An Atomistic Investigation of Adsorption of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on Gold with Nanoscale Topographies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
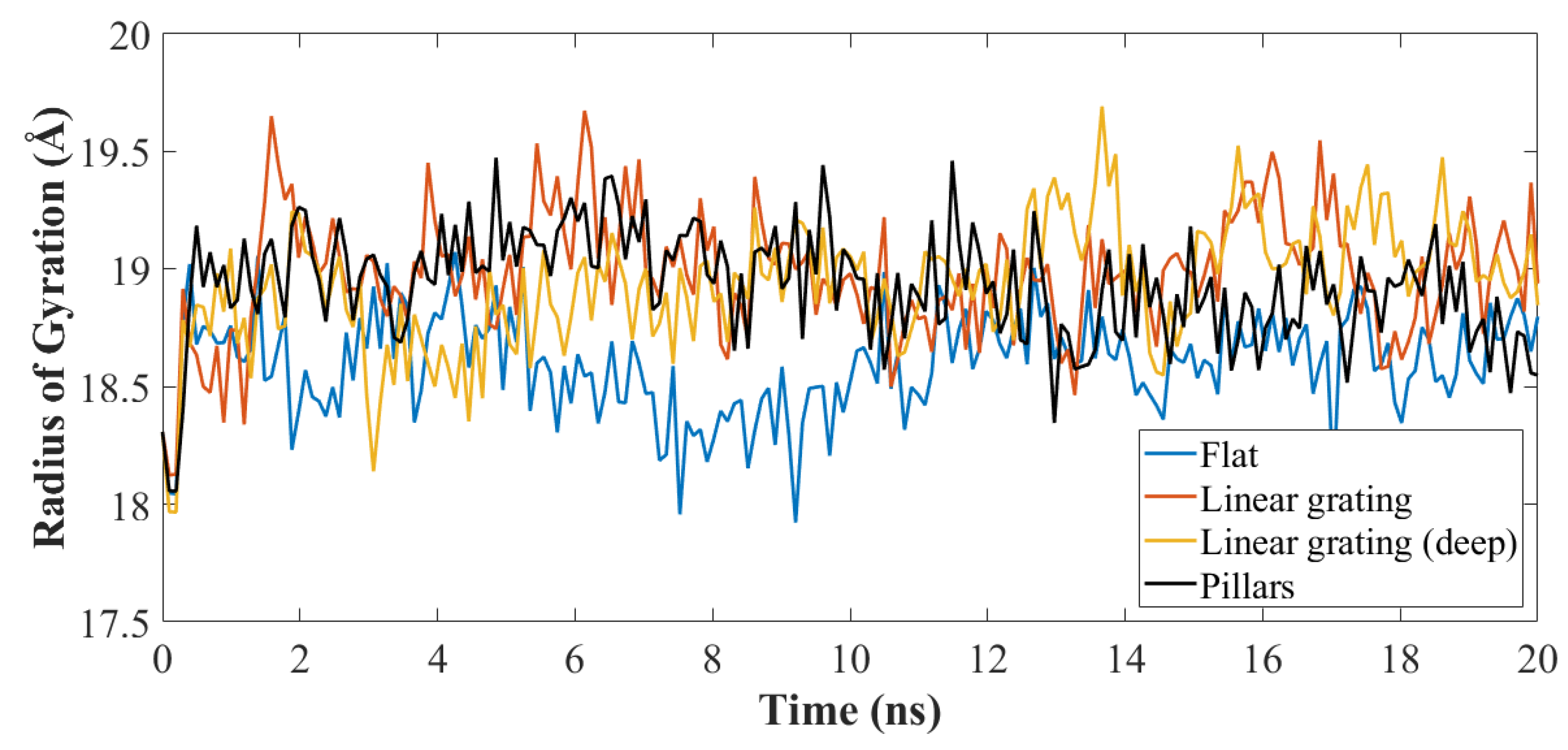
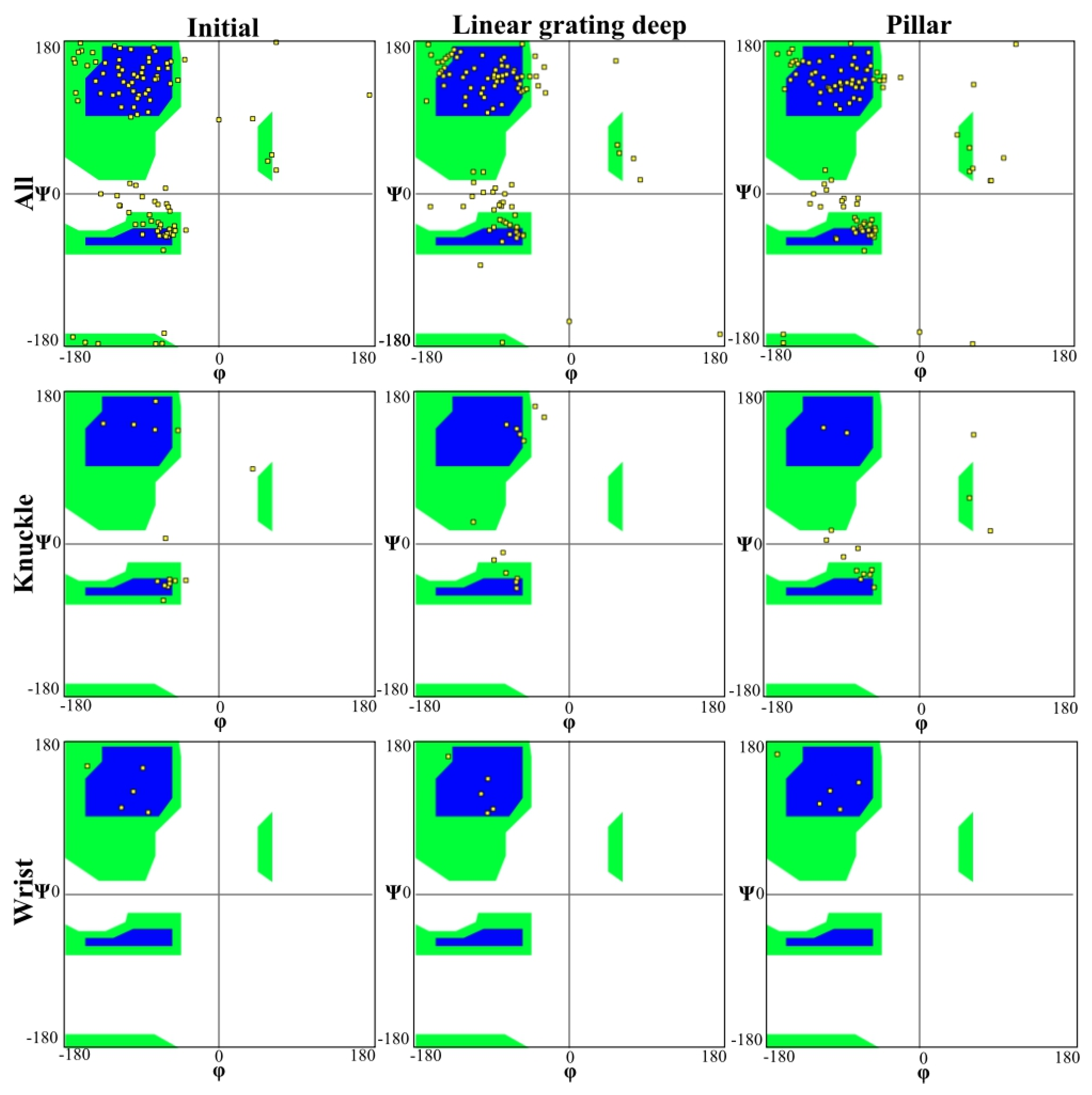
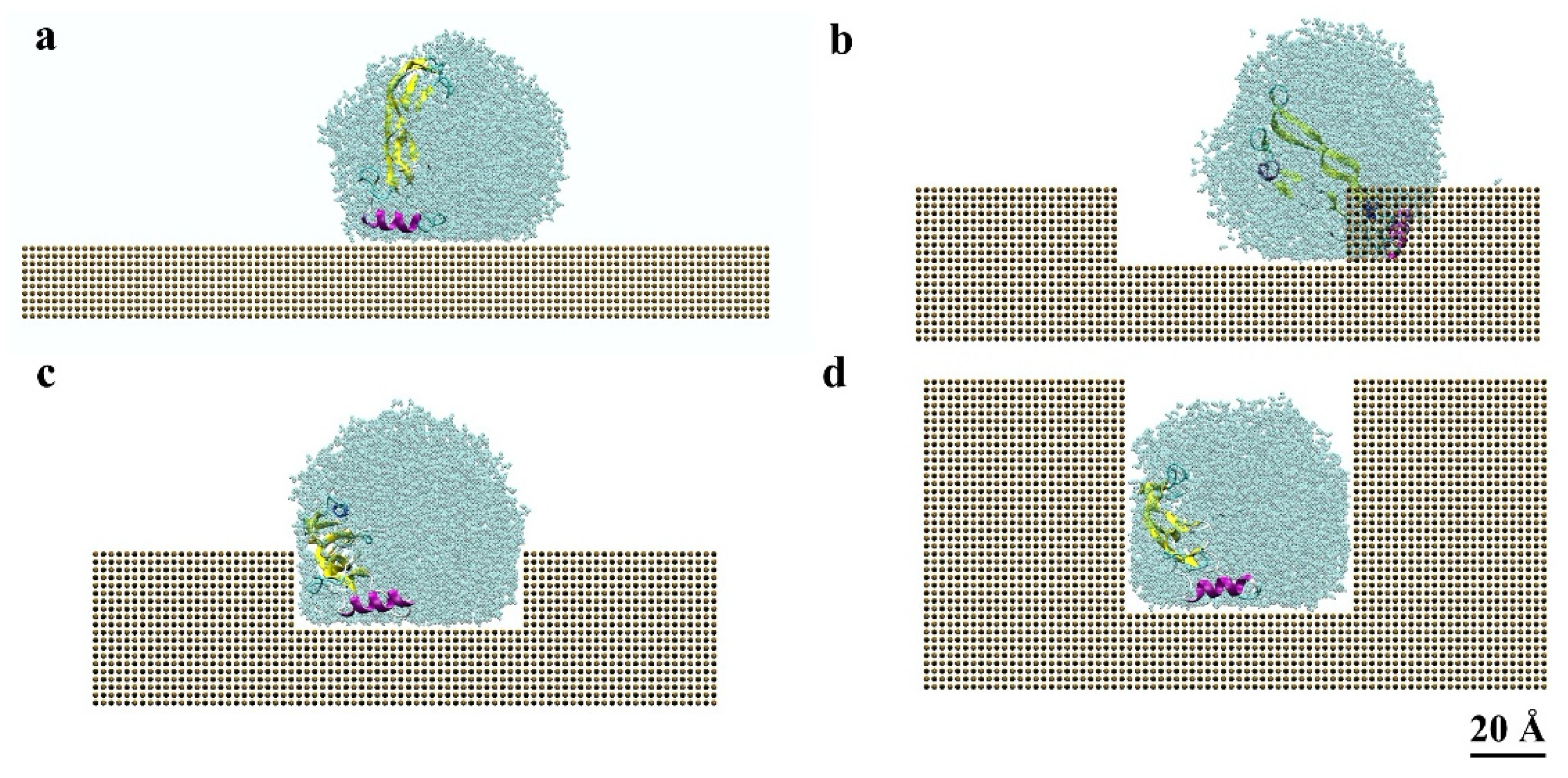
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quan, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J. Multiscale modeling and simulations of protein adsorption: Progresses and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 41, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Systematic approach to characterize the dynamics of protein adsorption on the surface of biomaterials using proteomics. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Xue, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, M.; Wang, K.; Xu, D. Effect of Hydroxyapatite Surface on BMP-2 Biological Properties by Docking and Molecular Simulation Approaches. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 3372–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquetti, I.; Desai, S. Adsorption Behavior of Bone Morphogenic Protein (BMP-2) on Nanoscale Topographies. In Proceedings of the ASME NanoEngineering for Medicine and Biology Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21–24 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, S.; Robertson, S.F.