Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of Al alloys: Influence of Material Processing to Improve Surface Roughness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
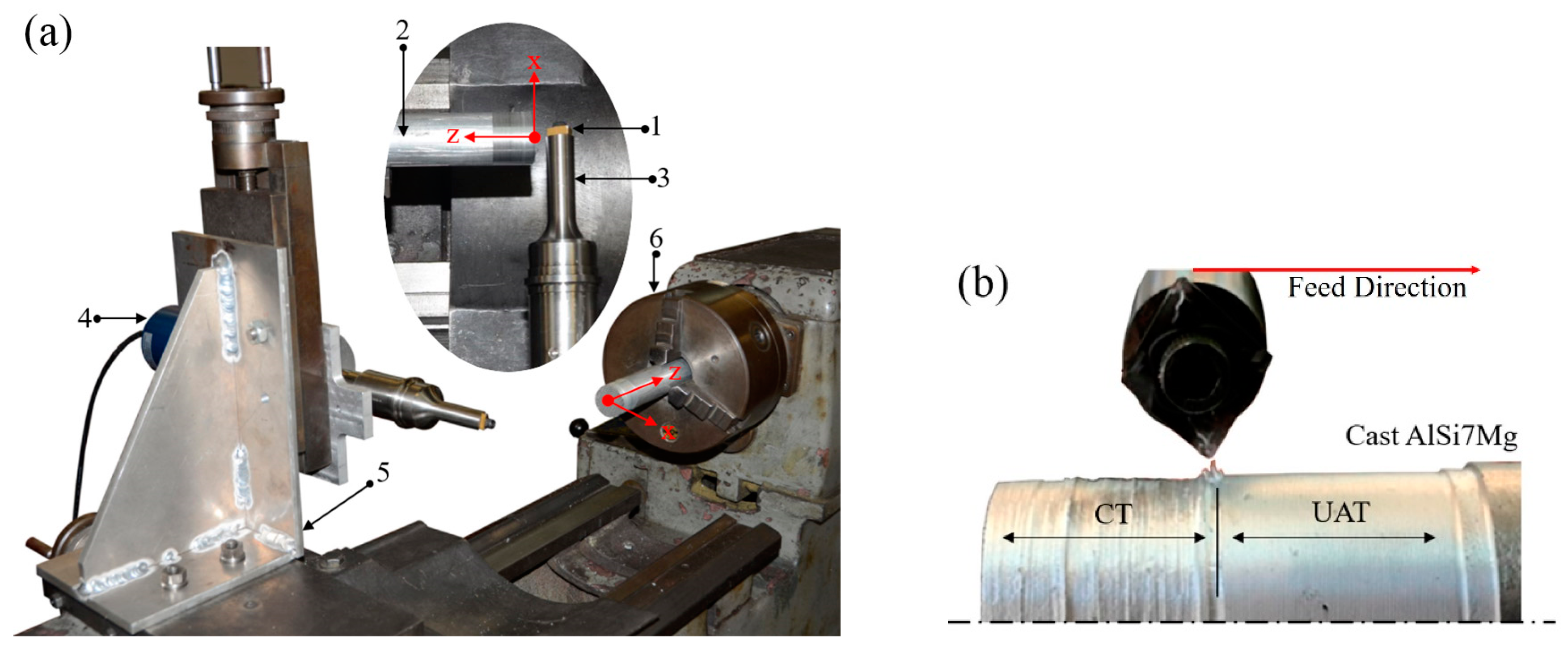
2.1. Experimental Description
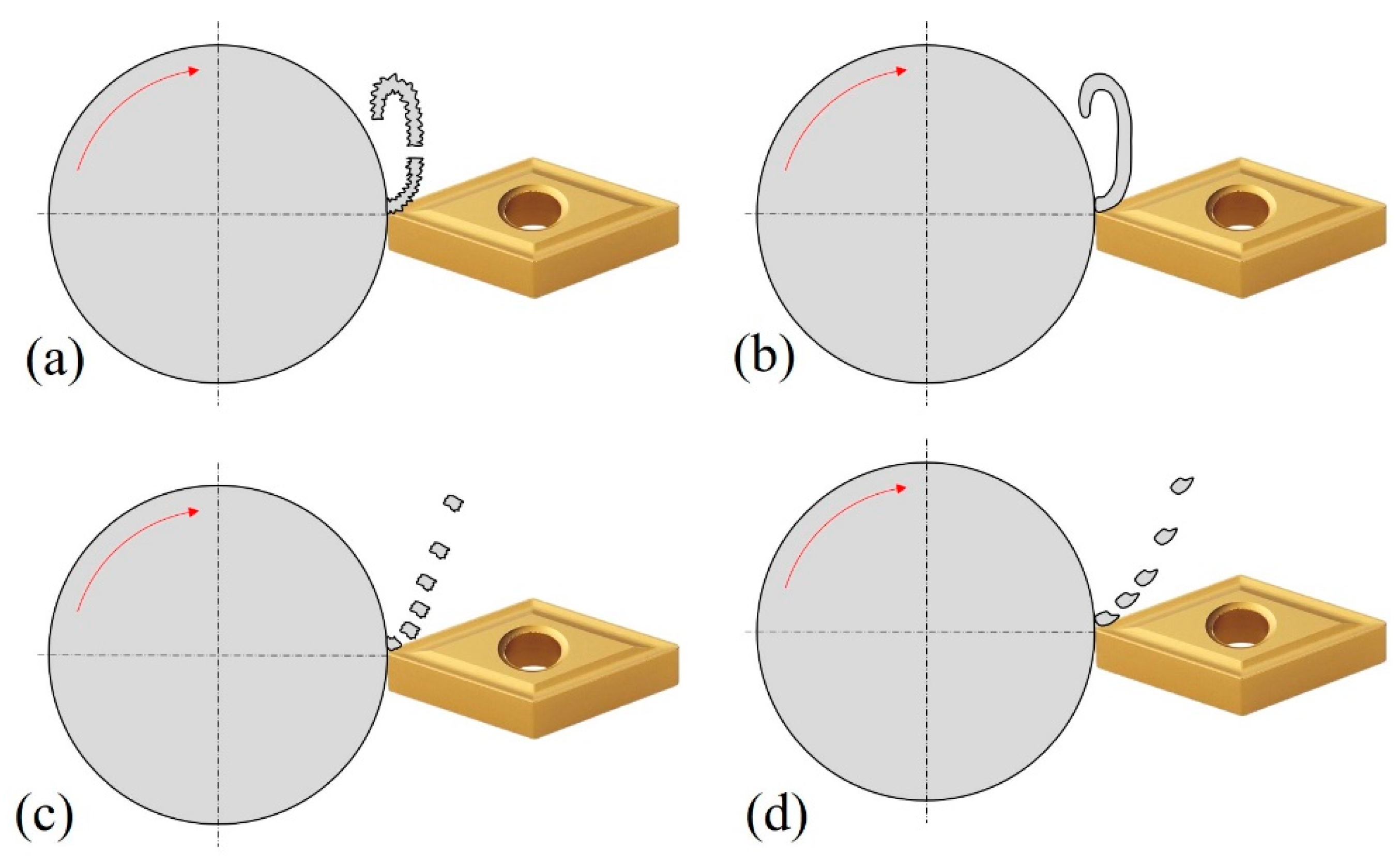
2.2. Specification of the Machining Process
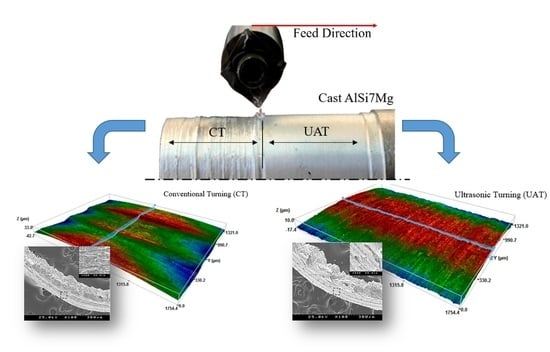
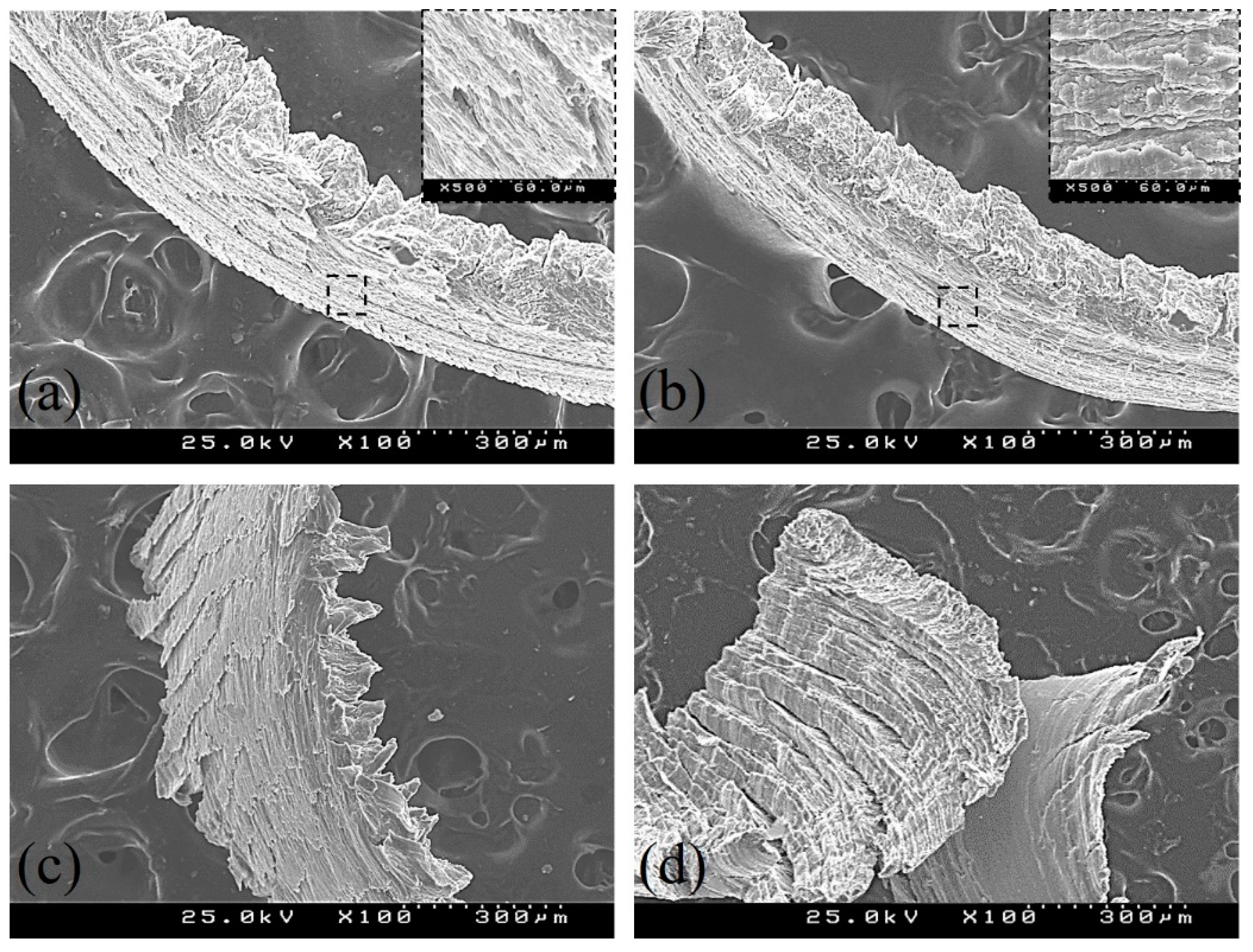
2.3. Post-Experimental Surface Characterization
2.4. Sample Casting and Testing
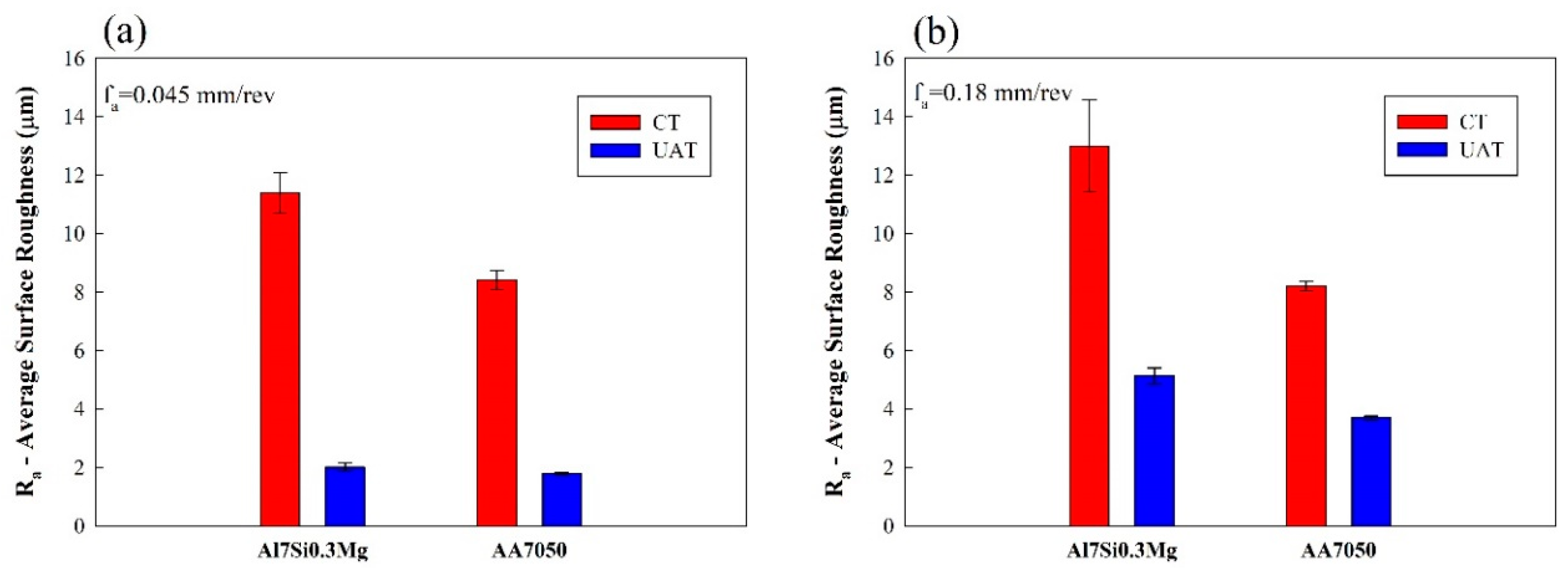
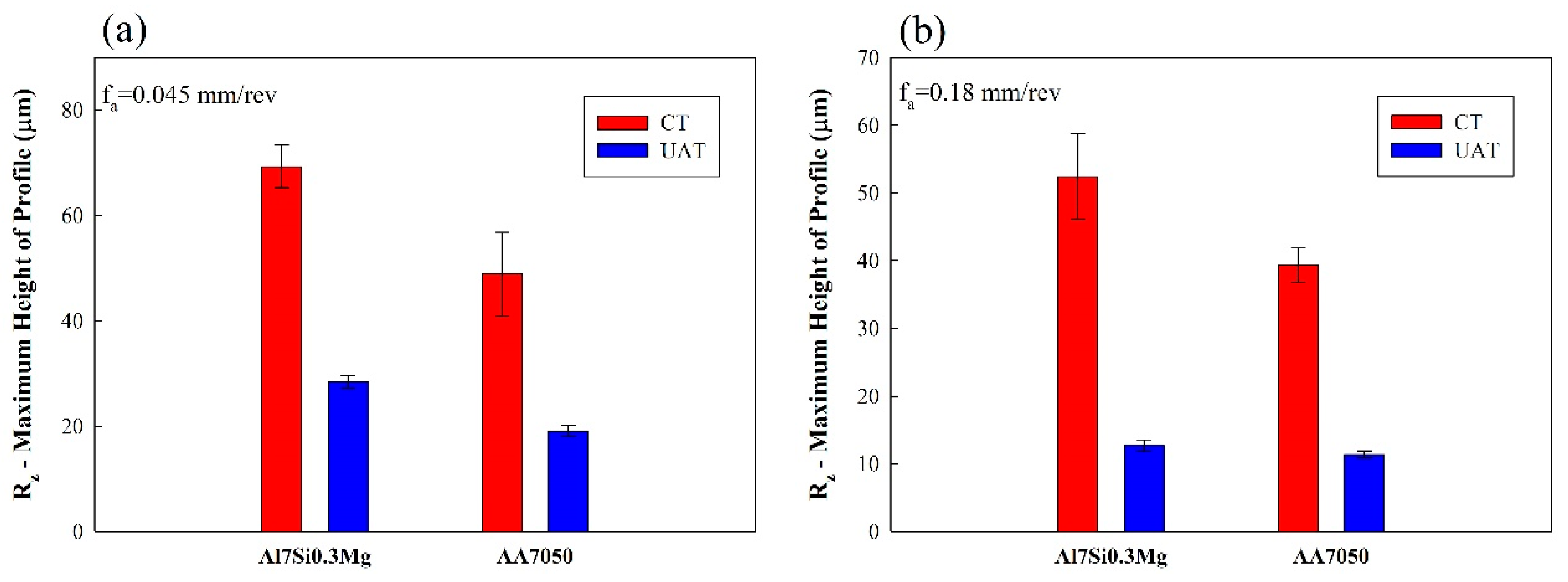
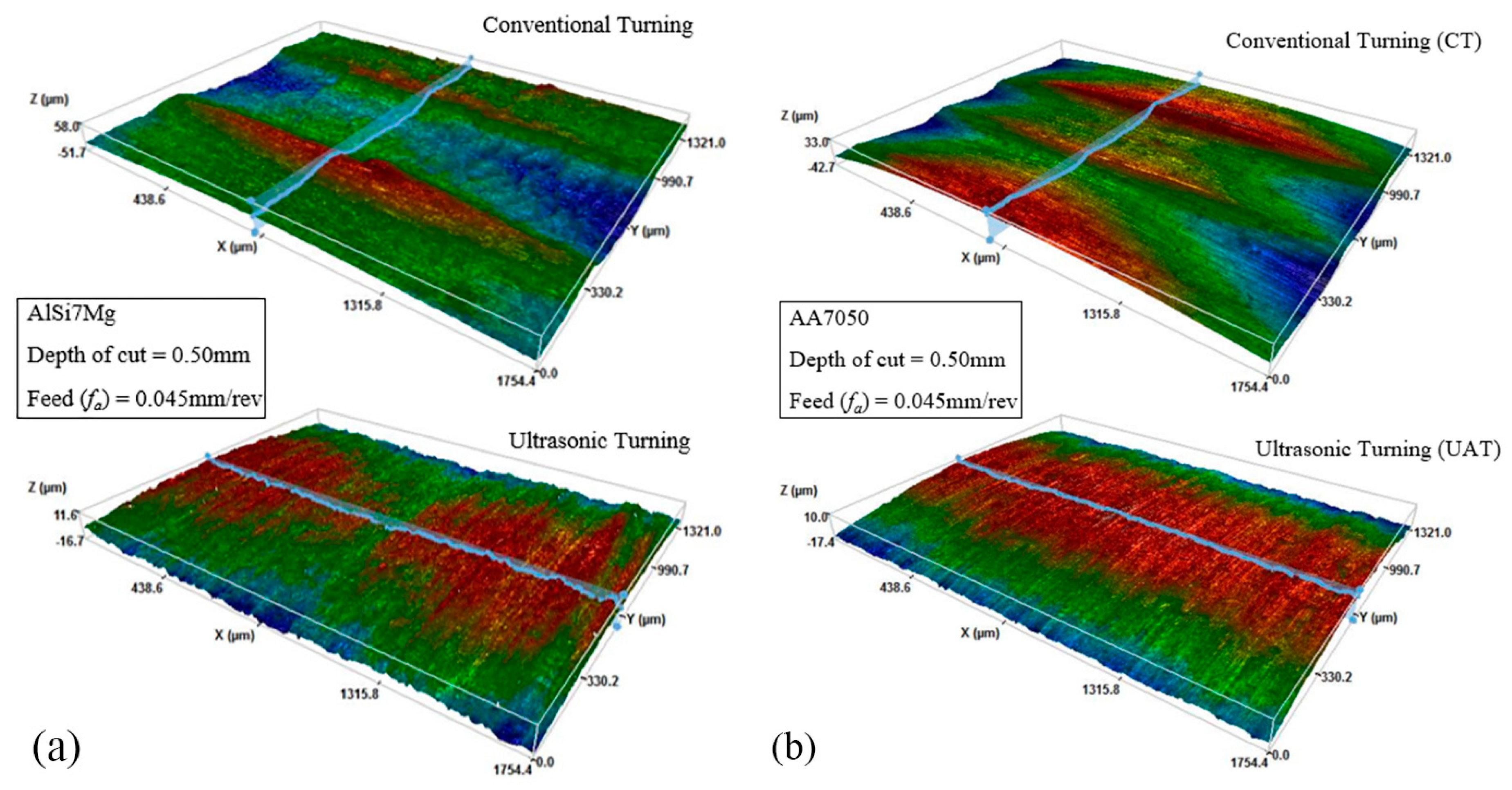
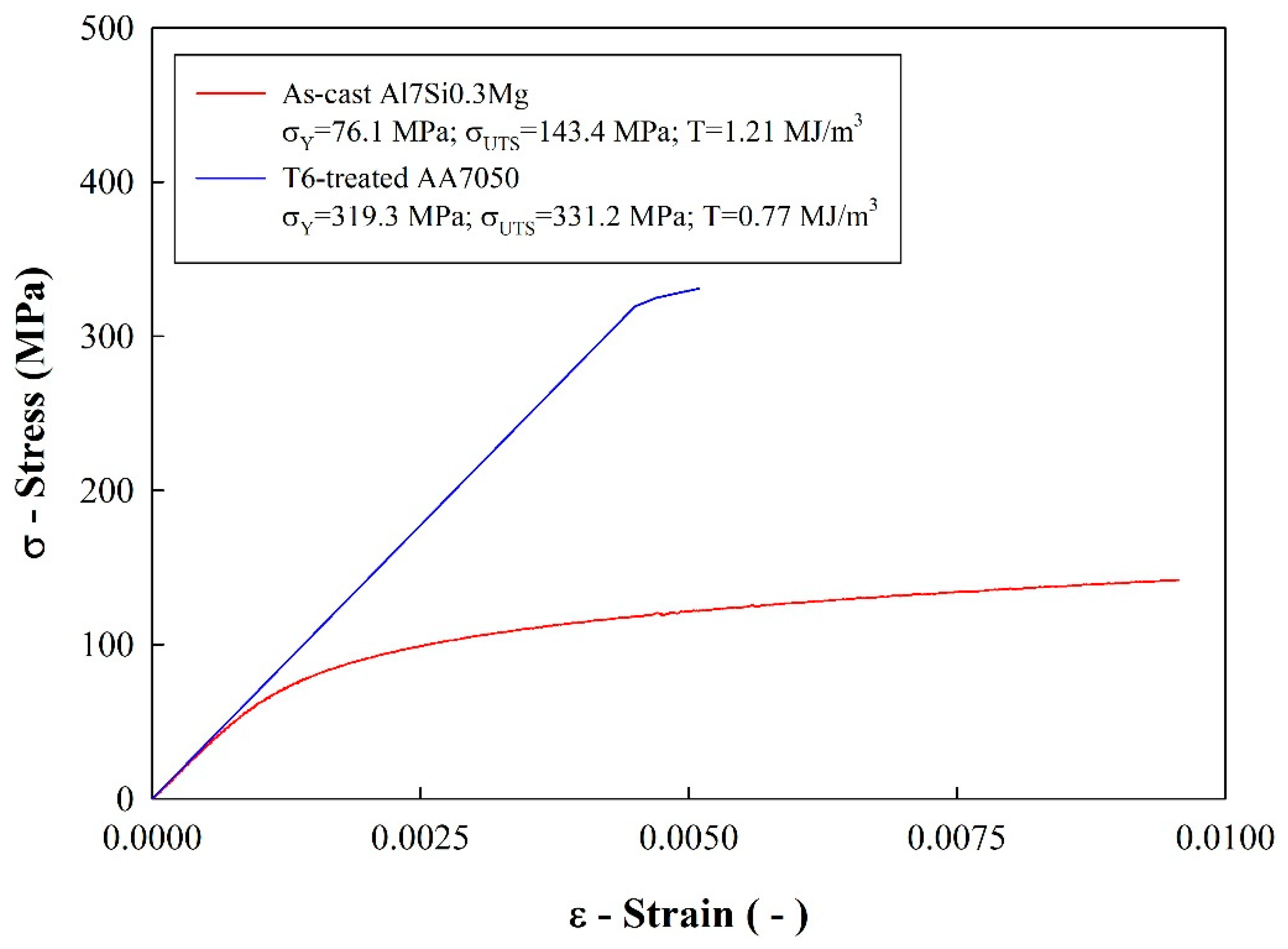
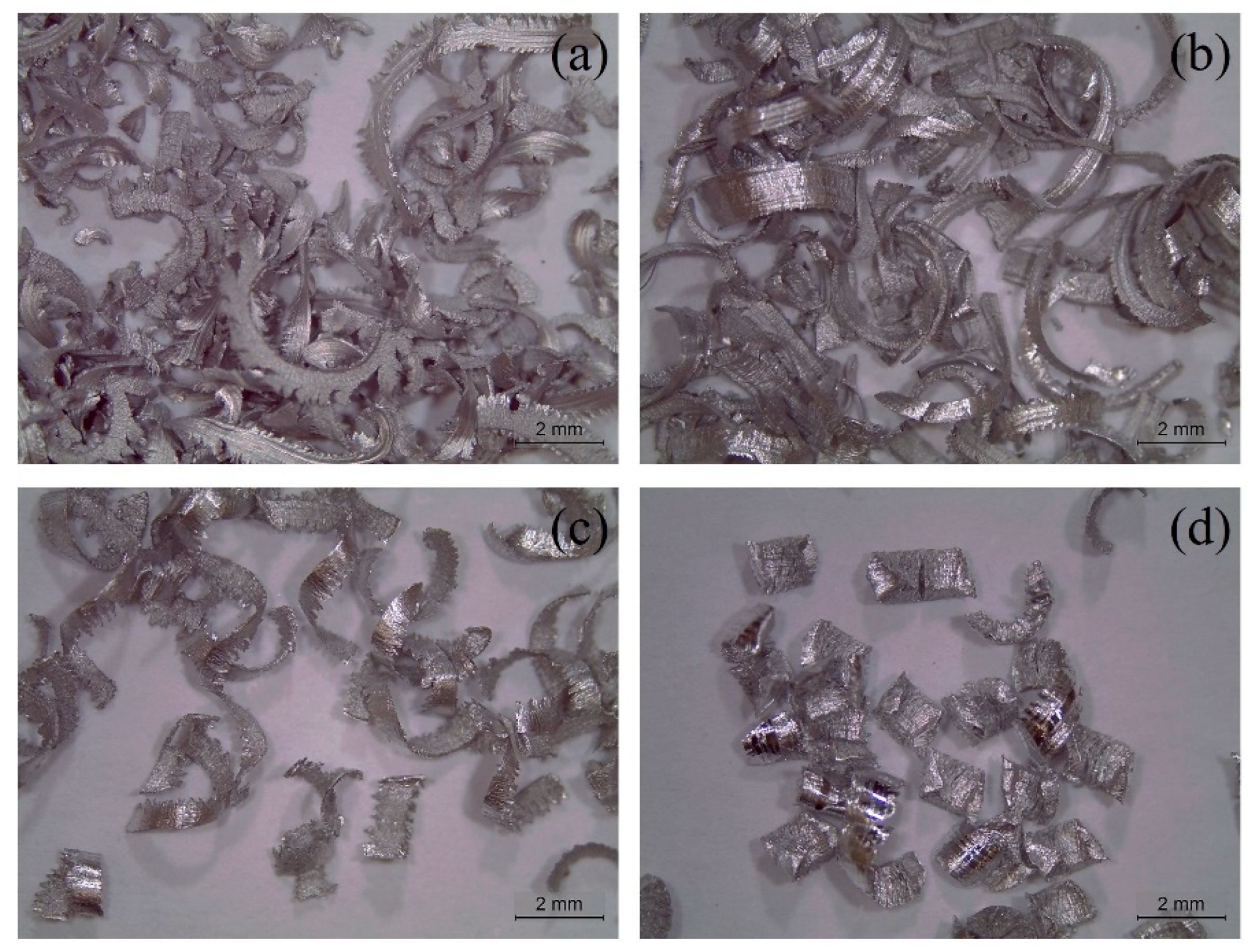
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brehl, D.E.; Dow, T.A. Review of vibration-assisted machining. Precis. Eng. 2008, 32, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.F.; Guo, Z.N.; Lian, H.S.; Liu, J.W.; Yao, Z.; Deng, Y. Experiments and simulations of micro-hole manufacturing by electrophoresis-assisted micro-ultrasonic machining. J. Manuf. Process. Technol. 2019, 264, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J. Ultrasonic machining—A comprehensive review. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2013, 17, 325–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ren, C.; Zou, Y.; Qin, X.; Lu, L.; Li, S. Mechanism for material removal in ultrasonic vibration helical milling of Ti 6Al 4V alloy. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 138, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Jiao, F. Microstructure of High-Performance Aluminum Alloy Surface Processed by the Single-Excitation Same-Frequency Longitudinal—Torsional Coupled Ultrasonic Vibration Milling. Materials 2018, 11, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted metal forming: Constitutive modelling of acoustoplasticity and applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 265, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaie, M.; Zahedi, A.; Akbari, J. Effect of Water-Based Nanolubricants in Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Grinding. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, H.; Grilo, J.; Oliveira, F.J.; Silva, R.F.; Girão, A.V. Influence of external loading on the resonant frequency shift of ultrasonic assisted turning: Numerical and experimental analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 101, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, E.D.; Bertolini, R.; Bruschi, S.; Ghiotti, A. Design and development of an ultrasonic vibration assisted turning system for machining bioabsorbable magnesium alloys. Procedia CIRP 2018, 77, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, F.H.; Gurgen, S.; Sofuoglu, M.A.; Celik, O.N.; Kushan, M.C. Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehbudi, P.; Baghlani, V.; Akbari, J.; Bushroa, A.R.; Mardi, N.A. Applying Ultrasonic Vibration to Decrease Drilling-Induced Delamination in GFRP Laminates. Procedia CIRP 2013, 6, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Zhang, J.; Shen, X.; Bai, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, J. Feasibility Study on Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Milling for Squamous Surface. Procedia CIRP 2016, 42, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehl, D.E.; Dow, T.A. Review of Vibration-Assisted Machining Methods for Precision Fabrication; North Carolina State University Raleigh: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Pandey, P.M. Optimization of machining and vibration parameters for residual stresses minimization in ultrasonic assisted turning of 4340 hardened steel. Ultrasonics 2016, 70, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimanimehr, H.; Nategh, M.J.; Najafabadi, A.F.; Zarnani, A. The