Respiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Criteria for Considering Studies in This Review
2.3. Search Strategies and Data Resources
2.4. Reviewing Procedure and Data Extraction
2.5. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
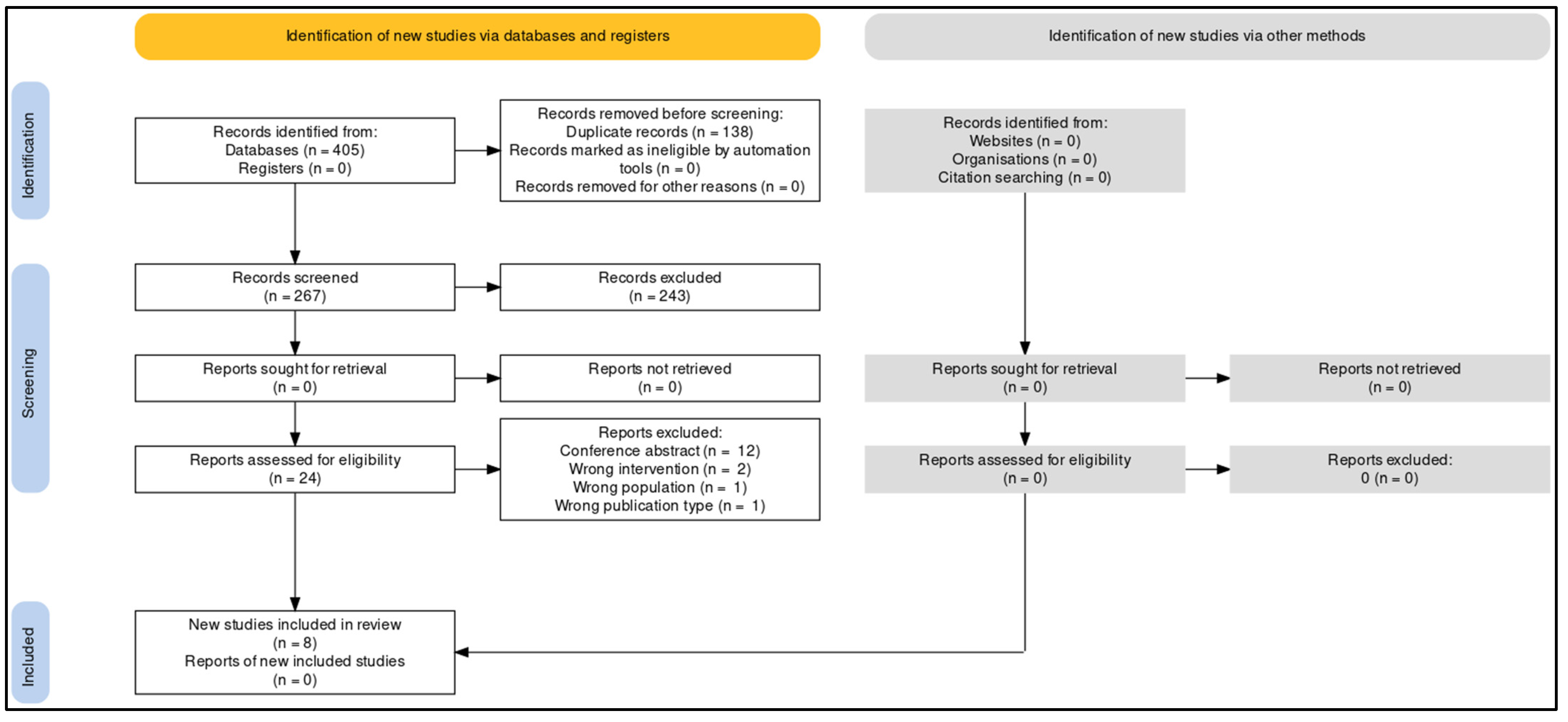
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.3. Participants
3.4. Characteristics of Training
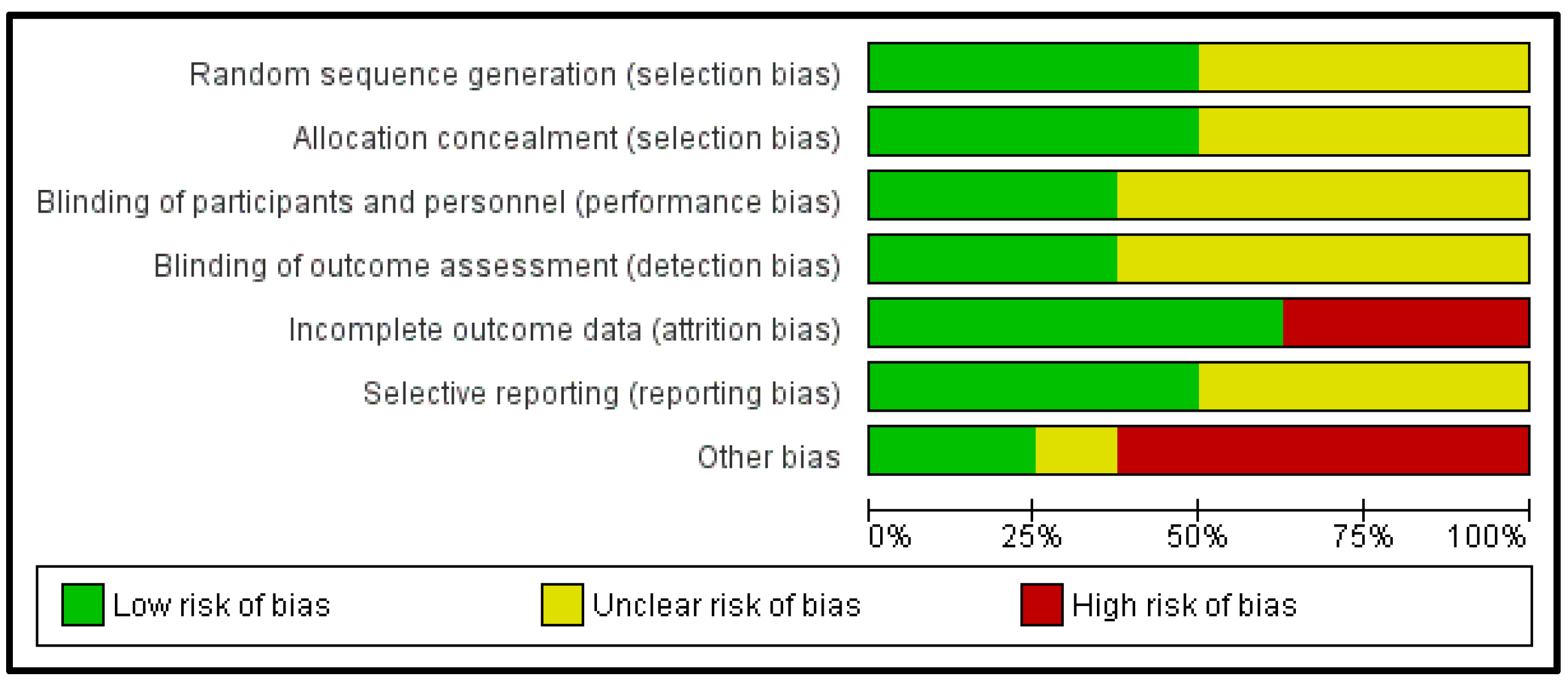
3.5. Methodological Quality Assessment
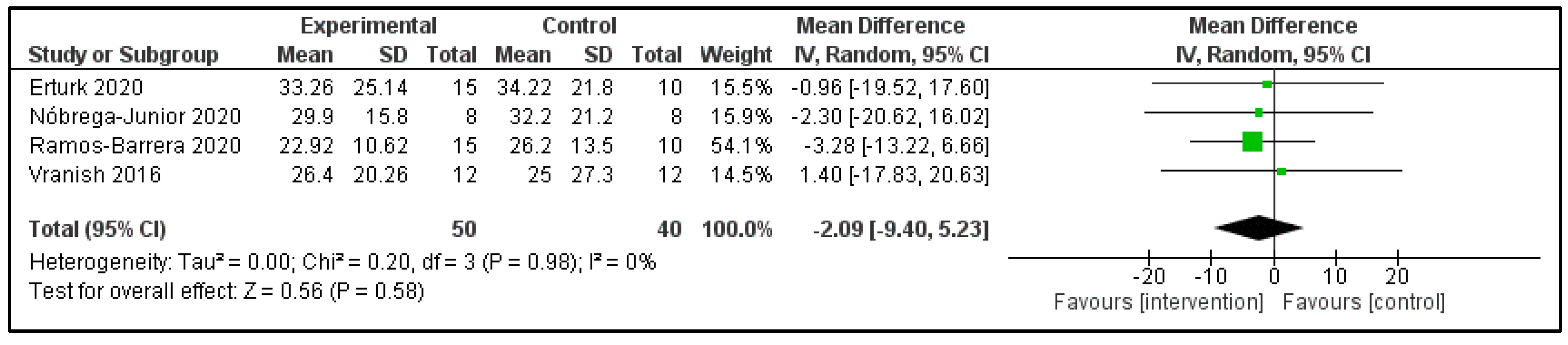
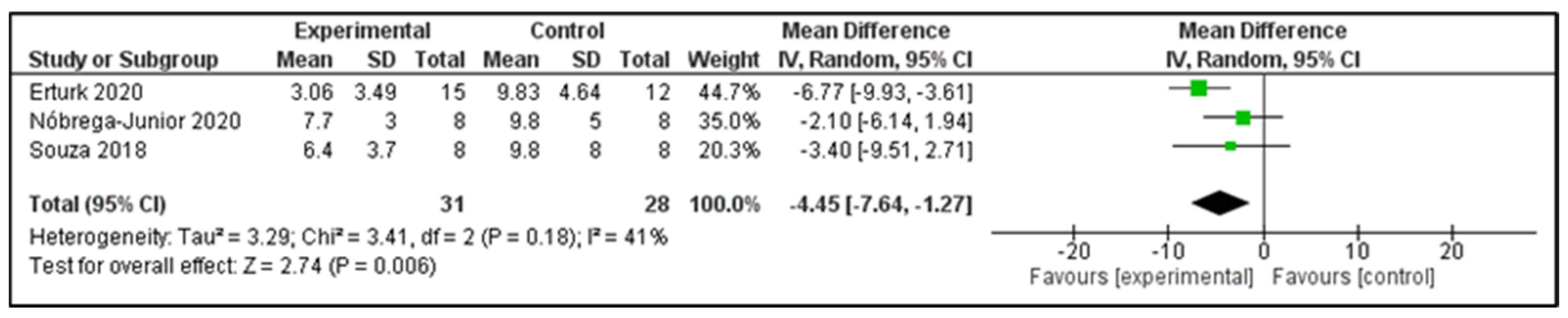
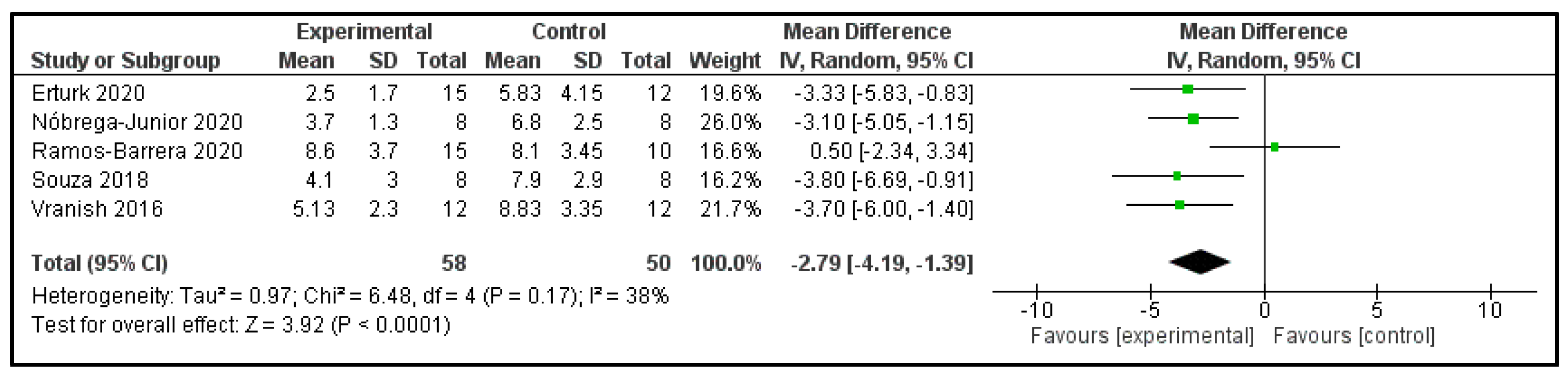
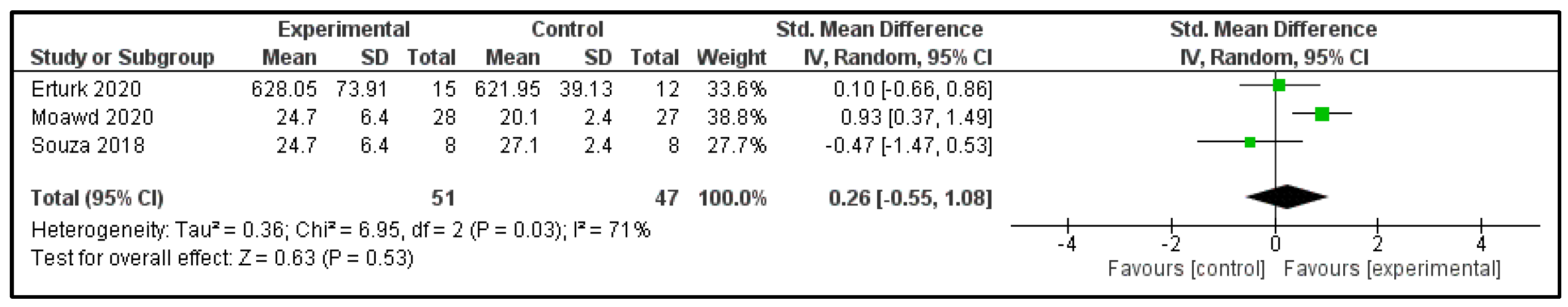
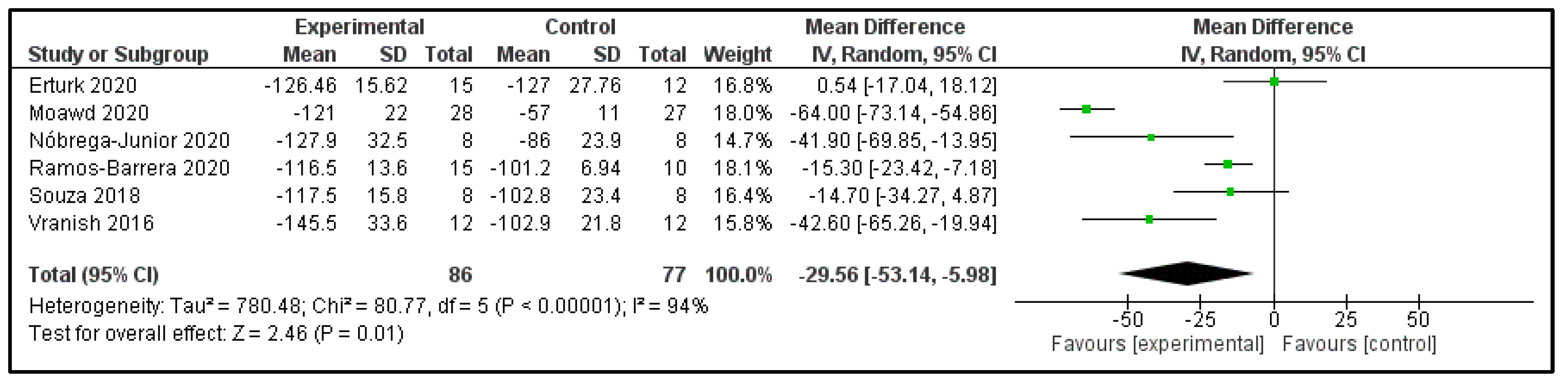
3.6. Main Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senaratna, C.V.; Perret, J.L.; Lodge, C.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Campbell, B.E.; Matheson, M.C.; Hamilton, G.S.; Dharmage, S.C. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in the general population: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 34, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, N.; Farré, R.; Gozal, D. Sleep Apnea Morbidity: A Consequence of Microbial-Immune Cross-Talk? Chest 2018, 154, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollicina, I.; Maniaci, A.; Lechien, J.R.; Iannella, G.; Vicini, C.; Cammaroto, G.; Cannavicci, A.; Magliulo, G.; Pace, A.; Cocuzza, S.; et al. Neurocognitive Performance Improvement after Obstructive Sleep Apnea Treatment: State of the Art. Behav. Sci. 2021, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; Punjabi, N.M. Diagnosis and Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause-Sorio, B.; An, E.; Aguila, A.P.; Martinez, F.; Aysola, R.S.; Macey, P.M. Inspiratory Muscle Training for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Protocol Development and Feasibility of Home Practice by Sedentary Adults. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 737493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniaci, A.; Di Luca, M.; Lechien, J.R.; Iannella, G.; Grillo, C.; Grillo, C.M.; Merlino, F.