Study of Corrosion Characteristics of AlMg3.5 Alloy by Hydrogen-Induced Pressure and Mass Loss Evaluation Under Simulated Cementitious Repository Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
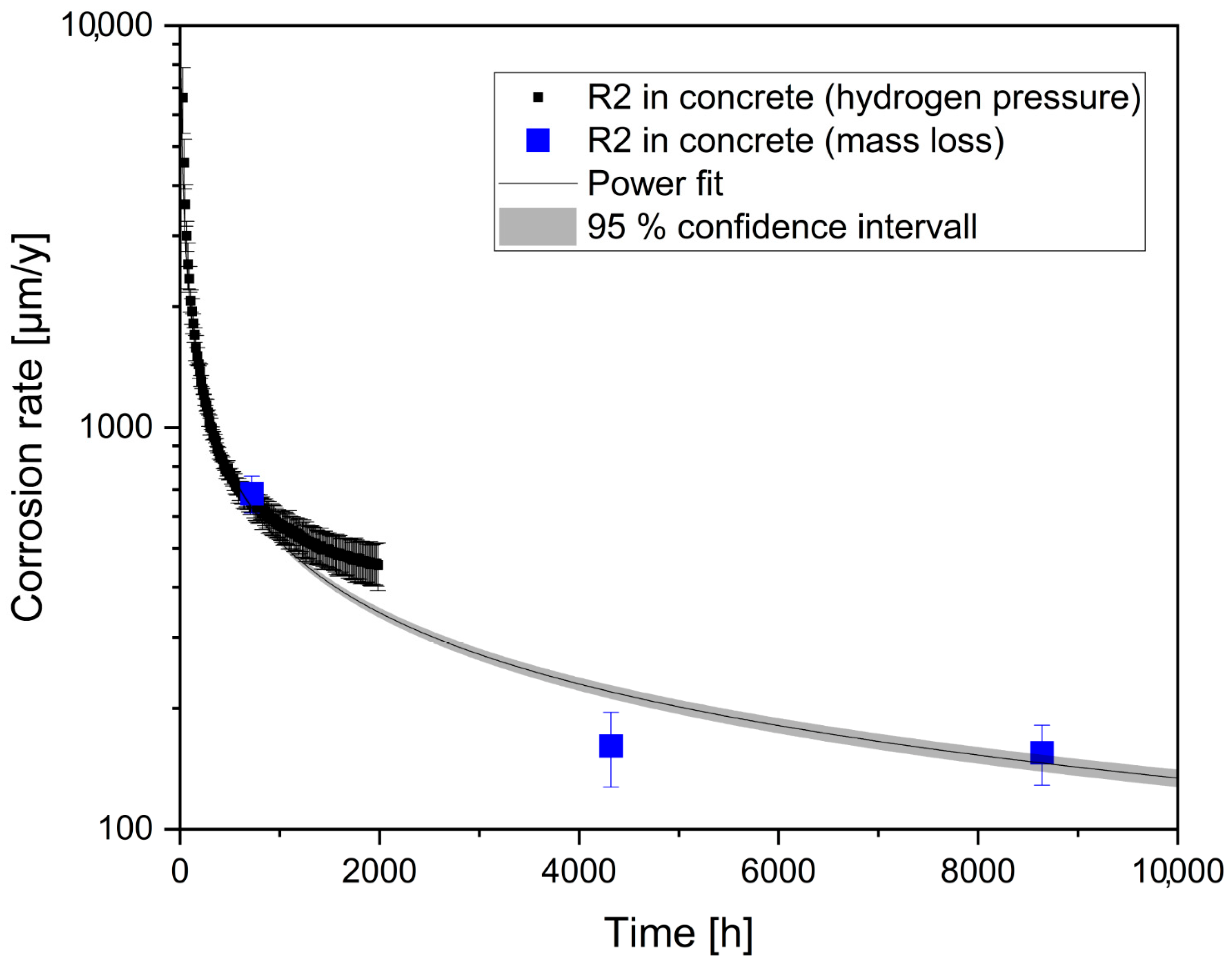
3.1. Corrosion Rates
3.2. X-Ray Imaging
4. Discussion
4.1. Corrosion Rates by H2-Induced Pressure Build-Up
4.2. Corrosion Rates by Mass Loss Evaluation
4.3. X-Ray Imaging
5. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herting, G.; Odnevall, I. Corrosion of Aluminium and Zinc in Concrete at Simulated Conditions of the Repository of Low Active Waste in Sweden. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2021, 2, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L.P. Management of radioactive waste: A review. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 6, 38. [Google Scholar]
- SSM (Swedish Radiation Safety Authority). Kingdom of Sweden—ARTEMIS. Self-Assessment Report 2023. In the IAEA Integrated Review Service for Radioactive Waste and Spent Fuel Management, Decommissioning and Remediation (ARTEMIS). 2023. Available online: www.ssm.se (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Kinoshita, H.; Swift, P.; Utton, C.; Carro-Mateo, B.; Marchand, G.; Collier, N.; Milestone, N. Corrosion of aluminium metal in OPC- and CAC-based cement matrices. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.; Glasser, F. Application of Portland cement-based materials to radioactive waste immobilization. Waste Manag. 1991, 12, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, M.; Lyon, S.; Thompson, G.; Ferguson, J. The long-term corrosion of aluminium in alkaline media. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezuber, H.; El-Houd, A.; El-Shawesh, F. A study on the corrosion behavior of aluminum alloys in seawater. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Yang, R.; Liu, Z. Active aluminum composites and their hydrogen generation via hydrolysis reaction: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, S.-I.; Moon, S.-M. Corrosion mechanism of pure aluminium in aqueous alkaline solution. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2000, 4, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, D.; Tepke, D.G. Corrosion of aluminum metal in concrete–A case study. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Cement Microscopy, ICMA, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28–31 March 2010; pp. 33–65. [Google Scholar]
- Husaini, M.; Usman, B.; Ibrahim, M.B. Evaluation of corrosion behaviour of aluminum in different environment. Bayero J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2018, 11, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauret, P.; Lacaze, P. Water corrosion studies of AlMg (5154) and AlCuMg (2024) aluminium alloys by gas chromatography. Corros. Sci. 1982, 22, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.H.; Vetrano, J.S.; Windisch, C.F. Stress Corrosion Cracking of Al-Mg and Mg-Al Alloys, December 2004. Corrosion 2004, 60, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Medhekar, N.V.; Frankel, G.S.; Birbilis, N. Corrosion mechanism and hydrogen evolution on Mg. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2015, 19, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Birbilis, N.; Scully, J.R. Accurate electrochemical measurement of magnesium corrosion rates; a combined impedance, mass-loss and hydrogen collection study. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 121, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curioni, M. The behaviour of magnesium during free corrosion and potentiodynamic polarization investigated by real-time hydrogen measurement and optical imaging. