Soil Inorganic Carbon Formation and the Sequestration of Secondary Carbonates in Global Carbon Pools: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Soil Depth (cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pool | 0–30 | 0–100 | 0–200 |
| SOC | 725 Pg | 1500 Pg | 2450 Pg |
| SIC | 250 Pg | 750 Pg | -- 1 |
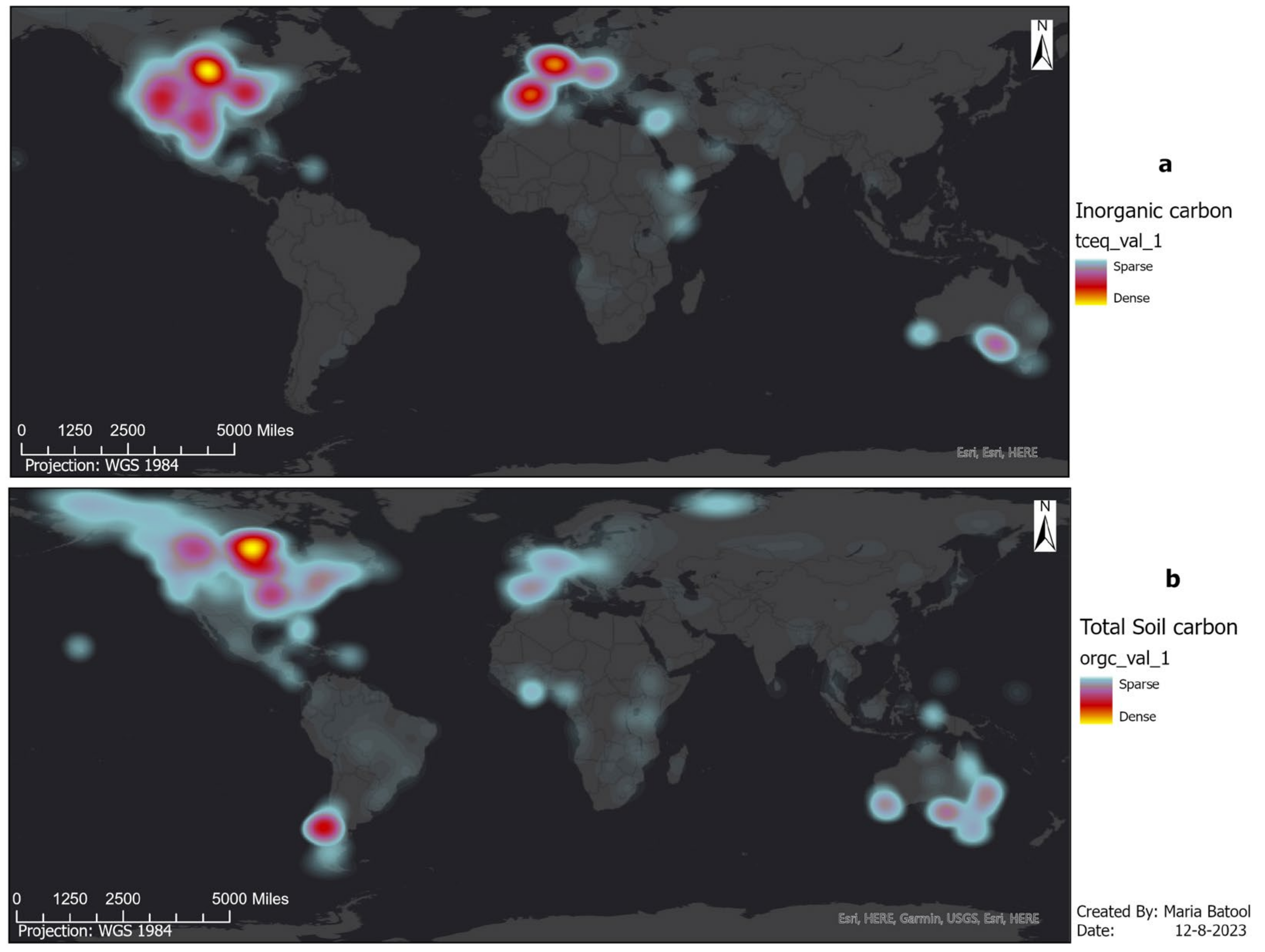
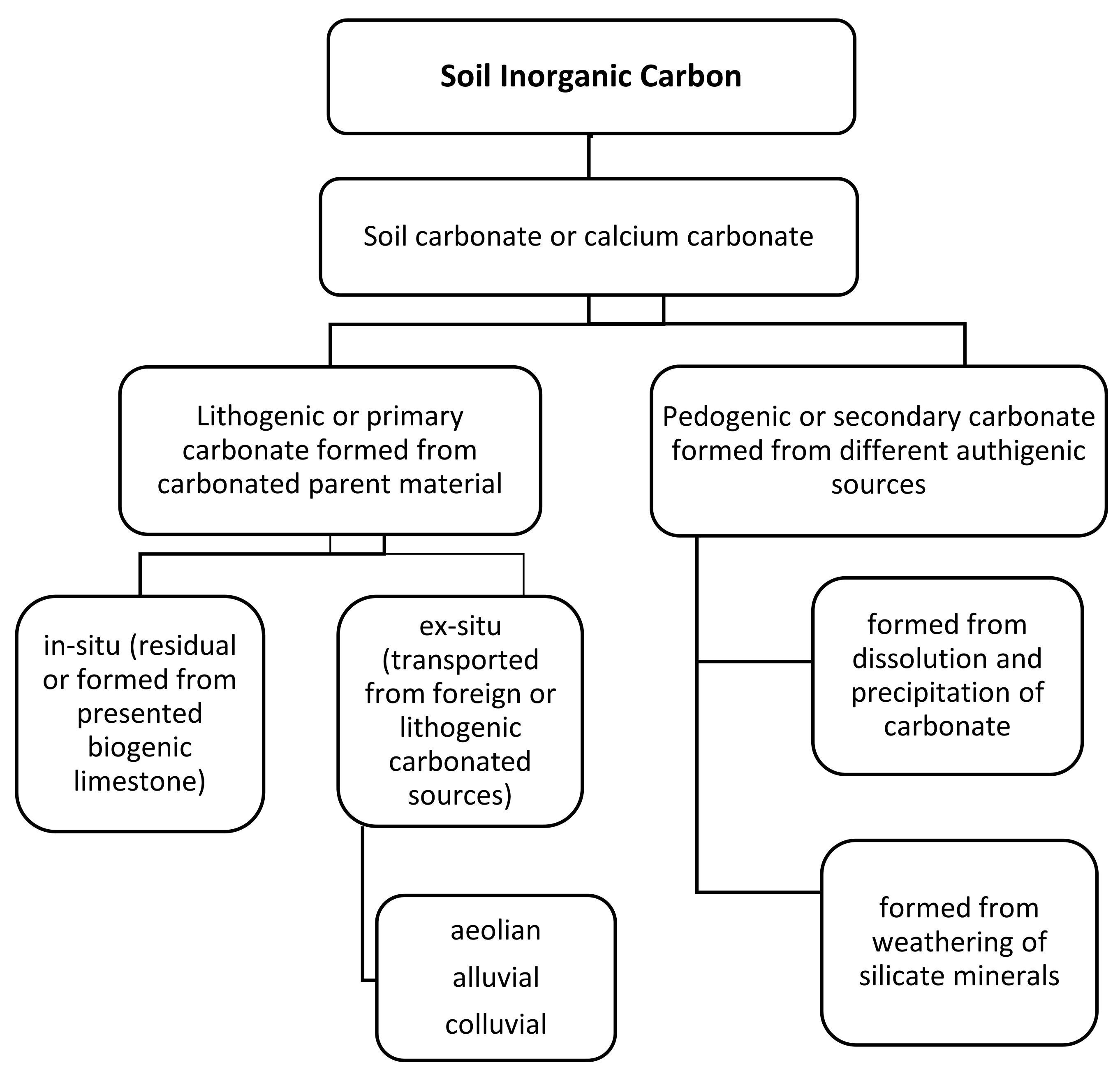
2. SIC and Its Importance
2.1. Carbonate Dissolution and Precipitation
2.2. Weathering and Metamorphism of Ca-Silicate Minerals
CaSiO3 + CO2 + H2O↓ ⟵⟶ H4SiO4 + 2HCO3− + Ca2+
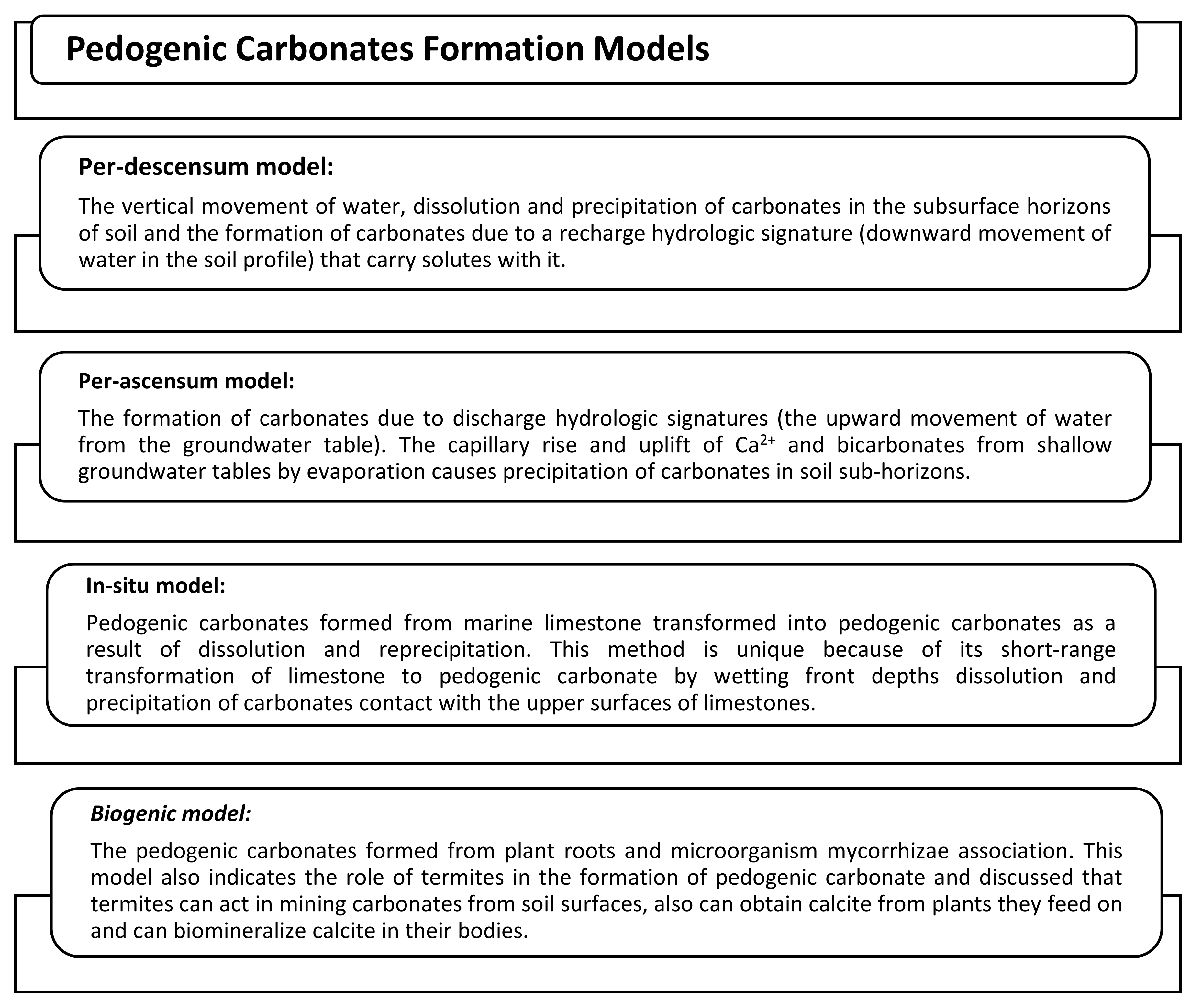
2.3. SIC Formation Models
2.4. Formation of Pedogenic or Secondary Carbonates
2.5. Factors Influencing SIC (Natural and Anthropogenic)
2.5.1. Soil pH
2.5.2. Wet Deposition of C2+ and Mg2+
3. Biogenetic Stages of Pedogenic Carbonate Accumulation in Drylands
3.1. Morphological Patterns
3.2. Environmental Patterns
4. Role of Stable Isotopes in Pedogenic Carbonate Dynamics
5. Land Management and Its Effect on Inorganic Carbon Sequestration
6. SIC and Global C Sequestration
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| U.S State/Country | BD 1 | STC 2 | SOC 3 | SIC 4 | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saskatchewan, Canada | N/D 5 | HiTDC 6 | HiTDC | IC 7 | [48] a |
| Northeastern Italy | PTF 8 | N/D | Dichromate oxidation and HiTDC | N/D | [86] [87] b |
| New Zealand | Claydon | A Leco WR-112 C analyser | fumigation extraction and dichromate oxidation | N/D | [88] |
| North Dakota, USA | Core method | N/D | N/D | Acid 9 | [77] [89] [90] c |
| Kursk, Russia | Oven-dried | HiTDC spectrometry by RPT 10 system | HiTDC spectrometry by RPT system | IC | [14] [91] |
| Kursk, Russia | Oven-dried | N/D | HiTDC spectrometry by RPT | N/D | [92] |
| North Dakota, USA | Core method | HiTDC | OC=TC-IC | Acid | [93] [89] [94] d |
| Maryland, USA | Core method | N/D | HiTDC | N/D | [95] |
| North Dakota, USA | Core method | N/D | Modified Mebius method | Acid | [18] [96] [94] |
| North Dakota, USA | Core method | HiTDC spectrometry by RPT System | HiTDC spectrometry by RPT system | Acid | [11] [90] |