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; De Vito, A.; Magliulo, G.; et al. Lateral pharyngoplasty vs. traditional uvulopalatopharyngoplasty for patients with OSA: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 2022, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Vasconcello-Castillo, L.; Puppo, H.; Cabrera-Aguilera, I.; Otto-Yáñez, M.; Rosales-Fuentes, J.; Vilaró, J. Effects of Exercise in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Clocks Sleep 2021, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, J.R.; Mugueta-Aguinaga, I.; Vilaró, J.; Rueda-Etxebarria, M. Myofunctional therapy (oropharyngeal exercises) for obstructive sleep apnoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD013449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Vilaró, J.; Martí, J.-D.; Garmendia, O.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; Romano-Andrioni, B.; Embid, C.; Montserrat, J.M. Effects of a Combined Community Exercise Program in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Otto-Yáñez, M.; Fregonezi, G.; Vilaró, J. Inspiratory muscle training in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 1663–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azambuja, A.D.C.M.; de Oliveira, L.Z.; Sbruzzi, G. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Patients With Heart Failure: What Is New? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.; Smith, L.; Anderson, C.; Ewing, N.; Gammack, A.; Pecover, M.; Sime, N.; Galley, H.F. The effect of Preoperative threshold inspiratory muscle training in adults undergoing cardiac surgery on postoperative hospital stay: A systematic review. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabero-Garrido, R.; del Corral, T.; Angulo-Díaz-Parreño, S.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; Martín-Casas, P.; Cleland, J.A.