Abstract
In a recent investigation the corrosion-fighting potential of five benzaldehyde derivatives were explored: 4-Formylbenzonitrile (BA1), 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde (BA2), 2-Hydroxy-5-methoxy-3-nitrobenzaldehyde (BA3), 3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde (BA4), and 4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (BA5). Benzaldehyde derivative (BA-2) showed a maximum inhibition efficiency of 93.3% at 500 ppm. Several techniques were used to evaluate these compounds’ ability to protect mild steel from corrosion in a 1 M HCl solution, including potentiodynamic polarization (PDP), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), adsorption isotherms, and computational methods. Supporting techniques Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and ultraviolet–visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy were also employed to validate the results. Despite sharing a common benzene ring, the molecules differ in their substituents, allowing for a comprehensive examination of the substituents’ impact on corrosion inhibition. PDP analysis disclosed that the inhibitors exhibited mixed-type inhibition behavior, interacting with anodic as well as cathodic reactions, influencing the corrosion process. EIS analysis revealed that benzaldehyde derivatives formed a protective passive film on the metal, exhibiting high corrosion resistance by shielding the alloy from corrosive attacks. The benzaldehyde inhibitors followed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, with high R² values near one, indicating a monolayer adsorption mechanism. DFT results indicate that BA 2 is the most effective inhibitor. FTIR and UV-vis spectroscopy revealed the molecular interactions between metal and benzaldehyde derivative molecules, providing insight into the binding mechanism. Experimental results support the outcomes obtained from the molecular dynamic (MD) simulations.
1. Introduction
Corrosion is a pervasive and insidious phenomenon that affects a variety of materials, particularly metals, leading to deterioration, damage, and ultimately failure [1]. Fe and mild steel are the most common metal and meat alloys, respectively, and are widely utilized in various industries due to their affordability and desirable mechanical properties. However, their susceptibility to corrosion in common environments, such as humid air, water, and acidic or salty media, can lead to significant degradation, weakening, and eventual failure [2,3]. Fe and mild steel are, however, highly corrosive in typical usage environments. Corrosion inhibitors are commonly used in the chemical industry to protect metal surfaces from corrosion and provide effective resistance to acidic solutions. Organic compounds with lone electron pairs, such as N, S, or O in a conjugated system, are widely recognized as acid inhibitors [4,5,6,7]. Passivation with thin film deposition, such as oxide or protective layers, is a tried-and-true method to increase corrosion resistance. These films serve as barriers, preventing corrosion and increasing material life. This technique, which is widely used with metals, increases durability and performance under harsh industrial or environmental conditions [8,9,10]. Corrosion inhibitors are chemicals that shield metals from corrosion in harsh environments by creating an inhibitive film onto the metallic surface [11]. Organic inhibitors adsorb onto metal surfaces, altering their properties, and quantum chemistry aids in the correlation of molecular efficiency with corrosion inhibition) [12]. Organic compounds bearing heteroatoms (such as N, O, P, or S), heterocycles, double bonds, and aromatic rings have been reported to inhibit the corrosion of metal in various corrosive medium [13,14,15]. These atomic groups or bonds enhance the electronic interactions between organic corrosion inhibitors and mild steel surfaces, enabling efficient adsorption of the inhibitors over the mild steel surface and enhancing their corrosion-protective properties [16]. Benzaldehyde derivatives show great promise as corrosion inhibitors because of their unique chemical structure, which features N, O, π-electron systems, and other electronegative atoms from different substituent groups. Notably, benzaldehydes are already widely used as precursors in the production of chemical additives and pharmaceutical products [17,18]. Organic compounds have an inhibitory effect due to their adsorption on metal surfaces [19,20]. The majority of commercial inhibitors used to prevent metal corrosion in various environments feature aldehyde, amine, nitrile, and hydroxyl groups [21,22,23]. BA 1, BA 2, BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5 have LD50 values of 100 mg/kg, 4702.74 mg/kg, 5367.44 mg/kg, 2340.30 mg/kg, and 1800 mg/kg, respectively, indicating that these compounds are environmentally friendly. Furthermore, their use as essential components in many pharmaceutical drugs suggests that they are non-toxic substances making them even more attractive as corrosion inhibitors. Previous studies have suggested that benzaldehyde derivatives could be used as corrosion inhibitors [24]. They investigated the corrosion inhibition N, N’-bis(n-hydroxybenzaldehyde)-1,3-propandiimine (n-HBP) and N, N’-bis(2-hydroxy,3-methoxybenzaldehyde)-1,3-propandiimine (H2L2) Schiff bases using electrochemical analysis (PDP and EIS). The results indicate that these compounds are extremely effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel, with inhibition efficiency improving as the inhibitor’s concentration increases. Polarization curves revealed that the studied inhibitors are mixed-type [25]. These compounds were employed as novel inhibitors of mild steel corrosion in 1-molar hydrochloric acid solution, with potentiodynamic polarization, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). According to the results, these inhibitors exhibit corrosion inhibition effectiveness values of 84% for NB and 94% for NPP, respectively, demonstrating good protective performance. The inhibition behavior of three benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone derivatives, namely p-methoxy benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone, p-carboxy benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone, and p-ethyl benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone for metal in 1 M hydrochloric acid solution was reported by [26].
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of five benzaldehyde derivatives (BA 1–5) as corrosion inhibitors for metal surfaces in acidic environments and improve corrosion protection strategies by examining their adsorption behavior, inhibition efficiency, and interaction mechanisms using quantum chemical calculations (DFT). Along with experimental studies, quantum chemical calculations were used to investigate the relationship between molecular structure and inhibition performance. Correlation analysis shows that the inhibitory effect of benzaldehyde derivatives is due to their electronic properties [27]. Corrosion in electrochemical energy technologies, such as batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors, is caused by redox reactions that deteriorate electrodes and other key components. This degradation reduces efficiency, shortens device lifespans, and raises safety issues. The goal of the research is to uncover weight loss of materials and corrosion mechanisms using methods such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), the potentiodynamic polarization (PDP) method, and surface characterization (FTIR and UV-vis spectroscopy). Protective coatings, corrosion-resistant material development, and chemical inhibitor use are all part of the remediation process. Understanding and controlling corrosion is critical for improving energy storage and conversion technologies’ performance, durability, and sustainability. Figure 1 illustrates the molecular structures of benzaldehyde derivative compounds.
Figure 1.
Structure of benzaldehyde derivatives.
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
The benzaldehyde derivatives were obtained directly from industry and used without further treatment or purification. The test solution 1 M hydrochloric acid was made by diluting 32% hydrochloric acid with deionized H2O. Various concentrations of the benzaldehyde compounds (100–500 ppm) were prepared by diluting it with distilled water. The experiment utilized a mild steel working electrode with a composition of 0.46% Mn, 0.26% Si, 0.17% carbon, 0.019% P, 0.017% sulfur, and the rest iron.
2.2. Weight Loss Study
In the weight loss experiment, the inhibitor concentration used was in the range of 100–500 ppm. The corrosion rate (CR), surface coverage (θ), and inhibition efficiency (%IE) were calculated according to Equation (1) [28,29], Equation (2) [30], and Equation (3) [31], respectively:
where W is the average weight loss of mild steel specimens from three parallel experiments, A is the total surface area of a single mild steel specimen, t is the immersion time in hours, and W0 and Wi are the weight loss values without and with inhibitor solutions, respectively.
2.3. Electrochemical Studies
All corrosion determinations were carried out using an Autolab galvanostat/potentiostat. In this study, Ag/AgCl was used as the reference electrode, a 1 cm² pure platinum electrode served as the counter electrode, and a 1 cm² metal specimen was used as the working electrode. Before electrochemical testing, the mild steel was allowed to corrode for 1800 s, during which the open circuit potential (OCP) was monitored and recorded. Potentiodynamic polarization (PDP) analysis was then taken by scanning the working electrode potential between −250 mV and +250 mV at a rate of 0.001 V/s. Additionally, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were performed using Autolab’s Frequency Response Analyzer (FRA) at the corrosion potential (Ecorr). The steel/electrolyte interface was analyzed by applying an alternating current (AC) signal between 100,000 and 0.1 Hz at an amplitude of 0.001 V. All experiments were conducted at a constant temperature of 303 K.
2.4. Spectroscopic Studies
FTIR spectroscopy was utilized to examine the pure and adsorbed inhibitor molecules using a Nicolet iS5 spectrophotometer equipped with an iD5 ATR. The initial step involved acquiring and recording the FTIR spectra of pure benzaldehyde derivatives. Subsequently, the FTIR spectra of the 500ppm benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors, one molar hydrochloric acid solution, and the mild steel sheets were obtained and recorded. The mild steel sheets were then subjected to a seven-day immersion in a solution containing 500 ppm of the inhibitors and 1 M HCl, followed by evaporation of the solution.
For UV–vis spectra, lately prewashed mild steels were immersed in a 500ppm solution of the investigated inhibitors for seven days. The film of benzaldehyde derivative molecules adsorbed onto the metallic surface was examined using a Cary 50 Ultraviolet-Visible Spectrophotometer. The UV-vis spectra of the benzaldehyde derivative compounds (500 ppm), and the remaining solution after 48 h of immersion in mild steel were recorded employing a Cary 50 Ultraviolet Spectrophotometer.
