Myxolipoma of the Popliteal Fossa: A Rare Tumor Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
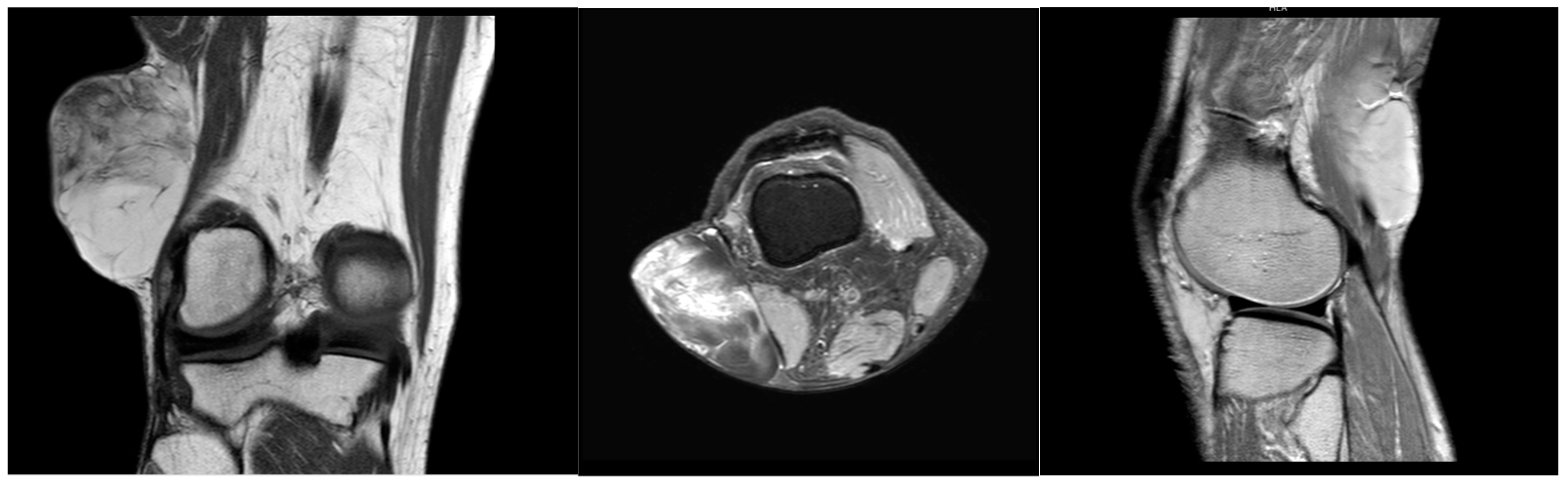
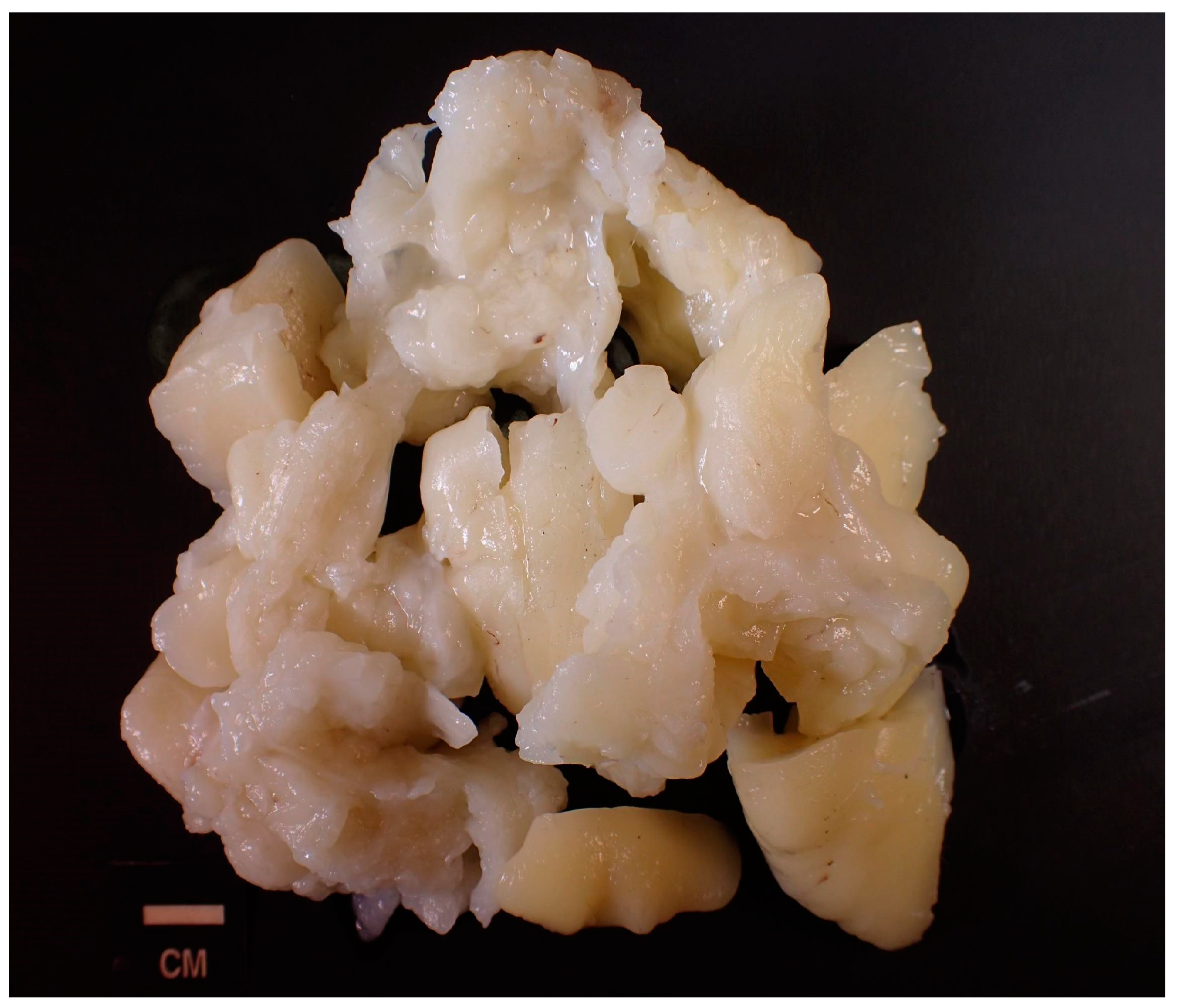
2. Detailed Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yohannan, T.M.; Goldberg, S.P.; Stamps, J.K.; Mathis, C.A.; Anthony Jr, C.L.; Lasater, O.E.; Knott-Craig, C.J. Cardiac myxolipoma in a child: Diagnosis and surgical management. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2012, 7, E113–E116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, G.M. Myxo-lipoma of the knee joint. Cal. State J. Med. 1914, 12, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakao, K.; Onishi, F.; Kiyama, M.; Minabe, T. The Growth Factors of Subcutaneous Benign Lipoma: Consideration from Anatomical Position of Occurrence. Plast. Reconstr. Surger-Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; James, S.L.; Davies, A.M.; Botchu, R. A diagnostic approach to popliteal fossa masses. Clin. Radiol. Vol. 2017, 72, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, G.; Ono, S.; Sekine, T.; Usami, S.; Ogawa, R. A Scoring System That Predicts Difficult Lipoma Resection: Logistic Regression and Tenfold Cross-Validation Analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 2575–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, S.; Garg, M.; Chaudhary, A.; Kalyan, M. Myxolipoma in the Neck—A Case Report with Review of Literature. Sch. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 9, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, L.; Yarrarapu, S.N.S.; Ameer, M.A.; Rosario-Collazo, J.A. Lipoma. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507906/ (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Cakiroglu, B.; Tas, T.; Esen, T.; Ates, L.; Aksoy, S.H. Myxolipoma of the renal capsule: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2015, 6, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasyev, S.G.; Dobrodeev AYu Avgustinovich, A.V.; Urmonov, U.B.; Samtsov Ye, N.; Frolova, I.G. Treatment of recurrent retroperitoneal myxolipoma. Khirurgiya 2021, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Guo, W.; Qu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Li, R. Characteristics of chondroid lipoma. Medicine 2019, 98, e15587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.E.; Aydıngöz, Ü.; Sökmensüer, C.; Karçaaltıncaba, M. Intramuscular chondroid lipoma: Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis by “fat ring sign”. Balkan Med. J. 2015, 32, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thway, K.; Flora, R.S.; Fisher, C. Chondroid lipoma: An update and review. Ann. Diag. Path. 2012, 16, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindblom, L.G.; Meis-Kindblom, J.M. Chondroid lipoma: An ultrastructural and immunohistochemical analysis with further observations regarding its differentiation. Hum. Pathol. 1995, 26, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannenbaum, M.; Colucci, P.G.; Baad, M.; Borczuk, A.C.; Steigman, S.A.; Kovanlikaya, A. Chondroid lipoma: Multimodality imaging in a 9-year-old female. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 49, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardhe, N.; Singh, N.; Bharadwaj, G.; Nayak, P.A. Spindle cell lipoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013010438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekhar, P.; Jose, M.; Dadhich, M.; Chatra, L.; Holla, V. Spindle cell lipoma: A case report and review of literature. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. 2012, 10, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldeira, P.; Bernardes, V.; Miranda, A.; Telles, D.; Batista, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Silva, T. Oral spindle cell lipomas. Open J. Stomatol. 2021, 1, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Chetty, R. Tumours composed of fat are no longer a simple diagnosis: An overview of fatty tumours with a spindle cell component. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, Y.; Nishio, J.; Nakayama, S.; Koga, K.; Aoki, M.; Yamamoto, T. Spindle Cell Lipoma and Pleomorphic Lipoma: An Update and Review. Cancer Diagn. Progn. 2023, 3, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huang, H.; He, S.; Wang, W.; Zhao, R.; Li, L.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, R. Spindle cell lipoma: Clinicopathologic characterization of 40 cases. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar]
- Horvai, A.E.; Link, T.M. Angiolipoma, in High-Yield Pathology. In Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology; Saunders, W.B., Ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2012; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Khubchandani, M.; Thosar, N.R.; Bahadure, R.N.; Baliga, M.S.; Gaikwad, R.N. Fibrolipoma of buccal mucosa. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2012, 3 (Suppl. 1), S112–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaghi, H.; Chokri, A.; Bouguezzi, A.; Abdeljelil, N.B.; Sioud, S.; Hentati, H.; Selmi, J. Oral fibrolipoma. Autops. Case Rep. 2023, 13, e2023431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, A.; Srivastava, A.; Jaiswal, R.; Gaur, A. Oral fibrolipoma: A rare clinicopathological entity. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2023, 27, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loubignac, F.; Bourtoul, C.; Chapel, F. Myxoid liposarcoma: A rare soft-tissue tumor with a misleading benign appearance. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, W.; He, X. Diagnosis and Prognosis of Retroperitoneal Liposarcoma: A Single Asian Center Cohort of 57 Cases. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, e7594027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baheti, A.D.; Tirumani, S.H.; Rosenthal, M.H.; Howard, S.A.; Shinagare, A.B.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Jagannathan, J.P. Myxoid Soft-Tissue Neoplasms: Comprehensive Update of the Taxonomy and MRI Features. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, H.; Ishiguro, M.; Nishio, J.; Aoki, M.; Yokoyama, R.; Yokoyama, K.; Taguchi, K.; Nabeshima, K. Extensive lipoma-like changes of myxoid liposarcoma: Morphologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular cytogenetic analyses. Virchows Arch. 2015, 466, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaricia, S.; Hirbe, A.C. Diagnosis and Treatment of Myxoid Liposarcomas: Histology Matters. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scapa, J.V.; Cloutier, J.M.; Raghavan, S.S.; Peters-Schulze, G.; Varma, S.; Charville, G.W. DDIT3 Immunohistochemistry Is a Useful Tool for the Diagnosis of Myxoid Liposarcoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, R.A.; Franchi, T.; Sohrabi, C.; Mathew, G.; Kerwan, A.; SCARE Group. The SCARE 2020 Guideline: Updating Consensus Surgical CAse REport (SCARE) Guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 84, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Myxoid Lipomas | Chondroid Lipoma | Spindle Cell Lipoma | Myxoid Liposarcoma | Angiolipoma | Fibrolipoma | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histology | Adipocytes surrounded by myxoid material | Embryonal fat and cartilage nests; myxohyaline stroma | Mature adipocytes accompanied by spindle cells, collagen fibers, mast cells, and areas of myxoid degeneration | Primitive mesenchymal cells mixed with signet rings or multivacuolated lipoblasts within “chicken-wire” capillary vasculature | Composed of mature fat with numerous small blood vessels, with fibrin thrombi present | Bundles of collagen fibers interspersed with lobules of adipocytes. |
| MRI | T1: homogeneous, low-intensity signal T2: Heterogeneous, high-intensity signal | T1: variable signals; T2: high signals. “Fat ring” on contrast-enhanced T2W MRI | Can appear low in fat, similar to the more aggressive myxoid liposarcoma | Multilobulated, heterogeneous mass T1: hypodense myxoid; enhances with contrast. Hyperdense fatty component (low percentage of tumor) T2: hyperdense myxoid component | T1: hypointense vascular elements; hyperintense fatty components T2: hyperintense vascular elements | High-intensity and well-encapsulated on both T1 and T2 imaging |
| IHC | - | Vimentin, S100, and CD68 | CD34 | DDIT3 | S100, CD31/34/61 | Vimentin, Ki-67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, Y.; Cao, J.; Nguyen, B.; Gero, M.; Jreije, K. Myxolipoma of the Popliteal Fossa: A Rare Tumor Case Report. Reports 2024, 7, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030058
You Y, Cao J, Nguyen B, Gero M, Jreije K. Myxolipoma of the Popliteal Fossa: A Rare Tumor Case Report. Reports. 2024; 7(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Yuchen, Jessica Cao, Brandon Nguyen, Melanie Gero, and Karim Jreije. 2024. "Myxolipoma of the Popliteal Fossa: A Rare Tumor Case Report" Reports 7, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030058
APA StyleYou, Y., Cao, J., Nguyen, B., Gero, M., & Jreije, K. (2024). Myxolipoma of the Popliteal Fossa: A Rare Tumor Case Report. Reports, 7(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports7030058






