Survival Times of Transplanted Kidneys Among Different Donor–Recipient Cohorts: The United States Registry Analysis from 1987 to 2018, Part 1: Gender and Ethnicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design, Setting, and Instrument for Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Kaplan Meier (KM)
2.2.2. Cox Proportional Hazard (Cox PH)
3. Results
3.1. Survival Times Regarding Gender Match of Donors and Recipients
3.2. Survival Times Regarding Ethnicity Match Among Donors and Recipients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coquillard, C.; Berger, J.; Daily, M.; Shah, M.; Mei, X.; Marti, F.; Gedaly, R. Combined liver–kidney transplantation for polycystic liver and kidney disease: Analysis from the United Network for Organ Sharing dataset. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, P.P.; Harhay, M.N.; Abt, P.L.; Levine, M.H.; Halpern, S.D. New Solutions to Reduce Discard of Kidneys Donated for Transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padela, A.I.; Rasheed, S.; Warren, G.J.W.; Choi, H.; Mathur, A.K. Factors associated with positive attitudes toward organ donation in Arab Americans. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, M.; Diena, D.; Dellepiane, S.; Guzzo, G.; Sardo, L.L.; Fop, F.; Segoloni, G.P.; Amoroso, A.; Magistroni, P.; Biancone, L. Long-Term Outcomes and Discard Rate of Kidneys by Decade of Extended Criteria Donor Age. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, C. Therapeutic cloning: Promises and issues. McGill J. Med. 2007, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, F.; Kachouie, N.N. Potential Impact of Donors’ Factors on Survival Times of Transplanted Hearts and Lungs. Transplant. Rep. 2019, 4, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachouie, N.N.; Hamad, F. Potential impact of OPTN plan in association with donors’ factors on survival times of transplanted kidneys. Transplant. Rep. 2020, 5, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, J.; Goel, M.; Khanna, P. Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2010, 1, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.T.; Wang, J.W. Statistical Methods for Survival Data Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 476. [Google Scholar]
- Collett, D. Modelling Survival Data in Medical Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegel, E.R. Survival analysis: A self-learning text. Technometrics 2006, 48, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, D.R. Regression models and lifetables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1972, 34, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R.; Lewis, P.A.W. Multivariate point processes. In Proceedings of the Sixth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability; University of California Press: Durham, NC, USA, 1972; Volume 3, pp. 401–448. [Google Scholar]
- Collett, D. Modelling Survival Data in Medical Research; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hamad, F.; Kachouie, N.N. A hybrid method to estimate the full parametric hazard model. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2019, 48, 5477–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.P.; Moeschberger, M.L. Statistics for Biology and Health. Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Survival probabilities (the Kaplan-Meier method). BMJ 1998, 317, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matloff, N. The Art of R programming: A Tour of Statistical Software Design; No Starch Press: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Puoti, F.; Ricci, A.; Nanni-Costa, A.; Ricciardi, W.; Malorni, W.; Ortona, E. Organ transplantation and gender differences: A paradigmatic example of intertwining between biological and sociocultural determinants. Biol. Sex Differ. 2016, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, P.; Van Thiel, D.H.; Gavaler, J.S.; Starzl, T.E. Effect of race upon organ donation and recipient survival in liver transplantation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1990, 35, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeier, M.; Döhler, B.; Opelz, G.; Ritz, E. The effect of donor gender on graft survival. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2570–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, R.R.; Foster, M.W. Community involvement in the ethical review of genetic research: Lessons from American Indian and Alaska Native populations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110 (suppl. 