2.5. Computational Studies
Quantum chemical calculations were used to study neutral benzaldehyde derivative molecules. The Density Functional Theory (DFT) was applied for computational studies, with the B3LYP/6-31G+(d, p) chemistry model selected. The hybrid functional B3LYP is described as follows [32]:
The symbols on the right part of Equation (4) represent the local Slater exchange, Vosko, Wilk, and Nussair local correlation, exchange gradient correction of Becke, modification of Lee, Yang, and Parr, exact Hartree–Fock exchange, and the local Slater exchange, respectively.
The Material Studio software’s Forcite module was employed to perform molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. An Fe crystal was selected from the Material Studio database The Fe (1 1 0) surface was chosen as the substrate based on previous studies, which highlighted its high stability and dense packing [33]. After relaxation, the Fe (110) surface was expanded into a (10 × 10) supercell, providing a larger area for the inhibitor to interact with the iron surface. A vacuum slab with zero thickness was introduced to the system. A simulation box with dimensions of 24.82 × 24.82 × 44.20 A3, consisting of 2 films, was formed by applying the layer builder module in Material Studio to better simulate real-world conditions [34,35,36]. The bottom layer consisted of iron atoms, while the top layer contained 491 water molecules (H2O) and 1 molecule of BA1, BA2, BA3, BA4, or BA5. Simulations were carried out using the COMPASSIII force field [37] with a time step of 1 femtosecond (fs) and a total simulation time of 1000 picoseconds (ps), under the NVT ensemble at a temperature of 303 K. After the simulation, the interaction energy between the inhibitor molecule and the mild steel surface was analyzed using the below Equation (5) [36]:
In this equation, represents the total energy of the system, is the combined energy of the iron surface and inhibitor free solution, is the energy of the inhibitor with the solution, and is the energy of the solution alone.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weight Loss Study
Weight loss measurements were used to study how different benzaldehyde derivative concentrations affected mild steel corrosion after 3 h of immersion in 1 M HCl at 30 °C. Table 1 displays the resulting corrosion parameters.

Table 1.
Corrosion parameters of mild steel following 3 h immersion in 1 M HCl solution in the absence and presence of different concentrations of benzaldehyde derivatives (BAs) at 303K.
As expected, the inhibition efficiency (%IE) of BA1, BA2, BA3, BA4, and BA5 increased as the inhibitor’s concentration increased (Figure 2a).
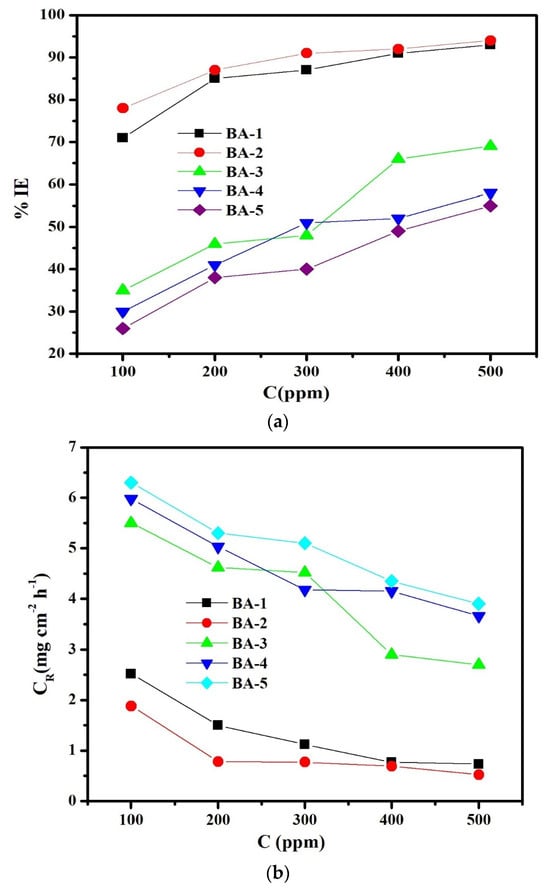
Figure 2.
(a). The inhibition efficiency of mild steel in 1 M HCl at 30 °C varied with inhibitor concentration, as measured by weight loss. (b). The corrosion rate of carbon steel in 1 M HCl at 30 °C varied with the inhibitor concentration, as measured by weight loss.
At the same concentrations, BA 2 and BA 1 demonstrated significantly higher inhibition efficiencies than BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5. Indeed, the inhibition efficiencies of BA 1 and BA 2 were more than 93% higher than that of other benzaldehyde derivatives (BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5). In fact, the increase in inhibition efficiency as the BAs concentration increased from 100 to 500 ppm could be attributed to increased surface coverage at higher concentrations caused by the adsorption of BAs molecules onto the metal surface. The inhibition efficiency is ordered as follows: BA 2 comes after BA 1, then BA 3, then BA 4, and finally BA 5. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show that as the concentration of BAs increases from 100 to 500 ppm, inhibition efficiency and corrosion rate both increase and decrease. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show that as the concentration of BAs increases from 100 to 500 ppm, the inhibition efficiency and corrosion rate decrease.
The corrosion rate (CR) decreased as the inhibitor concentration increased, most likely due to inhibitor adsorption at the metal/solution interface [38]. In the absence of inhibitors, the corrosion rate reached 8.52 mg cm−2 h−1, while in the presence of BAs 500 ppm, BA 1, BA 2, BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5, corrosion rates were lower at 0.73, 0.52, 2.70, 3.66, and 3.90 mg cm−2 h−1, respectively. Therefore, it can be concluded that the corrosion inhibition effectiveness followed the following order: BA 2 comes after BA 1, then BA 3, then BA 4, and finally BA 5.
3.2. OCP vs. Time
In the absence of applied potential or current, the OCP reflects the potential difference between the working electrode and the reference electrode. During the electrochemical corrosion evaluation of inhibitor molecules, OCP measurements are taken before EIS and PDP studies are conducted [39]. The open circuit potential (OCP) of the mild steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid with and without 500 ppm concentration of inhibitor was monitored for 30 min, and the results are shown in Figure 3. The purpose of this research was to look into changes in OCP values during the initial 30 min of immersion and determine if a 30 min waiting period is sufficient for the electrochemical system to reach a stable OCP. The OCP time profile can reveal which half-reaction is most influenced by the addition of benzaldehyde derivative molecules [16]. According to the results, a waiting interval of 1800 s (30 min) is adequate to achieve a stable OCP for most inhibitors, with the systems reaching stability within the first 1300 s. Initially, the OCP of the blank (without inhibitor) exhibited a slight increase over the first 300 s, possibly due to the creation of a metallic oxide film over the metallic surface [40]. After this initial period, the OCP of the blank stabilized. The OCP curves of BA 2, BA 3, and BA 5 shifted towards the anodic direction in the initial 140 s; the curves then stabilized after the 260 s, 460 s, and 670 s, respectively. The OCP curve for BA1 and BA4 has a slight curvature towards the anodic curve but is slightly more cathodic than the other inhibitors [41].
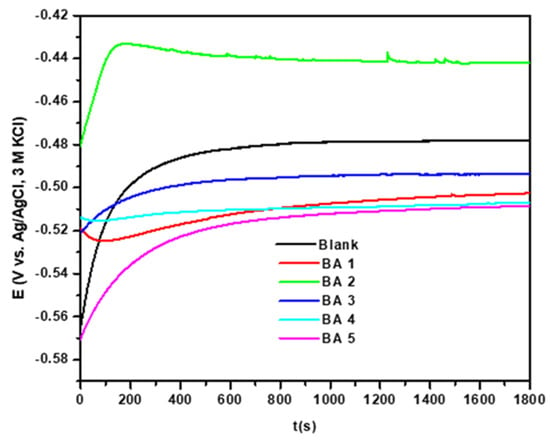
Figure 3.
OCP vs. time measurements in the presence and absence of inhibitors.
3.3. Potentiodynamic Polarization (PDP) Study
The reaction of mild steel was studied using a potentiodynamic polarization technique) in both inhibitor free (1 M HCl) and inhibited systems. The resulting PDP curves for benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors are shown in Figure 4. By examining the Tafel curves, the introduction of inhibitors to the hydrochloric acid solution led to an important reduction in corrosion current density for both anodic and cathodic curves, in comparison to the blank.
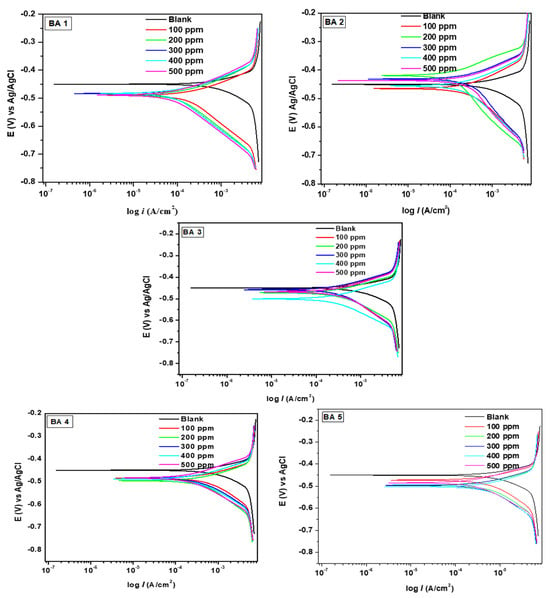
Figure 4.
