Discrepancy between Jun/Fos Proto-Oncogene mRNA and Protein Expression in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Collection and Preparation
2.2. Purification of Total RNA and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Real-Time RT-PCR
2.4. Preparation of Nuclear Extracts and Whole-Cell Extracts from Tissue Samples
2.5. ELISA-Based Jun/Fos Protein Quantitation
2.6. Antibodies, SDS-PAGE, and Western Blot Analyses
2.7. Immunohistology/In Situ Hybridization
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
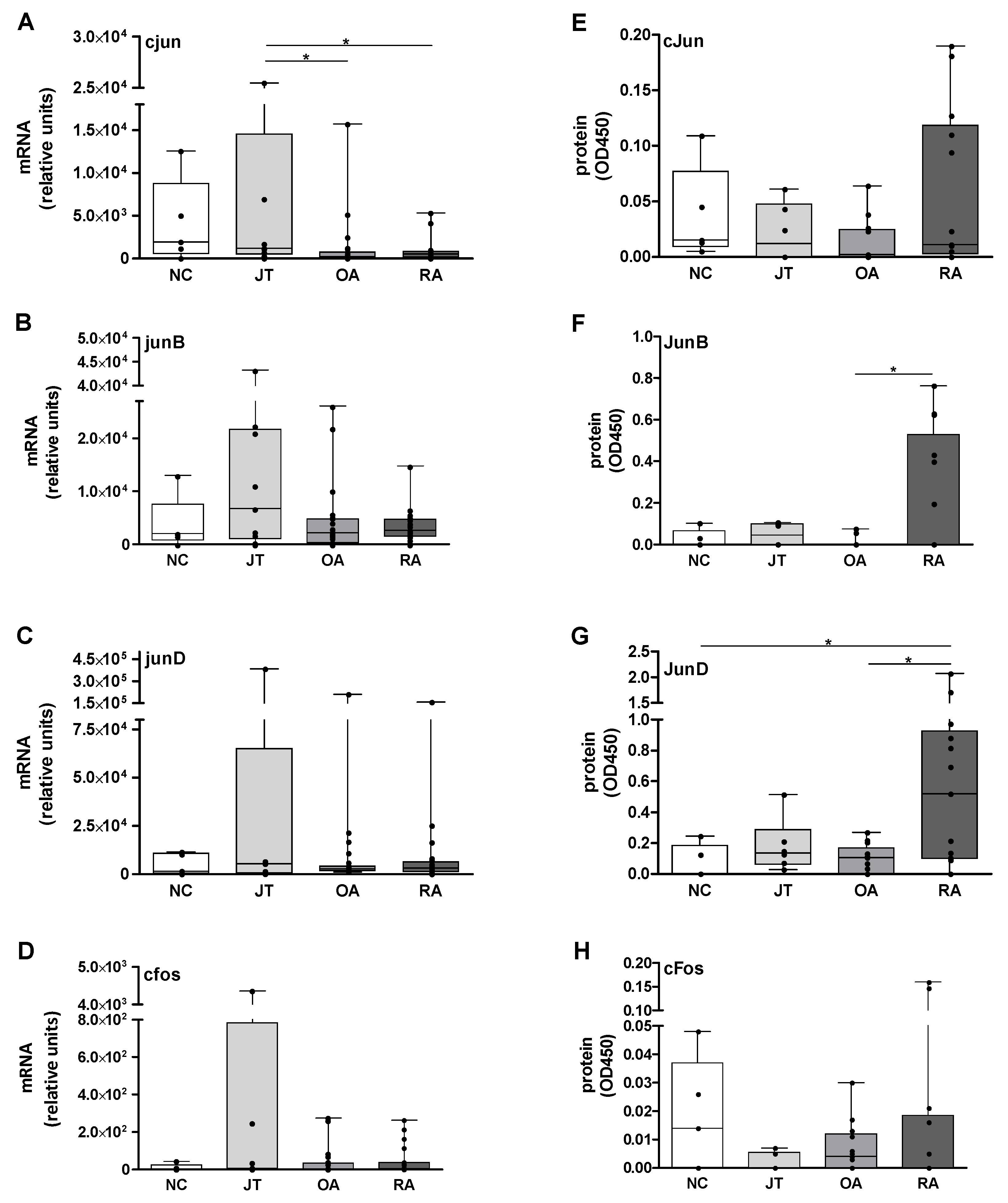
3.1. Quantitation of Jun and Fos mRNA Expression in the SM
3.2. Quantitation of Jun and Fos Protein Expression
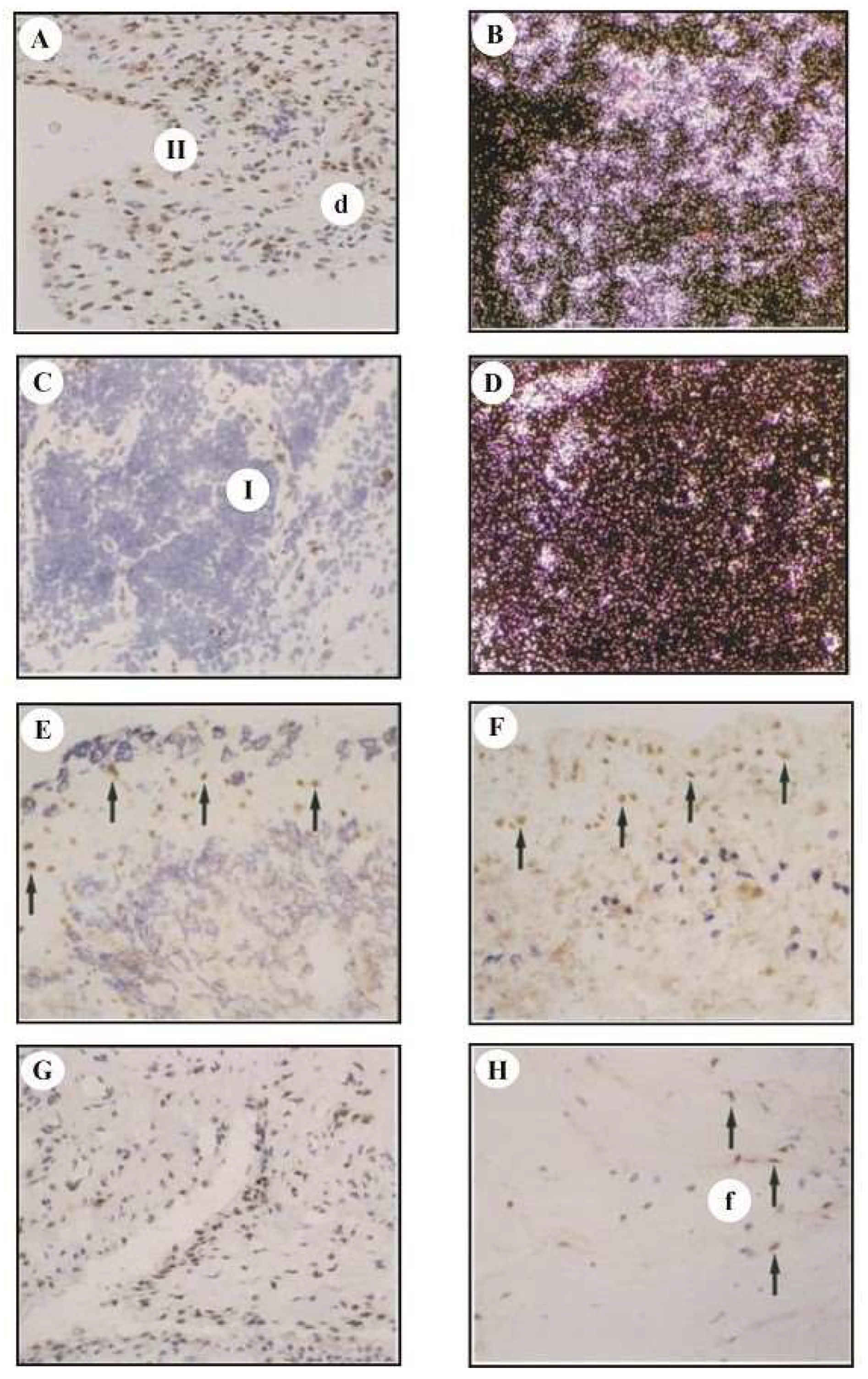
3.3. Analysis of cfos mRNA and cFos Protein Expression by In Situ Hybridization and Immunohistology
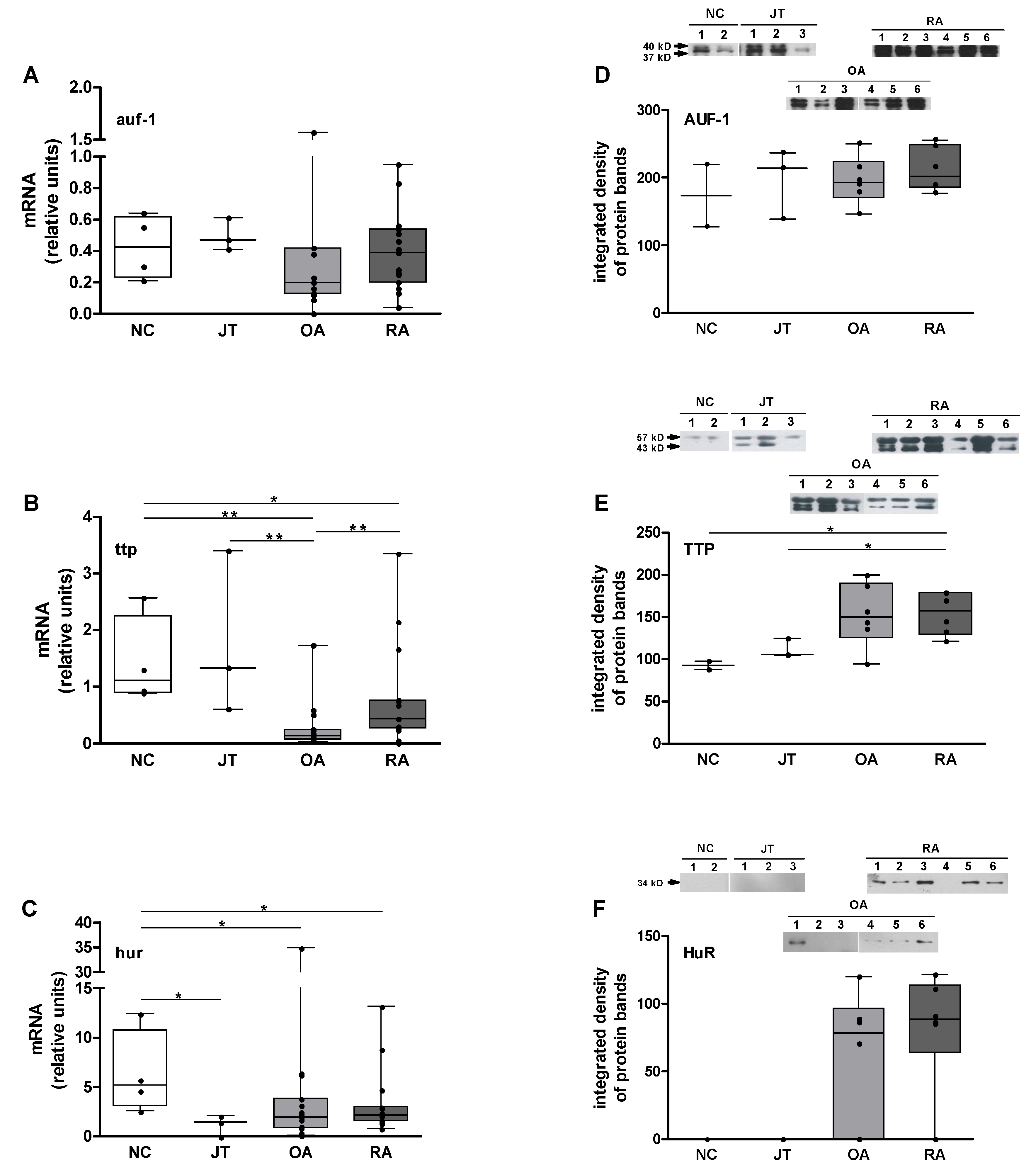
3.4. Quantitation of auf-1, ttp, and hur mRNA Expression
3.5. Quantitation of AUF-1, TTP, and HuR Protein Expression
3.6. Correlation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | activator protein |
| ARE | AU-rich elements |
| AUF | AU-rich element RNA-binding protein |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| FLS | fibroblast-like synoviocytes |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HuR | human antigen R |
| IL | interleukin |
| JT | joint trauma |
| NC | normal controls |
| OA | osteoarthritis |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RF | rheumatoid factor |
| SM | synovial membrane |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TTP | tristetraprolin |
References
- Bottini, N.; Firestein, G.S. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsalameh, S.; Amin, R.J.; Kunisch, E.; Jasin, H.E.; Kinne, R.W. Preferential induction of prodestructive matrix metalloproteinase-1 and proinflammatory interleukin 6 and prostaglandin E2 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via tumor necrosis factor receptor-55. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlers, D.; Siegling, A.; Buchner, E.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; Palombo-Kinne, E.; Emmrich, F.; Brauer, R.; Kinne, R.W. Expression of cytokine mRNA and protein in joints and lymphoid organs during the course of rat antigen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res.Ther. 2005, 7, R445–R457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunisch, E.; Chakilam, S.; Gandesiri, M.; Kinne, R.W. IL-33 regulates TNF-alpha dependent effects in synovial fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlers, D.; Beyer, A.; Koczan, D.; Wilhelm, T.; Thiesen, H.J.; Kinne, R.W. Constitutive upregulation of the TGF-b pathway in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res.Ther. 2007, 9, R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollbold, J.; Huber, R.; Pohlers, D.; Koczan, D.; Guthke, R.; Kinne, R.W.; Gausmann, U. Adapted Boolean network models for extracellular matrix formation. BMC Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, S.; Tsumiyama, K. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and c-Fos/AP-1. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanishi, Y.; Firestein, G.S. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: The role of synoviocytes. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2001, 27, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, R.W.; Boehm, S.; Iftner, T.; Aigner, T.; Vornehm, S.; Weseloh, G.; Bravo, R.; Emmrich, F.; Kroczek, R.A. Synovial fibroblast-like cells strongly express jun-B and C-fos proto-oncogenes in rheumatoid- and osteoarthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1995, 101, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, G. Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis Gene Expression Profile by Bioinformatics. Acta Reumatol. Port 2018, 43, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papoudou-Bai, A.; Hatzimichael, E.; Barbouti, A.; Kanavaros, P. Expression patterns of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) family members in lymphoid neoplasms. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 17, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, N.; Jordan, J.; Paul, S.; Reid, S.; Baenkler, H.W.; Sonnewald, S.; Bauerle, T.; Vera, J.; Schett, G.; Bozec, A. The AP-1 Transcription Factor c-Jun Promotes Arthritis by Regulating Cyclooxygenase-2 and Arginase-1 Expression in Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3605–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, R.; Kunisch, E.; Gluck, B.; Egerer, R.; Sickinger, S.; Kinne, R.W. Comparison of conventional and real-time RT-PCR for the quantitation of jun protooncogene mRNA and analysis of junB mRNA expression in synovial membranes and isolated synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Z. Rheumatol. 2003, 62, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostareck, D.H.; Ostareck-Lederer, A. RNA-Binding Proteins in the Control of LPS-Induced Macrophage Response. Front Genet. 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombrita, C.; Silani, V.; Ratti, A. ELAV proteins along evolution: Back to the nucleus? Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 56, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Xu, N.; Shyu, A.B. RNA stabilization by the AU-rich element binding protein, HuR, an ELAV protein. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3461–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Wan, C.; Bai, Y.; Sun, X.; Ma, J.; Zheng, F. TNF-alpha/calreticulin dual signaling induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation associated with HuR nucleocytoplasmic shuttling in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patial, S.; Blackshear, P.J. Tristetraprolin as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S. Recent advances in the role of RNA-binding protein, tristetraprolin, in arthritis. Immunol. Med. 2018, 41, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ross, E.A.; Naylor, A.J.; O’Neil, J.D.; Crowley, T.; Ridley, M.L.; Crowe, J.; Smallie, T.; Tang, T.J.; Turner, J.D.; Norling, L.V.; et al. Treatment of inflammatory arthritis via targeting of tristetraprolin, a master regulator of pro-inflammatory gene expression. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, A.; Suzuki, E.; Adachi, Y.; Murata, H.; Goto, D.; Kojo, S.; Matsumoto, I.; Zhong, L.; Nakamura, H.; Sumida, T. Expression of tristetraprolin (G0S24) mRNA, a regulator of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production, in synovial tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Maurino, S.M.; Rivero-Rodriguez, F.; Velazquez-Cruz, A.; Hernandez-Vellisca, M.; Diaz-Quintana, A.; De la Rosa, M.A.; Diaz-Moreno, I. RNA Binding Protein Regulation and Cross-Talk in the Control of AU-rich mRNA Fate. Front Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; McShane, D.J.; Fries, J.F.; Cooper, N.S.; Healey, L.A.; Kaplan, S.R.; Liang, M.H.; Luthra, H.S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.; Asch, E.; Bloch, D.; Bole, G.; Borenstein, D.; Brandt, K.; Christy, W.; Cooke, T.D.; Greenwald, R.; Hochberg, M. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlers, D.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; Franch, A.; Kuhlmann, J.; Brauer, R.; Emmrich, F.; Kinne, R.W. Differential clinical efficacy of anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies in rat adjuvant arthritis is paralleled by differential influence on NF-kappaB binding activity and TNF-alpha secretion of T cells. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, C.; Aicher, W.K.; Dinkel, A.; Peter, H.H.; Eibel, H. Characterization of SV40T antigen immortalized human synovial fibroblasts: Maintained expression patterns of EGR-1, HLA-DR and some surface receptors. Rheumatol. Int. 1997, 16, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed; Routledge: England, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sawilowsky, S. New effect size rules of thumb. J. Mod. Appl. Statist. Method. 