Abstract
The use of geopolymers for the solidification/stabilization (S/S) of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWI FA) is promising because the Cao in MSWI FA can provide an alkaline environment to facilitate geopolymer reactions and help to form the gel phase in the solidified body. This study investigated the role of CaO in MSWI FA in immobilizing common heavy metals, especially Cd2+ and Pb2+. Tests were performed to evaluate the effect of CaO on the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of the polymer and the leaching of heavy metals. The findings revealed that as the CaO content increased, the UCS of the geopolymer samples also rose, reaching a maximum 28-day UCS of 24.8 MPa at a CaO content of 31.5%. Additionally, higher CaO levels resulted in lower leaching concentrations of heavy metals in the stabilized material. When the CaO level is 32%, the levels of heavy metals that leach out are very low, with Pb2+ at 0. 02 mg/L and Cd2+ at 0. 01 mg/L, achieving a stabilization rate of over 93.6% for these ions. Moreover, the geopolymer’s characteristics were analyzed by XRD, FTIR, and SEM, and the immobilization mechanisms of Cd2+ and Pb2+ were identified as gelation, physical encapsulation, and chemical substitution.
1. Introduction
The principal pollutant emitted from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) units is fly ash, which is classed as hazardous waste. This is due to its elevated concentrations of heavy metals and dioxins, resulting in substantial environmental contamination [1,2,3]. Therefore, ensuring environmental safety by properly treating FA is a significant challenge. Currently, there are three primary methods for disposing of FA. Technologies for solidification and stabilization (S/S) techniques include the separation of components, extraction, and heat treatment [4]. Among them, FA S/S technology accounts for 80% of the current FA disposal market [5]. It is important to note that when FA is cured, the heavy metals (such as cadmium and lead) are not eliminated, but rather rendered stable. This approach raises significant concerns about the long-term safety and durability of pollutant leaching.
Recently, there has been a growing body of research dedicated to the solidification/stabilization (S/S) of FA in geopolymers. The outstanding structural stability and durability of the polymerization structure are the reasons behind this [6,7,8]. Under alkaline conditions, the breaking and recombination of Si-O and Al-O bonds create a three-dimensional (3D) network polymerization structure. This structure securely encapsulates the pollutants within the geopolymer, allowing for the safe and reliable disposal of FA. Additionally, the geopolymer can be reused, further enhancing environmental safety [9]. The geopolymer produced through geopolymerization exhibits excellent chemical stability, mechanical strength, low shrinkage, material stability, and environmental friendliness, making it a promising option for resource disposal [10,11].
Recent research has extensively examined the impact of elements like calcium and magnesium, as well as their derivatives, on the process of geopolymerization [12,13]. The amount and composition of calcium in the raw materials have a considerable impact on the reaction pathway and the physical characteristics of the resultant geopolymer. Similarly, the level of soluble silicate in the activating solution impacts the inclusion of calcium in the end product by regulating the pH of the solution and the ratio of calcium to silicon in the produced phases. More precisely, the pH has an effect on the relative stability of different precipitates that contain calcium [12].
At present, there is no systematic understanding of the mechanism of geopolymer solidification and stabilization of FA, and there are also differences in the mechanism of heavy metal S/S [14,15]. It is generally believed that there are two mechanisms for the solidification of heavy metal geopolymers: chemical binding and adsorption. Some studies [6,16,17] have suggested that chemical bonds between FA-based polymers and heavy metal ions can enhance the adsorption and encapsulation of heavy metals. This is because heavy metals transition from a free exchangeable and bound state to states bound to iron and manganese oxides, organic matter, and residues. This results in a closely bound and more stable geopolymer structure. Furthermore, limited research has been conducted on the effect of oxides on the composition of FA-based geopolymers used to cure or stabilize heavy metals.
This study employed geopolymers produced from FA to immobilize heavy metals, specifically, Cd2+ and Pb2+. An analysis was conducted to assess the immobilization characteristics of the composite geopolymer. This involved evaluating the unconfined compressive strength (UCS), chemical fractions, and leaching concentrations of heavy metals. In addition, the immobilization processes of heavy metals within the geopolymer were investigated using characterization techniques such as XRD, FTIR, and SEM. The main goals of this study were (i) to investigate the impact of different levels of CaO on the UCS of geopolymers; (ii) to evaluate how effectively heavy metals are immobilized at varying CaO levels; and (iii) to understand the mechanisms by which heavy metals are solidified and stabilized in the geopolymer matrix.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The waste-to-energy facility, owned by Everbright Environmental Protection (Shenyang) Energy Co., Ltd. (Shenyang, China), supplied the MSWI FA used in the experiments conducted for this study (Shenyang Daxin Domestic Waste Incineration Power Plant), and the chemical composition of different batches of FA in the MSWI plant are shown in Table S1.
Metakaolin (MK) is obtained at the Qingling Mineral Processing plant situated in Lingshou County, Hebei Province. MK is generated from the thermal treatment of kaolin (Al2O3·2SiO2·2H2O) to a temperature range of 600–900 °C for a duration of 2 h [18].
The alkaline activators employed in this investigation are water glass, sodium aluminate solution (NaAlO2), aluminum hydroxide solution (Al2(OH)3), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution. Sodium silicate, commonly referred to as water glass, is an inorganic compound represented by the chemical formula Na2O·nSiO2. Water glass, which is the aqueous solution of sodium silicate, is often used as a mineral adhesive. This soluble inorganic silicate has numerous applications. The modulus of sodium silicate, represented by the molar ratio n = SiO2/Na2O, serves as an indicator of its composition and is a significant parameter, often falling within the range of 1.5 to 3.5 [19]. It is necessary to adjust the modulus with sodium hydroxide solution when using it. Deionized water (18.2 Ω), waste water, and waste liquid such as landfill leachate, waste concentrate, waste alkali liquor, and municipal sewage are used as solvents for the geopolymerization reaction.
2.2. Synthesis of Geopolymer
The molds utilized for testing will be prepared in accordance with the subsequent procedures. Initially, precise ratios are employed to measure exact quantities of FA and a blend of mineral conditioner comprising geopolymer compounds and alkaline activators. The mixture is then put into a special stirrer and mixed for 100–120 s until a consistent and homogeneous texture is achieved. The readiness of the mixture can be determined by its viscosity and the absence of perceptible granules, ensuring a smooth and flowing consistency. The ingredients are stirred until the fluidity is just right, achieving a viscous texture. Subsequently, the concoction is transferred into a mold measuring 40 mm by 40 mm by 160 mm for the purpose of conducting tests. The mold is placed on a vibration table to vibrate and compact the cement mortar. The mold is allowed to stand in the air for 24 h. Finally, the prepared FA-based geopolymer is put in a curing box where the temperature and humidity stay the same (at about 20 °C and at least 95% humidity). The geopolymer samples are retrieved once the designated curing period has elapsed. The geopolymer samples were successfully prepared. The sequence of steps is depicted in Figure S1.