Potentiodynamic polarization curves for benzaldehyde derivative compounds for mild steel corrosion in 1 M HCl solution.
This shows that the inhibitors effectively decreased hydrogen formation and metal dissolution [42]. Notably, the anodic currents were minimal for the optimum concentration across all inhibitors, with the anodic curves exhibiting substantial inhibition, particularly at higher concentrations. This suggests that the benzaldehyde derivative molecules smoothly get deposited over the metallic surface, forming an inhibitive passive layer [43]. The inclusion of inhibitors did not significantly alter the shape of the anodic Tafel curves, suggesting that their presence had no effect on the corrosion reaction mechanism.
The data in Table 2 disclose a significant reduction in corrosion current density (Icorr) values when the benzaldehyde derivative molecule is added to the 1 M HCl solution; with a consistent decrease in Icorr, the inhibitor concentration increases. Meanwhile, the corrosion potential (Ecorr) values exhibit only a slight shift, indicating mixed type behavior. In this case, the small difference in Ecorr values between the uninhibited and inhibited systems (as depicted in Table 2) indicates a mixed-type inhibition mechanism. This implies that the benzaldehyde derivatives compounds under investigation are corrosion inhibitors of the mixed type, as they prevent mild steel from dissolving anodically and hydrogen gas from evolving cathodically. Icorr of the reaction is seen to decrease with the addition of the benzaldehyde derivatives inhibitors, which is a definite indicator of the benzaldehyde derivative molecule’s role in lowering the active sites over the mild steel surface. Since cathodic reactions are more likely to be prevalent when βc values are higher than βa values, inhibitors will have a greater impact on cathodic reaction sites.

Table 2.
Electrochemical polarization parameters for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution without and with various concentrations of benzaldehyde derivatives at 303 K.
As inhibitor concentrations rise, it is evident that the current density falls, indicating that the inhibitors under study are effective at inhibiting corrosion. All the inhibitors examined in this study exhibited notable protection efficiencies calculated using Equation (6) below:
Here I°corr and represent the corrosion current density without and with inhibitors, respectively.
The inhibition efficiencies of the compounds displayed a positive correlation with the benzaldehyde derivative concentration, with the highest inhibition efficiency obtained at a concentration of 500 ppm for all inhibitors. BA 2 at 500 ppm yields the highest result, 94%, as Table 1 illustrates. At maximum concentration, the decreasing order of inhibition performance of the benzaldehyde derivatives is BA2 > BA1 > BA3 > BA4 > BA5. The inhibitors BA 1 and BA 2 exhibit similar levels of inhibition performance across the concentration range studied. The BA 2 inhibitor demonstrated the maximum inhibition performance among all the derivatives of benzaldehyde in the research. The exceptional inhibition performance of BA 2 can be accredited to the sight of the nitro group at its cycle, which provides additional π-electrons, supplementing the π-electrons already present in the benzaldehyde ring. This enhances the inhibitor’s ability to interact with the steel surface, leading to improved corrosion protection. The synergistic effect of the nitro group and the benzaldehyde ring in BA 2 results in a more effective inhibitor–metal interaction, making it the most efficient inhibitor in the study. BA 3 has additional functional groups hydroxy (OH) at position two and methoxy at position five; these groups can introduce a bit of steric hindrance, which might slightly reduce the molecule’s ability to interact with the metallic surface [44]. This is because the steric barrier between the incoming and already adsorbed molecules may make it difficult for a particularly large molecule to fit into a partially occupied space on a metallic substrate [45].
3.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study
The fitted Nyquist plots illustrating mild steel corrosion with and without BAs in 1M HCl are presented in Figure 5,Figure 6 and Figure 7. The resulting Nyquist and Bode plots (phase angle vs. log f and log Z vs. log f) for metal in the absence and presence of various concentrations of the benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors are exhibited in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. The Nyquist plot shows a sequence of depressed semicircles, with each one’s center below the x-axis. The depressed Nyquist semicircle is a characteristic feature of solid electrodes, ascribed to the frequency dispersion caused by the roughness of the mild steel electrode surface. From the phase angle curves of the Bode plots, it can be observed that the curves of the inhibited system have an increased area under the curves and an increased value of the phase angle compared to the blank system. A high area under the curve for the inhibitors compared to the inhibitor-free system suggests that the maximum number of molecules of benzaldehyde derivatives were able to adsorb onto the metal surface and create a passive coating that protects the metal from acid exposure [46,47]. All inhibitors except BA 4 and BA 5 demonstrated consistent behavior. Notably, BA 5 stood out with significantly reduced inhibition performance values in both PDP and EIS tests, deviating from the expected trend.
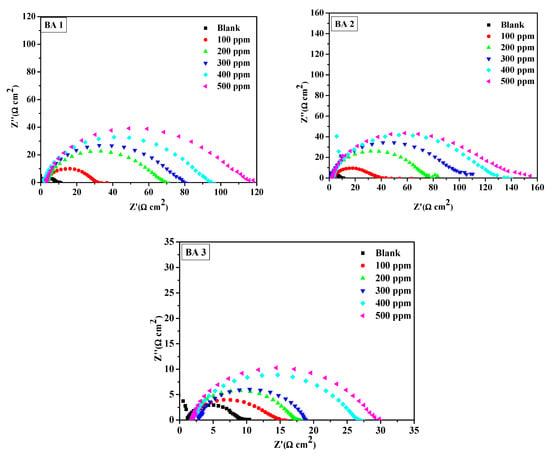
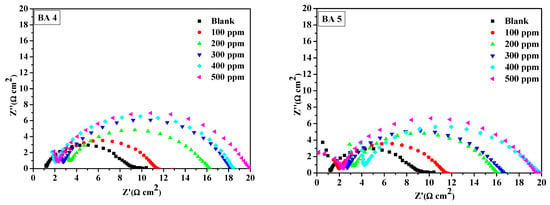
Figure 5.
Nyquist plot for mild steel in 1 M HCl at various concentrations of benzaldehyde derivatives (BA1, BA 2, BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5).
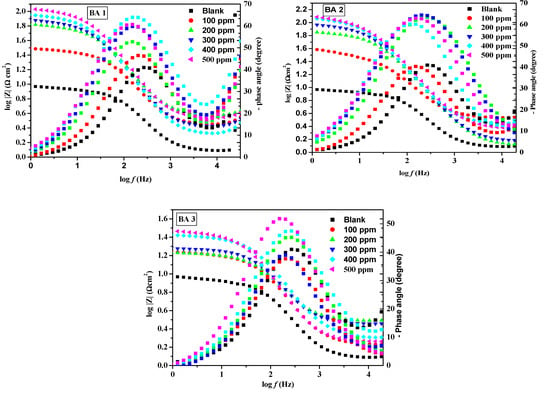
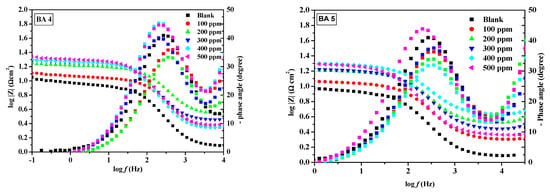
Figure 6.
Bode plot for mild steel in 1 M HCl at different concentrations of benzaldehyde derivatives (BA1, BA 2, BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5).
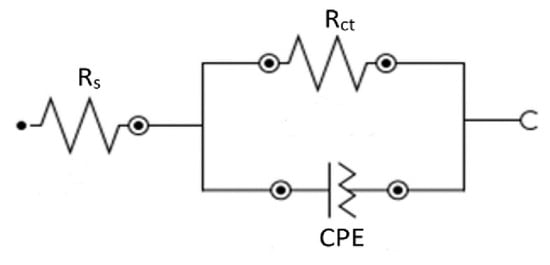
Figure 7.
Electrochemical equivalent circuit, applied for data fitting and analysis.
Figure 5 displays the Nyquist plots of the benzaldehyde derivatives, which were analyzed using equivalent circuits (Figure 7), which included solution resistance (Rs) and charge transfer resistance (Rct) in parallel with a constant phase element (CPE) to simulate the impedance behavior of all inhibitors. The CPE accounts for the frequency-independent phase shift between the applied AC potential and its current response, and its behavior is mathematically described by Equation (7), which characterizes the CPE’s impedance behavior.
Here, ω is the angular frequency (in rad), i is the imaginary number, and n is the CPE exponent, which can gauge the surface’s heterogeneity or roughness.
The double-layer capacitance (Cdl) values were calculated using Equation (8), which is shown below:
The impedance data in Table 3 obtained by fitting the Nyquist plots in Figure 5, reveal that as the benzaldehyde derivative concentration increases, the charge transfer resistance (Rct) of the inhibited system also increases. This suggests that the benzaldehyde derivatives molecules bind to the metal surface, preventing direct exposure to the acidic medium and thereby hindering the oxidation process. Corrosion inhibition efficiency was determined using Equation (9) below.

