Links between Sleep Apnoea and Insomnia in a British Cohort
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Sleep-Related Questionnaires
2.3. Statistical Analysis
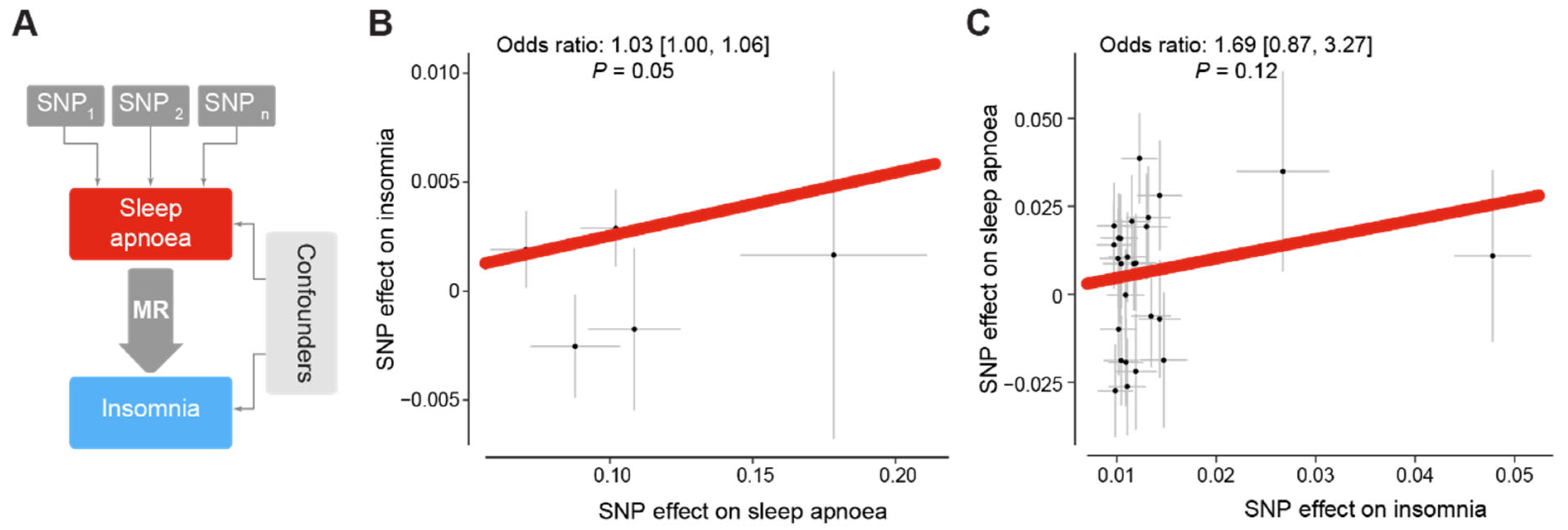
2.4. Mendelian Randomisation
3. Results
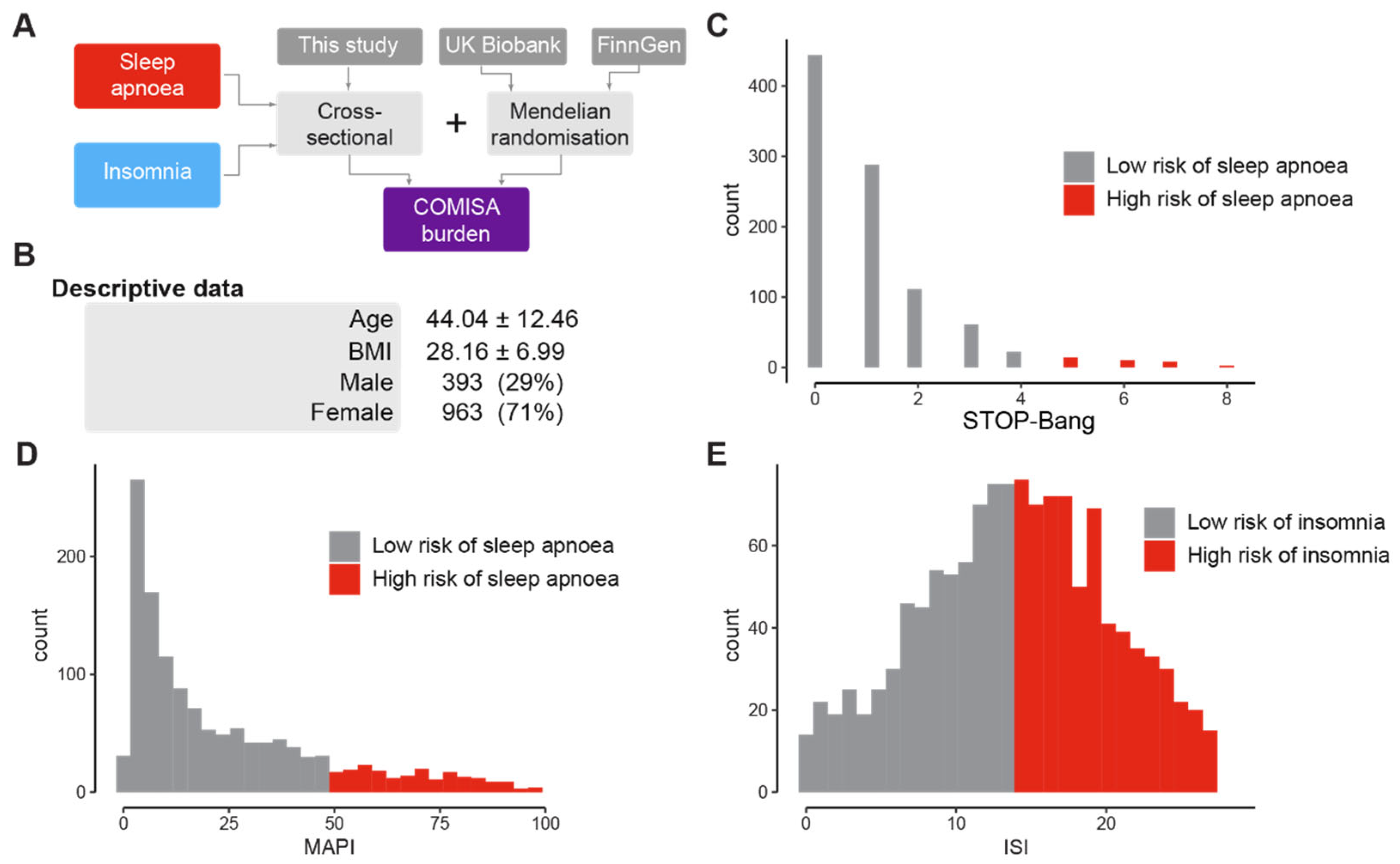
3.1. Prevalence of Sleep Apnoea, Insomnia, and COMISA in a British Population
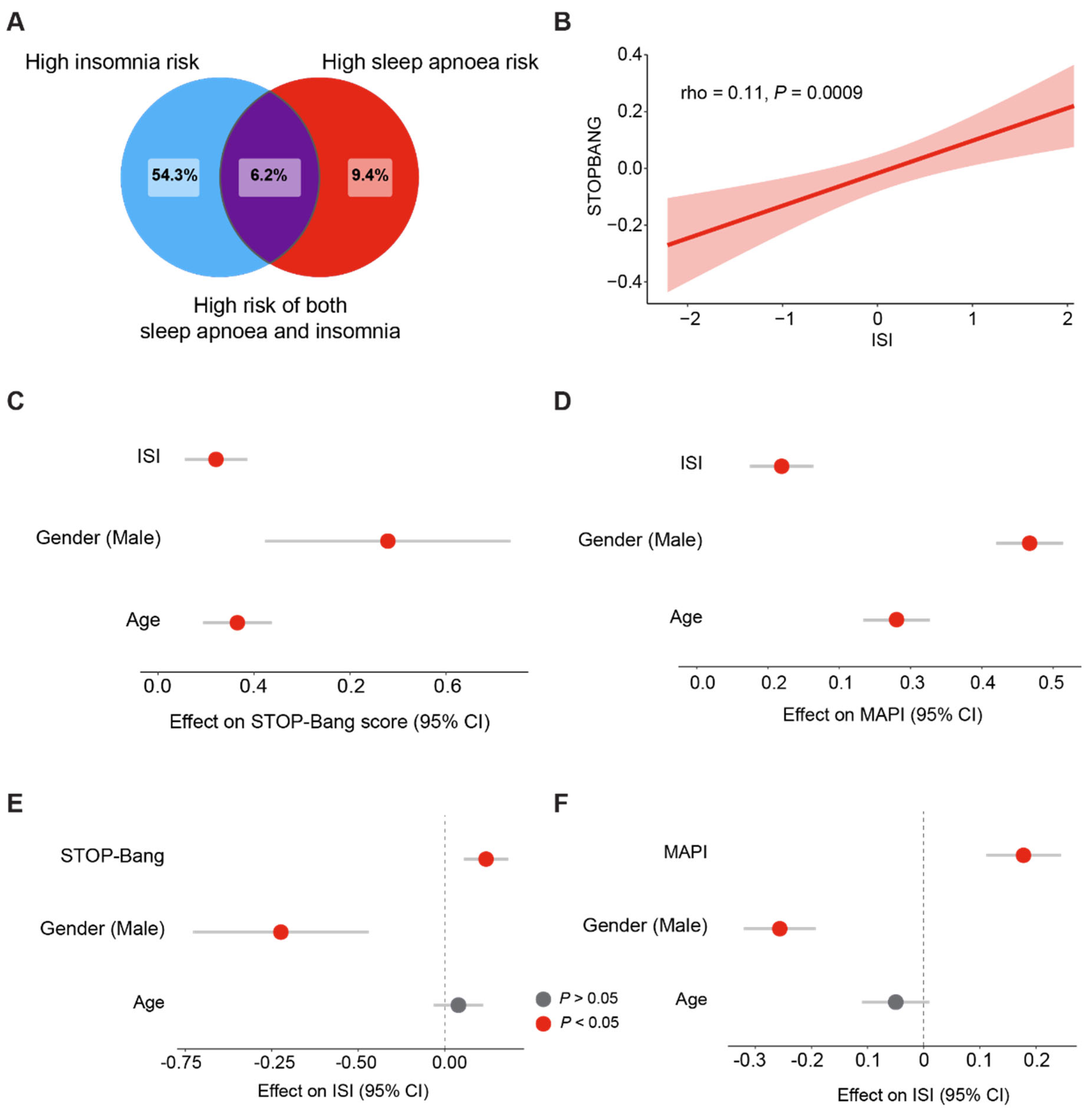
3.2. Sleep Apnoea Is a Putative Cause of Insomnia
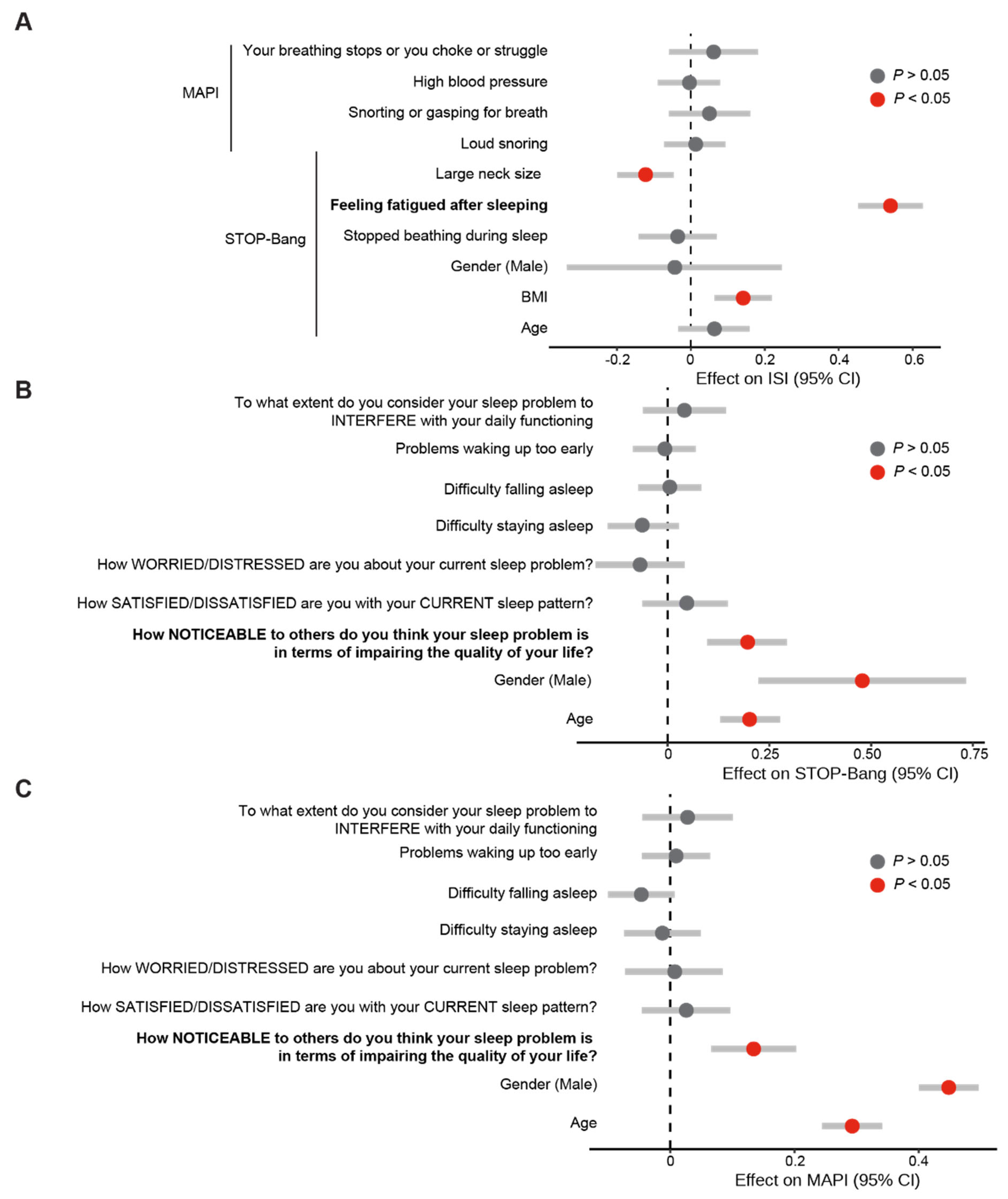
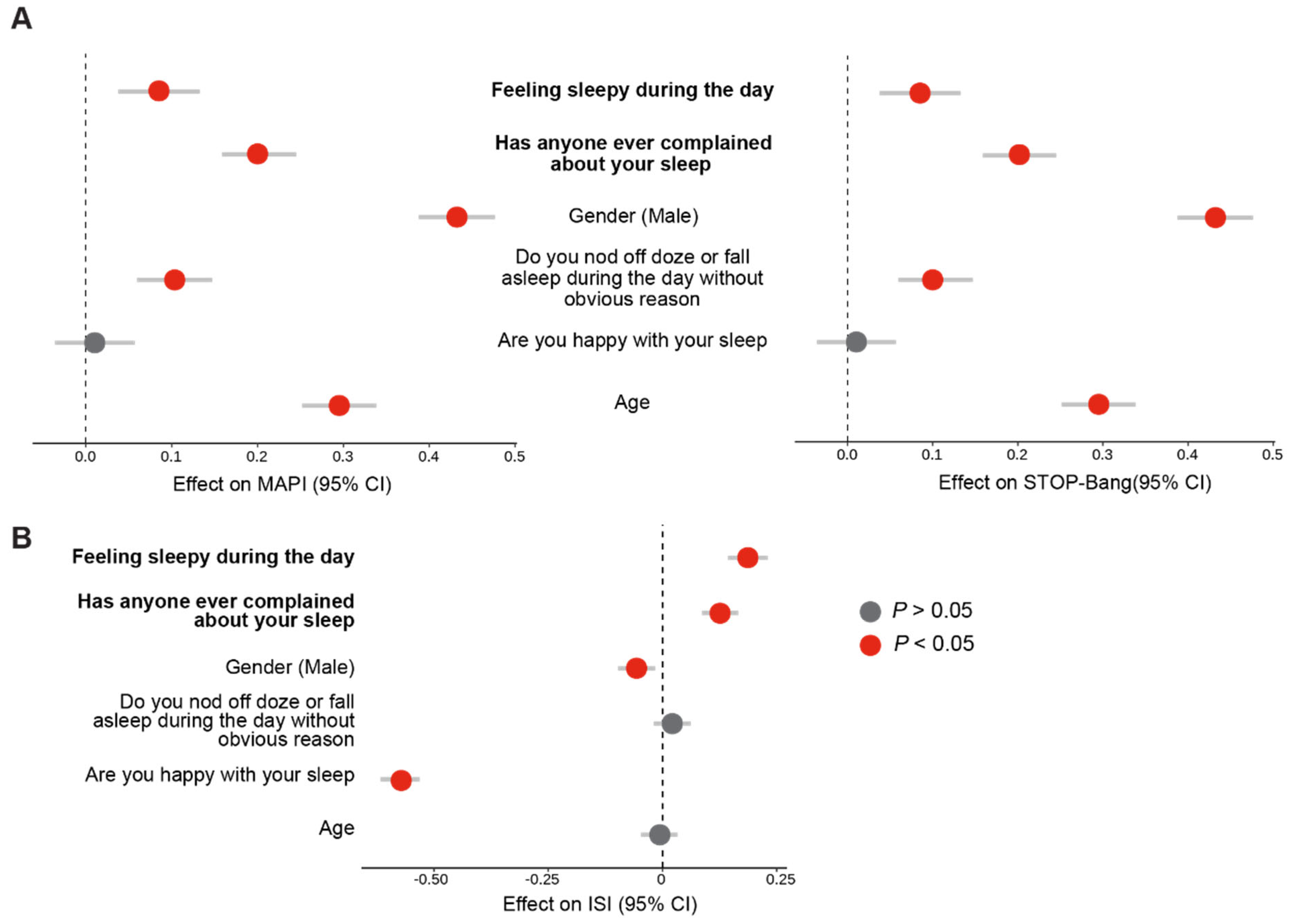
3.3. Fatigue and the Noticeability of Sleep Problems Are Markers of Poor Sleep
3.4. Validation of Fatigue and Noticeability of Sleep Problems as Reproducible Markers of Poor Sleep Using the SleepHubs Check-Up
4. Discussion
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wickwire, E.M.; Schnyer, D.M.; Germain, A.; Smith, M.T.; Williams, S.G.; Lettieri, C.J.; McKeon, A.B.; Scharf, S.M.; Stocker, R.; Albrecht, J.S.; et al. Sleep, Sleep Disorders, and Circadian Health following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Adults: Review and Research Agenda. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 2615–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, K.J.; Cooper, N.J. The effects of a poor night sleep on mood, cognitive, autonomic and electrophysiological measures. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2008, 7, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, K.; Gatti, S.; Wettstein, J.G.; Foster, R.G. Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulia, K.K.; Kumar, V.M. Sleep disorders in the elderly: A growing challenge. Psychogeriatrics 2018, 18, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.C.; Crawford, M.R. Insomnia and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sleep Med. Clin. 2013, 8, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke-Wold, B.P.; Smith, K.E.; Nguyen, L.; Turner, R.C.; Logsdon, A.F.; Jackson, G.J.; Huber, J.D.; Rosen, C.L.; Miller, D.B. Sleep