2.3. Leaching Concentration and Solidification Efficiency Calculation for Heavy Metals
A mass of 10 g of fly ash or geopolymer curing body was taken to be tested, the leaching agent was added according to the proportion of 20:1, it was placed on the turnover oscillator, the speed was adjusted to 30 ± 2 R/min, and it was oscillated for 18 ± 2 h. Subsequently, the concentration of heavy metals in the FA or solidified body was measured using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher sciscientific, iCE™ 3500, Waltham, MA, USA) to measure leaching. Refer to the information provided in Text S1 for further details.
2.4. Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS)
In this project, the UCS of geopolymers was measured by a cement constant stress pressure tester (Jinan Zhonglu Testing Machine Co., Ltd., DYE-300, Jinan, China). The test was carried out at a loading speed of 2400 ± 200 N/s until the cured specimen was completely destroyed.
2.5. Phase and Microstructural Analyses
X-ray diffraction (BRUKER, D8 Advance Plus, Rheinstetten, Germany) was used to analyze the mineralogical compositions of the geopolymer samples. The changes in the binding energy and valence electron states of components in the geopolymer were determined through the utilization of FTIR spectroscopy (Thermo Fisher Nicolet, IS20, Waltham, MA, USA). The shape and structure of the geopolymer were studied using a scanning electron microscope along with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (Hitachi, S4800, Tokyo, Japan). Comprehensive testing protocols are outlined in the supplemental information (SI).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of FA Content on the UCS of Geopolymers
The mechanical properties of geopolymers with varying FA contents were examined. The alkali activator was prepared by mixing sodium silicate solid powder and sodium hydroxide solution in a specific ratio, with the modulus and dosage of the activator, as well as the proportions of the FA and mineral regulator, kept constant. The FA content was adjusted to 50%, 60%, 70%, and 80%.
Figure 1 demonstrates a decrease in the UCS of the geopolymers over time (at 7, 14, and 28 days) when the concentration of FA was increased. At the point in time when the fine aggregate FA concentration was fifty percent, the 28-day UCS attained its highest value of 19.3 MPa. Conversely, at 80% FA content, the 28-day UCS dropped to its minimum value of 7.1 MPa. The decrease in the UCS with a higher FA content is attributed to the reduced amount of mineral modifier and lower silica–alumina content, which restrict the formation of the geopolymeric structure. This restrictive effect becomes more pronounced as the FA content increases, leading to a gradual decrease in the UCS of the geopolymer. Hence, the subsequent stage of the research will concentrate on examining the elements that influence the mechanical characteristics of the geopolymer at a precise level of 50% FA concentration.
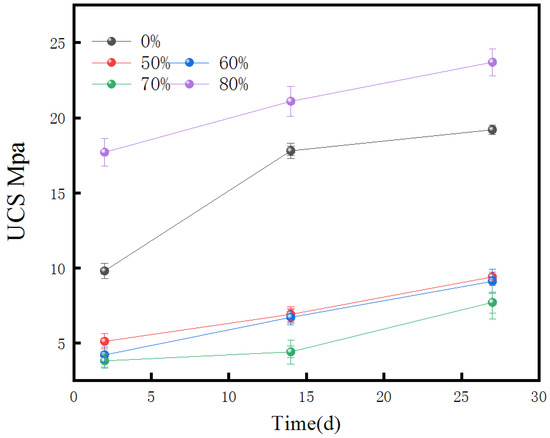
Figure 1.
Effect of different fly ash content on UCS of geopolymer.
3.2. The Effects of Oxidizing Agents on the UCS of Geopolymer Materials
3.2.1. Content of CaO
The CaO content is crucial in the geopolymerization process. According to Davidovits [20], the primary components of geopolymers are silicon and aluminum oxides, with a three-dimensional (3D) zeolite-like structure formed by SiO4 and Al2O3. The molar ratios of n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) and n(CaO)/(SiO2 + Al2O3) significantly affect the UCS of geopolymers.
CaO is primarily sourced from FA and slag. When the FA content is maintained at 50%, the CaO level can be adjusted by altering the slag content. For the purposes of this study, a CaO content between 20% and 25% is categorized as low, between 25% and 30% as medium, and above 30% as high. The variation in the UCS with different CaO contents was investigated. Table S1 presents the total component analysis of the FA. Everbright Shenyang Energy’s FA exhibits a high CaO proportion, with relatively lower SiO2 and Al2O3 levels, classifying it as high-calcium, low-silicon, and low-aluminum FA. Additionally, this FA contains high levels of Cl and SO3. Since Si and Al are essential for geopolymer chemistry, supplementary silica-rich aluminum materials are required to form the geopolymer. The elevated Cl and S content also negatively impacts the geopolymerization process.
When the concentration of CaO was raised from 20% to 25%, the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of the geopolymer consistently remained at a low level, measuring below 10 MPa. Nevertheless, with an increase in the CaO content, the UCS exhibited a consistent rising trend at 7, 14, and 28 days. A maximum UCS of 28.4 MPa was achieved after 28 days when the CaO concentration was 24.5%. When the FA content remains constant, greater amounts of CaO imply an increased amount of slag being added to the raw material. An increase in the CaO content results in its reaction with H2O in the alkaline activator, resulting in the formation of Ca(OH)2. Afterwards, Ca(OH)2 undergoes a reaction with CO2 in the atmosphere, resulting in the formation of compact crystalline structures such as CaCO3 [21,22]. Additionally, the Ca(OH)2 formed in water is alkaline, creating favorable conditions for the active reaction of MK [23]. The system’s silica–alumina content (mainly SiO2 and Al2O3) also increases. In a low-calcium system, the amount of calcium-rich geopolymer formed during polymerization is relatively low, with a large proportion being dispersed in phases rich in Si [24]. Therefore, the strength is primarily provided by Si-O-Si and Al-O-Si bonds. The strength of the geopolymer gradually improves as the quantity of Si-O-Si and Al-O-Si linkages in the system rises [25].
