The Ridge-Hurdle Negative Binomial Regression Model: A Novel Solution for Zero-Inflated Counts in the Presence of Multicollinearity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zero-Inflated Poisson (ZIP) Model
2.2. Zero-Inflated Negative Binomial (ZINB) Model
2.3. Hurdle Poisson Model
2.4. Hurdle Negative Binomial (Hurdle NB) Model
2.5. Ridge Zero-Inflated Poisson (Ridge ZIP) Model
2.6. Ridge Zero-Inflated Negative Binomial (Ridge ZINB) Model
- reducing variance and improving stability under multicollinearity
2.7. Proposed Ridge-Hurdle Negative Binomial (RHNB) Model
3. Simulation Study
3.1. Simulation Design
3.2. Results Discussion
3.2.1. Effectiveness Relative to Sample Size
3.2.2. Effectiveness Relative to the Number of Predictors
3.2.3. Effectiveness Relative to Correlation Coefficients
3.2.4. Effectiveness Relative to Intercept Logit
3.2.5. Effectiveness Relative to Overdispersion
4. Application
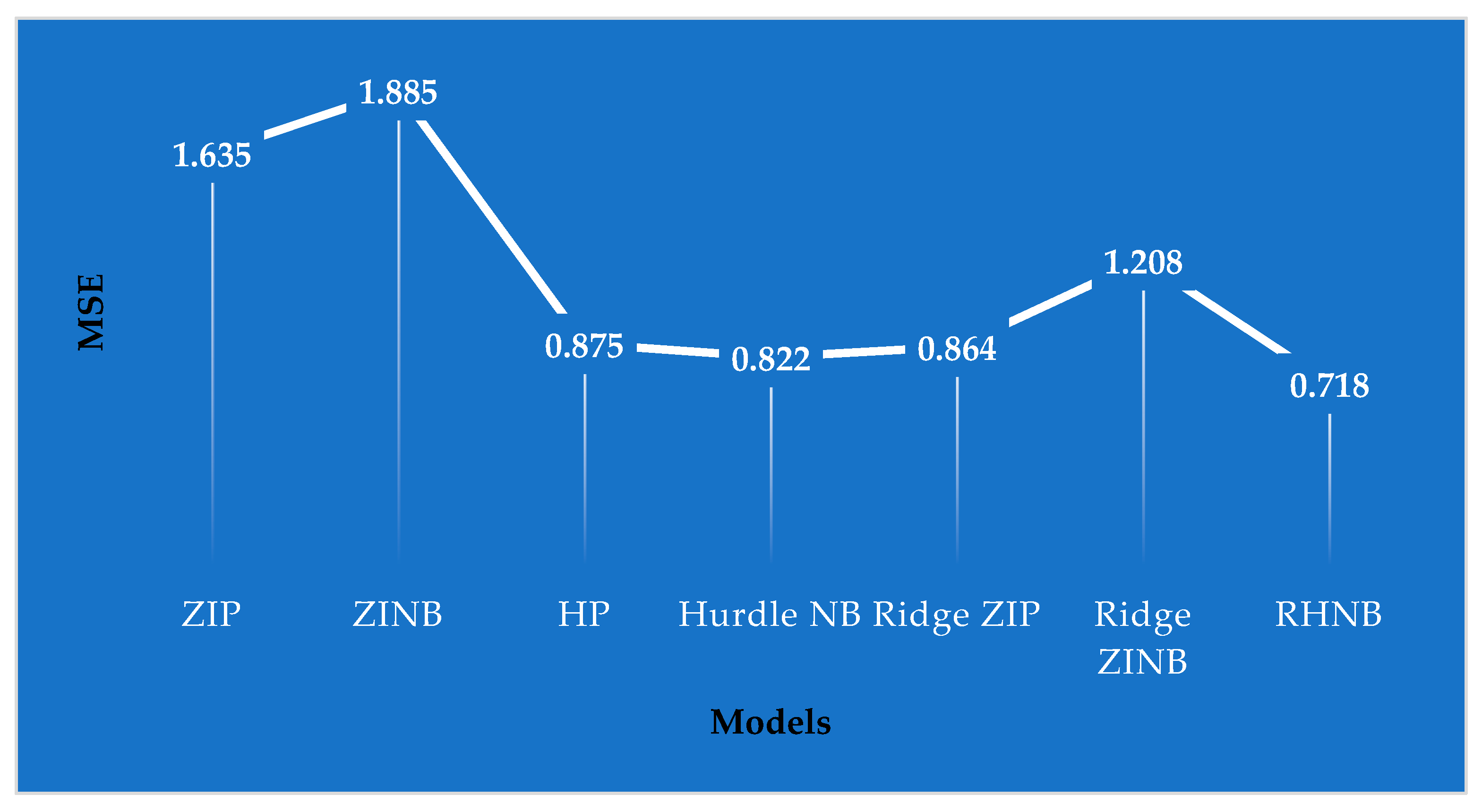
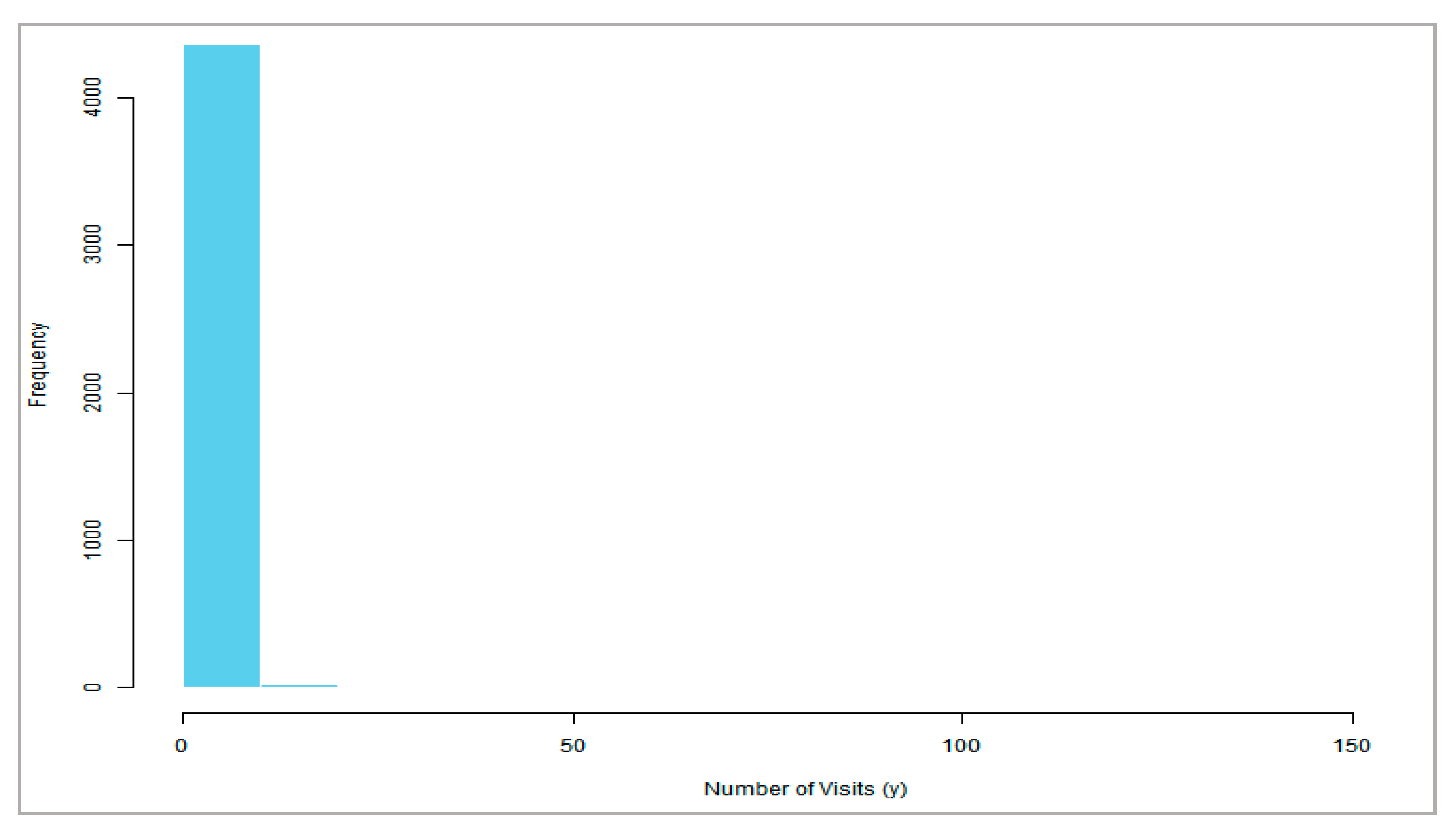
4.1. Wildlife Fish Data
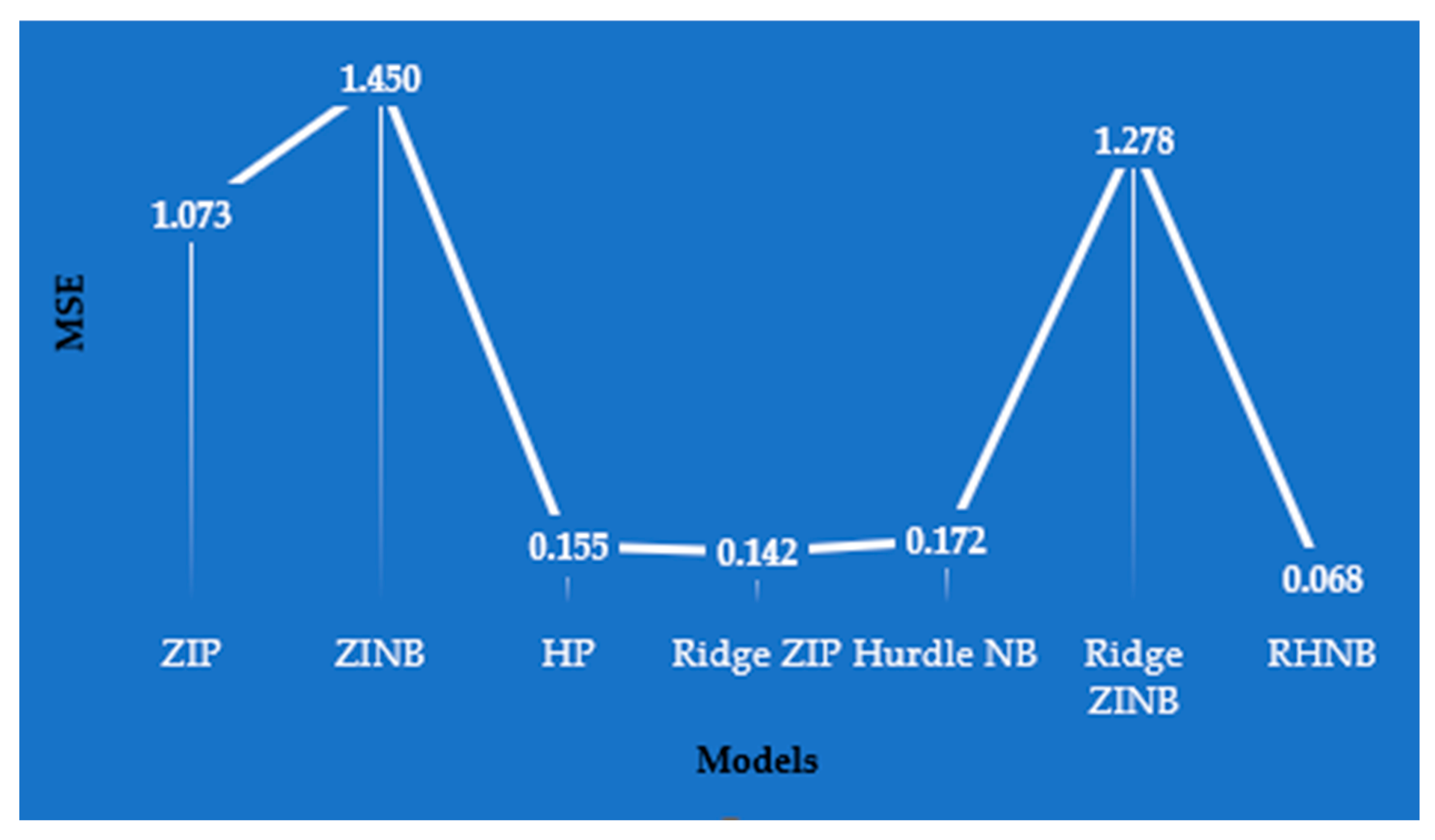
4.2. Medical Care Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Simulation Results Tables
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 6.146 | 0.406 | 0.224 | 0.368 | 0.191 | 0.156 |
| ZINB | 0.899 | 0.302 | 0.182 | 0.361 | 0.189 | 0.147 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 0.671 | 0.349 | 0.192 | 0.263 | 0.175 | 0.153 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 0.146 | 0.156 | 0.155 | 0.154 | 0.150 | 0.153 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 0.202 | 0.136 | 0.131 | 0.107 | 0.104 | 0.111 | |
| Hurdle NB | 0.604 | 0.204 | 0.121 | 0.250 | 0.156 | 0.124 | |
| RHNB | 0.063 | 0.057 | 0.056 | 0.085 | 0.058 | 0.041 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 872.117 | 1.356 | 0.334 | 425.184 | 0.467 | 0.181 |
| ZINB | 699.379 | 1.498 | 0.553 | 762.497 | 0.557 | 0.252 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 14.000 | 2.521 | 0.292 | 15.660 | 0.314 | 0.188 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 4.084 | 0.208 | 0.200 | 7.004 | 0.181 | 0.173 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 3.385 | 0.164 | 0.116 | 5.529 | 0.114 | 0.165 | |
| Hurdle NB | 14.262 | 2.426 | 0.189 | 11.638 | 0.304 | 0.248 | |
| RHNB | 0.070 | 0.059 | 0.058 | 0.055 | 0.051 | 0.036 | |
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 1.083 | 0.583 | 0.339 | 0.509 | 0.226 | 0.188 |
| ZINB | 0.947 | 0.478 | 0.215 | 0.519 | 0.213 | 0.167 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 1.146 | 0.550 | 0.310 | 0.434 | 0.223 | 0.192 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 0.167 | 0.177 | 0.179 | 0.144 | 0.162 | 0.168 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 0.172 | 0.158 | 0.128 | 0.120 | 0.096 | 0.116 | |
| Hurdle NB | 0.858 | 0.321 | 0.162 | 0.396 | 0.187 | 0.146 | |
| RHNB | 0.073 | 0.063 | 0.061 | 0.069 | 0.065 | 0.047 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 81.739 | 7.798 | 0.501 | 93.461 | 0.858 | 0.256 |
| ZINB | 92.304 | 7.765 | 0.617 | 96.643 | 1.189 | 0.388 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 27.219 | 7.694 | 0.456 | 10.644 | 0.499 | 0.253 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 9.695 | 2.193 | 0.318 | 2.184 | 0.288 | 0.225 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 7.884 | 1.080 | 0.306 | 1.588 | 0.266 | 0.219 | |
