Abstract
The ingestion of vegetables grown in soils or in cultivation substrate contaminated with heavy metals (HMs) and irrigated with wastewater is a potential problem for human health and food quality. The increasing disappearance of fertile soils has led to an increase in the practice of soil-less cultivation and the use of growing substrates, but the choice of the right substrate and its sustainable management is essential to ensure the production of quality and safe vegetables for all while minimizing the impact on the environment and human health. The present study measures the combined effects of different HMs (V, Ni, Cd, Pb, Cu, Cr) on microbial biomass, respiration, and enzyme activities (EAs) in an artificially contaminated commercial growing substrate. The concentrations of HMs were estimated by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy; enzyme activities via spectrophotometric assays; respiration via CO2 evolution; and microbial biomass C via the fumigation extraction method. The results showed a reduction in both respiration and all enzyme activities. The reduction in EAs highlighted a notable influence on microorganism-mediated C, N, S, and P cycles, strongly reducing substrate health. Microbial biomass did not show significant differences, but the increase in the metabolic quotient highlighted how the toxicity of HMs reduces the energy use efficiency of microbial metabolic processes.
1. Introduction
Sustainable nutrition for a constantly growing population and changes in consumption patterns are currently major global challenges. Agriculture is currently facing several significant environmental issues. One serious problem is soil erosion, which is mostly brought on by unsustainable farming methods. One outcome of this issue is the loss of productive land. The current agricultural revolution has applied innovative techniques, such as soil-less agriculture, irrigation with wastewater, and the intensive use of phytosanitary products such as fungicides, insecticides, and herbicides. Unfortunately, these methods pose a significant risk of contamination to soils, growing substrates, and both the surface and underground water used for irrigation [1,2,3]. Many of the phytosanitary products used in agriculture contain certain amounts of heavy metals (e.g., Cd and Pb) in their formulation, but although once applied they do not cause contamination in soils/substrates and plants, their prolonged use over time can cause contamination [4]. Similarly, prolonged irrigation with wastewater can also cause long-term contamination, as the treated water still retains some amount of heavy metals [5]. Through the food chain, air, and water, heavy metals in fields, soils, or agriculturally grown substrates can progressively reach humans. They also have an impact on plant growth and soil microflora [6,7,8]. Soil pollution is the third most significant issue for the proper development of soil functions in Europe and Eurasia [9].
Soil contamination by heavy metals can affect biodiversity by altering the structural balance of the microbial community present in the ecosystem and the composition of the different populations that make up this community [10]. Soil essentially acts as a collector or filter, where pollutants rapidly accumulate but are slowly removed. Metals are subject to a series of reactions that modify their bioavailability and, in turn, influence and modify the activity of microorganisms [11]. Certain metals are essential to microorganisms’ vital processes, acting as micronutrients, biochemical reaction catalysts, protein and bacterial cell wall stabilizers, and osmotic regulators. On the other hand, many metals, including cadmium, lead, mercury, and vanadium, are of no nutritive value and are potentially toxic even at low concentrations. Through covalent and ionic bonds, the toxicity of heavy metals results from their interactions with key cellular components. Accordingly, heavy metals in soil can pose potential environmental hazards [12].
Soil microbes show a certain ability to adapt to heavy metals [13,14,15]. For example, some studies indicate that heavy metals in soil may adversely affect biological processes, including soil enzymatic activities [16], microbial abundance [17], microbial activities [12], and the microbial community structure [18]. Previous studies have shown that soil enzymes facilitate chemical transformations and metabolic processes, such as nutrient cycling [19]. Soil enzymes are sensitive to heavy metal contamination and are a standard parameter for assessing soil quality in the presence of such contaminants [16]. For example, the inhibition of urease and phosphatase activities by heavy metals has been observed [16]. Furthermore, heavy metals significantly affect microbial community diversity and richness [16,18], altering soil microbial activities such as basal soil respiration and enzyme activity [16,20].
Different combinations of metals are often found at contaminated sites [21], but a full investigation of the long-term effects on soil microbial activity is lacking. It is essential to characterize the impact of mixed contaminants on soil microorganisms, understand their hazardous environmental effects, and develop appropriate bioremediation approaches.
Climate-change-related phenomena are a major challenge for agriculture today. They cause soil erosion, reduce agricultural production, and increase the pressure on water resources. Many European countries use greenhouses and nurseries for the soil-less production of fruit, vegetables, and cut flowers to meet current environmental problems and the growing demand for food. One of the most popular soil-less methods is the use of growing substrates. Several factors have contributed to their widespread adoption. Firstly, they allow for higher crop yields and enhanced production system management. On the contrary, in some regions of the world, such as southern Europe, where farmland has been lost, the use of alternative farming techniques is imperative to meet the population’s food needs, increase irrigation and fertigation efficiency, and control the use of pesticides [22].
The choice of the right growing substrate and its sustainable management are essential to ensure the production of quality and safe vegetables while minimizing the impact on the environment and human health. However, this system can also be harmful to the environment; the disposal of used growing substrates and the loss of excess nutrient solution that leaks from the growing mats are harmful. Heavy metals can affect the properties of the substrate and can also be transferred to different organs of the plant. The compositions of commercial growing substrates used in agriculture might vary. The most used materials can be divided into three groups: mineral (vermiculite, perlite); organic (blonde and black peat, tree bark, composted or not, other vegetable fibers, etc.); or synthetic (phenolic foams), giving them certain characteristics and properties. Depending on the origin of the materials, growing substrates can present low, adequate, or high amounts of heavy metals (HMs), which are required to be known for effective fertilizer application and quality control [23].