| North Dakota, USA | Core method | HiTDC | HiTDC | Acid | [8] [94] |
| California | Oven-dried | Costech ECS 4010 CHNS-O elemental analyzer | Mass spectrometry | Acid fumigation | [96] |
| Citation | Environment | Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Schaetzl et al. [46] | Temperate | Treating soil mixtures with HCl acid and measuring the evolved CO2; CaCO3 was determined, which is equivalent to a <2 mm fraction. |
| Rivadeneyra et al. [44] | Semiarid | X-ray dispersive energy microanalysis; the formation of carbonate crystals by Deleya halophila. |
| Landi et al. [48] | Semiarid | Europa Tracer/20 Mass spectrometer analysis and mineralogical analysis. |
| Bruckman et al. [97] | Forest land | Fourier transform midinfrared spectroscopy and powder X-ray diffraction. |
| Kolosz et al. [98] | Multiple environments | Roth-C and century model. |
| Allison & Moodie [99] | Multiple environments | Vacuum distillation and titration, acid neutralization, volumetric calcimeter, and pressure calcimeter methods, and a gravimetric method for the loss of CO2. |
| Mikhailova et al. [11] | Semiarid | Dry combustion mass spectrometry using the Robo-Prep Tracemass System. |
| Mikhailova & Post [14] | Semiarid | Electron microscope (SEM) model S-3500N for determining the elemental composition of CaCO3. |
| Country | Citation | Title of Study |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | Fitzpatrick and Merry [100] | Pedogenic Carbonate Pools and Climate Change in Australia. |
| Russia | Ryskov et al. [101] | The relationship between lithogenic and Pedogenic Carbonates Fluxes in Steppe Soils, and Regularities of Their profile dynamics for the last four millennia. |
| China | You et al. [102] | Profile storage and vertical distribution (0–150 cm) of soil inorganic carbon in croplands in Northeast China. |
| France | C. Grinand [103] | Prediction of soil organic and inorganic carbon contents at a national scale (France) using mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (MIRS). |
