Mean Field Bias-Aware State Updating via Variational Assimilation of Streamflow into Distributed Hydrologic Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model and Data Assimilation
2.1. Hydrological Model
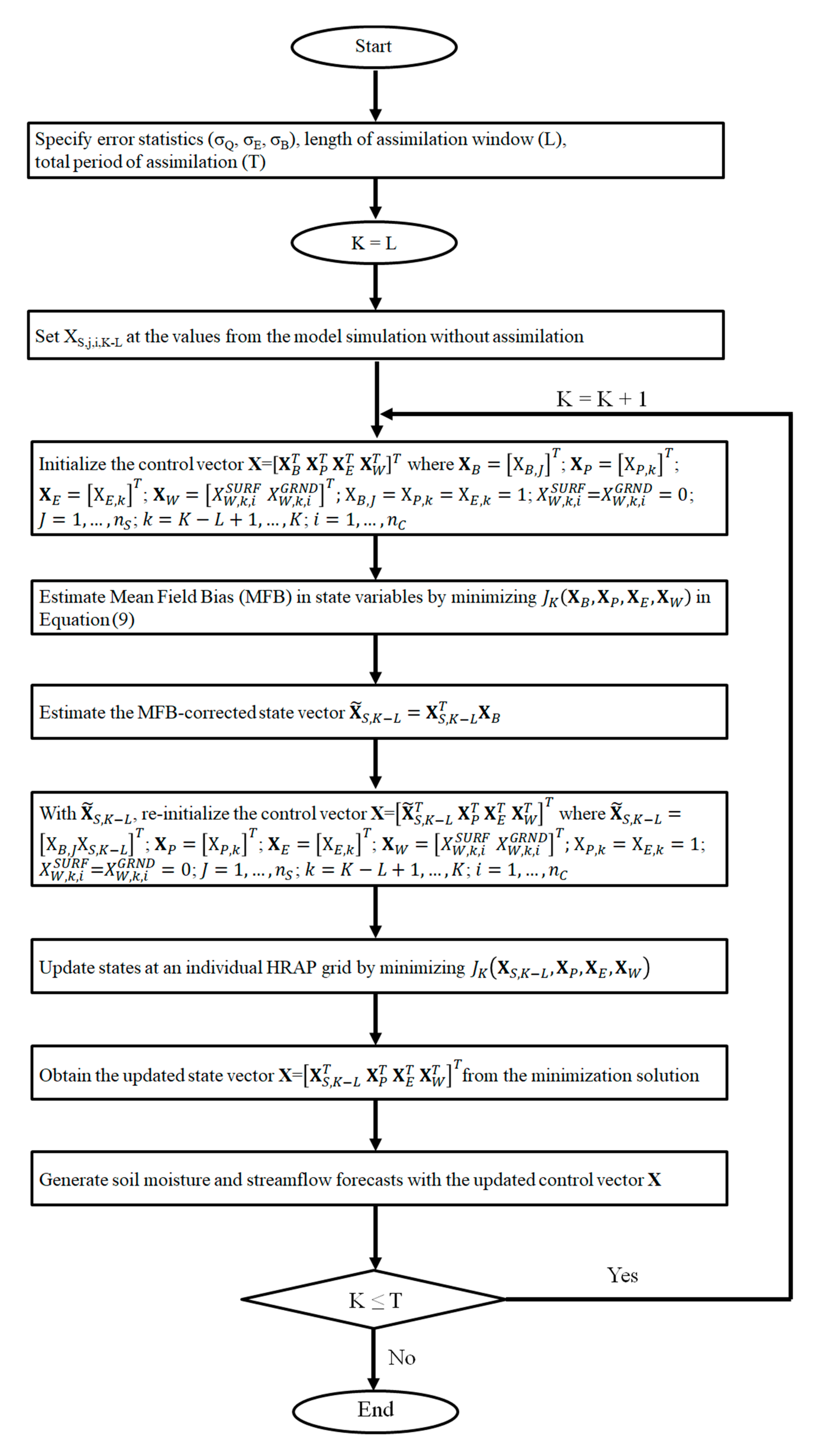
2.2. MFB-Aware Variational Data Assimilation, MVAR
2.3. Conventional Variational Data Assimilation, VAR
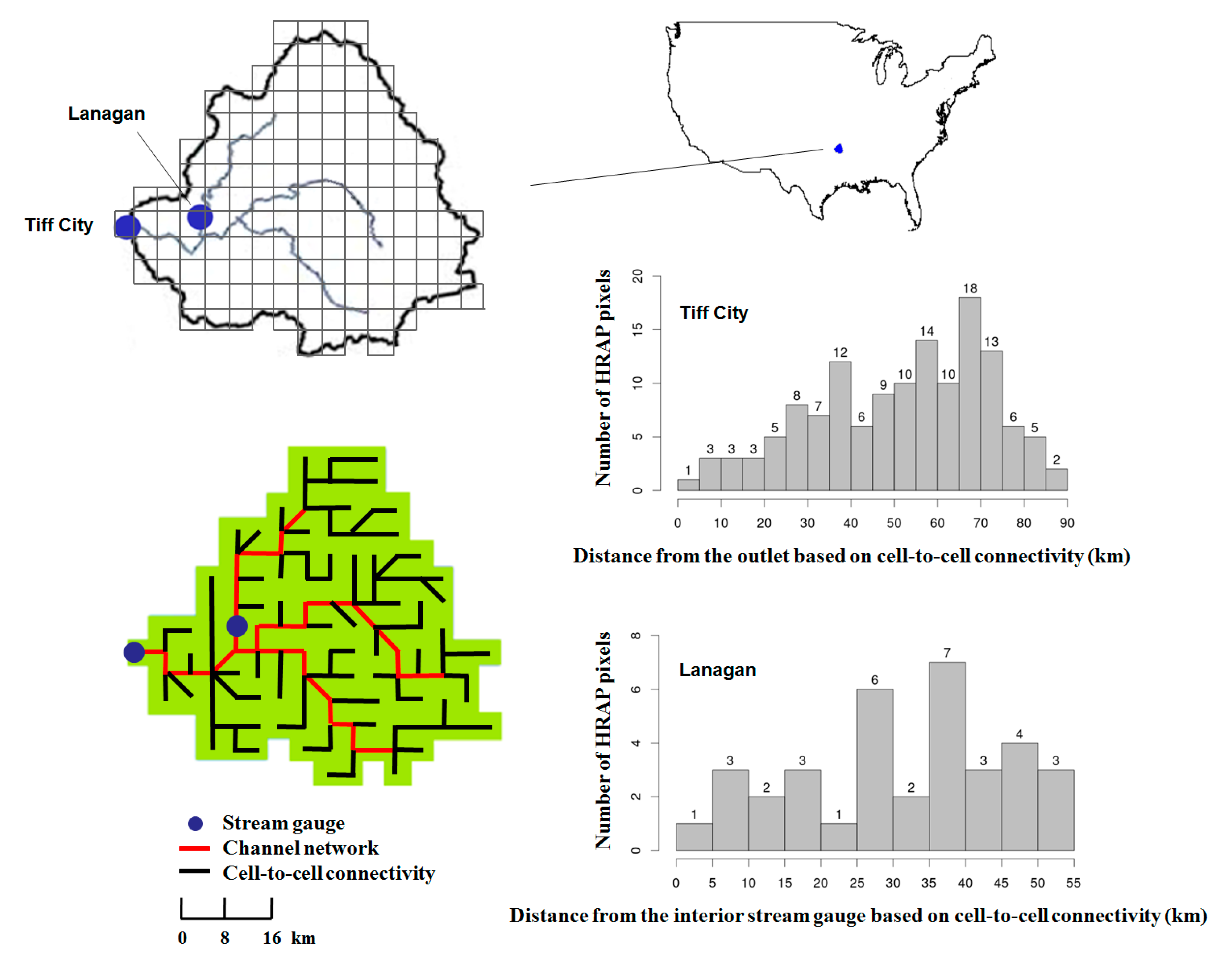
3. Study Area and Evaluation Metrics
3.1. Study Area
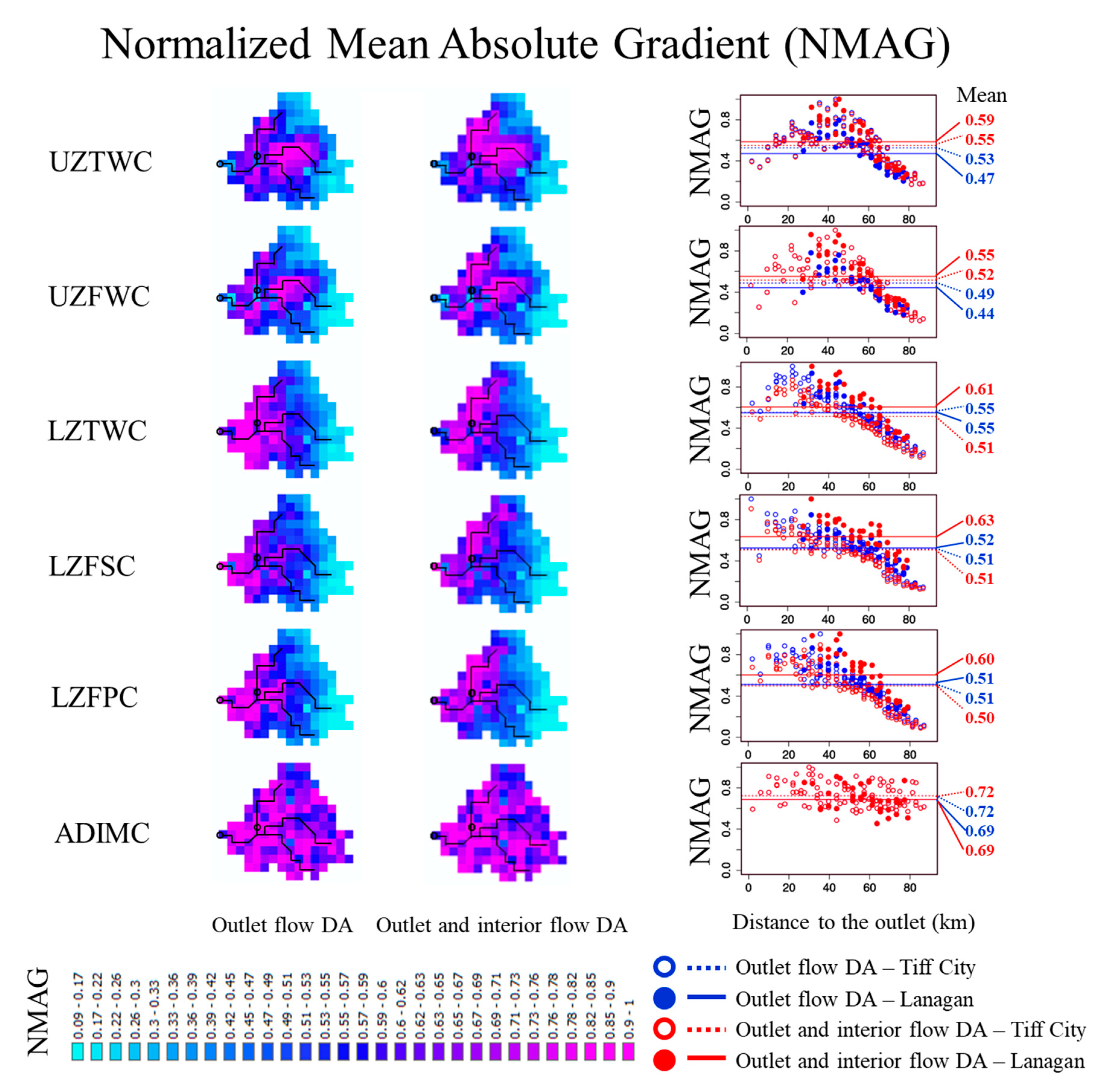
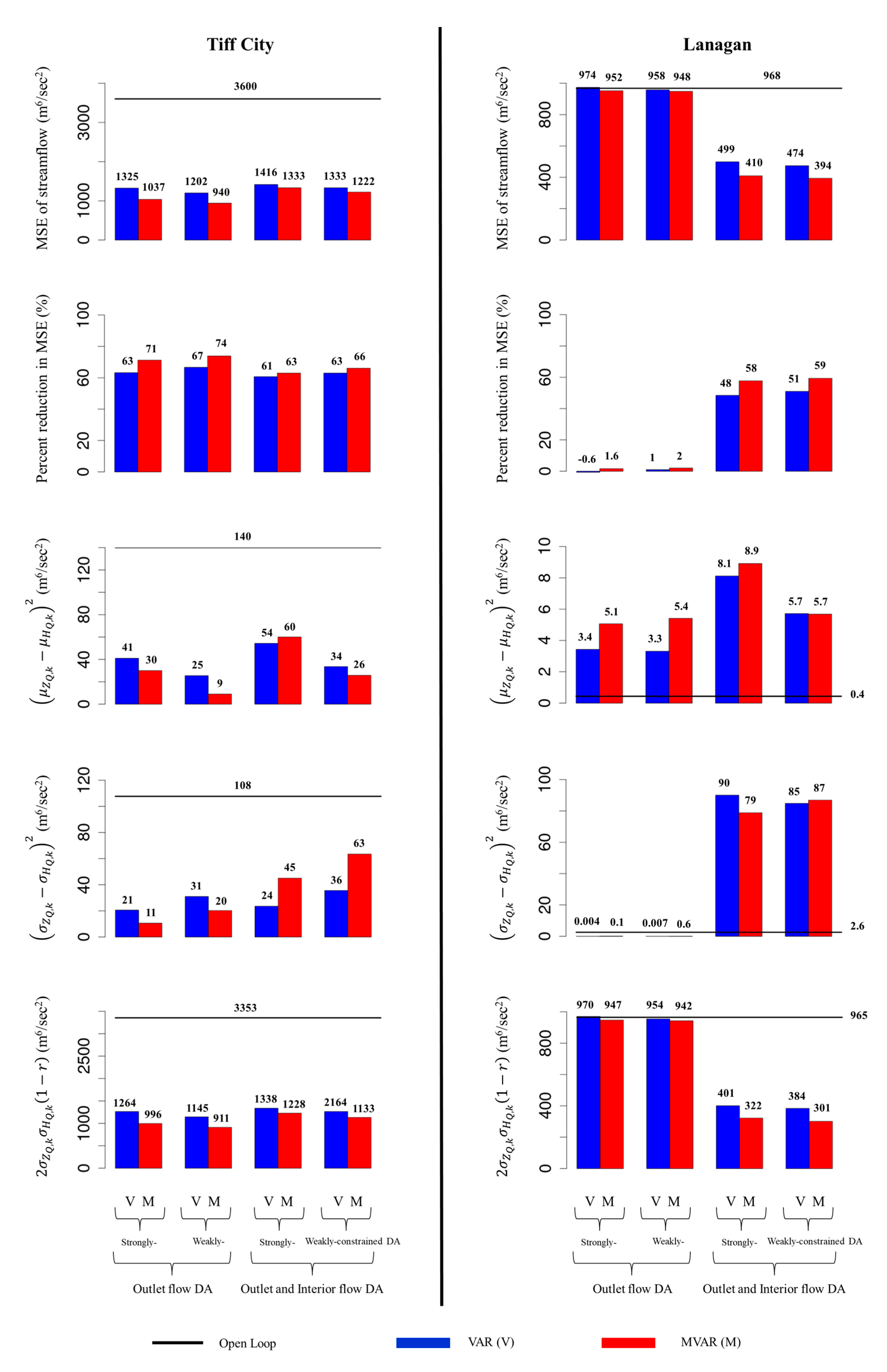
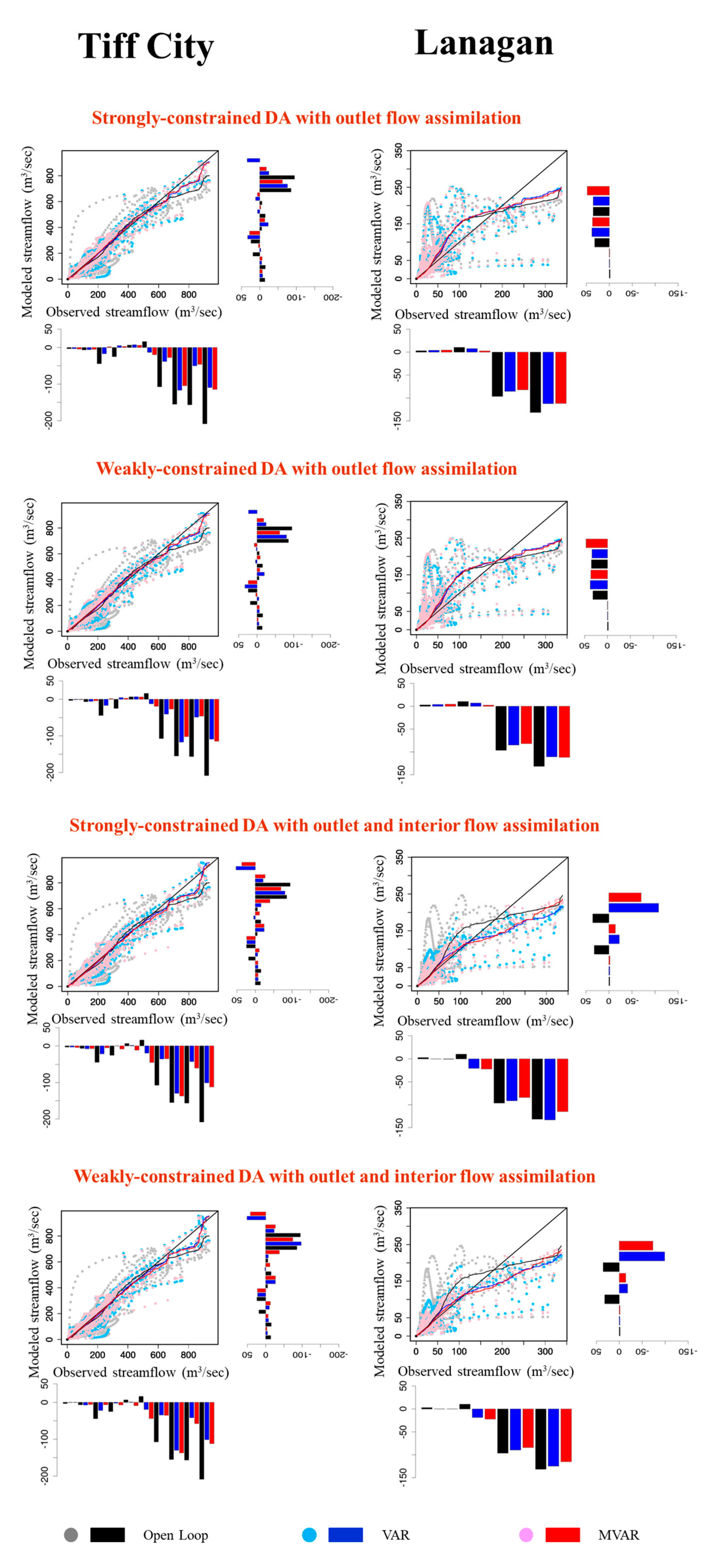
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
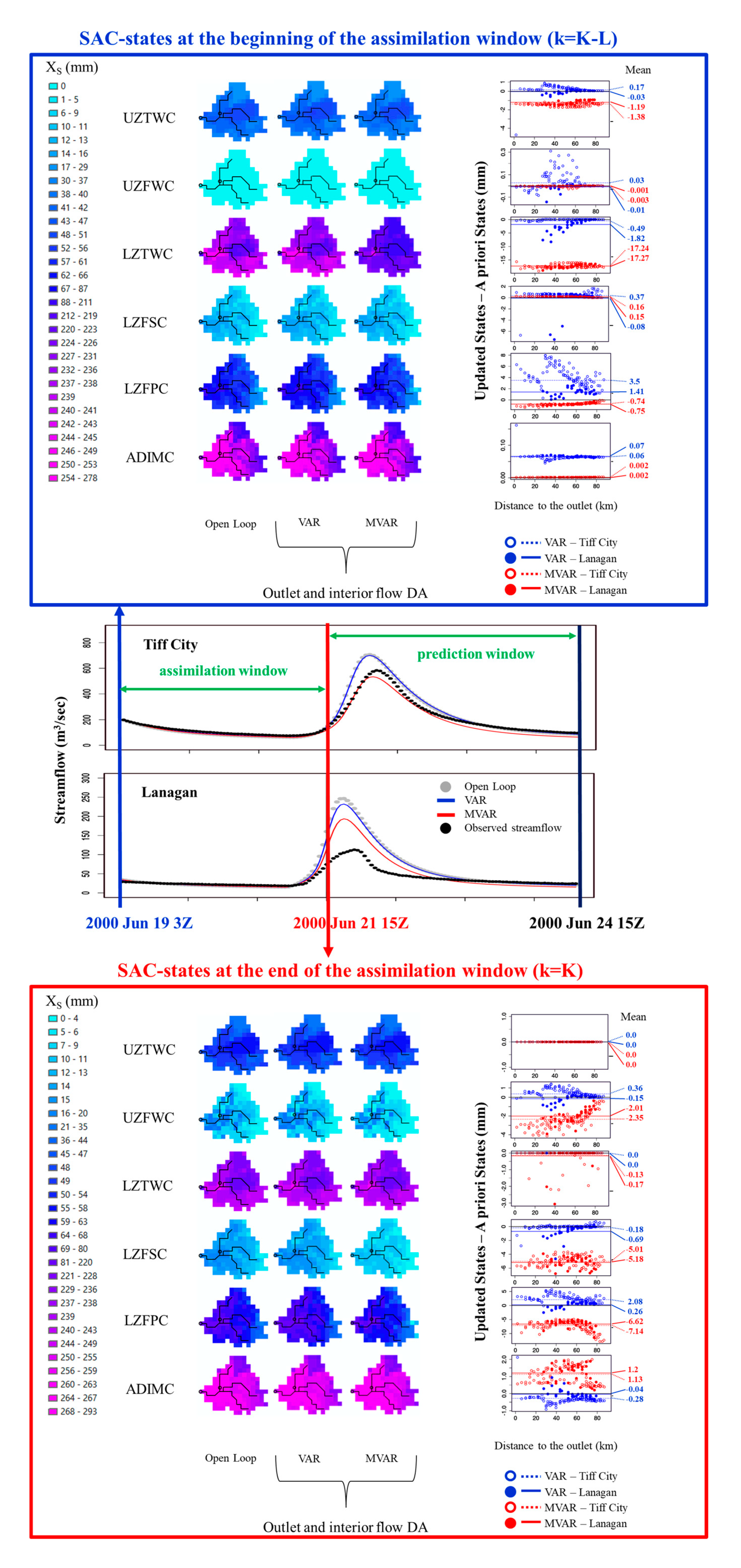
4.1. Illustrative Example
4.2. Model States
4.3. Model Structural Error
4.4. Streamflow
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kitanidis, P.K.; Bras, R.L. Real time forecasting of river flows. R. M. Parsons laboratory for water resources and hydrodynamics. Tech. Rep. 1978, 235, 324. [Google Scholar]
- Sittner, W.T.; Krouse, K.M. Improvement of Hydrologic Simulation by Utilizing Observed Discharge as an Indirect Input (Computed Hydrograph Adjustment Technique—CHAT); NOAA Tech. Memo. NWS HYDRO-38: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1979; p. 125.
- WMO. Simulated Real-Time Intercomparison of Hydrological Models. Operational Hydrology Rep. 38; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Georgakakos, K.; Smith, G.F. On improved operational hydrologic forecasting: Results from a WMO real-time forecasting experiment. J. Hydrol. 1990, 114, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C. Validation and intercomparison of different updating procedures for real-time forecasting, Nord. Hydrol. Res. 1998, 28, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhani, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Gupta, H.; Sorooshian, S. Uncertainty assessment of hydrologic model states and parameters: Sequential data assimilation using the particle filter. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W05012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J.; Koren, V. Assimilation of streamflow and in-situ soil moisture data into operational distributed hydrologic models: Effects of uncertainties in the data and initial model soil moisture states. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J.; Liu, Y.; Koren, V.; McKee, P.; Corby, R. Variational assimilation of streamflow into operational distributed hydrologic models: Effect of spatiotemporal scale of adjustment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2233–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shen, H.; Noh, S.J.; Kim, S.; Seo, D.-J.; Zhang, Y. Improving flood forecasting using conditional bias-penalized ensemble Kalman filter. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakovec, O.; Weerts, A.H.; Hazenberg, P.; Torfs, P.J.J.F.; Uijlenhoet, R. State updating of a distributed hydrological model with Ensemble Kalman Filtering: Effects of updating frequency and observation network density on forecast accuracy. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3435–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J. Assimilation of hydrologic and hydrometeorological data into distributed hydrologic model: Effect of adjusting mean field bias in radar-based precipitation estimates. J. Hydrol. 2014, 74, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasab, A.R.; Seo, D.-J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S. Comparative evaluation of maximum likelihood ensemble filter and ensemble Kalman filter for real-time assimilation of streamflow data into operational hydrologic models. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2663–2675. [Google Scholar]
- Dooge, J.C.I.; Napiôrkowsld, J.J. Applicability of diffusion analogy in flood routing. Acta Geophys. Pol. 1987, 35, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Zeng, F.; Gu, Y. Semi-analytical solutions to one-dimensional advection–diffusion equations with variable diffusion coefficient and variable flow velocity. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 221, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, B.; Seo, D.-J. Symbolic explicit solutions for 1-dimensional linear diffusive wave equation with lateral inflow and their applications. Water Resour. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Navon, I.M. Optimality of variational data assimilation and its relationship with the Kalman filter and smoother. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2001, 127, 661–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, G. Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 10143–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Reichle, R.H.; Houser, P.R.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Correcting for forecast bias in soil moisture assimilation with the ensemble Kalman filter. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W09410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D. Bias reduction in short records of satellite soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L19501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-J.; Breidenbach, J.P. Real-time correction of spatially nonuniform bias in radar rainfall data using rain gauge measurements. J. Hydrometeor. 2002, 3, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Seo, D.