This work aimed to study the combined effects of different HMs (chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), vanadium (V), lead (Pb), and cadmium (Cd)) on microbial biomass, respiration, and enzymatic activities in a substrate artificially contaminated by a mixed heavy metal solution prepared in the laboratory. This work is part of a larger study, the main objective of which is to evaluate the degree of accumulation of heavy metals in various organs of tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum), as well as the absorption of these metals and their translocation from the artificially contaminated substrate (data presented). To this end, a field study was carried out on tomato plants grown on a control growing substrate and on a substrate contaminated with heavy metals.
2. Materials and Methods
The facilities of the Isotopic Research Centre for Cultural and Environmental Heritage (CIRCE) of the University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli” (Caserta, Italy) were used for the experimental part of the present study.
In the study, a commercial substrate was used to grow tomato seedlings and groundwater for irrigation. The selected substrate composition was a mixture of coconut fiber, black and white peat, composted plant material, organic matter, and perlite, with 0.05 g root activator per liter of the substrate and 1 g fertilizer N-P-K 15-15-15 per liter of the substrate. Heavy metals were below the limits allowed for class A materials. Information on the substrate, composition, and physical–chemical properties are provided by the manufacturer. The main chemical–physical properties of the substrate are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical–physical properties of the commercial substrate before adding the contaminants.
The commercial growing substrate and irrigation water to be used in the experiment were analyzed for the presence of heavy metals (V, Ni, Cd, Pb, Cu, Cr) and their initial concentrations (substrate S0, irrigation water IW0) before the addition of homogeneously known amounts of solutions containing the heavy metals of interest to exceed the limits set by Italian Decree 115 Lgs.D. 75/2010 (Reorganization and revision of the regulations on fertilizers) for Cd, Ni, Pb, and Cu, and Lgs.D. 152/06 (Environmental regulations for Cr and V) and irrigated with contaminated water (according to Italian Legislative Decree 30/2009—Implementation of Directive 119 2006/118/EC on the protection of groundwater against pollution and deterioration) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Limit values for substrate according to Lgs.D. 75/2010—Reorganization and revision of the regulations on fertilizers for Cd, Ni, Pb, and Cu (column A), Lgs.D. 152/06—Environmental regulations for Cr and V (column A) and Lgs.D. 30/09 (column B) for groundwater.
One hundred and fifty kilograms of air-dried commercial growing substrate was weighed and loaded. The substrate was artificially contaminated by adding a solution containing heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, and V) and mixed thoroughly in a concrete mixer (EBERTH 180 L, 650 W, 32 rpm) for a uniform distribution of the heavy metal solution. Pb (500 mg kg−1 substrate) was added as Pb (NO3)2, Cd (15 mg kg−1 substrate) was added as Cd (NO3)2 · 4 H2O, Cu (500 mg kg−1 substrate) was added as Cu (NO3)2 · H2O, Cr (400 mg kg−1 substrate) was added as Cr NO3)2 · 9H2O, Ni (500 mg kg−1 substrate) was added as Ni (NO3)2 · 6 H2O, and V (50 mg kg−1 substrate) was added as VOSO4 · H2O. The water was artificially contaminated by adding Pb (12 µg L−1) as Pb (NO3)2, Cd (6 µg L−1) as Cd (NO3)2. 4 H2O, Cu (12 mg L−1) as Cu (NO3)2 ·H2O, as Cr (40 µg L−1) as Cr NO3)2 · 9H2O, Ni (20 µg L−1) as Ni (NO3)2 · 6 H2O, and V (50 µg L−1) as VOSO4 · H2O.
The substrate was stabilized for 30 days at a temperature of 24 °C and a humidity of 70% after homogenization.
A second analysis was carried out to determine the concentration of heavy metals in our substrate after stabilization (S1) and in the contaminated irrigation water (IW1) before planting the tomato seedlings in pots (Table 3).

Table 3.
Heavy metals tested in the initial (S0) and contaminated substrate (S1) (µg/g d.w. ± S.D.) and the initial (IW0) and contaminated irrigation water (IW1) (µg/L ± S.D.).
2.1. Experimental Design and Substrate Processing
The experimental design was carried out outdoors as shown in Figure 1. Twenty pots of ø50 cm and h60 cm were used and divided into 4 groups of 5 pots each. The first 5 pots were the control plot, where uncontaminated irrigation water and commercial growing substrate were used (Control). In the other 3 groups, i.e., the remaining 15 pots, different combinations of substrate, contaminated substrate, irrigation water, and contaminated irrigation water were used. Tomato seedlings were then planted and grown (4 per pot and 15 cm apart) to reproduce extreme contamination conditions in a controlled manner. Each pot was watered regularly every other day. The control plot and plot B were regularly irrigated with uncontaminated water, while plots A and C were irrigated with contaminated water. After about three months, from June to September (when the tomato plants were uprooted), the substrate was analyzed again. The substrate was collected at two depths, 0–15 and 15–30 cm, corresponding to the rhizosphere and the area immediately below it, respectively. Each sample was sieved (<2 mm) and divided into subsamples for determination of substrate chemical characteristics and substrate biological activities. Sub-samples used for enzyme activity measurements were stored at −80 °C until analysis.