| China | Pan and Guo [104] | Pedogenic Carbonate of aridic Soils in China and its Significance in Carbon Sequestration in terrestrial system. |
| India | Pal et al. [105] | Secondary Calcium Carbonate in Soils of arid and Semi-arid regions of India. |
| Turkey | Kapur et al. [106] | Carbonate Pools in Soils of the Mediterranean: A case study from Anatolia. |
| Japan | Nanko et al. [107] | Assessment of soil group, site, and climatic effects on soil organic stocks of topsoil in Japanese forests. |
| China | Nami et al. [108] | Soil inorganic carbon storage pattern in China. |
| Syria | Khalaf et al. [109] | Some calcareous soils Developed on Recent quaternary Basalt in Southeast Syria. |
| Tunisia | Houman [110] | Morphology, Distribution and Environmental Significance of Pedogenic Carbonates in Relict Soils of Tunisia. |
References
- Schlesinger, W.H. Carbon sequestration in soils: Some cautions amidst optimism. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, M.A.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Post, C.J.; Schlautman, M.A. Atmospheric Mg2+ wet deposition within the continental United States and implications for soil inorganic carbon sequestration. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2007, 59B, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, H.; Reich, P.F.; Kimble, J.M.; Beinroth, F.H.; Padmanabhan, E.; Moncharoen, P. Global carbon stocks. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zamanian, K.; Pustovoytov, K.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil Carbonates: The unaccounted, irrecoverable carbon source. Geoderma 2016, 384, 114817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegenthaler, U.; Sarmiento, J.L. Atmospheric carbon dioxide and the ocean. Nature 1993, 365, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.; Tignir, M.M.B.; Miller, H.L.J.; Chen, Z. (Eds.) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC 2007: The Scientific Basis Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC; Cambridge Univ. Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R.; Negassa, W.; Lorenz, K. Carbon sequestration in soil. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 15, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, H.; Berg, E.V.D.; Reich, P. Organic Carbon in Soils of the World. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil health and carbon management. Food Energy Secur. 2016, 5, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.; Post, C.; Cihacek, L.; Ulmer, M. Soil Inorganic Carbon Sequestration as a Result of Cultivation in the Mollisols; American Geophysical Union Publishers as part of the Geophysical Monograph Series; AGU: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 183, pp. 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilford, J.; de Caritat, P.; Bui, E. Modelling the abundance of soil calcium carbonate across Australia using geochemical survey data and environmental predictors. Geoderma 2015, 259–260, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Carbon management in agricultural soils. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Change 2007, 12, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.A.; Post, C.J. Effects of Land Use on Soil Inorganic Carbon Stocks in the Russian Chernozem. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varallyay, G. The Inorganic Carbon Cycle. In Proceedings of the IV. Alps-Adria Scientific Worksop, Portoroz, Slovenia, 28 February–5 March 2005; Volume 33, pp. 9–12. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/23787604 (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Tiessen, H.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Bettany, J.R. Cultivation effects on the amounts and concentration of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in grassland soils. Agron. J. 1982, 74, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.W. Carbonates. Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Cihacek, L.; Ulmer, M.G. Estimated soil organic carbon losses from long-term crop fallow in the Northern Great Plains of the U.S. In Soil Management and Greenhouse Effect, 1st ed.; Kimble, J.M., Levine, E.R., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihacek, L.; Ulmer, M.G. Effects of Tillage on Profile Soil Carbon Distribution