2009, 8, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, K.; Boccalini, P.; Moskowitz, M.A. Expression of c-fos-like immunoreactivity in brainstem after meningeal irritation by blood in the subarachnoid space. Neuroscience 1992, 49, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, Y.T.; Li, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Y.; Nguyen, P.; Chien, S. Shear stress-induced c-fos activation is mediated by Rho in a calcium-dependent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 303, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, H.; Hasunuma, T.; Kobata, T.; Inoue, H.; Muller-Ladner, U.; Gay, S.; Sumida, T.; Nishioka, K. In situ expression of protooncogenes and Fas/Fas ligand in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Aupperle, K.R.; Bennett, B.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. Jun N-terminal kinase in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 291, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aicher, W.K.; Dinkel, A.; Grimbacher, B.; Haas, C.; Seydlitz-Kurzbach, E.V.; Peter, H.H.; Eibel, H. Serum response elements activate and cAMP responsive elements inhibit expression of transcription factor Egr-1 in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Grimbacher, B.; Aicher, W.K.; Peter, H.H.; Eibel, H. Measurement of transcription factor c-fos and EGR-1 mRNA transcription levels in synovial tissue by quantitative RT-PCR. Rheumatol. Int. 1997, 17, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roivainen, A.; Soderstrom, K.O.; Pirila, L.; Aro, H.; Kortekangas, P.; Merilahti-Palo, R.; Yli-Jama, T.; Toivanen, A.; Toivanen, P. Oncoprotein expression in human synovial tissue: An immunohistochemical study of different types of arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 35, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. AP-1 and NF-kappaB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 1998, 28, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, H.; Fujisawa, K.; Kobata, T.; Hasunuma, T.; Maeda, T.; Asanuma, M.; Ogawa, N.; Inoue, H.; Sumida, T.; Nishioka, K. Direct evidence of high DNA binding activity of transcription factor AP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryseck, R.P.; Bravo, R. c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: Effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene 1991, 6, 533–542. [Google Scholar]
