Sentiment Analysis for Tourism Insights: A Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Research Topic: Exploring Tourist Sentiments on TripAdvisor
1.3. Tourism in Morocco
1.4. Main Results
2. Literature Review
2.1. Marrakech’s Tourist Attractions: Jemaa el-Fna and the Medina
2.2. Online Reviews
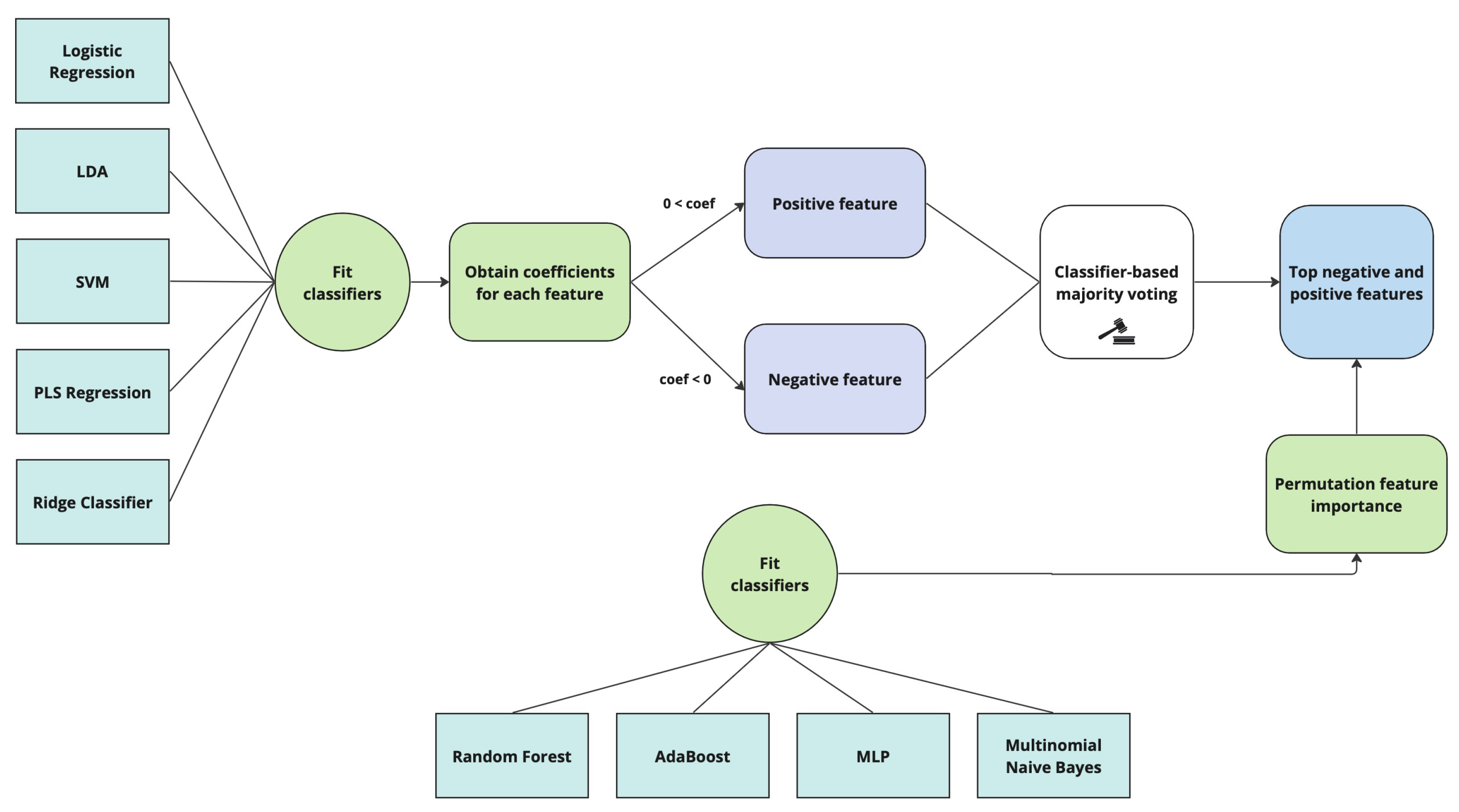
3. Methodology
3.1. ‘Voting’ Method
- Logistic Regression, based on maximum likelihood estimation for coefficient estimates, is commonly used for classification tasks.
- Ridge Classifier is based on the ridge regression incorporating a regularization that minimizes overfitting, especially when dealing with limited dataset samples. The cost function includes a penalty term, with a higher penalization leading to more robust coefficients [24].
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) maximizes the between-class variance, aiming at reducing the dimensionality and improving the classification in a lower-dimensional subspace [25].
- Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a classifier that identifies hyperplanes to separate classes while avoiding overfitting [26].
- Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) is based on latent orthogonal latent components used to fit a linear regression model. PLSR involves determining the optimal number of latent components, typically through cross-validation [27].
- Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), a standard neural network architecture, stands out for its ability to deal with non-linear problems [30].
- Random Forest, also an ensemble learning technique, aggregates decision trees using bootstrapping during the training process [33].
- The Naïve Bayes classifier relies on conditional probability and the assumption of feature independence to predict labels [34].
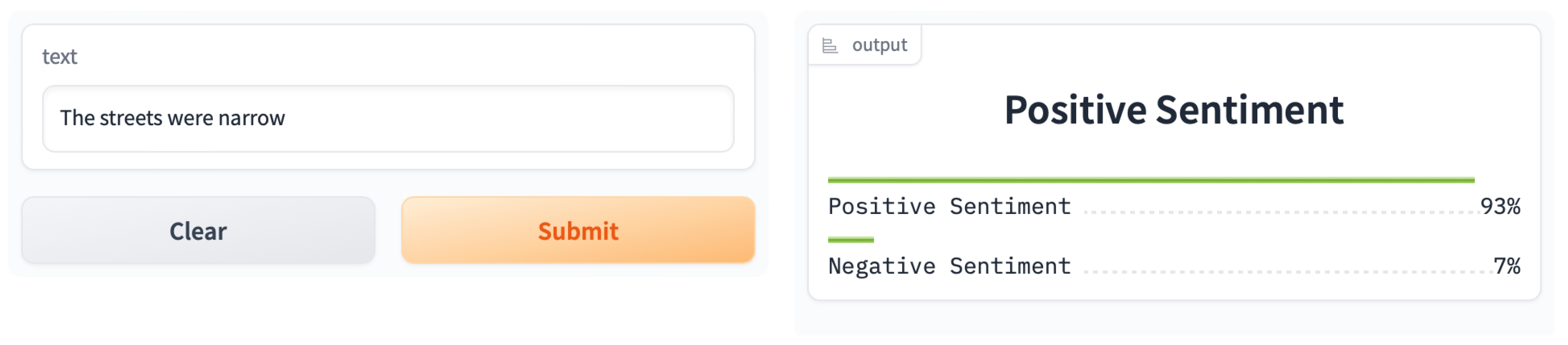
3.2. Large Language Models: Fine-Tuning SieBERT
4. Experimental Results: Comparisons with VADER and GPT-4o
5. Discussion: Public Policy Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huseynli, N. Econometric Analysis of the Relationship Between Tourism Revenues, Inflation and Economic Growth: The Case of Morocco and South Africa. Afr. J. Hosp. Tour. Leis. 2022, 11, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafik, K. The Tourism Sector and Territorial Development in Marrakech City-Morocco. Int. J. Humanit. Educ. Res. 2023, 5, 253–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Marc, B.; Omar, B.; Soulaimane, K.; Larbi, S. Exploring destination’s negative e-reputation using aspect based sentiment analysis approach: Case of Marrakech destination on TripAdvisor. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 40, 100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabdallaoui, I.; Guerouate, F.; Bouhaddour, S.; Saadi, C.; Sbihi, M. Advanced Exploratory Data Analysis for Moroccan Shopping Places in TripAdvisor. In Advanced Research in Technologies, Information, Innovation and Sustainability; Guarda, T., Portela, F., Augusto, M.F., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 257–271. [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia, A.; Luzon, M.V.; Herrera, F. Sentiment Analysis in TripAdvisor. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2017, 32, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.H.; Sigala, M.; Gretzel, U. Exploring TripAdvisor. In Open Tourism: Open Innovation, Crowdsourcing and Co-Creation Challenging the Tourism Industry; Egger, R., Gula, I., Walcher, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 239–255. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida-García, F. Current issues of tourism in Morocco. In Routledge Handbook of Tourism in Africa; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hutto, C.; Gilbert, E. VADER: A Parsimonious Rule-Based Model for Sentiment Analysis of Social Media Text. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1–4 June 2014; Volume 8, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. GPT-4o (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 4 Optimized). 2024. Available online: https://openai.com (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Escher, A.; Petermann, S.; Clos, B. Le Bradage de la Médina de Marrakech? In Le Maroc à la Veille du Troisième Millénaire 7 Défis, Chances et Risques d’un Développement Durable; Berriane, M., Kagermeier, A., Eds.; Actes du 6ème Colloque Maroco-Allemand de Paderborn 2000; Faculté des Lettres et des Science Humaines: Rabat, Morocco, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Saddou, H. Tourisme à Marrakech; Impacts économiques, socioculturels et environnementaux éminents. Espace Géogr. Soc. Marocaine 2019, 28/29, 221–251. [Google Scholar]
- Steenbruggen, J. Tourism geography: Emerging trends and initiatives to support tourism in Morocco. J. Tour. Hosp. 2016, 3, 224–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzac-Souali, A.C. Rumeurs et cohabitation en médina de Marrakech: L’étranger où on ne l’attendait pas. Hérodote 2007, 127, 64–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choplin, M.A.; Gatin, V. L’espace public comme vitrine de la ville marocaine: Conceptions et appropriations des places Jemaa El Fna à Marrakech, Boujloud à Fès et Al Mouahidine à Ouarzazate. Norois. Environ. Aménage. Soc. 2010, 214, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, L. Jemaa El-Fna ou l’exotisme durable. Géogr. Cult. 2009, 72, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keates, N. Deconstructing TripAdvisor. Wall Str. J. 2007, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.Z.K.; Zhao, S.J.; Cheung, C.M.K.; Lee, M.K.O. Examining the Influence of Online Reviews on Consumers’ Decision-Making: A Heuristic–Systematic Model. Decis. Support Syst. 2014, 67, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozen, I.; Raedts, M. The Effects of Online Customer Reviews and Managerial Responses on Travelers’ Decision-Making Processes. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2018, 27, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, A.Y.K.; Banerjee, S. Reliability of Reviews on the Internet: The Case of TripAdvisor. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering & Computer Science, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–25 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, P. User-Generated Content and Travel: A Case Study on TripAdvisor.Com. In Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2008; O’Connor, P., Höpken, W., Gretzel, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Stine, R.A. Sentiment Analysis. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2019, 6, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spärck Jones, K. A Statistical Interpretation of Term Specificity and Its Application in Retrieval. J. Doc. 1972, 28, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaiser, S.; Ali, R. Text Mining: Use of TF-IDF to Examine the Relevance of Words to Documents. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2018, 181, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.; Elgeldawi, E.; Zaki, A.; Galal, A. Sentiment Analysis for Arabic Reviews Using Machine Learning Classification Algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference, Aswan, Egypt, 8–9 February 2020; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Tharwat, A.; Gaber, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Linear Discriminant Analysis: A Detailed Tutorial. AI Commun. 2017, 30, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, M.; Chavan, P.; Tambade, S.; Shinde, S.V. A Review of Machine Learning Techniques Using Decision Tree and Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 12–13 August 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Krämer, N.; Sugiyama, M. The Degrees of Freedom of Partial Least Squares Regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2011, 106, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, F.; Muschalik, M.; Hüllermeier, E.; Hammer, B. Incremental permutation feature importance (iPFI): Towards online explanations on data streams. Mach. Learn. 2023, 112, 4863–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, C.; Freiesleben, T.; König, G.; Herbinger, J.; Reisinger, T.; Casalicchio, G.; Wright, M.N.; Bischl, B. Relating the Partial Dependence Plot and Permutation Feature Importance to the Data Generating Process. In Explainable Artificial Intelligence; Longo, L., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 1901, pp. 456–479. [Google Scholar]
- Nosratabadi, S.; Ardabili, S.; Lakner, Z.; Mako, C.; Mosavi, A. Prediction of Food Production Using Machine Learning Algorithms of Multilayer Perceptron and ANFIS. Agriculture 2021, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapire, R.E. Explaining AdaBoost. In Empirical Inference; Schölkopf, B., Luo, Z., Vovk, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kégl, B. Introduction to AdaBoost; Citeseer Publisher: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, I.; Baron, D.; Shahaf, S. Probabilistic Random Forest: A Machine Learning Algorithm for Noisy Data Sets. Astron. J. 2019, 157, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kumar, B.; Gaur, L.; Tyagi, A. Comparison between Multinomial and Bernoulli Naïve Bayes for Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Automation, Computational and Technology Management (ICACTM), London, UK, 24–26 April 2019; pp. 593–596. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, H. Cross-validated permutation feature importance considering correlation between features. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2022, 3, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condevaux, C.; Harispe, S.; Mussard, S. Fair and Efficient Alternatives to Shapley-based Attribution Methods. In Proceedings of the ECMLPKDD 2022-The European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Grenoble, France, 19–23 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Condevaux, C.; Harispe, S. LSG Attention: Extrapolation of pretrained Transformers to long sequences. In Proceedings of the PAKDD 2023—The 27th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Osaka, Japan, 25–28 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Naseer, M.; Hayat, M.; Zamir, S.W.; Khan, F.S.; Shah, M. Transformers in Vision: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, F.; Liu, N.; Deng, H.; Cai, H.; Wang, S.; Yin, D.; Du, M. Explainability for Large Language Models: A Survey. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2024, 15, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, J.; Heitmann, M.; Siebert, C.; Schamp, C. More than a Feeling: Accuracy and Application of Sentiment Analysis. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2023, 40, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a Distilled Version of BERT: Smaller, Faster, Cheaper and Lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Tourism Trends and Policies 2022; OECD: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kania, K.; Kałaska, M. Functional and spatial changes of souks in Morocco’s imperial cities in the context of tourism development. Misc. Geogr. 