Comparison of Linear and Beta Autoregressive Models in Forecasting Nonstationary Percentage Time Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
Preview of the Case Study
2. Statistical Methods
2.1. Linear Models
2.2. Beta Models
2.3. Forecasting
2.4. Non-Stationarity
2.5. Sequential Design
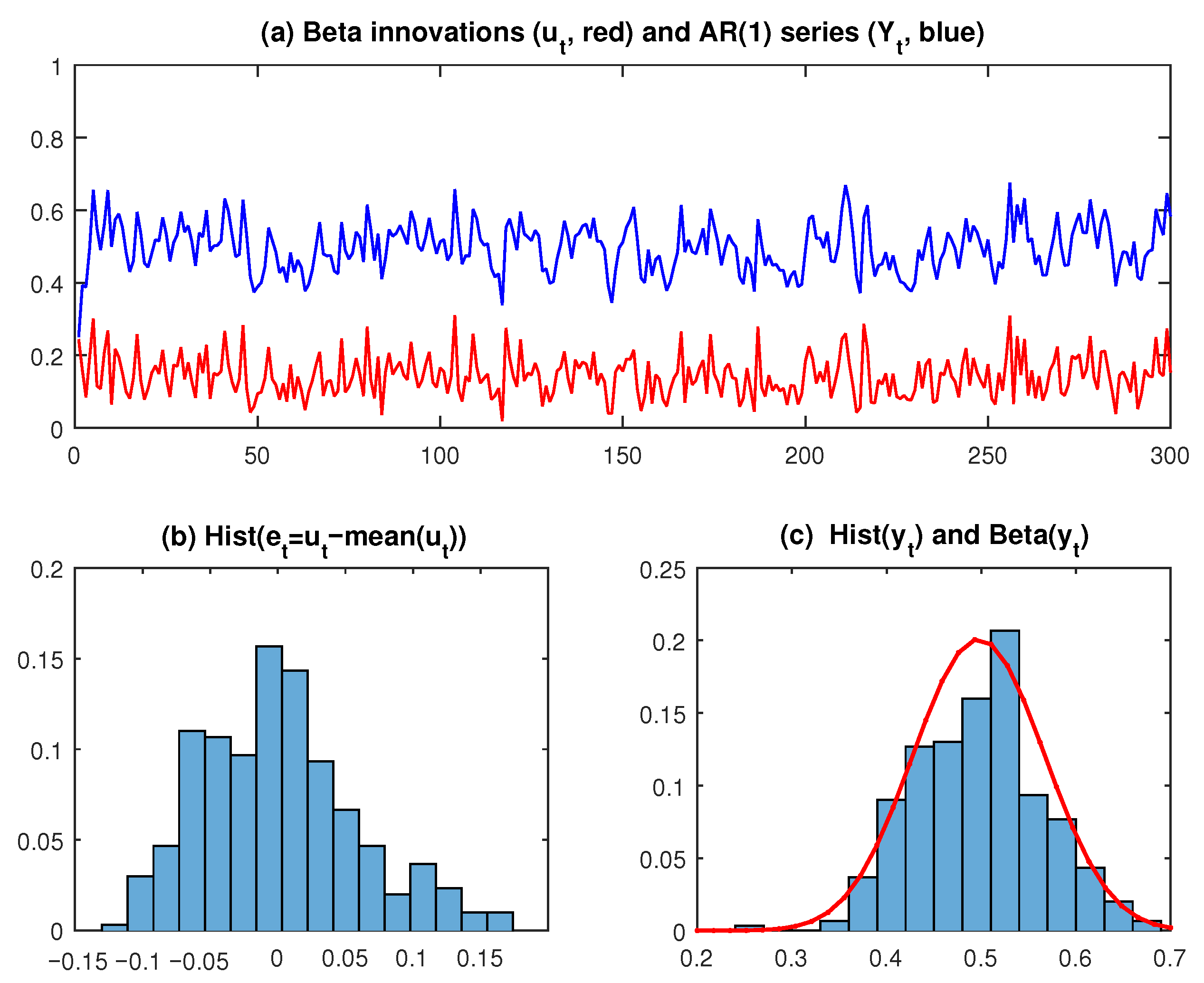
2.6. Simulation Studies
3. Applications to Real Data
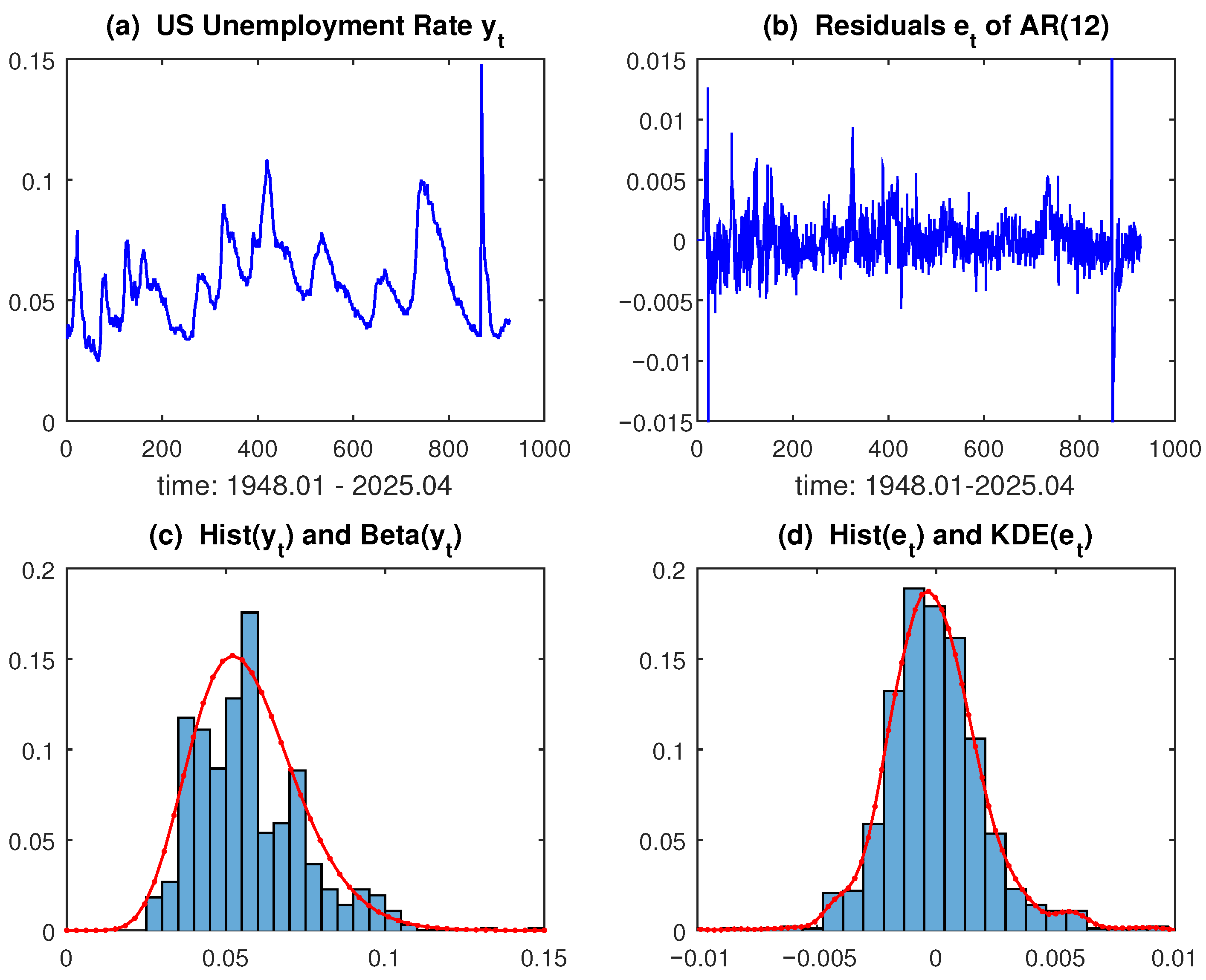