When the CaO content changes from 25% to 30%, there is a significant improvement in the UCS of the geopolymer, with most values surpassing 10 MPa at 28 days. Initially, as the CaO content increases, the UCS of the geopolymer at 7, 14, and 28 days rises, reaching a peak when the CaO content is around 27.0%, where the 28-day UCS reaches 23.9 MPa. Beyond this point, further increases in the CaO content lead to a decline in the UCS. The considerably higher UCS observed under a medium calcium content compared to low calcium content can be attributed to two main factors. Geopolymers are formed by organizing silica–oxygen tetrahedra and aluminum–oxygen tetrahedra in various sequences, with each pair of neighboring tetrahedra sharing a common oxygen atom. Guo et al. categorized the tetrahedral configurations into three distinct types: PS-type, PSS-type, and PSDS-type [26]. The connections that correlate are (-Si-O-Al-O-)/(-Si-O-Al-O-Si-O-)/(-Si-O-Al-O-Si-O-Si-O-). Out of them, the PSS type is recognized as the most robust chain type due to its elongated structure composed of silicon and aluminum. In a medium calcium system, the formation of these robust PSS-type chains is more favorable due to the optimal CaO content, which enhances the geopolymerization process. The CaO facilitates the formation of more stable and interconnected Si-O-Si and Al-O-Si bonds, contributing to the increased mechanical strength. Additionally, the presence of CaO in the right amount supports the formation of Ca(OH)2, which, in turn, reacts with CO2 to form CaCO3, further enhancing the density and strength of the geopolymer matrix. In contrast, in a low-calcium system, the formation of these long chain structures is less efficient due to insufficient CaO, leading to weaker and less interconnected Si-O-Si and Al-O-Si bonds. This results in lower UCS values. Similarly, in a high-calcium system, excessive CaO can result in the production of more Ca(OH)2 and CaCO3, which might disrupt the optimal geopolymer network, thus reducing the UCS. On one hand, the rise in the slag content components leads to a higher SiO2 concentration. Since the Si-O-Si bond is stronger than the Si-O-Al bond, this contributes to the potential for an increased UCS of the geopolymer. Alternatively, when exposed to alkaline activation, the raw materials consisting of CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3 undergo a chemical reaction that leads to the creation of C-S-H and C-(A)-S-H gel structures. These gels attach to the 3D zeolitic framework produced during the initial polymerization reaction, effectively filling in the gaps and enhancing the stability of the structure, therefore improving the UCS [18]. As the amount of CaO increases, the microstructure of the geopolymer undergoes a shift from a PS-type and PSS-type structure to that of a PSDS-type. Having this PSDS-type structure can weaken the stability of SiO4, leading to a decrease in the overall structural stability.
When the geopolymer system has a significant amount of calcium, the UCS initially rises and then declines. The UCS reaches its peak value of 24.8 MPa after a duration of 28 days, with the mass fraction of CaO being roughly 31.5%. This is a crucial juncture, because when calcium levels are elevated, slag accounts for over 30% of the overall cementitious materials, therefore establishing it as the dominating component in the system. Within this calcium-rich setting, sodium silicate experiences hydrolysis, resulting in the production of reactive SiO2. The SiO2, which is in an active state, undergoes a reaction with NaOH and the active silica–alumina compounds present in the slag and MK. This reaction results in the creation of a 3D gel structure known as C-(A)-S-H. The significance of this gel structure lies in its integration with the pre-existing 3D network composed of SiO2 and Al2O3 units. The interplay among these components leads to a more condensed and tightly packed microstructure. The C-(A)-S-H gels function as fillers, occupying the empty spaces within the geopolymer matrix. This procedure enhances the connections within the geopolymer, specifically the Si-O-Si and Al-O-Si connections, resulting in a general rise in UCS. Moreover, the inclusion of these gels in the 3D structure improves the robustness and longevity of the geopolymer. To summarize, the ideal CaO level of approximately 31.5% enhances the UCS by facilitating the creation of C-(A)-S-H gels, which strengthen the current geopolymeric structure. However, at this level, additional increments in the CaO concentration may result in component oversaturation, which can disrupt the ideal development of the gel and have a detrimental effect on the structural integrity and UCS of the geopolymer.
3.2.2. Effect of n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) Ratio on UCS of Geopolymer
The primary components of the geopolymer consist of a combination of Si and Al. The 3D network of the geopolymer is reminiscent of zeolite, which is composed of SiO4 and AlO4 units [27]. Therefore, Si and Al play an important role in the formation of the geopolymer structure. The ratio of n (SiO2)/n (Al2O3) has a great influence on the UCS of the geopolymer. This study investigated the impact of varying the n (SiO2)/n (Al2O3) ratios on the UCS of the geopolymer. The experiments were conducted under three distinct conditions: low calcium (CaO content 20–25%), medium calcium (CaO content 25–30%), and high calcium (CaO content 25–30%).
As depicted in Table 1, under the condition of low calcium, the strength of the geopolymer is generally low, and the UCS of 7 d, 14 d, and 28 d is below 10 MPa. With the increase in the n (SiO2)/n (Al2O3) ratio, the UCS of the geopolymer increases first and then decreases. When the ratio of n (SiO2)/n (Al2O3) is 4.3, the UCS of the 28 d geopolymer is the highest, which is 8.1 MPa. The silica–alumina present in the mineral regulator MK must be activated in order to take part in the polymerization reaction when the alkali concentration is high. On the other hand, the calcium–silica in the slag needs to participate in the activation reaction when the alkali concentration is low. Because there are many kinds of mineral regulators in the geopolymer, the experiment is carried out under the excitation condition of a medium and low alkali concentration. Therefore, under this condition, the strength of the geopolymer is generally low. At the mean time, there may be excessive SiO2 in the system, which will also affect the strength of the geopolymer.

Table 1.
Displays the impact of the ratio of n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) on the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) of geopolymer.
The UCS of the geopolymer materials measured at 7 d, 14 d, and 28 d, which corresponds to each of the n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) ratios, is substantially enhanced in comparison to that under the low-calcium condition and the medium-calcium condition. As the n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) ratio rises, the UCS of the geopolymer initially increases and subsequently decreases. The geopolymer’s 28 d UCS at 10.5 MPa is at its highest when the ratio of n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) is 4.3. In the medium calcium system, the active SiO2 and Al2O3 in the mineral regulator are important components of the 3D network structure of the geopolymer. The broken bonds of NaOH and SiO2 decomposed from the alkali activator will form an aluminosilicate gel structure with the active SiO2 and Al2O3 bonds in the regulator. The increase in the unit SiO4 in the geopolymer is beneficial to the flocculation reaction, and the macroscopic strength increases. However, when the unit SiO4 is too much, the depolymerization and polymerization in the geopolymerization reaction will produce some side effects, and the strength of the geopolymer will begin to decrease at this time.
Within the high-calcium condition, the molar ratio of n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) varied from 4.5 to 4.9, and the UCS of the geopolymer materials at various ages exhibited a notably greater value compared to that observed in the medium- and low-calcium conditions. The UCS of the geopolymer in the figure increases when the molar ratio of n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) is 4.7; the 28 d UCS of the geopolymer is the highest, which is 15.2 MPa. When the geopolymer process is subjected to elevated amounts of calcium, the CaO undergoes a chemical reaction with SiO2 and Al2O3 to produce a C-(A)-S-H gel that exhibits a certain degree of strength [28]. However, when the molar ratio of n(SiO2)/n(Al2O3) continues to increase, the Al2O3 content in the system decreases, resulting in the decrease in -Si-O-Al-bonds, and there is a part of unreacted SiO2, leading to a reduction in the strength of the geopolymer.
3.2.3. Effect of CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 on UCS of Geopolymer
The alkali activator has a modulus of 1.2, with a NaOH/Na2SiO3 ratio of 1:2, and a fixed FA concentration of 50%. The strength distribution of the geopolymer in the ternary system of SiO2-Al2O3-CaO under the conditions of low calcium, medium calcium and high calcium is shown in Figure 2d. It can be seen from the analysis of the figure that, on the whole, in the SiO2-Al2O3-CaO ternary system, with the change in the oxide composition in the raw material ratio, the strength distribution in the system shows three regions of high, medium, and low.