Table 3.
Electrochemical impedance parameters calculated by fitting the Nyquist plots with the equivalent circuit in absence and presence of different concentrations of benzaldehyde derivatives at 303 K.
Here, R°ct denotes the charge transfer resistance for the inhibitor-free system, while Rct refers to the charge transfer resistance for inhibited systems.
The trend in inhibition efficiencies (%IEEIS) at the maximum inhibitor concentration (500 ppm) is consistent with the order observed in polarization analysis; their inhibition efficiency ranking, from the highest to lowest, is as follows: BA 2 > BA 1 > BA 3 > BA 4 >BA 5. From the order, the inhibitors bearing nitrogen atoms tend to be effective for corrosion inhibition. The reduced inhibition efficiency of BA 4 and BA 5 can be attributed to the presence of fluorine, which alters the molecule’s electronic properties [48]. Fluorine’s electron withdrawing nature hinders the molecule’s ability to create a protective layer on metallic surfaces, leading to decreased corrosion protection. These results agreed favorably with other research reported on the metal corrosion inhibition in 1 M HCl [49]. The constant phase element was the next notable trend; the CPE constant (Q) values in the systems without an inhibitor were significantly higher than in the systems with an inhibitor, indicating that there might be a creation of an inhibitive layer or cover onto the metal surface by the benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors. The film shielded the mild steel surface from ions that might otherwise cause corrosion. The inhibited systems have n value close to 1.This is indicating that the CPE becomes equivalent to an ideal capacitor [50]. The BA 5 inhibitor has a lower CPE value than the blank. The decreased CPE exponent (n) on BA 5 inhibitor suggests adsorption over the metallic surface, resulting from the increased inhomogeneity of the working electrode (mild steel) surface in the systems with inhibitors [51].
3.5. Adsorption Isotherm
The adsorption process is widely recognized as the primary mechanism responsible for the organic molecules’ inhibitory effects. As a result, the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin adsorption isotherms were thoroughly examined to better understand the interactions between inhibitors and metal surfaces. The experimental study [52], in conjunction with Equations (10)–(12) [53,54,55], facilitated the analysis of the plots in Figure 8a–c to ascertain the adsorption isotherm that most precisely depicts the surface coverage (θ) (Table 1).
Here, the parameters ‘α’ and ‘n’ govern molecular interactions. Among the adsorption isotherms examined, the Langmuir model (Figure 8a) provided the best fit, with Table 4 showing a regression coefficient approaching unity for the benzaldehyde derivatives (BAs) inhibitor [56,57].
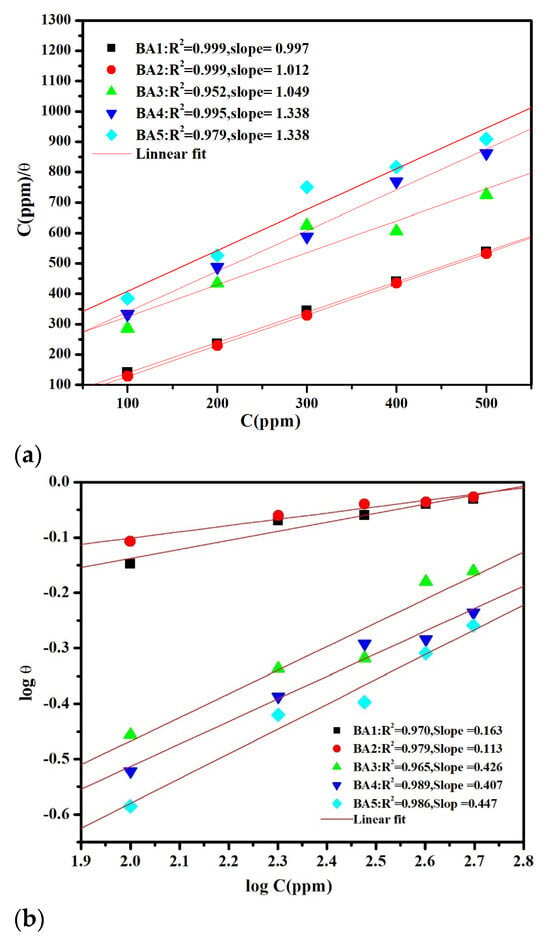
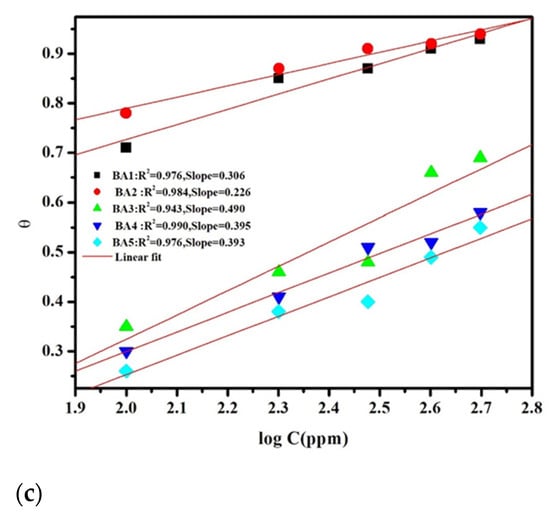
Figure 8.
(a). Langmuir adsorption isotherm plot for BA 1, BA 2, BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5. (b). Freundlich adsorption isotherm plot for BA 1, BA 2, BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5. (c). Temkin adsorption isotherm plot for BA 1, BA 2, BA 3, BA 4, and BA 5.

Table 4.
Isotherm parameters are graphically obtained from experimental observations.
Table 5 Shows the values of the constant of the adsorption/desorption (Kads) and Gibbs free energy. The benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors produced negative figures and high values, implying that the adsorption of the benzaldehyde derivative molecule over the metal surface was strong and spontaneous [57,58]. The equation used to calculate the change in Gibbs free energy is as follows in Equation (13) [29,30]:
where 55.5 stands for the water concentration in mol L−1 solution, T is the absolute temperature, and R is the universal gas constant.

Table 5.
Adsorption and interaction of the adsorbed inhibitor molecules over the mild steel surface in 1 M HCl medium.
Table 5 Depicts the values for Kads and ΔG0ads. High Kads values indicate strong adsorption of BA molecules on the mild steel surface. The observed ΔG0ads values span the range for physical and chemical adsorption, implying that the adsorption process involves both mechanisms [56].
3.6. Spectroscopic Analysis
3.6.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
Figure 9 displays the FTIR spectra of the pure benzaldehyde derivative (BA) inhibitors and the adsorbed BAs inhibitor molecules on the metal surface after seven days of exposure to 500 ppm benzaldehyde derivatives in 1 M HCl, providing insight into the interaction between the benzaldehyde derivatives and the metal surface through the analysis of the functional groups and adsorption mechanisms. The FTIR spectra of the pure benzaldehyde derivative molecules exhibit distinctive aromatic C-C stretching vibrations around 1500 cm−1 and a prominent absorption band between 1730 cm−1 and 1680 cm−1, which is ascribed to the stretching vibrations of the carbonyl C=O bond [59]. The C-H vibration bands are observed at 3000 cm−1 [60]. The spectra of pure BA1 show an absorption band around 2225 cm−1 caused by C≡N stretching, indicating the presence of a nitrile group (CN) [61], while for BA 2 and BA 3, the strong peak observed at about 1350 and 1550 cm−1 is believed to be the (C=N) nitro group [62]. For BA 3, the stretching frequency of the (O-H) group, which is about 3300 cm−1, can be observed [63]. From BA 4 and BA 5, the (C-F) stretching vibration can be observed around 1000 cm−1 and 1200 cm−1. Through careful observation of all the compounds, it can be noted that in the spectra of the adsorbed film, bands from 500 cm−1 to about 1500 cm−1 disappear as compared with the spectra of pure benzaldehyde derivatives. Since the C-C, and C=N visible vibration bands are around the region of 500 cm−1 to 1600 cm−1, it can be assumed that the metal interacted with the benzaldehyde derivatives inhibitors through the three functional groups. The hydroxyl group was identified as the broad and large peak seen in the adsorbed film spectra between 3500 cm−1 and 3100 cm−1, which is recorded for all inhibitors in the investigation. The absence of this peak in the pure spectra of the inhibitor’s molecule indicate that the inhibitor mild steel complex underwent the formation of new bonds [64].
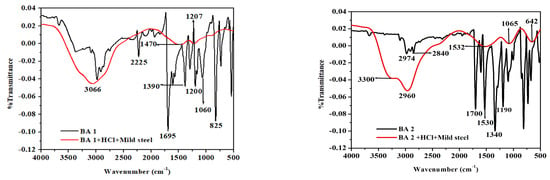
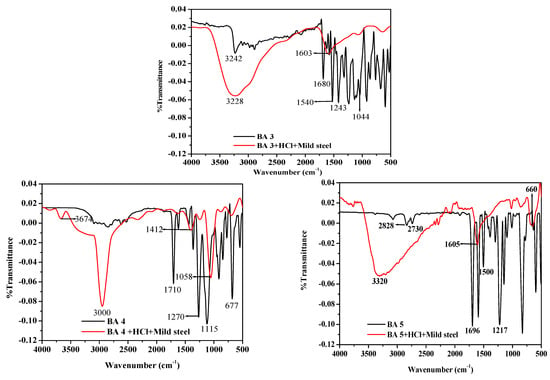
Figure 9.