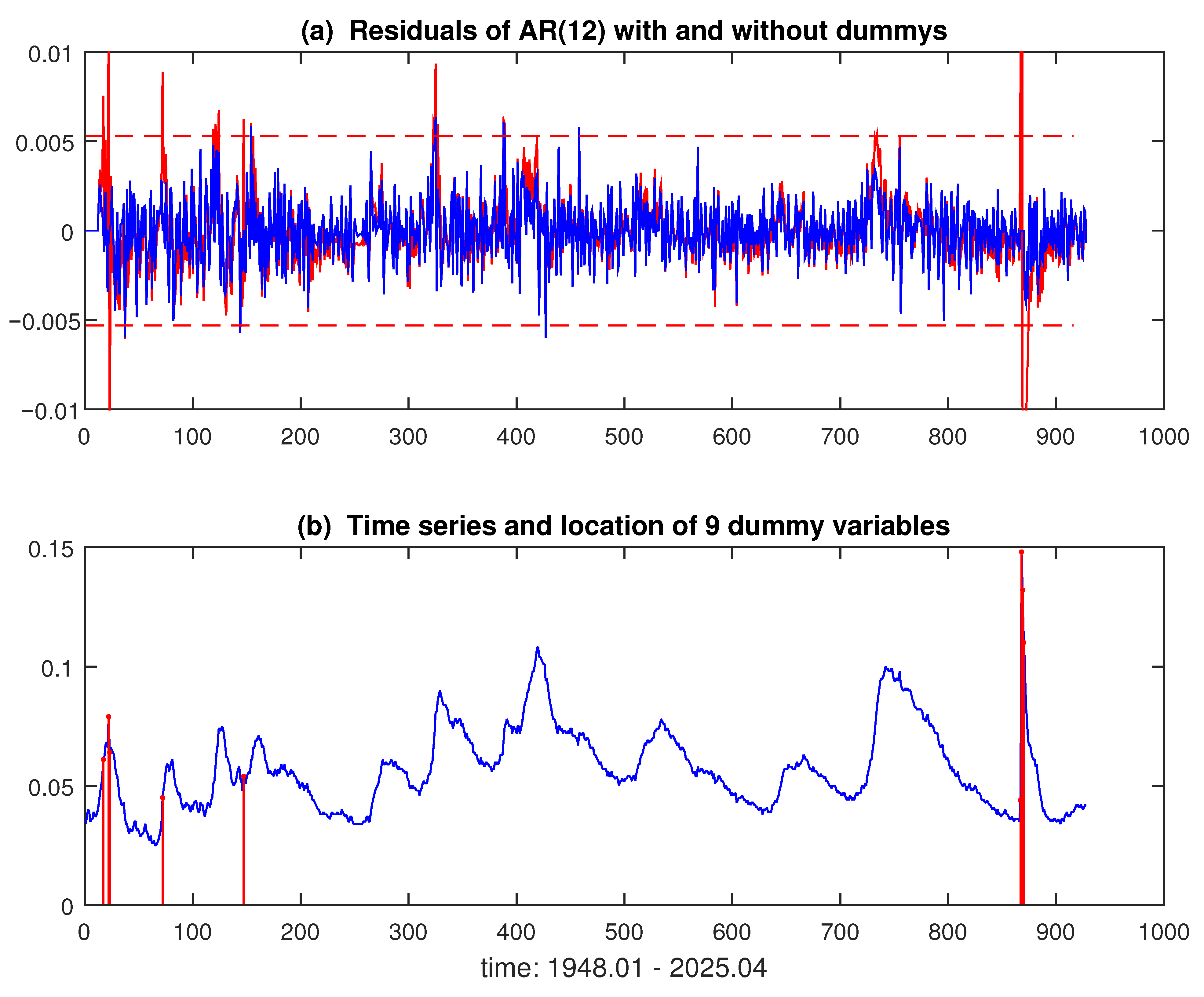
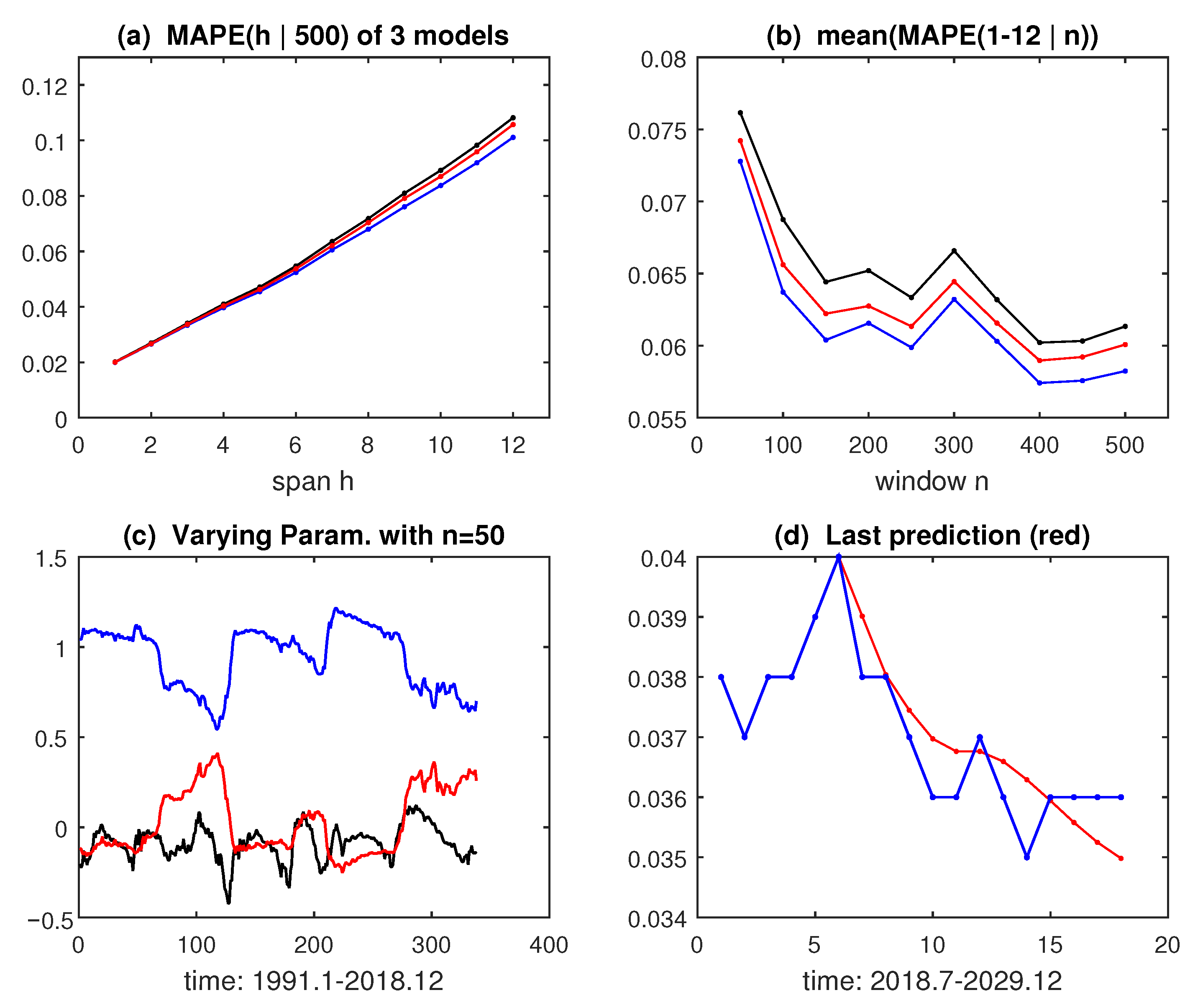
3.1. US Monthly Unemployment Rate
- (1)
- The span H of the predictors (10) is set to one year: ;
- (2)
- The out-of-sample forecasting period starts at = 517 (1991.01);
- (3)
- Models are estimated on , with sample sizes ;
- (4)
- At each , the parameters and forecasts are recomputed;
- (5)
- Prediction statistics are the mean absolute percentage errors (MAPE) (13c).