in the Northern Great Plains of the U.S. In Management of Carbon Sequestration in Soil, 1st ed.; Lal, R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdush, J.; Paul, V. A review on the possible factors influencing soil inorganic carbon under elevated CO2. CATENA 2021, 204, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N. Harmonized soil property values for broad-scale modelling (WISE30sec) with estimates of global soil carbon stocks. Geoderma 2016, 269, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z. Effects of land-use change on soil inorganic carbon: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2019, 353, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R.; Kimble, J.M. Pedogenic carbonates and the global carbon cycle. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailova, E.A.; Goddard, M.A.; Post, C.J.; Schlautman, M.A.; Galbraith, J.M. Potential Contribution of Combined Atmospheric Ca2+ and Mg2+ Wet Deposition Within the Continental U.S. to Soil Inorganic Carbon Sequestration. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monger, H.C.; Kraimer, R.A.; Khresat, S.; Cole, D.R.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Sequestration of inorganic carbon in soil and groundwater. Geology 2015, 43, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharififar, A.; Minasny, B.; Arrouays, D.; Boulonne, L.; Chevallier, T.; van Deventer, P.; Field, D.J.; Gomez, C.; Jang, H.-J.; Jeon, S.-H.; et al. Chapter Four—Soil inorganic carbon, the other and equally important soil carbon pool: Distribution, controlling factors, and the impact of climate change. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 178, pp. 165–231. ISBN 9780443192609. ISSN 0065-2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monger, H.C. Pedogenic Carbonates: Links between biotic and abiotic CaCO3. In Proceedings of the 17th WCSS, Bangkok, Thailand, 14–21 August 2002. Symposium no. 20, paper no. 897. [Google Scholar]
- Gile, L.H.; Grossman, R.B. The Desert Project Soil Monograph; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VA, USA, 1979; Doc. No. PB80-135304.