-J.; Demargne, J.; Brown, J.D.; Cong, S.; Schaake, J. Generation of ensemble precipitation forecast from single-valued quantitative precipitation forecast for hydrologic ensemble prediction. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-J.; Herr, H.D.; Schaake, J.C. A statistical post-processor for accounting of hydrologic uncertainty in short-range ensemble streamflow prediction. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2006, 3, 1987–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-J.; Saifuddin, M.M.; Lee, H. Conditional bias-penalized Kalman filter for improved estimation and prediction of extremes. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepurin, G.A.; Carton, J.A.; Dee, D. Forecast model bias correction in ocean data assimilation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2005, 133, 1328–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P. Bias and data assimilation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 3323–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; Wu, L.; He, M.; Regonda, S.; Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J. Verification of temperature, precipitation and streamflow forecasts from the NOAA/NWS Hydrologic Ensemble Forecast Service (HEFS): 1. Experimental design and forcing verification. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2869–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; He, M.; Regonda, S.; Wu, L.; Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J. Verification of temperature, precipitation and streamflow forecasts from the NOAA/NWS hydrologic ensemble forecast service (HEFS): 1. Streamflow verification. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2847–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Krajewski, W.F. Estimation of the mean field bias of radar rainfall estimates. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1991, 30, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-J.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Johnson, E.R. Real-time estimation of mean field bias in radar rainfall data. J. Hydrol. 1999, 223, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-J.; Kwon, H.-H.; Lima, C. A Bayesian partial pooling approach to mean field bias correction of weather radar rainfall estimates: Application to Osungsan weather radar in South Korea. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, V.; Reed, S.; Smith, M.; Zhang, Z.; Seo, D.-J. Hydrology laboratory research modeling system (HL-RMS) of the US national weather service. J. Hydrol. 2004, 291, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; McWilliams, J.C.; Ide, K.; Farrara, J.D. A multiscale variational data assimilation scheme: Formulation and illustration. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2015, 143, 3804–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.J.; Weerts, A.H.; Rakovec, O.; Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J. Assimilation of streamflow observations. In Handbook of Hydrometeorological Ensemble Forecasting; Duan, Q., Pappenberger, F., Thielen, J., Wood, A., Cloke, H.L., Schaake, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Seo, D.-J.; Noh, S.J. A weakly-constrained data assimilation approach to address rainfall-runoff model structural inadequacy in streamflow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnash, R.J.; Ferral, R.L.; McGuire, R.A. A Generalized Streamflow Simulation System: Conceptual Modeling for Digital Computers; US Department of Commerce National Weather Service and State of California Department of Water Resources: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1973.