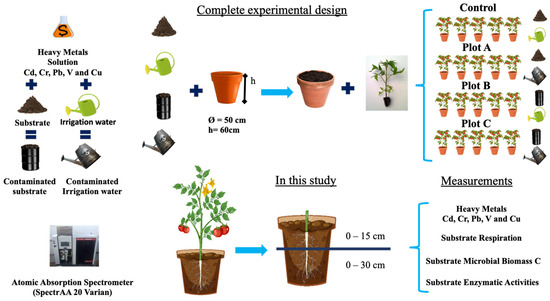
Figure 1.
Experimental design.
2.2. Substrate Heavy Metal Assays
Pulverized samples (250 mg per sample of the substrate) were mineralized using a combination of hydrogen peroxide and nitric acid (H2O2 50% v/v: HNO3 65% v/v = 1:3) in a microwave oven (Milestone—MLS 1200—Microwave Laboratory Systems).
After digestion, the solutions were diluted with deionized water to a final volume of 50 mL. The concentration of each element (V, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cu, and Cd) was measured using atomic absorption spectrometry (SpectrAA 20 Varian) using a graphite furnace and a flame. Heavy metal extraction and analyses were performed in triplicate and quantified using standard solutions (STD Analyticals, Carlo Erba, Milano, Italy).
Accuracy was checked by simultaneous analysis of standards (Resource Technology Corporation, Laramie, WY, USA). Recovery was greater than 90% [24].
2.3. Substrate Biological Properties
Substrate respiration was measured as CO2 evolution from the substrate at field humidity. Approximately 5 g of substrate was incubated for 2 d at 25 °C in complete darkness in airtight jars. The released CO2 was absorbed in NaOH solution (0.1 M) and its amount was determined by a two-phase titration with HCl (0.025 M) [25]. CO2 release from the substrate was expressed in μmol g−1 dry substrate d−1. All measurements were carried out in triplicate for each substrate sample. The water content of the substrates at the time of sampling was determined by oven drying the subsamples at 75 °C to a constant weight.
The substrate microbial biomass C was measured via the fumigation extraction method [26].
The metabolic quotient (qCO2) was calculated from respiration and Cmic (mgCO2 mgCmic−1 g h−1) [27].
The activities of the various substrate enzymes were based on the release and quantitative determination of the product in the reaction mixture when substrate samples were incubated with substrate and buffer solution. They were measured by the spectrophotometric method by using 4-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucopyranoside as a substrate for β-glucosidase activity (GLU) (EC 3.2.1.21) [28], 4-nitrophenyl phosphate bis (cyclohexylammonium) salt as a substrate for acid phosphomonoesterase (PHOac) (EC 3.1.3.2) and alkaline phosphomonoesterase activity (PHOal) (EC 3.1.3.1) [29], sodium caseinate as a substrate for protease activity (PRO) (EC 3.4.21.4) [30], p-nitrophenyl sulfate as a substrate for arylsulphatase activity (ARY) (E.C.3.1.6.1) [31] and p-nitrophenyl glycoside as a substrate for β-galactosidase activity (GAL) (EC 3.2.1.23) [28]. The substrate for dehydrogenase (DEH) (EC 1.1.1.x) was iodonitrotetrazolium chloride [32]. All enzyme activities are reported as μmol of product developed in one hour per gram of dry matter.
2.4. Statistics
All data measurements were performed in triplicate for each sample ± SD. The significance of differences was tested by an analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Tukey test (MINITAB INC 13). Correlations were determined using the simple Pearson correlation coefficient. The PCA analysis was conducted in the R environment [33] using the RStudio user interface [34] and the “survival” and “ranger” libraries [35].
3. Results
3.1. Heavy Metal Content
Figure 2 shows the assayed contents of V, Ni, Pb, Cd, Cu, and Cr in the treated substrates (plots A, B, C) and compares them to those of the control plot at two different depths (0–15 and 15–30 cm).
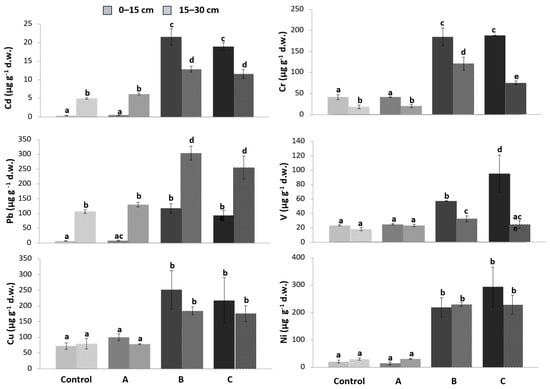
Figure 2.
Heavy metal content in substrate samples in the three plots (A, B, C) compared to the control at two depths: 0–15 (continuous color) and 15–30 cm (color with pattern fill). The intensity of the color is proportional to the degree of contamination. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between mean values at each sampling (p < 0.05).
The heavy metal content was significantly higher at 0–15 cm compared to 15–30 cm, except for Pb, which was higher at 15–30 cm. There is a significant increase from the control plot to plot C and, in general, significantly higher concentrations in the treatments using contaminated soil (B and C), both with and without spraying with contaminated water. Furthermore, these last treatments showed values higher than the limits proposed by the Italian Decree (Lgs.D.152/06—Part III and subsequent amendments) (Table 2—column A).
3.2. Soil Respiration
Figure 3 shows the CO2 evolution produced by the oxidation process of organic matter by the substrate microbial population in three different treatments (A, B, C) at two different depths (0–15 and 15–30 cm) compared to the control plot.
