Phosphorus Speciation in Long-Term Drained and Rewetted Peatlands of Northern Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Soil Sampling
2.2. Total Elements and Plant Available P Analyses
2.3. Sequential P Fractionation
2.4. Solution 31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and P K X-ray Absorption Near Edge Structure (XANES) Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Total Elements and Plant-Available P
3.2. Phosphorus Fractions Recovered by Different Methods
3.3. Solution 31P NMR
3.4. P K-Edge XANES
4. Discussions
4.1. Total Elements and Plant Available Phosphorus
4.2. Phosphorus Fractions
4.3. Solution 31P NMR and P K-XANES
4.4. Synthesis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, K.R.; DeLaune, R.D. Biogeochemistry of Wetlands: Science and Applications; Taylor and Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Joosten, H. European mires: A preliminary status report. Int. Mire Conserv. Group Memb. Newsl. 1997, 3, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lamers, L.P.M.; Vile, M.A.; Grootjans, A.P.; Acreman, M.C.; van Diggelen, R.; Evans, M.G.; Richardson, C.J.; Rochefort, L.; Kooijman, A.M.; Roelofs, J.G.M.; et al. Ecological restoration of rich fens in Europe and North America: From trial and error to an evidence-based approach. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paer, H.W. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater–marine continuum: Dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuar. Coast. 2009, 32, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.; Wells, C.; Macrae, M.; Price, J. Nutrient mineralisation and microbial functional diversity in a restored bog approach natural conditions 10 years post restoration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.; Gelbrecht, J.; Wagner, C.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Evaluation of phosphorus mobilization potential in rewetted fens by an improved sequential chemical extraction procedure. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsmann, D.M.; Kjaergaard, C. Phosphorus release from anaerobic peat soils during convective discharge−Effect of soil Fe: P molar ratio and preferential flow. Geoderma 2014, 223–225, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus dynamics: From Soil to Plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A critical review on soil chemical processes that control how soil pH affects phosphorus availability to plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, E.J.; Reddy, K.R. Phosphorus biogeochemistry of wetlands in agricultural watersheds. In Nutrient Management in Agricultural Watersheds: A Wetlands Solution; Dunne, E.J., Reddy, K.R., Carton, O.T., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Linquist, B.A.; Ruark, M.D.; Hill, J.E. Soil order and management practices control soil phosphorus fractions in managed wetland ecosystems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 90, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuukkanen, T.; Marttila1, H.; Kløve, B. Predicting organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentrations in runoff from peat extraction sites using partial least squares regression. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5860–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.; Gelbrecht, J.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Phosphorus retention at the redox interface of peatlands adjacent to surface waters in northeast Germany. Biogeochemistry 2004, 70, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, C.; Heiberg, L.; Jensen, H.S.; Hansen, H.C.B. Phosphorus mobilization in rewetted peat and sand at variable flow rate and redox regimes. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negassa, W.; Leinweber, P. How does the Hedley sequential phosphorus fractionation reflect impacts of land use and management on soil phosphorus: A review? J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierzynski, G.M.; McDowell, R.W.; Sims, J.T. Chemistry, Cycling, and Potential Movement of Inorganic Phosphorus in Soils. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment; Sims, J.T., Sharpley, A.S., Eds.; Agronomy Monograph 46; Agronomy Society of America, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, J. Peatlands Restoration in Germany—A Potential Win-Win-Win Solution for Climate Protection, Biodiversity Conservation and Land Use. Available online: https://www.teebweb.org (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Zerbe, S.; Steffenhagen, P.; Parakenings, K.; Timmermann, T.; Frick, A.; Gelbrecht, J.; Zak, D. Ecosystem Service Restoration after 10 Years of Rewetting Peatlands in NE Germany. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlichting, A.; Leinweber, P.; Meissner, R.; Altermann, M. Sequentially extracted phosphorus fractions in peat derived soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J.; Leinweber, P. Phosphorus in sequentially extracted fen peat soils: A K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy study. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2008, 171, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negassa, W.; Acksel, A.; Eckhardt, K.-U.; Regier, T.; Leinweber, P. Soil organic matter characteristics in drained and rewetted peatlands of northern Germany: Chemical and spectroscopic analyses. Geoderma 2019, 353, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations). Guidelines for Soil Description; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; SSSA Book Series 5; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- VdLUFA. Das VdLUFA Methodenbuch; VdLUFA Verlag: Darmstadt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tiessen, H.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Moir, J.O. Changes in organic and inorganic phosphorus composition of two grassland soils and their particle size fractions during 60–90 years of cultivation. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 34, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, H.; Moir, J.O. Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed; Carter, M.R., Gregorich, E.G., Eds.; Taylor and Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cade-Menun, B.J. Improved peak identification in 31P-NMR spectra of environmental samples with a standardized method and peak library. Geoderma 2015, 257–258, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergren, J.; Vincent, A.G.; Jansson, M.; Persson, P.; Ilstedt, U.; Gröbner, G.; Giesler, R.; Schleucher, J. High-resolution characterization of organic phosphorus in soil extracts using 2D 1H−31P NMR correlation spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3950–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prietzel, J.; Harrington, G.; Häusler, W.; Heister, K.; Werner, F.; Klysubun, W. Reference spectra of important adsorbed organic and inorganic phosphate binding forms for soil P speciation using synchrotron-based K-edge XANES spectroscopy. J. Synchrotron Rad. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Rad. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAS. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc. Version 9. Available online: https://support.sas.com/documentation/onlinedoc/91pdf/sasdoc_91/stat_ug_7313.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- Brünger, A.T. Free R value: A novel statistical quantity for assessing the accuracy of crystal structures. Nature 1992, 355, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pombal, X.P.; Muñoz, J.C.N.; Cortizas, A.M. Peat. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Chesworth, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rezanezhad, F.; Price, J.S.; Quinton, W.L.; Lennartz, B.; Milojevic, T.; Cappellen, P.V. Structure of peat soils and implications for water storage, flow and solute transport: A review update for geochemists. Chem. Geol. 2016, 429, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrock, C.N.; Cheshire, M.V.; Shand, C.A. The involvement of iron and aluminum in the bonding of phosphorus to soil humic acid. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1997, 28, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.; Velty, S.; Zeitz, J. The influence of degree of peat decomposition on phosphorus binding forms in fens. Mires Peat 2007, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Callery, O.; Brennan, R.B.; Healy, M.G. Use of amendments in a peat soil to reduce phosphorus losses from forestry operations. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, M.; Bergström, L.; Schmieder, F.; Kirchmann, H.; Condron, L.; Aronsson, H. Phosphorus leaching from an organic and a mineral arable soil in a rainfall simulation study. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.; Wagner, C.; Payer, B.; Augustin, J.; Gelbrecht, J. Phosphorus mobilization in rewetted fens: The effect of altered peat properties and implications for their restoration. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesman, A.W.; Turner, B.L.; Reddy, K.R. Forms of organic phosphorus in wetland soils. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 6697–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, E.; Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Heenan, M.; Wen, D. A structural equation model analysis of phosphorus transformations in global unfertilized and uncultivated soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.F.; Schlesinger, W.H. A literature review and evaluation of the Hedley fractionation: Applications to the biogeochemical cycle of soil phosphorus in natural ecosystems. Geoderma 1995, 64, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Post, W.M. Phosphorus transformations as a function of pedogenesis: A synthesis of soil phosphorus data using Hedley fractionation method. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shao, H.-B.; Sun, J.-N.; Chang, S.X. Phosphorus fractions and profile distribution in newly formed wetland soils along a salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta in China. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redel, Y.; Staunton, S.; Durán, P.; Gianfreda, L.; Rumpe, C.; Mora, M.L. Fertilizer P Uptake Determined by Soil P Fractionation and Phosphatase Activity. J. Soil Sci. Plant. Nut. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Jing, H.; Kaillou, L.; Qaswar, M.; Khan, M.N.; Jin, C. Changes in phosphorus fractions associated with soil chemical properties under long-term organic and inorganic fertilization in paddy soils of southern China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pätzold, S.; Hejcman, M.; Barej, J.; Schellberg, J. Soil phosphorus fractions after seven decades of fertilizer application in the Rengen Grassland Experiment. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, T.E.; Brookes, P.C. Changes in soil phosphorus forms through time in perennial versus annual agroecosystems. Agri. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 184, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jien, S.-H.; Baillie, I.; Hu, C.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Iizuka, Y.; Chiu, C.-Y. Forms and distribution of phosphorus in a placic podzolic toposequence in a subtropical subalpine forest, Taiwan. Catena 2016, 140, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.H.T.; Menegale, M.L.C.; Rodrigues, M.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Pavinato, P.S.; Foltran, E.C. Impacts of timber harvest intensity and P fertilizer application on soil P Fractions. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2019, 437, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltangheisi, A.; de Moraes, M.T.; Cherubin, M.R.; Alvarez, D.O.; de Souza, L.F.; Bieluczyk, W. Forest conversion to pasture affects soil phosphorus dynamics and nutritional status in Brazilian Amazon. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 194, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltran, E.C.; Rocha, J.H.T.; Bazani, J.H.; Goncalves, J.L.M.; Rodrigues, M.; Pavinato, P. Phosphorus pool responses under different P inorganic fertilizers for a eucalyptus plantation in a loamy Oxisol. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 435, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sperber, C.; Stallforth, R.; Preez, C.D.; Amelung, W. Changes in soil phosphorus pools during prolonged arable cropping in semiarid grasslands. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, L.E.; Parent, S.-É.; Ziadi, N. Biogeochemistry of soil inorganic and organic phosphorus: A compositional analysis with balances. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 141, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Bao, K.; Yu, X.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Q.; Lu, X. Forms and accumulation of soil P in a subalpine peatland of Mt. Changbai in Northeast China. Catena 2012, 92, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, K.; Gielen, G.; Luo, J.; He, L. Effect of 17 years of organic and inorganic fertilizer applications on soil phosphorus dynamics in a rice–wheat rotation cropping system in eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, D.; Herzog, C.; Hupfer, M. Effects of drying on phosphorus uptake in re-flooded lake sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.Z.; Whiteb, J.R.; Coghlan, C.C.; Reddy, K.R. Influence of hydropattern and vegetation on phosphorus reduction in a constructed wetland under high and low mass loading rates. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fang, F.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J. Spatial variations of soil phosphorus forms and the risks of phosphorus release in the water-level fluctuation zone in a tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahutomo, S.; Kovar, J.L.; Thompson, M.L. Phosphorus transformations in stream bank sediments in Iowa, USA, at varying redox potentials. J. Soil Sediment. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yang, P.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X. Spatial distribution and release of phosphorus in purple soils in the water fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. JFAE 2014, 12, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Bedrock, C.N.; Cheshire, M.V.; Chudek, J.A.; Goodman, B.A.; Shand, C.A. Use of 31P NMR to study the forms of phosphorus in peat soils. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 152, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.G.; Vestergren, J.; Gröbner, G.; Persson, P.; Schleucher, J.; Giesler, R. Soil organic phosphorus transformations in a boreal forest chronosequence. Plant Soil 2013, 367, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade-Menun, B.; Liu, C.W. Solution Phosphorus-31 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Soils from 2005 to 2013: A Review of Sample Preparation and Experimental Parameters. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 78, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizewski, F.; Liu, Y.-T.; Morris, A.; Hesterberg, D. Spectroscopic approaches for phosphorus speciation in soils and other environmental systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, S.; Hesterberg, D.; Chou, J.; Beauchemin, M.; Simard, R.R.; Sayers, D.E. Speciation of phosphorus in phosphorus-enriched agricultural soils using X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy and chemical fractionation. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J.; Abraham, M.; Amelung, W.; Baum, C.; Bol, R.; Kühn, O. Innovative methods in soil phosphorus research: A review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 43–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, D.A.; Williams, G.G. History of Chemical Fertilizer Development. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Ou, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, B.; Han, L.; Li, Y. Change in the distribution of phosphorus fractions in aggregates under different land uses: A case in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
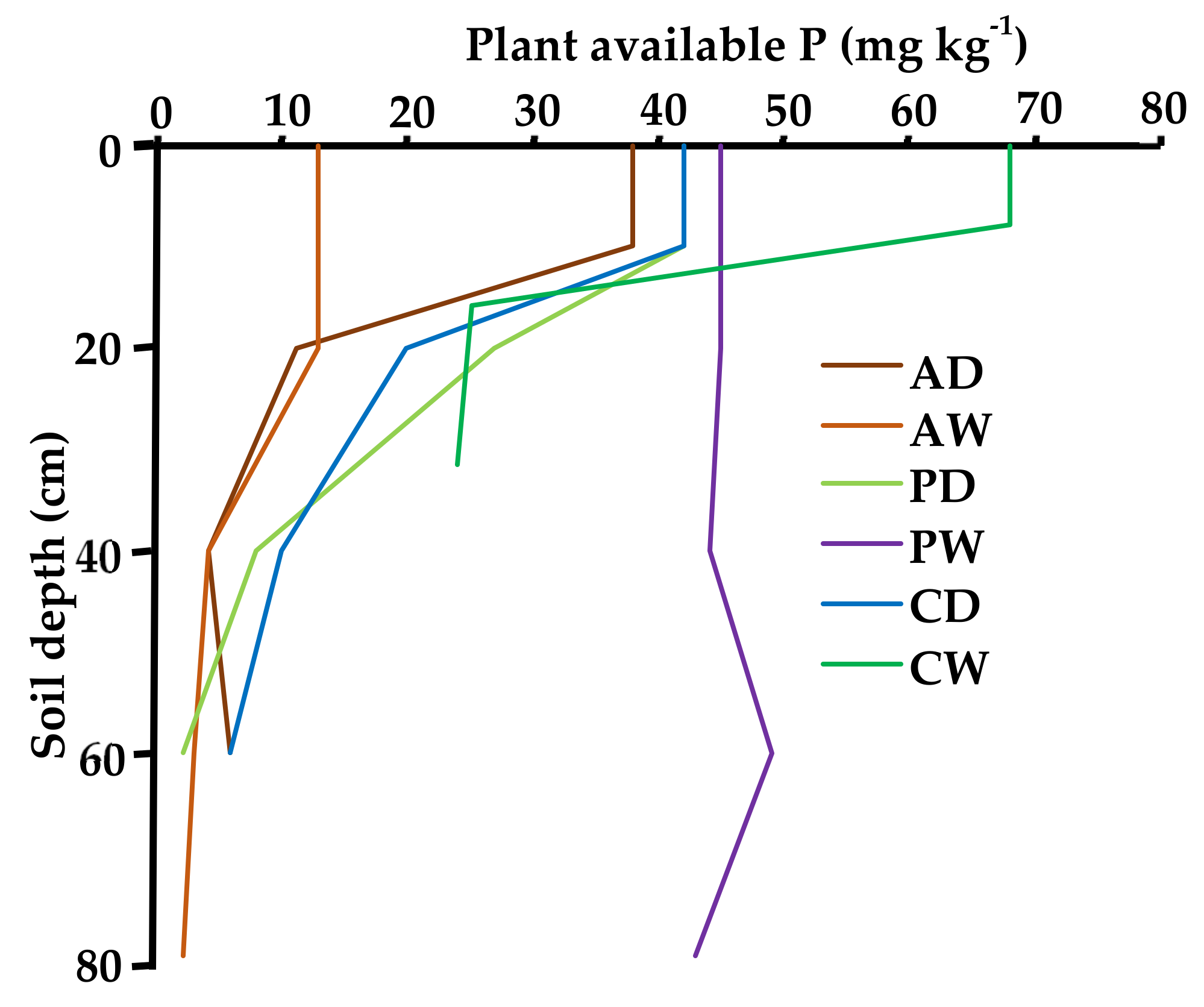


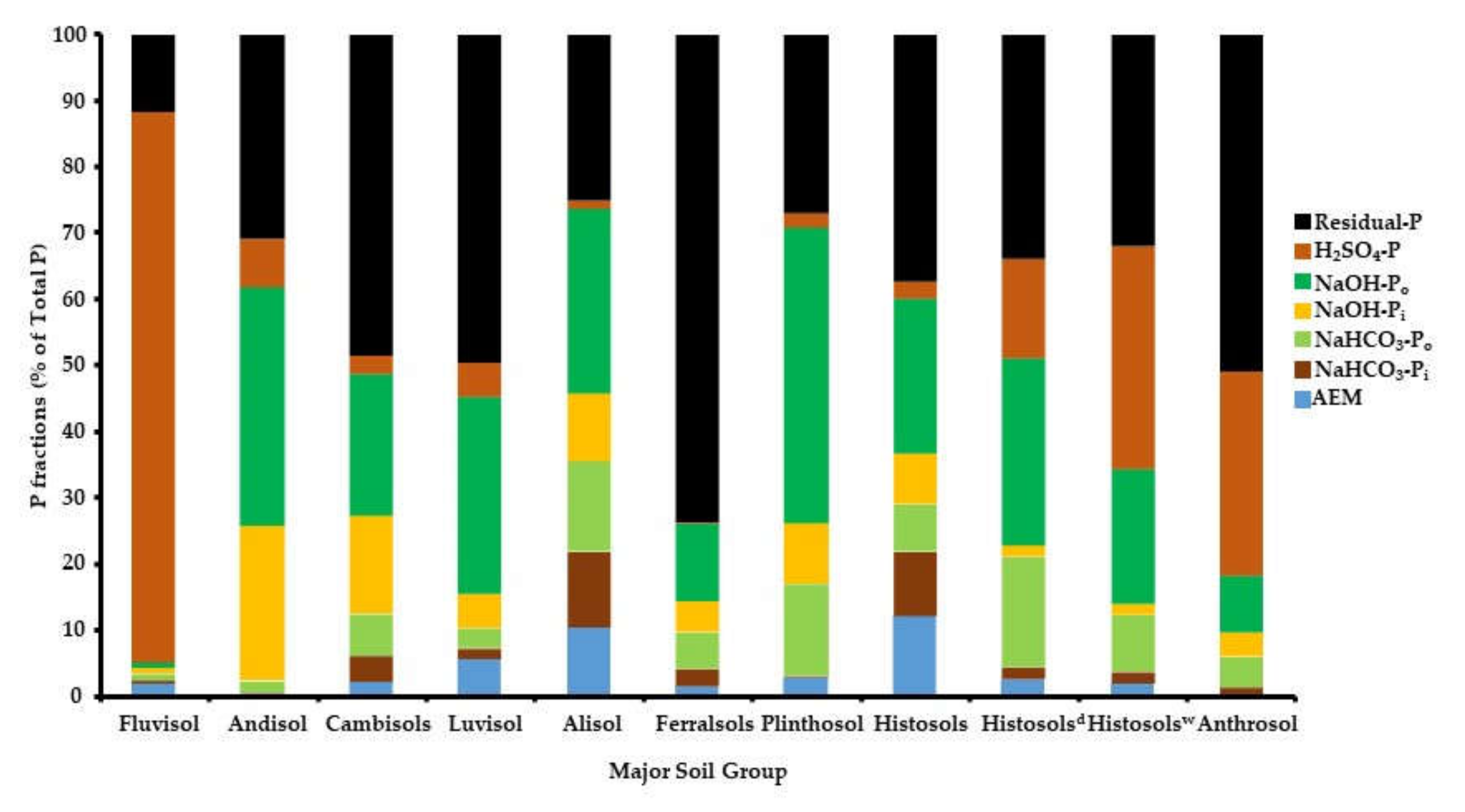
| (cm) | (mg P kg−1 Oven Dried Sample) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Depth | AEM-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaOH-Pi | H2SO4-Pi | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Po | H2SO4-Po | Residual-P |
| AD | 0–10 | 37 cd | 14 ef | 14 cdefh | 15 j | 213 b | 399 c | 52 efgh | 278 fgh |
| 10–20 | 21 hijk | 11 ef | 16 cdef | 13 j | 137 ef | 305 de | 57 defg | 114 ijk | |
| 20–40 | 24 fghijk | 12 ef | 12 efhi | 19 ij | 143 ed | 307 de | 71 d | 172 hij | |
| 40–60 | 22 ghijk | 7 f | 8 jk | 56 fg | 47 ij | 95 lkm | 47 fghi | 132 ijk | |
| AW | 0–20 | 38 bc | 39 b | 76 a | 319 a | 200 bc | 530 b | 121 b | 749 b |
| 20–40 | 28 defgh | 10 ef | 11 fhi | 76 e | 111 fg | 295 def | 74 cd | 347 ef | |
| 40–60 | 35 cde | 8 f | 10 hij | 51 gh | 84 gh | 193 hij | 62 def | 270 fgh | |
| 60–80 | 23 ghijk | 7 f | 10 hij | 24 ij | 56 hi | 126 jkl | 37 ijk | 169 hij | |
| CD | 0–10 | 33 cdef | 34 bc | 11 hij | 46 gh | 289 a | 326 d | 43 hij | 383 def |
| 10–20 | 27 efghi | 26 cd | 11 hij | 51 gh | 213 b | 248 efgh | 36 k | 64 jk | |
| 20–30 | 19 hijk | 13 ef | 12 cdefh | 74 ef | 132 ef | 225 ghi | 48 fghi | 106 ijk | |
| 30–40 | 20 hijk | 21 ed | 19 c | 77 e | 150 ed | 237 fgh | 44 ghij | 36 k | |
| 40–60 | 18 ijk | 14 ef | 7 k | 9 j | 95 g | 159 ijk | 17 m | 275 fgh | |
| CW | 0–10 | 47 ab | 50 a | 16 cdef | 75 e | 212 b | 403 c | 64 de | 581 c |
| 10–20 | 27 efghi | 28 bcd | 10 hij | 56 fg | 171 cd | 210 ghi | 32 kl | 224 ghi | |
| 20–30 | 26 fghij | 28 bcd | 12 efhi | 35 hi | 155 ed | 182 hij | 26 l | 146 ijk | |
| PD | 0–10 | 55 a | 35 bc | 56 b | 328 a | 280 a | 617 a | 235 a | 937 a |
| 10–20 | 31 cdefg | 26 cd | 54 b | 146 b | 109 fg | 268 defg | 98 bc | 168 hij | |