- Reed, S.M.; Maidment, D.R. Coordinate transformations for using NEXRAD data in GIS-based hydrologic modeling. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.M. Deriving flow directions for coarse-resolution (1–4 km) gridded hydrologic modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture, US General Soil Map (STATSGO2). Available online: https://data.nal.usda.gov/dataset/united-states-general-soil-map-statsgo2 (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Smith, M.B.; Seo, D.-J.; Koren, V.I.; Reed, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, Q.; Moreda, F.; Cong, S. The distributed model intercomparison project (DMIP): Motivation and experiment design. J. Hydrol. 2004, 298, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, V.; Smith, M.; Cui, Z. Physically-based modifications to the sacramento soil moisture accounting model. Part A: Modeling the effects of frozen ground on the runoff generation process. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3475–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y. Some basic formalisms in numerical variational analysis. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1970, 98, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanski, D. A general weak constraint applicable to operational 4DVAR data assimilation systems. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1997, 125, 2274–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, E.; Moore, A.M.; Arango, H.G.; Cornuelle, B.D.; Miller, A.J.; Powell, B.; Chua, B.S.; Bennett, A.F. Weak and strong constraint data assimilation in the inverse regional ocean modeling system (ROMS): Development and application for a baroclinic coastal upwelling system. Ocean Model. 2007, 16, 160–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhani, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V.; Houser, P.R. Dual state-parameter estimation of hydrological models using ensemble Kalman filter. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 28, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravela, S.; Emanuel, K.; McLaughlin, D. Data assimilation by field alignment. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2007, 230, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.J. On the concept of model structural error. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.-J.; Koren, V.; Cajina, N. Real-time variational assimilation of hydrologic and hydrometeorological data into operational hydrologic forecasting. J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


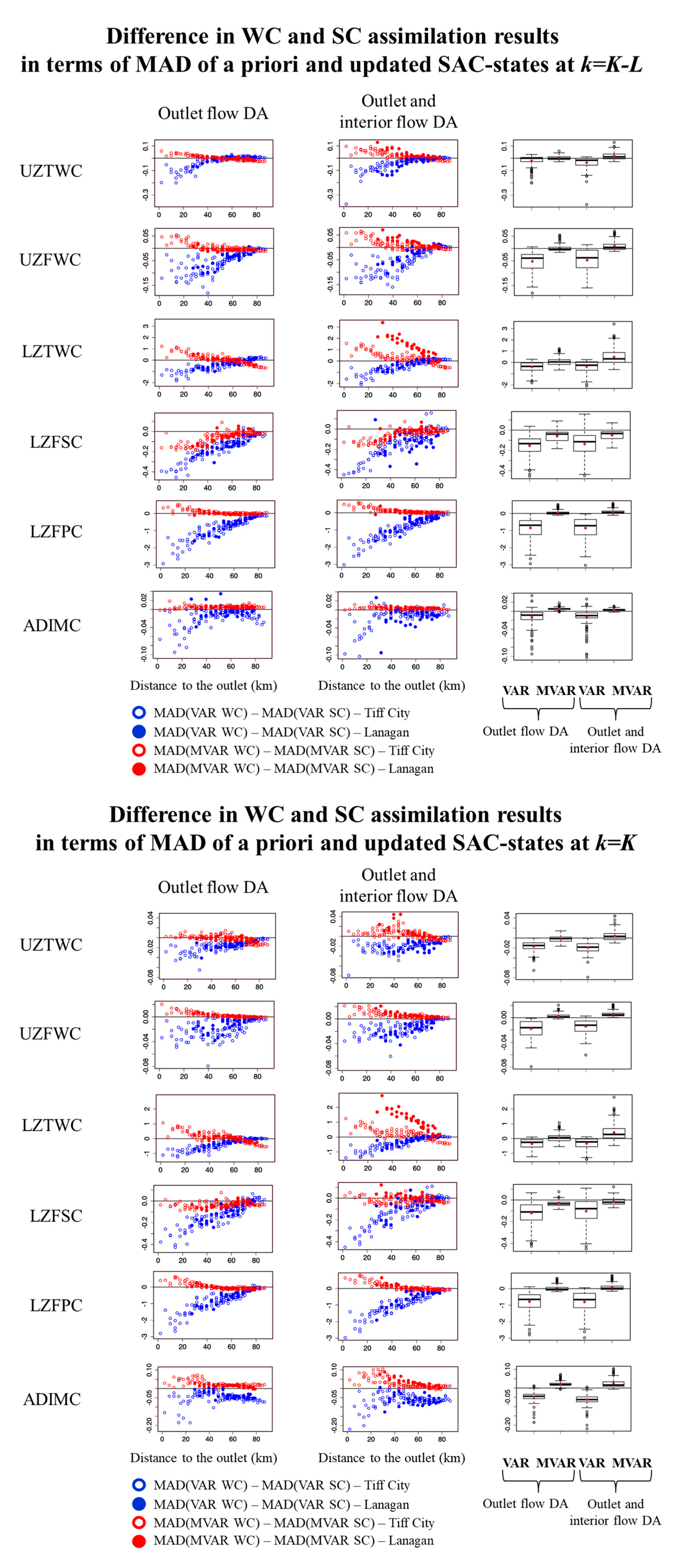
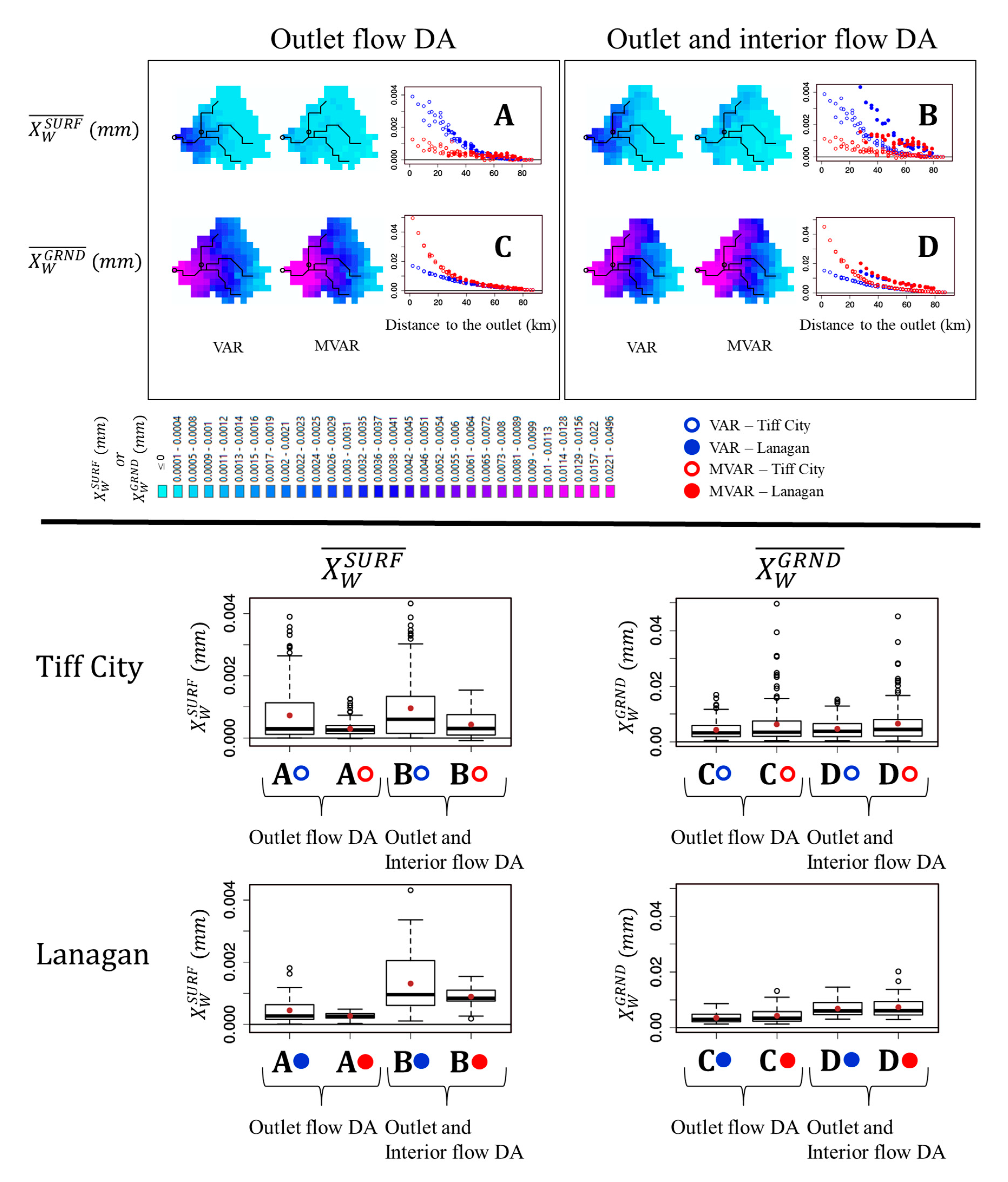
| SAC-SMA Model States | Description |
|---|---|
| UZTWC | Upper Zone Tension Water Content |
| UZFWC | Upper Zone Free Water Content |
| LZTWC | Lower Zone Tension Water Content |
| LZPFC | Lower Zone Primary Free Water Content |
| LZSFC | Lower Zone Supplemental Free Water Content |
| ADIMC | Additional impervious area water content |
| MFB-aware variational assimilation (MVAR) | |
| Step 1. Adjustment of mean field bias in model states | |
| Objective function | subject to |
| Control vector | |
| Step 2. Adjustment of individual model states at each HRAP cells | |
| Objective function | subject to |
| Control vector | |
| Conventional variational assimilation (VAR) | |
| Objective function | subject to |
| Control vector | |
| UZTWC | UZFWC | LZTWC | LZSFC | LZPFC | ADIMC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Begging of the assimilation window (k = K − L) Outlet flow assimilation | ||||||
| WC | 0.995(0.991) | 0.96(0.876) | 0.88(0.883) | 0.964(0.871) | 0.981(0.96) | 0.999(0.999) |
