Controlled Surface Wettability by Plasma Polymer Surface Modification
Abstract
1. Introduction
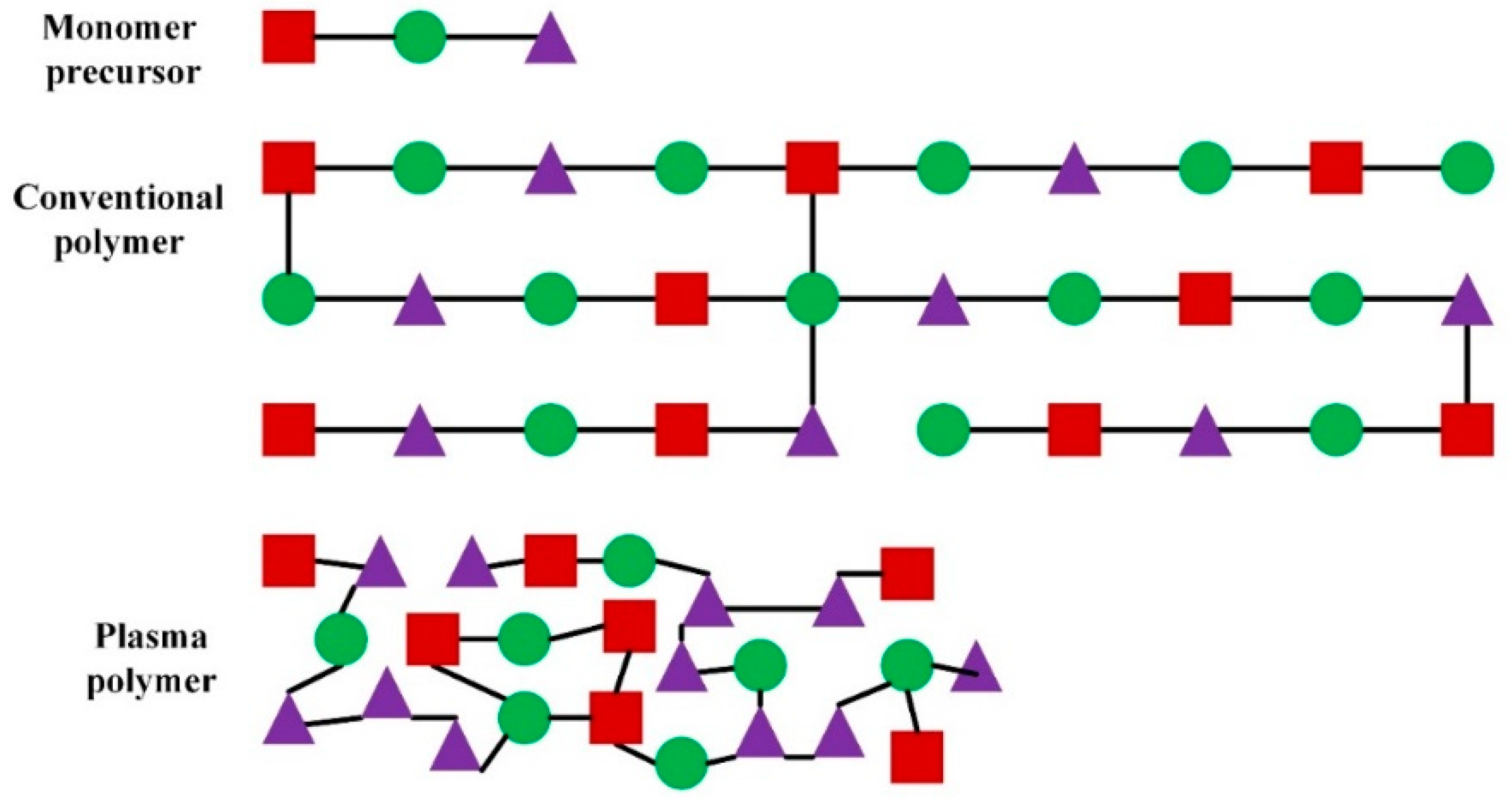
2. Plasma Polymerization
2.1. RF Plasma Polymerization
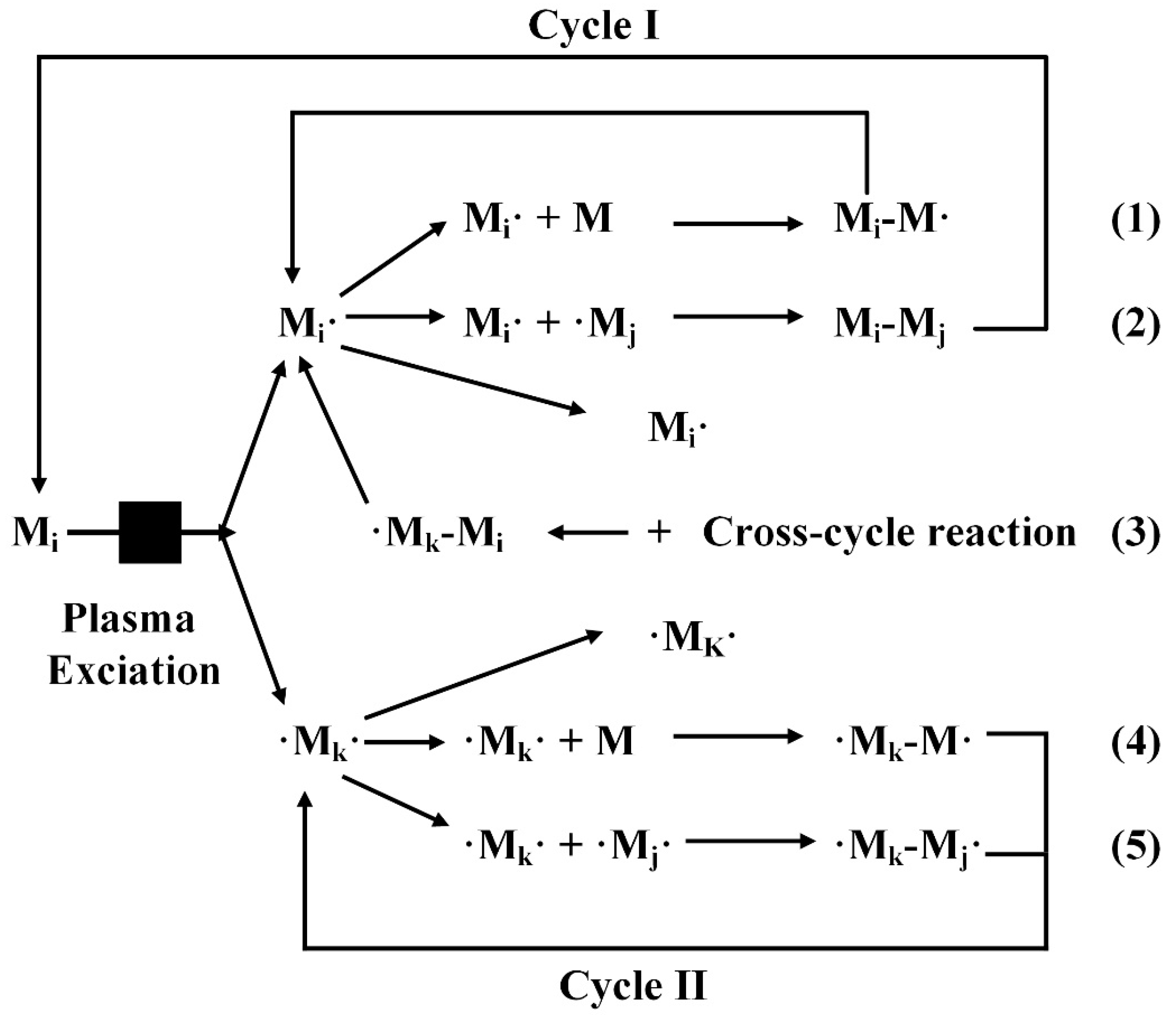
2.2. Growth Mechanisms of Plasma Polymerization
2.3. Influence of Plasma Parameters
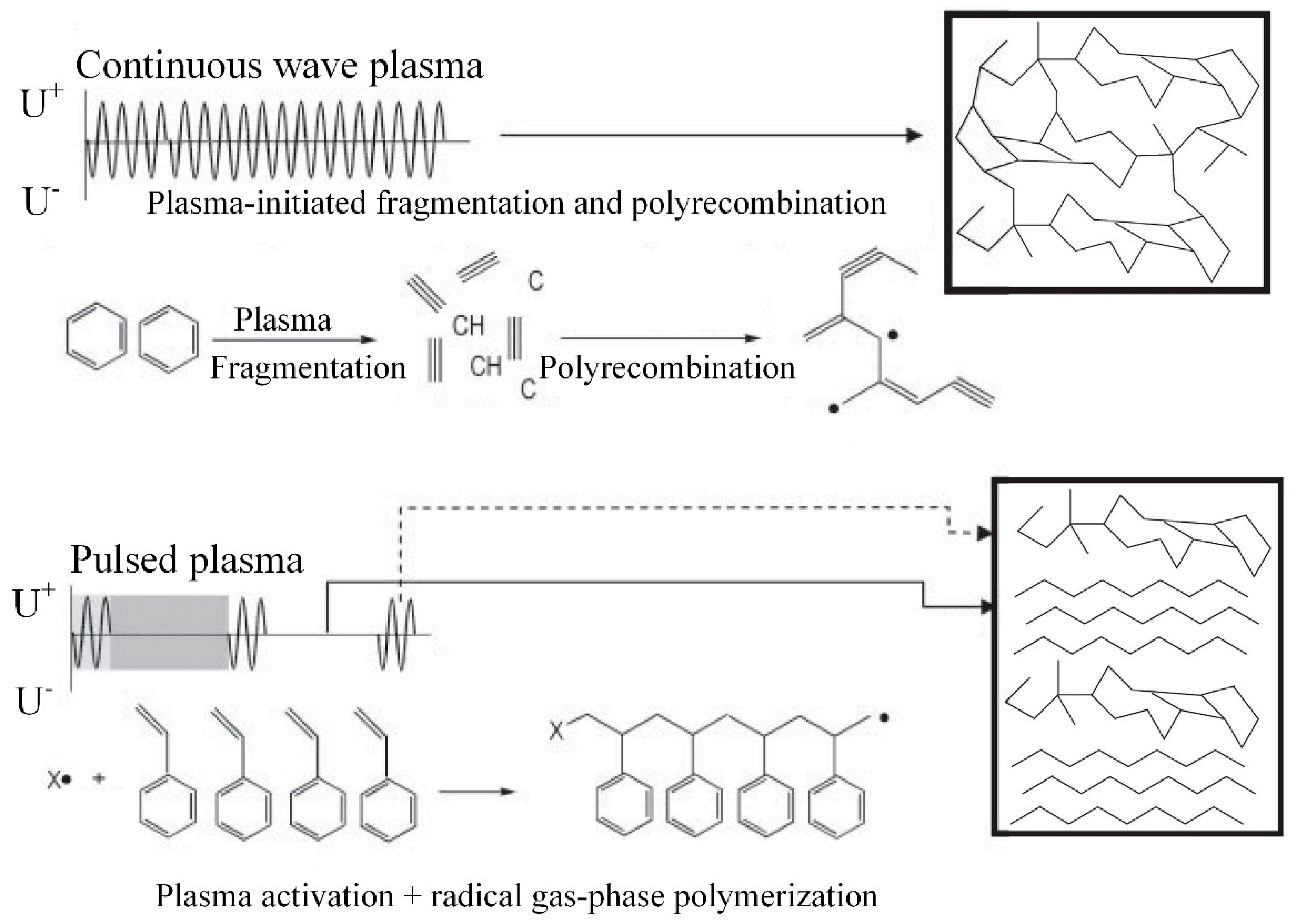
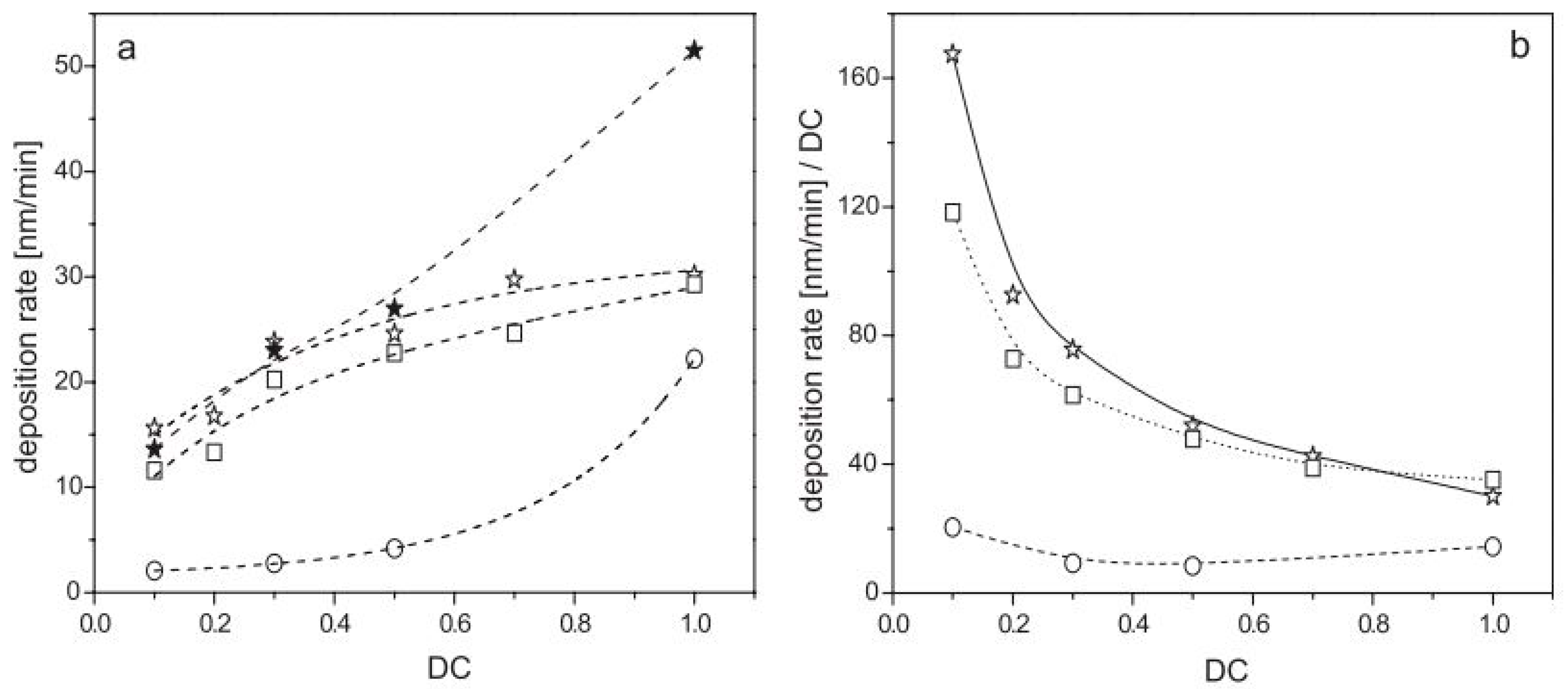
2.4. RF Pulsed Plasma Polymerization
| Initiation | M + plasma → M• | PW plasma (during tpulse-on) |
| M + plasma → A• + B• + C• + D• | CW plasma (fragmentation) | |
| Chain growth | M• + M → P• | PW plasma (during tpulse-off) |
| A• + B• + C• + D• → BDCA + ΔE | CW plasma (polyrecombination) |
2.5. Plasma Copolymerization
3. Surface Wettability
3.1. Static and Dynamic Wettability
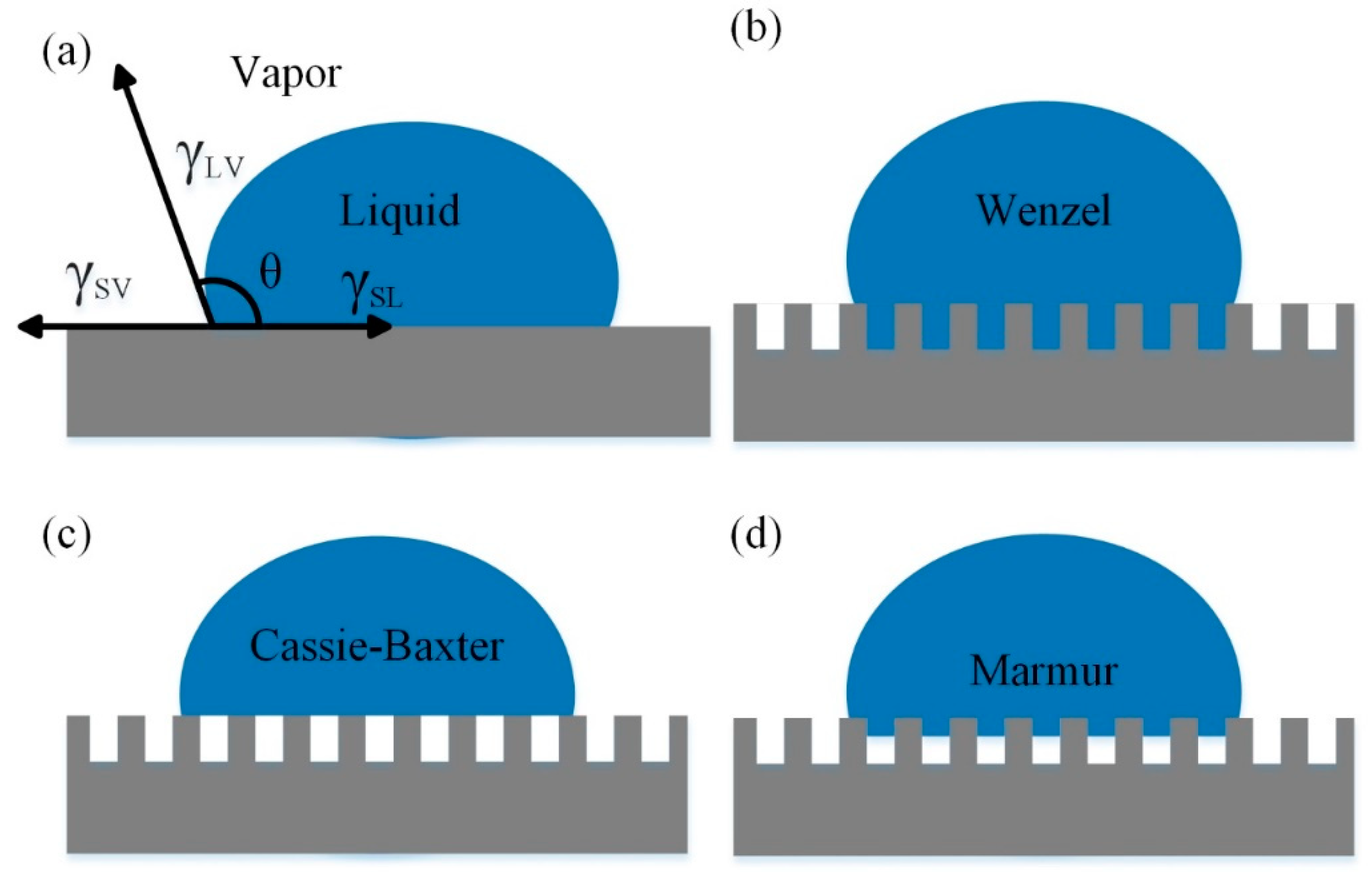
3.2. Theoretical Background
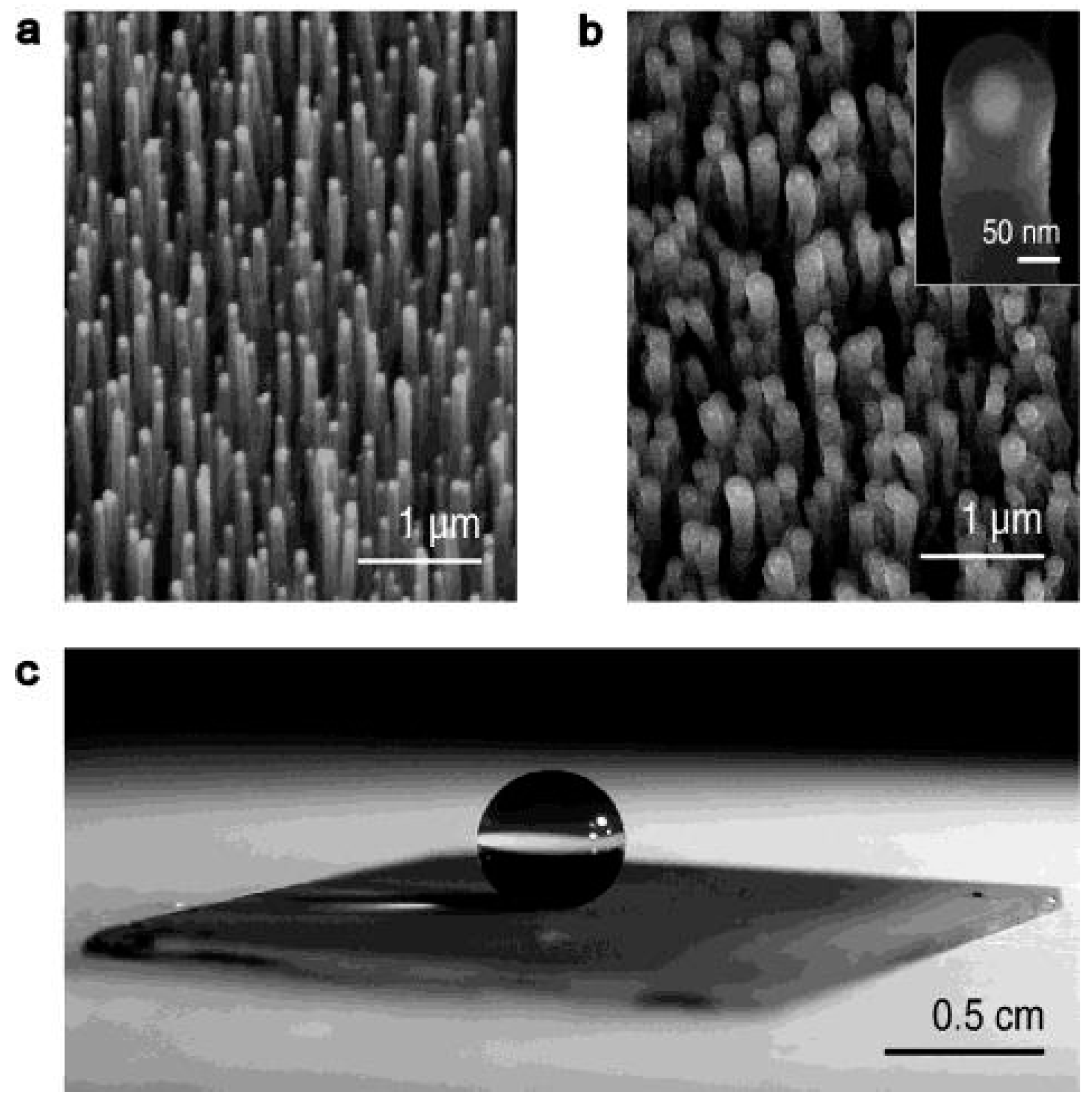
3.3. Textured Surface Wettability
4. Surface Functionalization of Plasma Polymer Coatings
4.1. Surface Processes During Plasma Functionalization
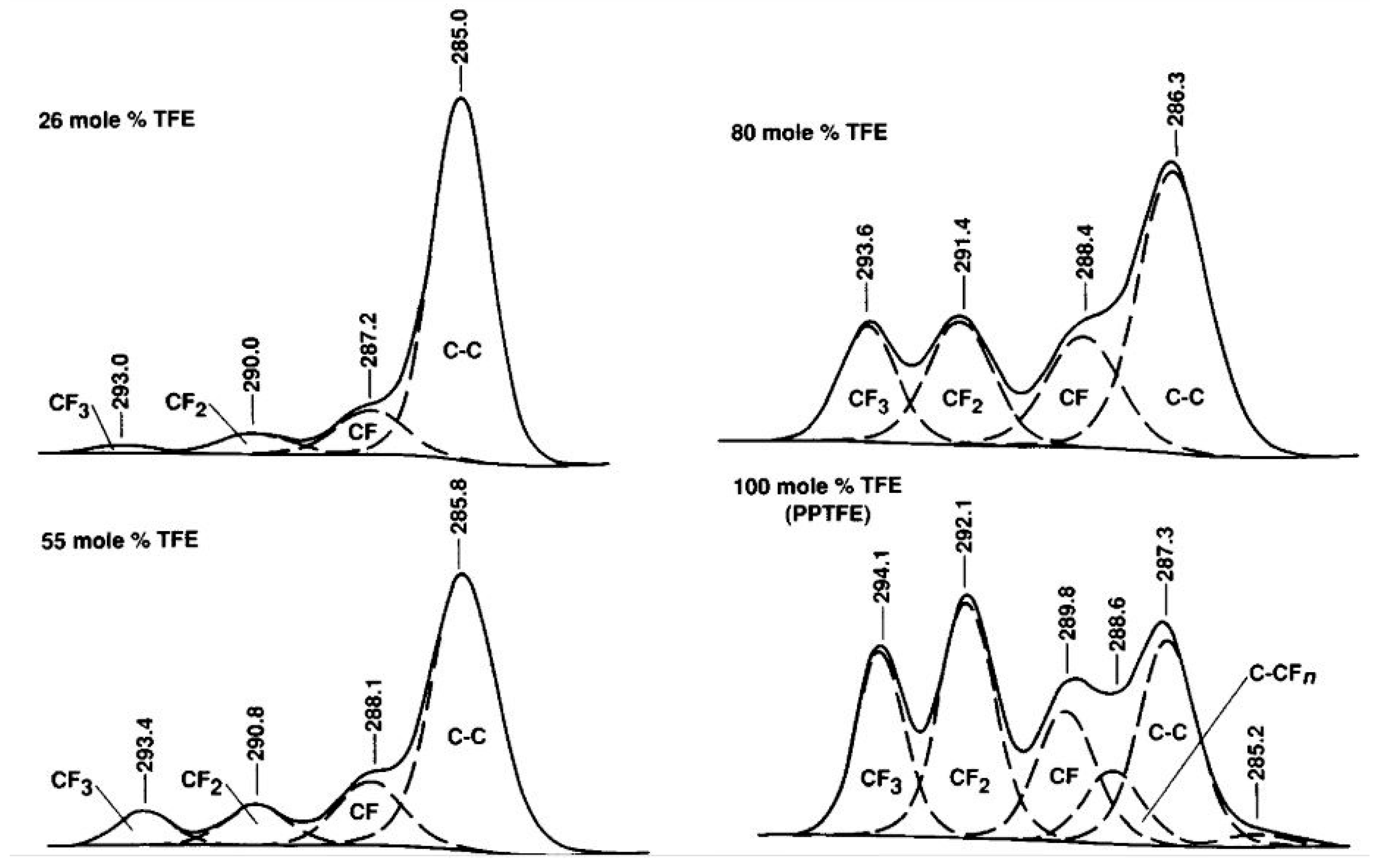
4.2. Functionalized Plasma Polymer Coatings
4.3. Functionalized Plasma Copolymer Coatings
5. Surface Wettability of Functionalized Polymer Coatings
5.1. Hydrophobic Polymer Coatings
5.2. Hydrophilic Polymer Coatings
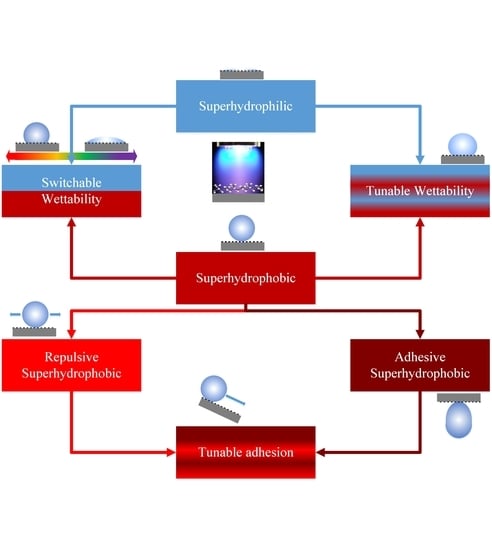
5.3. Tunable and pH-responsive Surface Wettability
6. Prominent Applications of Tunable Wettability and pH-responsiveness
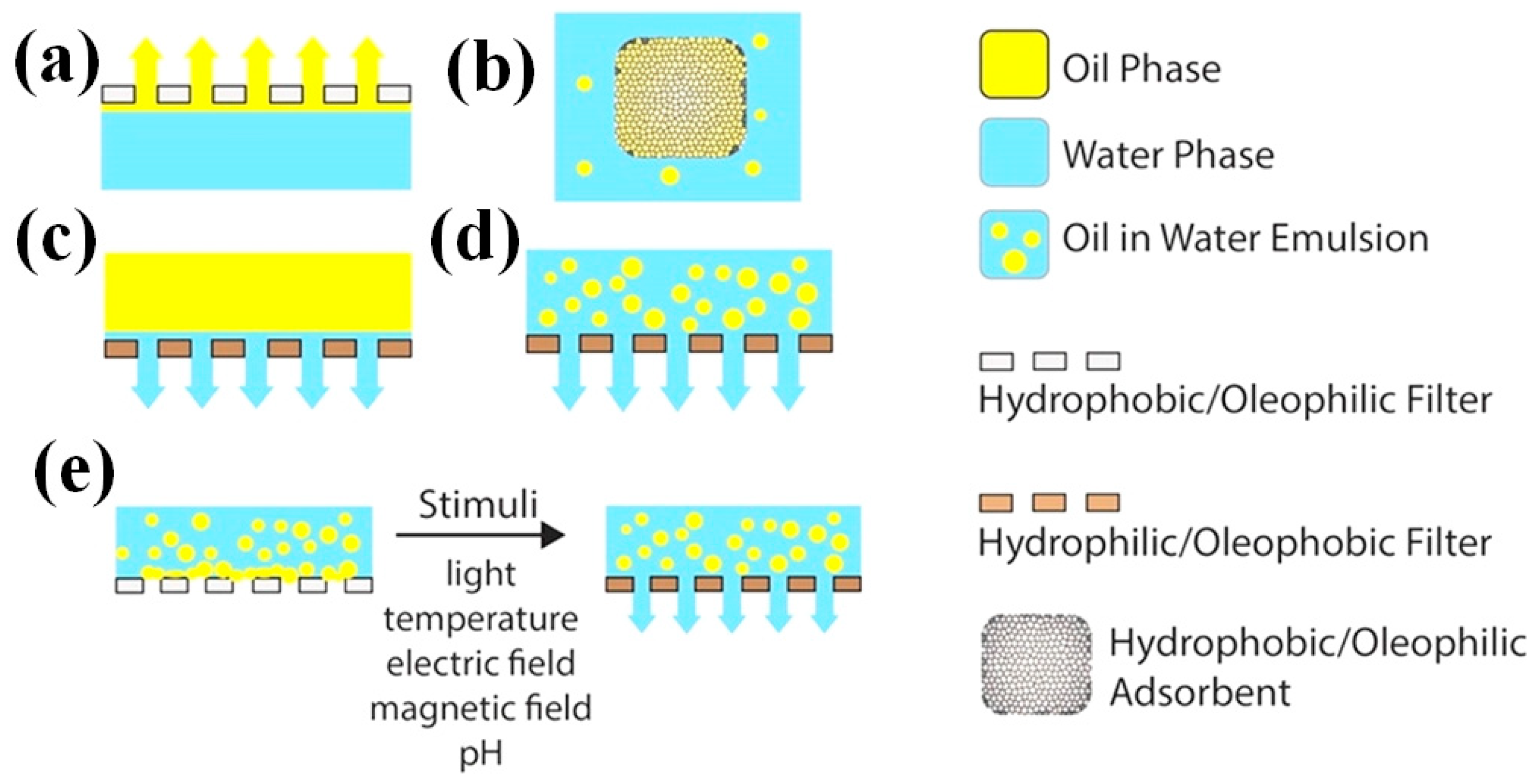
6.1. Oil-water Separation
6.2. pH-responsive Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.X.; Elimelech, M.; Lin, S.H. Environmental Applications of Interfacial Materials with Special Wettability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2132–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falde, E.J.; Yohe, S.T.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Superhydrophobic materials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siow, K.S.; Kumar, S.; Griesser, H.J. Low-Pressure Plasma Methods for Generating Non-Reactive Hydrophilic and Hydrogel-Like Bio-Interface Coatings—A Review. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Applications of bio-inspired special wettable surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifa, F.; Ershov, S.; Habibi, Y.; Snyders, R.; Dubois, P. Free-Radical-Induced Grafting from Plasma Polymer Surfaces. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3975–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denes, F. Macromolecular plasma-chemistry: An emerging field of polymer science. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 815–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odian, G. Principles of Polymerization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Ozaydin-Ince, G.; Coclite, A.M.; Gleason, K.K. CVD of polymeric thin films: Applications in sensors, biotechnology, microelectronics/organic electronics, microfluidics, MEMS, composites and membranes. Rep. Prog. Phys. Phys. Soc. 2012, 75, 016501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, R.; Gleason, K.K. Overview of Strategies for the CVD of Organic Films and Functional Polymer Layers. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2009, 15, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J. Mechanisms of Plasma Polymerization—Reviewed from a Chemical Point of View. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011, 8, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, A.; Neyts, E.; Gijbels, R.; van der Mullen, J. Gas discharge plasmas and their applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2002, 57, 609–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H. Glow discharge polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Macromol. Rev. 1981, 16, 199–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizer, Y.P.; Shneider, M.N.; Yatsenko, N.A. Radio-Frequency Capacitive Discharges; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jérôme, P.; Jacques, S.; Christoph, H.; Alan, H.; Laurent, S. The physics of plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition for large-area coating: Industrial application to flat panel displays and solar cells. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2000, 42, B353. [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki, N. Plasma Surface Modification and Plasma Polymerization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Bell, A.T. A Review of Recent Advances in Plasma Polymerization. Plasma Polym. 1979, 108, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Arora, B.; Choi, E.H. Utility of plasma: A new road from physics to chemistry. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelmore, A.; Steele, D.A.; Whittle, J.D.; Bradley, J.W.; Short, R.D. Nanoscale deposition of chemically functionalised films via plasma polymerisation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förch, R.; Zhang, Z.; Knoll, W. Soft Plasma Treated Surfaces: Tailoring of Structure and Properties for Biomaterial Applications. Plasma Process. Polym. 2005, 2, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J. Pulsed-Plasma Polymerization. In The Plasma Chemistry of Polymer Surfaces; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Chapter 12; pp. 377–456. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, H.; Hsu, T. Some aspects of plasma polymerization investigated by pulsed RF discharge. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1977, 15, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaraj, S.; Oran, U.; Friedrich, J.F.; Lippitz, A.; Unger, W.E.S. Surface Chemical Analysis of Plasma-Deposited Copolymer Films Prepared from Feed Gas Mixtures of Ethylene or Styrene with Allyl Alcohol. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, H.-G. Macromolecules: Volume 2: Synthesis, Materials, and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Förster, S.; Antonietti, M. Amphiphilic Block Copolymers in Structure-Controlled Nanomaterial Hybrids. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.J.; Jiang, L. Design and Creation of Superwetting/Antiwetting Surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspired superoleophobic and smart materials: Design, fabrication, and application. Prog. Mater Sci. 2013, 58, 503–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimittrakoolchai, O.U.; Supothina, S. Deposition of organic-based superhydrophobic films for anti-adhesion and self-cleaning applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.J. Contact angle, wetting, and adhesion: A critical review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1992, 6, 1269–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.N.; Birjandi, F.C.; Sargolzaei, J. Super-non-wettable surfaces: A review. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 448, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.T.; Wu, F.L.; Chen, W.Y. Super water- and oil-repellencies from silica-based nanocoatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 3377–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.J.; Zheng, Y.M.