2), 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, T.D.; Narva, A.S.; Stiles, S.K.; Karp, S.K.; Cass, A.; Ayanian, J.Z. Access to renal transplantation among American Indians and Hispanics. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 44, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, T.; Ishida, H.; Horita, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Toma, H.; Tanabe, K. Decrease of blood type antigenicity over the long-term after ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Transpl. Immunol. 2011, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K. A new concept of accommodation in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2005, 19, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Hotta, K.; Mitsuke, A.; Fukasawa, Y.; Tanabe, T.; Higuchi, H.; Takada, Y.; Harada, H. Long-Term Outcome of ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation in Patients Treated With Low-Dose Rituximab Regimen. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttarajappa, C.; Shapiro, R.; Tan, H.P. Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplantation: A Review. J. Transplant. 2012, 2012, 193724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

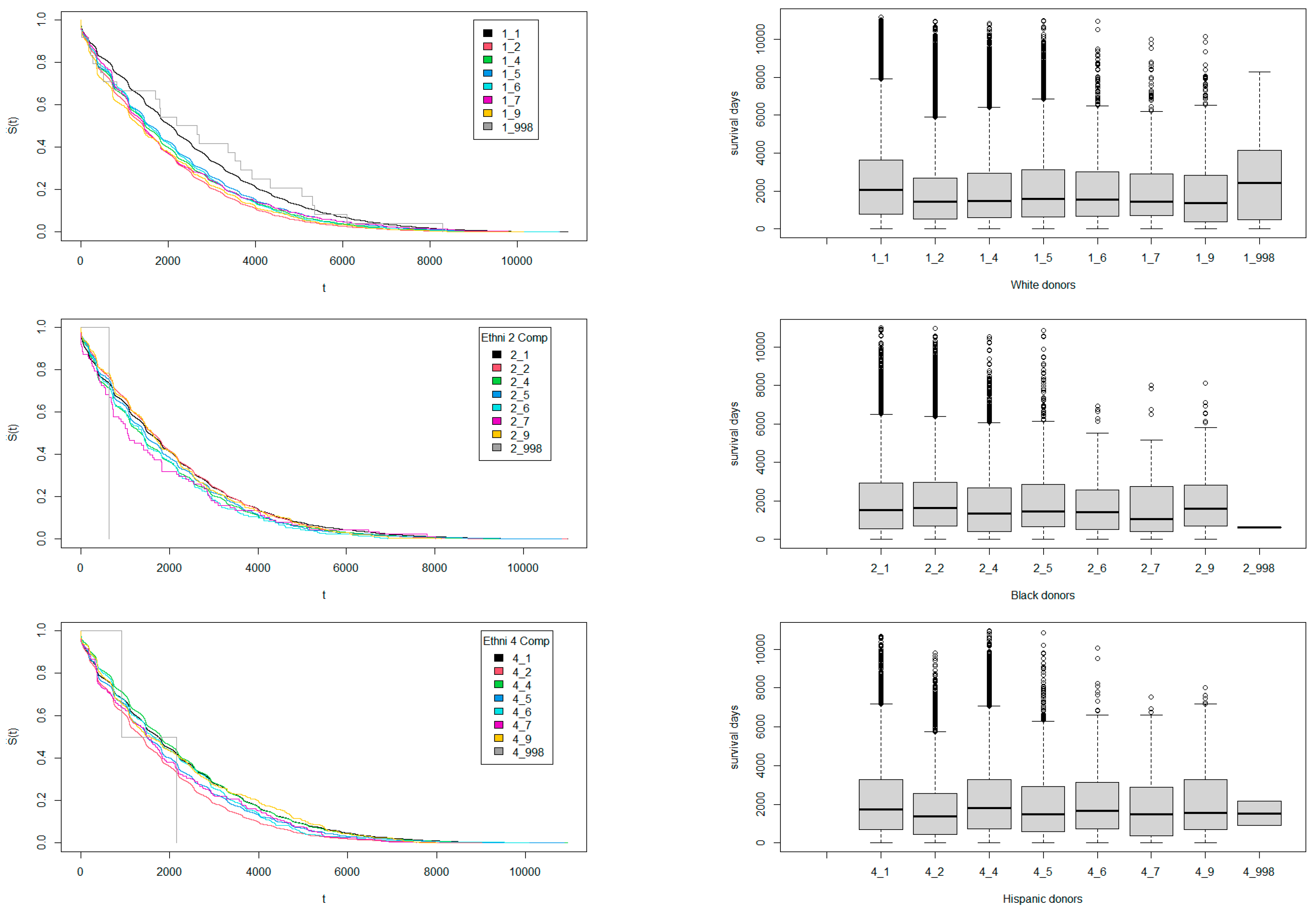
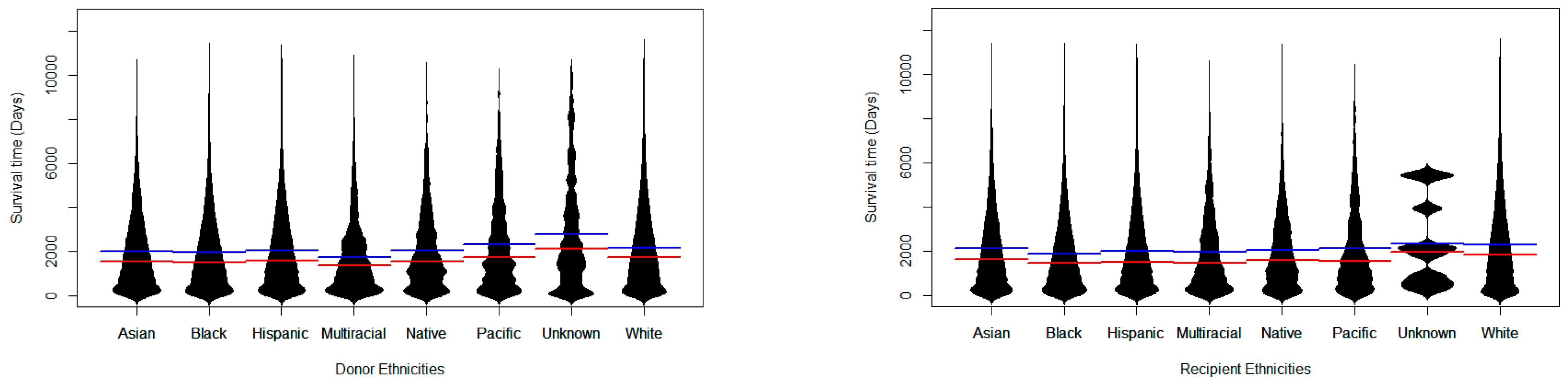
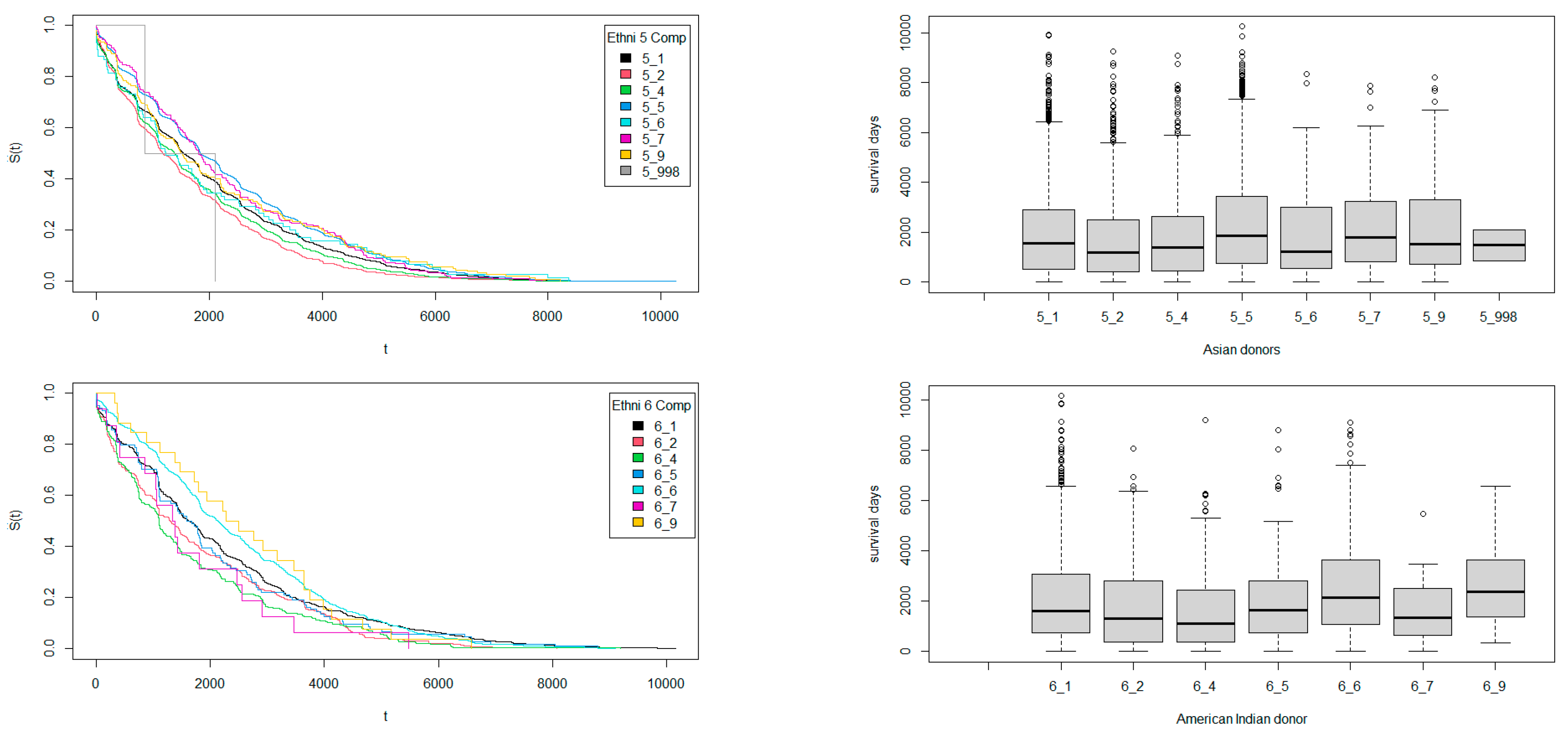
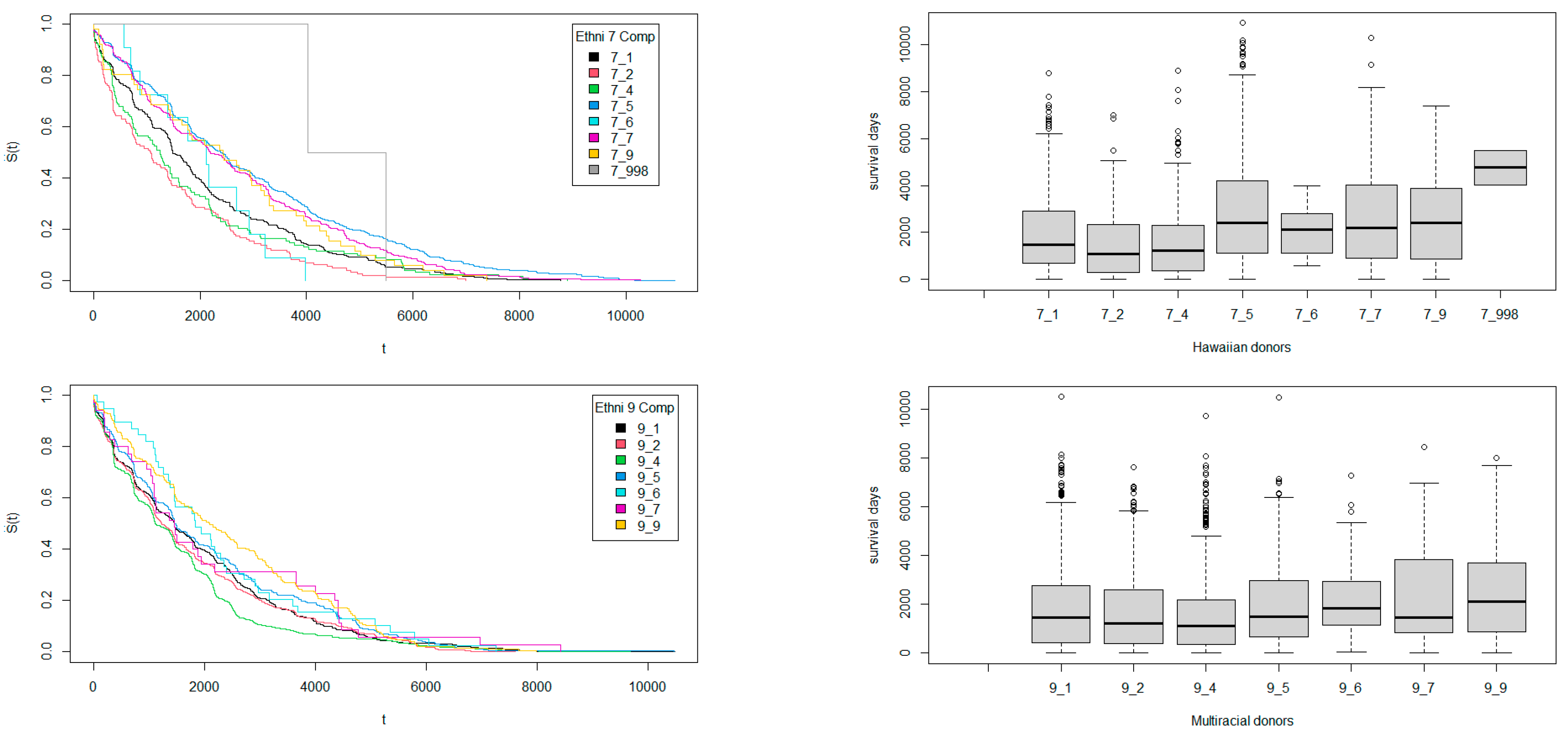
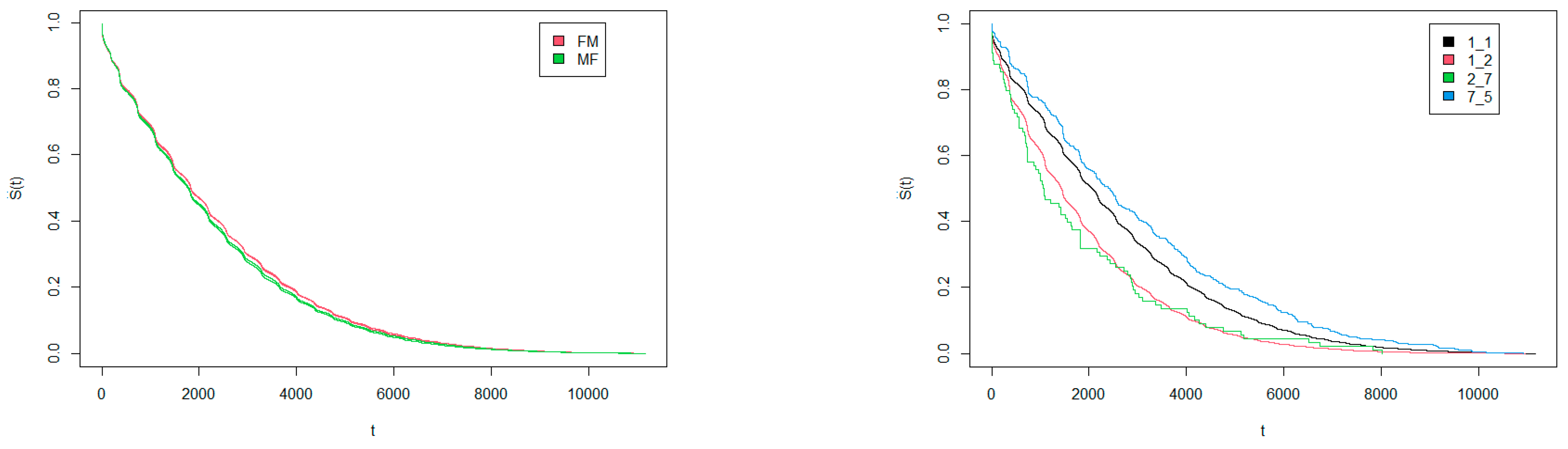
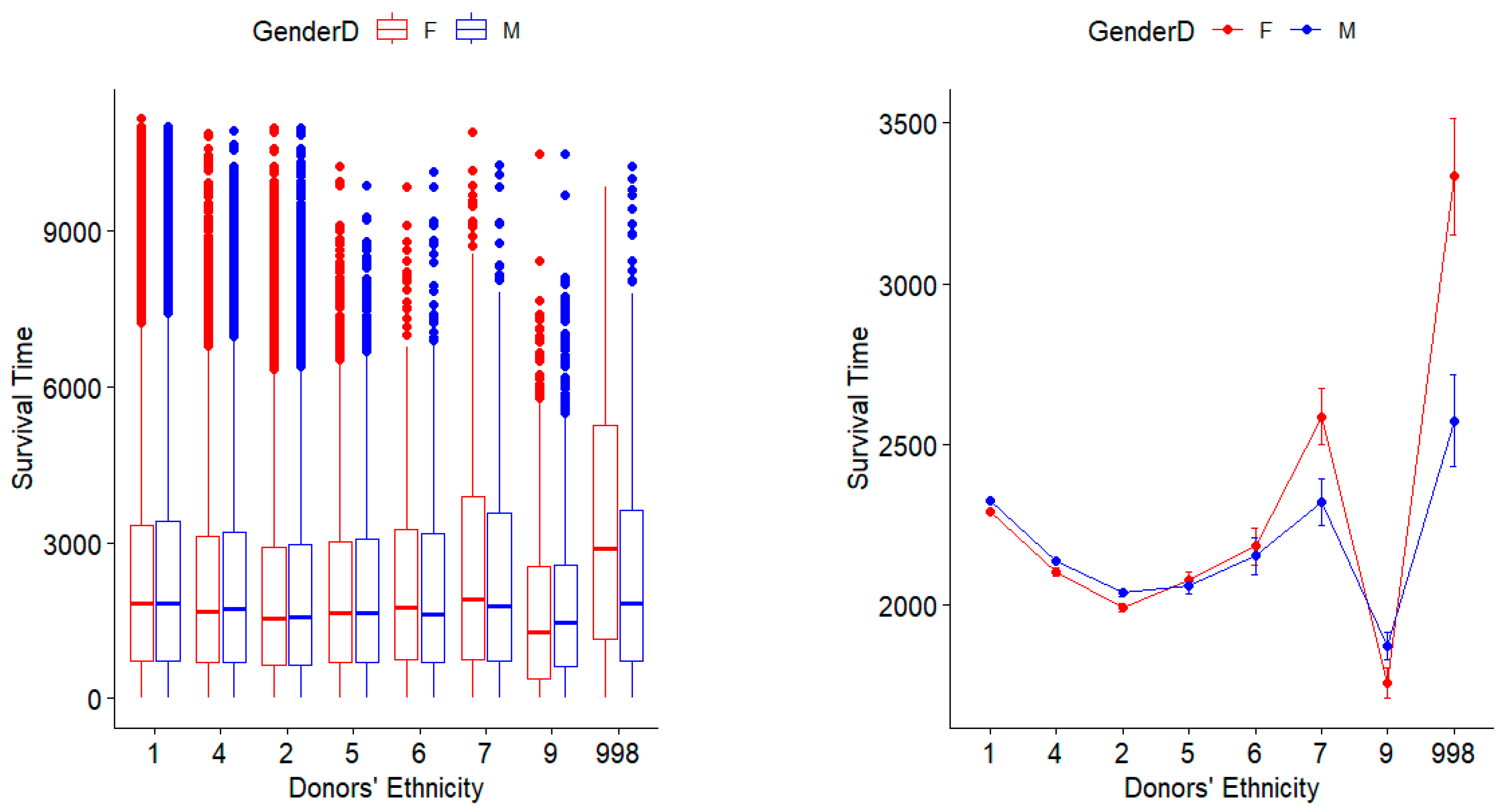

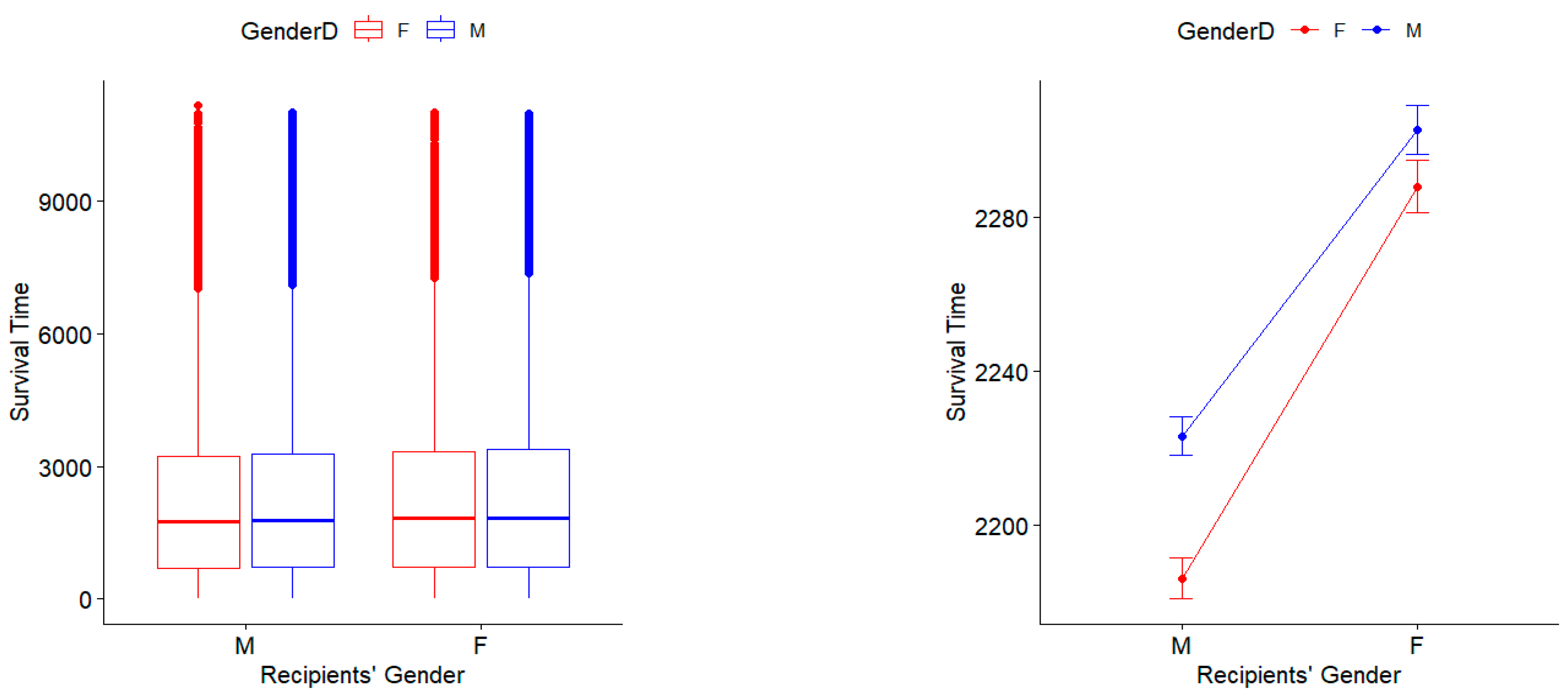

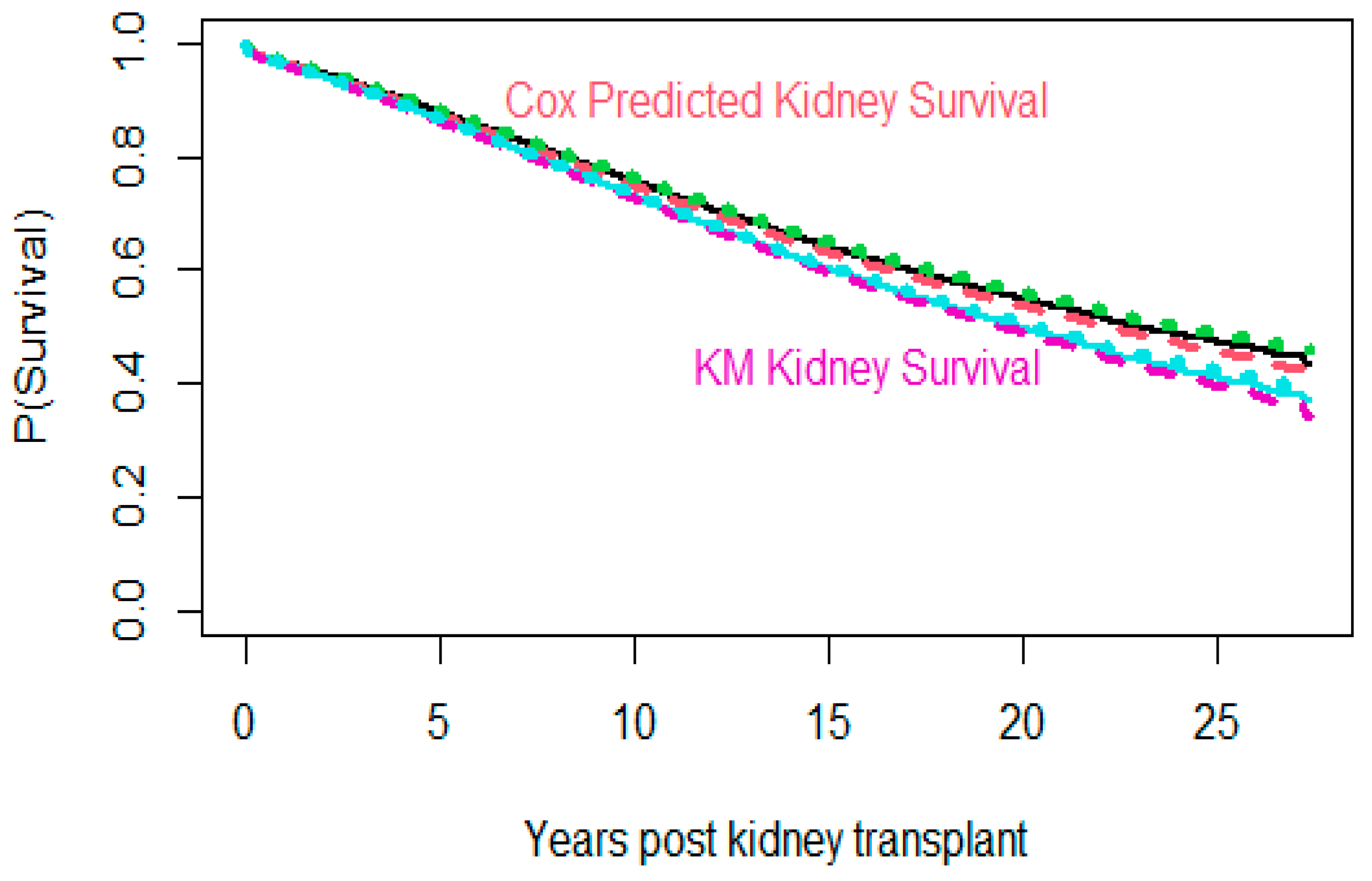