disruption and the sequelae associated with traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 55, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat, R.; Shah, V.D.; Redline, S.; Attia, P.; Walker, M.P. Broken sleep predicts hardened blood vessels. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, T. Insomnia: Definition, prevalence, etiology, and consequences. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2007, 3, S7–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystal, A.D.; Prather, A.A.; Ashbrook, L.H. The assessment and management of insomnia: An update. World Psychiatry 2019, 18, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, G.; Wille, M.; Hemels, M.E. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 9, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, I.; Glasser, M.; Polsek, D.; Leschziner, G.D.; Williams, S.C.R.; Morrell, M.J. Sleep apnoea and the brain: A complex relationship. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.-L.; et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: A literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, E.; Buysse, D.J. Insomnia: Prevalence, Impact, Pathogenesis, Differential Diagnosis, and Evaluation. Sleep Med. Clin. 2008, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylan, S.; Griffiths, S.; Grant, N.; Broomfield, N.M.; Evans, J.J.; Gardani, M. Incidence and prevalence of post-stroke insomnia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 49, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.N.; Bradley, A.J. Sleep disturbance in mental health problems and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2013, 5, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid-Valero, J.J.; Martínez-Selva, J.M.; Ribeiro do Couto, B.; Sánchez-Romera, J.F.; Ordoñana, J.R. Age and gender effects on the prevalence of poor sleep quality in the adult population. Gac. Sanit. 