| 20–40 | 20 hijk | 11 ef | 18 dc | 14 j | 31 ijk | 82 lm | 42 hijk | 277 fgh | |
| 40–60 | 16 k | 7 f | 15 cdefc | 14 j | 13 jk | 43 m | 39 ijk | 915 a | |
| PW | 0–20 | 27 efghi | 14 ef | 13 defh | 114 c | 59 hi | 234 fgh | 98 bc | 498 cd |
| 20–40 | 21 hijk | 7 f | 10 hij | 102 cd | 18 jk | 57 m | 43 hijk | 348 ef | |
| 40–60 | 22 ghijk | 8 f | 10 hij | 100 cd | 40 ij | 66l m | 59 def | 414 ed | |
| 60–80 | 18 jk | 6 f | 9 hijk | 83 de | 4 k | 42 m | 51 efgh | 337 efg | |
| SE | 3 | 4 | 3 | 6.8 | 11 | 24 | 9 | 42 | |
| (cm) | (mg P kg−1 Oven Dried Sample) | % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Depth | TP | TPi | TPo | TPi | TPo |
| AD | 0–10 | 1069 cd | 216 de | 852 bc | 21 fg | 79 ab |
| 40–60 | 471 e | 128 fg | 343 e | 27 ef | 73 bc | |
| AW | 0–20 | 1823 b | 795 b | 1027 b | 43 abc | 57 efg |
| 60–80 | 385 e | 84 g | 301 e | 21 fg | 79 ab | |
| CD | 0–10 | 1004 d | 444 c | 560 de | 44 ab | 56 fg |
| 40–60 | 587 e | 229 de | 358 e | 39 bcd | 61 def | |
| CW | 0–10 | 1291 c | 480 c | 811 bcd | 37 dc | 63 de |
| 20–30 | 638 e | 268 d | 370 e | 42 abc | 58 efg | |
| PD | 0–10 | 2618 a | 1241 a | 1377 a | 47 a | 53 g |
| 40–60 | 507 e | 101 g | 406 e | 20 g | 80 a | |
| PW | 0–20 | 966 d | 273 d | 692 cd | 28 ef | 72 bc |
| 60–80 | 596 e | 189 ef | 408 e | 32 de | 68 cd | |
| SE | 88 | 24 | 88 | 3 | 3 | |
| (mg P kg−1 Oven Dried Sample) | (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Depth (cm) | TPf | TPfi | TPfo | TPfi | TPfo | TPf |
| AD | 0–10 | 881 c | 186 ed | 696 b | 18 c | 67 a | 85 a |
| 40–60 | 263 ef | 51 fg | 213 c | 12 c | 51 abc | 62 abcd | |
| AW | 0–20 | 1500 b | 804 a | 697 b | 40 a | 50 abc | 74 abc |
| 60–80 | 296 e | 77 fg | 220 c | 18 c | 34 cd | 68 abcd | |
| CD | 0–10 | 907 c | 191 d | 715 b | 14 c | 50 abc | 63 abcd |
| 40–60 | 271 ef | 53 fg | 218 c | 12 c | 48 abc | 60 bcd | |
| CW | 0–10 | 1002 c | 324 c | 679 b | 34 ab | 46 bc | 68 abcd |
| 20–30 | 321 e | 188 de | 133 c | 22 bc | 17 d | 51 cde | |
| PD | 0–10 | 1833 a | 494 b | 1340 a | 21 bc | 57 ab | 79 ab |
| 40–60 | 143 f | 41 g | 103 c | 10 c | 24 d | 33 e | |
| PW | 0–20 | 663 d | 115 ef | 581 b | 21 bc | 54 abc | 62 abcd |
| 60–80 | 254 ef | 82 fg | 140 c | 8 c | 25 d | 45 de | |
| SE | 46 | 24 | 47 | 5 | 7 | 8 | |
| (cm) | (g kg−1 Oven Dried Sample) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Depth | Al | Fe | Ca | Mg | Mn |
| AD | 0–10 | 2.72 a | 2.87 d | 6.56 c | 0.25 e | 0.09 c |
| AW | 0–20 | 1.49 c | 26.09 a | 25.40 b | 0.49 c | 0.14 b |
| CD | 0–10 | 2.55 a | 7.42 c | 5.50 c | 0.78 b | 0.04 d |
| CW | 0–10 | 2.23 b | 2.92 d | 3.71 c | 2.21 a | 0.01 e |
| PD | 0–10 | 0.83 d | 11.34 b | 25.25 b | 0.41 d | 0.20 a |
| PW | 0–20 | 0.79 d | 1.09 e | 31.16 a | 0.85 b | 0.14 b |
| SE | 0.06 | 0.01 | 1.10 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| Chemical Shift (ppm) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.0–5.78 | 5.09–5.06 | 4.67–4.58 | 4.39–4.25 | 4.20–4.11 | 4.00–3.48 | 0.9–1.05 | −4.45–(−4.47) | ||||
