Effect of Heating Rate on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Quenched and Tempered 8620 Low Carbon Alloy Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
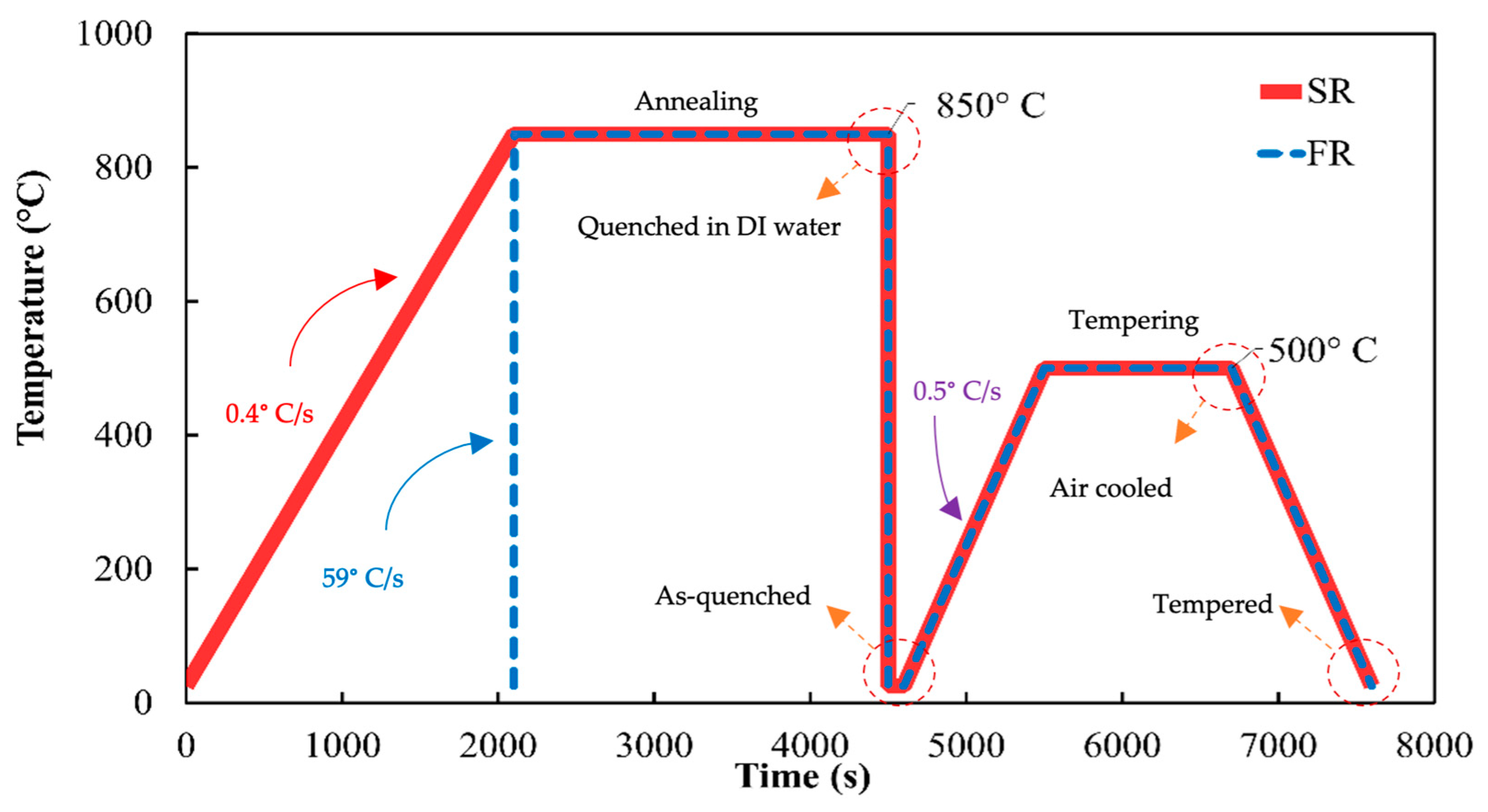
2.2. Heat Treatment
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Hardness Test
