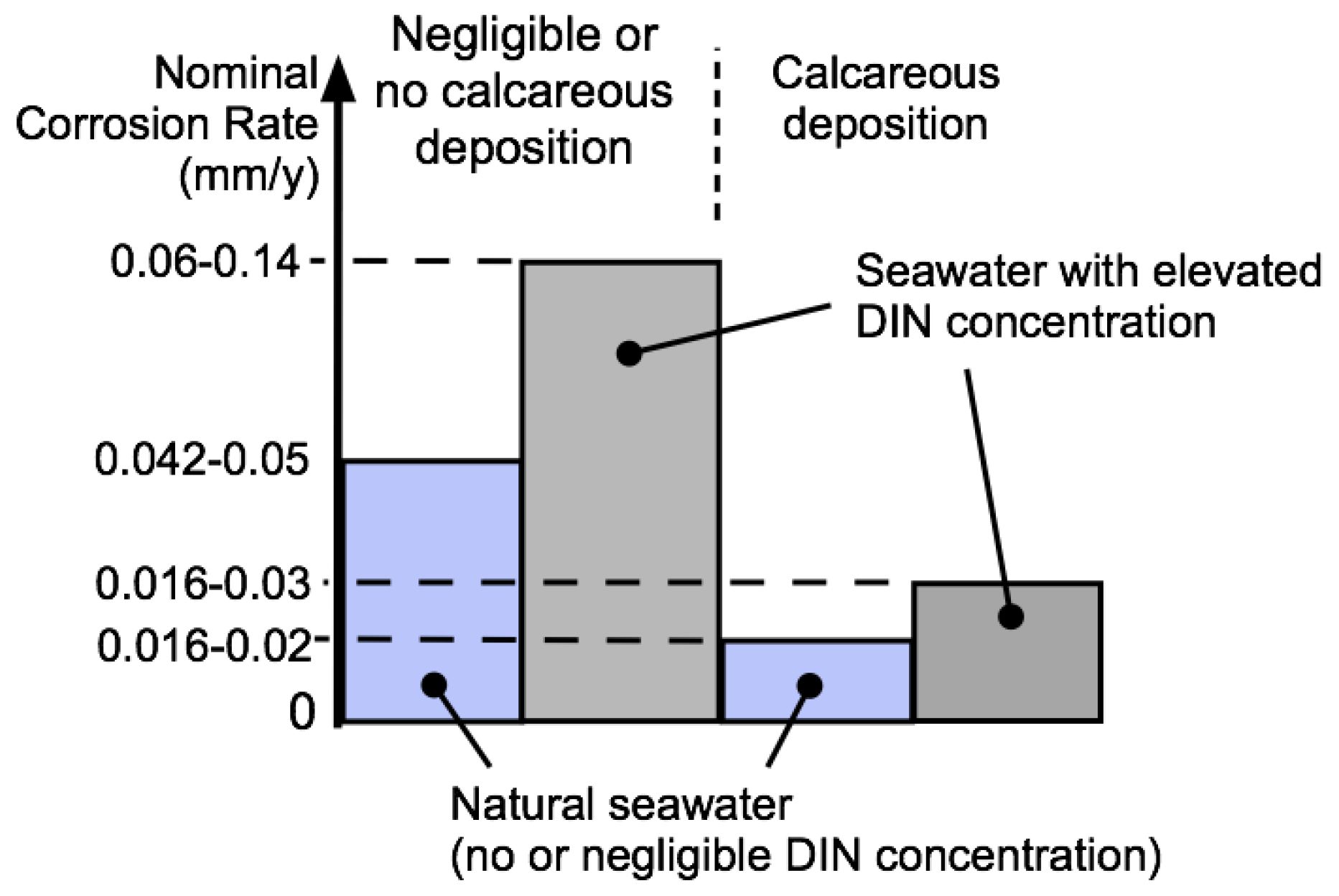
| 1 | Calcareous deposition | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| 2 | Seawater nutrient quality | Natural | Elevated DIN | Natural | Elevated DIN |
| 5 | Case numbers for estimates of rs | 1–3 | 14–20 | 23–25 | 36–37 |
| 6 | Number of individual data sets for rs | >25 | >8 | >3 | >11 |
| 7 | Approx. rate rs (mm/y) @ 12.5 °C | 0.042–0.05 | 0.06–0.14 | 0.016–0.02 | 0.016–0.03 |
| 8 | Approx. mean rs (mm/y) @ 12.5 °C | 0.049 | 0.077 | 0.016 | 0.022 |
| 9 | Approx. standard deviation (mm/y) | 0.0035 | 0.010 | 0.0017 | 0.0062 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melchers, R.E. Long-Term Marine Corrosion Under the Influence of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and Calcareous Conditions. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2025, 6, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6040046
Melchers RE. Long-Term Marine Corrosion Under the Influence of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and Calcareous Conditions. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2025; 6(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelchers, Robert E. 2025. "Long-Term Marine Corrosion Under the Influence of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and Calcareous Conditions" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 6, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6040046
APA StyleMelchers, R. E. (2025). Long-Term Marine Corrosion Under the Influence of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and Calcareous Conditions. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 6(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6040046