analysis of the Timoshenko transverse vibrations of workpiece in the ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning process and investigation of the machining error caused by this vibration. Precis. Eng. 2018, 54, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnakian, M.; Razfar, M.R.; Biglari, F.R. Multi-constrained optimization in ultrasonic-assisted turning of hardened steel by electromagnetism-like algorithm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 229, 1933–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, D. Influence of tool material and geometry on micro-textured surface in radial ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 152, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofti, M.; Amini, S.; Aghaei, M. Tool wear modeling in rotary turning modified by ultrasonic vibration. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2018, 87, 226–238. [Google Scholar]
- Lofti, M.; Amini, S.; Aghaei, M. 3D FEM simulation of tool wear in ultrasonic assisted rotary turning. Ultrasonics 2018, 88, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.-X.; Zhang, L.-C. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining: Principle, design and application. Adv. Manuf. 2015, 3, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.-G.; Tie, D. A Review on Grain Refinement of Aluminum Alloys: Progresses, Challenges and Prospects. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2017, 30, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebhota, W.S.; Jen, T.-C. Effects of Modification Techniques on Mechanical Properties of Al-Si Cast Alloys. In Aluminium Alloys—Recent Trends in Processing, Characterization, Mechanical Behavior and Applications; Sivasankaran, S., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3697-2. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, J.; Puga, H. Ultrasonic melt processing in the low pressure investment casting of Al alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 244, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, V.H.; Puga, H.; Meireles, J. Heat treatment as a route to tailor the yield-damping properties in A356 alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 729, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, N.Q.; Puga, H.; Barbosa, J.; Pinto, A.M.P. Grain refinement of Al-Mg-Sc alloy by ultrasonic treatment. Met. Mater. Int. 2015, 21, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.F.; Zhao, B.; Liu, C.S. Research on the influence of the cutting conditions on the surface microstructure of ultra-thin wall parts in ultrasonic vibration cutting. J. Manuf. Process. Technol. 