2.5. Electrochemical Test
3. Results and Discussion
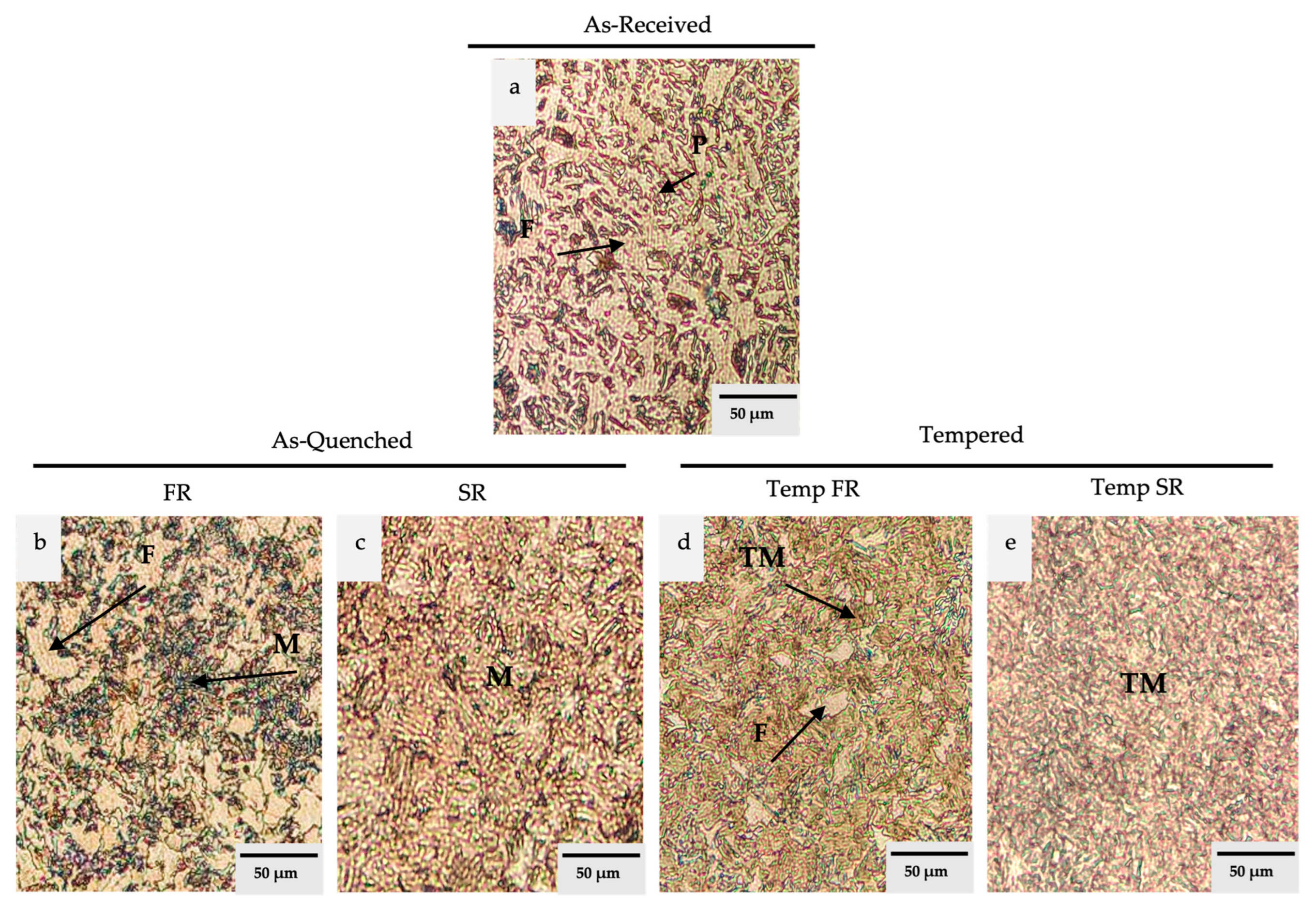
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Morphology
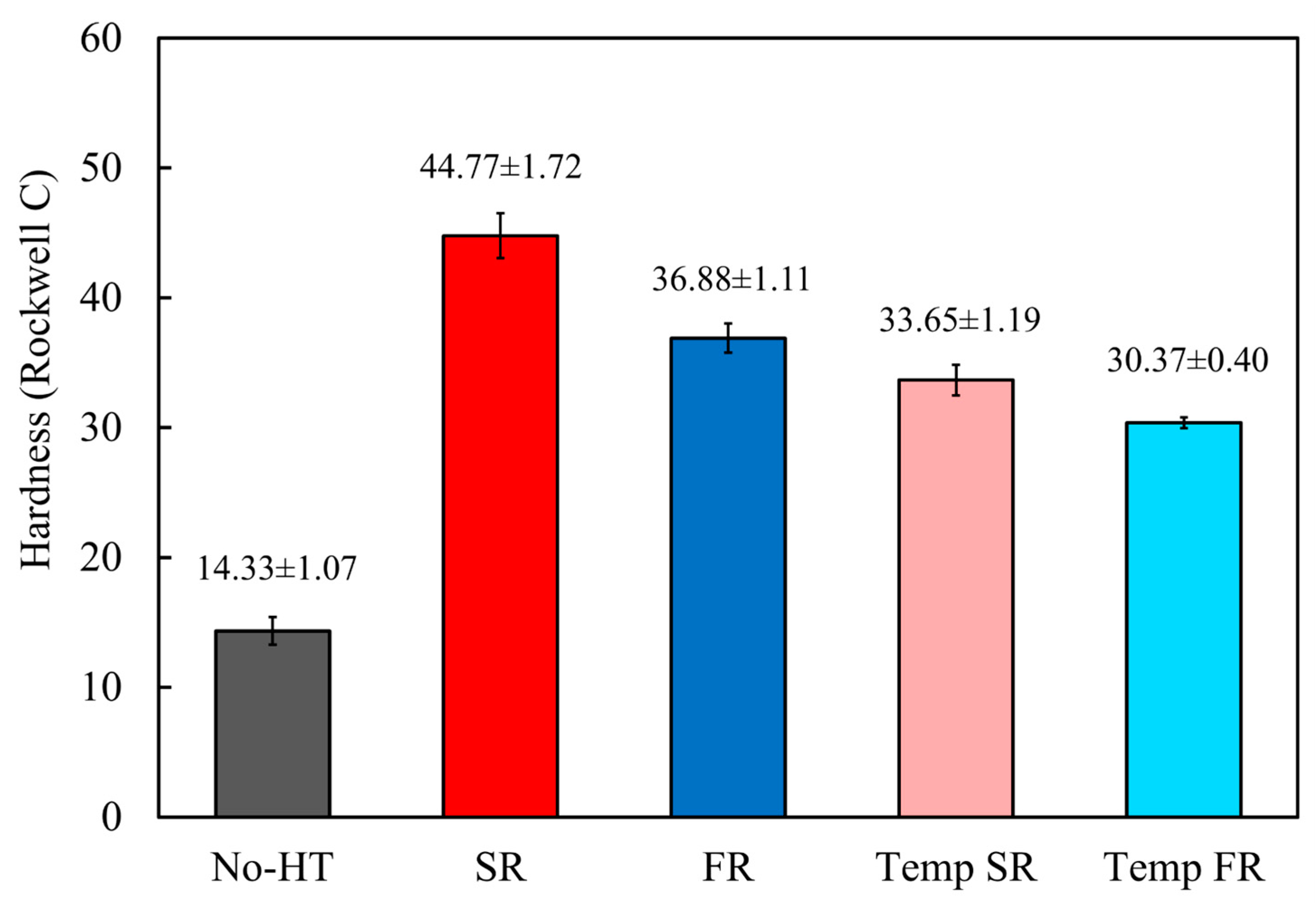
3.2. Mechanical Characterization
