Physico-Chemical Properties and Phosphorus Solubilization of Organomineral Fertilizers Derived from Sewage Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Organomineral Fertilizers (OMFs) Production
2.3. Physical Characterization
2.4. Fertilizer P Solubilization Dynamics
2.5. Sampling and Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical-Chemical Characterization
3.2. Leaching Column Experiment
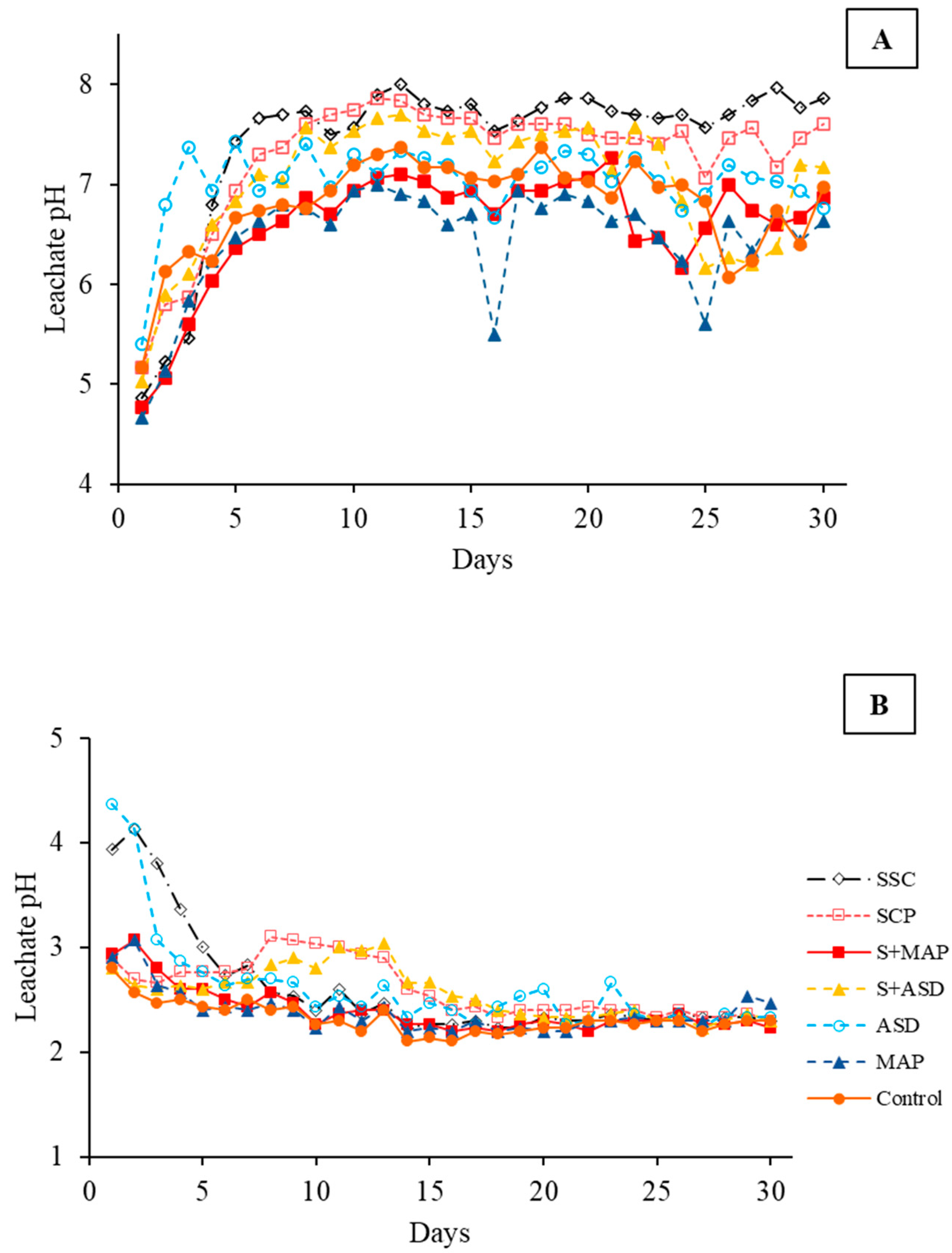
3.2.1. Leachate pH Values
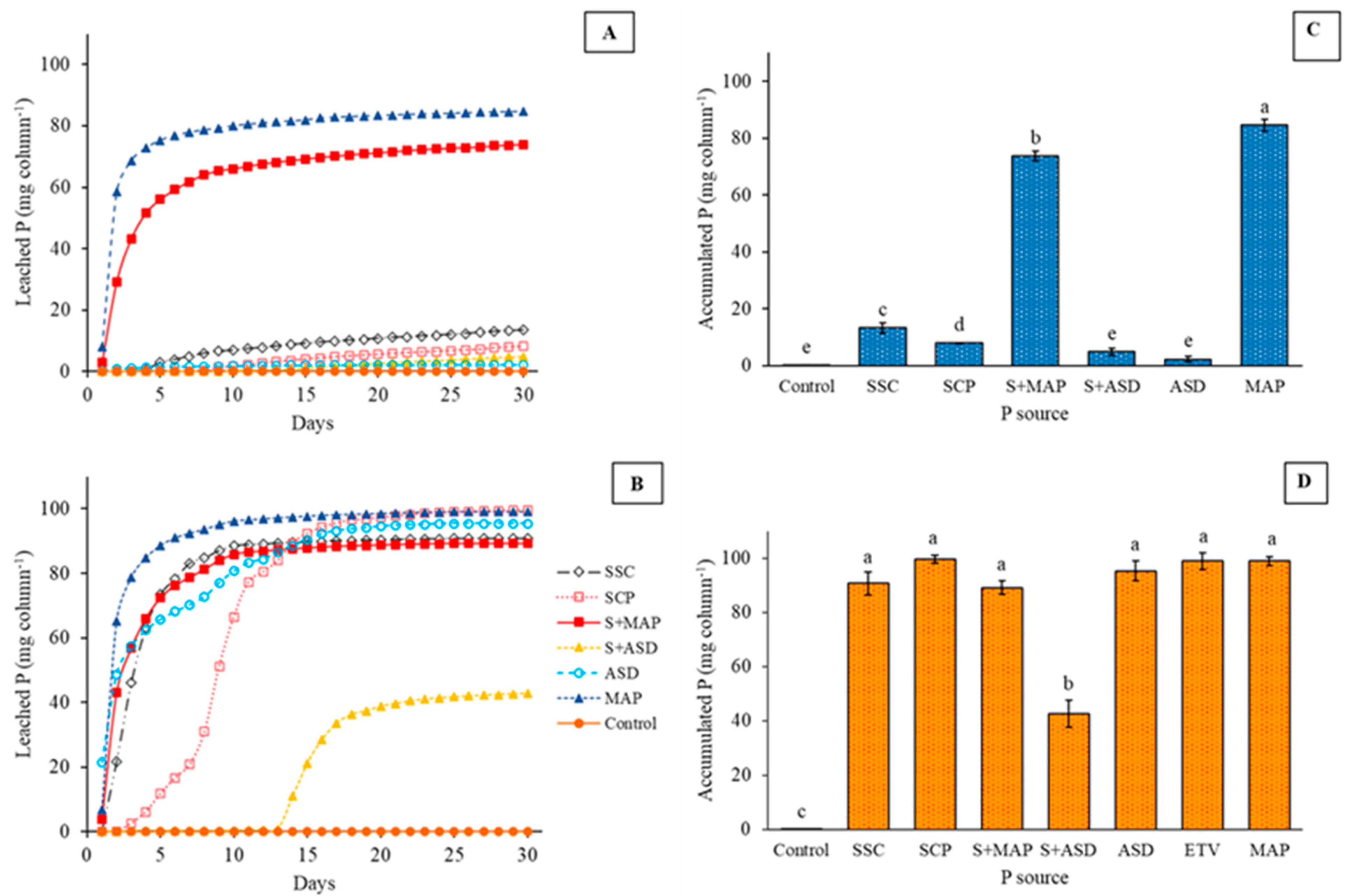
3.2.2. Fertilizer P Solubilization Dynamics
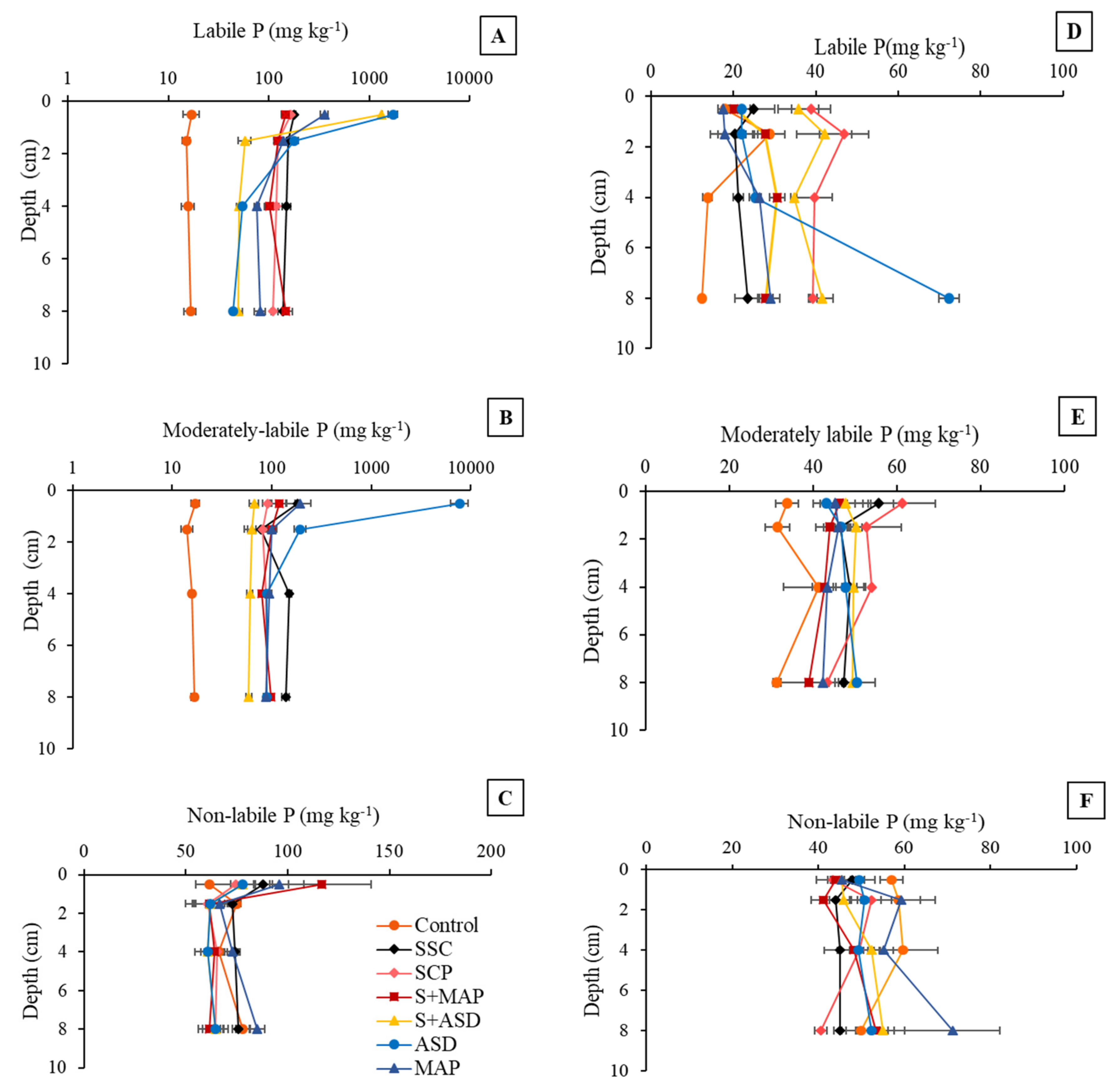
3.2.3. Soil P Lability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Syers, J.K.; Johnston, A.E.; Curtin, D. Efficiency of Soil and Fertilizer Phosphorus Use; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; ISBN 9789251059296. [Google Scholar]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.O.; White, S. The Story of Phosphorus: Global Food Security and Food for Thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smil, V. Phosphorus in the Environment: Natural Flows and Human Interferences. Energy Environ. 2000, 25, 53–88. [Google Scholar]
- Pavinato, P.S.; Cherubin, M.R.; Soltangheisi, A.; Rocha, G.C.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Revealing Soil Legacy Phosphorus to Promote Sustainable Agriculture in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, D.R.; Gatiboni, L.C.; Kaminski, J. Fatores Que Afetam a Disponibilidade Do Fósforo e o Manejo Da Adubação Fosfatada Em Solos Sob Sistema Plantio Direto. Cienc. Rural 2008, 38, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doydora, S.; Gatiboni, L.; Grieger, K.; Hesterberg, D.; Jones, J.L.; McLamore, E.S.; Peters, R.; Sozzani, R.; Van den Broeck, L.; Duckworth, O.W. Accessing Legacy Phosphorus in Soils. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.S.; Melo, L.C.A.; Vergütz, L.; Rodríguez-Vila, A.; Covelo, E.F.; Fernandes, A.R. Adsorption and Desorption Kinetics and Phosphorus Hysteresis in Highly Weathered Soil by Stirred Flow Chamber Experiments. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 162, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus Dynamics: From Soil to Plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Michel, E.; Nobile, C.; Lambers, H.; Kandeler, E.; Faucon, M.P. Response of Phosphorus Dynamics to Sewage Sludge Application in an Agroecosystem in Northern France. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 137, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M. Potential Benefits and Risks of Land Application of Sewage Sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talboys, P.J.; Heppell, J.; Roose, T.; Healey, J.R.; Jones, D.L.; Withers, P.J.A. Struvite: A Slow-Release Fertiliser for Sustainable Phosphorus Management? Plant Soil 2016, 401, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kooij, S.; van Vliet, B.J.M.; Stomph, T.J.; Sutton, N.B.; Anten, N.P.R.; Hoffland, E. Phosphorus Recovered from Human Excreta: A Socio-Ecological-Technical Approach to Phosphorus Recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A.; Edris, G.; Alalayah, W.M. Sludge Production from Municipal Wastewater Treatment in Sewage Treatment Plant. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.L.; de Souza, A.J.; Oliveira, F.C.; Coscione, A.R.; Viana, D.G.; Regitano, J.B. Chemical Attributes of Sewage Sludges: Relationships to Sources and Treatments, and Implications for Sludge Usage in Agriculture. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayara, T.; Basheer-Salimia, R.; Hawamde, F.; Sánchez, A. Recycling of Organic Wastes through Composting: Process Performance and Compost Application in Agriculture. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominko, H.; Gorazda, K.; Wzorek, Z. The Possibility of Organo-Mineral Fertilizer Production from Sewage Sludge. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, W.Y.; Chew, K.W.; Le, C.F.; Lam, S.S.; Chee, C.S.C.; Ooi, M.S.L.; Show, P.L. Sustainable Utilization of Biowaste Compost for Renewable Energy and Soil Amendments. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, J.J.; Hettiarachchi, G.M. A Review of the Latest in Phosphorus Fertilizer Technology: Possibilities and Pragmatism. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.; Peplinski, B.; Michaelis, M.; Kley, G.; Simon, F.G. Thermochemical Treatment of Sewage Sludge Ashes for Phosphorus Recovery. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, S.; Grunert, M.; Müller, S. Overview of Recent Advances in Phosphorus Recovery for Fertilizer Production. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.; Nelles, M.; Eichler-Löbermann, B. Phosphorus Application with Recycled Products from Municipal Waste Water to Different Crop Species. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, L.; Schaaf, T. Outotec (AshDec®) Process for P Fertilizers from Sludge Ash. In Phosphorus Recovery and Recycling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 221–233. ISBN 9789811080319. [Google Scholar]