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Super-antiwetting Interfaces with Special Liquid-Solid Adhesion. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.J.; Wang, S.T.; Wei, Z.X.; Song, Y.L.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Design of a Superoleophobic and Low Adhesive Water/Solid Interface. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extrand, C.W. Water contact angles and hysteresis of polyamide surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 248, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quéré, D. Wetting and Roughness. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Solid-Surface Characterization by Wetting. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2009, 39, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.T.; Chen, J.M.; Kuo, R.R.; Lin, T.S.; Wu, C.F. Influence of surface roughness on water- and oil-repellent surfaces coated with nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 240, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Francone, A.; Thamdrup, L.H.; Johanson, A.; Bilenberg, B.; Nielsen, T.; Guttmann, M.; Torres, C.M.S.; Kehagias, N. Design of Hierarchical Surfaces for Tuning Wetting Characteristics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7701–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Bhushan, B. Hierarchical roughness optimization for biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces. Ultramicroscopy 2007, 107, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bico, J.; Thiele, U.; Quéré, D. Wetting of textured surfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 206, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jai, C.; Ferencz, S.D.; Richard, B.T. Plasma Processing Approach to Molecular Surface Tailoring of Nanoparticles: Improved Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J. The Plasma Chemistry of Polymer Surfaces: Advanced Techniques for Surface Design; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kropewnicki, T.J.; Pender, J.T.; Fong, H.; Auglis, C.P.; Hung, R.; Shan, H. Substrate Cleaning Process. Google Patents US6440864B1, 27 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liston, E.M. Plasma treatment for improved bonding: A review. J. Adhes. 1989, 30, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardella, E.; Favia, P.; Gristina, R.; Nardulli, M.; d’Agostino, R. Plasma-Aided Micro-and Nanopatterning Processes for Biomedical Applications. Plasma Process. Polym. 2006, 3, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenka, V.; Miran, M. New developments in surface functionalization of polymers using controlled plasma treatments. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 293001. [Google Scholar]
- Liston, E.M.; Martinu, L.; Wertheimer, M.R. Plasma surface modification of polymers for improved adhesion: A critical review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1993, 7, 1091–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruvenket, S.; Rao, G.M.; Komath, M.; Raichur, A.M. Plasma surface modification of polystyrene and polyethylene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 236, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truica-Marasescu, F.; Wertheimer, M.R. Nitrogen-Rich Plasma-Polymer Films for Biomedical Applications. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, K.; Meyer-Plath, A.; Keller, D.; Besch, W.; Babucke, G.; Ohl, A. Plasma-Induced Surface Functionalization of Polymeric Biomaterials in Ammonia Plasma. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2001, 41, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeda, J.C.; de Mendez, M.; Legeay, G.; Brosse, J.C. Use of low temperature plasmas for polymer surface treatments. Rev. Gen. Electr. (Fr.) 1987, 5, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-K.; Lin, I.K.; Ko, F.-H.; Huang, C.-F.; Chen, K.-S.; Chan, C.-H.; Chang, F.-C. Behavior and surface energies of polybenzoxazines formed by polymerization with argon, oxygen, and hydrogen plasmas. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 4063–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Kim, K.S.; Park, C.E.; Ryu, C.M. Improvement of wettability and reduction of aging effect by plasma treatment of low-density polyethylene with argon and oxygen mixtures. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2002, 16, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.H.; Liu, C.C.; Park, S.M.; Jiang, H.Q.; Nealey, P.F.; Wendt, A.E. Surface Roughening of Polystyrene and Poly(methyl methacrylate) in Ar/O-2 Plasma Etching. Polymers 2010, 2, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.M.; Ko, T.M.; Hiraoka, H. Polymer surface modification by plasmas and photons. Surf. Sci. Rep. 1996, 24, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-P.; Yasuda, H. Ultrathin coating of plasma polymer of methane applied on the surface of silicone contact lenses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1988, 22, 919–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, F.G.; Granger, D.D.; Schmitz, A.E.; Miller, L.A. Plasma-polymerized films as moisture barriers for alkali halide optics. Thin Solid Films. 1981, 84, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.K.S.; Bico, J.; Teo, K.B.K.; Chhowalla, M.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Milne, W.I.; McKinley, G.H.; Gleason, K.K. Superhydrophobic Carbon Nanotube Forests. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, S.R.; Woodward, I.S.; Badyal, J.P.S.; Brewer, S.A.; Willis, C. Ultralow surface energy plasma polymer films. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teare, D.O.H.; Spanos, C.G.; Ridley, P.; Kinmond, E.J.; Roucoules, V.; Badyal, J.P.S.; Brewer, S.A.; Coulson, S.; Willis, C. Pulsed Plasma Deposition of Super-Hydrophobic Nanospheres. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4566–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasirci, N. Silicone polymerization by glow discharge application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 34, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasirci, N. Surface modification of charcoal by glow-discharge: The effect on blood cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1987, 34, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieg, K.W.; Wischmann, K.B. Plasma-polymerized organosilanes as protective coatings for solar front-surface mirrors. Sol. Energy Mater. 1980, 3, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Hirao, H. Plasma polymers containing sulfonate groups. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1987, 25, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Tasaka, S.; Yamada, Y. Plasma polymerization of cyano compounds. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1992, 30, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotsu, T. Cyano and Analogous Groups in Plasma Polymers from Nitrogen Monomers. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A—Chem. 1981, 15, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Oh-Ishi, K. Preparation of amino group-containing polymers by plasma polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1985, 23, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangindaan, D.; Kuo, W.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, S.-L.; Liu, H.-C.; Wang, M.-J. Plasma polymerization of amine-containing thin films and the studies on the deposition kinetics. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancarz, I.; Poźniak, G.; Bryjak, M.; Tylus, W. Modification of polysulfone membranes 5. Effect of n-butylamine and allylamine plasma. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaraj, S.; Oran, U.; Lippitz, A.; Unger, W.E.S. Surface Chemical Analysis of Plasma-Deposited Copolymer Films Prepared from Feed Gas Mixtures of Ethylene or Styrene with Allylamine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.A.; Wydeven, T.; Cormia, R.D. Plasma copolymerization of ethylene and tetrafluoroethylene. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1992, 30, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leezenberg, P.B.; Reiley, T.C.; Tyndall, G.W. Plasma induced copolymerization of hexafluoropropylene and octafluoropropane. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1999, 17, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Eyink, K.; Grant, J.T.; Enlow, J.; Tullis, S.; Bunning, T.J. PECVD Siloxane and Fluorine-Based Copolymer Thin Films. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2008, 14, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.J.; Jones, F.R.; Short, R.D. Plasma copolymerization as a route to the fabrication of new surfaces with controlled amounts of specific chemical functionality. Polymer 1996, 37, 5537–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.J.; Whittle, J.D.; Bullett, N.A.; Eves, P.; Mac Neil, S.; McArthur, S.L.; Shard, A.G. Plasma co-polymerisation of two strongly interacting monomers: Acrylic acid and allylamine. Plasma Process. Polym. 2005, 2, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotsu, T.; Tagaki, C.; Partridge, A. Plasma Copolymerization of Acrylic Acid with Hexamethyldisilazane. Plasmas Polym. 2002, 7, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, A.; Mix, R.; Schönhals, A.; Friedrich, J. Structure of Plasma-Deposited Copolymer Films Prepared from Acrylic Acid and Styrene: Part I Dependence on the Duty Cycle. Plasma Process. Polym. 2012, 9, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, A.; Mix, R.; Schönhals, A.; Friedrich, J. Structure of Plasma-Deposited Copolymer Films Prepared from Acrylic Acid and Styrene: Part II Variation of the Comonomer Ratio. Plasma Process. Polym. 2013, 10, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, C.; Poncin-Epaillard, F.; Debarnot, D. Plasma Copolymerization of Fluorinated and Acrylate Monomers: Kinetics and Chemical Structure Study. Plasma Process. Polym. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuma, A.; Quere, D. Superhydrophobic states. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Hill, R.M. Superhydrophobic surfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, E.; Dilks, A. Plasma polymerization of fluorocarbons in rf capacitively coupled diode system. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1981, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Hsu, T.S. Some aspects of plasma polymerization of fluorine-containing organic compounds. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1977, 15, 2411–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.-J.; Lee, Y. Characterization of fluorocarbon thin films deposited by ICP and PP. J. Surf. Anal. 2011, 17, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Furuya, K.; Nakanishi, R.; Okumura, H.; Makita, M.; Harata, A. Influence of substrate type on surface structure of polymeric perfluorocarbon in the initial stage of deposition in Ar/c-C4F8 plasmas. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 6028–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mundo, R.; De Benedictis, V.; Palumbo, F.; d’Agostino, R. Fluorocarbon plasmas for nanotexturing of polymers: A route to water-repellent antireflective surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5461–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsougeni, K.; Vourdas, N.; Tserepi, A.; Gogolides, E.; Cardinaud, C. Mechanisms of oxygen plasma nanotexturing of organic polymer surfaces: From stable super hydrophilic to super hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2009, 25, 11748–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.T.; Malkov, G.S.; Butoi, C.I.; Fisher, E.R. Comparison of pulsed and downstream deposition of fluorocarbon materials from C3F8 and c-C4F8 plasmas. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2004, 22, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelle, C.B.; Opila, R.; Kornblit, A. Plasma deposition of fluorocarbon thin films from c-C4F8 using pulsed and continuous rf excitation. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2005, 23, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelle, C.B.; Gleason, K.K. Pulsed plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition from CH2F2, C2H2F4, and CHClF2. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 1999, 17, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelle, C.B.; Limb, S.J.; Gleason, K.K. Electron spin resonance of pulsed plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposited fluorocarbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 82, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Träubel, H. Hydrophilic Polymers. In New Materials Permeable to Water Vapor; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 133–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Sunderland, B.; Xue, J.; Yan, S.; Zhao, W.; Folkard, M.; Michael, B.D.; Wang, Y. Study on hydrophilicity of polymer surfaces improved by plasma treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 3375–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkan, C.K.; Hammadeh, M.; Brück, S.; Park, H.W.; Veith, M.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Aktas, C. Plasma and short pulse laser treatment of medical grade PEEK surfaces for controlled wetting. Mater. Lett. 2013, 109, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Hatakeyama, T. Interaction between water and hydrophilic polymers. Thermochim. Acta 1998, 308, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, C.A. Hydrophilic polymers. In Specialty Polymers; Dyson, R.W., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Allméar, K.; Hult, A.; Rårnby, B. Surface modification of polymers. I. Vapour phase photografting with acrylic acid. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1988, 26, 2099–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Plummer, C.; Bisson, I.; Frey, P.; Hilborn, J. Plasma-induced graft polymerization of acrylic acid onto poly(ethylene terephthalate) films: Characterization and human smooth muscle cell growth on grafted films. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarratta, V.; Vohrer, U.; Hegemann, D.; Müller, M.; Oehr, C. Plasma functionalization of polypropylene with acrylic acid. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 174–175, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Tatoulian, M.; Morscheidt, W.; Arefi-Khonsari, F. Stable plasma polymerized acrylic acid coating deposited on polyethylene (PE) films in a low frequency discharge (70 kHz). React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronin, S.A.; Bradley, J.W.; Fotea, C.; Zelzer, M.; Alexander, M.R. Characterization of thin-film deposition in a pulsed acrylic acid polymerizing discharge. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2007, 25, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, A.; Mix, R.; Schönhals, A.; Friedrich, J.F. Structure of Plasma-Deposited Poly(acrylic acid) Films. Plasma Process. Polym. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, N.J.; Zhang, X.-S.; Chu, S.-G.; Zhu, F.-Y.; Seidel, H.; Zhang, H.-X. Tunable wetting behavior of nanostructured poly(dimethylsiloxane) by plasma combination treatments. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 221601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilgor, I.; Bilgin, S.; Isik, M.; Yilgor, E. Tunable wetting of polymer surfaces. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2012, 28, 14808–14814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Guo, Z. Inspired smart materials with external stimuli responsive wettability: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36623–36641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xia, F.; Sun, T.; Song, W.; Zhao, T.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L. Wettability switching between high hydrophilicity at low pH and high hydrophobicity at high pH on surface based on pH-responsive polymer. Chem. Commun. 2008, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wayland, B.B.; Fryd, M.; Winey, K.I.; Composto, R.J. pH-responsive nanostructures assembled from amphiphilic block copolymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6063–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.N.; Li, J.J.; Luo, Z.H. Toward Efficient Water/Oil Separation Material: Effect of Copolymer Composition on pH-Responsive Wettability and Separation Performance. Aiche J. 2016, 62, 1758–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Feng, L.; Wang, S.; Sun, T.; Song, W.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, L. Dual-Responsive Surfaces That Switch between Superhydrophilicity and Superhydrophobicity. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
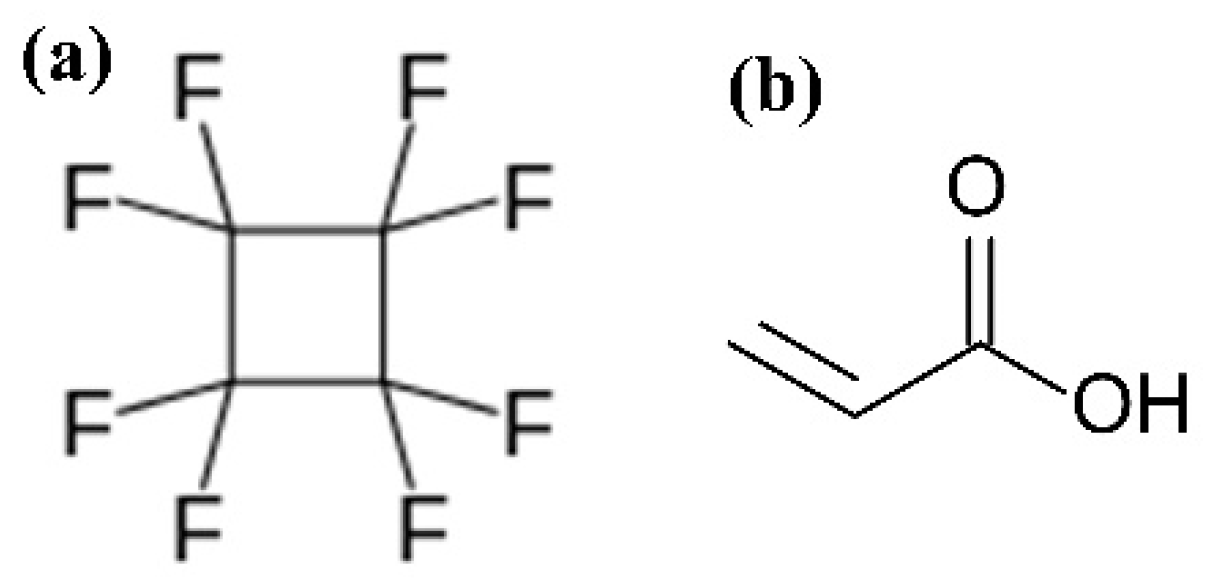
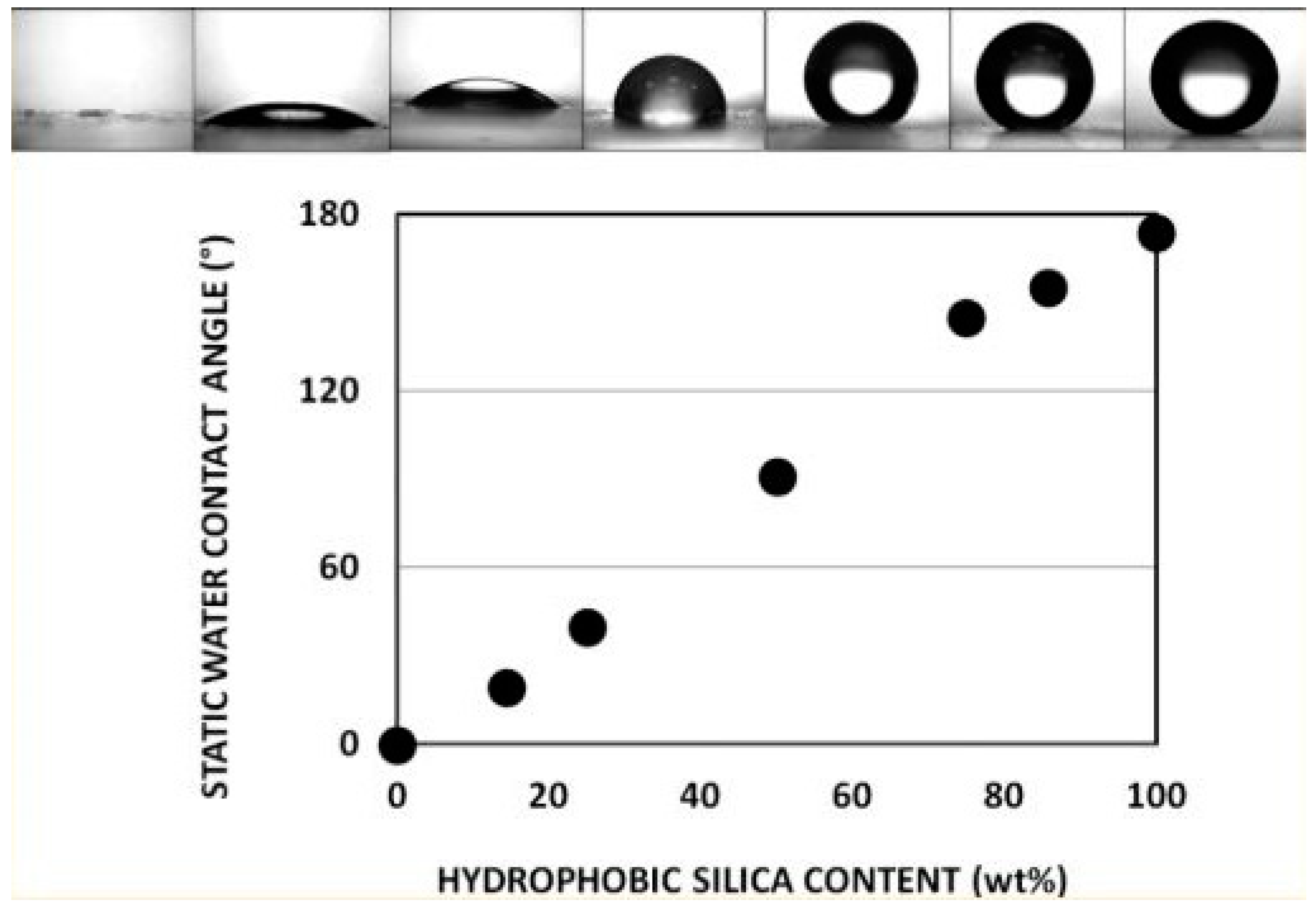
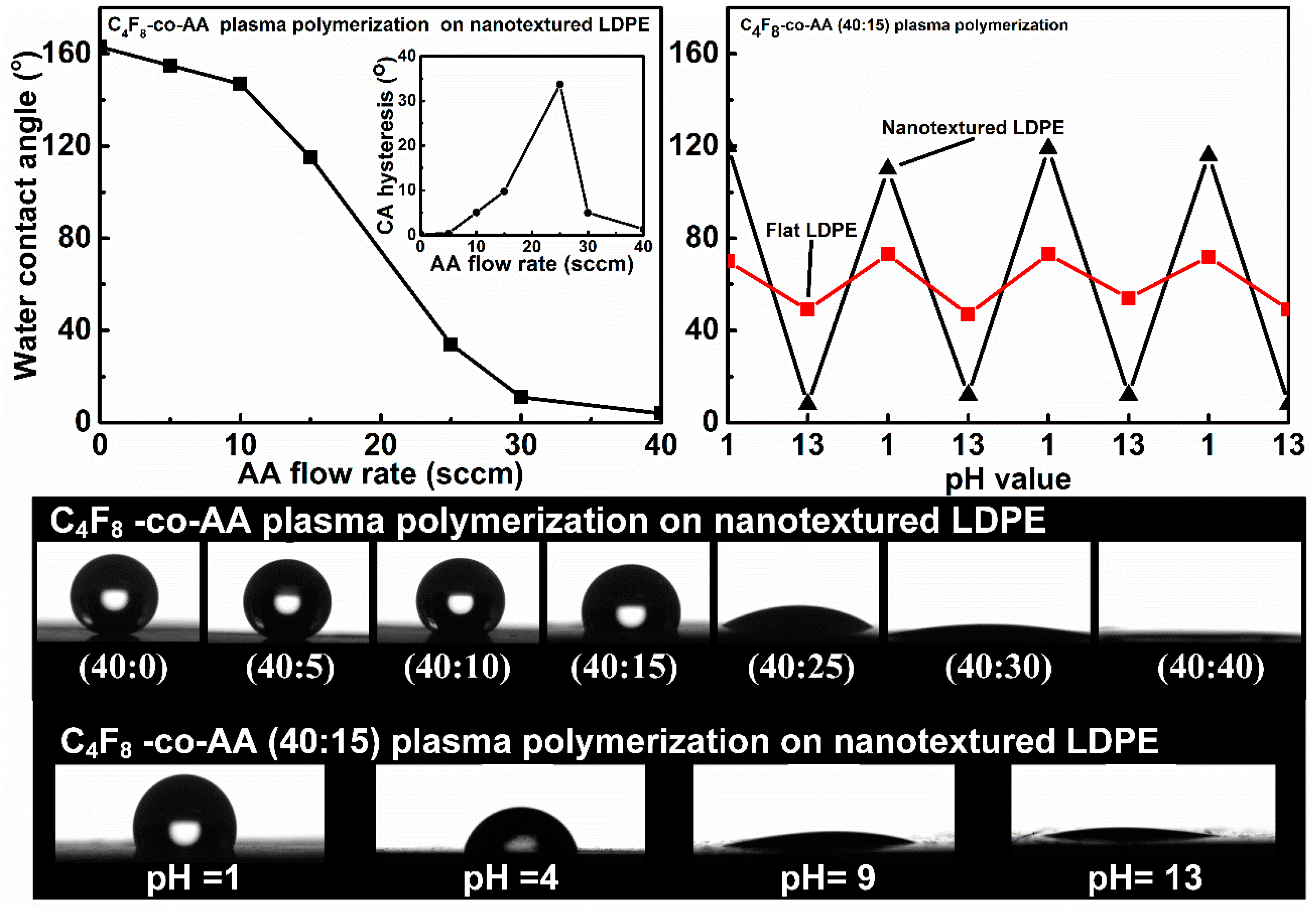
- Muzammil, I.; Li, Y.; Lei, M. Tunable wettability and pH-responsiveness of plasma copolymers of acrylic acid and octafluorocyclobutane. Plasma Process. Polym. 2017, 14, 1700053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammil, I.; Li, Y.; Lei, M. Cover Picture: Multifunctional Smart Polymer Coatings 10/2017. Plasma Process. Polym. 2017, 14, 1770019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammil, I.; Li, Y.P.; Li, X.Y.; Lei, M.K. Duty cycle dependent chemical structure and wettability of RF pulsed plasma copolymers of acrylic acid and octafluorocyclobutane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, N.