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 120, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Scenini, F.; Curioni, M. A study on magnesium corrosion by real-time imaging and electrochemical methods: Relationship between local processes and hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 198, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Atrens, A.; StJohn, D. An hydrogen evolution method for the estimation of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys. In Essential Readings in Magnesium Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- Schobel, M.; Ekberg, C.; Vollmer, T.R.; Puranen, A. Corrosion Characteristics of Studsvik R2 Al-Alloy by Hydrogen Evolution Under Simulated Repository Conditions. In Proceedings of the WM2025 Conference, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 9–13 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Galvele, J.R. Transport processes and the mechanism of pitting of metals. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1976, 123, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehira, S.; Kanamori, S.; Nagashima, K.; Saeki, T.; Visbal, H.; Fukui, T.; Hirao, K. Controllable hydrogen release via aluminum powder corrosion in calcium hydroxide solutions. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2013, 1, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, P. Diffusion in absorbing media. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1939, 171, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gerven, T.; Cornelis, G.; Vandoren, E.; Vandecasteele, C. Effects of carbonation and leaching on porosity in cement-bound waste. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, U. Evolution of pore water chemistry during degradation of cement in a radioactive waste repository environment. Waste Manag. 1992, 12, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, A.; Baston, G.; Glasser, F.; Hunter, F.; Smith, V. Modelling evolution in the near field of a cementitious repository. Mineral. Mag. 2012, 76, 3055–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasova, L.; Ojovan, M. Acoustic emission detection of microcrack formation and development in cementitious wasteforms with immobilised Al. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasova, L.; Ojovan, M. Characterisation of Al corrosion and its impact on the mechanical performance of composite cement wasteforms by the acoustic emission technique. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 375, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]





| Corrosion Rate [µm/y] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Month | 6 Months | 12 Months | 24 Months | |
| R2 alloy in concrete | 652 ± 44 * | 161 ± 34 ** | 155 ± 26 ** | - |
| R2 alloy in CW | 257 ± 33 * | 55 ± 8 ** | 3 ± 7 ** | - |
| Al in concrete [1] | 757 ± 333 | 164 ± 27 | 70 ± 11 | 114 ± 7 |
| Al in CW [1] | 1428 ± 178 | 214 ± 42 | 103 ± 17 | 54 ± 17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schobel, M.; Ekberg, C.; Retegan Vollmer, T.; Wennerlund, F.; Hedström, S.; Puranen, A. Study of Corrosion Characteristics of AlMg3.5 Alloy by Hydrogen-Induced Pressure and Mass Loss Evaluation Under Simulated Cementitious Repository Conditions. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2025, 6, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6030027
Schobel M, Ekberg C, Retegan Vollmer T, Wennerlund F, Hedström S, Puranen A. Study of Corrosion Characteristics of AlMg3.5 Alloy by Hydrogen-Induced Pressure and Mass Loss Evaluation Under Simulated Cementitious Repository Conditions. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2025; 6(3):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchobel, Marvin, Christian Ekberg, Teodora Retegan Vollmer, Fredrik Wennerlund, Svante Hedström, and Anders Puranen. 2025. "Study of Corrosion Characteristics of AlMg3.5 Alloy by Hydrogen-Induced Pressure and Mass Loss Evaluation Under Simulated Cementitious Repository Conditions" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 6, no. 3: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6030027
APA StyleSchobel, M., Ekberg, C., Retegan Vollmer, T., Wennerlund, F., Hedström, S., & Puranen, A. (2025). Study of Corrosion Characteristics of AlMg3.5 Alloy by Hydrogen-Induced Pressure and Mass Loss Evaluation Under Simulated Cementitious Repository Conditions. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 6(3), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd6030027