3.3. Corrosion Behavior of 8620 Steel Specimens
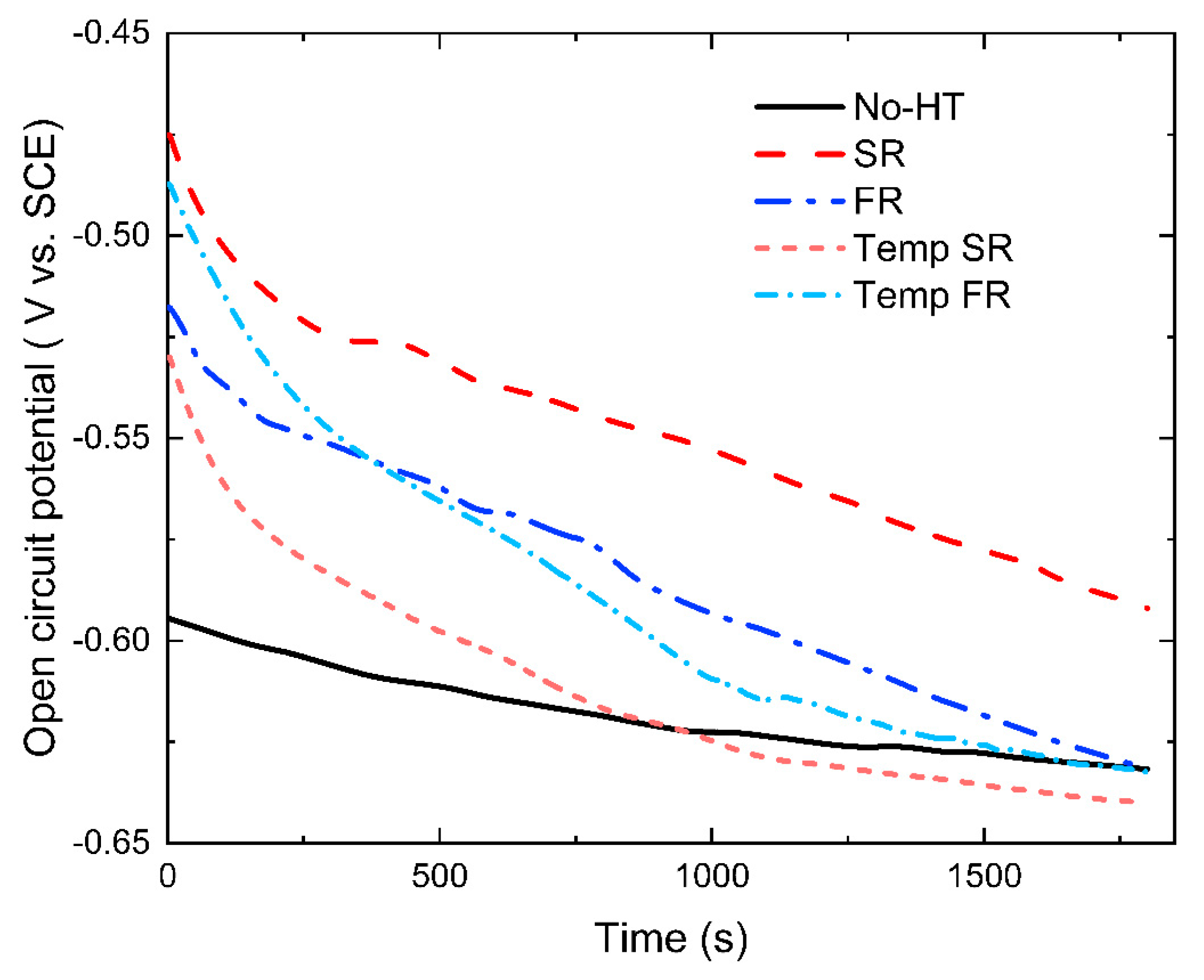
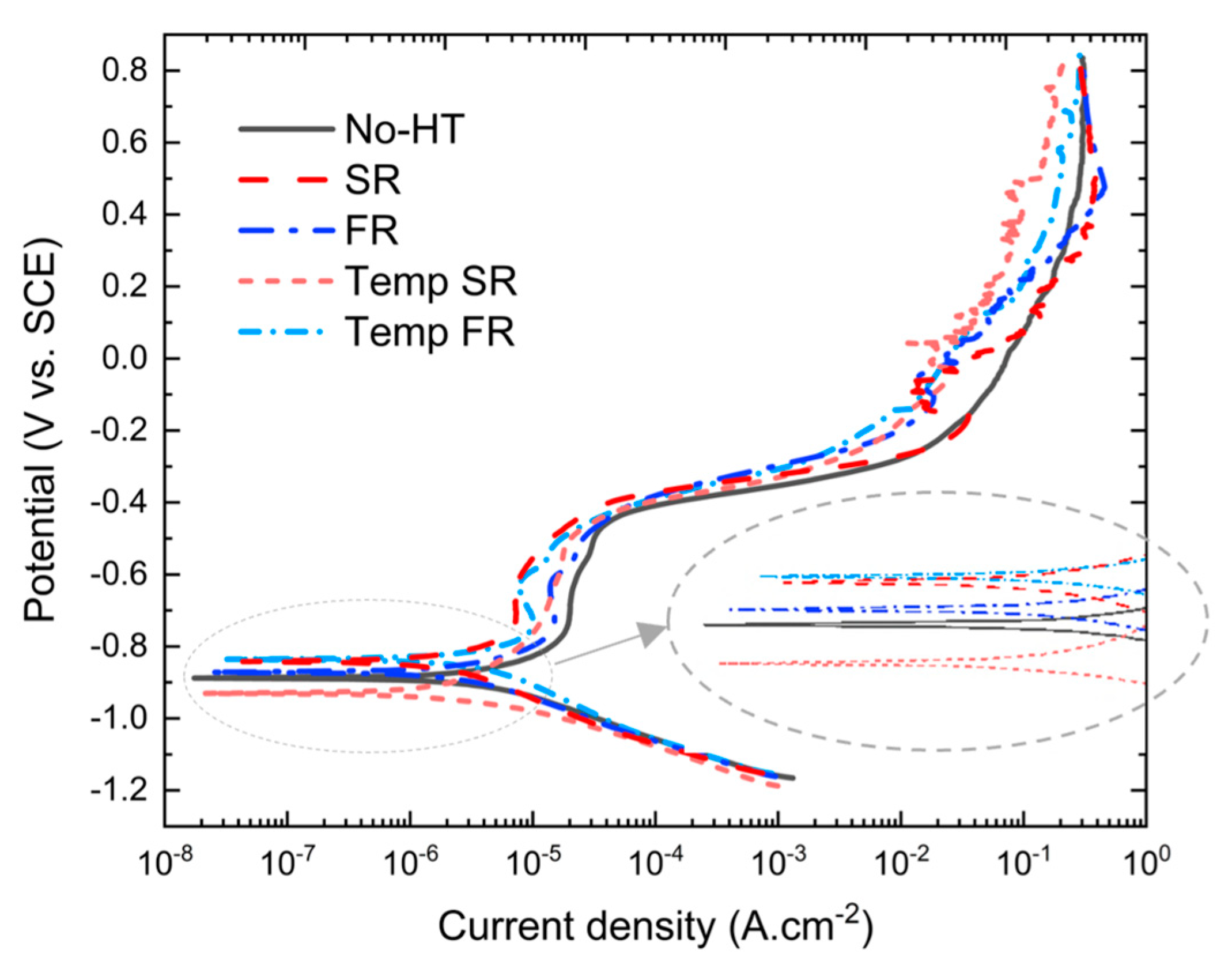
3.3.1. Open-Circuit Potential
3.3.2. Potentiodynamic Polarization
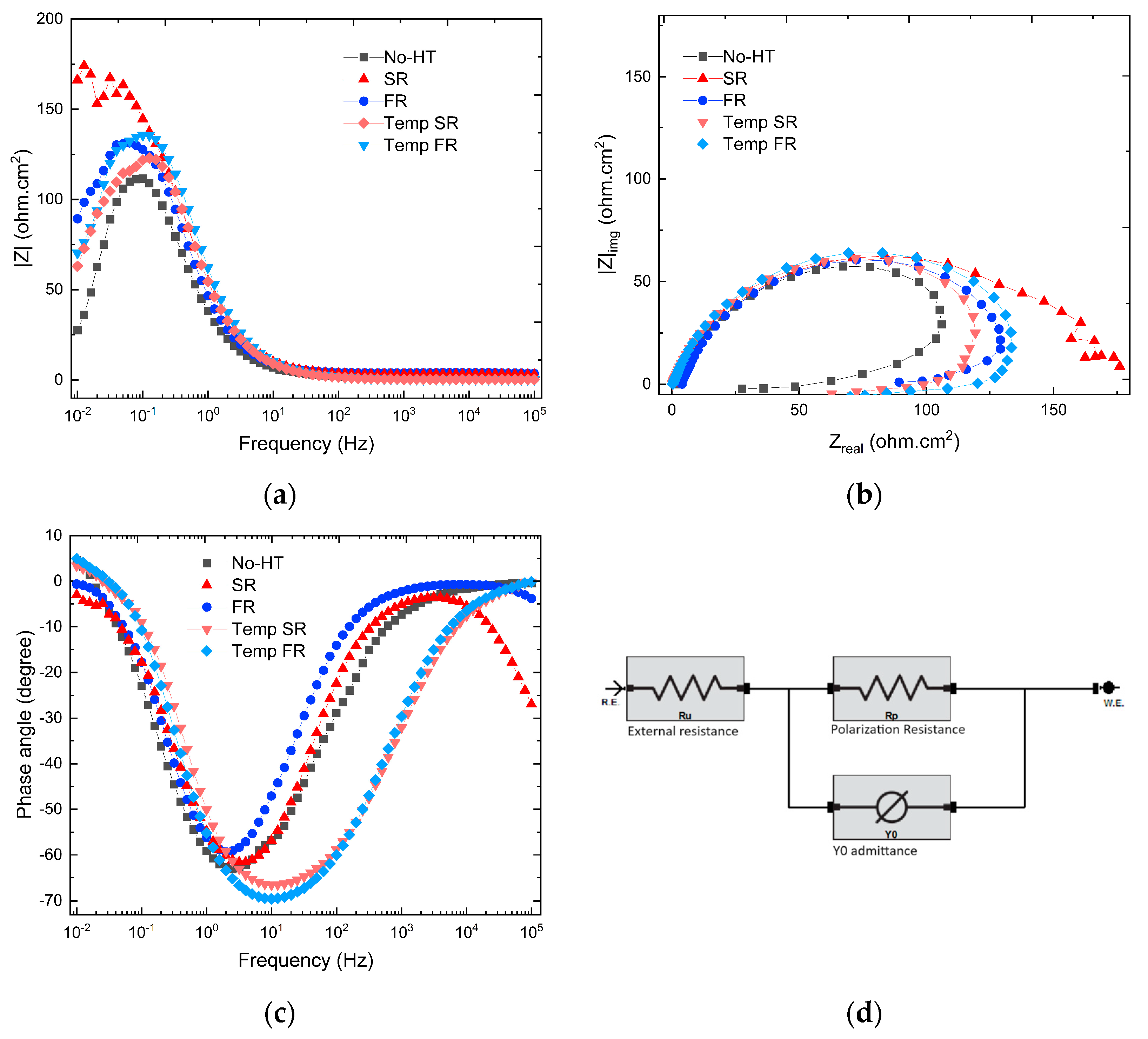
3.3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
- The formation of martensite significantly increased the hardness, with SR samples showing a hardness 8 HRC higher compared to FR. This was consistent with the higher martensite phase fraction observed, confirming the impact of phase transformation on mechanical properties.
- Following the tempering process, the hardness decreased from 44.77 to 33.65 HRC for SR and from 36.88 to 30.37 HRC for FR. It may be inferred that moderate tempering yields nearly identical effects on both martensite and the dual-phase of ferrite and martensite.