FTIR spectra of pure inhibitor and the surface product formed on mild steel in 1 M HCl containing benzaldehyde derivatives.
3.6.2. Ultraviolet–Visible Spectrometry
The interaction of the metal and inhibitor was studied using UV–visible spectroscopic analysis. The UV-vis absorption spectra of pure benzaldehyde derivatives and benzaldehyde derivatives with metal at the highest concentration of benzaldehyde derivatives (500 ppm) after seven days of immersion of a mild steel specimen are shown in Figure 10. Benzaldehyde derivatives exhibit peaks of absorption between 200 nm and 300 nm, which can be attributed to transitions [65]. For the mild steel, HCl, and inhibitor solutions, the noted shift in the position and absorbance of the absorption maximum indicates the interaction between the inhibitor molecules and the metal in the solution. The spectrum of BA 1 after immersion of mild steel shows a red-shift, with the sharp peak initially observed at 300 nm now appearing at 295 nm. The spectrum of BA 2 showed an apparent blue-shift after the steel specimens’ exposure, as the broad peak that is primarily centered at 320 nm now rises at 300 nm and shows a significant decrease in absorbance. For BA 3, before the immersion of mild steel, only one peak appeared at around 288 nm, but after immersion of mild steel, two absorption peaks appeared at 288 nm and 390 nm. A change was observed for BA 4: initially, a sharp peak was observed around 280 nm; after the mild steel was immersed, the peak appeared at 315 nm, shifting to the red region. The results of these experiments offer robust evidence for the complex formation between Fe2+ ions and the inhibitors in 1 M HCl solution [66]. UV-vis spectroscopic analysis confirms that a metal inhibitor complex protective layer forms over the mild steel surface, indicating the creation of a barrier that prevents corrosion.
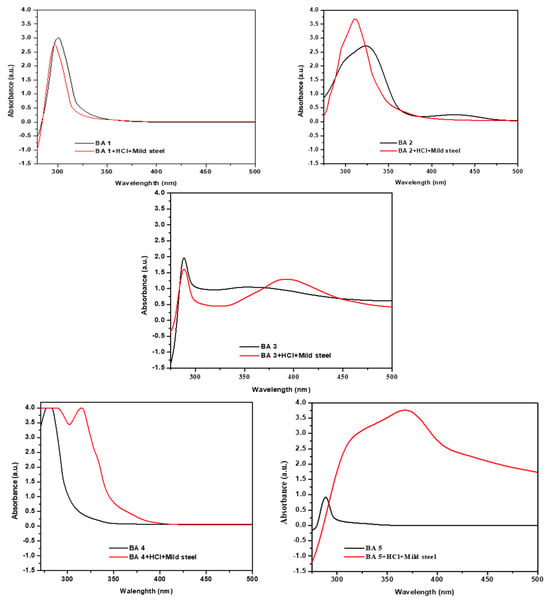
Figure 10.
UV-vis spectra of benzaldehyde derivative molecules in acidic solutions before and after exposure to mild steel.
3.7. Quantum Chemical Study
The optimized chemical structures of the benzaldehyde derivatives are depicted in Figure 11, with the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals shown in Figure 12, and the corresponding computed DFT parameters compiled in Table 6. High EHOMO values and low ELUMO values indicate high electron sharing and protection abilities, respectively [67,68]. Ionization energy (I, Equation (14)) and electron affinity (A, Equation (15)) can be interpreted as the negative values of EHOMO and ELUMO [69,70]:
I = ‒EHOMO
A = ‒ELUMO
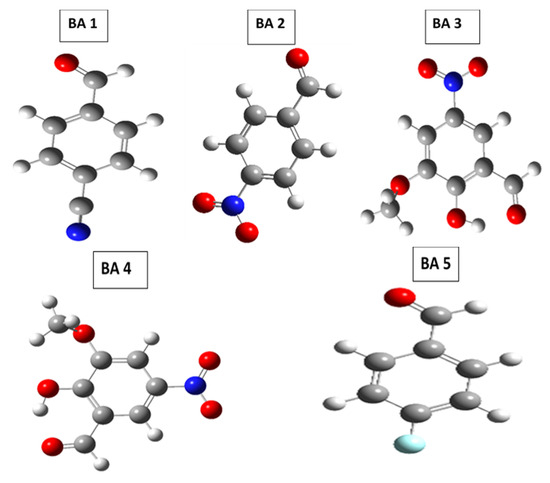
Figure 11.
Optimized molecular structure of benzaldehyde derivatives.
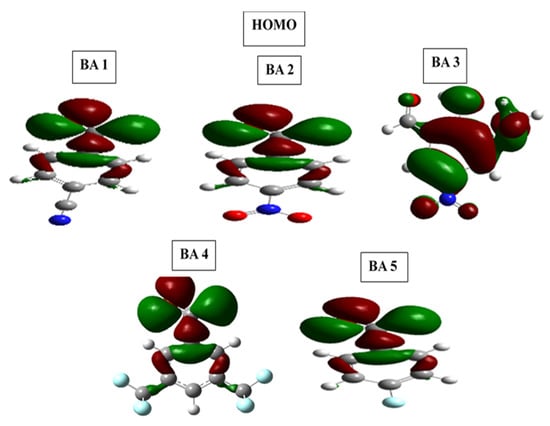
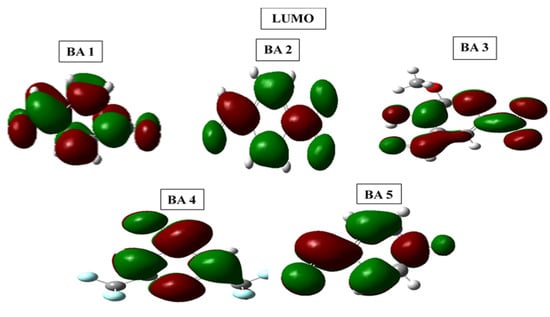
Figure 12.
Frontier molecular orbital diagrams HOMO and LUMO of benzaldehyde derivatives in 1 M HCl medium.

Table 6.
Calculated quantum chemical parameters of benzaldehyde derivatives.
The optimized structures of all molecules of benzaldehyde derivatives have near-planar geometries, which promote strong adsorption on the metal surface and increase inhibition performance [70]. For the benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors, the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) in BA1, BA2, BA3, BA4, and BA5 is primarily localized on the phenyl ring and carbonyl oxygen. In the case of benzaldehyde derivative inhibitor molecules, the HOMO for BA1, BA2, BA4, and BA5 is distributed over the phenyl ring and oxygen of the carbonyl group. However, the HOMO centers in BA3 are the phenyl ring, the methoxy (OCH3) group, and the heteroatom. However, the distribution of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) in BA-1 is over the phenyl ring, heteroatom of nitrile (CN), and carbonyl (CO) groups. In the case of BA2, the LUMO is distributed across all heteroatoms of the nitro functional group and the oxygen of the carbonyl group. In the BA-3 molecule, the LUMO is distributed among the hydroxyl (OH), carbonyl, and nitro groups. The benzene ring and the carbonyl heteroatom are included in the BA4 LUMO distribution. In the case of BA-5, the LUMO is distributed throughout the entire molecule, which includes the phenyl ring, carbonyl, and fluorine.
The energy gap (∆E) is an important indicator of inhibitor reactivity, with lower values indicating more electron-donating ability. BA2 has the lowest ∆E value compared to BA1, BA 3, BA4, and BA5, indicating a stronger interaction with the iron surface.
Table 6 exhibits the quantum chemical parameters, including global hardness (η), electronegativity (χ), global softness (σ) [71,72,73,74], and dipole moment (μ) [75,76]. The parameters are determined using the following equations:
The dipole moments of BA1, BA2, BA3, BA4, and BA5 are 2.70 D, 3.28 D, 2.49 D, 2.38 D, and 2.20 D, respectively, which are greater than that of the water molecule (1.88 D). This higher polarity facilitates the preferential adsorption of both inhibitors onto the metal surface, resulting in the displacement of water molecules and thus improving steel protection in acidic environments [77]. Further, quantum chemical properties are applied to examine the corrosion protection performance of benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors, including global hardness (η), electronegativity (χ), and global softness (σ). Equations (16)–(18) are utilized to ascertain these parameters, respectively. Molecules that are softer (higher σ) are thought to be significantly more reactive than those that are harder (lower σ) [5].
DFT calculations validated the experimental findings, confirming the efficacy of benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors. The analysis revealed that their planar geometry improves surface coverage and interaction with the metal, with optimized structures and HOMO-LUMO distributions (Figure 11 and Figure 12), emphasizing the importance of molecular geometry in corrosion inhibition. The agreement between experimental and DFT results provides a comprehensive understanding of the adsorption mechanisms, confirming the experimental findings and emphasizing the inhibitors’ effectiveness in corrosion protection.