- Chadwick, O.A.; Kelly, E.F.; Merritts, D.M.; Amundson, R.G. Carbon dioxide consumption during soil development. Biogeochemistry 1994, 24, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, T.M.; Breecker, D.O. The obscuring effects of calcite dissolution and formation on quantifying soil respiration. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2020, 34, e2020GB006584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heakal, M.S.; EI-Raies, S.A.A.; Al-Farraj, A.; Mashhady, A.S. Coprecipitation of Ca and Mg from a Carbonic System under Atmospheric Conditions. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderman, J. Can management induced changes in the carbonate system drive soil carbon sequestration? A review with a particular focus on Australia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 155, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Guo, Z.; Gao, Q.; Peng, C. Distribution of soil inorganic carbon storage and its changes due to agricultural land use activity in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamir, G.; Shenker, M.; Heller, H.; Bloom, P.R.; Fine, P.; Bar-Tal, A. Dissolution and re-crystallization processes of Active calcium carbonate in soil developed on tufa. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1606–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renforth, P.; Manning, D.A.C.; Lopez-Capel, E. Carbonate precipitation in artificial soils as a sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Raza, S.; Li, G.; Smith, P.; Zhu, Y.-G. Soil inorganic carbon sequestration through alkalinity regeneration using biologically induced weathering of rock powder and biochar. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2022, 4, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, R.A.; Lasaga, A.C.; Garrels, R.M. The carbonate-silicate geochemical cycle and its effect on atmospheric carbon dioxide over the past 100 million years. Am. J. Sci. 1983, 283, 641–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Richter, D.D.; Trumbore, S.E.; Jackson, R.B. Agricultural acceleration of soil carbonate weathering. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 5988–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. Carbon storage in the caliche of arid soils: A case study from Arizona. Soil Sci. 1982, 133, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urey, H.C. On the Early Chemical History of the Earth and the Origin of Life. Earth Atmos. Planet. Sci. 1952, 38, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlin, T.C. The Influence of Great Epochs of Limestone Formation upon the Constitution of the Atmosphere. J. Geol. 1898, 6, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monger, H.C.; Daugherty, L.A.; Lindemann, W.C.; Liddell, C.M. Microbial precipitation of pedogenic calcite. Geology 1991, 19, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Ramos-Cormenzana, A.; Delgado, G.; Delgado, R. Process of Carbonate Precipitation by Deleya halophila. Curr. Microbiol. 1996, 32, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Carbon sequestration in dryland ecosystems. Environ. Manag. 2004, 33, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaetzl, R.J.; Frederick, W.E.; Tomes, L. DIVISION S-5-PEDOLOGY Secondary Carbonates in Three Fine and Fine-loamy Alfisols in Michigan. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, F.J. Can We Control the Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere? Energy 1977, 2, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, A.; Mermut, A.R.; Anderson, D.W. Carbon Distribution in a Hummocky Landscape from Saskatchewan, Canada. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gile, L.H. Pedogenic Carbonate in Soils of the Isaacks’ Ranch Surface, Southern New Mexico. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. The formation of caliche in soils of the Mojave Desert, California. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 49, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.G.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, W.Z.; Gu, P.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.J. Review of progress in soil inorganic carbon research. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 100, 012129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, K.; Pustovoytov, K.; Kuzyakov, Y. Pedogenic carbonates: Forms and formation processes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 157, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaofei, J.; Wang, H. Relationships between soil pH and soil carbon in China’s carbonate soils. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.; Miao, N.; Wang, P.; Ju, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Dramatic loss of inorganic carbon by nitrogen-induced soil acidification in Chinese croplands. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3738–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X. Effects of soil pH and texture on soil carbon and nitrogen in soil profiles under different land uses in Mun River Basin, Northeast Thailand. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naorem, A.; Jayaraman, S.; Dalal, R.C.; Patra, A.; Rao, C.S.; Lal, R. Soil Inorganic Carbon as a Potential Sink in Carbon Storage in Dryland Soils—A Review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L. Chemical Equilibrium in Soils; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Gile, L.H.; Peterson, F.F.; Grossman, R.B. The K horizon—A master soil horizon of carbonate accumulation. Soil Sci. 1965, 99, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gile, L.H.; Hawley, J.W.; Grossman, R.B. Soils and Geomorphology in the Basin and Range Area of Southern New Mexico—Guidebook to the Desert Project; New Mexico Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources: Socorro, NM, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Monger, H.C.; Gallegos, R.A. Biotic and Abiotic Processes and Rates of Pedogenic Carbonate Accumulation in the Southwestern United States—Relationship to Atmospheric CO2 Sequestration. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hawley, J.W. The desert soil-geomorphology project. In Las Cruces Country; Seager, W.R., Clemons, R.E., Callender, J.F., Eds.; Guidebook, 26th Field Conference; New Mexico Geological Society: Socorro, NM, USA, 1975; pp. 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordt, L.C.; Wilding, L.P.; Hallmark, C.T.; Jacob, J.S. Stable carbon isotope composition of pedogenic carbonates and their use in studying pedogenesis. In Mass Spectrometry of Soils; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 133–154. [Google Scholar]