3.2. BR Hydroelectric Energy Storage
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Computational Aspects
- function [bb, Zb, R2, yf] = ARbeta(y, p, h)% PURPOSE: ML estimation and forecast of an AR(p) model% for stationary data 0 < yt < 1 having a Beta distribution% INPUT: y = n*1 vector of time series data in (0,1)% p = 1,2 … order of the lags of the AR(p)% h = 1,2 … number of forecasts% OUTPUT: bb = ML estimates of parameters% Zb = T-type statistics of significance% R2 = pseudo R-squared index% yf = fitted and forecast values% USAGE: [bb, Zb, R2, yf] = ARbeta(y, 6, 12)n = length(y);yl = log(y./(1-y));X = zeros(n-p,p);for i = 1:pX(:,i) = yl(p-i+1:n-i);endX = [ones(n-p,1), X];bl = inv(X’*X)*(X’*yl(p+1:n));ylo = X*bl;muo= 1./(1+1./exp(ylo));so = sum((yl(p+1:n)-ylo).^2)/(n-2*p-1);pho = mean(1./(so*(muo.*(1-muo))))-1;bo = [ bl; pho ];options = optimset(’MaxFunEvals’,1230,’MaxIter’,1230);[bb,∼,∼,∼,∼,H]= fminunc(@(b) betalike(b, X, y(p+1:n)), bo, options);Vb = diag(pinv(H));Zb = bb./sqrt(abs(Vb));yl1 = X*bb(1:p+1);mu1 = 1./(1+1./exp(yl1));R2 = corr(yl1,yl(p+1:n))^2;ylf = [yl(1:p); yl1; zeros(h,1)];for t = n+1:n+hylf(t) = bb(1)+ flip(bb(2:end-1))’*ylf(t-p:t-1);endyf = exp(ylf)./(1+exp(ylf));sf = std(y-yf(1:n));figure; subplot(211); plot(y,’-b’); hold on; plot(yf,’-r’)title(’(a) Original data Yt (blue), and beta AR fitted values (red)’)subplot(212); plot(yf(n-2*h:n+h),’.-r’); hold on; plot(y(n-2*h:n),’.-b’)plot(yf(n-2*h:n+h)+2*sf,’-k’); plot(yf(n-2*h:n+h)-2*sf,’-k’)title(’(b) Original data Yt (blue), and beta AR forecasts (red)’)xlabel(’Time: T-2h:T+h’)% Likelihood function ----------------------------------------------function ll = betalike(b, X, y)yo = X*b(1:end-1);mu = exp(yo)./(1+exp(yo));phi = b(end);ll = -sum(gammaln(phi) - gammaln(mu*phi) - gammaln((1-mu)*phi) + …(mu*phi-1).*log(y) + ((1-mu)*phi-1).*log(1- y) );
References
- Hurata, A.D. Predicting the unemployment rate using autoregressive integrated moving average. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2024, 11, 2293305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, C.; Oktay, Z.; Birecikli, B.; Bamya, S. Energy and economic analysis of a hydroelectric power plant. Eur. J. Eng. Technol. Res. 2023, 8, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, G.G.; Tang, Q.; Hosseini-Moghari, S.-M.; Liu, X.; Gebremicael, T.G.; Leng, G.; Kebede, A.; Xu, X.; Yun, X. Projected impacts of climate change on drought patterns over East Africa. Earth Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, R.; Berg, M. Forecasting future crime rates. J. Contemp. Crim. Justice 2024, 40, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillenzoni, C. Robust time-series analysis of the effects of environmental factors on the COVID-19 pandemic in the area of Milan (Italy) in the years 2020–2021. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2022, 4, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- East, S.D.; Zahed, M. Forecasting U.S. unemployment rates using ARIMA: A time series analysis from 1948 to 2019. In Proceedings of the SESUG Conference, Washinghton, DC, USA, 22–24 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. Forecasting USA unemployment rate based on ARIMA model. Adv. Econ. Manag. Political Sci. 2023, 49, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Saraf, N.; Bemporad, A. A bounded-variable least-squares solver based on stable QR updates. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 65, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieschnick, R.; McCullough, B.D. Regression analysis of variates observed on (0, 1): Percentages, proportions and fractions. Stat. Model. 2003, 3, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Mansson, K.; Kibria, B.M.G. On some beta ridge regression estimators: Methods, simulation and application. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2021, 91, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillenzoni, C. Forecasting unstable and nonstationary time series. Int. J. Forecast. 1998, 14, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.V.; Cribari-Neto, F. Beta autoregressive moving average models. Test 2009, 18, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Scher, V.; Bayes, F. Beta ARMA selection with application to modeling and forecasting stored hydroelectric energy. Int. J. Forecast. 2023, 39, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeileis, A. Why Use the Logit Link in Beta Regression? 2018. Available online: https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/337115/ (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Scher, V.T.; Cribari-Neto, F.; Bayer, F.M. Generalized ARMA model for double bounded time series forecasting. Int. J. Forecast. 2024, 40, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrot, A.; Pinson, P. On tracking varying bounds when forecasting bounded time series. Technometrics 2024, 66, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics Civilian Unemployment Rate. 2025. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/charts/employment-situation/civilian-unemployment-rate.htm (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 5th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. Asymptotic property of least squares estimators for explosive autoregressive models with a drift. Jour. Econ. Theory Econ. 2021, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- King, G.; Roberts, M.E. How robust standard errors expose methodological problems they do not fix, and What to do about it. Political Anal. 2015, 23, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operador Nacional do Sistema Elétrico Energia Armazenada. 2020. Available online: http://www.ons.org.br/historico/energia_armazenada.aspx (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- De Goeij, W.-J. Beta Regression, Matlab Code. 2009. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/24994 (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Grillenzoni, C. Beta Autoregressive Models for Forecasting Percentage Series. 2025. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/181667 (accessed on 31 August 2025).
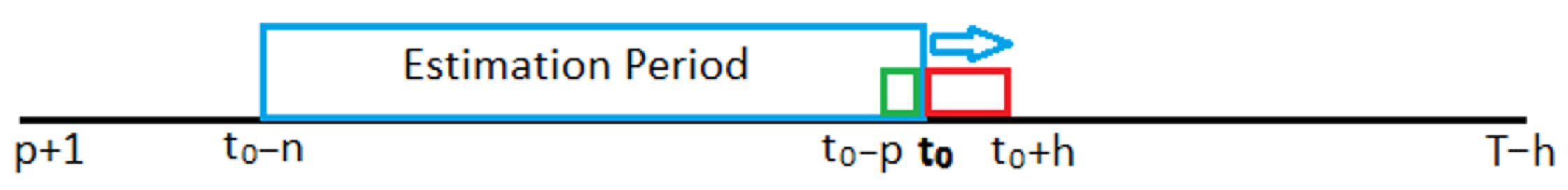



| (15a) | |||||||
| Model | Method | Bias | RMSE | N-test | Bias | RMSE | N-test |
| Linear (1a) | LS (3) | 0.0025 | 0.0255 | 0.133 | −0.0050 | 0.0511 | 0.1350 |
| Hybrid (7b) | LS (3) | −0.2494 | 0.2495 | 0.001 | −0.0074 | 0.0512 | 0.1307 |
| Beta (7c) | ML (9) | −0.2494 | 0.2495 | 0.001 | −0.0141 | 0.0521 | 0.1546 |
| (15b) | |||||||
| Model | Method | Bias | RMSE | N-test | Bias | RMSE | N-test |
| Linear (1a) | LS (3) | 0.0468 | 0.0669 | 0.0284 | 0.0487 | 0.0687 | 0.0326 |
| Hybrid (7b) | LS (3) | −0.0061 | 0.0495 | 0.0010 | −0.0009 | 0.0487 | 0.0010 |
| Beta (7c) | ML (9) | −0.0101 | 0.0493 | 0.0102 | 0.0012 | 0.0472 | 0.0936 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grillenzoni, C. Comparison of Linear and Beta Autoregressive Models in Forecasting Nonstationary Percentage Time Series. Forecasting 2025, 7, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast7040057
Grillenzoni C. Comparison of Linear and Beta Autoregressive Models in Forecasting Nonstationary Percentage Time Series. Forecasting. 2025; 7(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast7040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrillenzoni, Carlo. 2025. "Comparison of Linear and Beta Autoregressive Models in Forecasting Nonstationary Percentage Time Series" Forecasting 7, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast7040057
APA StyleGrillenzoni, C. (2025). Comparison of Linear and Beta Autoregressive Models in Forecasting Nonstationary Percentage Time Series. Forecasting, 7(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast7040057