| Ethnicity | White | Black | Hispanic | Asian | American Indian | Hawaiian | Multiracial | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 998 |
| Donor Gender | Recipient | Size n | Max Time | STD | Sample Proportion | Donor Gender | Recipient | Size n | Min Time | STD | Sample Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | 97,845 | 2303 | 1992 | 21.5% | M | M | 149,982 | 2223 | 1934 | 33% |
| F | F | 82,430 | 2288 | 1957 | 18% | F | M | 124,682 | 2186 | 1896 | 27% |
| Ethnicity | Ethnicity | ||||||||||
| Hawaiian | Asian | 529 | 2945 | 2354 | 0.1% | Hawaiian | Black | 143 | 1481 | 1499 | 0.03% |
| American Indian | American Indian | 674 | 2497 | 1816 | 0.15% | American Indian | Hispanic | 246 | 1629 | 1611 | 0.054% |
| White | White | 22,4104 | 2488 | 2067 | 49% | White | Black | 60,575 | 1837 | 1670 | 13.3% |
| Multi | Multi | 197 | 2432 | 1794 | 0.043% | Multi | Hispanic | 887 | 1539 | 1498 | 0.195% |
| Asian | Asian | 4673 | 2321 | 1862 | 1% | Asian | Black | 1586 | 1635 | 1501 | 0.35% |
| Hispanic | Hispanic | 27,504 | 2224 | 1835 | 6% | Hispanic | Black | 8884 | 1755 | 1576 | 1.95% |
| Black | Black | 34,656 | 2042 | 1739 | 7.62% | Black | Hawaiian | 88 | 1743 | 1815 | 0.02% |
| Donor Gender | Recipient | Sample Size | Max Expected Survival Time | KM STD | Sample Proportion | Donor Gender | Recipient | Sample Size | Min Expected Survival Time | KM STD | Sample Proportion | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | 97,845 | 2303 | 1992 | 21.5% | F | M | 124,682 | 2186 | 1896 | 27% | 2 × 10−16 |