- Stemann, J.; Adam, C.; Hermann, L. Production of Citrate Soluble Phosphates by Calcination of Secundary Phosphate Sources with a Sodium-Sulfuric Compound. U.S. Patent No. 10,259,752, 16 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brazil. RESOLUÇÃO No 498, DE 19 DE AGOSTO DE 2020. 2020; pp. 265–269. Available online: https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-n-498-de-19-de-agosto-de-2020-273467970 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- IFDC. Manual for Determining Physical Properties of Fertilizer; International Fertilizer Development Center: Muscle Shoals, AL, USA, 1986; ISBN 2053816600. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, H.G.; Jacomine, P.K.T.; Anjos, L.H.C.; Ovileira, V.Á.; Lumbreras, J.F.; Coelho, M.R.; Almeida, J.A.; Araújo Filho, J.C.; Oliveira, J.B.; Cunha, T.J.F. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 5th ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; ISBN 978-85-7035-198-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cantarella, H.; Quaggio, J.A.; Matos, D., Jr.; Boaretto, R.M.; van Raij, B. (Eds.) Boletim 100: Recomendações de Adubação e Calagem Para o Estado de São Paulo; Instituto Agronômico de Campinas: Campinas, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A Modified Single Solution Method for the Determination of Phosphate in Natural Waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in Inorganic and Organic Soil Phosphorus Fractions Induced by Cultivation Practices and by Laboratory Incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatiboni, L.C.; Kaminski, J.; Rheinheimer, D.d.S.; Flores, J.P.C. Biodisponibilidade de Formas de Fósforo Acumuladas Em Solo Sob Sistema Plantio Direto. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2007, 31, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, M.S. Solubilidade e Disponibilidade Do Fósforo de Fosfatos Naturais Com Origens Geológicas Diferentes. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, C.A.; Dos Santos, H.L.; De Franca, G.E.; Pitta, G.V.E.; Bahia Filho, A.F.C. Eficiencia Agronomica de Fosfatos Naturais Para a Cultura Do Sorgo-Granifero. I. Fosforo Total e Soluvel Em Acido Citrico e Granulometria. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 1986, 10, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Raniro, H.R.; Soares, T.d.M.; Adam, C.; Pavinato, P.S. Waste-Derived Fertilizers Can Increase Phosphorus Uptake by Sugarcane and Availability in a Tropical Soil#. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2022, 185, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemming, C.; Bruun, S.; Jensen, L.S.; Magid, J. Plant Availability of Phosphorus from Dewatered Sewage Sludge, Untreated Incineration Ashes, and Other Products Recovered from a Wastewater Treatment System. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2017, 180, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiema, J.; Cofie, O.; Impraim, R.; Adamtey, N. Processing of Fecal Sludge to Fertilizer Pellets Using a Low-Cost Technology in Ghana. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, L.; Jayathilake, N.; Fernando, S.; Gunawardena, S. Effects of Compost Particle Size, Moisture Content and Binding Agents on Co-Compost Pellet Properties. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, A.; Kianmehr, M.H. Factors Affecting Mechanical Properties of Biomass Pellet from Compost. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabil, L.G. Binding and Pelleting Characteristics Os Alfalfa, University of Saskatchewan. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kaliyan, N.; Morey, R.V. Factors Affecting Strength and Durability of Densified Biomass Products. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilvari, H.; de Jong, W.; Schott, D.L. Quality Parameters Relevant for Densification of Bio-Materials: Measuring Methods and Affecting Factors—A Review. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 120, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liang, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G. Co-Pelletization of Sewage Sludge and Biomass: The Density and Hardness of Pellet. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Li, K.; Nkoh, J.N.; He, X.; Xu, R.; Qian, W.; Shi, R.; Hong, Z. Effects of PH Variations Caused by Redox Reactions and PH Buffering Capacity on Cd(II) Speciation in Paddy Soils during Submerging/Draining Alternation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racz, G.J.; Soper, R.J. Reaction Products of Orthophosphates in Soils Containing Varying Amounts of Calcium and Magnesium. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1967, 47, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Johnston, C.; Armstrong, R.D.; Holloway, R.E. Mobility and Lability of Phosphorus from Granular and Fluid Monoammonium Phosphate Differs in a Calcareous Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Chen, Z.S. Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization of Sewage Sludge Compost in Soils with a Different Initial PH. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2009, 55, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouraiphy, A.; Amir, S.; El Gharous, M.; Revel, J.C.; Hafidi, M. Chemical and Spectroscopic Analysis of Organic Matter Transformation during Composting of Sewage Sludge and Green Plant Waste. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2005, 56, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.M.L.; Bertoncini, E.I.; Abreu-Junior, C.H. Composting Sewage Sludge with Green Waste from Tree Pruning. Sci. Agric. 2015, 72, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raniro, H.R.; Bettoni Teles, A.P.; Adam, C.; Pavinato, P.S. Phosphorus Solubility and Dynamics in a Tropical Soil under Sources Derived from Wastewater and Sewage Sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brännvall, E.; Wolters, M.; Sjöblom, R.; Kumpiene, J. Elements Availability in Soil Fertilized with Pelletized Fly Ash and Biosolids. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch, C.; Opp, C. Ecologically Relevant Phosphorus Pools in Soils and Their Dynamics: The Story so Far. Geoderma 2018, 325, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; McBeath, T.M.; Smernik, R.; Stacey, S.P.; Ajiboye, B.; Guppy, C. The Chemical Nature of P Accumulation in Agricultural Soils-Implications for Fertiliser Management and Design: An Australian Perspective. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antille, D.L.; Sakrabani, R.; Godwin, R.J. Phosphorus Release Characteristics from Biosolids-Derived Organomineral Fertilizers. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 2565–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatiboni, L.C. Disponibilidade de Formas de Fósforo Do Solo Às Plantas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, Santa Maria, Brazil, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rheinheimer, D.S.; Anghinoni, I.; Kaminski, J. Depleção Do Fósforo Inorgânico de Diferentes Frações Provocada Pela Extração Sucessiva Com Resina Em Diferentes Solos e Manejos. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2000, 24, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanzer, S.; Oberson, A.; Huthwelker, T.; Eggenberger, U.; Frossard, E. The Molecular Environment of Phosphorus in Sewage Sludge Ash: Implications for Bioavailability. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L. Organic Acids in the Rhizosphere—A Critical Review. Plant Soil 1998, 205, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.S.; Delai, L.B.; Sawaya, A.C.H.F.; Rosolem, C.A. Exudation of Organic Acid Anions by Tropical Grasses in Response to Low Phosphorus Availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, G.A.; Sarkar, D.; Brinton, S.R.; Elliott, H.A.; Martin, F.G. Phytoavailability of Biosolids Phosphorus. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptistella, J.L.C.; Llerena, J.P.P.; Domingues-Júnior, A.P.; Fernie, A.R.; Favarin, J.L.; Mazzafera, P. Differential Responses of Three Urochloa Species to Low Phosphorus Availability. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2021, 179, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil. Instrução Normativa No 61, de 8 de Julho de 2020. 2020; p. 33. Available online: https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/instrucao-normativa-n-61-de-8-de-julho-de-2020-266802148 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
| pH | O.M. | P resin | S | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Al3+ | H + Al | SB | CEC | V | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCl2 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ------------------------- mmolc kg−1 ------------------------ | ----- % ----- | ||||||||
| 4.6 | 14.0 | <6 | 9 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 22 | 8 | 30 | 27 | 20 |
| Sand | Silt | Clay | ||||||||||
| ---------- g kg−1 -------- | ||||||||||||
| 740 | 90 | 170 | ||||||||||
| Fertilizer | N | K2O | Ca | Mg | Na | P2O5 Total | P2O5 H2O | P2O5 HCi | P2O5 NaC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ---------------------------------------------- % ----------------------------------------- | |||||||||
| SSC | 3.73 | 1.10 | 3.08 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 2.46 | 0.4 | 2.20 | 2.30 |
| SCP | 3.73 | 1.10 | 3.08 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 2.46 | 0.4 | 2.20 | 2.30 |
| S + MAP | 5.91 | 0.77 | 2.16 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 17.34 | 13.48 | - | 17.21 |
| S + ASD | 2.61 | 0.64 | 4.36 | 0.76 | 3.34 | 6.75 | 0.49 | 6.22 | - |
| ASD | - | 0.33 | 9.50 | 1.50 | 11.00 | 16.60 | 0.70 | 15.60 | - |
| MAP | 11.00 | - | - | - | 52.00 | 44.00 | - | 52.00 | |
| Fertilizer | Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) | Humidity (%) | Density (g cm−3) | Resistance (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSC | - | - | 6.40 | 0.44 | - |
| SCP | 3.78 ± 0.14 | 15.50 ± 2.02 | 5.19 | 0.61 | 10.24 ± 2.12 |