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; López-De-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Respiratory muscle training improves exercise tolerance and respiratory muscle function/structure post-stroke at short term: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 65, 101596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Veasey, S.C.; Morgan, B.J.; O’Donnell, C.P. Pathophysiology of Sleep Apnea. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega-Júnior, J.C.N.; de Andrade, A.D.; de Andrade, E.A.M.; Andrade, M.D.A.; Ribeiro, A.S.V.; Pedrosa, R.P.; Ferreira, A.P.D.L.; de Lima, A.M.J. Inspiratory Muscle Training in the Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Sleep Quality and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2020, 12, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranish, J.R.; Bailey, E.F. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Sleep and Mitigates Cardiovascular Dysfunction in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Sleep 2016, 39, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.0; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.K.F.; de Andrade, A.M.; de Medeiros, A.I.C.; de Aguiar, M.I.R.; de Spiza Rpcja, T.D.; Pedrosa, R.P.; de Lima, A.M.J. Effectiveness of inspiratory muscle training on sleep and functional capacity to exercise in obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized controlled trial. Sleep Breath 2018, 22, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawd, S.A.; Azab, A.R.; Alrawaili, S.M.; AbdelBasset, W.K. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Associating Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Control Study. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5036585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-C.; Chiang, L.-L.; Ong, J.-H.; Tsai, K.-L.; Hung, C.-H.; Lin, C.