2019, 23, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L.B. ‘Tourist Price’ and Diasporic Visitors: Negotiating the Value of Descent. Valuat. Stud. 2015, 3, 119–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D. Tourism and Animal Welfare. Tour. Recreat. Res. 2015, 38, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stazaker, K.; Mackinnon, J. Visitor Perceptions of Captive, Endangered Barbary Macaques (Macaca sylvanus) Used as Photo Props in Jemaa El Fna Square, Marrakech, Morocco. Anthrozoös 2018, 31, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasethuntsa, B. Health and Hygiene Strategies for Tourism Promotion: Guidelines for Africa. J. Tour. Leis. Hosp. 2022, 4, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkumienė, D.; Atalay, A.; Safaa, L.; Grigienė, J. Sustainable Waste Management for Clean and Safe Environments in the Recreation and Tourism Sector: A Case Study of Lithuania, Turkey and Morocco. Recycling 2023, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yu, Q. Sense of Safety Toward Tourism Destinations: A Social Constructivist Perspective. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2022, 24, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n-Grams | Logistic Regression | Linear Discriminant Analysis | SVM | PLS Regression | Ridge Classifier | Final Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abuse | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| accept | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| acrobats | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| across | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| activity | Positive | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| worse | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| wrong | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative |
| years | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| yes | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| young | Negative | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive |
| Features | Sentiment |
|---|---|
| friendly | Positive |
| animal | Negative |
| night | Positive |
| harassed | Negative |
| overpriced | Negative |
| bill | Negative |
| fresh | Positive |
| money | Negative |
| charge | Negative |
| dirty | Negative |
| guide | Positive |
| lost | Positive |
| couldnt | Negative |
| Metrics | RoBERTa | SieBERT-Marrakech | DistilBERT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision label 0 | 97.79% | 98.04% | 96% |
| Recall label 0 | 96.81% | 96.69% | 98% |
| F-measure label 0 | 97.30% | 97.36% | 97% |
| Precision label 1 | 82.65% | 82.33% | 83% |
| Recall label 1 | 87.41% | 88.85% | 76% |
| F-measure label 1 | 84.97% | 85.47% | 79% |
| F-measure (macro) | 91.14% | 91.42% | 88% |
| Voting vs. Human | SieBERT-Marrakech vs. Human | GPT-4o vs. Human | Human vs. Human |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6435 | 0.8985 | 0.7182 | 0.9599 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voting | 0.835 | 0.83 | 0.835 |
| SieBERT-Marrakech | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.965 |
| VADER | 0.725 | 0.805 | 0.725 |
| GPT-4o | 0.895 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| Reviews | SieBERT-M | Voting | VADER | Human | GPT-4o |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Too busy, too pushy, too dirty, too many people coming to you to sell stuff, in the evening I found it scary…gazillion wonderful restaurants | N | P | P | N | N |
| Personally I do not see the charm of this square…This is one of those places you visit just to be able to cross it off the list and say that you have seen it. | N | P | P | N | N |
| A fast paced city square with merchants of all kinds, unfortunately with much of the merchandise being the same tourist junk. Nice experience…Lots of food stands etc. | P | N | P | P | N |
| This probably the nr 1 must see place in Marrakech even though its authenticity has been gradually eroded…a lot of confusion everywhere. | P | P | N | N | P |
| You must visit the most crowed square in Africa! There is always someone making “noises”…Also don’t “feed” the business of using monkeys or snakes. | P | N | P | P | N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charfaoui, K.; Mussard, S. Sentiment Analysis for Tourism Insights: A Machine Learning Approach. Stats 2024, 7, 1527-1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040090
Charfaoui K, Mussard S. Sentiment Analysis for Tourism Insights: A Machine Learning Approach. Stats. 2024; 7(4):1527-1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040090
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharfaoui, Kenza, and Stéphane Mussard. 2024. "Sentiment Analysis for Tourism Insights: A Machine Learning Approach" Stats 7, no. 4: 1527-1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040090
APA StyleCharfaoui, K., & Mussard, S. (2024). Sentiment Analysis for Tourism Insights: A Machine Learning Approach. Stats, 7(4), 1527-1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/stats7040090