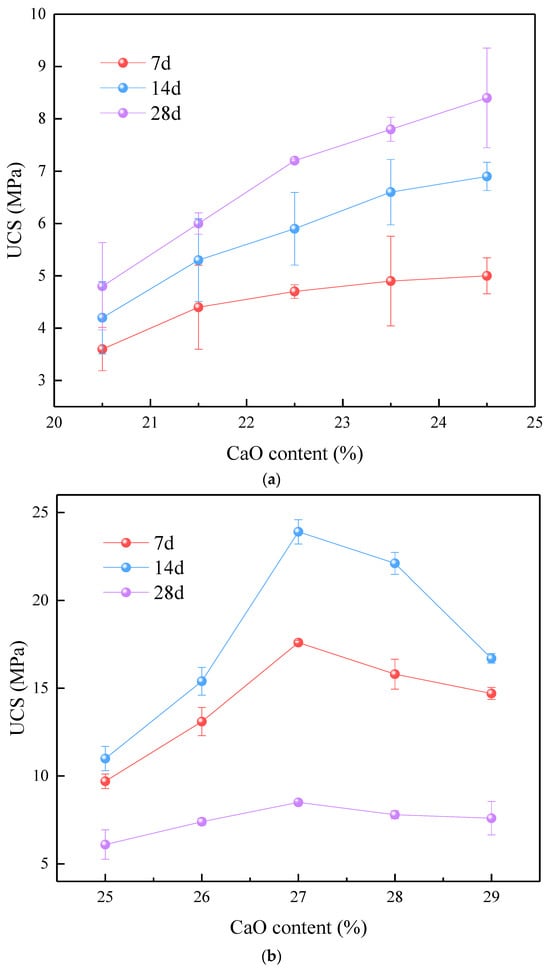
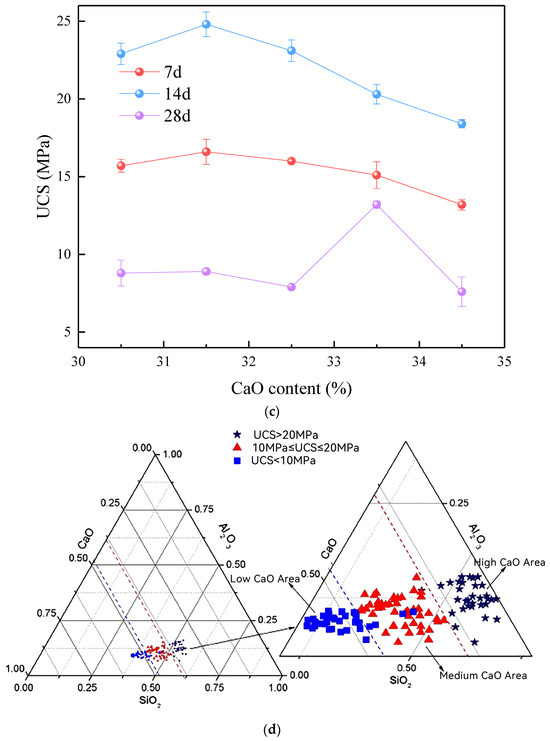
Figure 2.
The UCS of MSWI fly ash-based geopolymer: (a) low-CaO condition, (b) medium-CaO condition, (c) high-CaO condition, (d) ternary system of SiO2-Al2O3-CaO under the conditions of low, medium, and high CaO.
When the strength of the geopolymer is more than 20 MPa, the composition of SiO2 is between 0.40 and 0.60, the composition of Al2O3 is between 0.50 and 0.65, the composition of CaO is between 0.40 and 0.55, and the molar ratio of CaO/(SiO2 + Al2O3) changes between 0.94 and 1.21. When the strength of the geopolymer is between 10 MPa and 20 MPa, the composition of SiO2 is between 0.50 and 0.63, the composition of Al2O3 is between 0.45 and 0.60, and the composition of CaO is between 0.40 and 0.50. At this time, the CaO/(SiO2 + Al2O3) molar ratio changes between 0.67 and 0.91. When the strength of the geopolymer is less than 10 MPa, the composition of SiO2 is between 0.60 and 0.70, the composition of Al2O3 is between 0.40 and 0.55, and the composition of CaO is between 0.30 and 0.40, where the molar ratio of CaO/(SiO2 + Al2O3) varies from 0.43 to 0.66.
3.3. Leaching Results
Upon examining Figure 3a,b, it is evident that the levels of heavy metal ion leaching in geopolymers stabilized through geopolymerization are considerably reduced compared to the original FA. More precisely, the first FA contains a leaching concentration of Pb2+ at 2.48 mg/L and Cd2+ at 9.78 mg/L. By contrast, the levels of Pb2+ and Cd2+ leaching in the geopolymer are decreased to 0.25 mg/L and 0.15 mg/L, respectively. With an increase in the CaO content, there is a decrease in the concentrations of heavy metals leached in the geopolymer. At a CaO content of 32%, the leach solution included a Pb2+ concentration of 0.02 mg/L and a Cd2+ concentration of 0.01 mg/L. After geopolymerization, the solidification/stabilization (S/S) rate for Pb2+ and Cd2+ can reach 93.6%. The effective solidification of heavy metals by the geopolymer is attributed to the integration of these ions into the 3D network formed during geopolymerization. This integration significantly reduces the mobility and leachability of heavy metals. For example, Mallow’s [29] research suggests that incorporating heavy metal ions into the geopolymeric structure enhances their immobilization.
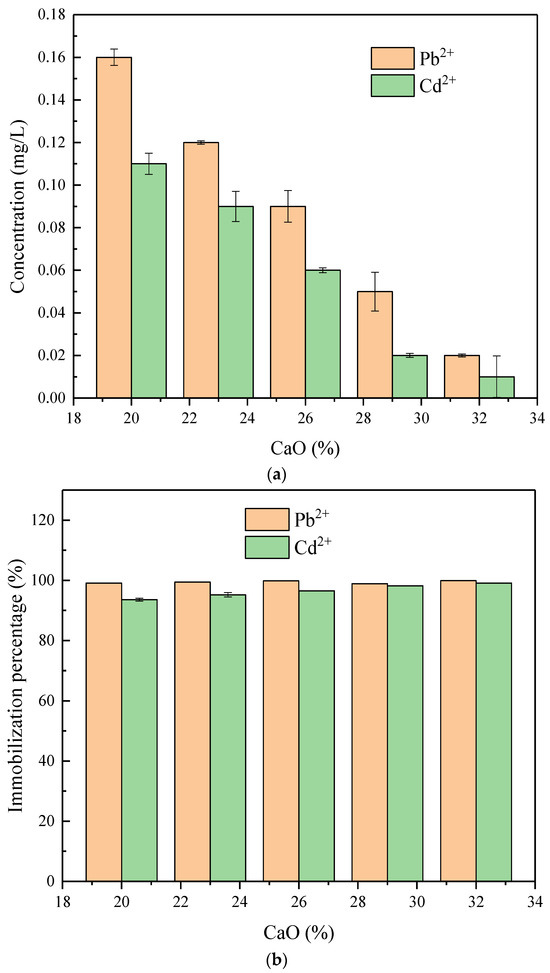
Figure 3.