| (cm) | Integrated area of the spectra (%). | Total P (%) | |||||||||
| Site | depth | Ortho | IHP | α-glycerol | β-glycerol | AMP | IHP | DNA | Pyro. | Pi | Po |
| AD | 0–10 | 41 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 9 | 10 | 3 | 6 | 47 | 53 |
| AW | 0–20 | 66 | 29 | 5 | 66 | 34 | |||||
| CD | 0–10 | 52 | 2 | 13 | 14 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 55 | 45 | |
| CW | 0–10 | 53 | 1 | 19 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 54 | 46 | ||
| PD | 0–10 | 55 | 4 | 12 | 16 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 59 | 41 | |
| PW | 0–20 | 25 | 5 | 15 | 26 | 8 | 15 | 6 | 31 | 69 | |
| (cm) | % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Depth | Best Fitted P Reference | P Species | Pi | Po | R-Factor # |
| AD | 0–10 | Al-phytate | 7 | 14 | 85 | 0.0017 |
| MgHPO4 | 14 | |||||
| IHP | 37 | |||||
| Ca-phytate | 41 | |||||
| 40–60 | Ca-phytate | 3 | 0 | 100 | 0.0679 | |
| Boehmite_IHP | 97 | |||||
| AW | 0–20 | Boehmite_IHP | 13 | 19 | 82 | 0.0017 |
| MgHPO4 | 19 | |||||
| Ca-phytate | 25 | |||||
| IHP | 44 | |||||
| 60–80 | Boehmite_IHP | 22 | 0 | 100 | 0.0093 | |
| Ca-phytate | 78 | |||||
| CD | 0–10 | Amorphous AlPO4 | 12 | 25 | 73 | 0.0043 |
| MgHPO4 | 15 | |||||
| IHP | 28 | |||||
| Ca-phytate | 45 | |||||
| 40–60 | Amorphous AlPO4 | 10 | 10 | 90 | 0.0033 | |
| Ca-phytate | 40 | |||||
| Boehmite_IHP | 50 | |||||
| CW | 0–10 | MgHPO4 | 17 | 34 | 66 | 0.0045 |
| Crystalline FePO4. | 17 | |||||
| Ca-phytate | 66 | |||||
| 20–30 | Crystalline-AlPO4 | 12 | 44 | 56 | 0.0512 | |
| Ca-phytate | 15 | |||||
| MgHPO4 | 32 | |||||
| IHP | 41 | |||||
| PD | 0–10 | Crytalline-FePO4 | 11 | 34 | 66 | 0.0031 |
| MgHPO4 | 23 | |||||
| Ca-phytate | 66 | |||||
| 40–60 | Boehmite_IHP | 28 | 0 | 100 | 0.0053 | |
| Ca-phytate | 72 | |||||
| PW | 0–20 | IHP | 5 | 0 | 100 | 0.0037 |
| Ca-phytate | 95 | |||||
| 60–80 | AlPO4-Crytalline | 10 | 67 | 32 | 0.0065 | |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 17 | |||||
| Ca-phytate | 32 | |||||
| MgHPO4 | 40 | |||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negassa, W.; Michalik, D.; Klysubun, W.; Leinweber, P. Phosphorus Speciation in Long-Term Drained and Rewetted Peatlands of Northern Germany. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4010011
Negassa W, Michalik D, Klysubun W, Leinweber P. Phosphorus Speciation in Long-Term Drained and Rewetted Peatlands of Northern Germany. Soil Systems. 2020; 4(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegassa, Wakene, Dirk Michalik, Wantana Klysubun, and Peter Leinweber. 2020. "Phosphorus Speciation in Long-Term Drained and Rewetted Peatlands of Northern Germany" Soil Systems 4, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4010011
APA StyleNegassa, W., Michalik, D., Klysubun, W., & Leinweber, P. (2020). Phosphorus Speciation in Long-Term Drained and Rewetted Peatlands of Northern Germany. Soil Systems, 4(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4010011