-Y. The effects of threshold inspiratory muscle training in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized experimental study. Sleep Breath 2020, 24, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erturk, N.; Calik-Kutukcu, E.; Arikan, H.; Savci, S.; Inal-Ince, D.; Caliskan, H.; Saglam, M.; Vardar-Yagli, N.; Firat, H.; Celik, A.; et al. The effectiveness of oropharyngeal exercises compared to inspiratory muscle training in obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized controlled trial. Hear Lung J. Cardiopulm. Acute Care 2020, 49, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Song, T.-T.; Bernard, J.R.; Liao, Y.-H. Short-term expiratory muscle strength training attenuates sleep apnea and improves sleep quality in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2017, 243, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Barrera, G.E.; DeLucia, C.M.; Bailey, E.F. Inspiratory muscle strength training lowers blood pressure and sympathetic activity in older adults with OSA: A randomized controlled pilot trial. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, C.E.; Crowley, E.P.; Ewing, G.B.; Burch, J.B.; Blair, S.N.; Durstine, J.L.; Davis, J.M.; Youngstedt, S.D. The Effect of Exercise Training on Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Sleep Quality: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sleep 2011, 34, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Kon, S.S.C.; Nolan, C.M.; Barker, R.E.; Simonds, A.K.; Morrell, M.J.; Man, W.D.-C. The epworth sleepiness scale: Minimum clinically important difference in obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 961–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, R.; Zeitzer, J.M. Physiological correlates of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale reveal different dimensions of daytime sleepiness. Sleep Adv. 2021, 2, zpab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F., III; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.M.; McCullough, C.A.; Bradbury, I.; Boyde, C.; Hume, D.; Yuan, J.; Quinn, F.; McDonough, S. Acupuncture and reflexology for insomnia: A feasibility study. Acupunct. Med. 2009, 27, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubay, G. Respiratory mass physiology and muscle power measurement. Thorax Surg. Bull. 2017, 10, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, K.D.; Caughey, W.G.; Nelluri, B.; Sharma, A.; Mookadam, F.; Mookadam, M. Effect of exercise training on sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Med. 2016, 116, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcante-Leão, B.L.; de Araujo, C.M.; Ravazzi, G.C.; Basso, I.B.; Guariza-Filho, O.; Taveira, K.V.M.; Santos, R.S.; Stechman-Neto, J.; Zeigelboim, B.S. Effects of respiratory training on obstructive sleep apnea: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, D.B.; Emperumal, B.C.P.; Grbach, V.X.; Padilla, D.M.; Enciso, R. Effects of respiratory muscle therapy on obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göhl, O.; Walker, D.J.; Walterspacher, S.; Langer, D.; Spengler, C.M.; Wanke, T.; Petrović, M.; Zwick, R.-H.; Stieglitz, S.; Glöckl, R.; et al. Atemmuskeltraining: State-of-the-Art. Pneumologie 2016, 70, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abodonya, A.M.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Awad, E.A.; Elalfy, I.E.; Salem, H.A.; Elsayed, S.H. Inspiratory muscle training for recovered COVID-19 patients after weaning from mechanical ventilation: A pilot control clinical study. Medicine 2021, 100, e25339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Munoz, P.; Lau, E.M.; Alison, J.A.; Brown, M.; Zheng, Y.; Corkery, P.; Wong, K.; Lindstrom, S.; Celermajer, D.S.; et al. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Inspiratory Muscle Strength and Functional Exercise Capacity in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Study. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, M.; Forget, P.; Couturaud, F.; Reychler, G. Effects of inspiratory muscle training in COPD patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 2178–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author, Year | Country | Group, n | Gender (M/F) | Age (Years) | BMI (kg/m2) | AHI (Events/h) | ESS | MIP (cmH2O) | MEP (cmH2O) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vranish and Bailey, 2016 | USA | IMT: 12 | 8/4 | 61.5 ± 3.9 | 27.0 ± 1.0 | 21.9 ± 4.4 | NR | 80.7 ± 7.1 | NR |