The results of the leaching test. (a) Determining the concentration of heavy metal ions released during leaching in the geopolymer. (b) The immobilization percentage of heavy metal ions in the geopolymer.
The 3D network of the geopolymer, composed of SiO4 and Al2O3 units, provides sites where heavy metal ions are effectively trapped. This structural incorporation reduces heavy metals’ leachability and improves the mechanical strength and durability of the geopolymer. As the amount of CaO increases, the creation of C-(A)-S-H gels becomes more dense, filling gaps and generating a more compact matrix. The process of densification improves the ability of the geopolymer matrix to bind and immobilize heavy metal ions, so effectively containing them and reducing their negative effects on the environment.
3.4. Immobilization Mechanisms of Heavy Mental
3.4.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
Figure 4a illustrates the XRD spectra of three materials including FA, FA-free geopolymer, and FA-based geopolymer. The MK sample’s X-ray energy spectrum demonstrates a distinct and substantial peak that is associated with crystallization in the 20 to 30 degree range [30]. This peak corresponds to the X-ray diffraction peaks of quartz (SiO2) and mullite (Al2O3), as verified through comparison with conventional X-ray films. The primary components identified in the X-ray images of the FA are Ca or Cl compounds. Furthermore, the presence of a tiny quartz phase is confirmed by the observation of smaller peaks between 50° and 60°, indicating that the FA has a specific gelling activity when stimulated by alkaline substances [26].
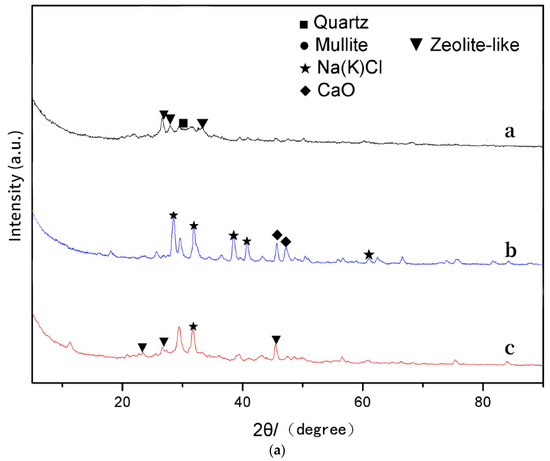
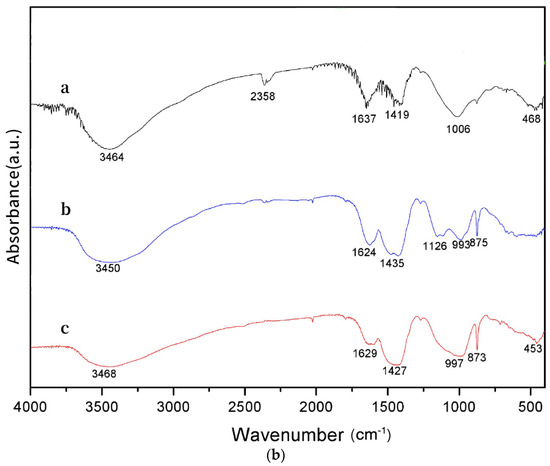
Figure 4.
Characteristics of geopolymers. (a) XRD (a: geopolymer, b: MSWI FA, c: geopolymer based on MSWI FA). (b) FTIR (a: geopolymer, b: MSWI FA, c: geopolymer based on MSWI FA).
The geopolymer’s X-ray spectrum reveals a concentrated peak of geopolymer gel within the 25° to 35° range in the absence of FA [31]. In contrast, the geopolymer had distinct peaks at 26.7° and 45.6° [32], which corresponded to hydrated calcium aluminosilicate. These findings indicate that the geopolymer containing FA is contaminated with heavy metals and other contaminants, which disrupt the process of polymerization. Furthermore, the occurrence of a peak at 29.2° [33] signifies the existence of a calcium silicate gel. The formation of this gel occurs when active silica from the raw material combines with calcium salts in the FA under basic conditions.
The geopolymer and the original FA’s X-ray patterns have been observed, and several significant deductions have been made. The diffraction peaks of the FA, which are normally found between 30° and 50°, become nearly imperceptible or noticeably reduced during the solidification process. The alteration is most noticeable in the distinct diffraction peaks of the chlorine salt crystals, which are initially conspicuous at 30° and 40° in the FA. Upon the FA’s involvement in the geopolymerization reaction, the X-ray diffraction pattern of the geopolymer exhibits characteristic peaks that are incorporated into its structure. This observation suggests that FA plays an active role in the creation of the geopolymer, rather than being a mere waste item in the process. The occurrence of these peaks indicates that certain detrimental chemicals in the FA, such as chlorine salts, are integrated into the polymer structure in a crystalline state throughout the reaction. By including FA, the leachability of dangerous compounds is decreased and it is shown that FA contributes to the composition and properties of the geopolymer. The process of solidifying these chemicals within the polymer matrix improves the environmental safety of the end material by trapping potential pollutants. Moreover, this event confirms the deductions made from prior research. Prior studies indicated that FA has a role in the creation of a durable and robust structure during geopolymerization. The present evidence substantiates this concept by demonstrating that the FA undergoes reactions with other constituents in the raw materials, resulting in the creation of novel crystalline phases inside the geopolymer framework. The results emphasize the dual function of FA as both a reactive agent and a potential source of hazardous compounds that are effectively neutralized by the reaction of geopolymerization. In summary, the lack of or reduction in diffraction peaks between 30° and 50° in the FA, coupled with the appearance of new peaks in the geopolymer, indicates the substantial contribution of FA in the geopolymerization reaction. This procedure ensures the successful integration of the FA into the geopolymer matrix, thereby effectively immobilizing hazardous chemicals and enhancing the material’s environmental security and structural strength.
3.4.2. Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) Analysis
In order to investigate the alterations of functional groups and chemical bonds during the interaction between the MSWI FA and geopolymer, infrared spectroscopy was conducted on the geopolymer, MSWI FA, and the curing body used for the studies. The test results are illustrated in Figure 4b.
The pictures clearly illustrate the creation of the geopolymer structure. An absorption peak with a rather wide range arises between the wavelengths of 3440–3450 cm−1 and 3450 cm−1 [15]. This peak corresponds to the stretching vibration of hydroxyl (-OH) groups in free water. The neighboring peak reflects the stretching vibration of hydroxyl groups in free water. Therefore, this suggests that a slight quantity of water is present in both the materials and the geopolymer. Liquid water within the geopolymer aids in reinforcing its strength and achieving a denser arrangement. The absorption peak at 1430 cm−1 is mainly associated with the C-O stretching vibration mode in the carbonate ion CO32−, and the formation of these carbonates may be due to the reaction of a large amount of calcium oxide with atmospheric carbon dioxide (carbonation) during fly ash combustion [8]. The bending vibration peak of Si-O-Si or O-Si-O in pure geopolymers occurs at a frequency of 468 cm−1, whereas the stretching vibration peak of Si-O-A (where A represents Si or Al) occurs at a frequency of 1006 cm−1. The MSWI FA-based geopolymers exhibit an extension vibration peak of Si-O-A in the range of 986–991 cm−1, and a symmetry vibration peak in the region of 873–875 cm−1. Furthermore, the system may exhibit bending vibration peaks of Si-O-Si or O-Si-O within the range of 449–455 cm−1 [34].