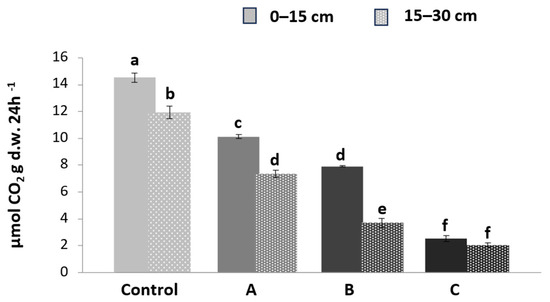
Figure 3.
CO2 evolution produced in three plots (A, B, C) compared to the control plot at two depths: 0–15 (continuous color) and 15–30 cm (color with pattern fill). The intensity of the color is proportional to the degree of contamination. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between mean values at each sampling (p < 0.05).
CO2 evolution was significantly higher in the 0–15 cm layer than in the 15–30 cm layer, as was found for heavy metals.
The treated samples show a significant decrease in the CO2 emissions ranging from 30 to 80% relative to the control. This reduction is much more pronounced in samples where both the substrate and the water were contaminated due to heavy metals, regardless of the depth at which the sample was taken. This shows how heavy metal contamination can inhibit microbial activity, reducing the decomposition of organic matter and hence CO2 evolution.
3.3. Microbial Biomass C (Cmic)
Figure 4 shows the microbial biomass content in the three different plots (A, B, C) at two different depths (0–15 and 15–30 cm) in comparison to the control plot. This parameter represents the carbon stored within the cellular structures of the microbial population, which acts as an indicator of soil quality. The data showed no statistically significant differences between the treatments or at the two different depths.
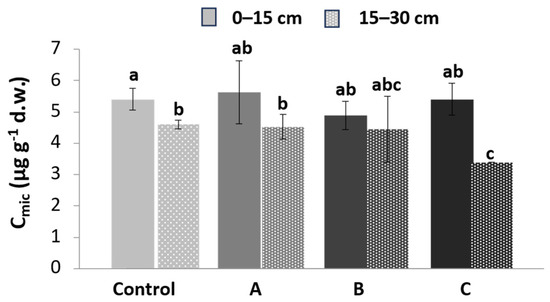
Figure 4.
Microbial biomass content, Cmic, in substrate samples in the three plots (A, B, C) compared to the control plot at two depths: 0–15 (continuous color) and 15–30 cm (color with pattern fill). The intensity of the color is proportional to the degree of contamination. Different letters above bars indicate significant differences between mean values at each sampling (p < 0.05).
3.4. qCO2 Index
The metabolic quotient (qCO2), an index of microbial metabolism, was calculated from substrate respiration and microbial biomass C. The reduced efficiency of optimizing available resources and increased selection pressure favor individuals that make better use of resources. This concept is expressed by qCO2 which represents the CO2 evolved from the microbial biomass per the unit of time and is expressed as (mg CO2 /mg Cmic*g soil)/h [36]. An increase in this index indicates stress or perturbations, while a decrease indicates the microorganisms are maximizing the resource yield. This index is therefore a “warning bell” of substrate microbial degradation [37].
Typically, metal contamination in the different treatments showed an increase in this index (Figure 5) at both sampling depths.
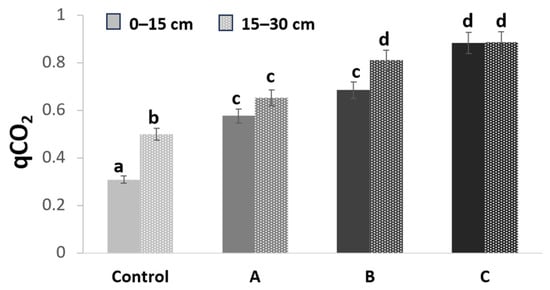
Figure 5.
qCO2 index expressed as (mg CO2 /mg Cmic*g soil)/h in substrate samples in the three plots (A, B, C) compared to the control plot at two depths: 0–15 (continuous color) and 15–30 cm (color with pattern fill). The intensity of the color is proportional to the degree of contamination. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between mean values at each sampling (p < 0.05).
3.5. Enzyme Activities
Figure 6 shows the enzymatic activities trends (EAs) tested at the two depths and for each treatment. In general, a significant reduction in enzyme activity was observed in contaminated substrates compared to the control plot. Regarding the two depths, the enzymatic activities were generally significantly higher in the 0–15 cm layer compared to the 15–30 cm layer, but they were inhibited with increasing contamination.
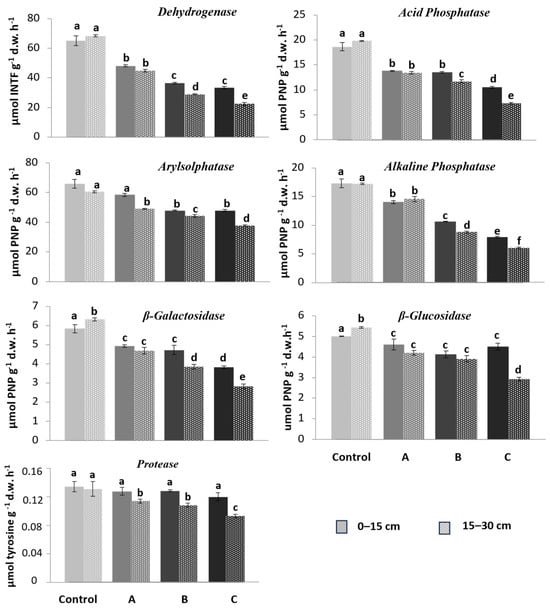
Figure 6.