DFT and experimental results support the efficacy of benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors, emphasizing the importance of planar geometry in improving metal interaction and surface coverage. Optimized structures and HOMO-LUMO distributions (Figure 11 and Figure 12) highlight the significance of molecular geometry in corrosion inhibition. The frontier molecular orbital energies are associated with a molecule’s donor acceptor ability. A molecule’s LUMO energy (ELUMO) indicates its electron-accepting ability, while HOMO energy (EHOMO) reflects its electron-donating capacity. Higher EHOMO and lower ELUMO suggest better donation and acceptance, respectively [78,79]. The EHOMO values reveal that these inhibitors possess high electron-donating ability, with BA4 exhibiting the highest EHOMO value among them. In addition, these inhibitors showed lower ELUMO values, indicating their ability to accept electrons, with BA 2 having the lowest value, signifying a high electron-accepting ability.
The energy gap (∆E) was also computed according to frontier orbital theory. The molecules with small values of the energy gap are expected to be more reactive than the ones with larger energy gap values [29,80]. The decreasing trend in the energy gap is BA 2 > BA 1 > BA 3 > BA 4 > BA 5. This trend shows that BA 2, BA 1, and BA 3 inhibitors have high reactivity and inhibition ability compared to BA 4 and BA 5 inhibitors; this order confirms that the molecules bearing nitrogen groups tend to be effective as corrosion inhibitors.
Experimental outcomes were adopted by Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations, confirming the effectiveness of the benzaldehyde derivative inhibitors. The DFT analysis disclosed that the planar geometry of the inhibitors is crucial for their corrosion inhibition properties, allowing them to cover a larger surface area and interact with the metal surface more effectively. The optimized structures of molecules and spatial distributions of HOMO and LUMO densities (Figure 11 and Figure 12) further highlighted the importance of geometric structures in determining their corrosion inhibition performance.
3.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations offer useful insights into the interactions between corrosion inhibitors and metal surfaces, proving to be an essential tool in corrosion research [21]. With advances in computational techniques, researchers can now investigate these interactions more thoroughly while using simplified models that retain high accuracy [37,81,82,83].
In Figure 13, the MD-optimized adsorption configurations of the molecules BA1– BA3 and BA4 –BA5 on the Fe (110) surface are displayed, respectively. The figure shows that all five molecules moved toward the metal surface, indicating a strong attraction between the molecules and iron. Each inhibitor adopts a parallel orientation that maximizes its contact with the surface, highlighting its high affinity for iron [36]. These configurations demonstrate the impact of molecular structure on the inhibitor’s performance. Notably, the presence of heteroatoms, such as nitrogen and oxygen, in all molecules, facilitates the approach of the molecules to the surface of iron. The parallel adsorption mode observed in these molecules enhances the binding strength, which is crucial for the creation of a stable, inhibitive layer that protects the metal from corrosion.
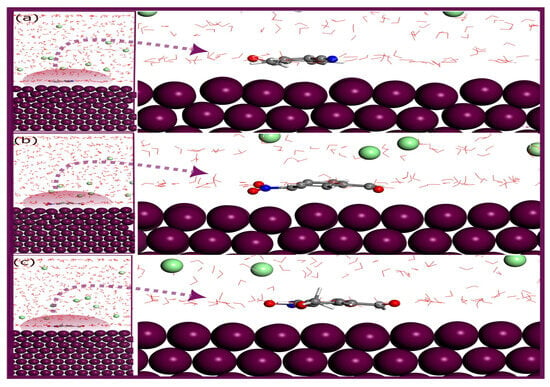
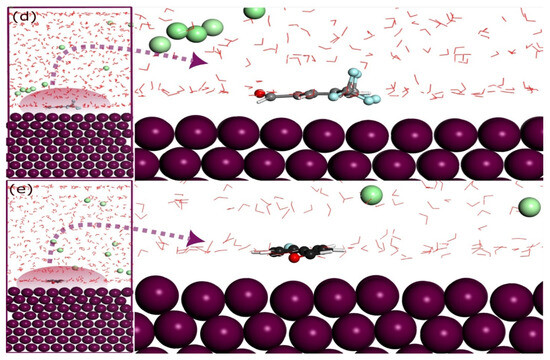
Figure 13.
Equilibrium configurations for the adsorption of (a) BA 1, (b) BA 2, and (c) BA 3 on the Fe (110) surface in solution by molecular dynamics. Equilibrium configurations for the adsorption of (d) BA 4, and (e) BA 5 on the Fe (110) surface in solution by molecular dynamics.
The heteroatoms, particularly nitrogen and oxygen, play a vital role in the adsorption process by providing lone pairs of electrons that interact with the Fe surface. Their positioning near the metal enables electron donation from the inhibitor to the metal, which strengthens the adsorption and aids in establishing a protective barrier against corrosive agents.
The interaction energies derived from MD simulations provide crucial evidence of the efficacy of these molecules as corrosion inhibitors. Among the five molecules, BA 2 exhibits the strongest interaction with the Fe (110) surface, with an interaction energy of −113.21 kcal/mol, followed by BA 1 at −104.33 kcal/mol, BA 3 at −95.47 kcal/mol, BA 4 at −81.74 kcal/mol, and BA 5 at −55.84 kcal/mol. The negative values for all three molecules indicate a highly favorable adsorption process on the Fe (110) surface [84]. This trend in interaction energies correlates well with experimental data, positioning BA 2 as the most effective inhibitor. The higher interaction energy of BA 2 suggests that it is more capable of forming a durable and protective film over the Fe surface, likely due to the positive impact of its nitro group.
The integration of MD simulations with DFT calculations offers a more in-depth view of how BA 1–BA 5 molecules of benzaldehyde derivatives interact with the Fe (110) surface in the presence of a solvent. The consistency between the reactivity patterns observed in both MD and DFT simulations underscores the significant role of the molecules’ electronic properties in their corrosion inhibition capabilities, further reinforcing the experimental findings. This alignment between computational and experimental data strengthens the confidence in the performance of these inhibitors, particularly in highlighting the superior performance of BA 2. However, the relatively weaker interaction of BA 5 suggests room for optimization in its molecular design to enhance its protective capacity.
4. Conclusions
This research investigated the corrosion inhibition properties and adsorption actions of five benzaldehyde derivatives on mild steel in 1 M HCl solution. A comprehensive approach was employed, combining electrochemical techniques, spectroscopic methods, scanning electron microscopy, and quantum chemical methods to evaluate the inhibitors’ performance. The study’s findings and conclusions are presented below. The inhibition efficiency of mild steel in 1 M HCl enhances as the concentration of benzaldehyde derivatives (BAs) increases, reaching 94 % at 500 ppm for BA 2. The inhibitors adsorb according to the Langmuir isotherm, with a negative ΔG°ads value indicating spontaneous adsorption.
According to PDP curves, all five benzaldehyde corrosion inhibitors demonstrated excellent inhibition performance for mild steel in 1 M HCl, with the highest concentration of 500 ppm, and the inhibition efficiency ranking of the five-benzaldehyde derivative (BA) inhibitors is as follows:
BA 2 > BA 1 > BA 3 > BA 4 > BA 5.
All these inhibitors interact with the mild steel surface through both cathodic and anodic sites, classifying them as mixed-type inhibitors. However, it is worth noting that in some cases, the cathodic site may be more dominant, while in others, the anodic site may be more prevalent, indicating a varying degree of interaction between the benzaldehyde derivatives molecules and the metal surface.
EIS outcome demonstrated that the five benzaldehyde derivatives corrosion inhibitors exhibited excellent performance in protecting metal against corrosion in one molar hydrochloric acid, with a maximum concentration of 500 ppm. Their inhibition efficiency order is as follows: BA 2 > BA 1 > BA 3 > BA 4 > BA 5.
The results of the Tafel and EIS analyses exhibited a remarkable correlation, indicating that all the inhibitors demonstrated substantial solution resistance and displayed exceptional corrosion inhibition ability for metal. The consistent trend across both analyses reaffirms the outstanding performance of the inhibitors in mitigating corrosion. Additionally, the findings suggest that these inhibitors have great potential for practical applications in corrosion protection. Both FTIR and UV-vis spectroscopy for all the studied benzaldehyde derivatives inhibitors demonstrated the interaction of inhibitors with a metal surface, indicating the potential creation of an inhibitor–mild steel complex formation.
The HOMO and LUMO analysis of the benzaldehyde derivatives corrosion inhibitors revealed that the benzaldehyde ring exhibits both electron-donating and electron-accepting capabilities. These heterocyclic compounds contain π-electrons from double bonds, as well as partially filled orbitals of N-atoms, which enable these inhibitors to engage in both electron donation and acceptance. Moreover, the quantum chemical calculations reveal that the studied inhibitors possess the essential electronic and structural properties required to interact strongly with the metal surface, underscoring their promising potential as effective corrosion inhibitors.
MD simulations confirmed BA 2 as the most effective inhibitor on Fe (110), with the strongest interaction energy. The results align with experimental data highlighting the role of molecular structure in enhancing corrosion inhibition performance. Thus, an overview about aromatic corrosion inhibitors ranging from micro to large to complex molecules obtained as plant extracts from natural and thus renewable resources is provided.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.B. and M.E.M.; methodology, T.H.B.; software, A.E.-K.; validation, T.H.B. and M.S.; formal analysis, T.H.B. and M.S.; investigation, T.H.B. and M.S.; data curation, T.H.B., A.E.-K. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, T.H.B. and M.S.; writing—review and editing, I.B. and M.E.M.; visualization, I.B. and M.E.M.; supervision, M.E.M.; project administration, M.E.M.; funding acquisition, I.B. and M.E.M.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Authors would like to acknowledge funding from North-West University and SASOL, South Africa.