| Ethnicity | Ethnicity | |||||||||||
| Hawaiian | Asian | 529 | 2945 | 2354 | 0.1% | Black | Hawaiian | 88 | 1743 | 1815 | 0.02% | 1.1 × 10−6 |
| White | White | 224,104 | 2488 | 2067 | 49% | White | Black | 60,575 | 1837 | 1670 | 13.3% | 2 × 10−16 |
| Ethnicity | Comparison | KLD | Wilcoxon p-Value | Overlap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian | Black | 0.048363 | 8.05398 × 10−45 | 0.84 |
| Asian | Hispanic | 0.014004 | 2.44724 × 10−7 | 0.78 |
| Asian | Multiracial | 0.047881 | 6.11082 × 10−5 | 0.88 |
| Asian | Native | 0.024184 | 0.2672166 | 0.87 |
| Asian | Pacific | 0.099293 | 0.8460493 | 0.93 |
| Asian | White | 0.035686 | 3.06276 × 10−29 | 0.91 |
| Black | Hispanic | 0.011565 | 1.68707 × 10−36 | 0.70 |
| Black | Multiracial | 0.168941 | 0.3556699 | 0.95 |
| Black | Native | 0.113502 | 9.0139 × 10−8 | 0.95 |
| Black | Pacific | 0.25474 | 4.83449 × 10−5 | 0.96 |
| Black | White | 0.023816 | 0 | 0.73 |
| Hispanic | Multiracial | 0.102914 | 0.02762855 | 0.94 |
| Hispanic | Native | 0.062604 | 0.1797135 | 0.93 |
| Hispanic | Pacific | 0.172042 | 0.1454121 | 0.95 |
| Hispanic | White | 0.01658 | 1.5662 × 10−155 | 0.82 |
| Multiracial | Native | 0.013971 | 0.009093587 | 0.64 |
| Multiracial | Pacific | 0.023005 | 0.008976896 | 0.66 |
| Multiracial | White | 0.129124 | 2.51715 × 10−16 | 0.96 |
| Native | Pacific | 0.048577 | 0.6404923 | 0.75 |
| Native | White | 0.096034 | 4.15114 × 10−10 | 0.96 |
| Pacific | White | 0.18096 | 0.000390374 | 0.97 |