| Placebo: 12 | 8/4 | 69.1 ± 3.4 | 28.5 ± 1.6 | 29.9 ± 8.9 | NR | 75.2 ± 3.9 | NR | ||
| Kuo et al., 2017 | Taiwan | EMT: 13 | 11/2 | 44.3 ± 2.9 | 24.9 ± 0.5 | 16.5 ± 2.2 | 9.8 ± 1.1 | NR | 134.8 ± 10.4 |
| Control: 12 | 10/2 | 48.0 ± 3.1 | 24.7 ± 0.8 | 14.6 ± 1.5 | 9.8 ± 0.9 | NR | 108.6 ± 11.6 | ||
| Souza et al., 2018 | Brazil | IMT: 8 | 4/4 | 54.8 ± 6.9 | NR | 27.6 ± 11.9 | 11.1 ± 4.5 | 85 ± 23.5 | 130.3 ± 35.8 |
| Placebo: 8 | 6/2 | 49.9 ± 11.6 | NR | 34.0 ± 18.4 | 11.1 ± 6.8 | 87.1 ± 23.7 | 115.4 ± 29.1 | ||
| Erturk et al., 2020 | Turkey | IMT: 15 | 9/6 | 49.7 ± 9.1 | 31.0 ± 5.4 | 30.0 ± 19.3 | 8.9 ± 4.4 | 80.9 ± 16.9 | 120.5 ± 21.3 |
| Control: 12 | 10/2 | 47.3 ± 7.3 | 32.1 ± 3.7 | 38.7 ± 24.0 | 9.7 ± 5.9 | 131.7 ± 23.5 | 148.9 ± 32.3 | ||
| Lin et al., 2020 | Taiwan | IMT: 16 | 13/3 | 47.9 ± 12.2 | 26.2 ± 3.3 | 29.0 ± 2.8 | 10.5 ± 5.7 | NR | NR |
| Control: 6 | 5/1 | 56.2 ± 11.5 | 27.3 ± 3.6 | 37.5 ± 14.1 | 13 ± 2.6 | NR | NR | ||
| Moawd et al., 2020 | Egypt | IMT: 28 | 20/8 | 55.5 ± 9.8 | 29.2 ± 3.9 | 32 ± 11.7 | NR | 56 ± 13 | NR |
| Placebo: 27 | 22/5 | 59.5 ± 4.8 | 27.9 ± 4.8 | 31 ± 10.8 | NR | 52 ± 10 | NR | ||
| Nóbrega-Júnior et al., 2020 | Brazil | IMT: 8 | 3/5 | 58.6 ± 5.6 | 33.4 (30.3–34.5) | 31.7 ± 15.9 | 12.5 ± 4.0 | 83.6 ± 26.5 | 124.8 ± 46.7 |
| Placebo 8 | 1/7 | 60.1 ± 2.7 | 32.7 (23.8–34.9) | 31.4 ± 20.8 | 14.9 ± 5.2 | 74.6 ± 25.4 | 101.6 ± 29.4 | ||
| Ramos-Barrera et al., 2020 | USA | IMT: 15 | 11/4 | 65.9 ± 6.0 | 30.7 ± 6.2 | NR | NR | 82.6 ± 12.5 | NR |
| Control: 10 | 6/4 | 69.7 ± 6.7 | 31.3 ± 6.5 | NR | NR | 85.6 ± 4.5 | NR |
| Author, Year | Device | Load | Comparison | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vranish J and Bailey F, 2016 | K3 series, POWERbreathe | 75% MIP | 15% MIP | 30 breaths/day | 6 weeks |