2017, 31, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Miller, E.; Prather, A.A.; Robinson, W.R.; Avery, C.L.; Yang, Y.C.; Haan, M.N.; Aiello, A.E. US acculturation and poor sleep among an intergenerational cohort of adult Latinos in Sacramento, California. Sleep 2018, 42, zsy246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, S.A.; Park, Y.-M.; McWhorter, K.L.; Sandler, D.P.; Jackson, C.L. Multiple poor sleep characteristics and metabolic abnormalities consistent with metabolic syndrome among white, black, and Hispanic/Latina women: Modification by menopausal status. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.S.; Cunningham, T.J.; Giles, W.H.; Croft, J.B. Trends in insomnia and excessive daytime sleepiness among U.S. adults from 2002 to 2012. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyster, F.S.; Buysse, D.J.; Strollo, P.J. Comorbid insomnia and obstructive sleep apnea: Challenges for clinical practice and research. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2010, 6, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Eldridge, F.L.; Dement, W.C. Insomnia with sleep apnea: A new syndrome. Science 1973, 181, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakow, B.; Melendrez, D.; Ferreira, E.; Clark, J.; Warner, T.D.; Sisley, B.; Sklar, D. Prevalence of insomnia symptoms in patients with sleep-disordered breathing. Chest 2001, 120, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.W.; Kim, K.T.; Moon, H.-J.; Korostyshevskiy, V.R.; Motamedi, G.K.; Yang, K.I. Comorbid Insomnia with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crönlein, T.; Geisler, P.; Langguth, B.; Eichhammer, P.; Jara, C.; Pieh, C.; Zulley, J.; Hajak, G. Polysomnography reveals unexpectedly high rates of organic sleep disorders in patients with prediagnosed primary insomnia. Sleep Breath Schlaf. Atm. 2012, 16, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Sullivan, K.; Hopkins, W.; Douglas, J. Frequency of insomnia report in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS). Sleep Med. 2004, 5, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, A.M.; Lack, L.C.; Catcheside, P.G.; Antic, N.A.; Chai-Coetzer, C.L.; Smith, S.S.; Douglas, J.A.; McEvoy, R.D. Developing a successful treatment for co-morbid insomnia and sleep apnoea. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 33, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, A.; Lack, L.; Bastien, C. Co-Morbid Insomnia and Sleep Apnea (COMISA): Prevalence, Consequences, Methodological Considerations, and Recent Randomized Controlled Trials. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, A.; Lack, L.; McEvoy, D. Refining the Measurement of Insomnia in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 1717–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastien, C.H.; Vallieres, A.; Morin, C.M. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Med. 2001, 2, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.M.; Belleville, G.; Bélanger, L.; Ivers, H. The Insomnia Severity Index: Psychometric indicators to detect insomnia cases and evaluate treatment response. Sleep 2011, 34, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagappa, M.; Liao, P.; Wong, J.; Auckley, D.; Ramachandran, S.K.; Memtsoudis, S.; Mokhlesi, B.; Chung, F. Validation of the STOP-Bang Questionnaire as a Screening Tool for Obstructive Sleep Apnea among Different Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.E.; Vana, K.D.; Goodwin, J.L.; Sherrill, D.L.; Quan, S.F. Identification of Patients with Sleep Disordered Breathing: Comparing the Four-Variable Screening Tool, STOP, STOP-Bang, and Epworth Sleepiness Scales. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2011, 7, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.C.; Venekamp, L.N.; Peeters, G.A.; Pijpers, A.; Pevernagie, D.A. Management of insomnia in sleep disordered breathing. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, F.; Abdullah, H.R.; Liao, P. STOP-Bang Questionnaire: A Practical Approach to Screen for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Chest 2016, 149, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Watach, A.; Varrasse, M.; King, T.S.; Sawyer, A.M. Clinical Trial Enrollment Enrichment in Resource-Constrained Research Environments: Multivariable Apnea Prediction (MAP) Index in SCIP-PA Trial. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maislin, G.; Pack, A.I.; Kribbs, N.B.; Smith, P.L.; Schwartz, A.R.; Kline, L.R.; Schwab, R.J.; Dinges, D.F. A survey screen for prediction of apnea. Sleep 1995, 18, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivetta, B.; Chen, L.; Nagappa, M.; Saripella, A.; Waseem, R.; Englesakis, M.; Chung, F. Use and Performance of the STOP-Bang Questionnaire for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Screening Across Geographic Regions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e211009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-Y.; Chang, L.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-J.; Tsai, P.-S. A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of three screening tools for insomnia. J. Psychosom. Res. 2016, 87, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingman, K.J.; Jungquist, C.R.; Perlis, M.L. Questionnaires that screen for multiple sleep disorders. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 32, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Travaglio, M.; Popovic, R.; Leal, N.S.; Martins, L.M. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases Predict Different COVID-19 Outcomes: A UK Biobank Study. Geriatrics 2021, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, N.S.