Substrate enzyme activity in substrate samples in the three plots (A, B, C) compared to the control plot at two depths: 0–15 (continuous color) and 15–30 cm (color with pattern fill). The intensity of the color is proportional to the degree of contamination. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between mean values at each sampling (p < 0.05).
DEH and ARY activities were shown to be the most sensitive to HM contamination, with reductions at a depth of 0–15 cm ranging from 30% to 50% and at 15–30 cm from 35% to 67%, respectively, between treatments A and C. The activities of PHOal, PHOac, GLU, and GAL showed an intermediate decrease of 15% to 20–30%, followed by PRO with a decrease of 10–20% (Figure 6).
Heavy metal contamination reduced the activities of all enzymes linearly, regardless of depth, in the following order: DEH < ARY < PHOac < PHOal < GAL < GLU < PRO.
3.6. Correlation between HMs and Biological Parameters, and PCA Analysis
The Pearson correlation coefficient enabled the evaluation of the relationships between the single HMs and the biological parameters tested (Table 4).

Table 4.
Correlations between soil biological parameters and HMs.
The microbial activity (CO2 evolution, enzyme activities, qCO2 index) appeared to be significantly inhibited by each metal. Regardless of the depth, Cd, Cu, Ni, and Cr were negatively correlated with all the biological parameters tested, while vanadium seemed to have no effect on ARY and DEH activity, and neither did Pb for PHOac, GLU, and GAL.
Furthermore, no correlations were found between the microbial biomass and the other biological parameters or with the heavy metals (Table 4).
A principal component analysis (PCA) was used to validate the results of this investigation (Figure 7). The first two components (Dim1 and Dim2) cumulatively represent 68.2% and 17.6% of the variability. The PCA findings indicate a clear differentiation between the four treatments (Control, A, B, C) (Figure 7a). Treatments B and C were more strongly affected by the heavy metal variables, whereas Control and A were more influenced by the biological properties tested (Figure 7b).
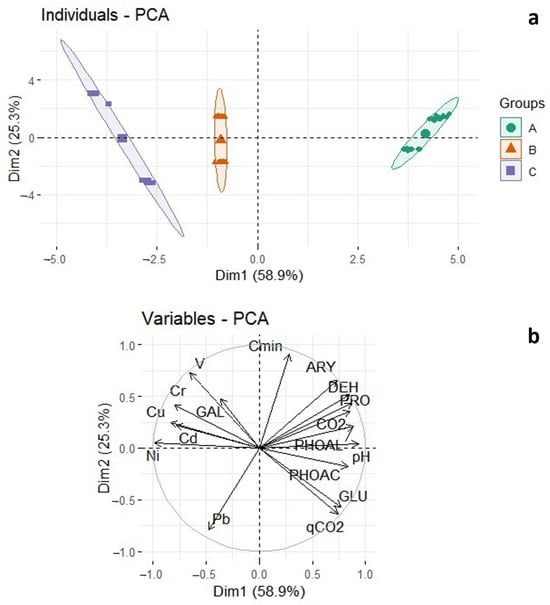
Figure 7.
Grouping of different treatments on the first two-dimensional plane (a) was achieved by utilizing variables derived from discriminant analysis (b) and employing a principal component analysis (PCA).
4. Discussion
The concentrations of all the heavy metals tested at both depths increased from the control grown substrate to the extreme treatment and appeared to be significantly higher in the layer corresponding to the rhizosphere than in the area immediately below, with the exception of lead (Figure 2). The substrate used for the cultivation contained, among other things, perlite. This component is an amorphous volcanic material composed mainly of ferrite, which is present in the substrate used and whose functions are to give structure to the soil and increase the porosity of the substrate and aeration, preventing its compaction and facilitating drainage. On the other hand, the substrate has a high content of organic matter, provided by peat and composted material mainly of plant origin. The abundant presence of organic matter in the substrate, which can support microbial growth, immobilizes the metals in the colloidal fraction of the soil [38]. The soils that receive the metals may adsorb them into the organic matter. The immediate effect is toxicity and a reduction in mobility, depending on the degree and strength of adsorption by soil aggregates. However, in soils with high metal accumulation, it has been observed that as the chemical–physical conditions of the soil change, the ability of the soil to retain the pollutant can also change [39]. In contrast to the other metals, lead showed higher concentrations in the deeper layer (15–30 cm). It is a contaminant with a high molecular weight, which precipitates as soon as it reaches the limit of its solubility. Simultaneously, it is adsorbed by organic matter, especially humic substances. In general, it has a very low mobility and tends to accumulate mainly in the first few centimeters of the soil. The presence of pearlite in the growing substrate used may have facilitated the migration of Pb to the deeper layer after adsorption by organic matter [40].
Microorganisms are the first living organisms affected by heavy metal contamination of soil. In our study, HM contamination significantly reduced both respiration (Figure 3) and enzymatic activities (Figure 6), demonstrating how these parameters can be used as indicators of substrate quality and indicators of HM contamination [41,42].
We found that HM contamination caused a decrease in the activities of each enzyme, and these decreases were enzyme-specific (Figure 6). ARY and DEH activities were more impaired. ARY is largely produced by bacteria [43] and is involved in the metabolism of fungal cell walls by catalyzing the degradation of their aromatic sulphate esters [43]. Since the intracellular activity of ARY is ~70% higher than its extracellular activity, we consider ARY to be mainly an endoenzyme. Furthermore, DEH, in which H is transferred from organic substrates to inorganic acceptors [43], reflects the intracellular activity of active microorganisms [44]. Since ARY and DEH are essentially endoenzymes more directly related to microbial metabolism, they are more affected by HM-contaminated substrates.