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Surface modification of biomaterials and biomedical devices using additive manufacturing. Acta Biomater. 2018, 66, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshy, K.S.; Snigdha, S.; Thomas, S. Plasma Modified Polymeric Materials for Scaffolding of Bone Tissue Engineering. In Non-Thermal Plasma Technology for Polymeric Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.F.; Gemming, S.; Seifert, G. Conformational Analysis of Aqueous BMP-2 Using Atomistic Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 115, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.; Bidanda, B.; Bártolo, P.J. Emerging Trends in the Applications of Metallic and Ceramic Biomaterials BT. In Bio-Materials and Prototyping Applications in Medicine; Bártolo, P.J., Bidanda, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-3-030-35876-1. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S.; Shankar, M.R. Emerging Trends in Polymers, Composites, and Nano Biomaterial Applications. In Bio-Materials and Prototyping Applications in Medicine; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Premarket Approval (PMA). Infuse Bone Graft, Lt-Cage Lumbar Tapered Fusion Device. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpma/pma.cfm?id=P000058 (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- US Food and Drug Administration. Premarket Approval (PMA—P000054). Infuse Bone Graft, Filler Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein, Collagen Scaffold, Osteoinduction. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpma/pma.cfm?id=P000054 (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- US Food and Drug Administration. Premarket Approval (PMA—P000053). Infuse Bone Graft, Bone Grafting Material, Dental, With Biologic Component. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpma/pma.cfm?id=P050053 (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- James, A.W.; LaChaud, G.; Shen, J.; Asatrian, G.; Nguyen, V.; Zhang, X.; Ting, K.; Soo, C. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2016, 22, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, E.H.; Pohl, T.L.M.; Haraszti, T.; Schwaerzer, G.K.; Hiepen, C.; Spatz, J.P.; Knaus, P.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A. Nanoscale control of surface immobilized BMP-2: Toward a quantitative assessment of BMP-mediated signaling events. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Harrison, B. Direct-Writing of Biomedia for Drug Delivery and Tissue Regeneration. In Printed Biomaterials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 71–89. ISBN 978-1-4419-1394-4. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S.; Perkins, J.; Harrison, B.S.; Sankar, J. Understanding release kinetics of biopolymer drug delivery microcapsules for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2010, 168, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Moore, A.; Harrison, B.; Sankar, J. Understanding microdroplet formations for biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 13–19 November 2009; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 15, pp. 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Tenkumo, T.; Vanegas Sáenz, J.R.; Nakamura, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Sokolova, V.; Epple, M.; Kamano, Y.; Egusa, H.; Sugaya, T.; Sasaki, K. Prolonged release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in vivo by gene transfection with DNA-functionalized calcium phosphate nanoparticle-loaded collagen scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekblad, T.; Liedberg, B. Protein adsorption and surface patterning. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, J. Experimental Control and Characterization of Protein Orientation on Surfaces. Prog. Chem. Beijing 2009, 21, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Valera, E.; Isaacs, M.J.; Kawakami, Y.; Belmonte, J.C.I.; Choe, S. BMP-2/6 Heterodimer Is More Effective than BMP-2 or BMP-6 Homodimers as Inductor of Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaito, T.; Morimoto, T.; Mori, Y.; Kanayama, S.; Makino, T.; Takenaka, S.; Sakai, Y.; Otsuru, S.; Yoshioka, Y.; Yoshikawa, H. BMP-2/7 heterodimer strongly induces bone regeneration