2002, 129, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Pandey, P.M. Recent advances in ultrasonic assisted turning: A step towards sustainability. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1222776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Pandey, P.M. Experimental investigations and statistical modeling of surface roughness during ultrasonic-assisted turning with self-lubricating cutting inserts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Eng. 2018, 232, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, R.; Amini, S.; Mohagheghian, N. Experimental study and empirical analysis on effect of ultrasonic vibration during rotary turning of aluminum 7075 aerospace alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hu, L. Development of an innovative device for ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. Ultrasonics 2015, 60, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, H. Experimental Investigation of Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Turning of 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel. Shock Vib. 2015, 2015, 817598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodrag, P. Multifrequency Ultrasonic Structural Actuators. European Patent EP1238715A1, 11 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, S.; Teimouri, R. Parametric study and multicharacteristic optimization of rotary turning process assisted by longitudinal ultrasonic vibration. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2017, 231, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, I.D.; Rowe, W.B.; Dimitrov, B.; Ohmori, H. Introduction. In Tribology of Abrasive Machining Processes; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 3–12. ISBN 978-1-4377-3467-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, C.; Rahman, M. Effect of machining parameters in ultrasonic vibration cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, R.; Hussain, M.S.; Maurotto, A.; Siemers, C.; Roy, A.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Analysis of a free machining α+β titanium alloy using conventional and ultrasonically assisted turning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, X.; Wu, R. Feasibility study of high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 247, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Rotation per minute, N (rpm) | 760 |
| Depth of cut, ap (mm) | 0.5 |
| Cutting speed, V (m/min) | 60 |
| Feed rate, fa (mm/rev) | 0.045; 0.18 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puga, H.; Grilo, J.; Carneiro, V.H. Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of Al alloys: Influence of Material Processing to Improve Surface Roughness. Surfaces 2019, 2, 326-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020024
Puga H, Grilo J, Carneiro VH. Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of Al alloys: Influence of Material Processing to Improve Surface Roughness. Surfaces. 2019; 2(2):326-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020024
Chicago/Turabian StylePuga, Hélder, José Grilo, and Vitor H. Carneiro. 2019. "Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of Al alloys: Influence of Material Processing to Improve Surface Roughness" Surfaces 2, no. 2: 326-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020024
APA StylePuga, H., Grilo, J., & Carneiro, V. H. (2019). Ultrasonic Assisted Turning of Al alloys: Influence of Material Processing to Improve Surface Roughness. Surfaces, 2(2), 326-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces2020024