PHOac and PHOal were the third and fourth most sensitive enzymes to HM contamination. They take part in the phosphorus cycle by catalyzing the release of phosphate (phosphomonoesterase) or pyrophosphate (phosphodiesterase) from organic matrices, making the element available for mineral nutrition of plants. Reduction could potentially be linked to metals interacting with amino acid residues present at the active site of the phosphatases, ultimately hindering their activity [43].
GALs and GLUs are the fifth and sixth most sensitive enzymes to heavy metal contamination. They are widely distributed in soils and are key enzymes in the carbon cycle. They hydrolyze organic matter, releasing glycosidic residues (glucose or galactose) that are used as an energy source by soil microorganisms as an energy source. Both enzymes are thought to be sensitive to HM contamination, but their response to increased HM levels is not well known due to a lack of data.
PROs appear to be the least sensitive enzymes to HM contamination. They are important enzymes in the soil nitrogen cycle. They promote protein degradation by hydrolyzing the C-N bond, releasing nitrogen in the form of ammonia.
In the past, mathematical models have been used in research to predict the interaction of heavy metals with various soil enzymes (urease, phosphatase, glucosidase...). In the case of PRO, the prediction models did not agree well with the experimental data obtained and the results were uncertain. The scatter of the observed results for these enzymes can be explained by the complexity of these enzymes and their responsiveness to changes in the soil, which are difficult to predict by such mathematically simplified models [45].
Thus, the observed data seem to indicate clear negative effects of HM exposure on all EAs, leading to changes in the soil C, N, P, and S cycles. ARY and DEH were the most affected by HM contamination (Figure 6). DEH is an enzyme associated with the C cycle that shifts H from organic substrates to inorganic acceptors [43,46] in microbial cells in vivo. In contrast to DEH, ARY acts by hydrolyzing organic sulfate esters [43,47], releasing S from organic material and controlling plant and microbial S availability [43,47]. As mentioned above, contamination with HMs has the potential to inhibit microbial C and S cycling processes, resulting in C and S limiting effects for microorganisms. This is particularly important as soils are increasingly being depleted due to the continuous depletion of S in agricultural crops and inadequate or no S fertilization [43,48]. In addition, HM exposure could lead to varying degrees of slowing of C cycling processes, as the activities of GLU and GAL appear to be less affected by HMs than DEH (Figure 6). This suggests that the overall soil microbial oxidation activity (as indicated by DEH activity) is more affected than cellulose degradation (GLU and GAL activity). In terms of N and P cycling, both PHOac and PHOal were affected by HM contamination, possibly resulting in reduced N and P cycling, respectively.
Substrate CO2 evolution also appears to be reduced in the presence of HMs. This was confirmed by the increase in the metabolic quotient, qCO2, in both treatments B and C (Figure 5). Indeed, the toxicity of HMs makes microbial metabolism less energy efficient, requiring more carbon to sustain it and reducing the amount of carbon available for microbial biomass [49,50].
In this study, significant negative correlations were observed between EA and total HMs (Table 4). In general, there is a negative correlation between the concentration of HMs and microbial activity. Some authors reported that the toxicity of HMs in soils decreased the activity of DEH, URE, CAT, and PHOac by between 5.3 and 74.8% compared to the control [51,52,53]. These studies suggest that an increase in the bioavailable fractions of HMs may inhibit the activities of soil enzymes by metal ions reacting with the sulfhydryl group of the enzyme or chelating with the enzyme substrate.
The application of HMs to soils has generally been associated with a decrease in microbial biomass and a change in microbial community composition [51,52,53]. In our study, this parameter did not show statistically significant differences between treatments (Table 4). There were no quantitative changes in the community, but there was probably a qualitative change in the community structure. Indeed, microbes respond differently to stress [54]; some more tolerant populations may survive, while others that are more susceptible may decline under environmental changes. In general, ammoniferous bacteria, along with some spore bacteria, cellulolytic bacteria and actinomycetes, are most sensitive to soil pollution but, at the same time, an increase in the number of bacteria in polluted soils has also been reported [55].
In the literature on the microbial community structure and diversity in soils, [51] emphasized that land use type, water content, HM content, pH, microbial biomass, respiration, and qCO2 were the most important parameters affecting the microbial community structure and diversity. The most dominant microbial species were Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Acidobacteria, and Chloroflexi. A high reactivity towards Cu, Cd, Zn, and Pb was observed in Chloroflexi, Firmicutes, and GAL15.
Applying principal component analysis to the results obtained indicates that irrigation with contaminated water (A) has a long-term effect that is not immediately apparent, whereas substrate contamination has a short-term effect. Thus, heavy metals added to the substrate had a greater effect on the microbial components than those artificially added to the irrigation water according to the PCA analysis and subsequent grouping of treatments along the x-axis. According to [56], soils with high levels of heavy metals tend to cluster together and distance themselves from those with low or no levels of contamination, which, in contrast, cluster based on the biological characteristics of the soil.