The geopolymer exhibits a shift towards shorter wavelengths in the absorption peak frequencies, indicating the transition of the Si-O-Si stretching vibration peak. This is because the modification is a result of Si favoring stronger bonding interactions with O over those with Al. This implies that the depolymerization reaction has occurred in the aluminosilicate or silicate [14]. The vibrational energy between the Si and O group and its surrounding environment is altered by the addition of heavy metal ions, which modifies the composition of the FA’s geopolymer. As a result, the vibration peak is displaced. The stretching vibration peak of Si-O-A in the geopolymer based on FA shifts towards lower wavenumbers as compared to traditional geopolymers (1006 cm−1–997 cm−1). This shift suggests that the structure has undergone depolymerization, providing evidence that FA, as a raw material, is not merely physically enclosed within the 3D cage structure but is actively involved in chemical reactions. However, even though the fly ash (FA) contained some chlorine and sulfur, no hydrated calcium chloroaluminate was found in the final product [35]. The absence of this product is most likely caused by the product being present in low concentrations or because the reaction forms hydration products that contain the chlorine and sulfur found in the FA [36].
The infrared spectrum investigation reveals that the presence of heavy metal ions in the fly ash (FA) does not affect the structure of SiO4. Instead, these ions are enclosed within the 3D cage-like structure generated by geopolymerization, which helps in their solidification. Further evidence of the geopolymer structure’s effective capacity to immobilize heavy metals in FA is provided by the heavy metal leaching test, which demonstrates that the solidification rates for Pb2+ and Cd2+ can exceed 93.6%.
3.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
An SEM image of the geopolymer in the low-calcium system is shown in Figure 5a. It can be seen from Figure 5a that the geopolymer shows a relatively dense amorphous structure. After a certain amount of magnification, it can be observed that in the low-calcium system, the geopolymer shows a 3D network structure, indicating that the incorporation of FA does not change the hydration products of the geopolymer. After further enlargement, it can be observed that the polymer in the cured body product shows a relatively dense network structure microscopically, and shows compression resistance macroscopically, as well as high strength, good impermeability, a low leaching concentration. It can also be observed that there are FA particles that do not fully participate in the reaction. As the geopolymerization structure of the geopolymer becomes more and more dense, the harmful heavy metals in the FA particles are effectively encapsulated inside the geopolymer under the simultaneous action of physical wrapping and chemical adsorption methods [37].
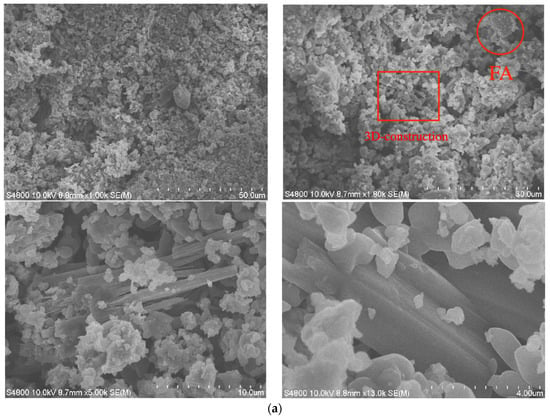

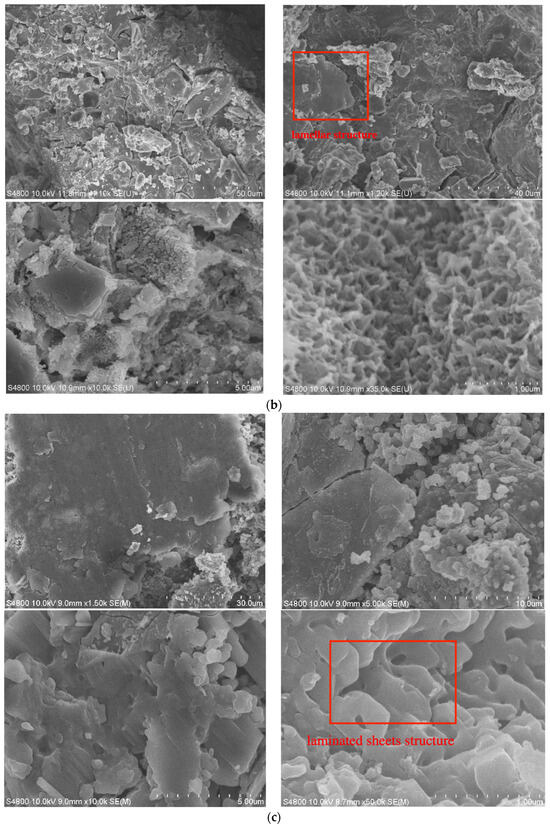
Figure 5.
SEM images of MSWI fly ash-based geopolymer: (a) low-CaO condition, (b) medium-CaO condition, (c) high-CaO condition.
The SEM image of the geopolymer in the medium-calcium system is shown in Figure 5b. As can be seen from Figure 5b, the lamellar structure of the geopolymer in the medium-calcium system is significantly enhanced in comparison to the low-calcium system. This is a direct result of the increased content of calcium oxide, which in turn leads to an increase in the C-S-H gel that is produced by the reaction between calcium and silicate. Meanwhile, a large number of 3D network structures can be observed in Figure 5b, and continuous cage structures can also be observed, indicating that in addition to the hydrated C-S-H gel formed by the CaO reaction, a C-A-S-H gel with a geopolymeric structure is also formed in the geopolymer, and the two are superimposed with each other [17]. In the case of interaction, the structure of the geopolymer is more compact. Furthermore, the toxic heavy metals in the FA are solidified in the geopolymerized network structure and cage structure.
The SEM images of the geopolymer in the high-calcium condition are depicted in Figure 5c. The majority of the fly ash particles in this system participate in the hydration process. These particles become significant components of the final geopolymer structure because of their involvement. The high-calcium content promotes good FA particle mixing and aids in the hydration process, which strengthens and stabilizes the geopolymer. The existence of different crystal structures in the FA leads to a reduced proportion of FA particles sticking to the geopolymer surface. These heterogeneous crystalline components do not participate in the hydration process. Instead, they are incorporated and immobilized inside the 3D network structure of the geopolymer, together with heavy metals. This encapsulation ensures that both the crystalline components and the heavy metals are integrated into the overall matrix, contributing to the stability and integrity of the geopolymer. In the high-calcium environment depicted in Figure 5c, there is a reduced presence of the aluminosilicate structure, primarily composed of calcium-alumino-silicate-hydrate (C-A-S-H) gel. The primary result of hydration is the formation of the calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) gel, which has a highly interconnected structure resembling laminated sheets. The geopolymers in the high-calcium systems exhibit a dense surface and high strength, qualities that can be attributed to its unique structure. This structure plays a crucial role in significantly enhancing the material’s exceptional endurance and durability [38].