- Reheis, M.C.; Kihl, R. Dust deposition in southern Nevada and California, 1984–1989: Relations to climate, source area, and source lithology. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 8893–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E. The stable isotopic composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationship to climate. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 71, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E.; Quade, I. Stable Carbon and Oxygen Isotopes in Soil Carbonates. Clim. Change Cont. Isot. Rec. 1993, 78, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.L.; Friedman, I.; Klieforth, H.; Hardcastle, K. Areal distribution of deuterium in eastern California precipitation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1979, 18, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.E. Further comments on using carbon isotopes in palaeosols to estimate the CO2 content of the palaeo-atmosphere. J. Geol. Soc. 1992, 149, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quade, I.; Cerling, T.E.; Bowman, J.R. Development of Asian monsoon revealed by marked ecological shift during the latest Miocene in northern Pakistan. Nature 1989, 342, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomons, W.; Mook, W.G. Isotope Geochemistry of Carbonate Dissolution and Reprecipitation in Soils. Soil Sci. 1976, 122, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monger, H.C.; Cole, D.R.; Gish, J.W.; Giordano, T.H. Stable carbon and oxygen isotopes in Quaternary soil carbonates as indicators of Eco geomorphic changes in the northern Chihuahuan Desert, USA. Geoderma 1998, 82, 137–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordt, L.; Hallmark, C.; Wilding, L.; Boutton, T. Quantifying pedogenic carbonate accumulations using stable carbon isotopes. Geoderma 1998, 82, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, L.L.; Cihacek, L.J.; Leistritz, F.A.; Faller, T.C.; Bangsund, D.A.; Sorensen, J.; Steadman, E.N.; Harju, J.A. The Contribution of Soils to Carbon Sequestration. 2005. Available online: https://undeerc.org/PCORPartners/Articles/ContributionSoils.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Olson, K.R.; Al-Kaisi, M.; Lal, R.; Cihacek, L. Impact of soil erosion on soil organic carbon stocks. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 61A–67A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R.; Al-Kaisi, M.; Lal, R.; Cihacek, L. Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics in Eroding and Depositional Landscapes. Open J. Soil Sci. 2016, 06, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entry, J.A.; Sojka, R.E.; Shewmaker, G.E. Irrigation Increases Inorganic Carbon in Agricultural Soils. Environ. Manag. 2004, 33, S309–S317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Kong, F.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xi, M. Soil inorganic carbon dynamic change mediated by anthropogenic activities: An integrated study using meta-analysis and random forest model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellajosula, G.; Cihacek, L.; Faller, T.; Schauer, C. Soil carbon change due to land conversion to grassland in a semi-arid environment. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, M.A.; Biondini, M. Mycorrhyzial hyphal length as a function of plant community richness and composition in restored northern tallgrass prairie (USA). Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 62, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermut, A.R.; Amundson, R.; Cerling, T.E. The Use of Stable isotopes in Studying Carbonate dynamics in Soils. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gile, L.H.; Peterson, F.F.; Grossman, R.B. Morphological and genetic sequences of carbonate accumulation in desert soils. Soil Sci. 1966, 101, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Wang, L.; Caracausi, A.; Galy, A.; Li, S.-L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.Q.; Liu, G.M.; Xu, S. Assessing the deep carbon release in an active volcanic field using hydrochemistry, δ13CDIC and Δ14CDIC. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2023, 128, e2023JG007435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, J.; Ding, H.; Yue, F.J.; Li, C.; Xu, S.; Li, S. Hydrological regulation of chemical weathering and dissolved inorganic carbon biogeochemical processes in a monsoonal river. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groshans, G.R.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Post, C.J.; Schlautman, M.A. Accounting for soil inorganic carbon in the ecosystem services framework for United Nations sustainable development goals. Geoderma 2018, 324, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.I.D.; Brito, L.M.; Nunes, L.J.R. Soil Carbon Sequestration in the Context of Climate Change Mitigation: A Review. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.J. The Great Plains Region. In Encyclopedia of the Great Plains; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2004; pp. xiii–xviii. ISBN 0-8032-4787-7. [Google Scholar]