| VARIABLES | Coef. | Exp. (Coef.) | SE (Coef.) | Z | Pr. (>|z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rcp.GENDER.M | 0.035125 | 1.035749 | 0.009902 | 3.547 | 0.000389 |
| Rcp.ETH2 | 0.669865 | 1.953973 | 0.011267 | 59.451 | <2 × 10−16 |
| Rcp.ETH4 | 0.11386 | 1.120595 | 0.016946 | 6.719 | 1.83 × 10−11 |
| Rcp.ETH5 | −0.156769 | 0.854901 | 0.027447 | −5.712 | 1.12 × 10−8 |
| Rcp.ETH6 | 0.408959 | 1.505249 | 0.049793 | 8.213 | <2 × 10−16 |
| Rcp.ETH7 | 0.423955 | 1.527993 | 0.071727 | 5.911 | 3.41 × 10−9 |
| Rcp.ETH9 | 0.362956 | 1.437573 | 0.06101 | 5.949 | 2.70 × 10−9 |
| Don.GENDER.M | −0.042959 | 0.957951 | 0.009784 | −4.391 | 1.13 × 10−5 |
| Don.ETH2 | 0.080228 | 1.083534 | 0.01428 | 5.618 | 1.93 × 10−8 |
| Don.ETH4 | −0.071019 | 0.931444 | 0.016565 | −4.287 | 1.81 × 10−5 |
| Don.ETH5 | 0.015543 | 1.015665 | 0.035109 | 0.443 | 0.658 |
| Don.ETH6 | −0.15537 | 0.856099 | 0.081832 | −1.899 | 0.058 |
| Don.ETH7 | 0.042052 | 1.042949 | 0.09636 | 0.436 | 0.663 |
| Don.ETH9 | −0.083577 | 0.91982 | 0.066516 | −1.256 | 0.209 |
| VARIABLES | Exp. (Coef.) | Exp. (Coef.) | Lower 0.95 | Upper 0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rcp.GENDER.M | 1.0357 | 0.9655 | 1.0158 | 1.056 |
| Rcp.ETH2 | 1.954 | 0.5118 | 1.9113 | 1.9976 |
| Rcp.ETH4 | 1.1206 | 0.8924 | 1.084 | 1.1584 |
| Rcp.ETH5 | 0.8549 | 1.1697 | 0.8101 | 0.9022 |
| Rcp.ETH6 | 1.5052 | 0.6643 | 1.3653 | 1.6596 |
| Rcp.ETH7 | 1.528 | 0.6545 | 1.3276 | 1.7586 |
| Rcp.ETH9 | 1.4376 | 0.6956 | 1.2756 | 1.6202 |
| Don.GENDER.M | 0.958 | 1.0439 | 0.9398 | 0.9765 |