3.4.4. Solidification Mechanism of Geopolymer
Geopolymers immobilize/stabilize heavy metal ions via three primary mechanisms: gelation, physical encapsulation, and chemical bonding [7,39]. When the formless aluminosilicate component dissolves in an alkaline environment, the SiO4 and AlO4 ions become dehydrated and undergo processes that result in polycondensation and gelation [40]. During the progression of the reaction, the amount of oligomeric gel rises, and the heavy metal cations become cemented inside the structure of the system due to the encapsulation effect, resulting in the desired solidification effect [41,42]. The abundant pore space and a significant surface area in the geopolymer enables it to capture heavy metal ions effectively. It should be emphasized that heavy metals do not consistently exist in their ionic state, as proposed by several researchers [43]. Thus, Pb2+, Cd2+, and other ions of the same nature can be immobilized by creating hydroxide precipitates [44]. In addition, Pb2+ can create silicate phases that help immobilize it [45]. However, a minority of specialists contend that the infrared spectrum measurements do not show any evidence of the hydroxide phase. In order to achieve a better understanding of this mechanism, additional experimental evidence is required. Investigations have shown that neither pure geopolymer nor geopolymer combined with FA results in the formation of new mineral varieties in their structure, but instead preserve many of the original features [46]. This indicates that the geopolymer after curing the heavy metal ion does not exhibit a large performance increase. Nevertheless, the initial condensed configuration can predominantly be maintained, hence augmenting its capacity to impede the migration of heavy metal ions. The precipitation of heavy metal hydroxides, carbonates, silicates, and aluminates is often regarded as a supplementary means to facilitate the hardening process [37]. Yet, it is also viewed as a sort of gel formation and physical protection, as it utilizes the gel process to adequately envelop and hold materials in position.
Geopolymers have the ability to create a distinct 3D network with a cage-like structure similar to zeolite. This is achieved through the process of alkali activation, which involves dissolving, breaking down, and then reassembling the polymer chains. The immobilization of heavy metal ions is greatly facilitated by this complex network. Heavy metal ions can contribute to the construction of the geopolymer skeleton structure by participating in ion replacement, which is facilitated by electrovalence balancing. Furthermore, these ions can also become cemented within the cage structure [47]. This ion replacement does not affect the original basic structure of SiO4 and AlO4. In the structure of the geopolymer, Al3+ shows electronegativity after combining with four O2−. To maintain electrovalence equilibrium, certain positive ions such as Na+ and K+ play a crucial role in forming essential components and ensuring stability. Some heavy metal ions in the FA can be replaced by these alkali metal ions to replace their sites in the structure, so that they can be stably solidified in the geopolymer structure [48]. This substitution is most significant for ions such as Pb2+ with radii close to those of Na+ and K+, and the radius of Pb2+ is 0.119 nm, the radius of Na+ is 0.095 nm, the radius of K+ is 0.138 nm, and the radius of Pb2+ is between those of Na+ and K+ and close to them, so the curing effect of Pb2+ is particularly significant, which also verifies the ion replacement mechanism. Some investigations have shown the potential for certain heavy metal ions to substitute components in the covalent framework of silicon and aluminum [49]. The fundamental process of immobilizing heavy metal ions is generally accepted to be initiated by their chemical interaction with the oxygen atoms at the end of the Al-O and Si-O bonds in the geopolymer structure.
4. Conclusions
This study examined the effectiveness of CaO in immobilizing Cd2+ and Pb2+ using a geopolymer made from MSWI FA. The results emphasize the crucial significance of CaO in effectively trapping heavy metals inside the geopolymer structure. This research yielded the following results and developments:
- (i)
- The role of CaO in the geopolymerization process was systematically explored. The findings revealed a direct relationship between the CaO concentration and the UCS of the geopolymer samples. The highest UCS, reaching 24.8 MPa at 28 days, was achieved with a CaO content of approximately 31.5%. Additionally, the UCS of the geopolymer exceeded 20 MPa when the molar ratio of CaO/(SiO2 + Al2O3) was between 0.94 and 1.21. This comprehensive understanding provides a theoretical basis for optimizing geopolymer solidification technology.
- (ii)
- The investigation revealed that augmenting the CaO content in the geopolymer had a substantial impact on diminishing the leaching concentrations of heavy metals, specifically, Pb2+ and Cd2+. At a CaO content of 32%, the concentrations of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in the leaching solution fell to 0.02 mg/L and 0.01 mg/L, respectively. This decrease was achieved with a solidification/stabilization (S/S) rate of 93.6%.
- (iii)
- Research on geopolymers, including techniques such as FTIR, XRD, and SEM, has demonstrated that they undergo an intricate sequence of alkali activation processes. This process results in the formation of a unique 3D network that comprises zeolite-looking cage structures. These structures play a vital function in the process of solidifying heavy metal ions, thereby ensuring their stability and preventing their movement. The comprehensive structural analysis confirms the superior performance of geopolymers in heavy metal immobilization and proposes methods for optimizing geopolymer formulations in high-calcium environments.
In summary, this study presents a new application pathway for the resource utilization of MSWI FA, characterized by economic efficiency, safety, low carbon emissions, clean energy, environmental protection, and circular economy. The innovative research methods and systematic analysis provide valuable theoretical and practical insights for further studies and practical applications in the field of geopolymer technology.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cleantechnol6030053/s1, Figure S1: Sample Schematic Diagram. Table S1: Total composition analysis of MWSI fly ash of different batches (%). Table S2: Heavy metal concentration of fly ash leaching test.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.R. and X.H. (Xiaomin Hu); methodology, X.H. (Xiaomin Hu); validation, X.H. (Xiang He), X.R. and F.W.; formal analysis, F.W.; investigation, F.W.; resources, X.H. (Xiaomin Hu); data curation, X.H. (Xiang He); writing—original draft preparation, X.R.; writing—review and editing, X.R.; visualization, F.W.; supervision, X.H. (Xiaomin Hu); project administration, X.H. (Xiaomin Hu); funding acquisition, X.H. (Xiaomin Hu). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Project] grant number [2022JH2/101300112] and The APC was funded by [2022JH2/101300112].