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Liang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Methodology for Robust Superhydrophobic Fabrics and Sponges from In Situ Growth of Transition Metal/Metal Oxide Nanocrystals with Thiol Modification and Their Applications in Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Seeger, S. Polyester Materials with Superwetting Silicone Nanofilaments for Oil/Water Separation and Selective Oil Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Kota, A.K.; Li, Y.; Sohani, A.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. On-Demand Separation of Oil-Water Mixtures. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3666–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A Novel Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Hydrogel-Coated Mesh for Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Guo, Z. pH-responsive bidirectional oil-water separation material. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9416–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Deng, L.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. PEG-b-PCL Copolymer Micelles with the Ability of pH-Controlled Negative-to-Positive Charge Reversal for Intracellular Delivery of Doxorubicin. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 4281–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.-J.; Dai, Y.-L.; Ma, P.-A.; Yang, D.-M.; Li, C.-X.; Hou, Z.-Y.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; Lin, J. Poly(acrylic acid)-Modified Fe3O4 Microspheres for Magnetic-Targeted and pH-Triggered Anticancer Drug Delivery. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 15676–15682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, R.; Wu, W.; Liu, B.; Jiang, X. Tumor Accumulation, Penetration, and Antitumor Response of Cisplatin-Loaded Gelatin/Poly(acrylic acid) Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Static Water Contact Angle (SWCA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| C2F6 | C3F8 | C4F8 | |
| PW (1kHz) | 103.8 ± 0.2° | 104.4 ± 0.5° | 98.8 ± 0.3° |
| PW (500 Hz) | 106.0 ± 1.0° | 101.5 ± 0.5° | 96.0 ± 0.1° |
| PW (200 Hz) | 74.5 ± 1.5° | 78.5 ± 0.5° | 81.5 ± 0.5° |
| CW | 102.0 ± 0.2° | 101.0 ± 0.5° | 112.0 ± 0.5° |
| Polymer Structural Feature | Water Solubility |
|---|---|
| Chain length increased | Decreases |
| Polar groups ratio increased | Increases |
| Polarity of polar group increased | Increases |
| Cross-linking increased | Decreases |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, M.; Dinh, D.K.; Abbas, Q.; Imran, M.; Sattar, H.; Ul Ahmad, A. Controlled Surface Wettability by Plasma Polymer Surface Modification. Surfaces 2019, 2, 349-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020026
Iqbal M, Dinh DK, Abbas Q, Imran M, Sattar H, Ul Ahmad A. Controlled Surface Wettability by Plasma Polymer Surface Modification. Surfaces. 2019; 2(2):349-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Muzammil, Duy Khoe Dinh, Qasim Abbas, Muhammad Imran, Harse Sattar, and Aqrab Ul Ahmad. 2019. "Controlled Surface Wettability by Plasma Polymer Surface Modification" Surfaces 2, no. 2: 349-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020026
APA StyleIqbal, M., Dinh, D. K., Abbas, Q., Imran, M., Sattar, H., & Ul Ahmad, A. (2019). Controlled Surface Wettability by Plasma Polymer Surface Modification. Surfaces, 2(2), 349-371. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020026