5. Conclusions
Given the results obtained, it can be concluded that (a) Heavy metal presence in treatments A, B, and C altered the microbial activity. Nonetheless, the most notable impact was perceived in treatments B and C, with both respiratory and enzymatic activities exhibiting a reduction. (b) No significant change in the microbial biomass was associated with the reduction in other biological parameters, but it might highlight an increase in the number of microorganisms more resistant to metals at the expense of the more sensitive ones, resulting in a change in the community only qualitatively and not quantitatively. (c) The increase in qCO2, the metabolic quotient, highlights how heavy metal toxicity reduces the energy use efficiency of microbial metabolic processes. In addition, the reduction in EAs in HM-contaminated soils showed a marked influence on microorganism-mediated C, N, S, and P cycling, severely reducing soil health. (d) The principal component analysis (PCA) suggests that the addition of heavy metals to the substrate had a greater effect on the microbial component than the metals added artificially through irrigation water. (e) The disposal or reuse of the growing substrate is a common practice, which in both cases should lead to associated control of the amount of heavy metals present. (f) It is important to properly formulate the growing substrates, paying attention to the materials used. (g) This study indicates that the biological properties and microbial communities of the substrate can be adversely affected by hypothetical contamination, either directly or by irrigation with contaminated water over time. (h) We must not lose sight of the heavy metals present in water from industrial processes, even though it is treated before being used as irrigation water by farmers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P. and M.A.-R.; writing—review and editing, S.P. and M.A.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Giovanni Bartoli (University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”, Di. C.D.E.A.) and Antonietta Fioretto (University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli”, Di.S.T.A.Bi.F.) for their assistance in fieldwork and data curation. The authors wish to express their gratitude to Roberto J. Cabrera-Puerto (Evaluation and Restoration of Agricultural and Forestry Systems Research Group, Forest Engineering Department, University of Córdoba) for his invaluable assistance during the PCA statistical analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fussy, A.; Papenbrock, J. An Overview of Soil and Soilless Cultivation Techniques-Chances, Challenges and the Neglected Question of Sustainability. Plants 2022, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaimy, M.A.; Shahin, S.A.; Vranayova, Z.; Zelenakova, M.; Abdel-Hamed, E.M.W. Long-Term Impact of Wastewater Irrigation on Soil Pollution and Degradation: A Case Study from Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Malyan, S.K.; Baram, S.; Sharma, J.; Singh, R.; Pugazhendhi, A. Industrial wastes: Fly ash, steel slag, and phosphogypsum-potential candidates to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from paddy fields. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 124824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raven, P.H.; Hassenzahl, D.M.; Hager, M.C.; Gift, N.Y.; Berg, L.R. Environment, 9th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-119-62472-1. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, M.; Pineda, M.; Yargeau, V. Sensitivity of the LuminoTox tool to monitor contaminants of emerging concern in municipal secondary wastewater effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, M.; Surendran, U.; Raja, P.; Kumar, A.; Senapathi, V. A review of heavy metals accumulation pathways, sources and management in soils. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtić, S.; Zahirović, Ć.; Čivic, H.; Karić, L.; Furković, J. Uptake of heavy metals by tomato plants (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) and their distribution inside the plant. Agric. For. 2018, 64, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Eugenio, N.; McLaughlin, M.; Pennock, D. Soil Pollution: A Hidden Reality; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; 142p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, K.; Luo, C. Differential response of the soil nutrients, soil bacterial community structure and metabolic functions to different risk areas in Lead-Zine tailings. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1131770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra Caracciolo, A.; Terenzi, V. Rhizosphere Microbial Communities and Heavy Metals. Microorganisms 2021, 8, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Schutte, B.J.; Ulery, A.; Deyholos, M.K.; Sanogo, S.; Lehnhoff, E.A.; Beck, L. Heavy Metal Contamination in Agricultural Soil: Environmental Pollutants Affecting Crop Health. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Meng, D.; Li, J.; Yin, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Cheng, C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, M. Response of soil microbial communities and microbial interactions to long-term heavy metal contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Liu, C.; Li, B.; Dong, Y. Trifolium repens L. regulated phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by promoting soil enzyme activities and beneficial rhizosphere associated microorganisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeboah, J.O.; Shi, G.; Shi, W. Effect of heavy metal contamination on soil enzymes activities. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2021, 9, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changchao, L.; Quan, Q.; Gan, Y.; Dong, J.; Fang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Effects of heavy metals on microbial communities in sediments and establishment of bioindicators based on microbial taxa and function for environmental monitoring and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosławiecka, A.K.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. The Effect of Heavy Metals on Microbial Communities in Industrial Soil in the Area of Piekary Śląskie and Bukowno (Poland). Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, K.; Luo, Y.; Du, L.; Tian, R.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Shao, W.; et al. Responses of Soil Enzyme Activity to Long-Term Nitrogen Enrichment and Water Addition in a Typical Steppe. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrani, D.; Ajmone-Marsan, F.; Corti, G.; Cocco, S.; Cardelli, V.; Adamo, P. Heavy metal load and effects on biochemical properties in urban soils of a medium-sized city, Ancona, Italy. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3425–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutam Mukherjee, A.; Ramesh Wanjari, U.; Eladl, M.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Elsherbini, D.M.A.; Sukumar, A.; Kannampuzha, S.; Ravichandran, M.; Renu, K.; Vellingiri, B.; et al. Mixed contaminants: Occurrence, interactions, toxicity, detection, and remediation. Molecules 2022, 27, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmakçı, R.; Salık, M.A.; Çakmakçı, S. Assessment and Principles of Environmentally Sustainable Food and Agriculture Systems. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, C.A.D.; van Raij, B.; Abreu, M.F.D.; González, A.P. Routine soil testing to monitor heavy metals and boron. Sci. Agric. 2005, 62, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Bartoli, G.; Alvarez Romero, M.; Mottola, S.; Fioretto, A. Trace metals accumulation in Fragaria ananassa and its possible use as a bioaccumulator. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 475–482. [Google Scholar]