| Don.ETH2 | 1.0835 | 0.9229 | 1.0536 | 1.1143 |
| Don.ETH4 | 0.9314 | 1.0736 | 0.9017 | 0.9622 |
| Don.ETH5 | 1.0157 | 0.9846 | 0.9481 | 1.088 |
| Don.ETH6 | 0.8561 | 1.1681 | 0.7292 | 1.005 |
| Don.ETH7 | 1.0429 | 0.9588 | 0.8635 | 1.2598 |
| Don.ETH9 | 0.9198 | 1.0872 | 0.8074 | 1.0479 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kachouie, N.N.; Despeignes, A.; Breininger, D. Survival Times of Transplanted Kidneys Among Different Donor–Recipient Cohorts: The United States Registry Analysis from 1987 to 2018, Part 1: Gender and Ethnicity. Stats 2025, 8, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8010001
Kachouie NN, Despeignes A, Breininger D. Survival Times of Transplanted Kidneys Among Different Donor–Recipient Cohorts: The United States Registry Analysis from 1987 to 2018, Part 1: Gender and Ethnicity. Stats. 2025; 8(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKachouie, Nezamoddin N., Alain Despeignes, and Daniel Breininger. 2025. "Survival Times of Transplanted Kidneys Among Different Donor–Recipient Cohorts: The United States Registry Analysis from 1987 to 2018, Part 1: Gender and Ethnicity" Stats 8, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8010001
APA StyleKachouie, N. N., Despeignes, A., & Breininger, D. (2025). Survival Times of Transplanted Kidneys Among Different Donor–Recipient Cohorts: The United States Registry Analysis from 1987 to 2018, Part 1: Gender and Ethnicity. Stats, 8(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats8010001