| Hurdle NB | 26.916 | 3.396 | 0.345 | 6.039 | 0.471 | 0.246 | |
| RHNB | 0.338 | 0.054 | 0.032 | 0.053 | 0.047 | 0.040 | |
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 35.598 | 0.900 | 0.520 | 1.050 | 0.320 | 0.236 |
| ZINB | 3.270 | 0.698 | 0.338 | 1.081 | 0.295 | 0.192 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 2.828 | 0.959 | 0.539 | 0.835 | 0.324 | 0.253 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 0.203 | 0.182 | 0.207 | 0.190 | 0.161 | 0.176 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 0.392 | 0.178 | 0.143 | 0.153 | 0.106 | 0.114 | |
| Hurdle NB | 1.759 | 0.511 | 0.245 | 0.621 | 0.265 | 0.174 | |
| RHNB | 0.088 | 0.067 | 0.060 | 0.128 | 0.085 | 0.074 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 95.822 | 45.154 | 0.953 | 63.818 | 1.107 | 0.819 |
| ZINB | 48.022 | 27.661 | 0.984 | 13.268 | 1.292 | 0.474 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 55.013 | 3.105 | 0.938 | 19.409 | 0.779 | 0.334 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 18.737 | 1.184 | 0.337 | 6.902 | 0.271 | 0.227 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 14.367 | 1.070 | 0.233 | 3.969 | 0.198 | 0.196 | |
| Hurdle NB | 35.742 | 2.425 | 0.464 | 5.397 | 0.738 | 0.250 | |
| RHNB | 0.051 | 0.040 | 0.032 | 0.052 | 0.041 | 0.029 | |
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 62.282 | 3.347 | 2.041 | 4.283 | 1.092 | 0.612 |
| ZINB | 59.227 | 2.046 | 1.826 | 4.451 | 0.852 | 0.378 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 53.279 | 1.503 | 1.300 | 3.504 | 0.641 | 0.708 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 7.347 | 0.232 | 0.205 | 0.915 | 0.388 | 0.307 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 3.107 | 0.274 | 0.193 | 0.783 | 0.330 | 0.141 | |
| Hurdle NB | 50.644 | 1.056 | 0.741 | 2.244 | 0.515 | 0.341 | |
| RHNB | 0.117 | 0.082 | 0.070 | 0.221 | 0.113 | 0.102 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 159.496 | 21.902 | 6.955 | 77.842 | 8.615 | 2.191 |
| ZINB | 181.909 | 14.263 | 8.638 | 82.632 | 9.955 | 2.081 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 63.205 | 9.728 | 4.219 | 39.622 | 6.061 | 1.257 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 42.266 | 5.180 | 3.169 | 11.012 | 1.338 | 0.288 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 35.939 | 3.882 | 2.595 | 8.304 | 0.499 | 0.209 | |
| Hurdle NB | 57.773 | 6.268 | 3.836 | 15.620 | 5.675 | 0.793 | |
| RHNB | 1.050 | 0.040 | 0.027 | 0.285 | 0.051 | 0.024 | |
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 540.361 | 0.593 | 0.249 | 187.591 | 0.196 | 0.119 |
| ZINB | 670.843 | 4.823 | 0.161 | 271.596 | 0.213 | 0.115 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 35.106 | 0.523 | 0.226 | 25.376 | 0.177 | 0.115 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 0.132 | 0.165 | 0.155 | 0.127 | 0.122 | 0.132 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 77.343 | 2.589 | 0.115 | 29.410 | 0.100 | 0.092 | |
| Hurdle NB | 1.647 | 0.292 | 0.101 | 1.451 | 0.159 | 0.088 | |
| RHNB | 0.069 | 0.050 | 0.042 | 0.039 | 0.029 | 0.014 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 136.156 | 10.505 | 0.415 | 68.248 | 14.224 | 0.147 |