- Morari, F.; Lugato, E.; Berti, A.; Giardini, L. Long-term effects of recommended management practices on soil carbon changes and sequestration in north-eastern Italy. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 22, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wösten, J.H.M.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Rawls, W.J. Pedotransfer functions: Bridging the gap between available basic soil data and missing soil hydraulic characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.J.; Tate, K.R.; Scott, N.A.; Feltham, C.W. Land-use change: Effects on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus pools and fluxes in three adjacent ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.R.; Hartage, K.H. Bulk Density. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1, 2nd ed.; Klute, A., Ed.; SSSA book series; American Society of Agronomy ASA and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, L.G.; Bremner, J.M. A simple titrimetric method for determination of inorganic carbon in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1972, 36, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasyeva, E.A. Chernozems of the Middle Russian Upland; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1966; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailova, E.A.; Noble, R.R.P.; Post, C.J. Comparison of soil organic carbon recovery by Walkey–Black and dry combustion methods in the Russian chernozem. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2003, 34, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, C.; Cihacek, L.J. Relationships Between Soil Carbon and Soil Texture in the Northern Great Plains. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, J.C.; Bremner, J.M. A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in the soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1988, 19, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.M.; Rabenhorst, M.C. Organic carbon dynamics in soils of Mid-Atlantic barrier island landscapes. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, Y.B.; Ryals, R. Soil carbon response to long-term biosolids application. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckman, V.J.; Wriessnig, K. Improved soil carbonate determination by FT-IR and X-ray analysis. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, K.; Peter, M.; Ehsan, J.; Saran, S.; David, M. A Multipurpose Soil Inorganic Carbon Prediction Model. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, Toulouse, France, 10–14 July 2016; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, L.E.; Moodie, C.D. Carbonate. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Norman, A.G., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, R.W.; Merry, R.H. Pedogenic. Carbonate Pools and Climate Change in Australia. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ryskov, Y.A.; Borisov, A.V.; Oleinik, S.A.; Rykova, E.A.; Demkin, V.A. The relationship between lithogenic and Pedogenic Carbonates Fluxes in Steppe Soils, and the Regularities of Their profile dynamics for the last four millenia. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- You, M.; Han, X.; Hu, N.; Du, S.; Doane, T.A.; Li, L.-J. Profile storage and vertical distribution (0–150 cm) of soil inorganic carbon in croplands in northeast China. CATENA 2020, 185, 104302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinand, C.; Barthès, B.G.; Brunet, D.; Kouakoua, E.; Arrouays, D.; Jolivet, C.; Caria, G.; Bernoux, M. Prediction of soil organic and inorganic carbon contents at a national scale (France) using mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (MIRS). Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Guo, T. Pedogenic Carbonate of aridic Soils in China and its Significance in Carbon Sequestration in Terrestrial System. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, D.K.; Dasong, G.S.; Vadivelu, S.; Ahuja, R.L.; Bhattacharyya, T. Secondary Calcium Carbonate in Soils of arid and Semi-arid regions of India. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kapur, S.; Saydam, C.; Akca, E.; Cavusgil, V.S.; Karaman, C.; Atalay, I.; Ozsoy, T. Carbonate Pools in Soils of the Mediterranean: A case study from Anatolia. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nanko, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Miura, S.; Ishizuka, S.; Sakai, Y.; Levia, D.F.; Ugawa, S.; Nishizono, T.; Kitahara, F.; Osone, Y.; et al. Assessment of soil group, site and climatic effects on soil organic carbon stocks of topsoil in Japanese forests. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, N.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Yu, G.; Zhang, W.; Jobbágy, E. Soil inorganic carbon storage pattern in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, S.; Revel, J.C.; Guiresse, M.; Kaemmerer, M. Some calcareous soils Developed on Recent quaternary Basalt in Southeast Syria. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Houman, B. Morphology, Distribution and Environmental Significance of Pedogenic Carbonates in Relict Soils of Tunisia. In Global Climate Change and Pedogenic Carbonates; Lewis Publishers, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batool, M.; Cihacek, L.J.; Alghamdi, R.S. Soil Inorganic Carbon Formation and the Sequestration of Secondary Carbonates in Global Carbon Pools: A Review. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010015
Batool M, Cihacek LJ, Alghamdi RS. Soil Inorganic Carbon Formation and the Sequestration of Secondary Carbonates in Global Carbon Pools: A Review. Soil Systems. 2024; 8(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatool, Maria, Larry J. Cihacek, and Rashad S. Alghamdi. 2024. "Soil Inorganic Carbon Formation and the Sequestration of Secondary Carbonates in Global Carbon Pools: A Review" Soil Systems 8, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010015
APA StyleBatool, M., Cihacek, L. J., & Alghamdi, R. S. (2024). Soil Inorganic Carbon Formation and the Sequestration of Secondary Carbonates in Global Carbon Pools: A Review. Soil Systems, 8(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010015