Data Availability Statement
No data was used for the research described in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ovri, J.E.O. Corrosion: A Precursor to Environmental stability in the Niger delta of Nigeria, 36th Inaugural lecture. Delta 2020, 3, 4–877. [Google Scholar]
- Ebenso, E.E.; Oguzie, E.E. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic media by some organic dyes. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2163–2165. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, M.; Javidani, M.; Heidari, M.; Jahazi, M. Enhancing the tribological performance of tool steels for wood-processing applications: A comprehensive review. Metals 2023, 13, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y. Organic Compounds as Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in HCl Solution: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2022, 15, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyari, M.M.; Hiwa, M.Q. Corrosion inhibition efficiency and quantum chemical studies of some organic compounds: Theoretical evaluation. Corros. Rev. 2023, 41, 427–441. [Google Scholar]
- Kadhim, A.; Betti, N.; Al-Bahrani, H.A.; Al-Ghezi, M.K.S.; Gaaz, T.; Kadhum, A.H.; Alamiery, A. A mini review on corrosion, inhibitors and mechanism types of mild steel inhibition in an acidic environment. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2021, 10, 861–884. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.J.; Li, S.N.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.H.; Lu, L.D. Computational and electrochemical studies of some amino acid compounds as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 6255–6265. [Google Scholar]
- Prabakar, S.R.; Hwang, Y.H.; Bae, E.G.; Lee, D.K.; Pyo, M. Graphene oxide as a corrosion inhibitor for the aluminum current collector in lithium ion batteries. Carbon 2013, 52, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.Y.; Belau, L.; Seo, H.; Somorjai, G.A. Improved oxidation resistance of Ru/Si capping layer for extreme ultraviolet lithography reflector. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2011, 29, 041602. [Google Scholar]
- Shwetha, K.M.; Praveen, B.M.; Devendra, B.K. A review on corrosion inhibitors: Types, mechanisms, electrochemical analysis, corrosion rate and efficiency of corrosion inhibitors on mild steel in an acidic environment. Results Surf. Interfaces 2024, 16, 100258. [Google Scholar]
- Sherif, E.S.M. The role of corrosion inhibitors in protecting metallic structures against corrosion in harsh environments. Role Colloid. Syst. Environ. Prot. 2014, 509–526. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, M.I.; Saad, A.F.; Shaaban, M.R.; Jahdaly, B.A.; Hazazi, O.A. New insight into the mechanism of the inhibition of corrosion of mild steel by some amino acids. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A. Molecular structural aspects of organic corrosion inhibitors: Experimental and computational insights. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 1227, 129374. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, C.; Haque, J.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E. Aqueous phase environmentally friendly organic corrosion inhibitors derived from one step multicomponent reactions: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 18–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Quraishi, M.A.; Nik, W.B.W.; Srivastava, V. Triazines as a potential class of corrosion inhibitors: Present scenario, challenges and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114747. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Amiery, A.A.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Alobaidy, A.H.M.; Mohamad, A.B.; Hoon, P.S. Novel corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in HCl. Mater. 2014, 7, 662–672. [Google Scholar]
- Satrio, J.A.B.; Doraiswamy, L.K. Production of benzaldehyde: A case study in a possible industrial application of phase-transfer catalysis. J. Chem. Eng. 2001, 82, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemifard, A.G.; Moore, D.E.; Mohammadi, A.; Kebriyaeezadeh, A. Capillary gas chromatography determination of benzaldehyde arising from benzyl alcohol used as preservative in injectable formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 31, 685–691. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazy, M.A.; Hasan, A.M.; Emara, M.M.; Bakr, M.F.; Youssef, A.H. Evaluating four synthesized Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitors on the carbon steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid. Corr. Sci. 2012, 65, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, P.; Obot, I.B.; Yadav, M. Functionalized 2-hydrazinobenzothiazole with carbohydrates as a corrosion inhibitor: Electrochemical, XPS, DFT and Monte Carlo simulation studies. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 931–940. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Chen, W.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Inhibition effect of 4-amino-antipyrine on the corrosion of copper in 3 wt.% NaCl solution. Corr. Sci. 2012, 57, 270–278. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, S.A.; Metwally, M.S.; Selim, S.R.; Bedair, M.A.; Abbas, M.A. Corrosion inhibition and adsorption behavior of new Schiff base surfactant on steel in acidic environment: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 4311–4320. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Mazumder, M.J.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ansari, K.R. Chitosan-cinnamaldehyde Schiff base: A bioinspired macromolecule as corrosion inhibitor for oil and gas industry. Int. J. Bio. Macromole. 2020, 158, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.; Zaafarany, I.; Fouda, A.S.; Abd El-Kader, D. Inhibition of zinc corrosion by some benzaldehyde derivatives in HCl solution. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Arrousse, N.; Salim, R.; Houari, G.A.; Hajjaji, F.E.; Zarrouk, A.; Rais, Z.; Taleb, M.; Chauhan, D.S. Experimental and theoretical insights on the adsorption and inhibition mechanism of (2E)-(acetylamino)-3-(4-nitrophenyl) prop-2-enoic acid and 4-nitrobenzaldehyde on mild steel corrosion. Chem. Sci. J. 2020, 132, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.H.; Chen, Y. Experimental and theoretical studies of benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acid media. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1177, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, U.J.; Jha, P.C.; Lone, M.Y.; Shah, R.R.; Shah, N.K. Electrochemical and theoretical investigation of the inhibitory effect of two Schiff bases of benzaldehyde for the corrosion of aluminium in hydrochloric acid. J. Mole. Struct. 2016, 1125, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.K.; Haque, J.; Salghi, R.; Lgaz, H.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Quraishi, M.A. Spiro [indoline-3,4′-pyrano [2,3-c] pyrazole] derivatives as novel class of green corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium: Theoretical and experimental approach. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, M.; Zondi, Z.; Mashuga, M.E.; Bahadur, I.; Kumar, S.; Haque, J.; Pandey, S.K.; Mohammad, F.; El-khlifi, A. Calotropis procera Latex Extract as an Effective Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in Acidic Medium: Experimental and Quantum Chemical Approaches. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 20, e70010. [Google Scholar]
- Saranya, J.; Sowmiya, M.; Sounthari, P.; Parameswari, K.; Chitra, S.; Senthilkumar, K. N-heterocycles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acid medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Manivel, A.; Ramkumar, S.; Wu, J.J.; Asiri, A.M.; Anandan, S. Exploration of (S)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo [d] thiazole-2,6-diamine as feasible corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic media. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, H.; Cavallo, L. Re-evaluation of the Mn (Salen) mediated epoxidation of alkenes by means of the B3LYP* density functional. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 3747–3753. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Obot, I.B.; Zheng, X.; Shen, X.; Qiang, Y.; Kaya, S.; Kaya, C. Theoretical insight into an empirical rule about organic corrosion inhibitors containing nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur atoms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 406, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lgaz, H.; Lee, H. Interfacial adsorption mechanism of hydroxycinnamic acids on iron surfaces: A computational perspective toward eco-friendly corrosion mitigation strategies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 644, 158763. [Google Scholar]
- Lgaz, H.; Lee, H. Computational Exploration of Phenolic Compounds in Corrosion Inhibition: A Case Study of Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol. Materials 2023, 16, 6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Lgaz, H.; Verma, D.K.; Ebenso, E.E.; Bahadur, I.; Quraishi, M.A. Molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations as powerful tools for study of interfacial adsorption behavior of corrosion inhibitors in aqueous phase: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 99–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wazzan, N.; Obot, I.B.; Lgaz, H.; Safi, Z.; Al-Qurashi, O. Multiscale computational modeling of phytochemicals for iron corrosion inhibition: Bridging DFT, SCC-DFTB, and molecular dynamics for eco-friendly solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 406, 125070. [Google Scholar]
- Obot, I.B.; Obi-Egbedi, N.O. Anti-corrosive properties of xanthone on mild steel corrosion in sulphuric acid: Experimental and theoretical investigations. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, D.K.; Quraishi, M.A. Electrochemical investigation of substituted pyranopyrazoles adsorption on mild steel in acid solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8194–8210. [Google Scholar]
- Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Mashuga, M.E.; Ebenso, E.E. Surface protection activities of some 6-substituted 3-chloropyridazine derivatives for mild steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid: Experimental and theoretical studies. Surf. Interfac. 2018, 12, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, A.; Abdouss, M.; Farhadian, A.; Guo, L.; Neshati, J. Development of a Novel Thermally Stable Inhibitor Based on Furfuryl Alcohol for Mild Steel Corrosion in a 15% HCl Medium for Acidizing Application. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 11030–11044. [Google Scholar]