- Due to the presence of almost 100% martensitic phases, the corrosion rate for SR was reported to be nearly half that of No-HT. However, following tempering, the EIS results indicated that polarization resistance decreased by almost 380 Ω for the Temp SR, while Temp FR improved. Compared with the FR samples, the Temp FR samples had a 300 Ω gain in polarization resistance and a twofold reduction in Cdl. This phenomenon is likely demonstrated by the increase in martensite to tempered martensite, from 44.6% in SR to 72.3% in Temp SR, which figuratively enhances the overall corrosion response.
- The tempering heat treatment on Temp FR suggested a noble effect on corrosion characteristics. The Temp FR also had a superior corrosion rate, RP, and Cdl to the as-quenched SR.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osório, W.R.; Peixoto, L.C.; Garcia, L.R.; Garcia, A. Electrochemical Corrosion Response of a Low Carbon Heat Treated Steel in a NaCl Solution. Mater. Corros. 2009, 60, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Yen, H.W.; Lee, Y.L. Corrosion Behavior and Surface Analysis of 690 MPa-Grade Offshore Steels in Chloride Media. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wei, G.; Gao, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Fang, X.; Chen, Y. Tuning the Pitting Performance of a Cr-13 Type Martensitic Stainless Steel by Tempering Time. Corros. Sci. 2022, 203, 110346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, A.J.; Marinescu, I.D.; Basudan, I.M.; Alqahtani, B.M.; Tharwan, M.Y. Ball-Burnishing Factors Affecting Residual Stress of AISI 8620 Steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatiwach, V.; Angkurarach, L.; Juijerm, P. Effect of Intercritical Annealing on Deformation Behavior and Flow Stress Predictive Models of AISI 8620 Steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 13488–13501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Su, Z.G.; Gao, X.X.; Yang, Y.L.; Sun, S.J. Corrosion Characteristics of Boronized AISI 8620 Steel in Oil Field Water Containing H 2S 1. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2012, 48, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, M.; Tekeli, S. The Effect of Martensite Volume Fraction and Particle Size on the Tensile Properties of a Surface-Carburized AISI 8620 Steel with a Dual-Phase Core Microstructure. Mater. Charact. 2002, 49, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdeja, L.F.; Verdeja, J.I.; González, R. Machinability improvement through heat treatment in 8620 low-carbon alloyed steel. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2009, 13, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Duran, E.I.; Ros-Yanez, T.; Castro-Cerda, F.M.; Petrov, R.H. The Influence of the Heating Rate on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Peak Annealed Quenched and Partitioned Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 797, 140061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Lu, W.; Rao, X. Effect of Ultra-Fast Heating on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cold-Rolled Low-Carbon Low-Alloy Q&P Steels with Different Austenitizing Temperature. Mater. Charact. 2022, 191, 112086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Duran, E.I.; Bliznuk, V.; Ros-Yanez, T.; Iquilio-Abarzua, R.; Castro-Cerda, F.M.; Petrov, R.H. Improvement of the Strength-Ductility Balance in Ultrafast Heated Steels by Combining High-Temperature Annealing and Quenching and Partitioning Process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 827, 142045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, J.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, P. Effect of Heating Rate on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TRIP-Aided Multiphase Steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 614, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavoine, M.; Dumont, M.; Drillet, J.; Hébert, V.; Maugis, P. Combined Effect of Heating Rate and Microalloying Elements on Recrystallization during Annealing of Dual-Phase Steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Met. Mater. Sci. 2018, 49, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggiotti, M.; Albini, L.; Stornelli, G.; Tiracorrendo, G.; Landi, L.; Di Schino, A. Ultra-Fast Heating Treatment Effect on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Magnetic Characteristics of Non-Oriented Grain Electrical Steels. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Dhokey, N.B. Refinement of Tempered Martensite Structure and Its Effect on Wear Mechanism in SAE 8620. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2016, 10, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, Y.; Lian, T.S.; Tseng, L.Y.; Lin, K.M. The Corrosion Behaviors of Heat-Treated SAE 8620 Steels. Mater. Sci. Forum 2008, 575–578, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapek, Ş.H.; Polat, Ş.; Zor, S. Effect of Tempering Temperature and Microstructure on the Corrosion Behavior of a Tempered Steel. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2013, 49, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Sun, S.; Fabijanic, D.; Barr, C.; Liu, Q.; Walker, K.; Matthews, N.; Orchowski, N.; Easton, M.; Brandt, M. In-Situ Quench and Tempering for Microstructure Control and Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Laser Cladded AISI 420 Stainless Steel Powder on 300M Steel Substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 333, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskari, M.; Järvenpää, A.; Karjalainen, P. The Effect of Heating Rate and Temperature on Microstructure and R-Value of Type 430 Ferritic Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 941, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xiao, D.; Luo, D.; Tuo, C.; Wu, H. Effect of Quenching and Tempering on Mechanical Properties and Impact Fracture Behavior of Low-Carbon Low-Alloy Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, R.G.; Santos, A.P.; Soares, R.B.; dos Santos Silva, K.H.; Nascimento, J.P.; de Freitas Cunha Lins, V. Effect of Gamma Radiation on the Electrochemical Behavior of AISI 8620 Steel Coated with Diamond-Like Carbon. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 6226–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera Hernández, H.; Reynoso, M.R.; González, C.T.; Morán, O.G.; Hernández, G.M.; Mandujano Ruiz, A.; Morales Hernández, J.; Orozco Cruz, R. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): A Review Study of Basic Aspects of the Corrosion Mechanism Applied to Steels. In Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy; InTech Open: London, UK, 2020; pp. 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domanski, M.; Webb, J. A Review of Heat Treatment Research. Lithic. Technol. 2007, 32, 153–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, M.; Magazzino, C. A Machine Learning Analysis of the Relationship among Iron and Steel Industries, Air Pollution, and Economic Growth in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuz, E.H.; Noor-A-Alam, M.; Haider, W.; Shabib, I. Improving the Mechanical and Electrochemical Performance of Additively Manufactured 8620 Low Alloy Steel via Boriding. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2023, 4, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulanda, D.M.; Cortés, J.G.; Pérez, M.A.; García, G. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AISI 8620 Steel Processed by ECAP. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2014, 1611, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ghosh, P.K.; Kumar, S. Thermal and Metallurgical Characteristics of Surface Modification of AISI 8620 Steel Produced by TIG Arcing Process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 240, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, R.R.; Girina, O.A.; Fonstein, N.M. Effect of Heating Rate on the Austenite Formation in Low-Carbon High-Strength Steels Annealed in the Intercritical Region. Met. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Met. Mater. Sci. 2011, 42, 3680–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggiotti, M.; Albini, L.; Di Nunzio, P.E.; Di Schino, A.; Stornelli, G.; Tiracorrendo, G. Ultrafast Heating Heat Treatment Effect on the Microstructure and Properties of Steels. Metals 2022, 12, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.; Geary, A.L. Electrochemical Polarization: I. A Theoretical Analysis of the Shape of Polarization Curves. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1957, 104, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, M.; Saengdeejing, A.; Muto, I.; Chen, Y.; Masuda, H.; Katayama, H.; Doi, T.; Kawano, K.; Miura, H.; Sugawara, Y.; et al. First-Principles Analysis of the Inhibitive Effect of Interstitial Carbon on an Active Dissolution of Martensitic Steel. Corros. Sci. 2020, 163, 108251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, N.; Tabata, S.; Kawata, H. Excess Solute Carbon and Tetragonality in As-Quenched Fe-1Mn-C (C:0.07 to 0.8 Mass Pct) Martensite. Met. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Met. Mater. Sci. 2020, 51, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Sarkar, A.; Mehtani, H.K.; Raut, P.; Prakash, A.; Prasad, M.J.N.V.; Samajdar, I.; Parida, S. Microstructure and Aqueous Corrosion in Carbon Steel: An Emerging Correlation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösing, I.; Cramer, L.; Steinbacher, M.; Zoch, H.W.; Thöming, J.; Baune, M. Influence of Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Martensitic Stainless Steel. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 65317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.B.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.C.; Yu, L.M.; Ma, Z.Q.; Liu, C.X.; Li, H.J. Effect of Microstructure Variation on the Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel in 3.5wt% NaCl Solution. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, F. Significantly Improved Corrosion Resistance of Mg-15Gd-2Zn-0.39Zr Alloys: Effect of Heat-Treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, E.; Rafsanjani-Abbasi, A.; Imani, A.; Hosseinpour, S.; Davoodi, A. Correlation of Surface Volta Potential with Galvanic Corrosion Initiation Sites in Solid-State Welded Ti-Cu Bimetal Using AFM-SKPFM. Corros. Sci. 2018, 140, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lv, Z.; Lu, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, X. Correlation of Micro-Galvanic Corrosion Behavior with Corrosion Rate in the Initial Corrosion Process of Dual Phase Steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 3310–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, P.K.; Misra, S.; Mondal, K. Comparative Corrosion Behavior of Five Microstructures (Pearlite, Bainite, Spheroidized, Martensite, and Tempered Martensite) Made from a High Carbon Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.P.; Kumar, P.; Manna, M.K.; Chakraborti, P.C. Microstructural Influence on the Electrochemical Corrosion Behaviour of Dual-Phase Steels in 3.5% NaCl Solution. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2488–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, N.; Vega, C.; Pébère, N.; Lacaze, J.; Brito, J.L. CO2 Corrosion Resistance of Carbon Steel in Relation with Microstructure Changes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 156, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushimi, K.; Yanagisawa, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kawano, T.; Kimura, M. Microelectrochemistry of Dual-Phase Steel Corroding in 0.1 M Sulfuric Acid. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 114, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staicopolus, D.N. The Role of Cementite in the Acidic Corrosion of Steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1963, 110, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrivà-Cerdán, C.; Ooi, S.W.; Joshi, G.R.; Morana, R.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Akid, R. Effect of Tempering Heat Treatment on the CO2 Corrosion Resistance of Quench-Hardened Cr-Mo Low-Alloy Steels for Oil and Gas Applications. Corros. Sci. 2019, 154, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuz, E.H.; Maruf, M.A.; Haider, W.; Shabib, I. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance of TiZrN-Coated Additively Manufactured 8620 Low-Alloy Steel in Nitrate Salt Solution and Salt Bath. Coatings 2023, 13, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igual Muñoz, A.; García Antón, J.; Guiñón, J.L.; Pérez Herranz, V. The Effect of Chromate in the Corrosion Behavior of Duplex Stainless Steel in LiBr Solutions. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 4127–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taweesup, K.; Visuttipitukul, P.; Yongvanich, N.; Lothongkum, G. Corrosion Behavior of Ti-Cr-N Coatings on Tool Steel Substrates Prepared Using DC Magnetron Sputtering at Low Growth Temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschorn, B.; Orazem, M.E.; Tribollet, B.; Vivier, V.; Frateur, I.; Musiani, M. Determination of Effective Capacitance and Film Thickness from Constant-Phase-Element Parameters. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6218–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Momeni, M.; Kosari, A.; Zakeri, M.; Moayed, M.H. A Comparative Study of Critical Pitting Temperature (CPT) of Stainless Steels by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS), Potentiodynamic and Potentiostatic Techniques. Corros. Sci. 2012, 59, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Cr | Ni | Mn | Mo | Si | C | S | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wrought 8620 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.035 | Bal. |
| Samples | Ecorr (mV) | icorr (μA/cm2) | βA (mV/Decade) | βC (mV/Decade) | RP (Ω·cm2) | Corrosion Rate (mpy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-HT | −872.3 ± 24.9 | 12.15 ± 0.95 | 805.1 ± 79.4 | 246.8 ± 36.0 | 6.72 ± 0.75 | 5.55 ± 0.43 |
| SR | −851.3 ± 14.2 | 6.36 ± 0.53 | 760.3 ± 58.9 | 196.9 ± 15.9 | 9.51 ± 1.12 | 2.91 ± 0.23 |
| FR | −870.9 ± 7.3 | 9.91 ± 0.44 | 1035 ± 99.7 | 214.6 ± 38.6 | 7.72 ± 0.78 | 4.53 ± 0.20 |
| Temp SR | −935.5 ± 18.1 | 5.39 ± 0.95 | 552.4 ± 33.2 | 127.1 ± 10.6 | 8.52 ± 1.87 | 2.91 ± 0.69 |
| Temp FR | −839.2 ± 2.6 | 3.97 ± 0.46 | 511.4 ± 13.1 | 162.1 ± 08.1 | 13.51 ± 1.05 | 1.81 ± 0.21 |
| Samples | Polarization Resistance (Ω) | Y0 (μS-sα cm−2) | α (0 < α < 1) | Cdl (F × 104) | Goodness of Fit (10−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-HT | 945.2 ± 157.6 | 522 ± 54 | 0.839 ± 0.015 | 3.055 | 2.61 ± 1.6 |
| SR | 1377.2 ± 59.8 | 497 ± 59 | 0.822 ± 0.007 | 5.003 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| FR | 931.1 ± 171.6 | 479 ± 81 | 0.801 ± 0.020 | 7.589 | 2.46 ± 1.61 |
| Temp SR | 989.8 ± 165.4 | 285 ± 54 | 0.837 ± 0.012 | 6.601 | 1.05 ± 0.96 |
| Temp FR | 1234.0 ± 158.2 | 273 ± 8 | 0.870 ± 0.028 | 3.600 | 1.34 ± 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tajmiri, S.; Haider, W.; Shabib, I. Effect of Heating Rate on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Quenched and Tempered 8620 Low Carbon Alloy Steel. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2024, 5, 370-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd5030016
Tajmiri S, Haider W, Shabib I. Effect of Heating Rate on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Quenched and Tempered 8620 Low Carbon Alloy Steel. Corrosion and Materials Degradation. 2024; 5(3):370-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd5030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleTajmiri, Sina, Waseem Haider, and Ishraq Shabib. 2024. "Effect of Heating Rate on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Quenched and Tempered 8620 Low Carbon Alloy Steel" Corrosion and Materials Degradation 5, no. 3: 370-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd5030016
APA StyleTajmiri, S., Haider, W., & Shabib, I. (2024). Effect of Heating Rate on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Quenched and Tempered 8620 Low Carbon Alloy Steel. Corrosion and Materials Degradation, 5(3), 370-386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cmd5030016