Data Availability Statement
The authors are available to provide study data upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Liaoning Haitiange Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. did not fund this study and does not have any conflict of interest with the authors of this study, and Author Fan Wang participated in this study only as an employee of the company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sun, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, G. A Review on the Management of Municipal Solid Waste Fly Ash in American. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ma, G.X.; Yuan, G.L. Content Analysis of Heavy Metals in Fly Ash from One Shanghai Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Plant. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 531, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Incineration Fly Ash as an Important Source of Heavy Metal Pollution in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Han, M.; Zhang, R. A Mini-Review of Heavy Metal Recycling Technologies for Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marieta, C.; Martín-Garin, A.; Leon, I.; Guerrero, A. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash: From Waste to Cement Manufacturing Resource. Materials 2023, 16, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hu, W.; Shi, H. Microstructure and Self-Solidification/Stabilization (S/S) of Heavy Metals of Nano-Modified CFA–MSWIFA Composite Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna Galiano, Y.; Fernández Pereira, C.; Vale, J. Stabilization/Solidification of a Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Residue Using Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Rout, P.K. Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 3213–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rożek, P.; Król, M.; Mozgawa, W. Geopolymer-Zeolite Composites: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wang, M.; Fu, S.; Jia, D.; Yan, S.; Yuan, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Si/Al Ratio on the Structure and Properties of Metakaolin Based Geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14416–14422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer Technology: The Current State of the Art. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.K.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Microanalysis of Calcium Silicate Hydrate Gel Formed within a Geopolymeric Binder. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 3851–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.; Lukey, G.; van Deventer, J. The Effect of Calcium Sulphate Hemihydrate on the Geopolymerisation of Metakaolin. In Chemeca 2003: Products and Processes for the 21st Century, Proceedings of the 31st Australasian Chemical Engineering Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 1 January 2003; Institution of Engineers: Barton, Australia, 2003; pp. 845–851. [Google Scholar]
- El-Eswed, B.I.; Yousef, R.I.; Alshaaer, M.; Hamadneh, I.; Al-Gharabli, S.I.; Khalili, F. Stabilization/Solidification of Heavy Metals in Kaolin/Zeolite Based Geopolymers. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 137, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Jin, H.; Zhang, W.; Xing, F.; Tang, L. Synthesis of Geopolymer Using Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash and Steel Slag: Hydration Properties and Immobilization of Heavy Metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Jaarsveld, J.G.S.; Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Schwartzman, A. The Potential Use of Geopolymeric Materials to Immobilise Toxic Metals: Part II. Material and Leaching Characteristics. Miner. Eng. 1999, 12, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Zhou, Y.L.; Chang, Q.; Qu, H.Q. Study on the Factors of Affecting the Immobilization of Heavy Metals in Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, W. A Comparative Study on Fly Ash, Geopolymer and Faujasite Block for Pb Removal from Aqueous Solution. Fuel 2016, 185, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, P.; Nazarko, M.; Włosińska, E.; Kanciruk, A.; Zarębska, K. Synthesis of Geopolymers Derived from Fly Ash with an Addition of Perlite. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Inorganic Polymeric New Materials. J. Therm. Anal. 1991, 37, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-Y.; Alrefaei, Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Dai, J.-G. Recent Advances in Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the N-A-S-H Geopolymer System: Modeling, Structural Analysis, and Dynamics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 122196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Anwer, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, J.-W. Decontamination of Radioactive Cesium-Contaminated Soil/Concrete with Washing and Washing Supernatant—Critical Review. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Bai, C.; Wang, M.; He, P. Effects of Si/Al Ratios on the Bulk-Type Zeolite Formation Using Synthetic Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer with Designated Composition. Crystals 2021, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Yu, Q. Understanding the Gel Compatibility and Thermal Behavior of Alkali Activated Class F Fly Ash/Ladle Slag: The Underlying Role of Ca Availability. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 170, 107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Abdel-Gawwad, H.A.; García, S.R.V.; Israde-Alcántara, I. Fabrication and Characterization of Thermally-Insulating Coconut Ash-Based Geopolymer Foam. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Pan, Y.; Bai, Y.; Sasaki, K. Immobilization of Strontium in Geopolymers Activated by Different Concentrations of Sodium Silicate Solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 24298–24308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Nakama, S.; Sasaki, K. Immobilization of Cesium in Fly Ash-Silica Fume Based Geopolymers with Different Si/Al Molar Ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provis, J.L. Alkali-Activated Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallow, W.A. Fixation of Haxardous Wastes and Related Products. U.S. Patent No. 5,976,244, 2 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.; Guo, B.; Zhang, H.; Sasaki, K. Effect of Si/Al Molar Ratio on the Immobilization of Selenium and Arsenic Oxyanions in Geopolymer. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Wang, F.; He, X.; Hu, X. Resistance and Durability of Fly Ash Based Geopolymer for Heavy Metal Immobilization: Properties and Mechanism. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 12580–12592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y. Effects of Si/Al Ratio on the Efflorescence and Properties of Fly Ash Based Geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunsheng, Z.; Wei, S.; Qianli, C.; Lin, C. Synthesis and Heavy Metal Immobilization Behaviors of Slag Based Geopolymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Lei, X. Reduction/Immobilization Processes of Hexavalent Chromium Using Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Yan, F. Synthesis and Mechanical Properties of Metakaolinite-Based Geopolymer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 268, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.W.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. Structural Reorganisation of Class F Fly Ash in Alkaline Silicate Solutions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 211, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Jaarsveld, J.G.S.; Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Lorenzen, L. Factors Affecting the Immobilization of Metals in Geopolymerized Flyash. Met. Mater. Trans. B 1998, 29, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Jaarsveld, J.G.S.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The Effect of Metal Contaminants on the Formation and Properties of Waste-Based Geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Galiano, Y.; Leiva, C.; Arenas, C.; Fernández-Pereira, C. Fly Ash Based Geopolymeric Foams Using Silica Fume as Pore Generation Agent. Physical, Mechanical and Acoustic Properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 500, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Pereira, C.; Luna, Y.; Querol, X.; Antenucci, D.; Vale, J. Waste Stabilization/Solidification of an Electric Arc Furnace Dust Using Fly Ash-Based Geopolymers. Fuel 2009, 88, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, C.; Luna-Galiano, Y.; Leiva, C.; Vilches, L.F.; Arroyo, F.; Villegas, R.; Fernández-Pereira, C. Development of a Fly Ash-Based Geopolymeric Concrete with Construction and Demolition Wastes as Aggregates in Acoustic Barriers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhou, F.; Lu, M.; Hou, H.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, T. Early Solidification/Stabilization Mechanism of Heavy Metals (Pb, Cr and Zn) in Shell Coal Gasification Fly Ash Based Geopolymer. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. Pb2+ and Cr3+ Immobilization Efficiency and Mechanism in Red-Mud-Based Geopolymer Grouts. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S. Influence of Calcium Content on Structure and Strength of MSWI Bottom Ash-Based Geopolymer. Mag. Concr. Res. 2019, 71, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Facile Preparation of Slag or Fly Ash Geopolymer Composite Coatings with Flame Resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Lin, J.; Fang, L.; Ma, R.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y. Formulation of Sludge Incineration Residue Based Geopolymer and Stabilization Performance on Potential Toxic Elements. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Guo, B.; Sasaki, K. Immobilization Mechanism of Se Oxyanions in Geopolymer: Effects of Alkaline Activators and Calcined Hydrotalcite Additive. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, C.; Yao, S.; Guo, B.; Zhang, H. Immobilization Mechanism of Cesium in Geopolymer: Effects of Alkaline Activators and Calcination Temperature. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Rao, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, E.-H. Lightweight Aerated Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Incorporating Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Bottom Ash as Gas-Forming Agent. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).