- Papa, S.; Curcio, E.; Lombardi, A.; D’Oriano, P.; Fioretto, A. Soil microbial activity in three evergreen oak (Quercus ilex) woods in a Mediterranean area. In Developments in Soil Science; Violante, A., Huang, P.M., Bollag, J.M., Gianfreda, L., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherland; Boston, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 28B, pp. 229–237. ISSN 0166-2481. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.H.; Domsch, K.H. The metabolic quotient for CO2 (qCO2) a specific activity parameter to assess the effects of environmental conditions, such as pH, on the microbial biomass of forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1993, 25, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Glucosidases and galactosidases in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, J.N.; Bulter, J.H.A. Short-term assays of soil proteolytic enzyme activities using proteins and dipeptide derivatives as substrates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Arylsulfatase activity of soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1970, 34, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Mersi, W.; Schinner, F. An improved and accurate method for determining the dehydrogenase activity of soils with iodonitrotetrazolium chloride. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1991, 11, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. R Studio: Integrated Development for R; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Fox, J.; Carvalho, M.S. The RcmdrPlugin. Survival Package: Extending the R Commander Interface to Survival Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 49, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.N.; Waqas, M.A.; Rahman, S. Microbial metabolic quotient is a dynamic indicator of soil health: Trends, implications, and perspectives. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2022, 55, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananyeva, N.D.; Ivashchenko, K.V.; Sushko, S.V. Microbial indicators of urban soils and their role in the assessment of ecosystem services: A review. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, M.; Hu, W.; Chen, L.; Ai, S. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and their immobilization at micro-scale interfaces among diverse soil components. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintorini, M.M.; Widyatmoko, H.; Sinaga, E.; Aliyah, N. Effect of pH on metal mobility in the soil. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 737, 012071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, I.; Dorronsoro, C. Contaminación por Metales Pesados. En Tecnología de Suelos. Universidad de Granada. Departamento de Edafología y Química Agrícola. 2005. Available online: http://edafologia.ugr.es (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Geng, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Hou, H. A New Method for Ecological Risk Assessment of Combined Contaminated Soil. Toxics 2023, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnikova, T.; Kolesnikov, S.; Khoroshaev, D.; Tsepina, N.; Evstegneeva, N.; Timoshenko, A. Assessment of the Health of Soils Contaminated with Ag, Bi, Tl, and Te by the Intensity of Microbiological Activity. Life 2023, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, H.; Meli, P.; Butler, B.; Paolini, J.; Matus, F.; Merino, C.; Cornejo, P.; Kuzyakov, Y. Meta-analysis of heavy metal effects on soil enzyme activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Greco, S.; Ceccanti, B. Ecological significance of the biological activity in soil. Soil Biochem. 2017, 6, 293–356. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, P.; Mao, L.; Zhi, Y.E.; Shi, W.J. Assessment of effects of heavy metals combined pollution on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure: Modified ecological dose–response model and PCR-RAPD. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilakiya, T.; Swarnapriya, R.; Pugalendhi, L.; Geethalakshmi, V.; Lakshmanan, A.; Kumar, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Carbon Accumulation, Soil Microbial and Enzyme Activities in Elephant Foot Yam-Based Intercropping System. Agriculture 2023, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.M.; Khan, K.S.; Billah, M.; Akhtar, M.S.; Rukh, S.; Alam, S.; Munir, A.; Mahmood Aulakh, A.; Rahim, M.; Qaisrani, M.M.; et al. Organic Amendments and Elemental Sulfur Stimulate Microbial Biomass and Sulfur Oxidation in Alkaline Subtropical Soils. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucheta, A.R.; Lambais, M.R. Sulfur in agriculture. Rev. Bras. De Ciência Do Solo 2012, 36, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Sarkar, B.; Sik Ok, Y.; Zhang, W.; Rumpel, C.; Sparks, D.; Farrell, M.; Hall, T.; et al. Microbial functional diversity and carbon use feedback in soils as affected by heavy metals. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, L.; Yu, M.; Afzal, M.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.; Xu, J. Nitrogen combined with biochar changed the feedback mechanism between soil nitrification and Cd availability in an acidic soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisca, F.M.; Glatstein, D.A. Environmental application of basic oxygen furnace slag for the removal of heavy metals from leachates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Physicochemical features, metal availability and enzyme activity in heavy metal-polluted soil remediated by biochar and compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.P.; Yang, J.E.; Kim, S.C. Heavy metal remediation in soil with chemical amendments and its impact on activity of antioxidant enzymes in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and soil enzymes. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; Lou, W.; Zeng, W.; Liu, T.; Yin, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Mathivanan, K.; et al. Soil microbial community assembly model in response to heavy metal pollution. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylo, A.; Almeida Pereira, S.I.; Benidire, L.; El Khalil, H.; Castro, P.M.; Ouvrard, S.; Schwartz, C.; Boularbah, A. Trace and major element contents, microbial communities, and enzymatic activities of urban soils of Marrakech city along an anthropization gradient. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; Huang, K.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Z. An improved weighted index for the assessment of heavy metal pollution in soils in Zhejiang, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).