| ZINB | 120.916 | 18.819 | 0.528 | 46.596 | 6.385 | 0.366 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 90.868 | 19.959 | 0.385 | 3.038 | 2.557 | 0.136 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 68.451 | 0.268 | 0.227 | 11.926 | 0.240 | 0.211 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 52.083 | 7.739 | 0.293 | 9.443 | 7.978 | 0.220 | |
| Hurdle NB | 85.981 | 3.190 | 0.236 | 3.196 | 2.417 | 0.125 | |
| RHNB | 0.781 | 0.062 | 0.060 | 0.034 | 0.025 | 0.017 | |
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 292.209 | 0.937 | 0.435 | 222.253 | 0.241 | 0.160 |
| ZINB | 208.681 | 0.684 | 0.247 | 472.061 | 0.397 | 0.134 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 158.013 | 0.917 | 0.424 | 66.112 | 0.242 | 0.162 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 0.223 | 0.204 | 0.242 | 0.207 | 0.216 | 0.193 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 15.563 | 0.176 | 0.143 | 14.220 | 0.150 | 0.095 | |
| Hurdle NB | 15.127 | 1.678 | 0.154 | 0.942 | 0.223 | 0.103 | |
| RHNB | 0.140 | 0.082 | 0.058 | 0.092 | 0.061 | 0.051 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 558.922 | 238.307 | 0.820 | 95.895 | 13.309 | 0.267 |
| ZINB | 331.164 | 118.676 | 22.851 | 73.794 | 17.524 | 0.659 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 26.671 | 17.324 | 0.801 | 2.672 | 2.531 | 0.251 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 98.440 | 0.368 | 0.398 | 40.858 | 0.228 | 0.281 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 28.347 | 6.460 | 5.327 | 41.582 | 13.158 | 0.283 | |
| Hurdle NB | 5.510 | 1.018 | 0.451 | 2.672 | 2.502 | 0.202 | |
| RHNB | 0.759 | 0.250 | 0.115 | 0.071 | 0.048 | 0.029 | |
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 574.206 | 1.761 | 0.976 | 317.659 | 1.399 | 0.882 |
| ZINB | 443.453 | 1.174 | 0.869 | 94.783 | 0.605 | 0.786 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 120.674 | 1.076 | 0.793 | 34.198 | 0.417 | 0.340 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 35.565 | 0.443 | 0.317 | 10.521 | 0.323 | 0.315 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 15.327 | 0.261 | 0.163 | 8.729 | 0.189 | 0.135 | |
| Hurdle NB | 82.297 | 0.975 | 0.546 | 18.508 | 0.359 | 0.236 | |
| RHNB | 0.448 | 0.108 | 0.100 | 0.147 | 0.073 | 0.067 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 747.036 | 74.734 | 1.551 | 95.486 | 12.151 | 1.413 |
| ZINB | 422.694 | 60.561 | 1.177 | 25.926 | 10.058 | 1.163 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 96.235 | 5.940 | 1.086 | 13.300 | 1.937 | 1.009 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 36.803 | 2.726 | 0.362 | 8.046 | 1.296 | 0.740 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 21.693 | 1.424 | 0.325 | 5.178 | 1.085 | 0.532 | |
| Hurdle NB | 57.651 | 2.679 | 0.674 | 10.711 | 1.347 | 0.987 | |
| RHNB | 0.438 | 0.200 | 0.122 | 0.586 | 0.436 | 0.079 | |
| Models | Intercept Logit | Overdispersion Parameter = 1 | Overdispersion Parameter = 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Sample Size | ||||||
| 100 | 200 | 500 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| ZIP | 1 | 678.909 | 8.075 | 4.038 | 804.014 | 2.087 | 1.843 |