| Kuo YC et al., 2017 | EMST150, Aspire products | 75% MEP | 0% MEP | 25 breaths/day (5 days/w) | 5 weeks |
| Souza AKF et al., 2018 | POWERbreathe classic light | 50–60% MIP | 20% MIP | 90 breaths/day (7 days/w) | 12 weeks |
| Erturk et al., 2020 | IMT Threshold | 30% MIP | No intervention | 15 min twice a day (7 days/w) | 12 weeks |
| Lin et al., 2020 | IMT Threshold | 30% MIP | NR | 30–45 min/day (5 days/w) | 12 weeks |
| Moawd et al., 2020 | TRAINAIR®, Project Electronics Ltd., UK | 75% MIP | ≤10% MIP | 120 breaths/day (3 days/w) | 12 weeks |
| Nóbrega-Júnior et al., 2020 | POWERbreathe classic light | 50% MIP–2 weeks60% MIP–2 weeks75% MIP–4 weeks | 0% MIP | 180 breaths/day (7 days/w) | 8 weeks |
| Ramos-Barrera et al., 2020 | K3 series, POWERbreathe | 75% MIP | 15% MIP | 30 breaths/day | 6 weeks |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Castro, R.; Solis-Navarro, L.; Puppo, H.; Alcaraz-Serrano, V.; Vasconcello-Castillo, L.; Vilaró, J.; Vera-Uribe, R. Respiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clocks & Sleep 2022, 4, 219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4020020
Torres-Castro R, Solis-Navarro L, Puppo H, Alcaraz-Serrano V, Vasconcello-Castillo L, Vilaró J, Vera-Uribe R. Respiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clocks & Sleep. 2022; 4(2):219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Castro, Rodrigo, Lilian Solis-Navarro, Homero Puppo, Victoria Alcaraz-Serrano, Luis Vasconcello-Castillo, Jordi Vilaró, and Roberto Vera-Uribe. 2022. "Respiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Clocks & Sleep 4, no. 2: 219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4020020
APA StyleTorres-Castro, R., Solis-Navarro, L., Puppo, H., Alcaraz-Serrano, V., Vasconcello-Castillo, L., Vilaró, J., & Vera-Uribe, R. (2022). Respiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clocks & Sleep, 4(2), 219-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep4020020