| S + MAP | 4.16 ± 0.23 | 16.63 ± 2.22 | 3.98 | 0.67 | 8.08 ± 1.38 |
| S + ASD | 3.90 ± 0.12 | 19.12 ± 2.30 | 4.09 | 0.71 | 6.00 ± 1.96 |
| ASD | - | - | 0.00 | 1.17 | - |
| MAP | 3.80 ± 0.48 | - | 1.87 | 1.13 | 6.90 ± 1.19 |
| Treatment | Leached P | Labile P | Moderately Labile P | Non-Labile P | Recovered P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ---------------------------------- (%) -------------------------------- | |||||
| Leaching with deionized water | |||||
| Control | 1.9 | 12.3 | 31.3 | 54.5 | 100.0 |
| SSC | 42.7 | 23.8 | 21.5 | 12.0 | 29.0 |
| SCP | 36.9 | 27.6 | 20.5 | 15.1 | 20.2 |
| S + MAP | 84.1 | 7.1 | 5.1 | 3.7 | 82.3 |
| S + ASD | 24.5 | 43.3 | 15.4 | 16.3 | 18.5 |
| ASD | 3.5 | 19.0 | 69.4 | 8.0 | 60.3 |
| MAP | 85.2 | 5.7 | 5.1 | 4.0 | 93.2 |
| Leaching with citric acid | |||||
| Control | 0.2 | 14.4 | 33.4 | 52.0 | 100.0 |
| SSC | 94.0 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 91.7 |
| SCP | 94.0 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 100.7 |
| S + MAP | 91.9 | 3.6 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 90.2 |
| S + ASD | 85.9 | 3.9 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 47.3 |
| ASD | 92.8 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 97.7 |
| MAP | 93.9 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 2.9 | 100.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinoza, A.L.d.F.; Raniro, H.R.; Leite, C.N.; Pavinato, P.S. Physico-Chemical Properties and Phosphorus Solubilization of Organomineral Fertilizers Derived from Sewage Sludge. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040100
Espinoza ALdF, Raniro HR, Leite CN, Pavinato PS. Physico-Chemical Properties and Phosphorus Solubilization of Organomineral Fertilizers Derived from Sewage Sludge. Soil Systems. 2023; 7(4):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040100
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinoza, Andre Luiz de Freitas, Henrique Rasera Raniro, Camille Nunes Leite, and Paulo Sergio Pavinato. 2023. "Physico-Chemical Properties and Phosphorus Solubilization of Organomineral Fertilizers Derived from Sewage Sludge" Soil Systems 7, no. 4: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040100
APA StyleEspinoza, A. L. d. F., Raniro, H. R., Leite, C. N., & Pavinato, P. S. (2023). Physico-Chemical Properties and Phosphorus Solubilization of Organomineral Fertilizers Derived from Sewage Sludge. Soil Systems, 7(4), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040100