| ZINB | 708.676 | 4.747 | 2.200 | 890.000 | 2.569 | 1.122 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 66.509 | 2.554 | 1.189 | 421.420 | 2.104 | 0.891 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 12.326 | 1.514 | 0.874 | 22.211 | 1.953 | 0.536 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 8.847 | 1.039 | 0.365 | 16.261 | 0.618 | 0.307 | |
| Hurdle NB | 27.635 | 1.832 | 0.951 | 73.422 | 1.508 | 0.657 | |
| RHNB | 1.009 | 0.659 | 0.315 | 0.937 | 0.334 | 0.140 | |
| ZIP | 2 | 492.554 | 190.133 | 6.664 | 190.918 | 96.810 | 2.828 |
| ZINB | 235.260 | 88.416 | 5.770 | 136.842 | 82.092 | 2.376 | |
| Hurdle Poisson | 49.965 | 8.778 | 2.225 | 30.201 | 9.722 | 1.922 | |
| Ridge ZIP | 44.265 | 2.662 | 1.909 | 18.829 | 2.169 | 0.936 | |
| Ridge ZINB | 34.371 | 1.857 | 1.602 | 13.374 | 1.194 | 0.514 | |
| Hurdle NB | 45.966 | 4.459 | 2.021 | 25.873 | 3.190 | 1.314 | |
| RHNB | 19.144 | 0.967 | 0.512 | 1.573 | 0.552 | 0.311 | |
Appendix B. Real Data Results
| Predictors | ZIP | ZINB | Hurdle Poisson | Hurdle NB | Ridge ZIP | Ridge ZINB | Ridge Hurdle NB | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | |
| nofish | −0.04 | 0.14 | −0.09 | 0.17 | −0.05 | 0.14 | −0.03 | 0.17 | −0.11 | 0.04 | −0.08 | 0.05 | −0.03 | 0.05 |
| livebait | 0.43 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.30 | 0.66 | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.38 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| camper | −0.04 | 0.11 | −0.01 | 0.14 | −0.12 | 0.10 | −0.09 | 0.14 | −0.03 | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| persons | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.03 |
| child | −0.71 | 0.13 | −0.38 | 0.16 | −0.48 | 0.13 | −0.24 | 0.16 | −0.32 | 0.04 | −0.23 | 0.05 | −0.03 | 0.05 |
| xb | 0.99 | 0.03 | 1.17 | 0.07 | 0.95 | 0.04 | 1.09 | 0.07 | 0.78 | 0.02 | 0.91 | 0.03 | 0.61 | 0.03 |
| zg | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.02 |
| Predictors | ZIP | ZINB | Hurdle Poisson | Hurdle NB | Ridge ZIP | Ridge ZINB | Ridge Hurdle NB | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | Coef. | SE | |
| emergency | −0.08 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.09 | −0.09 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.14 | −0.08 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.000012 |
| hospital | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 0.000015 |
| health | 0.05 | 0.03 | −0.30 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.06 | −0.08 | 0.25 | −0.05 | 0.03 | −0.30 | 0.02 | −0.13 | 0.000024 |
| chronic | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.000029 |
| adl | −0.47 | 0.03 | −0.68 | 0.15 | −0.48 | 0.06 | −1.02 | 0.23 | −0.50 | 0.03 | −0.60 | 0.02 | −0.57 | 0.000023 |
| region | −0.09 | 0.05 | −0.16 | 0.05 | −0.09 | 0.02 | −0.23 | 0.08 | −0.15 | 0.05 | −0.16 | 0.04 | −0.19 | 0.000033 |
| age | −0.27 | 0.04 | −0.56 | 0.10 | −0.24 | 0.04 | −0.16 | 0.16 | −0.57 | 0.04 | −0.55 | 0.04 | −0.18 | 0.000092 |
| afam | 1.25 | 0.02 | 1.07 | 0.17 | 1.23 | 0.06 | 2.07 | 0.32 | 0.89 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 0.71 | 0.000004 |
| gender | 0.26 | 0.03 | −0.01 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.03 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.000018 |