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fedele, G.; Martins, L.M. Paracetamol Is Associated with a Lower Risk of COVID-19 Infection and Decreased ACE2 Protein Expression: A Retrospective Analysis. COVID 2021, 1, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fedele, G.; Celardo, I.; Loh, S.H.Y.; Martins, L.M. Parp mutations protect from mitochondrial toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travaglio, M.; Yu, Y.; Popovic, R.; Selley, L.; Leal, N.S.; Martins, L.M. Links between air pollution and COVID-19 in England. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, R.; Yu, Y.; Leal, N.S.; Fedele, G.; Loh, S.H.Y.; Martins, L.M. Upregulation of Tribbles decreases body weight and increases sleep duration. Dis. Model Mech. 2023, 16, dmm049942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Glymour, M.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Kang, H.; Morrison, J.; Munafò, M.R.; Palmer, T.; Schooling, C.M.; Wallace, C.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco M, F.; Minelli, C.; Zhao, Q.; Lawlor, D.A.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.; Smith, G.D. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: Moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlRasheed, M.M.; Fekih-Romdhane, F.; Jahrami, H.; Pires, G.N.; Saif, Z.; Alenezi, A.F.; Humood, A.; Chen, W.; Dai, H.; Bragazzi, N.; et al. The prevalence and severity of insomnia symptoms during COVID-19, A global systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2022, 100, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, M.; Lanquart, J.-P.; Loas, G.; Hubain, P.; Linkowski, P. Prevalence and risk factors of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in insomnia sufferers: A study on 1311 subjects. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakow, B.; Romero, E.; Ulibarri, V.A.; Kikta, S. Prospective Assessment of Nocturnal Awakenings in a Case Series of Treatment-Seeking Chronic Insomnia Patients: A Pilot Study of Subjective and Objective Causes. Sleep 2012, 35, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, M. The factor structure of the twelve item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12): The result of negative phrasing? Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2008, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.-N.; Zong, Q.-Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, Y.-F.; Ng, C.H.; Chen, L.-G.; Xiang, Y.-T. Gender Difference in the Prevalence of Insomnia: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 577429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutte-Rodin, S.; Broch, L.; Buysse, D.; Dorsey, C.; Sateia, M. Clinical Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Insomnia in Adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2008, 4, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Barnet, J.H.; Palta, M.; Hagen, E.W.; Hla, K.M. Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmisson, H.; Sveinsdottir, E.; Lange, N.; Magnusdottir, S. Insomnia symptoms in primary care: A prospective study focusing on prevalence of undiagnosed co-morbid sleep disordered breathing. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 63, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morphy, H.; Dunn, K.M.; Lewis, M.; Boardman, H.F.; Croft, P.R. Epidemiology of insomnia: A longitudinal study in a UK population. Sleep 2007, 30, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Buysse, D.J.; Thompson, W.; Scott, J.; Franzen, P.L.; Germain, A.; Hall, M.; Moul, D.E.; Nofzinger, E.A.; Kupfer, D.J. Daytime symptoms in primary insomnia: A prospective analysis using ecological momentary assessment. Sleep Med. 2007, 8, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glidewell, R.N.; Renn, B.N.; Roby, E.; Orr, W.C. Predictors and patterns of insomnia symptoms in OSA before and after PAP therapy. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.C.; Olatunji, B.O. A systematic review of sleep disturbance in anxiety and related disorders. J. Anxiety Disord. 2016, 37, 104–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neckelmann, D.; Mykletun, A.; Dahl, A.A. Chronic Insomnia as a Risk Factor for Developing Anxiety and Depression. Sleep 2007, 30, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnin, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Antic, N.A.; Catcheside, P.; Chai-Coetzer, C.L.; McEvoy, D.; Vakulin, A. The impact of ethnicity on the prevalence and severity of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 41, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wing, Y.-K. Sex Differences in Insomnia: A Meta-Analysis. Sleep 2006, 29, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.S.; Levsen, M.P.; McCrae, C.S. A meta-analysis of associations between obesity and insomnia diagnosis and symptoms. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 40, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, P.; Pepin, J.; Bettega, G.; Veale, D.; Ferretti, G.; Deschaux, C.; Levy, P. Relationship between body mass index, age and upper airway measurements in snorers and sleep apnoea patients. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y. Links between Sleep Apnoea and Insomnia in a British Cohort. Clocks & Sleep 2023, 5, 552-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030036
Yu Y. Links between Sleep Apnoea and Insomnia in a British Cohort. Clocks & Sleep. 2023; 5(3):552-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yizhou. 2023. "Links between Sleep Apnoea and Insomnia in a British Cohort" Clocks & Sleep 5, no. 3: 552-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030036
APA StyleYu, Y. (2023). Links between Sleep Apnoea and Insomnia in a British Cohort. Clocks & Sleep, 5(3), 552-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep5030036