| SC | 0.996(0.99) | 0.969(0.853) | 0.902(0.863) | 0.966(0.854) | 0.993(0.95) | 0.999(0.999) |
| Outlet and interior flow assimilation | ||||||
| WC | 0.992(0.99) | 0.952(0.859) | 0.817(0.838) | 0.956(0.828) | 0.977(0.944) | 0.999(0.998) |
| SC | 0.994(0.989) | 0.963(0.837) | 0.854(0.817) | 0.961(0.823) | 0.99(0.935) | 0.999(0.998) |
| End of the assimilation window (k = K) Outlet flow assimilation | ||||||
| WC | 0.999(0.999) | 0.845(0.765) | 0.913(0.97) | 0.872(0.85) | 0.947(0.932) | 0.997(0.996) |
| SC | 0.999(0.999) | 0.842(0.752) | 0.931(0.951) | 0.883(0.841) | 0.959(0.926) | 0.997(0.995) |
| Outlet and interior flow assimilation | ||||||
| WC | 0.998(0.999) | 0.821(0.754) | 0.88(0.966) | 0.814(0.768) | 0.928(0.909) | 0.996(0.994) |
| SC | 0.999(0.999) | 0.834(0.733) | 0.912(0.945) | 0.831(0.768) | 0.943(0.901) | 0.997(0.994) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Shen, H.; Seo, D.-J. Mean Field Bias-Aware State Updating via Variational Assimilation of Streamflow into Distributed Hydrologic Models. Forecasting 2020, 2, 526-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2040028
Lee H, Shen H, Seo D-J. Mean Field Bias-Aware State Updating via Variational Assimilation of Streamflow into Distributed Hydrologic Models. Forecasting. 2020; 2(4):526-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Haksu, Haojing Shen, and Dong-Jun Seo. 2020. "Mean Field Bias-Aware State Updating via Variational Assimilation of Streamflow into Distributed Hydrologic Models" Forecasting 2, no. 4: 526-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2040028
APA StyleLee, H., Shen, H., & Seo, D.-J. (2020). Mean Field Bias-Aware State Updating via Variational Assimilation of Streamflow into Distributed Hydrologic Models. Forecasting, 2(4), 526-548. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast2040028