| married | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.06 | −0.16 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | −0.13 | 0.000010 |
| school | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | −0.04 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | −0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −0.04 | 0.000144 |
| income | −0.03 | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.02 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −0.06 | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.04 | −0.06 | 0.000048 |
| employed | −0.16 | 0.02 | −0.19 | 0.18 | −0.13 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.29 | −0.22 | 0.02 | −0.15 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.000004 |
| insurance | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.07 | −0.24 | 0.32 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.47 | 0.02 | −0.18 | 0.000012 |
| medicaid | −0.05 | 0.02 | −0.15 | 0.22 | −0.05 | 0.09 | −0.37 | 0.41 | −0.07 | 0.02 | −0.12 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.000003 |
Appendix C. Residual Analysis of Medical Care Data
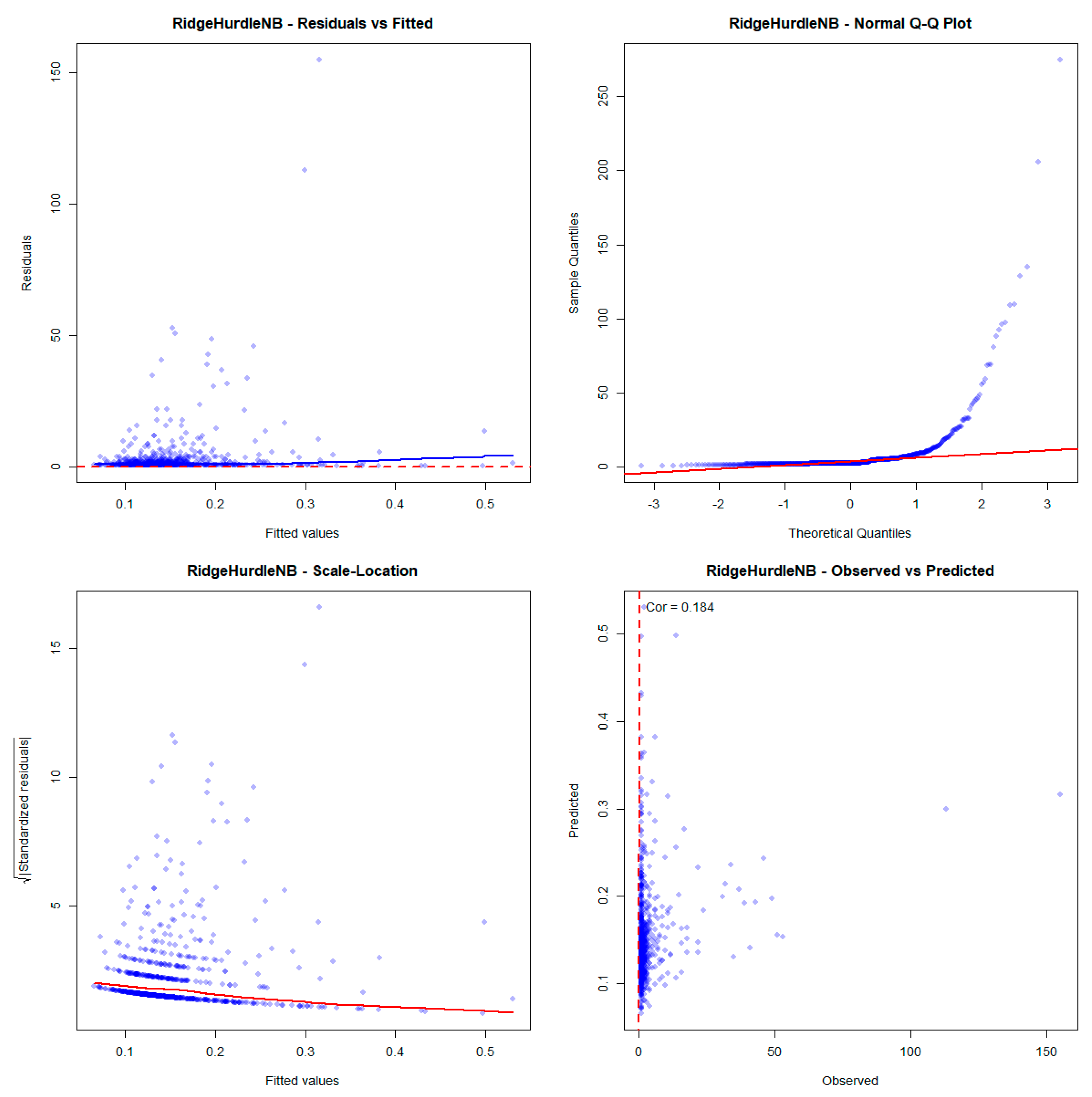
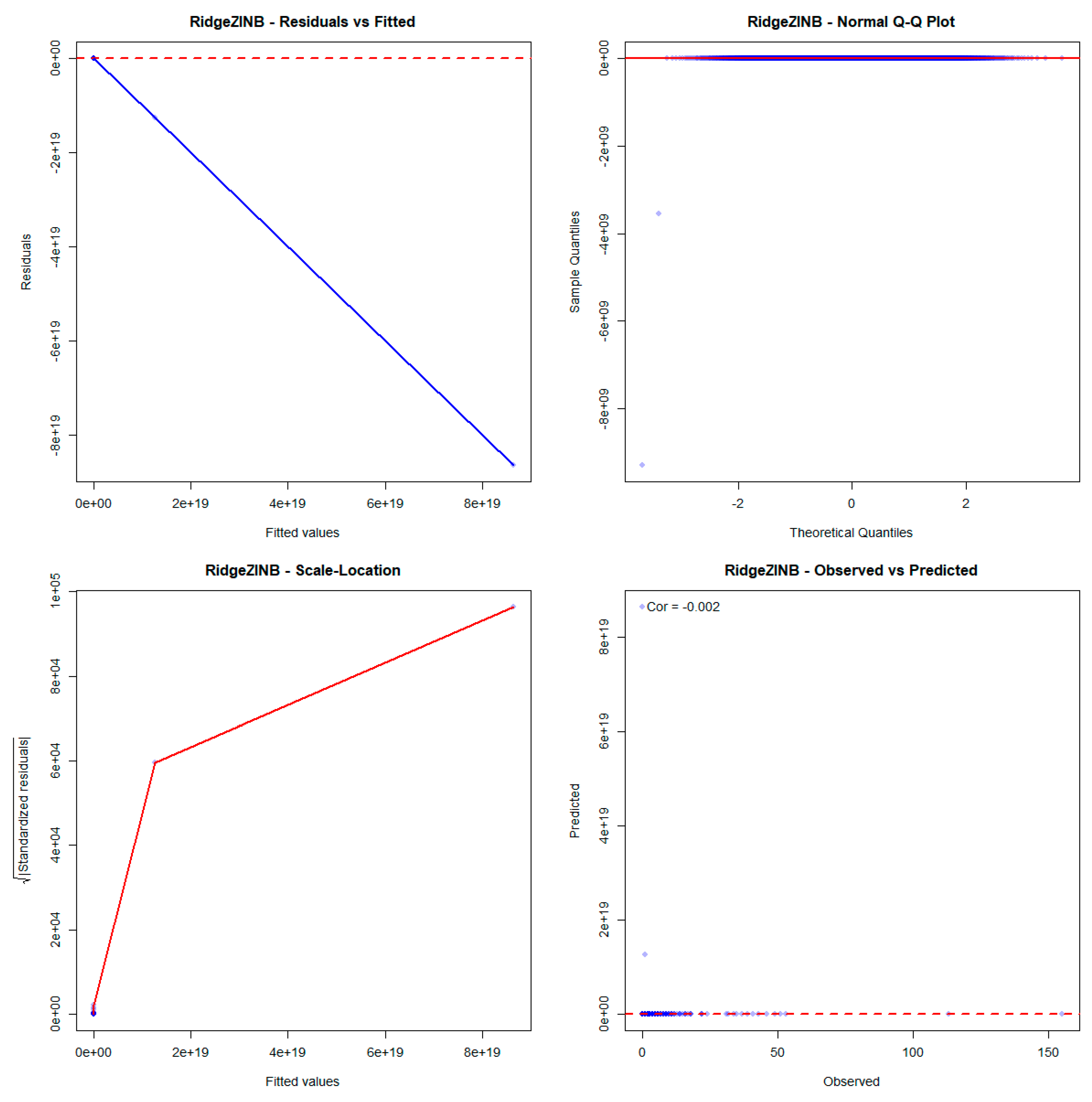
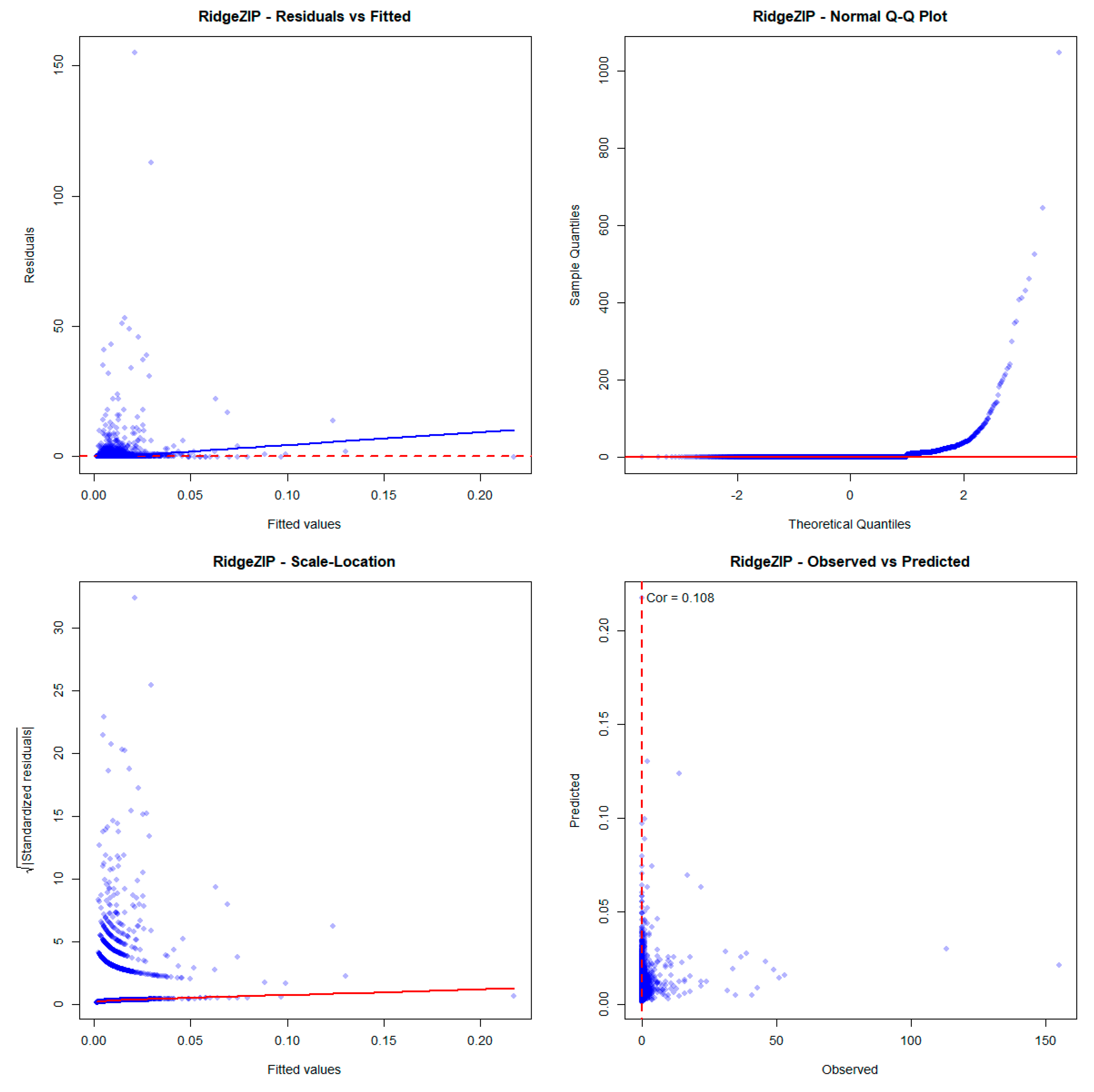
References
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Regression Analysis of Count Data, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schober, P.; Vetter, T.R. Count data in medical research: Poisson regression and negative binomial regression. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 132, 1378–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, M.N.; Abonazel, M.R.; Amin, M.; Kibria, B.G.; Afzal, N. A new Stein estimator for the zero-inflated negative binomial regression model. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, e7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D. Zero-inflated Poisson regression, with an application to defects in manufacturing. Technometrics 1992, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridout, M.; Demétrio, C.G.; Hinde, J. Models for count data with many zeros. In Proceedings of the International Biometric Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 14–18 December 1998; Volume 19, pp. 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, W.H. Accounting for Excess Zeros and Sample Selection in Poisson and Negative Binomial Regression Models; NYU Working Paper; New York University: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Amalia, R.N.; Sadik, K.; Notodiputro, K.A. A study of ZIP and ZINB regression modeling for count data with excess zeros. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1863, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, D.; Mannering, F. The statistical analysis of crash-frequency data: A review and assessment of methodological alternatives. Transp. Res. A 2010, 44, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Trivedi, P.K. Demand for medical care by the elderly: A finite mixture approach. J. Appl. Econ. 1997, 12, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonazel, M.R.; El-Sayed, S.M.; Saber, O.M. Performance of robust count regression estimators in the case of overdispersion, zero inflated, and outliers: Simulation study and application to German health data. Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.E.; Martin, S.W.; Wannemuehler, K.A.; Plikaytis, B.D. On the use of zero-inflated and hurdle models for modeling vaccine adverse event count data. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2006, 16, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.X. A comparison of zero-inflated and hurdle models for modeling zero-inflated count data. J. Stat. Distrib. Appl. 2021, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullahy, J. Specification and testing of some modified count data models. J. Econom. 1986, 33, 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, J.G. Some statistical models for limited dependent variables with application to the demand for durable goods. Econometrica 1971, 39, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Mannering, F.L.; Kim, D.K. Statistical modeling of highway safety data: Hurdle models revisited. Anal. Methods Accid. Res. 2021, 30, 100165. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Paterson, A.D.; Turpin, W.; Xu, W. Assessment and selection of competing models for zero-inflated microbiome data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Agresti, A. Random effect models for repeated measures of zero-inflated count data. Stat. Model 2005, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Mukerjee, R.; Chatterjee, S. Bayesian analysis of zero-inflated regression models. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2012, 142, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famoye, F.; Singh, K.P. Zero-inflated generalized Poisson regression model with an application to domestic violence data. J. Data Sci. 2006, 4, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurmu, S.; Trivedi, P.K. Excess zeros in count models for recreational trips. J. Appl. Econ. 1996, 11, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, R. Econometric Analysis of Count Data, 5th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbe, J.M. Negative Binomial Regression, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Peck, E.A.; Vining, G.G. Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis, 5th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; Marquéz, J.R.G.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Leitão, P.J.; et al. Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 2013, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerl, A.E.; Kennard, R.W. Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 1970, 12, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, B.M.G.; Månsson, K.; Shukur, G. A simulation study of some biasing parameters for the ridge type estimation of Poisson regression. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2015, 44, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ullah, M.A.; Amin, M. Poisson regression diagnostics with ridge estimation. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2023, 52, 4174–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, E.A.; Abonazel, M.R.; Taha, I.M. Ridge estimators for the negative binomial regression model with application. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Conference on Statistics, Computer Science, and Operation Research, Cairo, Egypt, 3–5 December 2018; pp. 