- Foletta, V.C.; Segal, D.H.; Cohen, D.R. Transcriptional regulation in the immune system: All roads lead to AP-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 63, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Kwok, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, W.K.; Her, Y.M.; Son, H.J.; Kim, E.K.; Ryu, J.G.; et al. The Fos-Related Antigen 1-JUNB/Activator Protein 1 Transcription Complex, a Downstream Target of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3, Induces T Helper 17 Differentiation and Promotes Experimental Autoimmune Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ding, N.; Guo, J.; Xia, J.; Ruan, Y. Dysregulation of TTP and HuR plays an important role in cancers. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 14451–14461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballo, E.; Lai, W.S.; Blackshear, P.J. Feedback inhibition of macrophage tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by tristetraprolin. Science 1998, 281, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, M.; D’Silva, N.J.; Kirkwood, K.L. Tristetraprolin regulates interleukin-6 expression through p38 MAPK-dependent affinity changes with mRNA 3’ untranslated region. J. Interferon. Cytokine. Res. 2011, 31, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loupasakis, K.; Kuo, D.; Sokhi, U.K.; Sohn, C.; Syracuse, B.; Giannopoulou, E.G.; Park, S.H.; Kang, H.; Ratsch, G.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor dynamically regulates the mRNA stabilome in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahmadi, W.; Al-Ghamdi, M.; Al-Haj, L.; Al-Saif, M.; Khabar, K.S. Alternative polyadenylation variants of the RNA binding protein, HuR: Abundance, role of AU-rich elements and auto-Regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3612–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchen, C.R.; Brook, M.; Saklatvala, J.; Clark, A.R. The stability of tristetraprolin mRNA is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 and by tristetraprolin itself. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32393–32400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmadi, W.; Al-Ghamdi, M.; Al-Souhibani, N.; Khabar, K.S. miR-29a inhibition normalizes HuR over-expression and aberrant AU-rich mRNA stability in invasive cancer. J. Pathol. 2013, 230, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, N.; Frenzel, L.; Alsaleh, G.; Suffert, G.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Sibilia, J.; Pfeffer, S.; Wachsmann, D. miR-346 controls release of TNF-alpha protein and stability of its mRNA in rheumatoid arthritis via tristetraprolin stabilization. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhlmuller, B.; Kunisch, E.; Franz, J.; Martinez-Gamboa, L.; Hernandez, M.M.; Pruss, A.; Ulbrich, N.; Erdmann, V.A.; Burmester, G.R.; Kinne, R.W. Detection of oncofetal h19 RNA in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolilli, C.; Kabala, P.A.; Grabiec, A.M.; Rossato, M.; Lai, W.S.; Fossati, G.; Mascagni, P.; Steinkuhler, C.; Blackshear, P.J.; Reedquist, K.A.; et al. Control of cytokine mRNA degradation by the histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Beyond transcriptional regulation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Cardoso, S.C.; Bekker, C.P.J.; Boes, M.; Radstake, T.; Angiolilli, C. CXCL4 is a driver of cytokine mRNA stability in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouhara, K.; Munenaga, S.; Kajiya, M.; Takeda, K.; Matsuda, S.; Sato, Y.; Hamamoto, Y.; Iwata, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Akutagawa, K.; et al. The induced RNA-binding protein, HuR, targets 3’-UTR region of IL-6 mRNA and enhances its stabilization in periodontitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 192, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalaj, K.; Ahn, S.H.; Bidarimath, M.; Nasirzadeh, Y.; Singh, S.S.; Fazleabas, A.T.; Young, S.L.; Lessey, B.A.; Koti, M.; Tayade, C. A balancing act: RNA binding protein HuR/TTP axis in endometriosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, R.; Hummert, C.; Gausmann, U.; Pohlers, D.; Koczan, D.; Guthke, R.; Kinne, R.W. Identification of intra-group, inter-individual, and gene-specific variances in mRNA expression profiles in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, R.; Panterodt, T.; Welz, B.; Christmann, M.; Friesenhagen, J.; Westphal, A.; Pietsch, D.; Brand, K. C/EBPbeta-LAP*/LAP Expression Is Mediated by RSK/eIF4B-Dependent Signalling and Boosted by Increased Protein Stability in Models of Monocytic Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huber, R.; Stuhlmüller, B.; Kunisch, E.; Kinne, R.W. Discrepancy between Jun/Fos Proto-Oncogene mRNA and Protein Expression in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Membrane. J 2020, 3, 181-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/j3020015
Huber R, Stuhlmüller B, Kunisch E, Kinne RW. Discrepancy between Jun/Fos Proto-Oncogene mRNA and Protein Expression in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Membrane. J. 2020; 3(2):181-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/j3020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuber, René, Bruno Stuhlmüller, Elke Kunisch, and Raimund W. Kinne. 2020. "Discrepancy between Jun/Fos Proto-Oncogene mRNA and Protein Expression in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Membrane" J 3, no. 2: 181-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/j3020015
APA StyleHuber, R., Stuhlmüller, B., Kunisch, E., & Kinne, R. W. (2020). Discrepancy between Jun/Fos Proto-Oncogene mRNA and Protein Expression in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Membrane. J, 3(2), 181-194. https://doi.org/10.3390/j3020015