in the absence of increased soft tissue inflammation. Spine J. 2018, 18, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, D.I.; Nove, J.; Kerns, K.M.; Kaufman, R.J.; Rosen, V.; Cox, K.A.; Wozney, J.M. Heterodimeric Bone Morphogenetic Proteins Show Enhanced Activity In Vitro and In Vivo. Growth Factors 1996, 13, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, T.; Kaito, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Kashii, M.; Makino, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Yoshikawa, H. The bone morphogenetic protein-2/7 heterodimer is a stronger inducer of bone regeneration than the individual homodimers in a rat spinal fusion model. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mücksch, C.; Urbassek, H.M. Adsorption of BMP-2 on a hydrophobic graphite surface: A molecular dynamics study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 510, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, T.; Pan, H. Understanding Adsorption-Desorption Dynamics of BMP-2 on Hydroxyapatite (001) Surface. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mücksch, C.; Urbassek, H.M. Enhancing Protein Adsorption Simulations by Using Accelerated Molecular Dynamics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.F.; Gemming, S.; Seifert, G. Molecular dynamics simulations of BMP-2 adsorption on a hydrophobic surface. Mater. Werkst. 2010, 41, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, T.; Nayeem, S.M. Computational analysis on conformational dynamics of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquetti, I.; Desai, S. Orientation effects on the nanoscale adsorption behavior of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on hydrophilic silicon dioxide. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marquetti, I.; Desai, S. Molecular modeling the adsorption behavior of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on hydrophobic and hydrophilic substrates. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 706, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquetti, I.; Desai, S. Adsorption Behavior of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on a Graphite Substrate for Biomedical Applications. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 11, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Lou, Y.; Li, T.; Lin, Z.; Sun, S.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Gu, Y. Molecular dynamics simulations of adsorption and desorption of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on textured hydroxyapatite surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanti, F.; Pedone, A.; Menziani, M.C. Multiscale Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Multiple Protein Adsorption on Gold Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Towns, J.; Cockerill, T.; Dahan, M.; Foster, I.; Gaither, K.; Grimshaw, A.; Hazlewood, V.; Lathrop, S.; Lifka, D.; Peterson, G.D.; et al. XSEDE: Accelerating Scientific Discovery. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2014, 16, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKerell, A.D.; Bashford, D.; Bellott, M.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Evanseck, J.D.; Field, M.J.; Fischer, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Ha, S.; et al. All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, R.; Sarikaya, M.; Schulten, K. Genetically engineered gold-binding polypeptides: Structure prediction and molecular dynamics. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utesch, T.; Daminelli, G.; Mroginski, M.A. Molecular dynamics simulations of the adsorption of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on surfaces with medical relevance. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13144–13153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.D.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, D.R.; Waldeck, H.; Kao, W.J. Protein Adsorption to Biomaterials. In Biological Interactions on Materials Surfaces; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
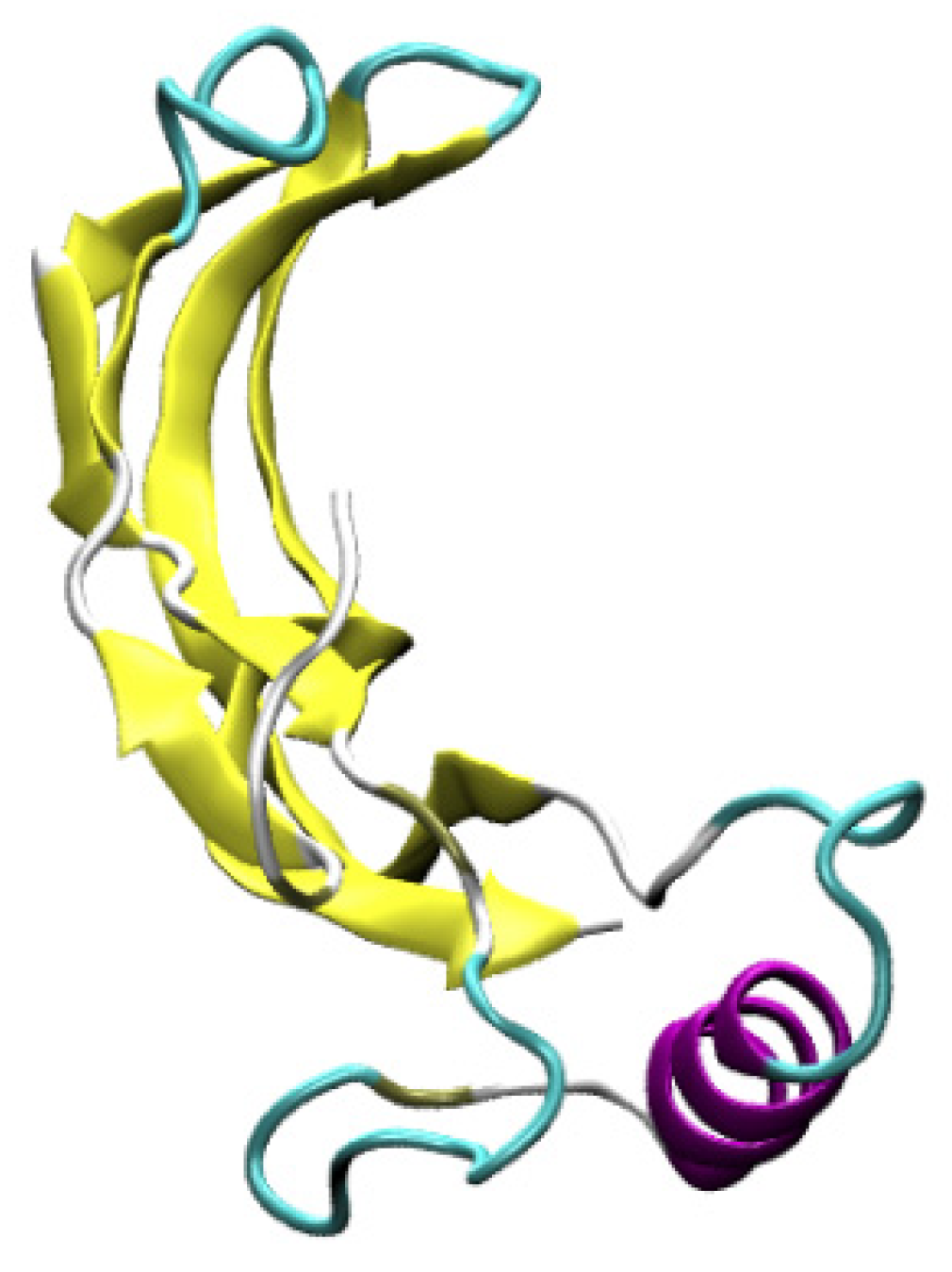
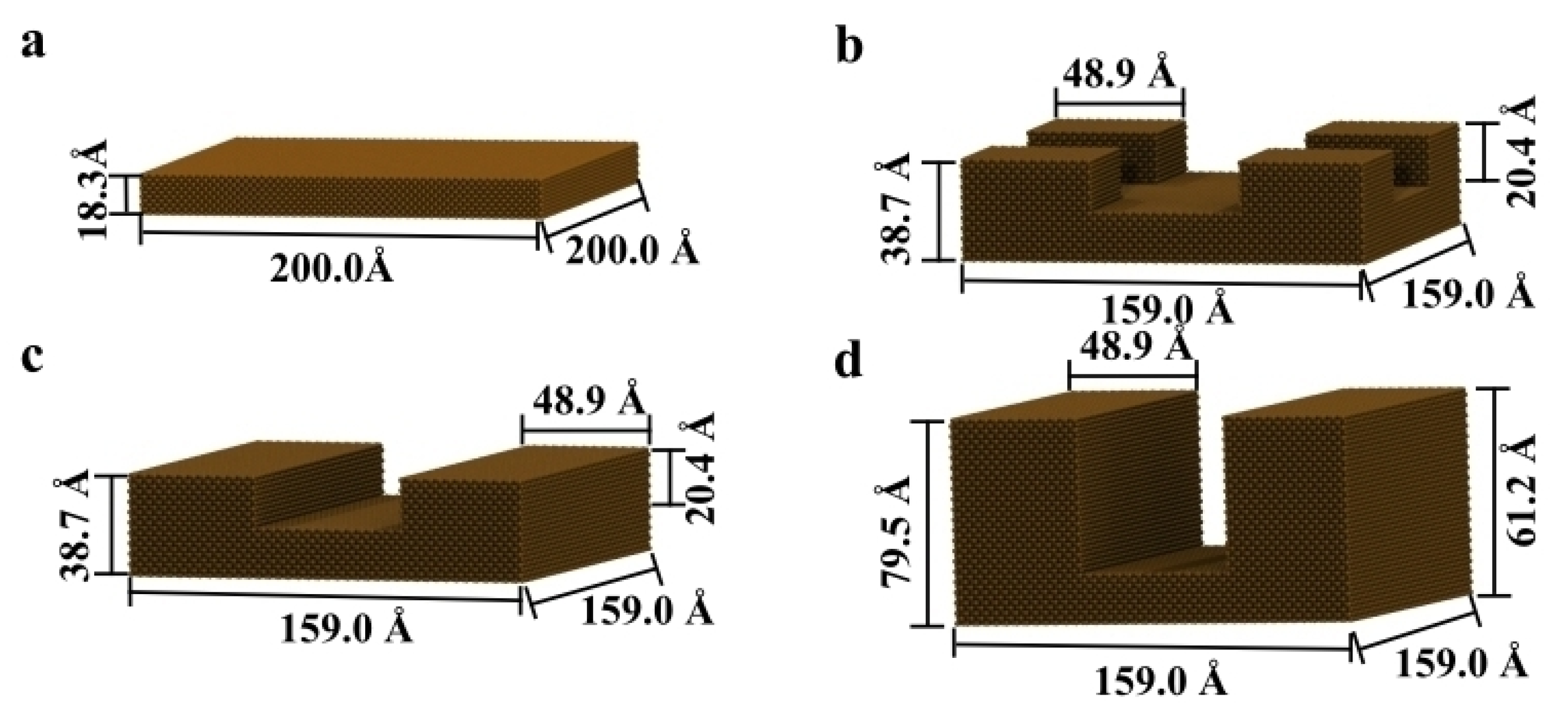
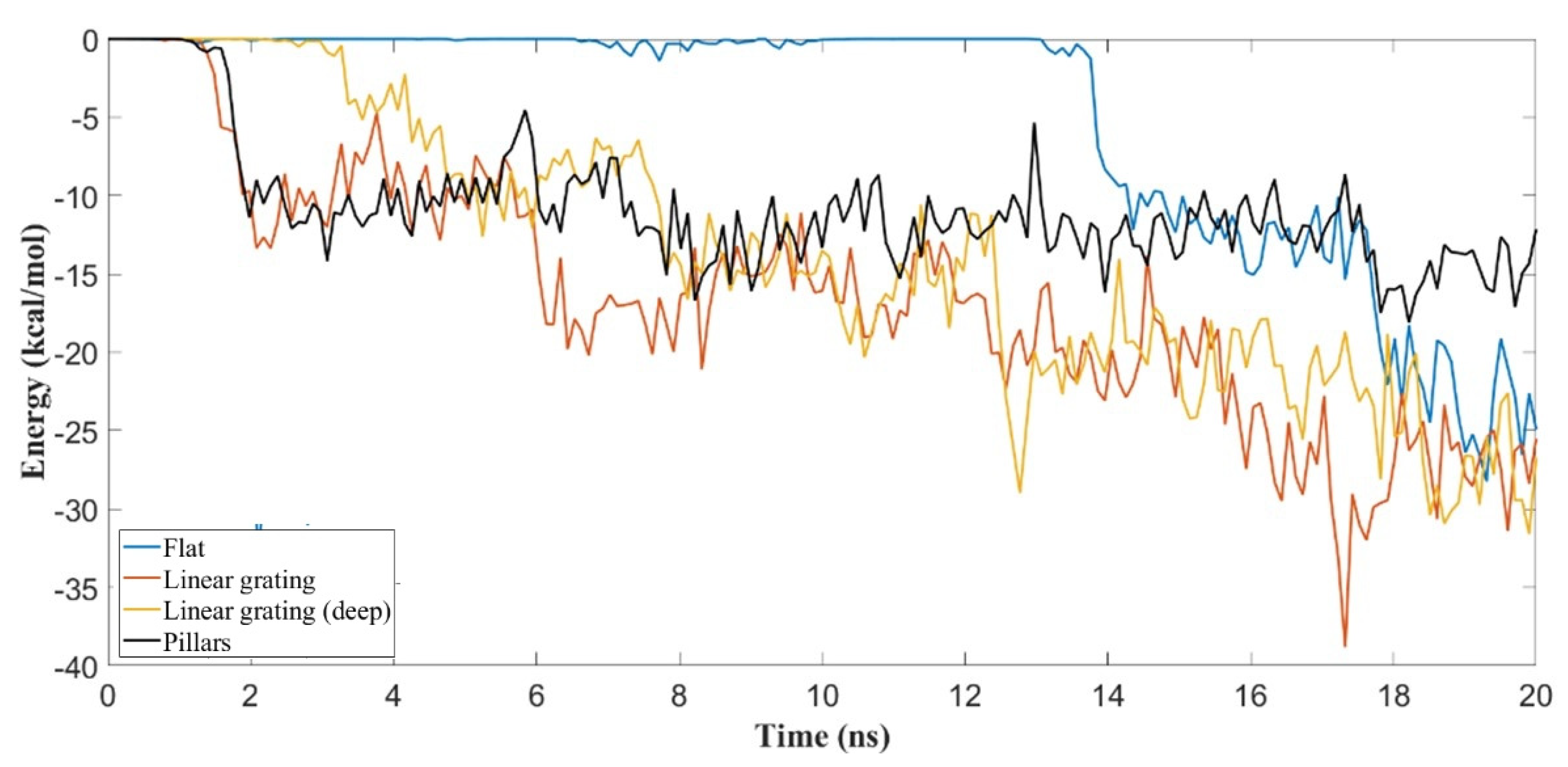
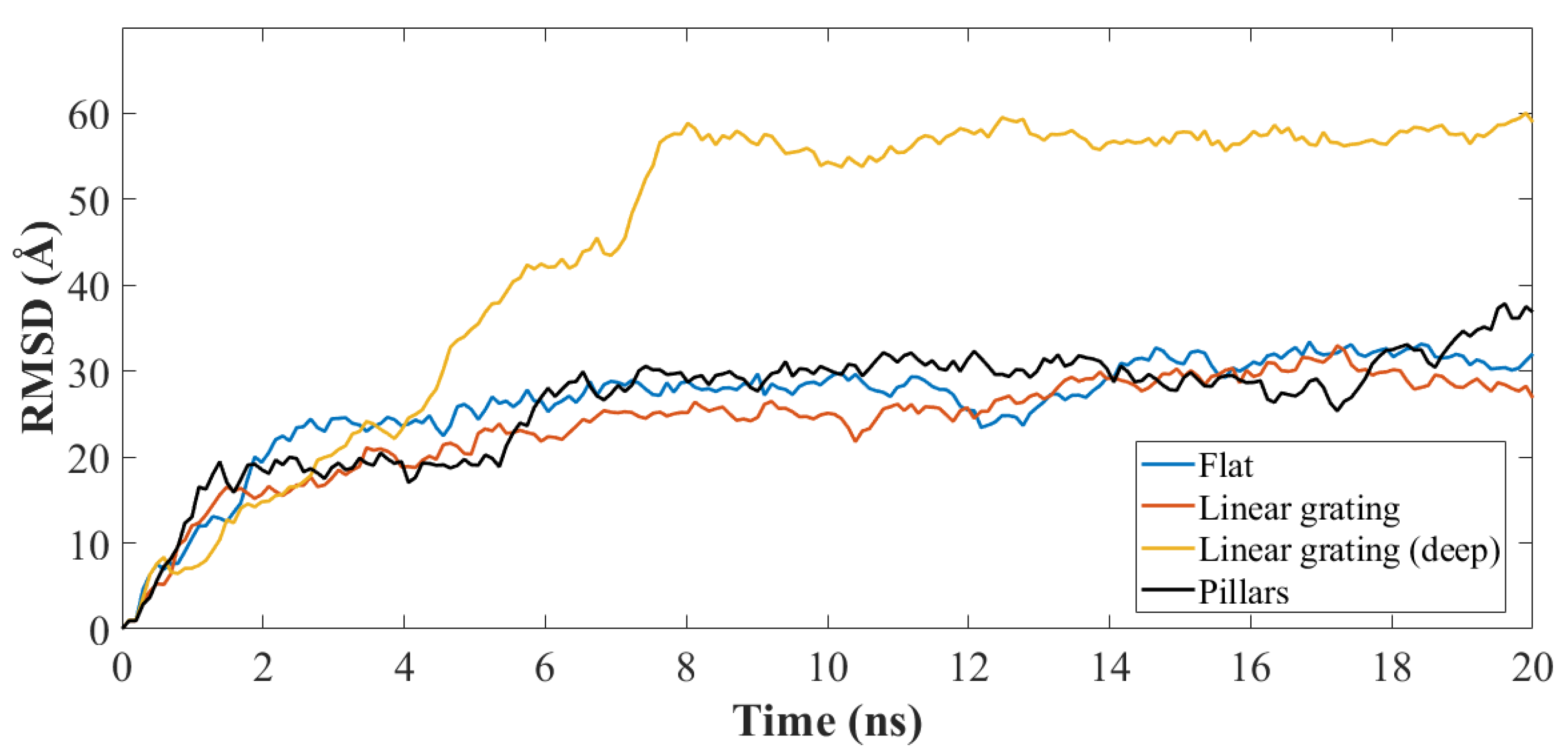
| Secondary | Initial | After 20 ns | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Structure | Flat | Pillar | Linear Grating | Linear Grating Deep |
| α-helix | 10.38% | 10.38% | 15.09% | 11.32% | 9.43% |
| 310-helix | 0.00% | 0.00% | 2.83% | 2.83% | 0.00% |
| β-sheet | 44.34% | 44.34% | 38.68% | 38.68% | 40.57% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marquetti, I.; Desai, S. An Atomistic Investigation of Adsorption of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on Gold with Nanoscale Topographies. Surfaces 2022, 5, 176-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces5010010
Marquetti I, Desai S. An Atomistic Investigation of Adsorption of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on Gold with Nanoscale Topographies. Surfaces. 2022; 5(1):176-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces5010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarquetti, Izabele, and Salil Desai. 2022. "An Atomistic Investigation of Adsorption of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on Gold with Nanoscale Topographies" Surfaces 5, no. 1: 176-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces5010010
APA StyleMarquetti, I., & Desai, S. (2022). An Atomistic Investigation of Adsorption of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on Gold with Nanoscale Topographies. Surfaces, 5(1), 176-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces5010010