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.N.; Afzal, N.; Amin, M.; Batool, A. Modified ridge-type estimator for the zero inflated negative binomial regression model. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2024, 53, 5305–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Khan, A.; Amanullah, M.; Bakr, M.E.; Alshangiti, A.M.; Balogun, O.S.; Yusuf, M. A new modified biased estimator for Zero inflated Poisson regression model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGough, S.F.; Incerti, D.; Lyalina, S.; Copping, R.; Narasimhan, B.; Tibshirani, R. Penalized regression for left-truncated and right-censored survival data. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 5487–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibria, B.M.G.; Månsson, K.; Shukur, G. A Ridge Regression Estimator for the Zero-Inflated Poisson Model; CESIS Working Paper; Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kibria, B.M.G.; Månsson, K.; Shukur, G. Some ridge regression estimators for the zero-inflated Poisson model. J. Appl. Stat. 2013, 40, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzbaşi, B.; Asar, A. Ridge type estimation in the zero-inflated negative binomial regression. Econom. Methods Appl. 2018, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Qasim, M.; Månsson, K.; Amin, M.; Kibria, B.M.G.; Sjölander, P. Biased adjusted Poisson ridge estimators—Method and application. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2020, 44, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladeitan, B.B.; Adebimpe, O.; Lukman, A.F.; Oludoun, O.; Abiodun, O.E. Modified Kibria–Lukman (MKL) estimator for the Poisson regression model: Application and simulation. F1000Research 2021, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raihan, M.A.; Alluri, P.; Wu, W.; Gan, A. Estimation of bicycle crash modification factors (CMFs) on urban facilities using zero-inflated negative binomial models. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 123, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaktha, N. Properties of Hurdle Negative Binomial Models for Zero-Inflated and Overdispersed Count Data. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.Y.; Hastie, T. L1-regularization path algorithm for generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. B. 2007, 69, 659–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taweel, Y.; Algamal, Z. Almost unbiased ridge estimator in the zero-inflated Poisson regression model. TWMS J. Appl. Eng. Math. 2022, 12, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Kibria, B.M.G. Performance of some new ridge regression estimators. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2003, 32, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.A.; Kibria, B.M. Some one and two parameter estimators for the multicollinear Gaussian linear regression model: Simulations and applications. Surv. Math. Appl. 2023, 18, 183–221. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.A.; Kibria, B.G. Performance of some estimators for the multicollinear logistic regression model: Theory, simulation, and applications. Res. Stat. 2024, 2, 2364747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayem, H.M.; Aziz, S.; Kibria, B.M.G. Comparison among ordinary least squares, ridge, lasso, and elastic net estimators in the presence of outliers: Simulation and application. Int. J. Stat. Sci. 2024, 24, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, N.; Kibria, B.M. Performance of some improved estimators and their robust versions in presence of multicollinearity and outliers. Sankhya B 2025, 87, 173–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D.; MacKenzie, D.; Villouta, E. Modelling skewed data with many zeros: A simple approach combining ordinary and logistic regression. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2005, 12, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Tang, W.; Wang, W.; Paul, C. Structural zeroes and zero-inflated models. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2014, 26, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoli, W.; Conceição, K.S.; Andrade, M.G.; Louzada, F. A Bayesian approach for some zero-modified Poisson mixture models. Stat. Model. 2020, 20, 467–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheety, M.I.; Nayem, H.M.; Kibria, B.M.G. An unbiased convex estimator depending on prior information for the classical linear regression model. Stats 2025, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayem, H.M.; Aziz, S.; Kibria, B.M.G. Evaluating estimator performance under multicollinearity: A trade-off between MSE and accuracy in logistic, lasso, elastic net, and ridge regression with varying penalty parameters. Stats 2025, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Chen, Q. An iterative and shrinking generalized ridge regression for ill-conditioned geodetic observation equations. J. Geod. 2024, 98, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Du, J.H.; Tibshirani, R.J. Optimal ridge regularization for out-of-distribution prediction. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.01233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifollahi, S.; Bevrani, H.; Algamal, Z.Y. Shrinkage estimators in zero-inflated Bell regression model with application. J. Stat. Theory Pract. 2025, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeileis, A.; Kleiber, C.; Jackman, S. Regression models for count data in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 27, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nayem, H.; Kibria, B.M.G. The Ridge-Hurdle Negative Binomial Regression Model: A Novel Solution for Zero-Inflated Counts in the Presence of Multicollinearity. Stats 2025, 8, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8040102
Nayem H, Kibria BMG. The Ridge-Hurdle Negative Binomial Regression Model: A Novel Solution for Zero-Inflated Counts in the Presence of Multicollinearity. Stats. 2025; 8(4):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8040102
Chicago/Turabian StyleNayem, HM, and B. M. Golam Kibria. 2025. "The Ridge-Hurdle Negative Binomial Regression Model: A Novel Solution for Zero-Inflated Counts in the Presence of Multicollinearity" Stats 8, no. 4: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8040102
APA StyleNayem, H., & Kibria, B. M. G. (2025). The Ridge-Hurdle Negative Binomial Regression Model: A Novel Solution for Zero-Inflated Counts in the Presence of Multicollinearity. Stats, 8(4), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8040102