- Lowmunkhong, P.; Ungthararak, D.; Sutthivaiyakit, P. Tryptamine as a corrosion inhibitor of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Döner, A.; Solmaz, R.; Özcan Kardaş, M.G. Experimental and theoretical studies of thiazoles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in sulphuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2902–2913. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, C.; Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Ebenso, E.E.; Quraishi, M.A. Substituents effect on corrosion inhibition performance of organic compounds in aggressive ionic solutions: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 251, 100–118. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, S.; Metikoš-Huković, M. A nonlinear kinetic model introduced for the corrosion inhibitive properties of some organic inhibitors. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2003, 33, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, H.L. CO2 Corrosion of Steel in Formate Brines for Well Applications. Presented at the CORROSION 2004, New Orleans, LA, USA, 27 March–1 April 2004. NACE-04357. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrouk, A.; Hammouti, B.; Zarrok, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Warad, I. Thermodynamic study of metal corrosion and inhibitor adsorption processes in copper/N-1-naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride monomethanolate/nitric acid system: Part 2. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2012, 38, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, D.; Row, T.N.G. Role of organic fluorine in crystal engineering. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2011, 13, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, A.; Anitha, P.; Gnanavel, S.; Angaiah, S. Development of 1-phenyl-3-(4-(pyridin-4-ylmethyl) phenyl) urea derivatives as robust corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M HCl environment: Insight from, molecular, experimental, and microscopic-scale modelling approaches. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111648. [Google Scholar]
- Iroha, N.B.; Maduelosi, N.J. Corrosion inhibitive action and adsorption behaviour of justicia secunda leaves extract as an eco-friendly inhibitor for aluminium in acidic media. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 13019–13030. [Google Scholar]
- Mashuga, M.E.; Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Lgaz HEl-Sayed, M.; Sherif Eno, E. Ebenso Aminomethylpyridazine isomers as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 MHCl: Electrochemical DFT, Monte Carlo simulation studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117882. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, P. Inhibitory action of extract of ankado (Calotropis gigantea) leaves on mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 437–447. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y. Experimental and theoretical evaluation of N,N-Bis (2-pyridylmethyl) aniline as a novel corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 59, 526–535. [Google Scholar]
- Dkhireche, N.; Galai, M.; El Kacimi, Y.; Rbaa, M.; Ouakki, M.; Lakhrissi, B.; Touhami, M.E. New quinoline derivatives as sulfuric acid inhibitor’s for mild steel. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 111–135. [Google Scholar]
- Adejo, S.O.; Ahile, J.U.; Gbertyo, J.A.; Kaior, A.; Ekwenchi, M.M. Resolution of adsorption characterisation ambiguity through the Adejo-Ekwenchi adsorption isotherm: A case study of leaf extract of Hyptis suaveolen poit as green corrosion inhibitor of corrosion of mild steel in 2 M HCl. J. Emerg. Trends Eng. Appl. Sci. 2014, 5, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Ansari, K.R.; Quraishi, M.A.; Kaya, S.; Banerjee, P. The effect of an N-heterocyclic compound on corrosion inhibition of J55 steel in sweet corrosive medium. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 6303–6313. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, M.; Ansari, K.R.; Haque, J.; Srivastava, V.; Quraishi, M.A.; Mazumder, M.A. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of substituted triazines and their corrosion inhibition behavior on N80 steel/acid interface. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2020, 57, 2157–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Manimegalai, S.; Manjula, P. Thermodynamic and adsorption studies for corrosion inhibition of mild steel in aqueous media by Sargasam swartzii (brown algae). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, L.F.C.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Velozo, E.S.; Nesbitt, M. Vibrational spectroscopic study of brazilin and brazilein, the main constituents of brazilwood from Brazil, Vib. Spectrosc. 2002, 28, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- James, C.; Raj, A.A.; Reghunathan, R.; Jayakumar, V.S.; Joe, I.H. Structural conformation and vibrational spectroscopic studies of 2, 6-bis (p-N,N-dimethyl benzylidene) cyclohexanone using density functional theory. JRSPAF 2006, 37, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, M.P.; Sandford, S.A.; Allamandola, L.J. The infrared spectra of nitriles and related compounds frozen in Ar and H2O. Astrophys. J. 1997, 476, 932. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, I.P.S. Spectral Studies of Compounds Containing the Carboxylate Ion, Nitro and Related Groupings. Ph.D. Thesis, The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Badger, R.M.; Bauer, S.H. Spectroscopic studies of the hydrogen bond I. A photometric investigation of the association equilibrium in the vapor of acetic acid. J. Chem. Phys. 1937, 5, 605–608. [Google Scholar]
- Olasunkanmi, L.O.; Kabanda, M.M.; Ebenso, E.E. Quinoxaline derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium: Electrochemical and quantum chemical studies. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2016, 76, 109–126. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, K.; Ohashi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Aizawa, T.; Adschiri, T.; Arai, K. Estimation of local density augmentation and hydrogen bonding between pyridazine and water under sub-and supercritical conditions using UV-vis spectroscopy. Anal. Sci. 2006, 11, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Rbaa, M.; Benhiba, F.; Obot, I.B.; Oudda, H.; Warad, I.; Lakhrissi, B.; Zarrouk, A. Two new 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives as an efficient corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid: Synthesis, electrochemical, surface morphological, UV–visible and theoretical studies. J. Mole. Liq. 2019, 276, 120–133. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E.; Bahadur, I. A green and sustainable approach for mild steel acidic corrosion inhibition using leaves extract: Experimental and DFT studies. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2018, 4, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Sayin, Koray, and Duran Karakaş. Quantum chemical studies on the some inorganic corrosion inhibitors. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lukovits, I.; Kalman, E.; Zucchi, F. Corrosion inhibitors correlation between electronic structure and efficiency. Corrosion 2001, 57, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, M.; Ansari, K.R.; Srivastava, V.; Chauhan, D.S.; Haque, J.; Quraishi, M.A. Chromeno naphthyridines based heterocyclic compounds as novel acidiz-ing corrosion inhibitors: Experimental, surface and computational study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114825. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, R.G. Absolute electronegativity and hardness correlated with molecular or-bital theory. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8440. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, R.G. Absolute electronegativity and hardness: Application to inorganic chemistry. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 734. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, R.G.; and Pearson, R.G. Absolute hardness: Companion parameter to absolute electronegativity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 7512. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, M.; Sri-vastava, V.; Quraishi, M.A.; Chauhan, D.S.; Ansari, K.R.; Haque, J. Qui-no-line Carbonitriles as Novel Inhibitors for N80 Steel Corrosion in Oil-Well Acidizing: Experimental and Computational Insights. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2021, 57, 228–244. [Google Scholar]
- Lebrini, M.; Lagrenee, M.; Traisnel, M.; Gengembre, L.; Vezin, H.; Bentiss, F. Enhanced corrosion resistance of mild steel in normal sulfuric acid medium by 2,5-bis (n-thienyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazoles: Electrochemical, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy andtheoretical studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 9267–9276. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Gong, M.; Yin, L. Experi-mental and theoretical studies of two imidazoli-um-based ionic liquids as inhibitors for mild steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2015, 95, 168–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Meng, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Cao, D. Experimental and theo-retical studies of benzothiazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in 1 M HCl. Corros. Sci. 2016, 112, 563–575. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrouk, A.; Hammouti, A.B.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Salghi, R.; Zarrok, H.; Jama, C.; Bentiss, F. Corrosion inhibition performance of 3, 5-diamino-1, 2, 4-triazole for protection of copper in nitric acid solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 5997–6011. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, N.O.; Ebenso, E.E. Quantum chemical studies on the inhibition potentials of some penicillin compounds for the corrosion of mild steel in 0.1 M HCl. J. Mol. Model. 2010, 16, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, K.R.; Ramkumar, S.; Chauhan, D.S.; Salman, M.; Nalini, D.; Srivastava, V.; Quraishi, M.A. Macrocyclic compounds as green corrosion inhibitors for aluminium: Electrochemical, surface and quantum chemical studies. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2018, 7, 443–459. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, N.; Pahuja, P.; Lgaz, H.; Chung, I.M.; Selwal, K.; Singhal, S.; Lata, S. PVP oxime-TiO2-adenine as a hybrid material: Decent synthesis and depiction with advanced theoretical measurements for anticorrosive behavior and antibacterial potentiality. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 278, 438–451. [Google Scholar]
- Lgaz, H.; Salghi, R.; Subrahmanya Bhat, K.; Chaouiki, A.; Shubhalaxmi, S.J. Correlated experimental and theoretical study on inhibition behavior of novel quinoline derivatives for the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 244, 154–168. [Google Scholar]
- Lgaz, H.; Bhat, K.S.; Salghi, R.; Jodeh, S.; Algarra, M.; Hammouti, B.; Ali, I.H.; Essamri, A. Insights into corrosion inhibitionbehavior of three chalcone derivatives for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 238, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Lgaz, H.; Lee, H.; Kaya, S.; Salghi, R.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Chafiq, M.; Bazzi, L.; Ko, Y.G. Unraveling Bonding Mechanisms andElectronic Structure of Pyridine Oximes on Fe(110) Surface: Deeper Insights from DFT, Molecular Dynamics and SCC-DFTTight Binding Simulations. Molecules 2023, 28, 3545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).