Concomitant Thoracic Spinal Hemangioma and Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Case Report and Technical Note
Abstract
1. Introduction and Clinical Significance
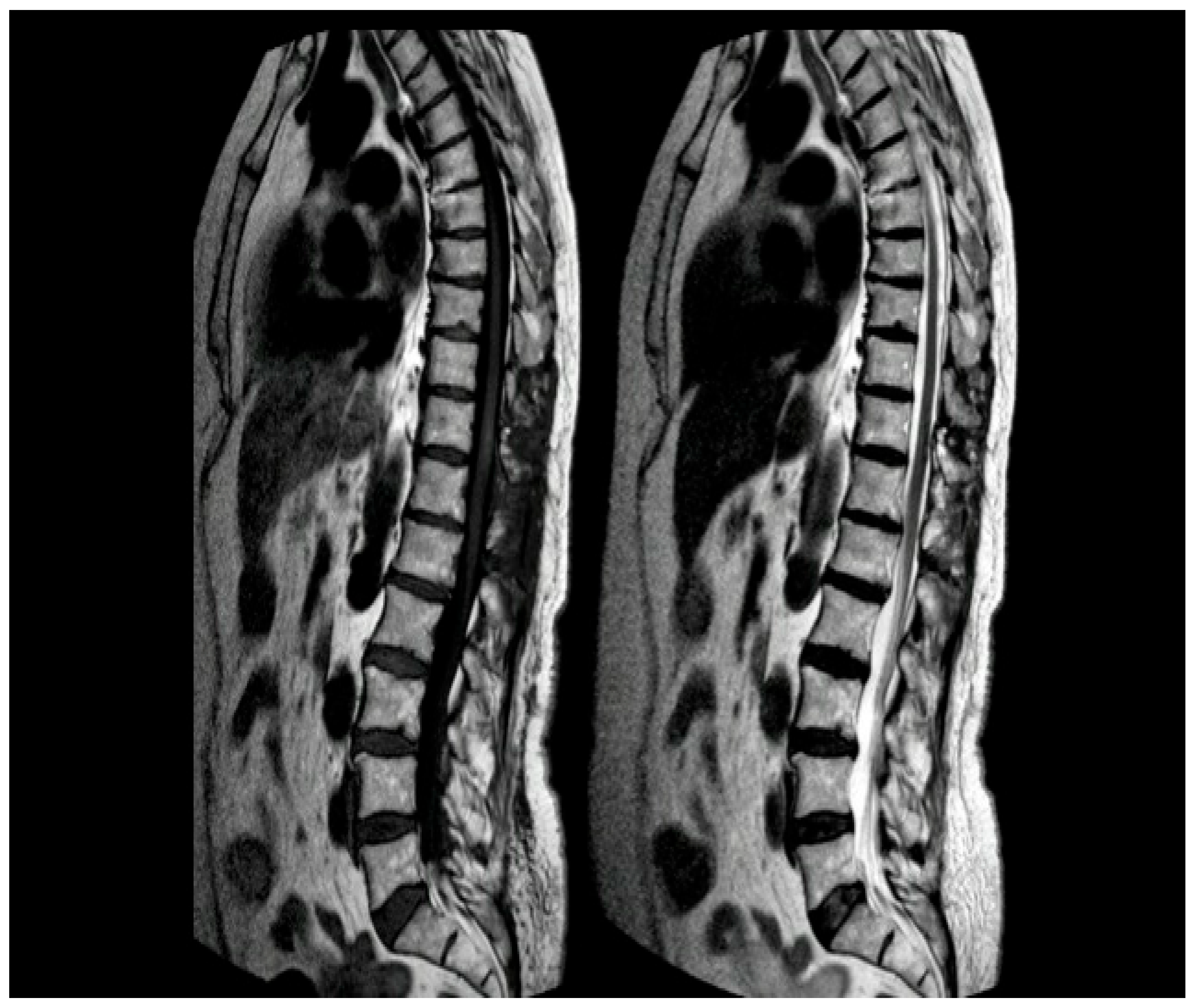
2. Case Presentation
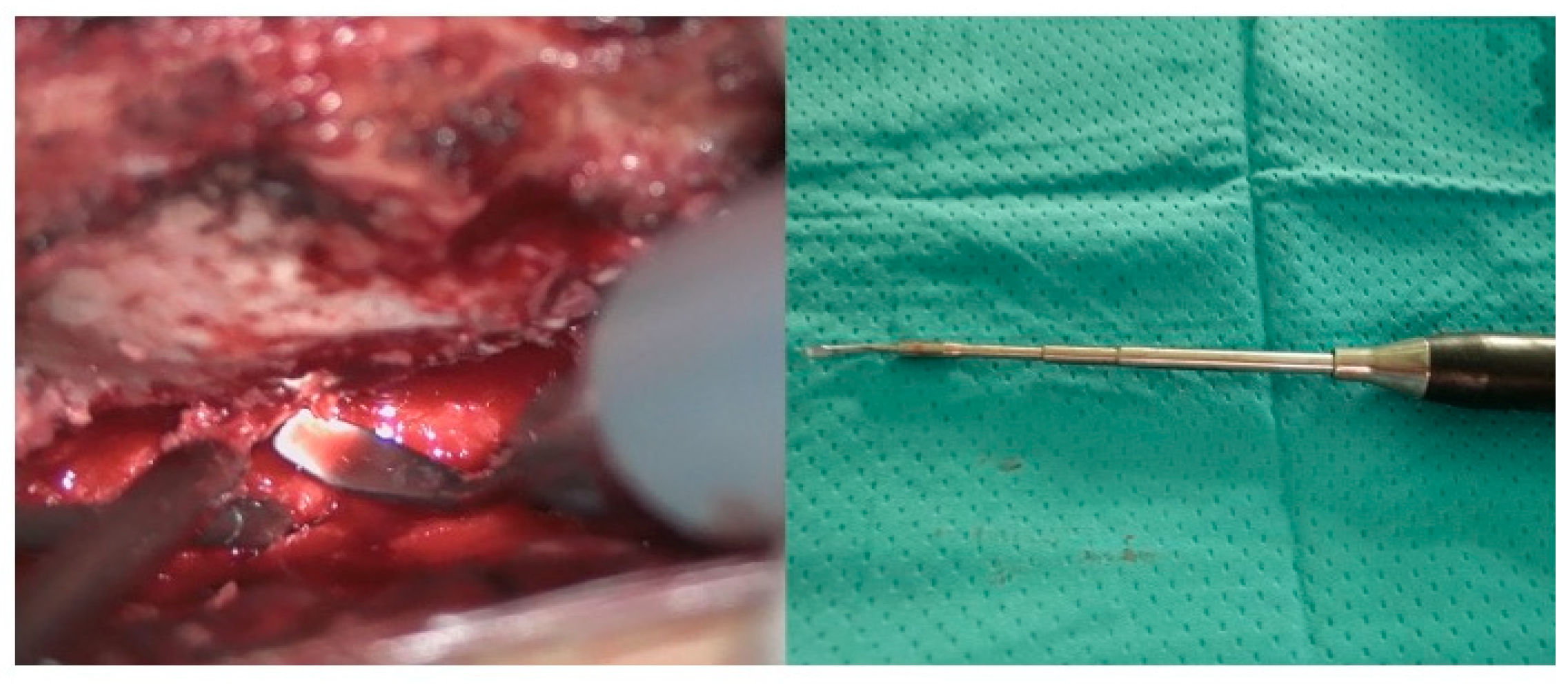
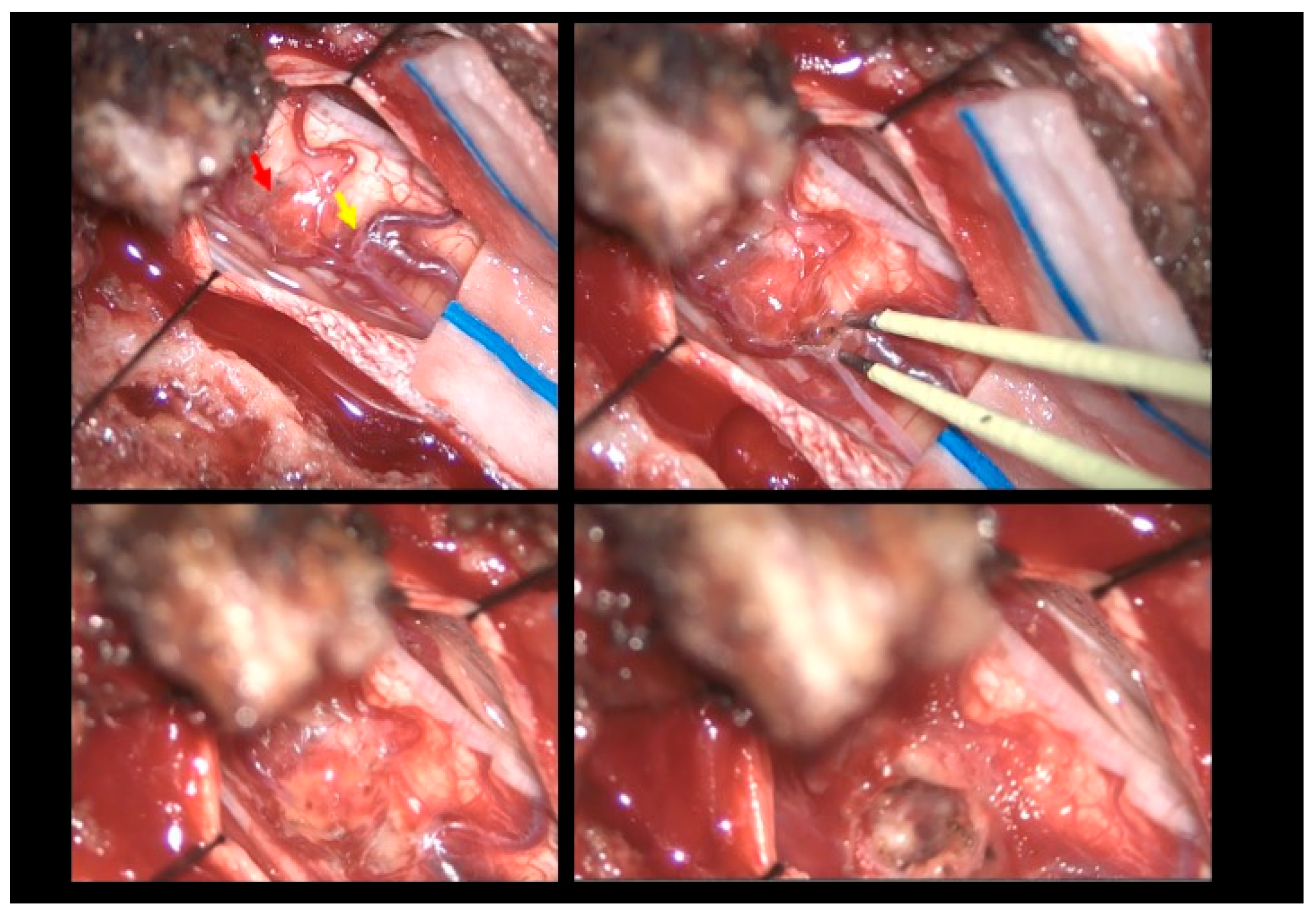
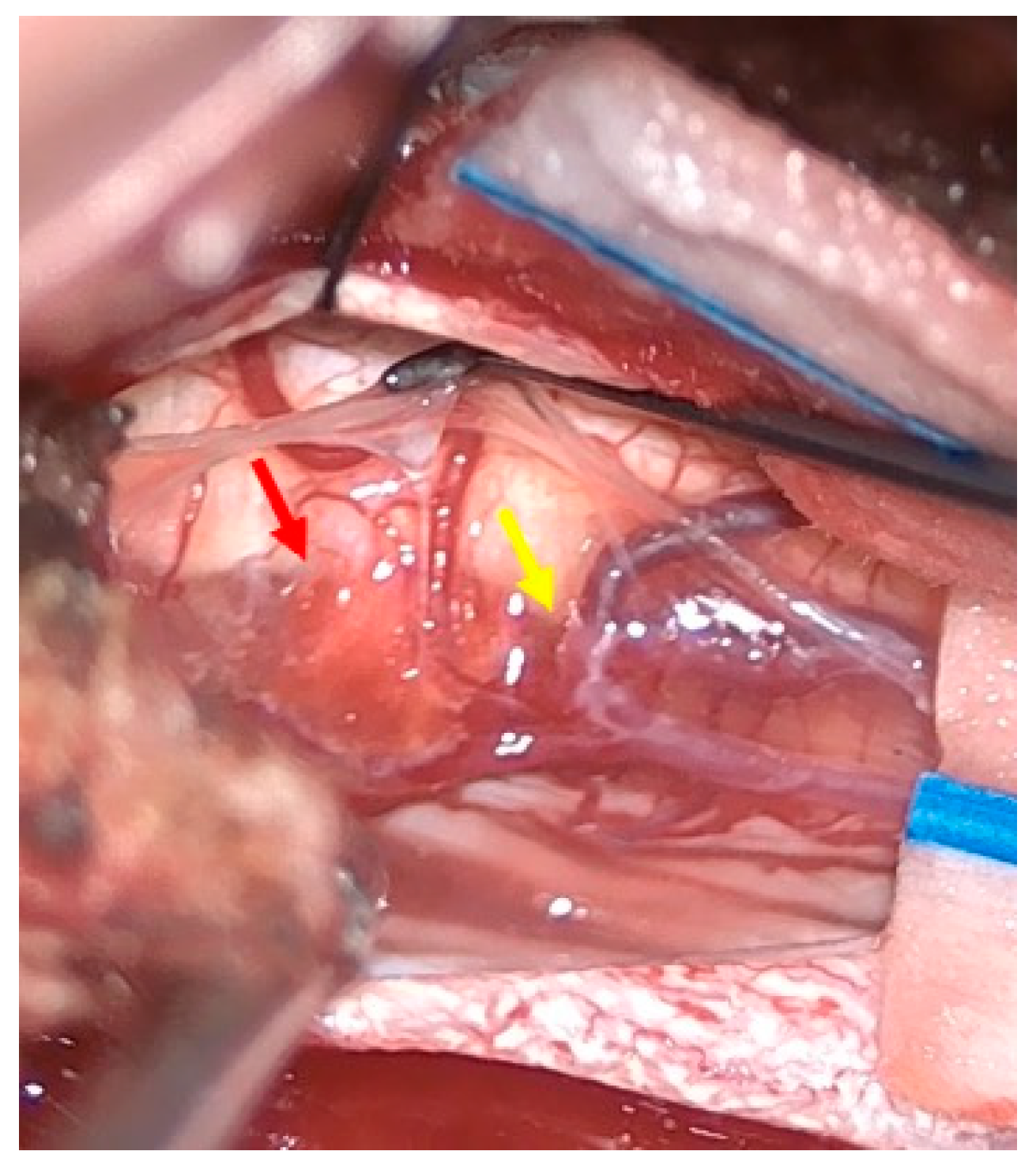
2.1. Surgical Technique
2.2. Postoperative Course
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SDAVF | Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula |
| AVF | Arteriovenous fistula |
| AVM | Arteriovenous malformation |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| DSA | Digital subtraction angiography |
References
- Bostroem, A.; Thron, A.; Hans, F.J.; Krings, T. Spinal vascular malformations–typical and atypical findings. Zentralbl. Neurochir. 2007, 68, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canavero, S.; Pagni, C.A.; Duca, S.; Bradac, G.B. Spinal intramedullary cavernous angiomas: A literature meta-analysis. Surg. Neurol. 1994, 41, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, I.; Pamir, M.N. Spinal Cavernomas: Outcome of Surgically Treated 10 Patients. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 672. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neurology/articles/10.3389/fneur.2017.00672/full (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Binkert, C.A.; Kollias, S.S.; Valavanis, A. Spinal cord vascular disease: Characterization with fast three-dimensional contrast-enhanced MR angiography. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.W.; Rodesch, G.; Luo, C.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Alvarez, H.; Lasjaunias, P.L. Concomitant Conus Medullaris Arteriovenous Malformation and Sacral Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Filum Terminale. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2002, 8, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, C. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Ren, J.; Ye, M. Concomitant Thoracic Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula and Spinal Cavernous Malformation. World Neurosurg. 2024, 181, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talenti, G.; Vitale, G.; Cester, G.; Della Puppa, A.; Faggin, R.; Causin, F. Rare association between spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas and dysraphisms: Report of two cases and review of the literature with a focus on pitfalls in diagnosis and treatment. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2017, 23, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotakopoulos, G.; Kivelev, J.; Andrade-Barazarte, H.; Tjahjadi, M.; Goehre, F.; Hernesniemi, J. Outcome in Patients with Spinal Cavernomas Presenting with Symptoms Due to Mass Effect and/or Hemorrhage: Conservative versus Surgical Management: Meta-analysis of Direct Comparison of Approach-Related Complications. World Neurosurg. 2021, 152, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiger, H.J.; Turowski, B.; Hänggi, D. Prognostic factors for the outcome of surgical and conservative treatment of symptomatic spinal cord cavernous malformations: A review of a series of 20 patients. Neurosurg. Focus. 2010, 29, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacoangeli, A.; Alsagheir, M.; Aiudi, D.; Gladi, M.; Di Rienzo, A.; Esposito, D.P.; Diab, M.; Naas, H.; Eldellaa, A.; Gigante, A.; et al. Microendoscopic Tailored Spine Decompression as a Less-Invasive, Stability-Preserving Surgical Option to Instrumented Correction in Complex Spine Deformities: A Preliminary Multicenter Experience. World Neurosurg. 2024, 186, e142–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzini, A.; Legnani, F.; Beretta, E.; Prada, F.; DiMeco, F.; Visintini, S.; Franzini, A. Piezoelectric Surgery for Dorsal Spine. World Neurosurg. 2018, 114, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Lawton, M.T.; Du, R.; Shwe, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, H. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in response to venous hypertension. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. A pivotal role of the vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway in the formation of venous hypertension-induced dural arteriovenous fistulas. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 3301–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, L. Local chronic hypoperfusion secondary to sinus high pressure seems to be mainly responsible for the formation of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uranishi, R.; Nakase, H.; Sakaki, T. Expression of angiogenic growth factors in dural arteriovenous fistula. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 91, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.T.; Jacobowitz, R.; Spetzler, R.F. Redefined role of angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of dural arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 87, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetts, S.W.; Moftakhar, P.; English, J.D.; Dowd, C.F.; Higashida, R.T.; Halbach, V.V. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas and intrathecal venous drainage: Correlation between digital subtraction angiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and clinical findings. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2012, 16, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassler, W.; Thron, A.; Grote, E. Hemodynamics of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. An intraoperative study. J. Neurosurg. 1989, 70, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Hong, T.; Zhang, H. Angioarchitecture and genetic variants of spinal cord cavernous malformations and associated developmental venous anomalies: A case report. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2023, 39, 1945–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vecchioni, S.; Iacoangeli, A.; Galli, E.G.; Vissani, M.; Marini, A.; Benigni, R.; Luzi, M.; Trignani, R. Concomitant Thoracic Spinal Hemangioma and Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Case Report and Technical Note. Reports 2025, 8, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8020074
Vecchioni S, Iacoangeli A, Galli EG, Vissani M, Marini A, Benigni R, Luzi M, Trignani R. Concomitant Thoracic Spinal Hemangioma and Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Case Report and Technical Note. Reports. 2025; 8(2):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8020074
Chicago/Turabian StyleVecchioni, Stefano, Alessio Iacoangeli, Elia Giacomo Galli, Massimo Vissani, Alessandra Marini, Roberta Benigni, Michele Luzi, and Roberto Trignani. 2025. "Concomitant Thoracic Spinal Hemangioma and Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Case Report and Technical Note" Reports 8, no. 2: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8020074
APA StyleVecchioni, S., Iacoangeli, A., Galli, E. G., Vissani, M., Marini, A., Benigni, R., Luzi, M., & Trignani, R. (2025). Concomitant Thoracic Spinal Hemangioma and Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Case Report and Technical Note. Reports, 8(2), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8020074





